Submitted:
13 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
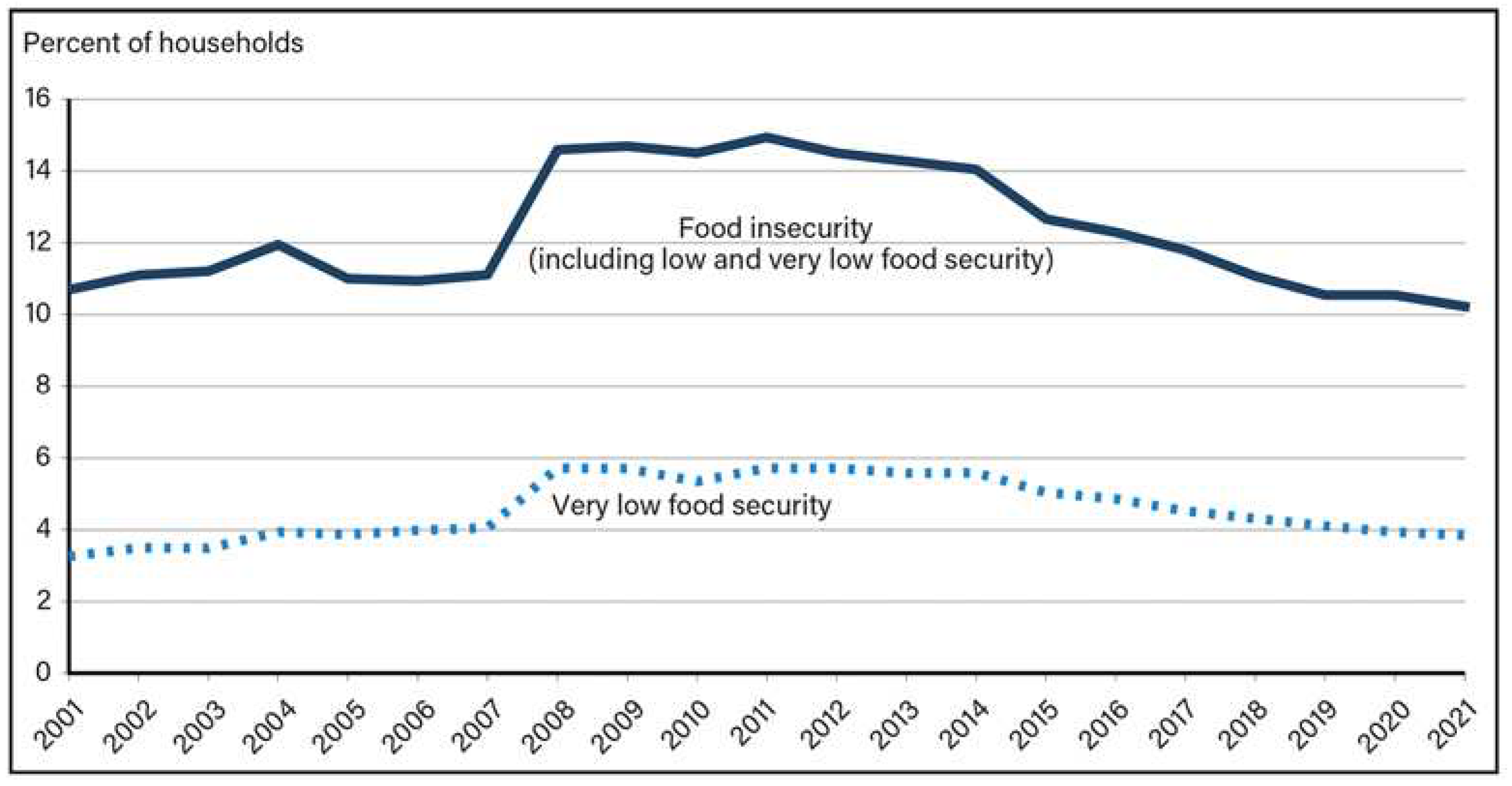
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regression Analysis
| Food insecurity | |||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| Independent Variable | 0 | X11 | X12 |
| 1 | X21 | X22 | |
3. Application Example
3.1. Study Region and Data Collection
| Variable | Notation | Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Male | Male | 1 = Male, 0 otherwise |
| Age ≤ 38.6 (USA 2020 Median age: 38.6α) | Age_386 | 1 if Age ≤ 38.6, 0 otherwise |
| Age in-between 38.6 and 50 | Age_38650 | 1 if 38.6 < Age ≤ 50, 0 otherwise |
| Age in-between 50-65 | Age_5065 | 1 if 50 < Age ≤ 65, 0 otherwise |
| Age > 65 | Age_65 | 1 if Age > 65, 0 otherwise |
| Income ≤ $21,960 (below poverty with a mean family size of 3β) | Inc_p | 1 if Income ≤ $21,960, 0 otherwise |
| Income $21,960 to $67,521 (Median household income in the USA was $67,521 in 2020γ) | Inc_pm | 1 if $21,960 < Income ≤ $67,521, 0 otherwise |
| Income > $67,521 | Inc_m | 1 if Income > $67,521, 0 otherwise |
