1. Introduction
Industrial robots were first created in the 1950s and have since been developed for about 60 years. Due to their ability to replace humans in relatively simple and repetitive tasks, they are widely used in various major fields [
1]. In recent years, FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays) have proven to be advantageous in the field of image processing due to their ability to perform real-time pipeline operations and achieve high real-time performance. FPGAs are widely utilized across industries for their programmability, enabling rapid prototyping, iterative development, and easy adaptation to changing requirements. The trend of employing FPGAs for image processing in machine vision is on the rise. Nowadays, machine vision utilizing neural networks for target recognition and sorting is extensively adopted in sorting lines within automated factories. GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are designed to accelerate image and video processing. While most neural networks run on GPUs, their high power consumption and cost are limiting factors [
2], making them unsuitable for extensive use in large automated factories. However, in various scenarios, such as small platforms, the substantial power consumption and high cost are not feasible for users. Neural network-based machine vision for target recognition and sorting often demands significant resources, such as CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks) [
3], which not only consume substantial resources but also slow down processing speed due to the multitude of multiplication units required for convolutional operations.
After the industrial robot system completes the recognition task, ensuring the robot’s accuracy in locating the grasping target and improving the robustness of the design method remains a challenging task. The traditional approach employing robotic arms, which use predetermined movement routes and grasping positions for task execution, exhibits limited adaptability [
4]. In contemporary industrial production, time-optimal planning algorithms are utilized to complete corresponding paths in the shortest time, such as PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) algorithms and genetic algorithms [
5]. In multi-objective optimal trajectory planning, the accuracy of late curve control tends to diminish as runtime increases, resulting in reduced accuracy of the robotic arm system and increased overall mechanical loss [
6]. This scenario is less than ideal for practical engineering applications. Considering the aforementioned factors, the demand for designing a low-cost, low-power consumption, low-resource consumption, high real-time item identification, and sorting system with tangible economic benefits and practical value is particularly prominent for small and medium-sized enterprises or individuals. The system designed in this paper possesses the following advantages.
The hardware configuration of the entire system includes an FPGA development board, a vision camera, and a robotic arm grasping system. This setup eliminates the need for high power consumption and a large computer mobile platform, making it well-suited for the requirements of small enterprises or individuals;
The entire system is built on an FPGA, utilizing fundamental components such as counters, registers, and LUT (Look-Up Table) modules. This design significantly reduces system resources and power consumption when compared to GPUs;
In terms of algorithm implementation, the vision component employs traditional morphology for real-time parallel processing through pipeline operations, while the grasping segment utilizes an enhanced cubic B-spline algorithm for trajectory planning. This comprehensive system exhibits strong real-time performance and high operational stability.
2. Related Works Analysis
For items on industrial assembly lines, the application of industrial robots for recognition and grasping has garnered significant attention from researchers. In this section, we will provide a detailed analysis and summary, categorizing it into the visual component and the grasping segment.
2.1. Visual Section
The solutions in the vision section can be broadly divided into two categories: traditional morphological recognition algorithms and neural network-based image recognition algorithms [
7]. Many researchers have proposed various algorithms and methods. Tang et al. [
8] proposed a method to extract color features and shape features of items and use the BP (Backpropagation) neural network for the classification and recognition of items. The method has an accuracy rate of about 95%. The paper also compared the classification by selecting only color features and the classification by selecting only shape features; the accuracy rate was less than 84%, underscoring the importance of considering multiple features for classification judgments. In comparison to [
8], Wang et al. [
9] added the extraction of texture features, resulting in improved recognition accuracy to some extent. Both above methods are implemented based on software without hardware deployment, which imposes certain limitations on recognition speed. For image recognition, the deployment of neural networks to hardware generally involves GPUs, ensuring the algorithm’s implementation and fast recognition speed, but at the cost of higher power and resource consumption [
1]. In [
10], the neural network is deployed on hardware and image segmentation is performed using a bounding box regression algorithm. Deploying the neural network to hardware implementation can effectively enhance the real-time performance of the system.
In contrast to the neural network-based image recognition algorithm, the traditional morphological recognition algorithm does not require a large number of computing units as in a neural network, resulting in reduced resource consumption
2.2. Grabbing Section
Numerous domestic and international experts and scholars have conducted extensive in-depth studies and research on various aspects of robotic arm trajectory planning, including time-optimal, energy-optimal, impact-optimal, and integrated optimal approaches.
Chowdhury et al. [
11] reduced the multivariate interpolation problem to a joint polynomial approximation issue, thereby performing polynomial interpolation for robotic arm trajectory planning. However, this method requires specific constraints to be configured within each segmentation interval, leading to increased complexity in calculations, especially with a large number of nodes. Park and Kyung-Jo [
12] employed Fourier series and polynomial functions for path design to mitigate vibration. Cao et al. [
13] analyzed convergence based on B-spline curves but noted that errors in B-spline fitting could lead to end effector deviations.
Building upon the analysis of the aforementioned relevant works, this paper employs a threshold classifier, instead of a neural network, for classification judgment in the recognition part. This approach significantly reduces resource consumption and minimizes the required number of operations. For the grasping part, the paper adopts the improved cubic B-spline curve for trajectory planning, benefiting from continuous second-order derivatives and adherence to the path points, thus satisfying the requirements of robotic arm trajectory planning.
In FPGA hardware implementation, the unique advantage of high-speed parallel computing is harnessed to achieve a rapid recognition system. While the speed may be slightly lower than that of GPU recognition, FPGA’s power consumption is significantly reduced.
3. Overall System Design
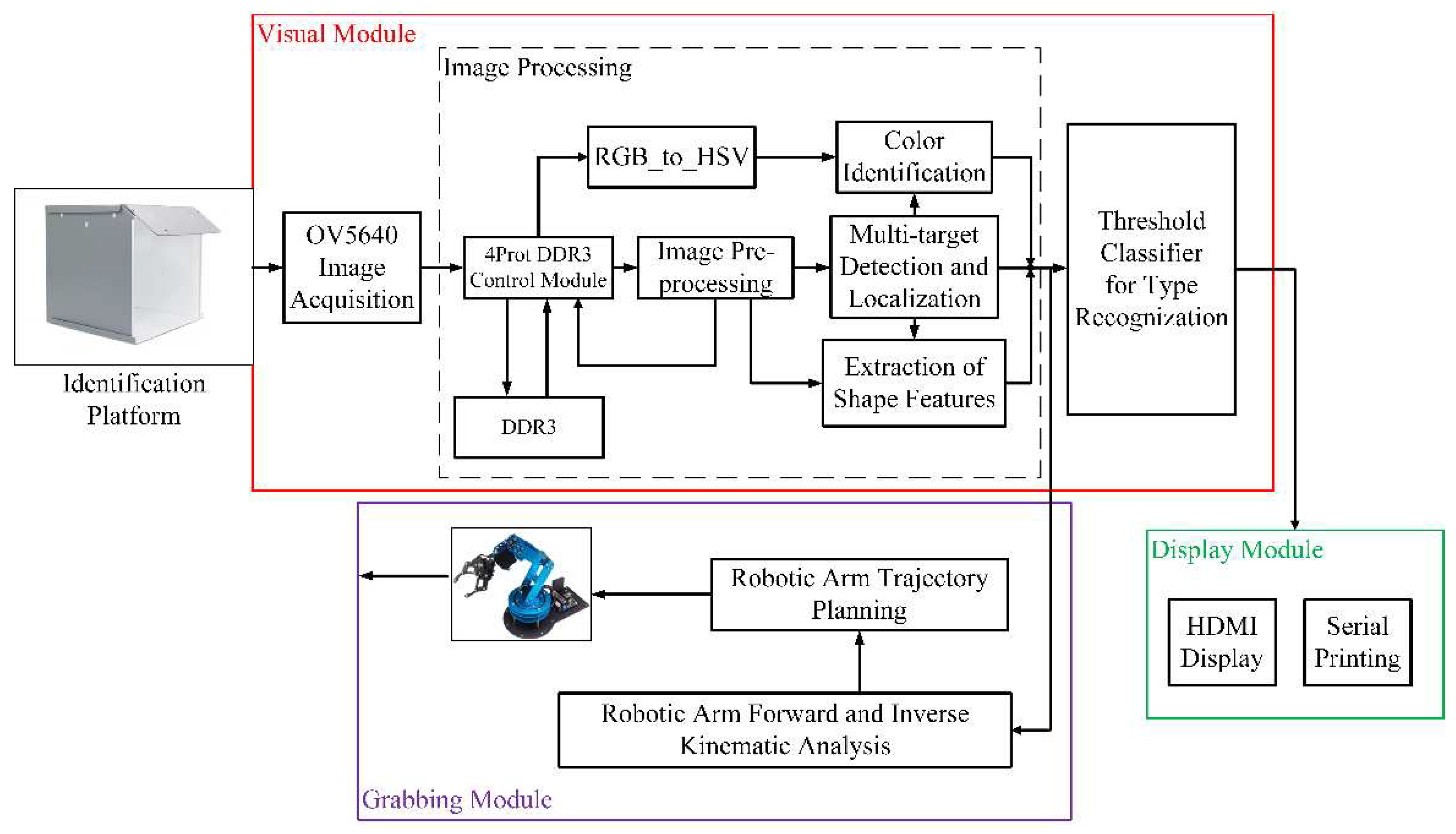
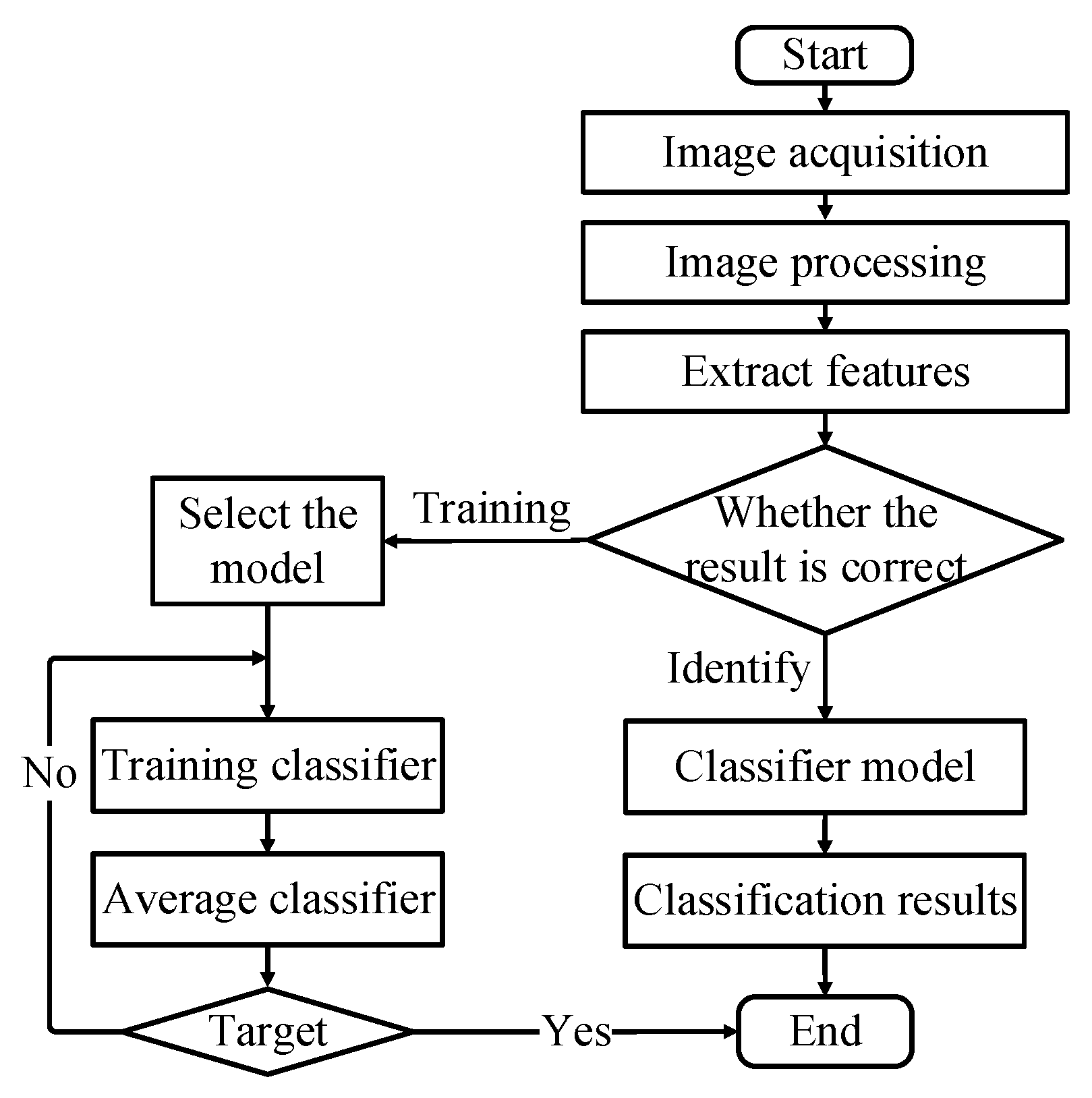
The overall design of the proposed system adopts a morphological recognition method. The system’s overall block diagram is depicted in
Figure 1. The framework comprises three main modules: the visual module, the grasping module, and the display module.
In the visual module, the system initially captures the scene using an OV5640 camera. The OV5640, manufactured by OmniVision Technologies Inc., 500W pixels, supports up to QSXGA (2592x1944) photo function, 1080P video image output, supports autofocus function, automatic exposure control (AEC). To extract the shape features of fruit objects, the system computes the background frame difference when the scene changes. This algorithm is implemented using a four-channel DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3) control module, employing the morphological filtering algorithm to eliminate noise and smoothen the image curve of the items. DDR3, a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM), finds use in computer systems and succeeded DDR2. It was prevalent in personal computers, laptops, servers, and other computing devices. Subsequently, multi-target detection and localization algorithm enable the segmentation, position extraction, and quantitative detection of multiple items. Meanwhile, the color identification of objects is achieved through HSV (Hue, Saturation, and Value) color space transformation combined with location information. The HSV color model is widely utilized in computer graphics, image processing, and color-related applications due to its intuitive and perceptually uniform color representation. Extracted object shape features, along with color features, facilitate object recognition using a pre-trained threshold classifier. Ultimately, the visual module identifies the object and transmits the corresponding object coordinate data to the six-degree-of-freedom robotic arm for further grasping function.
In the grasping module, the FPGA completes the forward and inverse kinematic analysis of the robotic arm and the trajectory planning. Subsequently, the robotic arm receives signals from the FPGA, enabling the sorting of corresponding objects on a simulated assembly line.
The display module showcases information from both the visual and grasping modules. The HDMI display presents details such as color, type, quantity, coordinate information, and whether the fruit has undergone sorting.
This system is designed around the characteristics of FPGA to fully utilize its computation and extension abilities. The image processing algorithm is implemented on an FPGA, with the OV5640 and the robotic arm serving as an external device to capture signals and perform the sorting operation. Once image processing is completed, a threshold classifier which is implemented in FPGA is utilized to determine the object’s category and color. The positional information is processed by FPGA to perform forward and inverse kinematic analysis and robotic arm trajectory planning to grab objects.
Through system architecture design and overall debugging, the system meets the expected requirements. The system is applicable to a large range of target categories. Because of the wide variety of fruits with different colors and shapes, the system utilizes fruits as representative objects for identification and sorting purposes. The system encompasses the following major steps in the overall operation, and their details are represented in the following four subsections.
3.1. Image Processing
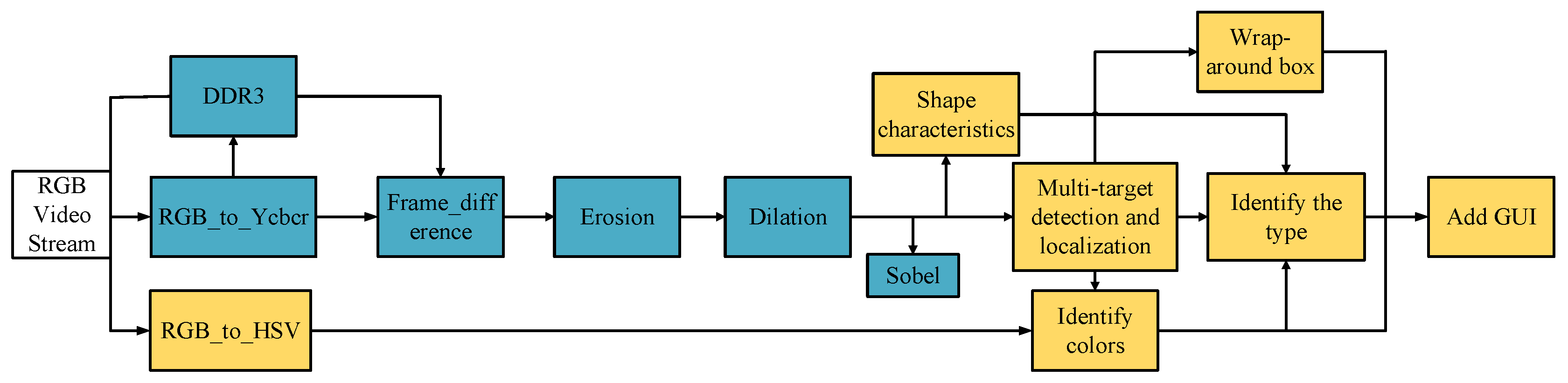
The image processing module is the core of this system, as shown in
Figure 2. After real-time detection by the OV5640, the grayscale Y required for image processing is obtained by RGB to YCbCr conversion. The grayscale of the background frame is saved to DDR3 memory, and the grayscale data of multiple fruits placed against the background is obtained by computing the difference with the current frame. The difference grayscale data of the background frame is then sequentially filtered through erosion and expansion [
14]. Sobel edge detection is also applied to the filtered image in the image preprocessing section to obtain the perimeter of the fruit [
15]. After the frame scan localization, the position information of each fruit is utilized to add frames around each fruit. Simultaneously, the color of each localized fruit is identified using the HSV color model via the RGB to HSV algorithm.
The boundary information, edge pixel points, and internal pixel points of each fruit obtained after image preprocessing are tallied to acquire shape features such as the long axis, short axis, perimeter, and area of each fruit. Further calculations yield second-order features like roundness, eccentricity, and body ratio. Ultimately, the acquired color features (Hue, Saturation, and Value) and shape features (Roundness, Eccentricity, and body Ratio) are combined to ascertain the fruit type using a trained threshold classifier (as discussed in
Section 3.2).
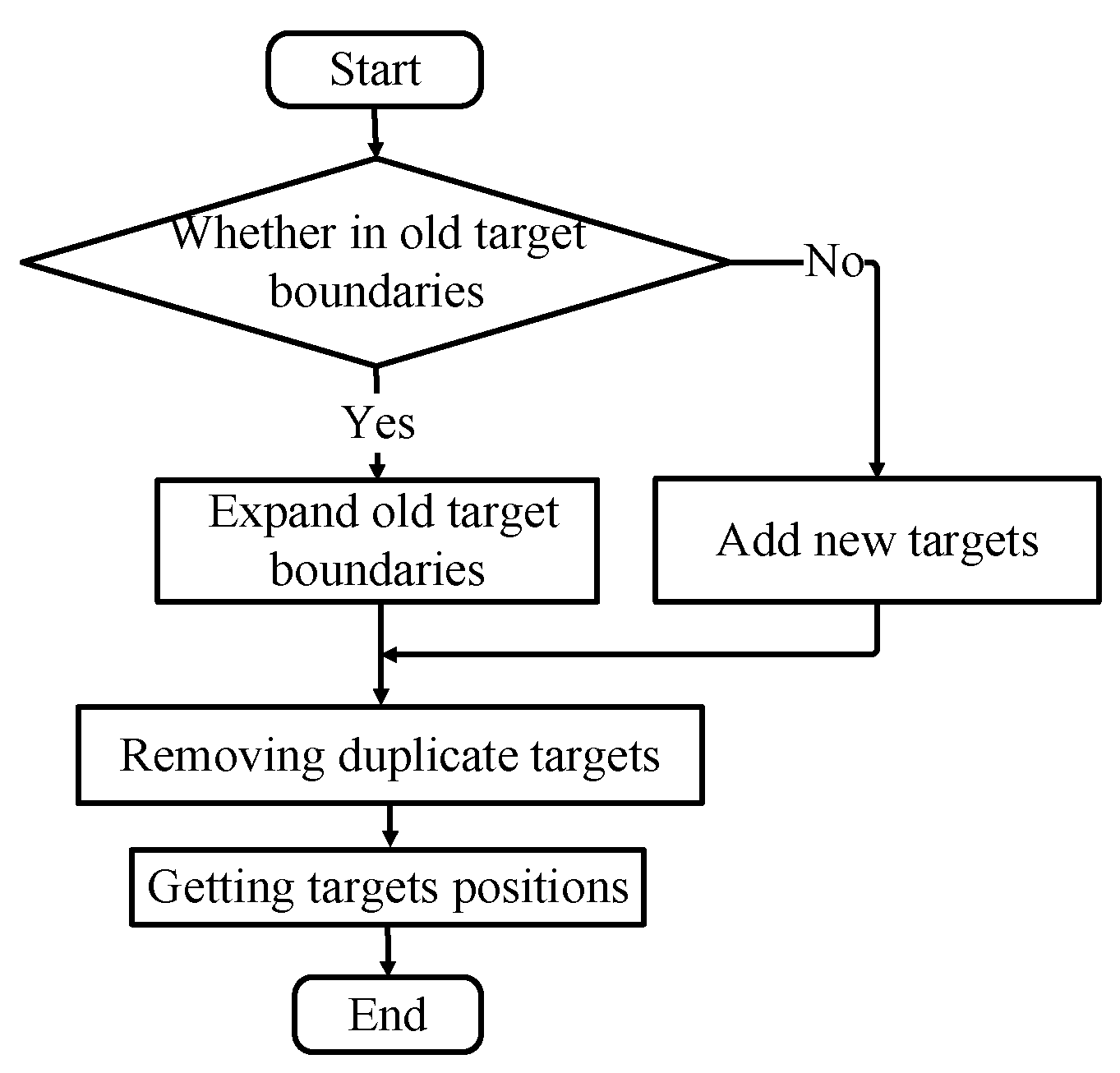
Following morphological filtering, target segmentation and quantity statistics are achieved by assessing the distances between each target. The fruits positioned on the detection platform are assessed, and the position coordinates of each fruit are real-time extracted based on the assessment outcome. The image is also binarized. Upon scanning the first white pixel, if the current target list is of black pixels, the pixel is automatically appraised during the subsequent white pixel scan. Upon detection, it first establishes whether the pixel pertains to an existing target. If not, it’s identified as a new target; if it does, it’s classified as an old target, and the target’s boundary is expanded according to the current pixel position information.
After observation, when the line field scan completes a frame, some specially shaped fruits, such as bananas, may appear and be identified as two overlapping targets. Therefore, each target needs to be compared to determine whether there is overlap. If overlap is detected, it is considered a duplicate target, and its boundary is merged to eliminate the duplication. The algorithm’s flowchart is depicted in
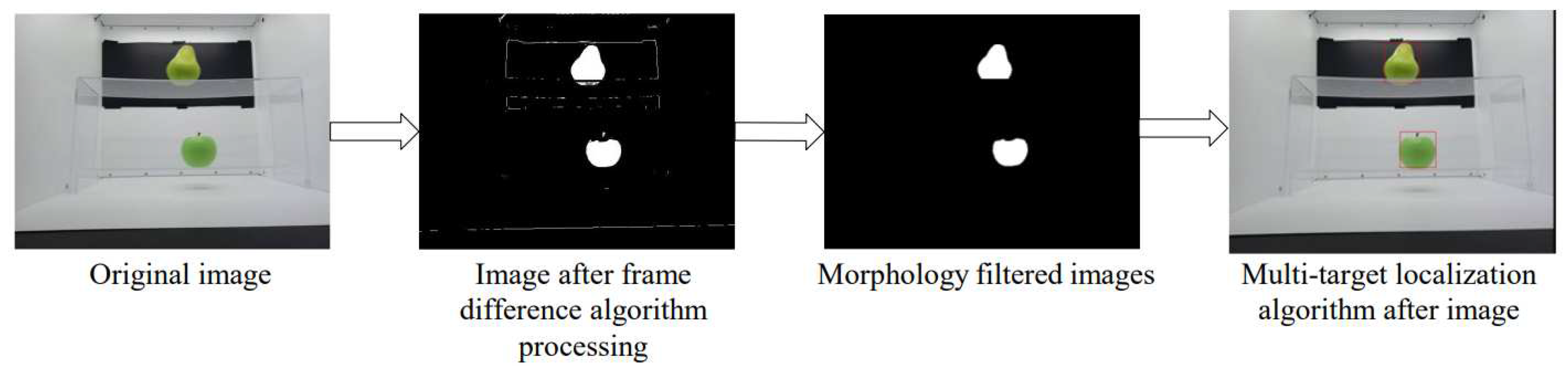
Figure 3. The images of apples and pears are input to the image processing module according to the flow, and the verification of the image processing effect is displayed in
Figure 4.
3.2. Threshold classifier
After preprocessing the captured fruit images, feature extraction is also required. Here, the color features and shape features of fruits are primarily extracted. The color features are obtained through the color recognition module, allowing the system to perform an initial classification of fruits based on color. However, the core of fruit recognition lies in extracting the shape features of fruits.
Figure 5 illustrates the comprehensive flowchart of fruit type recognition.
As evident from
Figure 5, pattern recognition primarily encompasses two aspects: training and testing, with the training of images being particularly crucial. The training algorithm plays a pivotal role in handling the training data. The recognition classification algorithm, which involves training and testing the extracted features, constitutes the essence of the fruit recognition system. The thresholds employed for recognition are established through a threshold classifier’s training. In this system, each threshold parameter is derived from multiple training sessions involving different fruits. The training outcomes are detailed in
Section 4.1 of the Experiment Results.
3.3. Robotic arm forward and inverse kinematic analysis
In the context of robotics and kinematics, ‘D-H’ represents Denavit-Hartenberg. The Denavit-Hartenberg (D-H) method is a widely employed mathematical technique for illustrating the relationship between successive links in a robotic manipulator or robotic arm. It aids in defining the coordinate frames and kinematic parameters for each joint, facilitating efficient and systematic kinematic analysis. In this paper, a modified D-H coordinate system is utilized to depict the positional and angular relationship between two sets of jointed connecting rods, and a mathematical model along with a coordinate system for the robotic arm is established. In the modified D-H coordinate system, the linkage length ai-1, four parameters of linkage twist αi-1, linkage offset di, and joint rotation angle θi are employed to depict the system, and the D-H parameter table is constructed based on the robotic arm model employed in the experiment.
After determining the D-H parameters and the homogeneous transformation matrix, a mathematical model of the kinematic equations of the robot arm was established. In the forward kinematic analysis, the orientation of the end effector relative to the coordinate system is obtained from the linkage parameters in
Table 1, and the positional coordinate matrix of connecting rod i and connecting rod i-1 is shown in Equation (1).
To achieve the grasping of the object, it is necessary to ensure that the robotic arm is in the desired position. The position of the end effector is determined by sequentially multiplying the position coordinate matrices of each linkage [
16]. The desired position of the robotic end effector is shown in Equation (2). The n
x, n
y and n
z are the three direction cosine of the end effector’s x-axis of coordinates, with respect to the base-fixed coordinate system. The o
x, o
y and o
z are the three direction cosine of the end effector’s y-axis of coordinates, with respect to the base-fixed coordinate system. The a
x, a
y and a
z are the three direction cosine of the end effector’s z-axis of coordinates, with respect to the base-fixed coordinate system.The symbol ‘p’ indicates the end effector’s coordinates, positioned relative to the base-fixed coordinate system. Additional details are provided in [
16].
In inverse kinematics, the goal is to determine the angles of each joint of the robotic arm based on the known positional coordinates. In this paper, the analysis is focused solely on the main body of the robotic arm. The coordinates of the end point P are defined as (Px, Py) in the XOY plane, and these coordinates are obtained according to the D-H model, as shown in Equations (3) and (4).
In the inverse kinematics solution, the coordinates of the end point P are known, and l3, l4, and l5 are the inherent parameters of the D-H model. Through calculations, the formula (5) can be derived, and similarly, other angles can be obtained. These angles can be used to control servos and achieve coordinated position control.
3.4. Robotic arm trajectory planning
To maintain a stable state during the movement of the robotic arm and at the same time achieve efficient gripping, the trajectory of the robotic arm needs to be planned. This paper focuses on the variation of position, velocity and acceleration of the robotic arm in the joint space, as well as the trajectory planning of the rotating joint over time. Trajectory planning involves the time series planning of velocity and acceleration during the movement of the robotic arm to ensure that the trajectory curve of the robotic arm at any moment is smooth and the speed is controllable, avoiding unnecessary sudden changes in position, velocity and acceleration. At the same time, the motion trajectory of each joint of the robotic arm is planned so that the end effector can complete the task under the work requirements during the motion process. By controlling the roles of each joint at the same time, it ensures that the end effector performs the task by the optimal path. Reasonable motion trajectory planning helps to improve the accuracy of the end position of the robotic arm, thus ensuring the operational efficiency of the robot in high-precision motion. Then a smooth path point position function is derived using the following two steps.
In recent years, for the problem of free curve interpolation points in the field of robotic arm research, studies have been conducted on interpolation using the B-spline curve algorithm, which is relatively more advantageous than the polynomial interpolation algorithm, but due to the fact that the B-spline fitting the fitted curves do not necessarily pass through all the given interpolation points. In order to ensure that the B-spline curve passes through all control points, this paper employs an improved cubic B-spline interpolation algorithm for point-to-point trajectory planning [
18]. This approach mitigates the impact of interpolation operations in both joint and Cartesian spaces, ultimately enhancing motion accuracy and quality. The expression for L
3i+1 concerning time ‘t’ is depicted in Equation (6), and the same principle applies to L
3i+2, L
3i+3.
In Equation (6), L3i+1 represents a segment of the trajectory curve of the cubic B-spline, while Di, Di+1, Di+2, and Di+3 serve as the control points along the trajectory curve. The provided Equation (6) smoothly fits the given path, ensuring adherence to velocity, acceleration, and the duration of the movement. This enables the planning of an optimal path.
4. Experiment Result
Image processing and object recognition are pivotal technologies in this research. The morphological recognition method and image segmentation techniques employed in this study can find application in image processing for the surrounding environment of vehicles, encompassing tasks like road, vehicle, and pedestrian detection. The system we have designed possesses the capability to recognize a wide array of objects. Through a straightforward replacement of these objects with road, vehicle, or pedestrian categories and the provision of suitable training, the system can be tailored for autonomous driving applications. Furthermore, by incorporating the enhanced motion trajectory planning algorithm to govern the actions of the robotic arm, it can be seamlessly integrated with path planning and vehicle control within autonomous driving systems, thereby enabling object grasping and placing operations.
4.1. Experimental Setup and Data
Based on the above design plan, the physical system was fabricated and built, as shown in
Figure 6 below, and testing of the system was started.
For this study, the color features and shape features of fruits are the primary focus. The color recognition module takes in the color characteristics of fruits, enabling the identification of fruits with distinct colors such as kiwi fruits characterized by their brown hue, and facilitating an initial classification of fruits based on color. The color thresholds, derived from pertinent experiments, are detailed in
Table 2.
The shape characteristics of the fruit constitute a fundamental basis for fruit species identification. Various shape attributes contribute to this, including fruit size, fruit circumference, fruit area, fruit roundness, fruit eccentricity, and more. These shape features play a pivotal role in the identification process within the design.
Given that first-order shape features are susceptible to effects from rotation, scaling, and translation, it becomes imperative to extract shape features with RST (Rotation, Scaling, and Translation) invariance. Consequently, second-order shape features such as body ratio, roundness, and eccentricity are predominantly employed. The calculation Equations (7), (8), and (9) are provided below.
where O represents roundness, f denotes body ratio, which is the ratio of the long axis to the short axis, e stands for eccentricity, S signifies area, L represents perimeter, H corresponds to the long axis, and W represents the short axis. In the discrimination process, the measured roundness is normalized in the actual code by expanding the roundness value from 1 to 256. This normalization simplifies discrimination and enhances the accuracy of the threshold.
Table 3 presents the data obtained for each feature measurement.
4.2. Experimental Result
The experimental setup and training data have been completed. The next step involves conducting a robot arm grasping experiment to test the system’s robustness, calculate resource consumption, and measure recognition speed.
As the parameters of each joint of the robotic arm used in this paper serve as direct inputs and the system requires real-time capabilities, the trajectory planning method chosen is joint space. The LeArm 6-degree-of-freedom high-performance programmable robotic arm studied in this simulation is a six-axis structured rotary joint manufactured by Hiwonder. The arm structure comprises 6 digital servos with alloy grippers, an aluminum alloy stand, and an all-metal rotating base. The body is equipped with 6 high-precision digital servos, providing 6 degrees of freedom. The robotic arm’s gripper structure is modeled using Solidworks software and produced using a 3D printer.
Based on the established mathematical model and D-H parameter table, this system conducts simulated object grasping experiments in the Matlab simulation environment. It adopts the improved cubic B-spline interpolation algorithm for trajectory planning and selects four path points as experiment constraints. The constraint points and joint parameter table are presented in
Table 4.
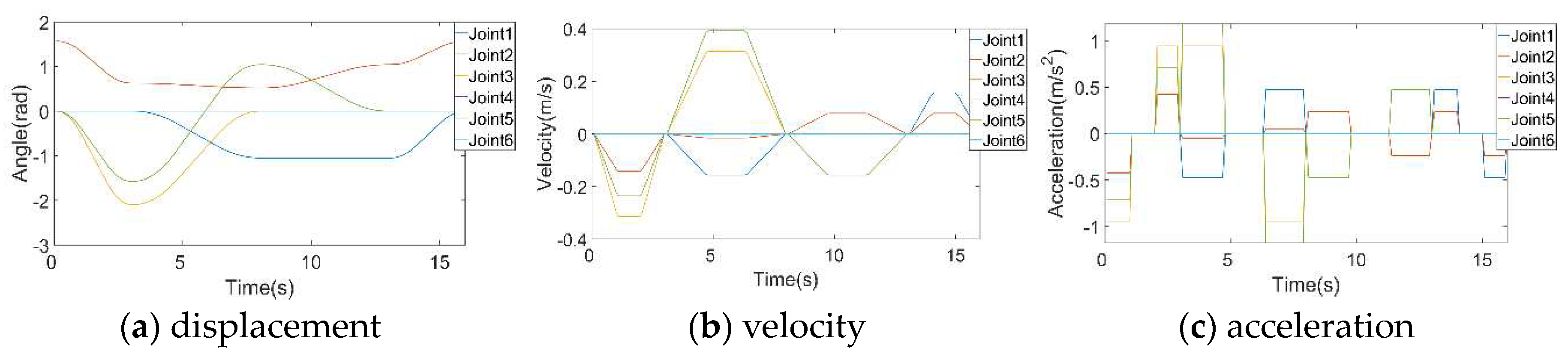
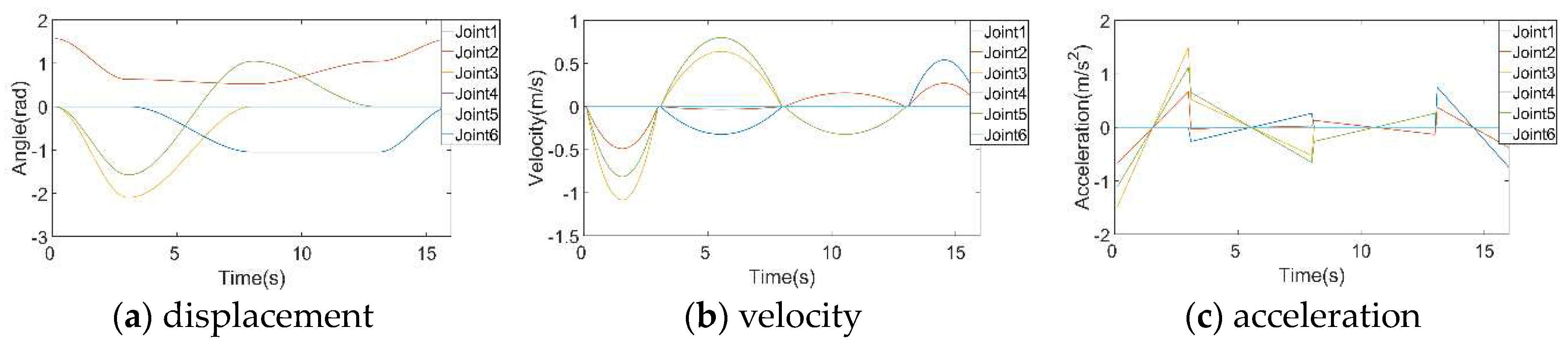
In this paper, the time of joint motion is set at each of the four constraint points. P0 represents the initial random position of the robotic arm, P1 signifies the position of the robotic arm after a reset, P2 corresponds to the position of the target object for the robotic arm, and P3 denotes the arrival position of the sorting robotic arm. These points collectively form the entire process of robotic arm grasping and sorting. The polynomial interpolation algorithm and the modified cubic B-spline interpolation algorithm are utilized to determine the pose of the robotic arm, encompassing displacement, velocity, and acceleration, as illustrated in
Figure 7.
Figure 7a and
Figure 8adisplay the positional changes of the robotic arm’s joints during the gripping of an object using the two algorithms. These figures illustrate the trajectory trends of the robotic arm’s joints over time. The two trajectories exhibit substantial consistency. Comparing
Figure 7b and
Figure 8b, it becomes apparent that the cubic B-spline curve results in higher maximum velocity and acceleration. This adjustment is made to complete trajectory planning within the same timeframe. However, the improved cubic B-spline interpolation algorithm yields smoother curves, effectively reducing impact during the motion process. It addresses sudden parameter changes in the motion of each joint, enhancing stability and accuracy. Notably, an increase in the number of interpolation functions corresponds to a proportional rise in overall system computation. Thus, the improved cubic B-spline interpolation algorithm is a stable and efficient trajectory planning approach.
By recognizing and sorting different fruits multiple times at various locations within the recognition area, we achieve high accuracy in both recognition and sorting. The majority of fruits exhibit a high recognition and sorting accuracy, resulting in an impressive overall recognition success rate of 97.69% and a sorting success rate of 96.46%. These outcomes showcase the system’s robustness, as depicted in
Table 5.
As displayed in
Table 5, both recognition accuracy and sorting accuracy remain consistently above 96%. In terms of the recognition component, it can be observed that higher accuracy is still achieved for items with brighter colors or more distinct shapes. For instance, the yellow pear may encounter recognition judgment errors due to its shape similarity to the green pear, despite the minor difference in their actual colors. Concerning the sorting aspect, superior grasping accuracy is observed for items closely resembling spheres or squares, while smaller objects like grapes and figs may incur grasping errors. This is attributed to the utilization of the traditional morphological recognition approach, which significantly reduces system resources compared to neural network schemes.
Furthermore, the entire system is constructed on an FPGA development board utilizing fundamental components such as adders, multipliers, counters, registers, and Look-Up Tables (LUTs). Consequently, the system demonstrates substantially reduced resource utilization and power consumption. Although the CNN-based recognition system [
19] and the YOLOv3-based recognition system [
2] exhibit higher accuracy rates of approximately 99% and a mean Average Precision (mAP) of about 90.78%, respectively, compared to our method, the resource usage of our approach amounts to only about 1/10 of that employed in [
19] and [
2].
In addition, when considering recognition speed, the average recognition speed of the hardware-deployed CNN neural network recognition system is approximately 900ms, while the YOLOv3 neural network recognition system, deployed to hardware and optimized, achieves an average recognition speed of about 54.76ms. In contrast, our system demonstrates an average recognition speed of approximately 25.26ms. A comprehensive performance comparison is presented in
Table 6. Compared to the systems introduced in [
20] and [
21], our system attains comparable or slightly higher accuracy while demanding fewer resources (FF, LUT). Furthermore, when contrasted with the system outlined in [
22], our approach offers a substantial advantage in terms of recognition speed. Additionally, in comparison with the system described in [
23], our system achieves relatively higher accuracy without compromising recognition speed. Moreover, when evaluated against the system detailed in [
24], our approach significantly reduces resource consumption while effectively fulfilling the intended functionality.
