Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test material
2.2. Sequencing process
2.3. Raw Data Processing and Comparison with Reference Genome Sequence
2.4. Analysis of differential gene expression (DEGs)
2.5. Analysis of GO functional enrichment
2.6. Analysis of KEGG Pathway enrichment
2.7. Analysis of cSNP structure
2.8. Analysis of eggNOG
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of RNA-seq sequence
3.2. Functional annotation of genes
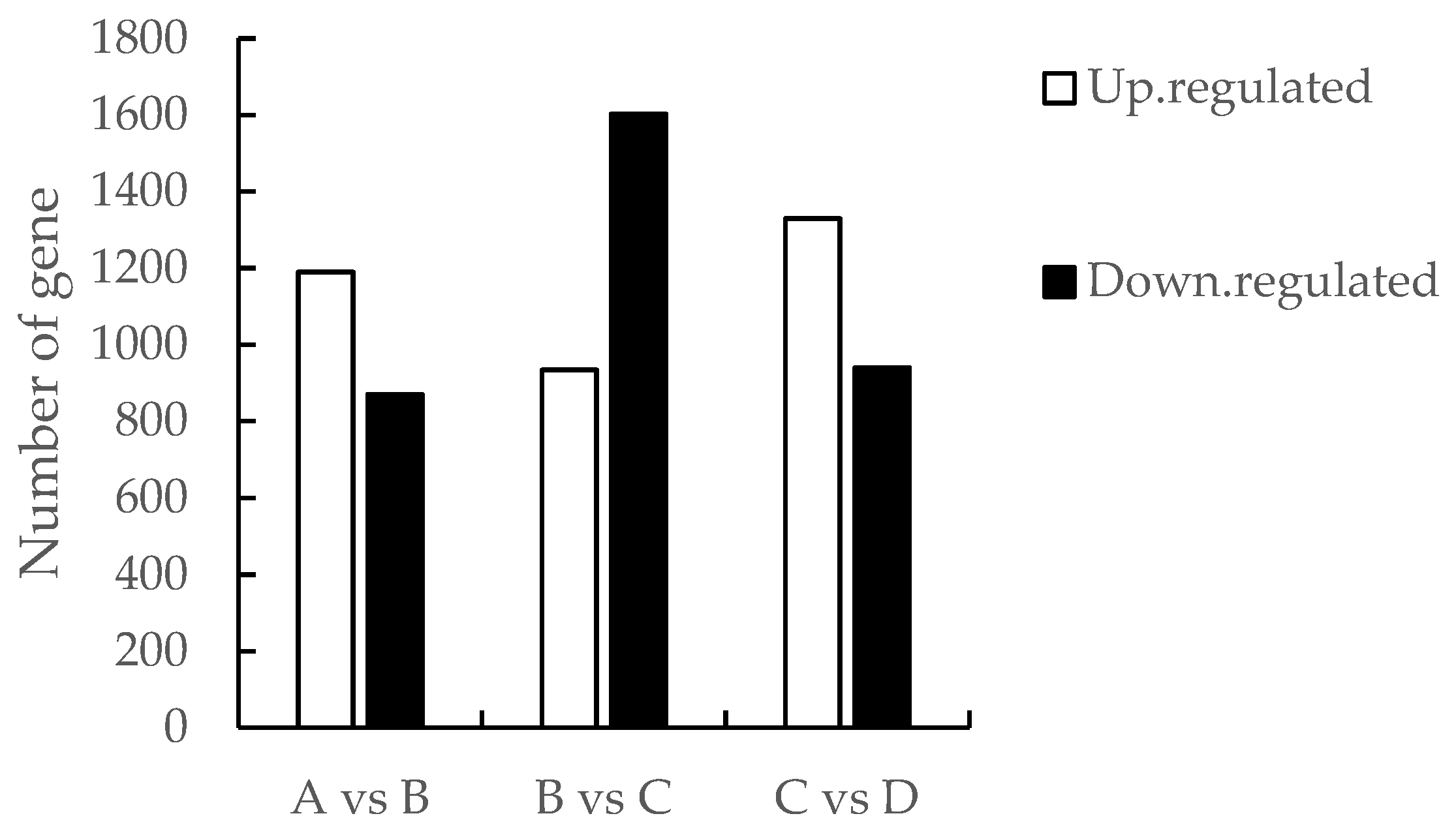
3.3. Domporisom of differentials expressed genes
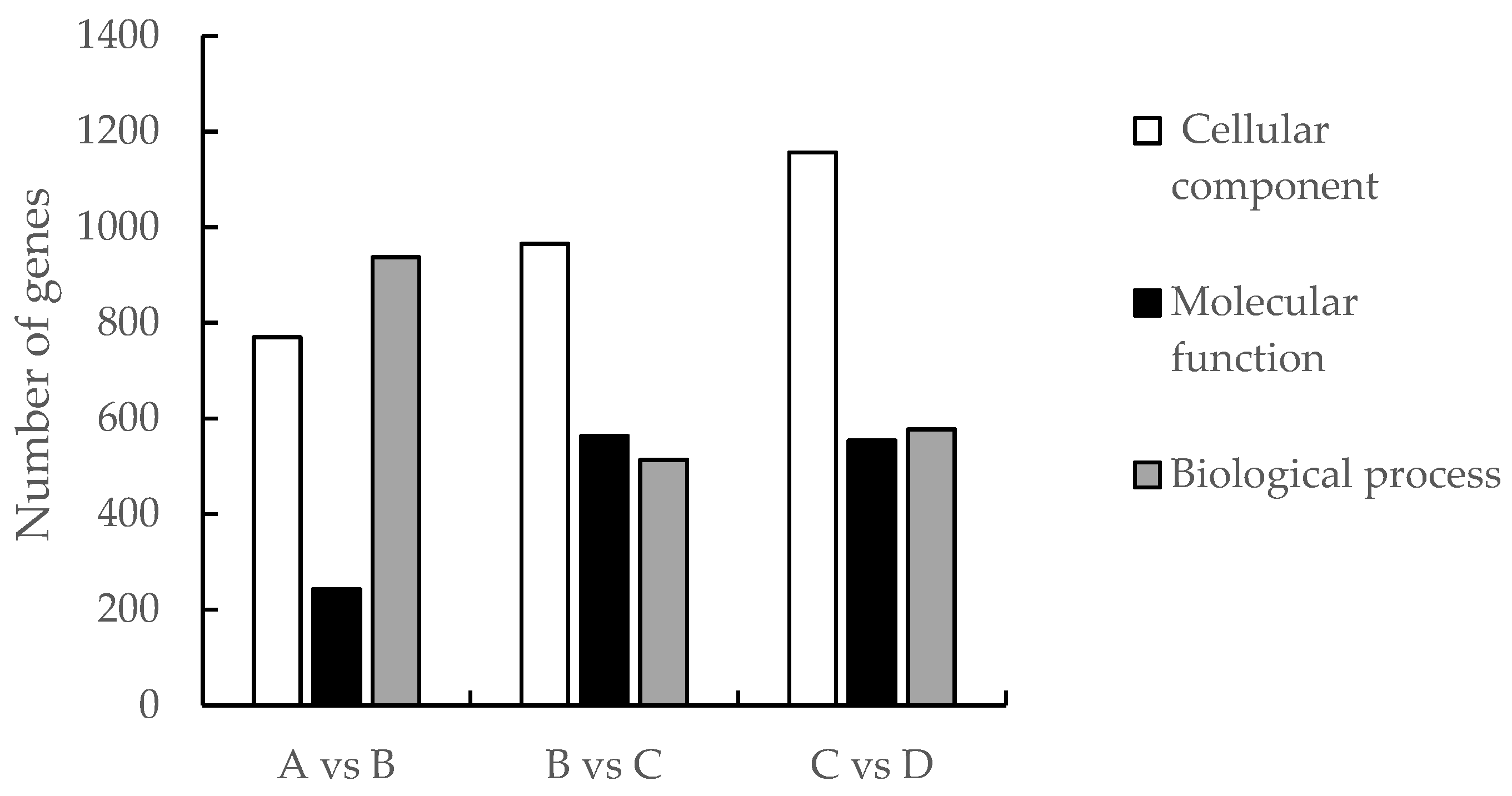
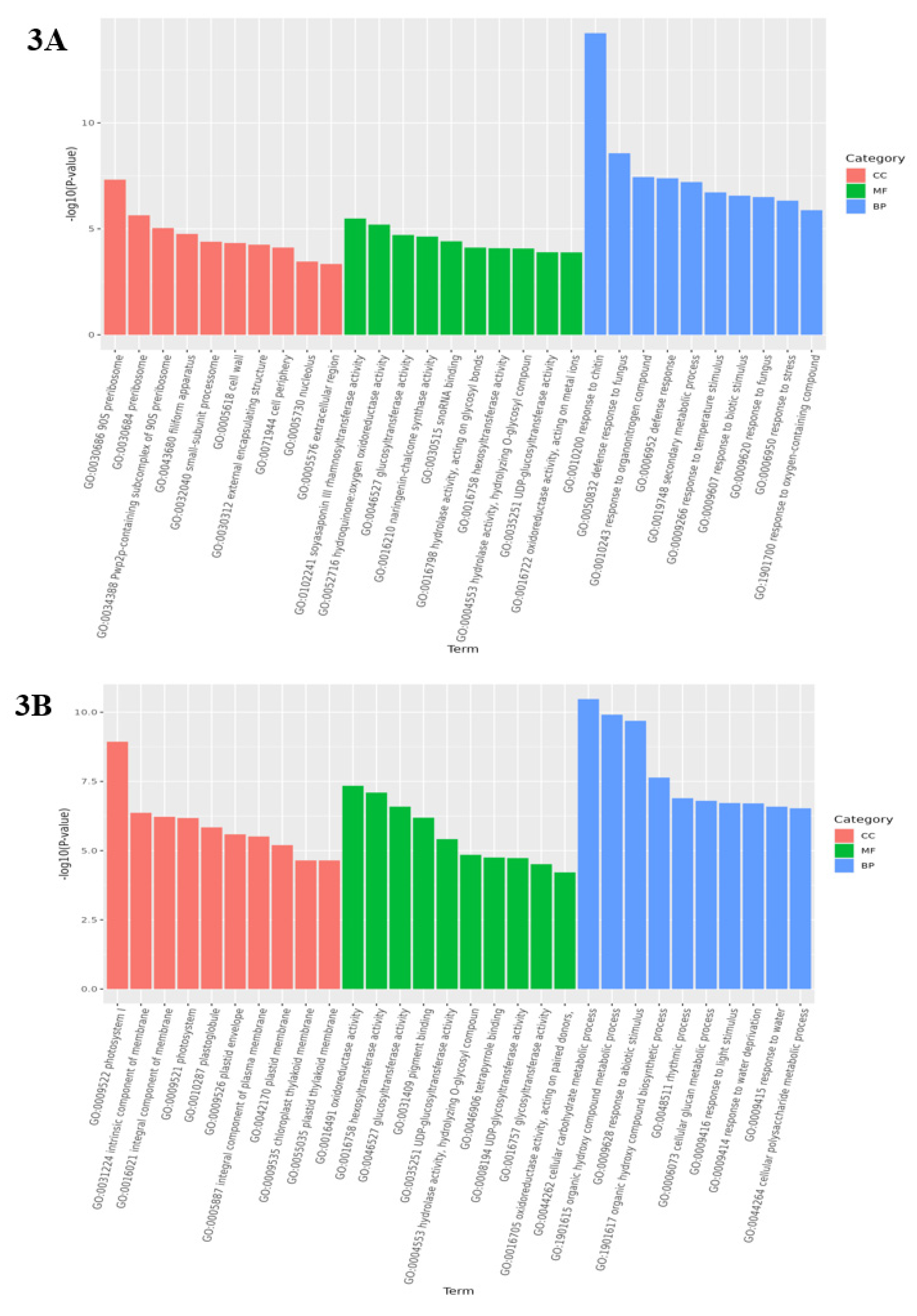
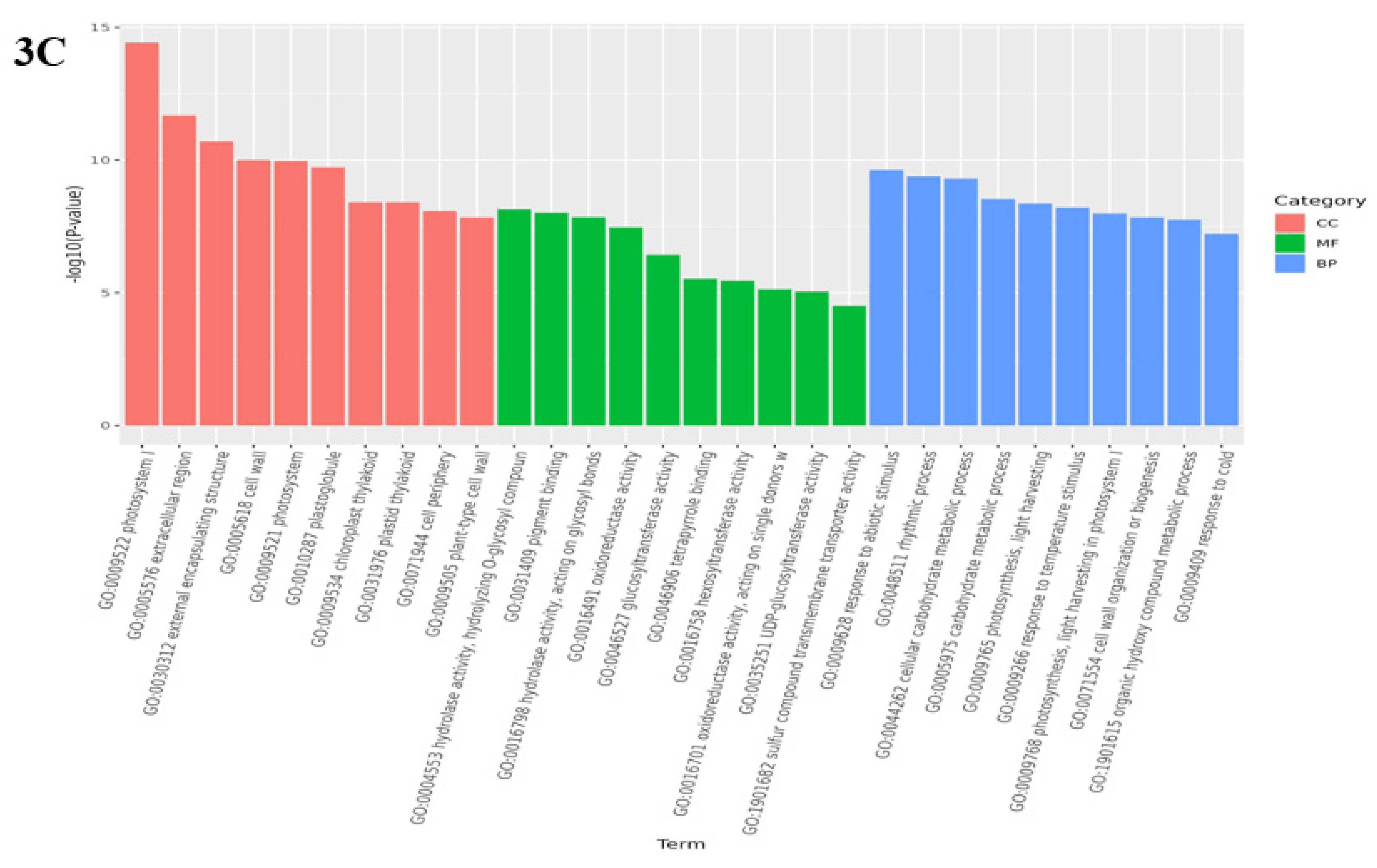
3.4. Analysis of GO function enrichment of differential genes
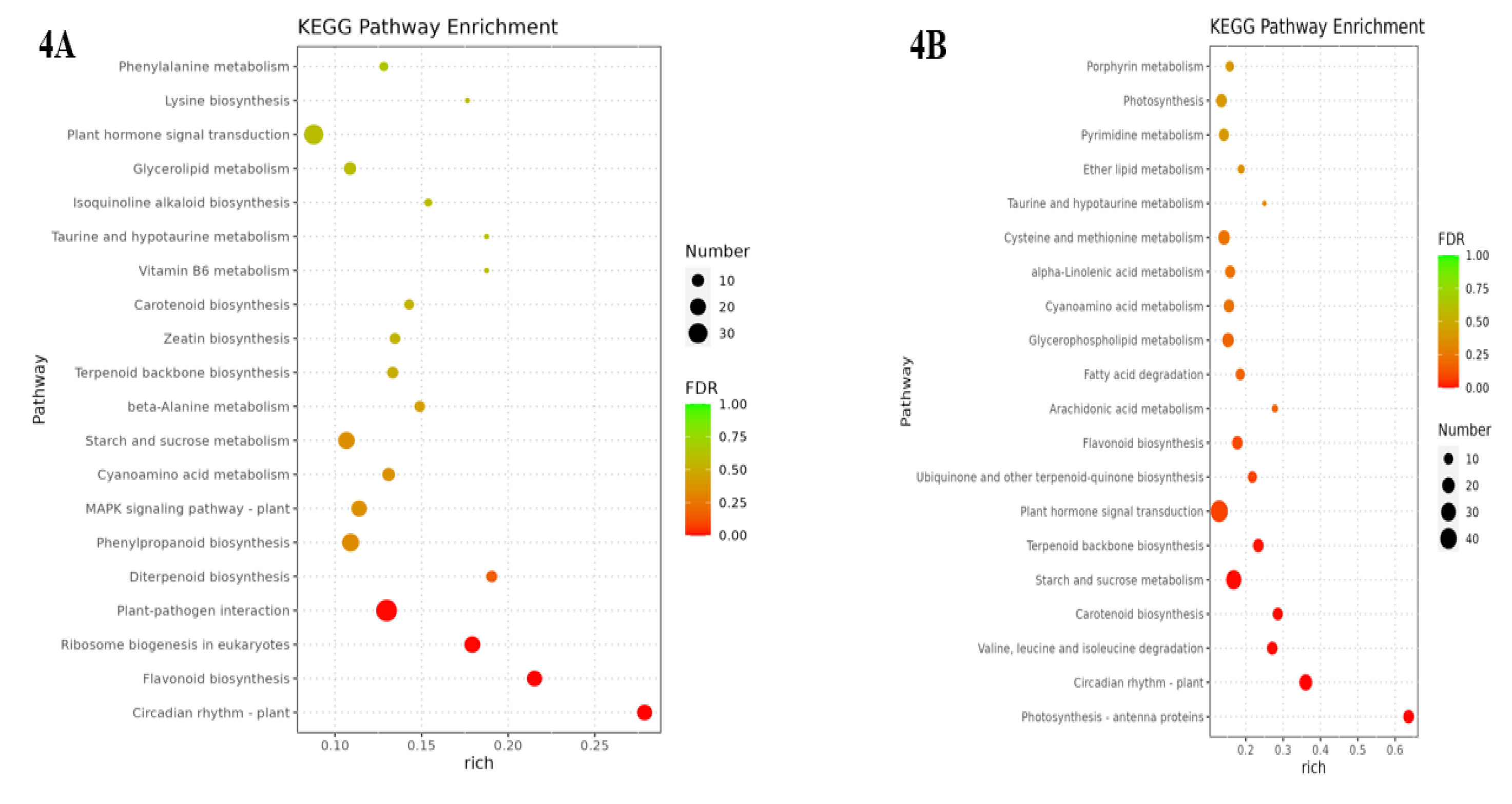
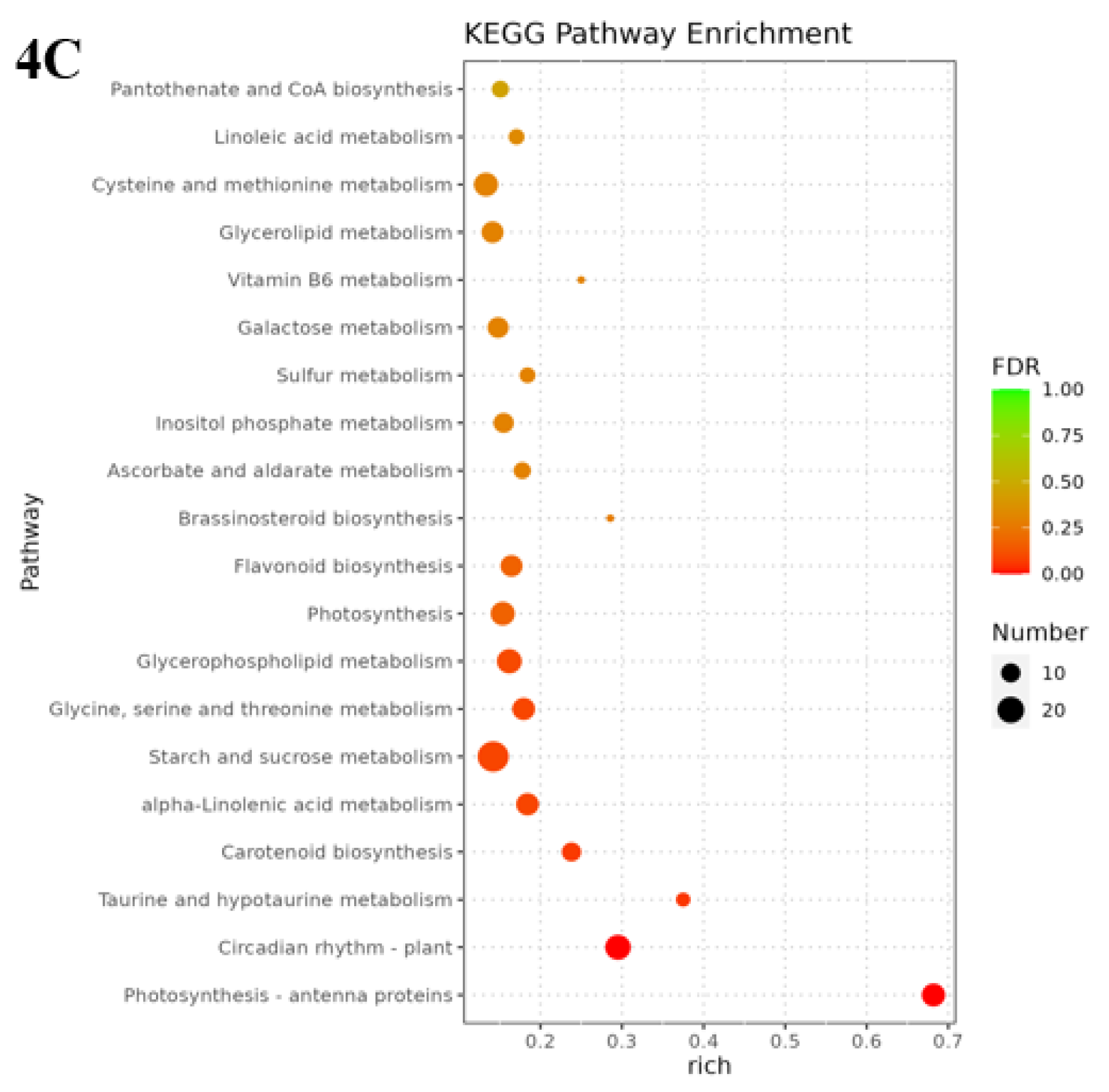
3.5. Analysis of KEGG pathway of differential genes
3.6. Analysis of cSNP
3.7. Functional classification of eggNOG
3.8. Photoperiod-related differentials expressed genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, H.S.; Lei, T.; Shun, X.W.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L.J.; Ku, L.X.; Chen, Y.H. Integrating transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of photoperiod-sensitive in near isogenic maize line under long-day conditions. J. Intege. Age. 2019, 18, 1211-1221. [CrossRef]
