Submitted:
08 August 2023
Posted:
09 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental animals and sample collection
2.2. Sequence splicing and ASV annotation
2.3. Extraction of serum samples
2.4. Chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis
2.4.1. Chromatographic conditions
2.5. Statistical analysis
2.5.1. Analysis of microbiota diversity and composition differences
2.5.2. Construction of cecal microbial co-abundance groups
2.5.3. Serum metabolomics analysis
3. Results
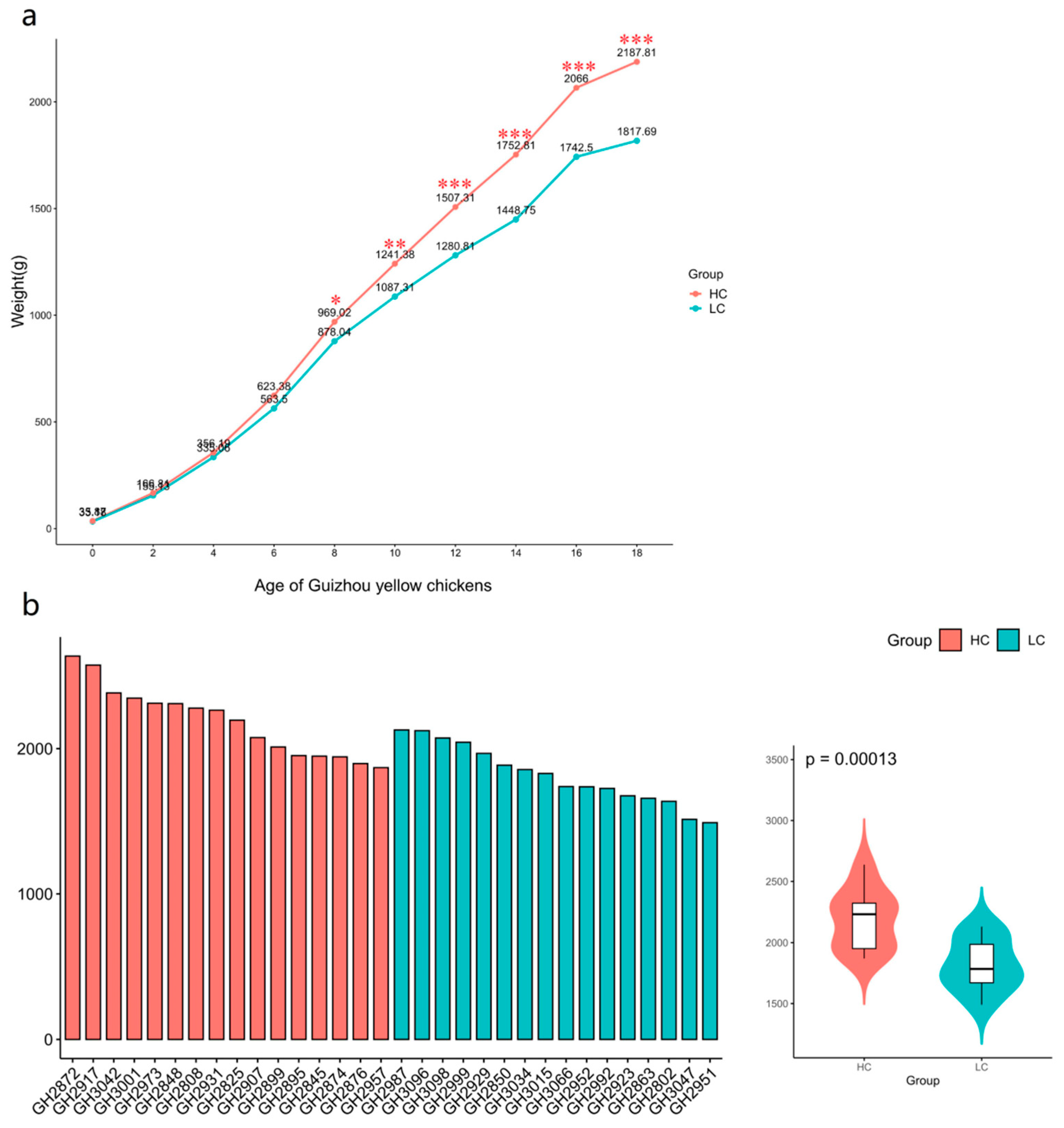
3.1. Growth performance of the study chickens
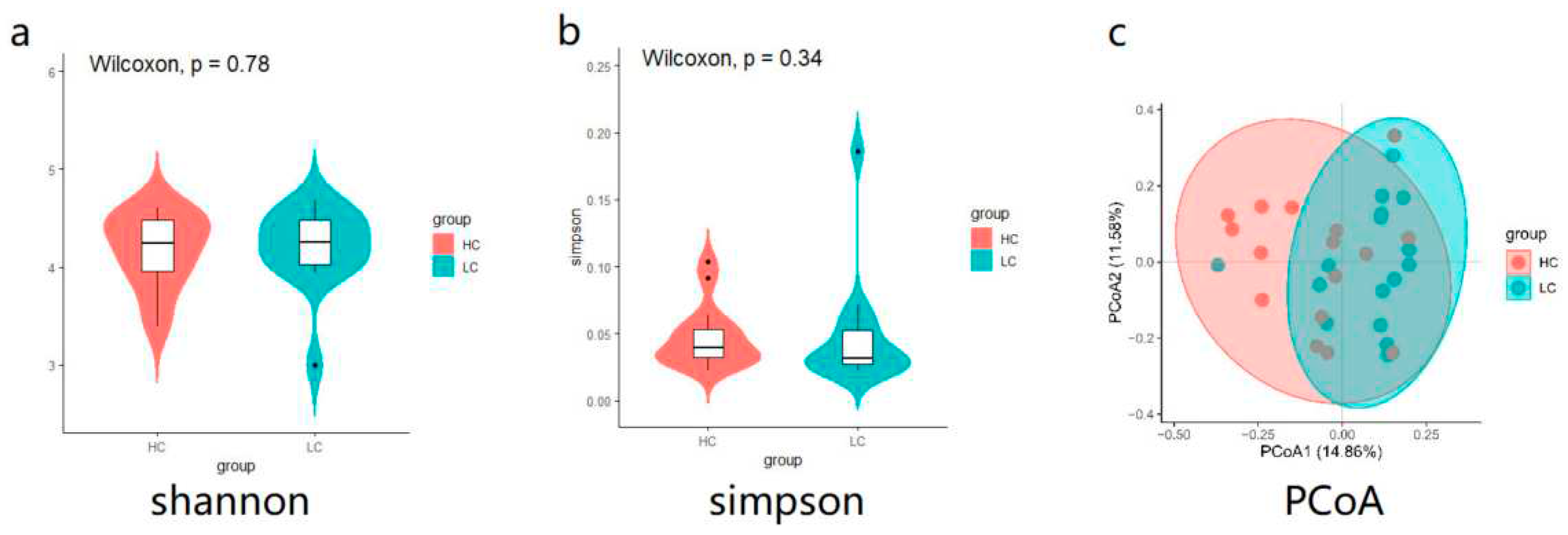
3.2. Cecal microbial diversity in high versus low weight chickens
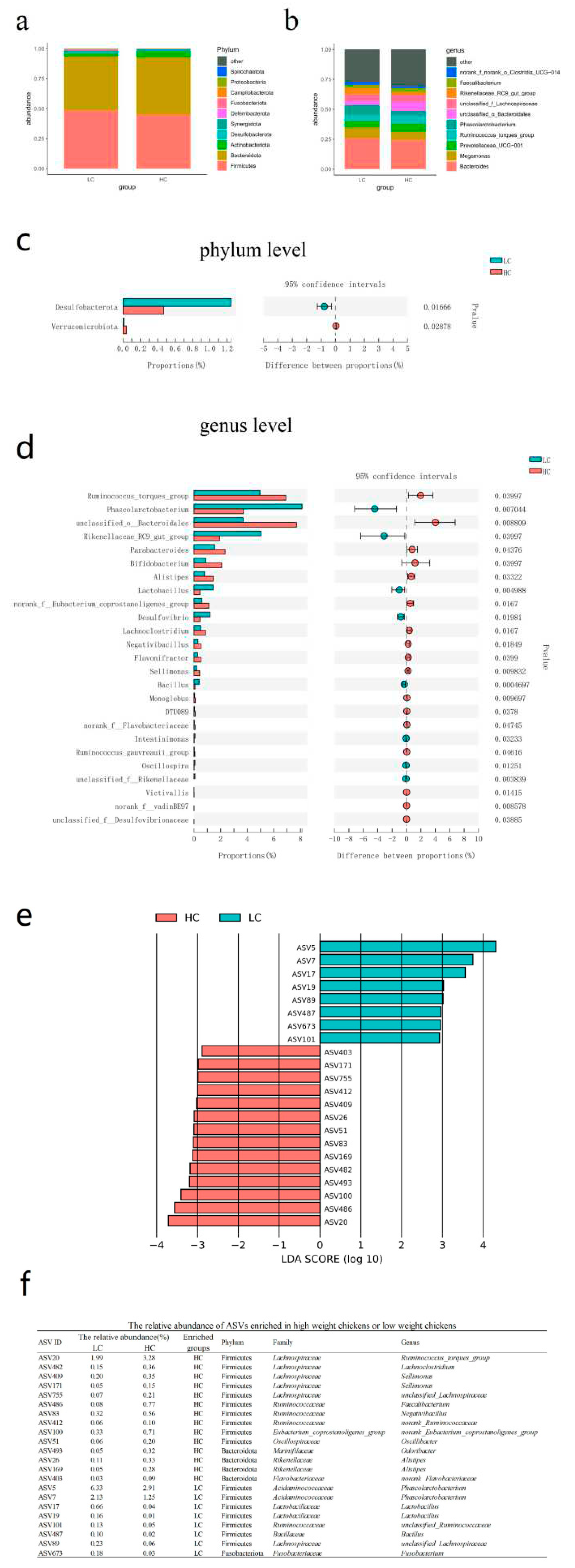
3.3. Bacteria differentially abundant in HC versus LC
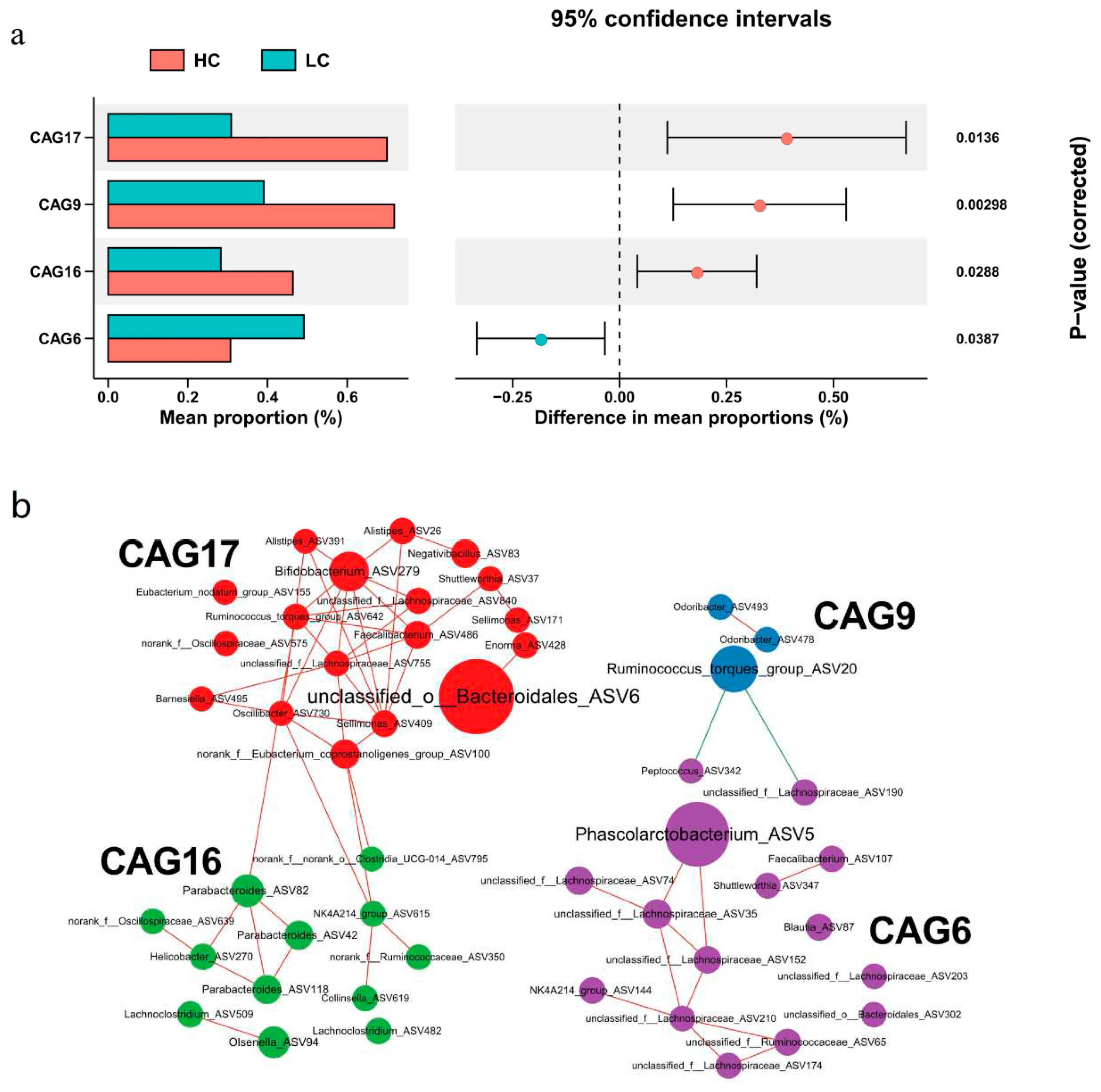
3.4. Identification of co-abundance groups (CAG) associated with body weight
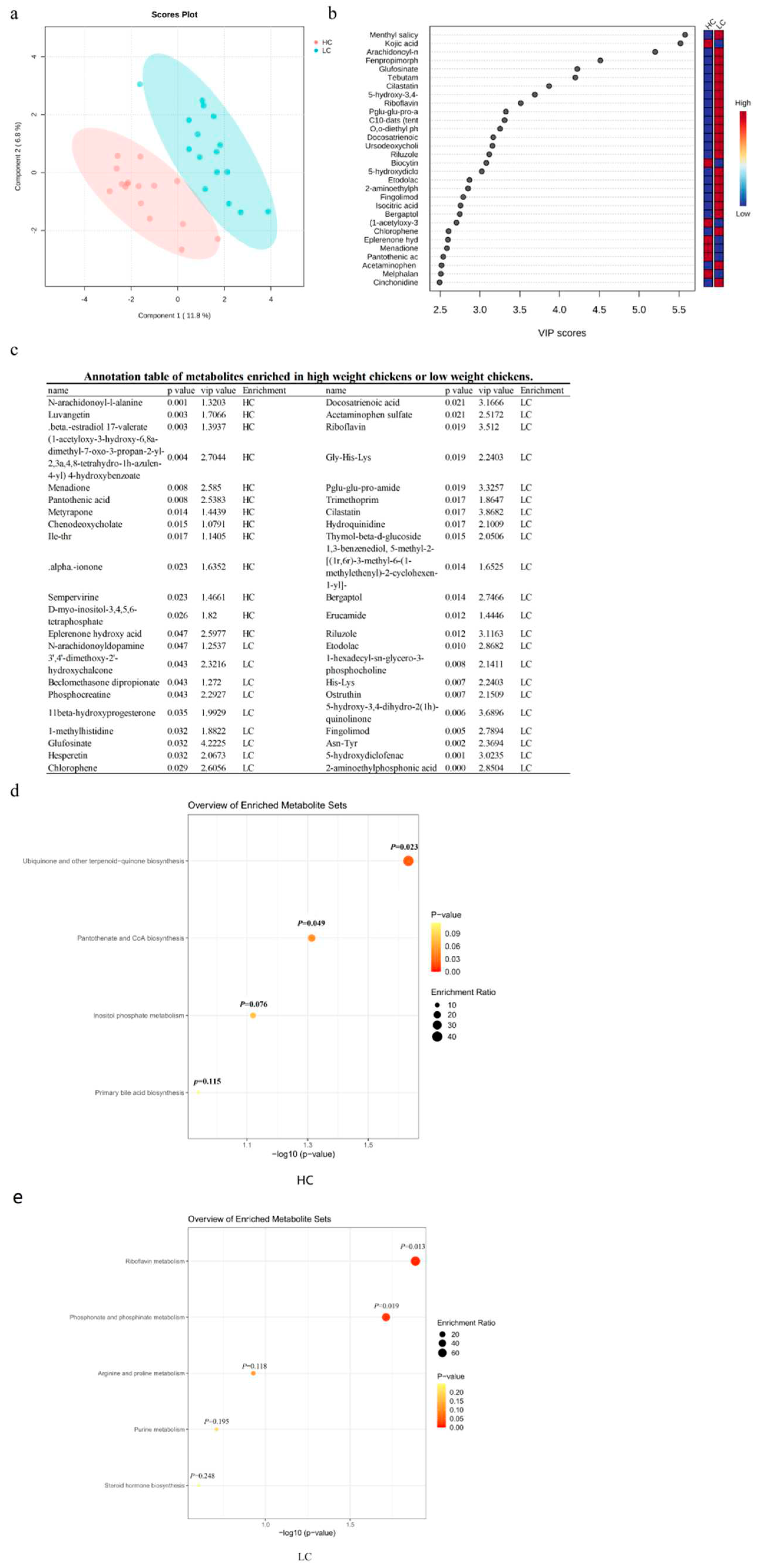
3.5. Differential serum metabolites between HC and LC
3.6. Correlation analysis reveals relationships between the cecal microbiota and serum metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, M.; Conchedda, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Cinardi, G.; Linard, C.; Nicolas, G.; Thanapongtharm, W.; D'Aietti, L.; Wint, W.; Newman, S.H.; et al. Income disparities and the global distribution of intensively farmed chicken and pigs. Plos One 2015, 10, e0133381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoro, J.; Muasya, T.K.; Mbuza, F.; Mbuthia, J.; Kahi, A.K. Farmers' breeding practices and traits of economic importance for indigenous chicken in RWANDA. Trop Anim Health Prod 2018, 50, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Xing, T.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. The effect of breed and age on the growth performance, carcass traits and metabolic profile in breast muscle of Chinese indigenous chickens. Foods 2022, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, F. Effects of different raising systems on growth performance, carcass, and meat quality of medium-growing chickens. J Appl Anim Res 2017, 1, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Bian, C.; Tian, Y.; Sun, G.; Han, R.; Liu, X.