Submitted:
09 August 2023
Posted:
09 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
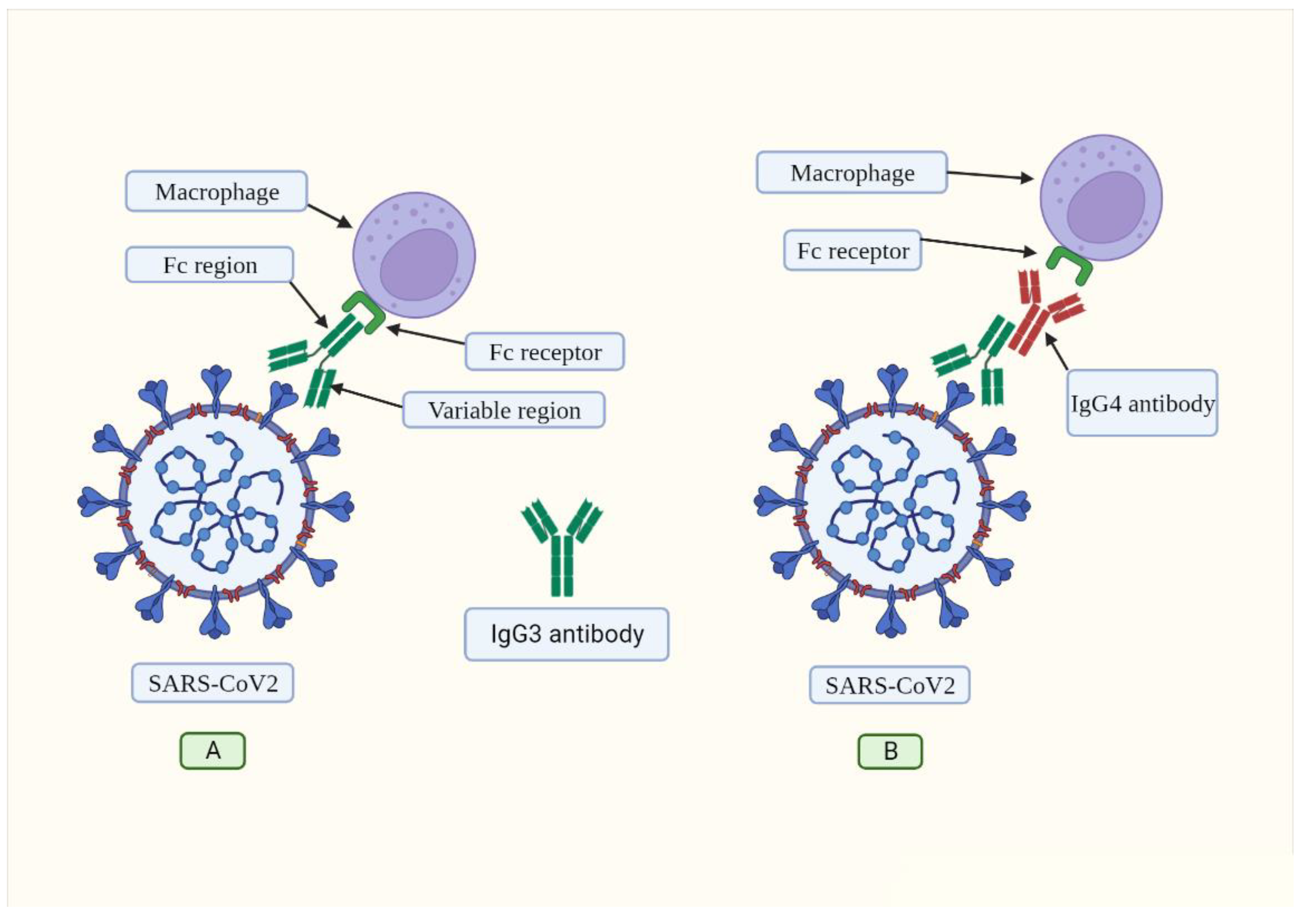
2. IgG4 antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 may help it to evade the immune system
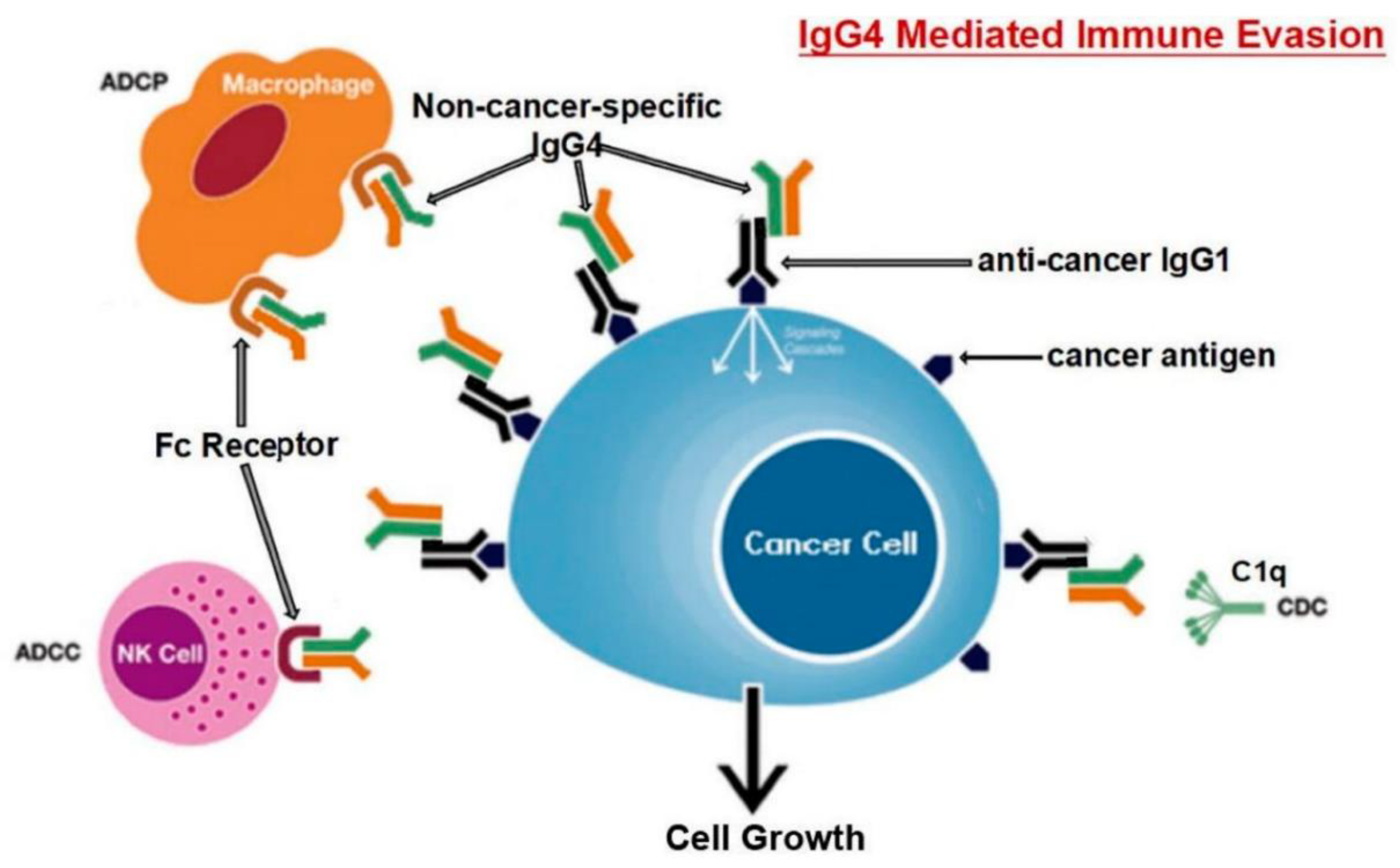
3. Mechanisms of the IgG4-induced immune evasion in SARS-CoV-2 infection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desimmie, B.A.; Raru, Y.Y.; Awadh, H.M.; He, P.; Teka, S.; Willenburg, K.S. Insights into SARS-CoV-2 Persistence and Its Relevance. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q.; Jia, Z.S. Viral (hepatitis C virus, hepatitis B virus, HIV) persistence and immune homeostasis. Immunology 2014, 143, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussani, R.; Zentilin, L.; Correa, R.; Colliva, A.; Silvestri, F.; Zacchigna, S.; Collesi, C.; Giacca, M. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients seemingly recovered from COVID-19. J Pathol 2023, 259, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grey, H.M.; Kunkel, H.G. H Chain Subgroups of Myeloma Proteins and Normal 7s Gamma-Globulin. J Exp Med 1964, 120, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, W.D.; Fahey, J.L. Subclasses of Human Gamma-2-Globulin Based on Differences in the Heavy Polypeptide Chains. Science 1964, 146, 400–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayumi, M.; Kuritani, T.; Kubagawa, H.; Cooper, M.D. IgG subclass expression by human B lymphocytes and plasma cells: B lymphocytes precommitted to IgG subclass can be preferentially induced by polyclonal mitogens with T cell help. J Immunol 1983, 130, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, P.; Rosen, L.B.; Zhang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Dorgham, K.; Philippot, Q.; Rosain, J.; Beziat, V.; et al. Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Netea, M.G.; Rovina, N.; Akinosoglou, K.; Antoniadou, A.; Antonakos, N.; Damoraki, G.; Gkavogianni, T.; Adami, M.E.; Katsaounou, P.; et al. Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients with Severe Respiratory Failure. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Gonzalez, J.; Edwards, K.; Mallajosyula, V.; Buzzanco, A.S.; Sherwood, R.; Buffone, C.; Kathale, N.; Providenza, S.; Xie, M.M.; et al. Proinflammatory IgG Fc structures in patients with severe COVID-19. Nat Immunol 2021, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.L.; Ehrbar, D.J.; Hunt, D.T.; Girardin, R.C.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Payne, A.F.; Sowizral, M.; Varney, S.; Kulas, K.E.; Demarest, V.L.; et al. Serological analysis reveals an imbalanced IgG subclass composition associated with COVID-19 disease severity. Cell Rep Med 2021, 2, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.D.; da Costa, H.H.M.; Correa, V.A.; de, S.L.A.K.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; De Gaspari, E.; Hong, M.A.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; Prudencio, C.R. Assessment of avidity related to IgG subclasses in SARS-CoV-2 Brazilian infected patients. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 17642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Jia, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; et al. The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 632814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irrgang, P.; Gerling, J.; Kocher, K.; Lapuente, D.; Steininger, P.; Habenicht, K.; Wytopil, M.; Beileke, S.; Schafer, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Class switch toward noninflammatory, spike-specific IgG4 antibodies after repeated SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Sci Immunol 2023, 8, eade2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Torre, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Strollo, M.; Ramirez, G.A.; Dagna, L.; Tresoldi, M.; group, C.O.-B.s. Serum IgG4 level predicts COVID-19 related mortality. Eur J Intern Med 2021, 93, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Torre, E.; Campochiaro, C.; Cavalli, G.; De Luca, G.; Napolitano, A.; La Marca, S.; Boffini, N.; Da Prat, V.; Di Terlizzi, G.; Lanzillotta, M.; et al. Interleukin-6 blockade with sarilumab in severe COVID-19 pneumonia with systemic hyperinflammation: an open-label cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2020, 79, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Torre, E.; Della-Torre, F.; Kusanovic, M.; Scotti, R.; Ramirez, G.A.; Dagna, L.; Tresoldi, M. Treating COVID-19 with colchicine in community healthcare setting. Clin Immunol 2020, 217, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Torre, E.; Lanzillotta, M.; Campochiaro, C.; Cavalli, G.; De Luca, G.; Tomelleri, A.; Boffini, N.; De Lorenzo, R.; Ruggeri, A.; Rovere-Querini, P.; et al. Respiratory Impairment Predicts Response to IL-1 and IL-6 Blockade in COVID-19 Patients With Severe Pneumonia and Hyper-Inflammation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 675678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xia, T.; Shin, W.J.; Yu, K.M.; Jung, W.; Herrmann, A.; Foo, S.S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Viral Mimicry of Interleukin-17A by SARS-CoV-2 ORF8. mBio 2022, 13, e0040222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, J.N.; Benson, E.M. The