- Kathleen, G.; Robertson, C.M.; Integrating circadian dynamics with physiological processes in plants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 598-610. [CrossRef]
- Fernando, A.; George, C.; The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 627-639. [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.S.; Akane, K.; Takato, I.; Circadian Clock and Photoperio5-15dic Flowering in Arabidopsis: CONSTANS Is a Hub for Signal Integration. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 5-15. [CrossRef]
- Soledad, P.; Nathanael, N.; Fran, R.; Weller, J.L.; Bond, Donna.M.; Macknight, R.C. A Point Mutation in Phytochromobilin synthase Alters the Circadian Clock and Photoperiodic Flowering of Medicago truncatula. Plants 2022, 11, 239-239. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.S.; Rugnone, L.M.; Kay, A.S. Light Perception: A Matter of Time. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 363-385. [CrossRef]
- Viker, K.B.; Steele, M.B.; Iankov, I.D.; Concilio, S.C.; Ammayappan, A.; Bolon B.; Jenks N.J.; Goetz, M.P.; Panagioti E.; Federspiel, M.J.; et al. Preclinical safety assessment of MV-s-NAP, a novel oncolytic measles virus strain armed with an H. pylori immunostimulatory bacterial transgene. Mol. Ther-Meth. D. 2022, 26, 532-546. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, G.Y. Functional analysis of ZmDWF1, a maize homolog of the Arabidopsis brassinosteroids biosynthetic DWF1/DIM gene. Plant Sci. 2004, 167, 743-751. [CrossRef]
- Laurie, R.E.; Diwadkar, P.; Jaudal M.; Zhang, L.L.; Hecht, V.; Wen, J.Q.; Tadege, M.; Mysore K.S; Putterill, J.; Weller, J.L.; et al. The Medicago FLOWERING LOCUS T homolog, MtFTa1, is a key regulator of flowering time. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2207-24. [CrossRef]
- Putterill, J.; Varkonyi-Gasic, E. FT and florigen long-distance flowering control in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33: 77-82. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, A.; Thomson, G.; Kerr-Phillips, M.; Phan, C.; Krueger, T.; Jaudal, M.; Wen J.Q.; Mysore, K. S.; Putterill, J. Overexpression of Medicago MtCDFd1_1 Causes Delayed Flowering in Medicago via Repression of MtFTa1 but Not MtCO -Like Genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1148. [CrossRef]
- Jaudal, M.; Wen, J.Q.; Mysore, K.S; Putterill, J. Medicago PHYA promotes flowering, primary stem elongation and expression of flowering time genes in long days. BMC plant biol. 2020, 20(1): 329. [CrossRef]
- Thomson, G.; Zhang, L.L.; Wen, J.Q.; Mysore, K.S.; Putterill, J. The Candidate Photoperiod Gene MtFE Promotes Growth and Flowering in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634091-634091. [CrossRef]
- Liew, L. C.; Hecht, V.; Sussmilch, F. C.; Weller, J.L. The Pea Photoperiod Response Gene STERILE NODES Is an Ortholog of LUX ARRHYTHMO. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165(2): 648-657. [CrossRef]
- Rubenach, A.J.S.; Hecht, V.; Vander, S.J.K.; Liew, L.C.; Aubert, G.; Burstin, J.; Weller J. L. EARLY FLOWERING3 Redundancy Fine-Tunes Photoperiod Sensitivity. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 2253-2264. [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Hecht, V. F.; Picard, K. Isolation and functional analysis of CONSTANS-LIKE genes suggests that a central role for CONSTANS in flowering time control is not evolutionarily conserved in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 486. [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.J.; Watanabe, S.; Yamada, T.; Tsubokura, Y.; Nakashima, H.; Zhai, H.; Anai. T.; Sato. S.; Yamazaki, T.; Lv, S.X. Positional cloning and characterization reveal the molecular basis for soybean maturity locus E1 that regulates photoperiodic flowering. P.N.A.S. 2012, 109, E2155-64. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, B.J.; Ma, L.M.; Zhang, S.W.; Zhai, H.; Xu, X.; Hou, W.S.; Xia, Z.J.; Wu, C.X.; Sun, S.; Wu, T.T.; et al. Functional diversification of Flowering Locus T homologs in soybean: GmFT1a and GmFT2a/5a have opposite roles in controlling flowering and maturation. New phytol. 2018, 217, 1335-1345. [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; Yamagishi, N.; Zhao, C.; Takeshima, R.; Kasai, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanazawa, A.; Yoshikawa, N.; Liu, B.H.; Yamada, T.; et al. The Soybean-Specific Maturity Gene E1 Family of Floral Repressors Controls Night-Break Responses through Down-Regulation of FLOWERING LOCUS T Orthologs. Plant physiol. 2015, 168, 1735-46. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Zhai, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tian, X.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wu, H.Y.; Lv, S.X.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Functional conservation and diversification of the soybean maturity gene E1 and its homologs in legumes. Sci. rep. 2016, 6, 29548. [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.L.; Liu, X.G.; Jia, W.; Liu, H.J.; Li, W. Q.; Peng, Y.; Du, Y.F.; Wang, Y.B.; Yin, Y.J.; Zhang, X.H. et al. ZmCOL3 a CCT gene represses flowering in maize by interfering with the circadian clock and activating expression of ZmCCT, J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 465-480. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Muszynski, M. G.; Danilevskaya, O.N. The FT-like ZCN8 Gene Functions as a Floral Activator and Is Involved in Photoperiod Sensitivity in Maize. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 942-960. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Li, C.X.; Hu, W.; Lau, M.Y.; Lin, H.Q.; Rockwell, N.C.; Martin, S.S.; Jernstedt, J.A.; Lagarias, J.C.; Dubcovsky, J. Phytochrome C plays a major role in the acceleration of wheat flowering under long-day photoperiod. P.N.A.S. 2014, 111, 10037-44. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884-i890. [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B. A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq, Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621-8. [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Catherine, A.B.; Judith, A.B.; David, B.; Heather, B.; Cherry, J.M.; Allan, P.D.; Kara, D.; Selina, S.D.; Janan T.E.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25-29. [CrossRef]
- Minoru, K.; Susumu, G.; Shuichi, K.; Yasushi, O.; Masahiro, H. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. N.A.R. 2004, 32: D277-80. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Xie, W.B.; Li, J.; Zhou, F.S.; Zhang, Q.F. A whole-genome SNP array (RICE6K) for genomic breeding in rice. Plant biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 28-37. [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D. et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644-52. [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.C.K.; EMishra, P. GIGANTEA - An Emerging Story. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, G.G.; Dean, C.; Arabidopsis, the Rosetta Stone of Flowering Time? Sci. 2002, 296(5566): 285-289. [CrossRef]
- Chentao, L. Blue light receptors and signal transduction. Plant cell 2002, 14Suppl, S207-25.
