Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Husbandry
2.2. Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.3. Larvae Dissociation
2.4. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
3. Results
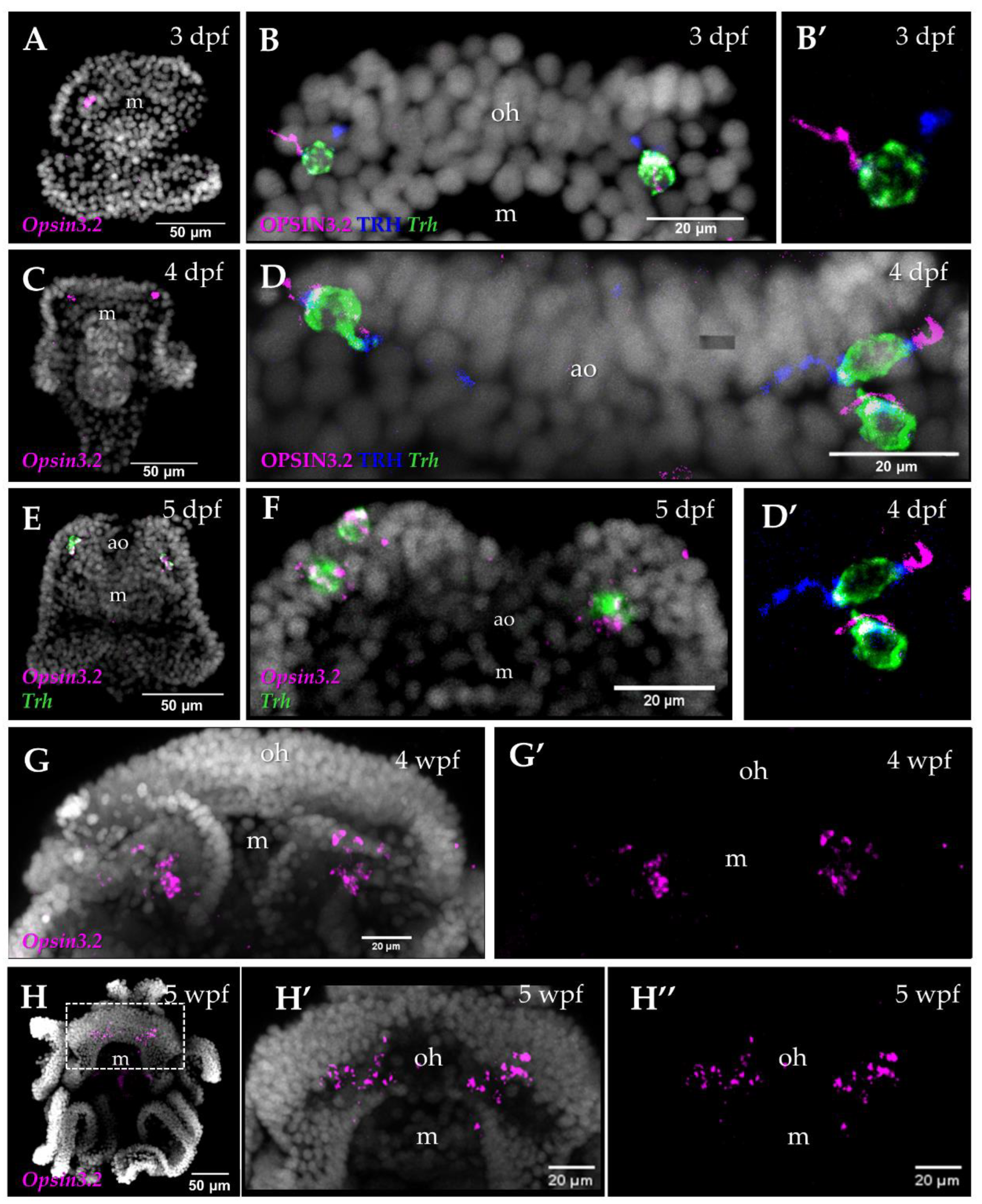
3.1. Expression Pattern of Opsin3.2 (Go-Opsin) during Larval Development
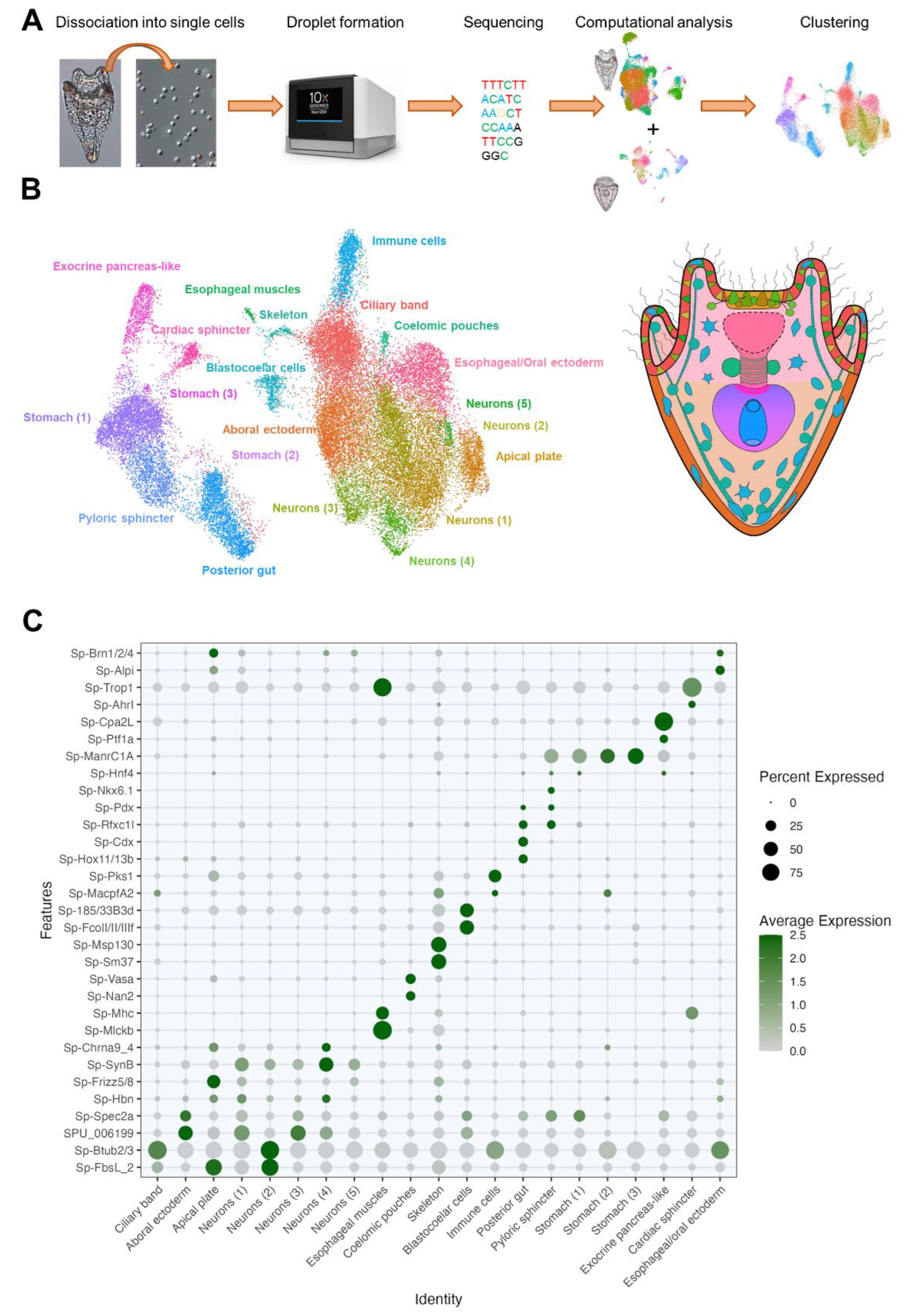
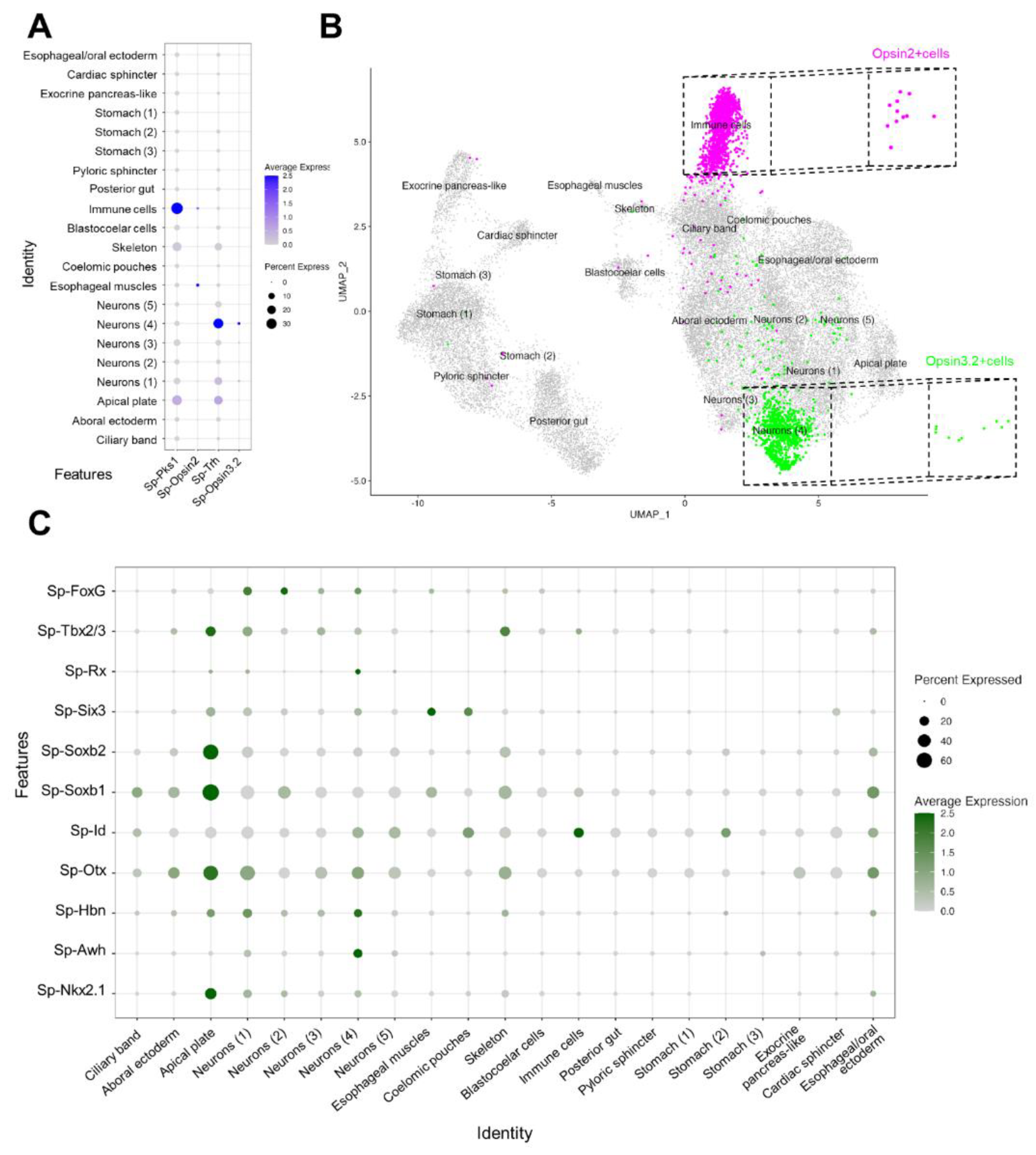
3.2. Characterization of the Go-Opsin3.2 and the Opsin2 Positive Cell Types at a Single Cell Resolution
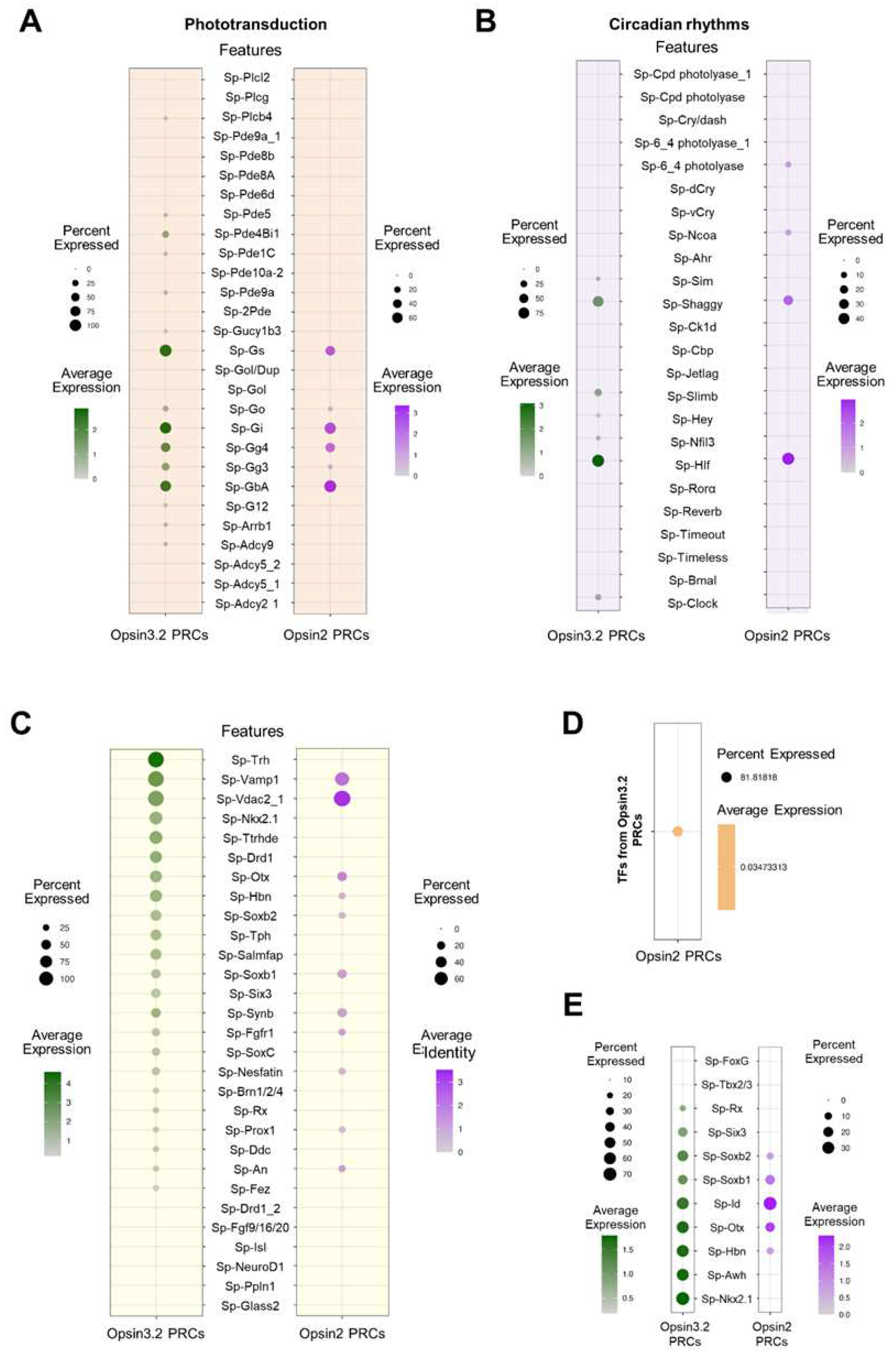
3.3. Molecular Signature of Photoreceptor Cells in S. purpuratus Larvae
4. Discussion
4.1. Opsin3.2 Cells Characterization during S. purpuratus Larval Development
4.2. Opsin3.2 cells utilize an ancestral gene regulatory toolkit
4.3. Opsin3.2 Cells as Sensory and Neurosecretory Unit
4.4. Opsin3.2 Cells Possible Function(s)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Häfker, N.S.; Andreatta, G.; Manzotti, A.; Falciatore, A.; Raible, F.; Tessmar-Raible, K. Rhythms and Clocks in Marine Organisms. Annual Review of Marine Science 2023, 15, 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitaterna, M.H.; Takahashi, J.S.; Turek, F.W. Overview of Circadian Rhythms. Alcohol Res Health 2001, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dawson, A.; King, V.M.; Bentley, G.E.; Ball, G.F. Photoperiodic Control of Seasonality in Birds. Journal of Biological Rhythms 2001, 16, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeValois, R.L.; DeValois, K.K. Spatial Vision; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780199872220. [Google Scholar]