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic determinism of growth traits in a Gushi-Anka F2 chicken population. Heredity (Edinb) 2021, 126, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tobe, K. The gut microbiome: a core regulator of metabolism. J Endocrinol 2023, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Li, N.; Duan, X.; Niu, H. Interaction between the gut microbiome and mucosal immune system. Mil Med Res 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevelline, B.K.; Kohl, K.D. The gut microbiome influences host diet selection behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.a. 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Carrasco, J.M.; Casanova, N.A.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Microbiota, gut health and chicken productivity: What is the connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ansari, A.R.; Akhtar, M.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Cui, L.; Nafady, A.A.; Elokil, A.A.; Abdel-Kafy, E.M.; et al. Caecal microbiota could effectively increase chicken growth performance by regulating fat metabolism. Microb Biotechnol 2022, 15, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Akhtar, M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liang, Y.; Shi, D.; Cheng, R.; Cui, L.; Hu, Y.; Nafady, A.A.; et al. Chicken jejunal microbiota improves growth performance by mitigating intestinal inflammation. Microbiome 2022, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Lan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cao, G.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immunity, short chain fatty acid production, antioxidant capacity, and cecal microflora in broilers. Poult Sci 2021, 100, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathima, S.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Adams, D.; Selvaraj, R.K. Gastrointestinal microbiota and their manipulation for improved growth and performance in chickens. Foods 2022, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, R.; Ansari, A.R.; Elokil, A.A.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Nafady, A.A.; Liu, H. Sex differences in growth performance are related to cecal microbiota in chicken. Microb Pathog 2021, 150, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Long, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Metabolic and inflammatory linkage of the chicken cecal microbiome to growth performance. Front Microbiol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Rosa, F.; Rossi, N.; Martin, T.C.; Mohney, R.P.; Li, W.; de Rinaldis, E.; Bell, J.T.; Venter, J.C.; et al. Interplay between the human gut microbiome and host metabolism. Nat Commun 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bäckhed, F. Diet–microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; McLean, J.A. Untargeted metabolomics strategies-Challenges and emerging directions. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Fang, S.; Wei, H.; He, M.; Fu, H.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, H.; et al. Prevotella copri increases fat accumulation in pigs fed with formula diets. Microbiome 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.Y.; Sun, H.Z.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, J.X.; Guan, L.L. Multi-omics reveals that the rumen microbiome and its metabolome together with the host metabolome contribute to individualized dairy cow performance. Microbiome 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, B.