- Li, R.N.; Li, T.; Wu, X.; Yao, X.Y.; Ai, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, Z.C.; Huang, X.Z. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Expression Profiling of the CONSTANS-like Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Genes-Basel. 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
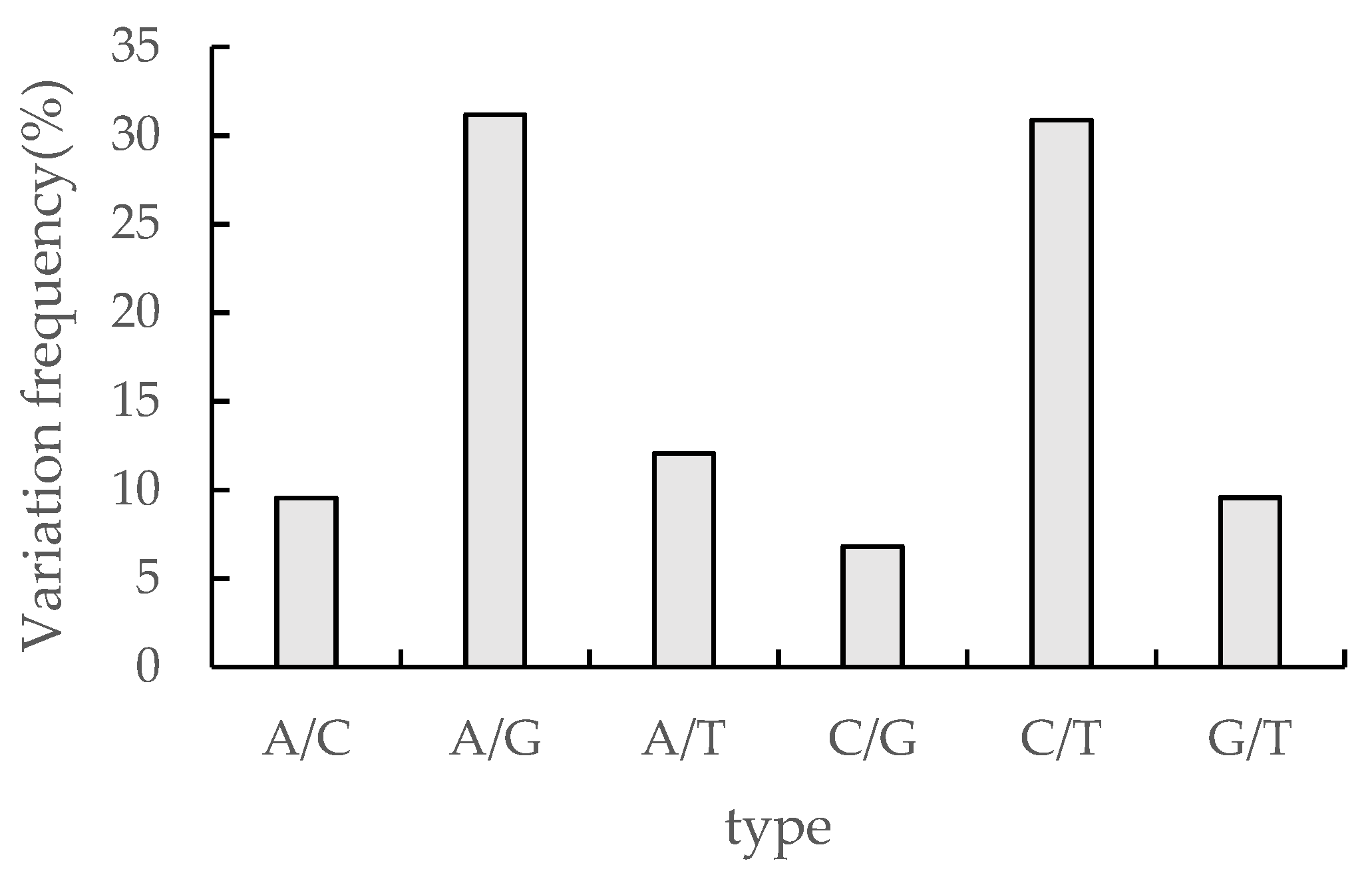
| Sample | Reads No. | Clean Reads No. | Q30 (%) | Total_ Mapped (%) | Multiple_ Mapped (%) | Uniquely_ Mapped (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A_1 | 45425876 | 45101984 | 94.84 | 92.87% | 4.00% | 96.00% |
| A_2 | 44676462 | 44323034 | 94.58 | 93.74% | 4.46% | 95.54% |
| A_3 | 46069654 | 45525622 | 93.61 | 91.77% | 4.31% | 95.69% |
| B_1 | 42730730 | 42144712 | 93.01 | 91.69% | 15.13% | 94.87% |
| B_2 | 46843152 | 46205678 | 93.06 | 91.11% | 3.31% | 96.69% |
| B_3 | 42296358 | 41995038 | 94.49 | 92.05% | 3.81% | 96.19% |
| C_1 | 43099064 | 42532114 | 93.16 | 90.75% | 4.20% | 95.80% |
| C_2 | 44530066 | 44066860 | 94.06 | 90.39% | 3.74% | 96.26% |
| C_3 | 44945554 | 44437312 | 93.76 | 90.85% | 3.99% | 96.01% |
| D_1 | 46751856 | 46319452 | 94.13 | 92.00% | 4.03% | 95.97% |
| D_2 | 43762322 | 43326008 | 94.04 | 92.00% | 5.02% | 94.98% |
| D_3 | 52817612 | 52325294 | 93.96 | 91.76% | 3.33% | 96.67% |
| Database | Number | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CC | 16395 | 51.39 |
| BP | 17067 | 53.49 |
| eggNOG _ Category | 28072 | 87.99 |
| Ensembl | 31901 | 100 |
| MF | 16059 | 50.34 |
| Eggnog | 29689 | 93.06 |
| Pathway | 6110 | 19.15 |
| GO | 18101 | 56.74 |
| KEGG | 11288 | 35.38 |
| Swissprot | 26028 | 81.58 |
| NR | 31894 | 99.97 |
| Functional classification | Number of genes/each | Percentage /% |
|---|---|---|
| RNA processing and modification | 753 | 2.82 |
| Chromatin structure and dynamics | 270 | 1.01 |
| Energy production and conversion | 674 | 2.52 |
| Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning | 296 | 1.11 |
| Amino acid transport and metabolism | 851 | 3.18 |
| Nucleotide transport and metabolism | 207 | 0.77 |
| Carbohydrate transport and metabolism | 1312 | 4.91 |
| Coenzyme transport and metabolism | 275 | 1.03 |