role of human interleukin-6 in B-cell isotype regulation and differentiation. Cell Immunol 1990, 125, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Noma, T.; Kou, K.; Yoshizawa, I.; Yata, J. Regulation of human IgG subclass production by cytokines: human IgG subclass production enhanced differentially by interleukin-6. Immunology 1995, 84, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Dulak, N.A.; Trzcinski, R. Disguised aspects of IgG4. Eur J Intern Med 2022, 95, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirula, A.; Glaser, S.M.; Kalled, S.L.; Taylor, F.R. What is IgG4? A review of the biology of a unique immunoglobulin subtype. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2011, 23, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, S.K.; Burbelo, P.D.; Chetchotisakd, P.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; Kiertiburanakul, S.; Shaw, P.A.; Kirk, J.L.; Jutivorakool, K.; Zaman, R.; Ding, L.; et al. Adult-onset immunodeficiency in Thailand and Taiwan. N Engl J Med 2012, 367, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Bastard, P.; Bolze, A.; Jouanguy, E.; Zhang, S.Y.; Effort, C.H.G.; Cobat, A.; Notarangelo, L.D.; Su, H.C.; Abel, L.; et al. Life-Threatening COVID-19: Defective Interferons Unleash Excessive Inflammation. Med 2020, 1, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Bastard, P.; Liu, Z.; Le Pen, J.; Moncada-Velez, M.; Chen, J.; Ogishi, M.; Sabli, I.K.D.; Hodeib, S.; Korol, C.; et al. Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrestier, R.; Bastard, P.; Belmondo, T.; Voiriot, G.; Urbina, T.; Luyt, C.E.; Gervais, A.; Bizien, L.; Segaux, L.; Ben Ahmed, M.; et al. Auto-antibodies against type I IFNs in > 10% of critically ill COVID-19 patients: a prospective multicentre study. Ann Intensive Care 2022, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Diaz, A.; Romero, M.; Mendez, N.V.; Landin, A.M.; Blomberg, B.B. Effects of age on H1N1-specific serum IgG1 and IgG3 levels evaluated during the 2011-2012 influenza vaccine season. Immun Ageing 2013, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavacini, L.A.; Kuhrt, D.; Duval, M.; Mayer, K.; Posner, M.R. Binding and neutralization activity of human IgG1 and IgG3 from serum of HIV-infected individuals. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2003, 19, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, M.S.; Zimmerman, M.G.; Kauffman, R.C.; Mantus, G.; Linderman, S.L.; Hudson, W.H.; Vanderheiden, A.; Nyhoff, L.; Davis, C.W.; Adekunle, O.; et al. Rapid Generation of Neutralizing Antibody Responses in COVID-19 Patients. Cell Rep Med 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, L.; Martinuzzi, D.; Hyseni, I.; Benincasa, L.; Molesti, E.; Casa, E.; Lapini, G.; Piu, P.; Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; et al. Comparative analyses of SARS-CoV-2 binding (IgG, IgM, IgA) and neutralizing antibodies from human serum samples. J Immunol Methods 2021, 489, 112937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C.; Dieges, P.H.; Knul-Bretlova, V.; Vooren, P.; Aalbers, M.; van Leeuwen, J. IgG4 as a blocking antibody. Clin Rev Allergy 1983, 1, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoguina, J.S.; Weyand, E.; Larbi, J.; Hoerauf, A. T regulatory-1 cells induce IgG4 production by B cells: role of IL-10. J Immunol 2005, 174, 4718–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefowicz, S.Z.; Lu, L.F.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol 2012, 30, 531–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduro, M.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Tissue Tregs. Annu Rev Immunol 2016, 34, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, M.; Arrigoni, A.; Rossetti, G.; Gruarin, P.; Ranzani, V.; Politano, C.; Bonnal, R.J.P.; Provasi, E.; Sarnicola, M.L.; Panzeri, I.; et al. Transcriptional Landscape of Human Tissue Lymphocytes Unveils Uniqueness of Tumor-Infiltrating T Regulatory Cells. Immunity 2016, 45, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plitas, G.; Konopacki, C.; Wu, K.; Bos, P.D.; Morrow, M.; Putintseva, E.V.; Chudakov, D.M.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer. Immunity 2016, 45, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, A.M.; Kiner, E.; Ergun, A.; Park, J.S.; Asinovski, N.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Kilcoyne, A.; Paoluzzi-Tomada, E.; Weissleder, R.; Mathis, D.; et al. Identification and validation of a tumor-infiltrating Treg transcriptional signature conserved across species and tumor types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E10672–E10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.M.; Hsing, L.; Pham, T.T.; Rudensky, A.Y. Coordination of early protective immunity to viral infection by regulatory T cells. Science 2008, 320, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanan, M.; Raynor, J.; Sholl, A.; Wang, M.; Chougnet, C.; Cardin, R.D.; Hildeman, D.A. Tissue-specific control of latent CMV reactivation by regulatory T cells. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1006507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan-Pena, S.; Leon, J.; Chowdhary, K.; Michelson, D.A.; Vijaykumar, B.; Yang, L.; Magnuson, A.M.; Chen, F.