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G. Integration of lipidomics and metabolomics for in-depth understanding of cellular mechanism and disease progression. J Genet Genomics 2020, 47, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Misra, B.B.; Liang, L.; Bi, D.; Weng, W.; Wu, W.; Cai, S.; Qin, H.; Goel, A.; Li, X.; et al. Integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis reveals a novel interplay between commensal bacteria and metabolites in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4101–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mou, T.; Rao, Y.; Yang, D.; Long, G.; Lin, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, F. Determination and correlation analysis of body size, slaughter performance, meat quality of Guizhou yellow chicken (in Chinese). Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2021, 49, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Niu, H.; Tian, R.; Wang, H.; Pang, H.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Alterations in the gut microbiome and metabolism with coronary artery disease severity. Microbiome 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, A.; Chan, E.K.F. Combining partial correlation and an information theory approach to the reversed engineering of gene co-expression networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Fang, S.; He, M.; Huang, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Huang, L. Age-based dynamic changes of phylogenetic composition and interaction networks of health pig gut microbiome feeding in a uniformed condition. Bmc Vet Res 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Yang, H. Microbial community mapping in intestinal tract of broiler chicken. Poult Sci 2017, 96, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lkhagva, E.; Chung, H.J.; Hong, J.; Tang, W.; Lee, S.I.; Hong, S.T.; Lee, S. The regional diversity of gut microbiome along the GI tract of male C57BL/6 mice. Bmc Microbiol 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoman, C.J.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.; Sipos, M.; Goldenfeld, N.D.; White, B.A. The microbiome of the chicken gastrointestinal tract. Anim Health Res Rev 2012, 13, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Ansari, A.R.; Akhtar, M.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Cui, L.; Nafady, A.A.; Elokil, A.A.; Abdel Kafy, E.S.M.; et al. Caecal microbiota could effectively increase chicken growth performance by regulating fat metabolism. Microb Biotechnol 2022, 15, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Galperin, M.Y. A genomic update on clostridial phylogeny: Gram-negative spore formers and other misplaced clostridia. Environ Microbiol 2013, 15, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogal, A.; Louca, P.; Zhang, X.; Wells, P.M.; Steves, C.J.; Spector, T.D.; Falchi, M.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. Circulating levels of the short-chain fatty acid acetate mediate the effect of the gut microbiome on visceral fat. Front Microbiol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bai, Y.; Tao, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, S. Fiber-rich foods affected gut bacterial community and short-chain fatty acids production in pig model. J Funct Foods 2019, 57, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Calderón, P.; Wiedemann, L.; Benítez-Páez, A. The microbiota composition drives personalized nutrition: Gut microbes as predictive biomarkers for the success of weight loss diets. Front Nutr 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.M.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The Genus Alistipes: Gut Bacteria With Emerging Implications to Inflammation, Cancer, and Mental Health. Front Immunol 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Rehman, A.; Dittrich, M.; Groen, A.K.; Hermanns, H.M.; Seyfried, F.; Beyersdorf, N.; Dandekar, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Geier, A. Fecal SCFAs and SCFA-producing bacteria in gut microbiome of human NAFLD as a putative link to systemic T-cell activation and advanced disease. United European Gastroenterol J 2018, 6, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kononen, E.; Rautio, M.; Liu, C.; Bryk, A.; Eerola, E.; Finegold, S.M. Alistipes onderdonkii sp. nov. and Alistipes shahii sp. nov., of human origin. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006, 56, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Yang, X.; Yu, J. Intake of total saponins and polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum affects the gut microbiota in diabetic rats. Phytomedicine 2017, 26, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, B.; Yoo, J.E.; Lee, Y.M.; Ko, G. Sellimonas intestinalis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2016, 66, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Price, J.; Arze, C.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Schirmer, M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Poon, T.W.; Andrews, E.; Ajami, N.J.; Bonham, K.S.; Brislawn, C.J.; et al. Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature 2019, 569, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, F.; Heller, A.; Rippke, F.; Tausch, I. Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. Am J Clin Dermatol 2002, 3, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liang, S.; Wu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xing, G.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, M.; et al. Effects of pantothenic acid on growth performance and antioxidant status of growing male white Pekin ducks. Poult Sci 2020, 99, 4436–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, E.; Ito, J.; Wu, Z.; Nakamura, T.; Wahida, A.; Doll, S.; Tonnus, W.; Nepachalovich, P.; Eggenhofer, E.; Aldrovandi, M.; et al. A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2022, 608, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.H.; Amoah, K.; Leng, Q.Y.; Zheng, J.H.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, L. Poultry response to heat stress: Its physiological, metabolic, and genetic implications on meat production and quality including strategies to improve broiler production in a warming world. Front Vet Sci 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ou, Z.; Peng, Y. Phascolarctobacterium faecium abundant colonization in human gastrointestinal tract. Exp Ther Med 2017, 14, 3122–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.M.; Shah, T.; Deshpande, S.; Jakhesara, S.J.; Koringa, P.G.; Rank, D.N.; Joshi, C.G. High through put 16S rRNA gene-based pyrosequencing analysis of the fecal microbiota of high FCR and low FCR broiler growers. Mol Biol Rep 2012, 39, 10595–10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; An, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; et al. Effects of different ambient temperatures on caecal microbial composition in broilers. Pol J Microbiol 2021, 70, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaboli, G.; Huang, X.; Feng, X.; Ahn, D.U. How can heat stress affect chicken meat quality? -a review. Poult Sci 2019, 98, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A. Heat stress management in poultry. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 2021, 105, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vich, V.A.; Imhann, F.; Collij, V.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Gurry, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Jiang, X.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; et al. Gut microbiota composition and functional changes in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Sci Transl Med 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Yuan, Y.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Differences in Gut Microbiota in Patients With vs Without Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 930–946.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Quan, K.; Feng, C.; Zhang, T.; He, Q.; Kwok, L.; Chen, Y. The Lactobacillus gasseri G098 strain mitigates symptoms of DSS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