- Verasztó, C.; Gühmann, M.; Jia, H.; Rajan, V.B.V.; Bezares-Calderón, L.A.; Piñeiro-Lopez, C.; Randel, N.; Shahidi, R.; Michiels, N.K.; Yokoyama, S.; et al. Ciliary and Rhabdomeric Photoreceptor-Cell Circuits Form a Spectral Depth Gauge in Marine Zooplankton. eLife 2018, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, D. Evolution of Eyes and Photoreceptor Cell Types. International Journal of Developmental Biology 2003, 47, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, D.; Wittbrodt, J. Reconstructing the Eyes of Urbilateria. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2001, 356, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargrave, P.A.; McDowell, J.H.; Curtis, D.R.; Wang, J.K.; Juszczak, E.; Fong, S.L.; Mohana Rao, J.K.; Argos, P. The Structure of Bovine Rhodopsin. Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism 1983, 9, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terakita, A. The Opsins. Genome Biology 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schertler, G.F.X.; Villa, C.; Henderson, R. Projection Structure of Rhodopsin. Nature 1993, 362, 770–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aniello, S.; Delroisse, J.; Valero-Gracia, A.; Lowe, E.K.; Byrne, M.; Cannon, J.T.; Halanych, K.M.; Elphick, M.R.; Mallefet, J.; Kaul-Strehlow, S.; et