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; et al. Profound Treg perturbations correlate with COVID-19 severity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenstein, J.; Melderis, S.; Nosko, A.; Warkotsch, M.T.; Richter, J.V.; Ramcke, T.; Herrnstadt, G.R.; Scheller, J.; Yan, I.; Mittrucker, H.W.; et al. A Novel Role for IL-6 Receptor Classic Signaling: Induction of RORgammat(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs with Enhanced Suppressive Capacity. J Am Soc Nephrol 2019, 30, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhont, S.; Derom, E.; Van Braeckel, E.; Depuydt, P.; Lambrecht, B.N. The pathophysiology of 'happy' hypoxemia in COVID-19. Respir Res 2020, 21, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciabene, A.; Peng, X.; Hagemann, I.S.; Balint, K.; Barchetti, A.; Wang, L.P.; Gimotty, P.A.; Gilks, C.B.; Lal, P.; Zhang, L.; et al. Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature 2011, 475, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElvaney, O.J.; McEvoy, N.L.; McElvaney, O.F.; Carroll, T.P.; Murphy, M.P.; Dunlea, D.M.; Ni Choileain, O.; Clarke, J.; O'Connor, E.; Hogan, G.; et al. Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020, 202, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, M.J.; Vignali, P.D.A.; Mullett, S.J.; Overacre-Delgoffe, A.E.; Peralta, R.M.; Grebinoski, S.; Menk, A.V.; Rittenhouse, N.L.; DePeaux, K.; Whetstone, R.D.; et al. Metabolic support of tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells by lactic acid. Nature 2021, 591, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway Jr, C.A.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Pathogens have evolved various means of evading or subverting normal host defenses. In Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease. 5th edition, Garland Science: 2001.
- Rispens, T.; Meesters, J.; den Bleker, T.H.; Ooijevaar-De Heer, P.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P.W.; Labrijn, A.; Aalberse, R.C. Fc-Fc interactions of human IgG4 require dissociation of heavy chains and are formed predominantly by the intra-chain hinge isomer. Mol Immunol 2013, 53, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, P.; Gilbert, A.E.; Josephs, D.H.; Ali, N.; Dodev, T.; Saul, L.; Correa, I.; Roberts, L.; Beddowes, E.; Koers, A.; et al. IgG4 subclass antibodies impair antitumor immunity in melanoma. J Clin Invest 2013, 123, 1457–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; et al. An immune evasion mechanism with IgG4 playing an essential role in cancer and implication for immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