| Lipid transport and metabolism | 618 | 2.31 |
| Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis | 998 | 3.73 |
| Transcription | 2194 | 8.20 |
| Replication, recombination and repair | 1236 | 4.62 |
| Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis | 183 | 0.68 |
| Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones | 2123 | 7.94 |
| Inorganic ion transport and metabolism | 608 | 2.27 |
| Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism | 1126 | 4.21 |
| Function unknown | 9008 | 33.68 |
| Signal transduction mechanisms | 2669 | 9.98 |
| Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport | 794 | 2.97 |
| Defense mechanisms | 302 | 1.13 |
| Extracellular structures | 8 | 0.03 |
| Nuclear structure | 7 | 0.03 |
| Cytoskeleton | 233 | 0.87 |
| Gene | Unigene Code | FPKM | Gene expression model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Branching stage |
B the present bud stage |
C the first flowering stage |
D and the blooming stage |
A vs B | B vs C | C vs D | ||
| GI | gene-LOC11410562 | 22.45 | 52.22 | 1.45 | 27.22 | Up | Down | Up |
| CO | gene-LOC11435974 | 0.19 | 1.17 | 4.61 | 0.43 | Up | - | Down |
| PHYA | gene-LOC25500742 | 12.89 | 26.25 | 6.01 | 12.42 | - | Down | Up |
| PHYB | gene-LOC11420025 | 12.71 | 11.89 | 16.79 | 13.27 | - | - | - |
| CRY1 | gene-LOC11428875 | 138.89 | 162.06 | 165.35 | 134.21 | - | - | - |
| CRY2 | gene-LOC25484452 | 51.70 | 69.89 | 80.66 | 56.78 | - | - | - |
| TOC1 | gene-LOC11422615 | 32.28 | 56.06 | 66.98 | 33.86 | Up | - | - |
| ELF3 | gene-LOC11431402 | 1.47 | 2.93 | 16.78 | 1.20 | - | Up | Down |
| LHY | gene-LOC11432385 | 469.08 | 192.19 | 806.17 | 415.10 | Down | Up | - |
| Col2 | gene-LOC25497637 | 129.53 | 122.78 | 174.20 | 134.80 | - | - | - |
| Col13 | gene-LOC11434778 | 22.92 | 31.47 | 56.71 | 17.66 | - | - | Down |
| Col4 | gene-LOC11431452 | 169.85 | 104.34 | 163.58 | 146.27 | - | - | - |
| Col5 | gene-LOC11425462 | 131.48 | 191.78 | 251.04 | 195.10 | - | - | - |
| Col6 | gene-LOC25498015 | 20.00 | 17.68 | 5.79 | 16.2 | - | Down | Up |
| Col9 | gene-LOC11415514 | 3.25 | 2.32 | 57.72 | 2.85 | - | Up | Down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