al. Opsin Evolution in the Ambulacraria. Marine Genomics 2015, 24, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirson, S.N.; Halford, S.; Foster, R.G. The Evolution of Irradiance Detection: Melanopsin and the Non-Visual Opsins. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2009, 364, 2849–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.L.; Blasic, J.R.; Bok, M.J.; Cameron, E.G.; Pringle, T.; Cronin, T.W.; Robinson, P.R. Shedding New Light on Opsin Evolution. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2011, 279, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichida, Y.; Matsuyama, T. Evolution of Opsins and Phototransduction. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2009, 364, 2881–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arendt, D. The Enigmatic Xenopsins. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delroisse, J.; Mallefet, J.; Flammang, P. De Novo Adult Transcriptomes of Two European Brittle Stars: Spotlight on Opsin-Based Photoreception. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.D.; Pairett, A.N.; Pankey, M.S.; Serb, J.M.; Speiser, D.I.; Swafford, A.J.; Oakley, T.H. The Last Common Ancestor of Most Bilaterian Animals Possessed at Least Nine Opsins. Genome Biology and Evolution 2016, 8, 3640–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.E.; Feuda, R.; Mellott, D.O.; Burke, R.D.; Peter, I.S. Ciliary Photoreceptors in Sea Urchin Larvae Indicate Pan-Deuterostome