5. Conclusions
FPGAs offer significant application value in image processing due to their ability to execute real-time pipeline operations with the utmost efficiency. The proposed system in this paper leverages FPGA development boards to achieve enhanced recognition outcomes while optimizing resource utilization and effectively orchestrating the robotic arm to accomplish sorting duties. Moreover, when juxtaposed with recognition approaches like neural networks, the presented system boasts rapid recognition speed, minimal resource consumption, and exceptional portability. With its cost-effectiveness and adaptability across diverse scenarios, this system exhibits promising potential for small-scale production. Its implementation stands to substantially bolster production automation and markedly amplify sorting efficiency.
Given the attributes of low power consumption, high real-time performance, and minimal resource utilization inherent in this devised system, this study underscores its viability in addressing relatively straightforward sorting tasks across an array of application settings. By delving into the realms of image recognition and trajectory planning, the system adeptly executes requisite operations while keeping power consumption to a minimum. A prime example of its utility lies in tasks like container sorting by port forklifts or material handling at construction sites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W., Y.H. and Z.W.; methodology, Y.W. and J.C.; software, Y.W., Y.H. and J.C.; validation, Y.W., Y.H., J.C. and Z.W.; formal analysis, Y.W. and J.C.; investigation, Y.W., J.C. and Y.Z; resources, Y.W., J.C. and Z.W.; data curation, Y.W. and J.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W., Y.H. and J.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and Z.W.; visualization, Y.W., Y.H. and J.C.; supervision, Y.H.; project administration, Y.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Project of Wuhan University of Technology Chongqing Research Institute (No. YF2021-06), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61801341) and 2022 Independent Innovation Research Fund of School of Information Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology (No. 2022-XX-B1-08).
Data Availability Statement
The simulation data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, Y. Z.; Wu, C. Y.; Hu, X. D. Study of Web-based integration of pneumatic manipulator and its vision positioning. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A, 2005, 6, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Hong, H.; Liu, J. FPGA-based Deep Learning Acceleration for Visual Grasping Control of Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Xining, China; 2021; pp. 881–886. [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa, H.; Yamashita, T.; Watanabe, H. A study on object detection method from manga images using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Workshop on Advanced Image Technology (IWAIT), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2018, pp.1-4.
- Zhu, L.; Lin, H.; Wu, W.J. Machine vision-based workpiece positioning for industrial robots. J. Chinese Computer Science, 2016, 8, 1873–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.F. Trajectory planning of vibration suppression for rigid-flexible hybrid manipulator based on PSO algorithm. J. Control and Decision, 2014, 29, 632–638. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A. Y.; Jang, G.; Choi, Y. Infinitely differentiable and continuous trajectory planning for mobile robot control. In Proceedings of the 2013 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI), Jeju, Korea (South), 2013; pp. 357–361. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Tan, L.; Xu, X. Three-dimensional recognition method of fruit target based on PointNet++. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM), Ma’anshan, China; 2022; pp. 496–500. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y. A Research on the Fruit Recognition Algorithm Based on the Multi-Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE), Harbin, China; 2020; pp. 1865–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Jin, C.; Hu, M.; Ren, F. Fruit recognition based on multi-feature and multi-decision. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems, Shenzhen; 2014; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Latha, R. S.; Sreekanth, G. R.; Rajadevi, R.; Nivetha, S. K.; Kuma, K. A.; Akash, V.; Bhuvanesh, S.; Anbarasu, P. Fruits and Vegetables Recognition using YOLO. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India; 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M. F. I.; Jeannerod, C. P.; Neiger, V.; Schost, É. ; Villard,G. Faster Algorithms for Multivariate Interpolation with Multiplicities and Simultaneous Polynomial Approximations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory, 2015, 61, 2370–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Kyung-Jo, P.; Park, Y.S. Fourier-based optimal design of a flexible manipulator path to reduce residual vibration of the endpoint. J. Robotica, 1993, 11, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; He, X.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, J.; Shi, G. Study on the reverse design of screw rotor profiles based on a B-spline curve. J. Advances in Mechanical Engineering. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y. Real-Time Image Filtering and Edge Detection Method Based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China; 2022; pp. 1168–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. R.; Jeon, J. W. Sobel Edge based Image Template Matching in FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics Asia (ICCE-Asia), Seoul, Korea (South), 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B. Choi, J. Lee. “Time-optimal trajectory planning for a robot system under torque and impulse constraints,” 30th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 2004. IECON 2004, Busan, Korea (South), vol. 2,2004, pp. 1058-1063.
- Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ming, L. Interpolation method of NURBS and its offset curve. J. Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 41, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- L, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, W.; Hao, L. Smooth and collision-free trajectory generation in cluttered environments using cubic B-spline form. J. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2022, 169, 104606. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Xiang, Z. Acceleration and optimization of artificial intelligence CNN image recognition based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China; 2022; pp. 1946–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, A.; Nose, Y. Development of an Autonomous Driving Robot Car Using FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (FPT), Naha, Japan; 2018; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, A. Autonomous Driving System implemented on Robot Car using SoC FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Auckland, New Zealand, pp. 1-4; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Honda, K.; Amano, H. FPGA Design for Autonomous Vehicle Driving Using Binarized Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (FPT), Naha, Japan, 2018, pp. 425-428.
- Hao, C.; Sarwari, A.; Jin, Z.; Abu-Haimed, H.; Sew, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, B.; Fu, D.; Gu, J.; Chen, D. A Hybrid GPU + FPGA System Design for Autonomous Driving Cars. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS), Nanjing, China, 2019, pp. 121-126.
- Takasaki, K.; Hisafuru, K.; Negishi, R.; Yamashita, K.; Fukada, K.; Wakaizumi, T.; Togawa, N. An autonomous driving system utilizing image processing accelerated by FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Auckland, New Zealand, 2021, pp. 1-4.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).