| Education level with no degree | Edu_nd | 1 if Education with no degree, 0 otherwise |
| Education level with associate degree and aboveθ but below bachelor level | Edu_ad | 1 if Education with a degree below undergraduate, 0 otherwise |
| Education level with bachelors and above degree | Edu_bd | 1 if Education with undergraduate and above degree, 0 otherwise |
| Received food stamp in the last 12 months | Food_S | 1 if received food stamp in last 12 months, 0 otherwise |
| Variable | Aggregated States | |||||||||||||||
| Northeast States | Midwest States | Southern States | Western States | |||||||||||||
| Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | |
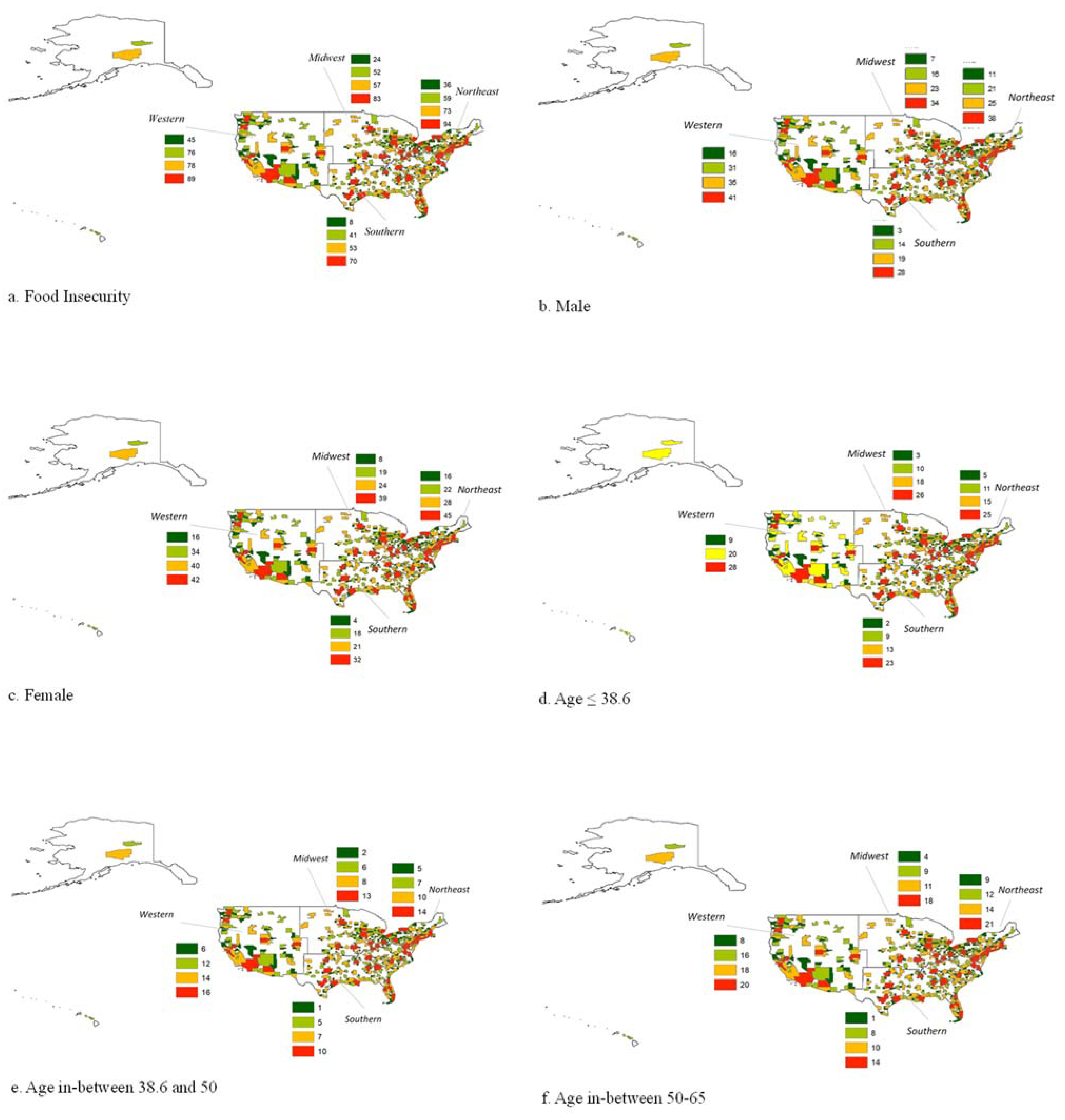
| Food Insecurity (consists of aggregated affirmative responses to - ‘worry food would run out’, ‘food didn't last’, ‘couldn't afford to eat balanced meals’, and ‘cut the size of meals or skip meals’) |
94 | 73 | 59 | 36 | 83 | 52 | 57 | 24 | 70 | 53 | 41 | 8 | 89 | 78 | 76 | 45 |
| Male | 38 | 25 | 21 | 11 | 34 | 16 | 23 | 7 | 28 | 19 | 14 | 3 | 41 | 35 | 31 | 16 |