Cell Type Conservation. BMC Biology 2021, 19, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vöcking, O.; Kourtesis, I.; Tumu, S.C.; Hausen, H. Co-Expression of Xenopsin and Rhabdomeric Opsin in Photoreceptors Bearing Microvilli and Cilia. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shichida, Y.; Imai, H. Visual Pigment: G-Protein-Coupled Receptor for Light Signals. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 1998, 54, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, D.; Terakita, A.; Ishikawa, T.; Tsukahara, Y.; Maeda, A.; Shichida, Y. A Novel G(o)-Mediated Phototransduction Cascade in Scallop Visual Cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1997, 272, 22979–22982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gühmann, M.; Jia, H.; Randel, N.; Verasztó, C.; Bezares-Calderón, L.A.; Michiels, N.K.; Yokoyama, S.; Jékely, G. Spectral Tuning of Phototaxis by a Go-Opsin in the Rhabdomeric Eyes of Platynereis. Current Biology 2015, 25, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, D.; Tessmar-Raible, K.; Snyman, H.; Dorresteijn, A.W.; Wittbrodf, J. Ciliary Photoreceptors with a Vertebrate-Type Opsin in an Invertebrate Brain. Science 2004, 306, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmik, Z.; Ruzickova, J.; Jonasova, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Vopalensky, P.; Kozmikova, I.; Strnad, H.; Kawamura, S.; Piatigorsky, J.; Paces, V.; et al. Assembly of the Cnidarian Camera-Type Eye from Vertebrate-like Components. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2008, 105, 8989–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, J.S.; Pearse, V.B. Vision in Cubomedusan Jellyfishes. Science 1978, 199, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, K.; Kaul-Strehlow, S.; Ullrich-Lüter, E.; Stach, T. Structure and Ultrastructure of Eyes of Tornaria Larvae of Glossobalanus Marginatus. Organisms Diversity and Evolution 2015, 15, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich-Luter, E.M.; Dupont, S.; Arboleda, E.; Hausen, H.; Arnone, M.I. Unique System of Photoreceptors in Sea Urchin Tube Feet. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2011, 108, 8367–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopalensky, P.; Pergner, J.; Liegertova, M.; Benito-Gutierrez, E.; Arendt, D.; Kozmik, Z. Molecular Analysis of the Amphioxus Frontal Eye Unravels the Evolutionary Origin of the Retina and Pigment Cells of the Vertebrate Eye. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2012, 109, 15383–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, D.E. Eye Evolution and Its Functional Basis. Visual Neuroscience 2013, 30, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, G.L.; Hardie, R.; Laughlin, S.B. Phototransduction and the Evolution of Photoreceptors. Current Biology 2010, 20, R114–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.; Angerer, L.; Elphick, M.; Humphrey, G.; