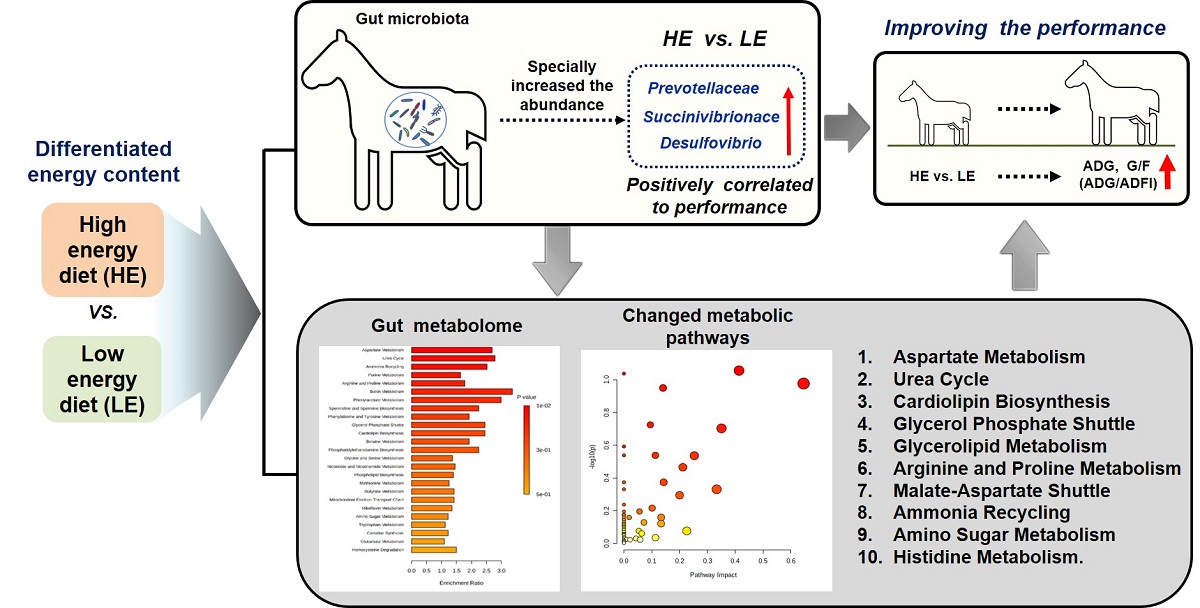
Little information is available regarding the impacts of dietary energy level on the gut microbiota and metabolites of donkeys. This studied aimed to explore the effects of dietary energy content on growth performance, intestinal microbiome and metabolome of Dezhou donkeys. Thirty-six 9-month-old male Dezhou donkeys were assigned to two groups fed low or high content energy diets (LE or HE). Results showed that donkeys fed HE had improved (P < 0.05) the average daily gain (ADG) and feed efficiency (G/F), compared with those receiving LE diet. Compared to the LE group, feeding HE specially increased the abundances of unidentified_Prevotellaceae (P = 0.02) while decreased the richness of unidentified_Ruminococcaceae (P = 0.05) of donkeys. Compared to LE group, feeding HE diet significantly (P < 0.05) affected the metabolic pathways involving the aspartate metabolism and urea cycle. In addition, the increased bacteria and metabolites in the HE-fed group exhibited a positive correlation with improved growth performance of donkeys. Taken together, feeding HE diet increased the richness of some specific bacteria and upregulated growth-related metabolic pathways, which contributed to the augmented growth performance of donkeys. Thus, it is a recommendable dietary strategy to feed HE diet to fattening donkey for superior production performance and feed efficiency.