| Female | 45 | 28 | 22 | 16 | 39 | 19 | 24 | 8 | 32 | 21 | 18 | 4 | 42 | 40 | 34 | 16 |
| Age ≤ 38.6 (USA 2020 Median age: 38.6) | 25 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 26 | 10 | 18 | 3 | 23 | 13 | 9 | 2 | 28 | 20 | 20 | 9 |
| Age in-between 38.6 and 50 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 13 | 6 | 8 | 2 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 6 |
| Age in-between 50-65 | 21 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 18 | 9 | 11 | 4 | 14 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 20 | 18 | 16 | 8 |
| Age ≥ 65 | 23 | 14 | 13 | 8 | 17 | 8 | 10 | 6 | 14 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 19 | 22 | 17 | 9 |
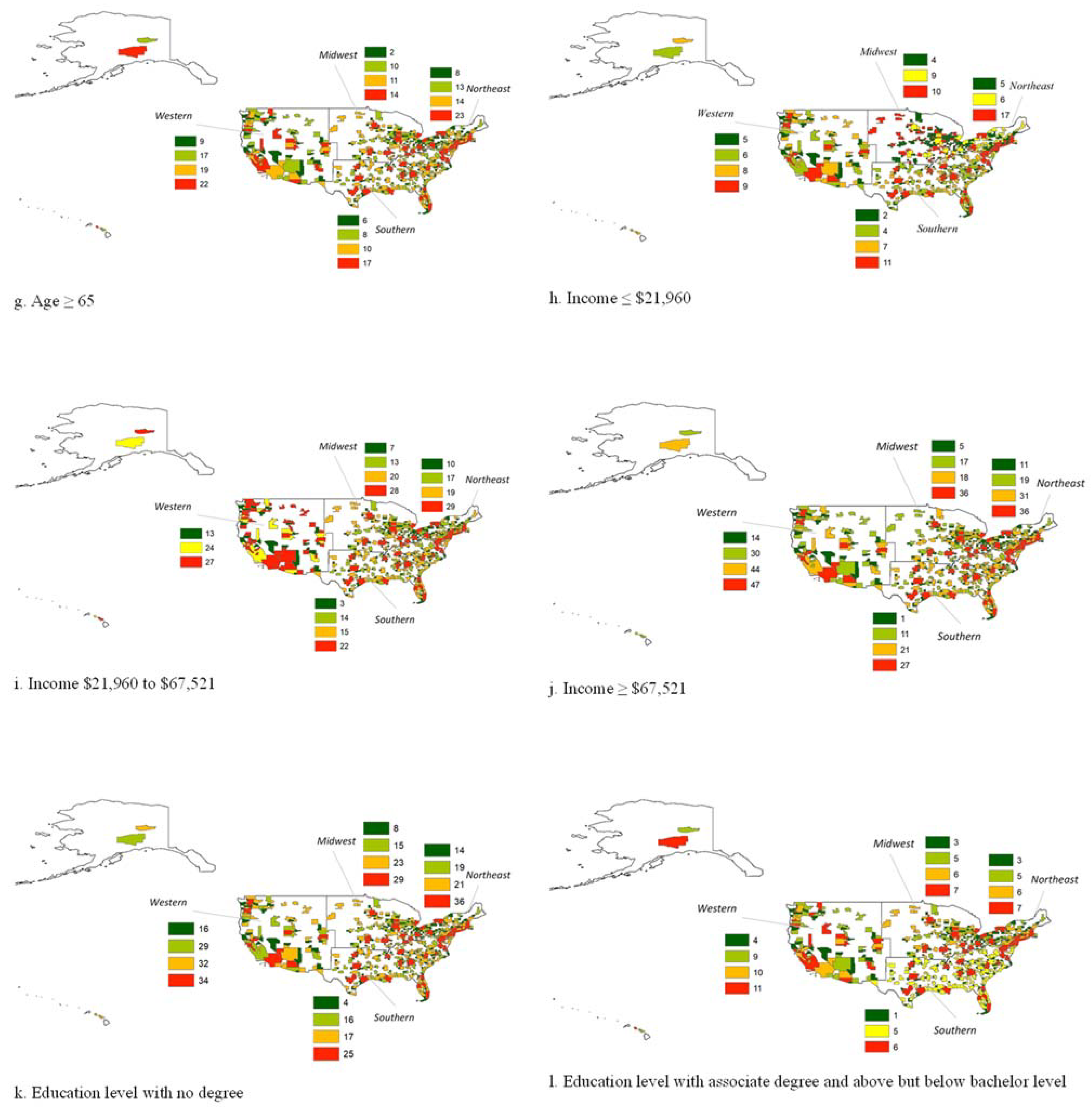
| Income ≤ $21,960 (below poverty with a mean family size of 3) | 17 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 11 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 9 | 6 | 8 | 5 |
| Income $21,960 to $67,521 (Median household income in the USA was $67,521 in 2020) | 29 | 17 | 19 | 10 | 28 | 13 | 20 | 7 | 22 | 15 | 14 | 3 | 27 | 24 | 27 | 13 |
| Income ≥ $67,521 | 36 | 31 | 19 | 11 | 36 | 18 | 17 | 5 | 27 | 21 | 11 | 1 | 47 | 44 | 30 | 14 |
| Education level with no degree | 36 | 21 | 19 | 14 | 29 | 15 | 23 | 8 | 25 | 17 | 16 | 4 | 34 | 29 | 32 | 16 |
| Education level with associate degree and above but below bachelor level | 7 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 4 |
| Education level with bachelors and above degree | 39 | 25 | 19 | 10 | 37 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 29 | 19 | 11 | 2 | 40 | 34 | 23 | 11 |
| Received food stamp in the last 12 months (2019) | 15 | 9 | 11 | 19 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 9 | 15 | 24 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 17 |
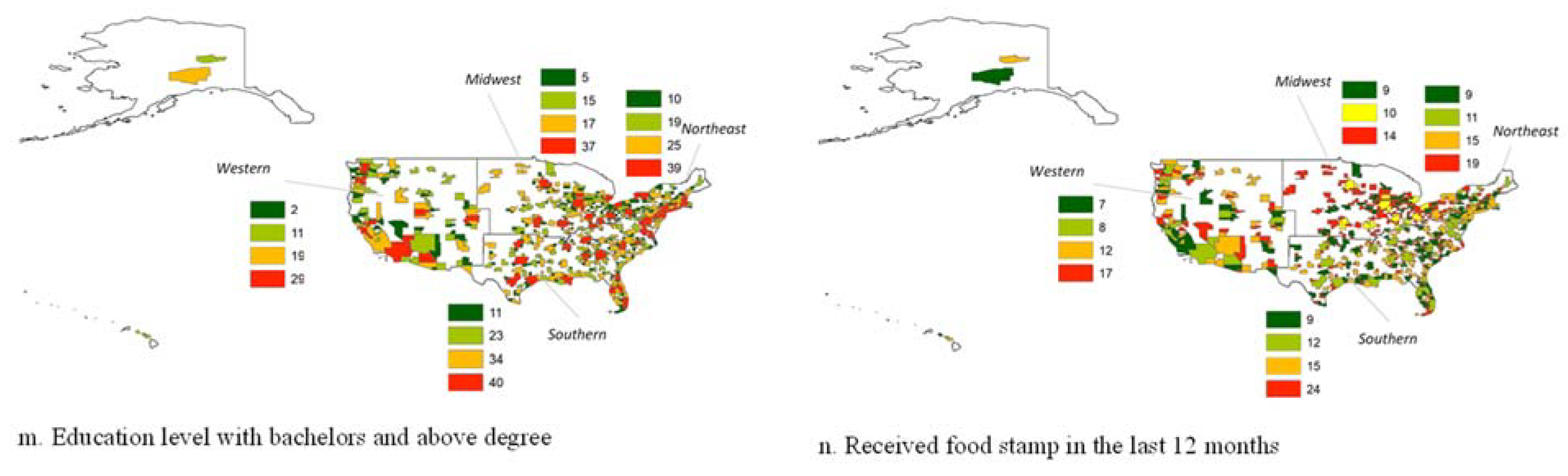
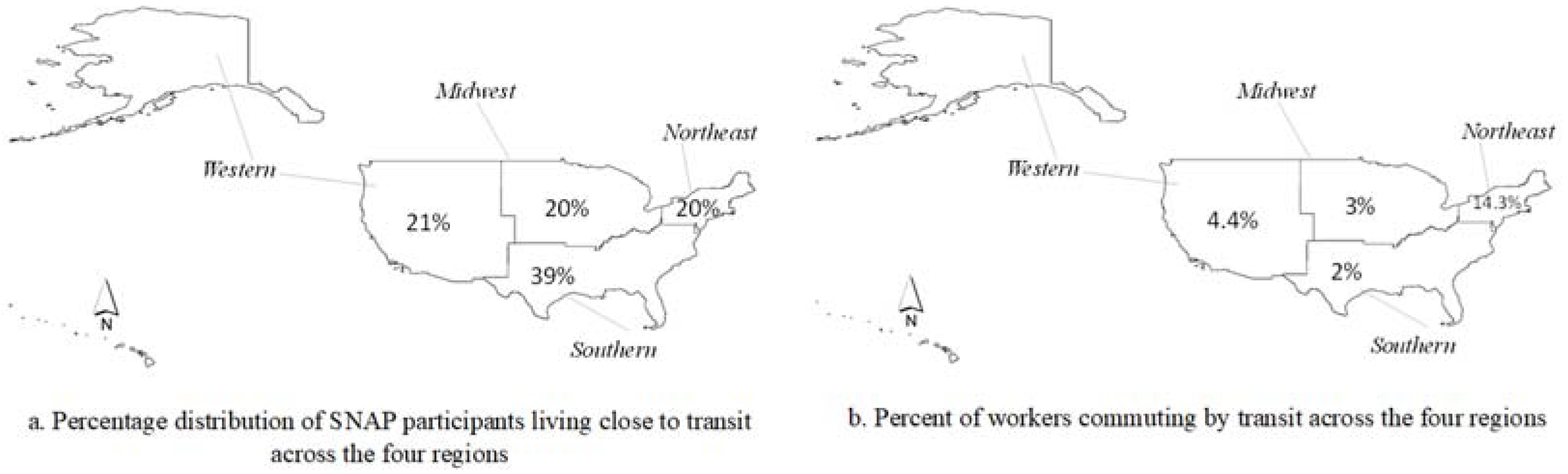
Results and Discussion
| Variables | Northeast States | Midwest States | Southern States | Western States | ||||||||||||
| Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | |
| Males | -0.505* (0.223) | 1.356 (0.658) | -0.688* (0.306) | |||||||||||||
| Age_386 | 0.79 (0.227) | 0.933 (0.317) | 1.482 (0.444) | 0.803 (0.306) | 1.578 (0.551) | 0.923 (0.217) | 0.71 (0.261) | 0.749 (0.238) | 0.513 (0.198) | 1.228 (0.387) | 1.123 (0.232) | |||||
| Age_38650 | 1.101 (0.269) | 1.792 (0.35) | 1.824* (0.48) | 1.484 (0.505) | 1.839 (0.63) | 1.205 (0.25) | 0.597 (0.291) | 0.854 (0.223) | 1.325 (0.42) | 1.334* (0.26) | 1.588 (0.682) | |||||
| Age_5065 | 0.661 (0.221) | 1.081 (0.323) | 0.975 (0.438) | 1.32 (0.455) | 1.119 (0.545) | 0.967 (0.223) | 0.891 (0.281) | 0.897 (0.244) | 0.611 (0.209) | 1.106* (0.243) | ||||||
| Inc_p | 2.454 (0.299) | 2.636 (0.396) | 2.188 (0.524) | 1.863 (0.355) | 1.904 (0.491) | 2.209 (0.445) | 2.707 (0.845) | 2.239 (0.27) | 1.824 (0.339) | 2.679 (0.372) | 1.906 (0.222) | 3.204 (0.495) | 1.918 (0.245) | |||
| Inc_pm | 1.879 (0.273) | 1.93 (0.296) | 1.269 (0.465) | 1.445 (0.3) | 1.506 (0.38) | 1.633 (0.418) | 2.046 (0.794) | 1.784 (0.241) | 1.563 (0.254) | 1.88 (0.351) | 1.295 (0.185) | 2.213 (0.416) | 0.89 (0.202) | |||
| Edu_nd | 0.692* (0.201) | 1.05* (0.401) | 0.866* (0.25) | 1.343 (0.333) | 0.800* (0.19) | 0.753* (0.241) | 0.739 (0.18) | 0.855* (0.355) | 0.731 (0.201) | 1.365 (0.68) | ||||||
| Edu_ad | 0.597* (0.305) | 0.834 (0.235) | ||||||||||||||
| Food_S | 1.095 (0.201) | 1.086 (0.302) | 2.168 (0.358) | 2.571 (0.905) | 1.759 (0.252) | 1.872 (0.369) | 1.401 (0.254) | 1.149 (0.489) | 1.055 (0.189) | 1.434 (0.255) | 1.47 (0.207) | 1.514 (0.707) | 1.315 (0.179) | 0.984 (0.192) | 1.874 (0.501) | |
| Variables | Northeast States | Midwest States | Southern States | Western States | ||||||||||||
| Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | Large central metro | Large fringe metro | Medium and small metro | Nonmetropolitan | |
| Males | 0.605 | 4.05 | 0.501 | |||||||||||||
| Age_386 | 2.204 | 2.542 | 4.4 | 2.233 | 4.846 | 2.518 | 2.033 | 2.115 | 1.67 | 3.416 | 3.073 | |||||
| Age_38650 | 3.009 | 6 | 6.195 | 4.412 | 6.291 | 3.335 | 1.47 | 1.817 | 2.349 | 3.764 | 3.798 | 4.893 | ||||
| Age_5065 | 1.938 | 2.947 | 2.65 | 3.745 | 3.063 | 2.631 | 2.437 | 2.453 | 1.843 | 2.184 | 3.023 | |||||
| Inc_p | 11.118 | 13.452 | 8.926 | 6.443 | 6.678 | 9.137 | 14.497 | 8.82 | 5.848 | 14.329 | 6.579 | 25.532 | 6.797 | |||
| Inc_pm | 6.228 | 6.809 | 3.577 | 4.242 | 4.488 | 5.132 | 7.577 | 5.867 | 4.684 | 6.61 | 3.613 | 9.17 | 2.439 | |||
| Edu_nd | 1.969 | 2.856 | 2.378 | 3.818 | 2.254 | 2.008 | 2.097 | 2.378 | 2.082 | 3.87 | ||||||
| Edu_ad | 1.867 | 2.329 | 2.294 | |||||||||||||
| Food_S | 2.85 | 3.026 | 8.682 | 13.021 | 5.712 | 6.467 | 4.047 | 3.178 | 2.927 | 4.443 | 4.432 | 4.209 | 3.766 | 2.013 | 2.661 | 6.739 |
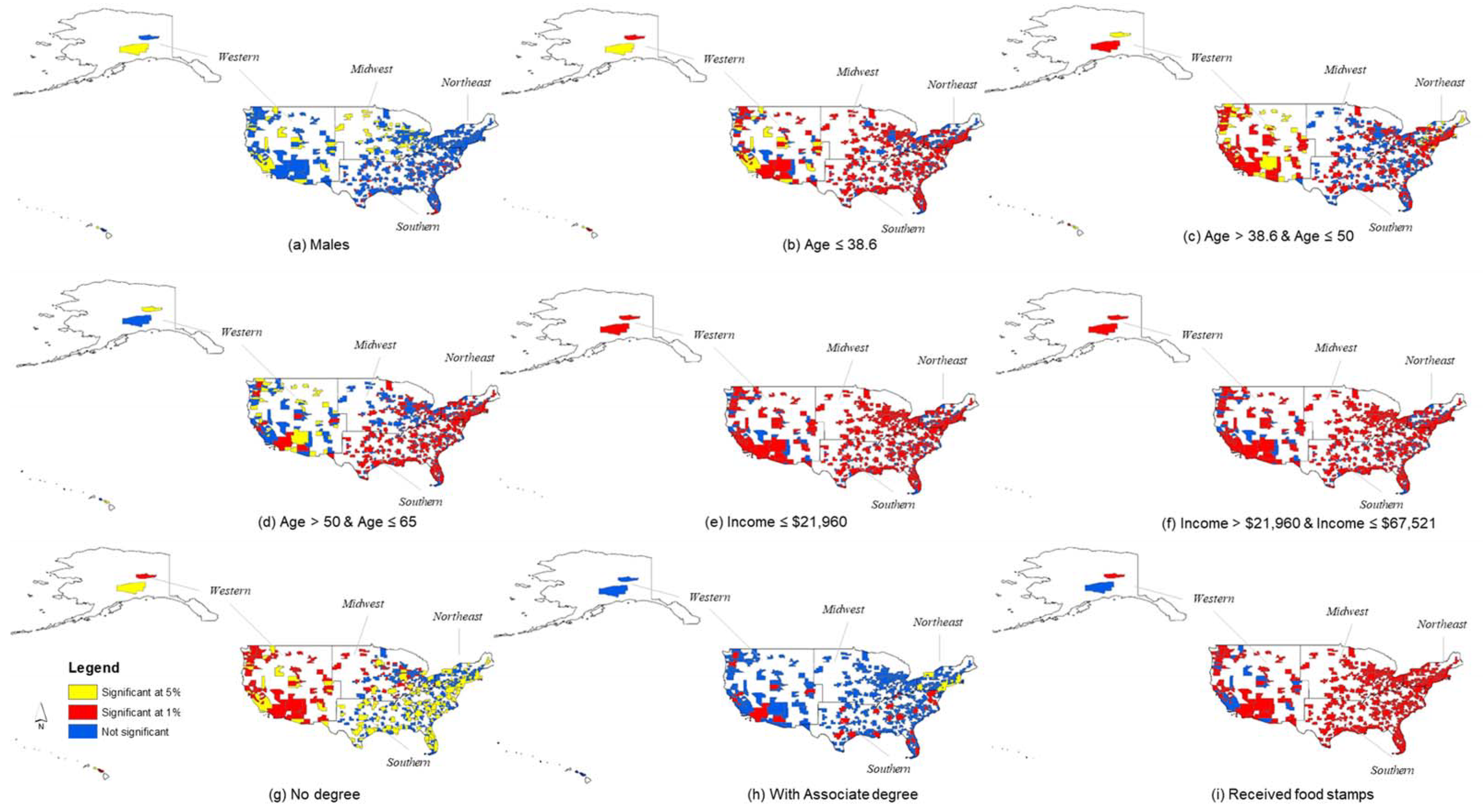
Conclusion and Future Research
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- 2013 National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Urban–Rural Classification Scheme for Counties, https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/sr_02/sr02_166.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), 2020, https://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS/Dataset_Documentation/NHIS/2020/srvydesc-508.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Poverty income threshold of $21,960 for a family size of 3: https://www.statista.com/statistics/183657/average-size-of-a-family-in-the-us/.
- US Department of Health and Human Services 2021, https://aspe.hhs.gov/topics/poverty-economic-mobility/poverty-guidelines/prior-hhs-poverty-guidelines-federal-register-references/2021-poverty-guidelines.
- Statistica.com, https://www.statista.com/statistics/241494/median-age-of-the-us-population/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Food and Nutrition Service, United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), https://www.fns.usda.gov/pd/snap-state-activity-reports (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Pruitt, S., Leonard, T., Xuan, L., Amory, R., Higashi, R., Nguyen, O., & Swales, S. (2016). Who is food insecure? Implications for targeted recruitment and outreach, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005–2010. Retrieved June 6, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Larson, J. ; Moseley, W. G. Reaching the limits: a geographic approach for understanding food insecurity and household hunger mitigation strategies in Minneapolis-Saint Paul, USA. GeoJournal, 2012; 77, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Feeding America, https://map.feedingamerica.org/?_ga=2.156318203.1397879697.1691855096-248042924.1691855096 (accessed on August 10, 2023).
- Coleman-Jensen, A., Rabbitt, M. P., Gregory, C. A., & Singh, A. (2022). Household food security in the United States in 2021. Economic Research Report Number 309, US Department of Agriculture, accessed on July 23, 2023, https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/104656/err-309.pdf.
- International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI). https://www.ifpri.org/topic/food-security (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- HungerMap, World Food Programme (WFP), https://static.hungermapdata.org/insight-reports/2022-04-25/rbbsummary.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2022).
- Prosekov, A. Y.; Ivanova, S. A. Food security: The challenge of the present. Geoforum, 2018; 91, 73-77. [CrossRef]
- SNAP Eligibility, Food and Nutrition Service, United States Department of Agriculture, https://www.fns.usda.gov/snap/recipient/eligibility, (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Welch, T. F. Equity in transport: The distribution of transit access and connectivity among affordable housing units. Transport policy, 2013; 30, 283-293. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Woo, M. The relationship between transit rich neighborhoods and transit ridership: Evidence from the decentralization of poverty. Applied Geography, 2017; 86, 183-196. [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.;Huang, Y.; Yip, T. L.; Li, V. J. . Does rail transit development gentrify neighborhoods? Evidence from Hong Kong. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2022; 155, 354-372. [CrossRef]
- Derakhti, L.; Baeten, G. Contradictions of transit-oriented development in low-income neighborhoods: The case study of Rosengård in Malmö, Sweden. Urban Science, 2020; 4(2), 20.
- Gupta, S., “How can Delhi provide affordable housing near transit to its poor”, DownToEarth, https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/governance/how-can-delhi-provide-affordable-housing-near-transit-to-its-poor-73619 (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Sharp, S. “Affordable Housing Rises Next to Blue Line in Long Beach”, Urbanize Los Angeles, 2018, “Affhttps://la.urbanize.city/post/affordable-housing-rises-next-blue-line-long-beach (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- Burrows, M.; Burd, C.; McKenzie, B. Commuting by public transportation in the United States: 2019. American Community Survey Reports 2021, 802.
- Baek, D., 2016. The effect of public transportation accessibility on food insecurity. Eastern Economic Journal, 2016; 42(1), 104-134.
- Gundersen, C.; Kreider, B.; Pepper, J. The economics of food insecurity in the United States. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy, 2011; 33(3), 281-303. [CrossRef]
- Baek, D. (2014). Essays on Poverty and Infant Health. Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College.
- Martinez, J. C.; Clark, J. M.; Gudzune, K. A. Association of personal vehicle access with lifestyle habits and food insecurity among public housing residents. Preventive medicine reports, 2019; 13, 341-345. [CrossRef]
- Swayne, M. R., & Lowery, B. C. (2021). Integrating transit data and travel time into food security analysis: A case study of San Diego, California. Applied Geography, 131, 102461. [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M., Petteway, R., Bacetti, L., Barbot, O., 2011. Healthy Baltimore 2015, 1st ed. Baltimore City Health Department, Baltimore City. http://health.baltimorecity.gov/ sites/default/files/HealthyBaltimore2015_Final_Web.pdf, (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Patil, G. R. ; Sharma, G. Overweight/obesity relationship with travel patterns, socioeconomic characteristics, and built environment. Journal of Transport & Health, 2021; 22, 101240. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





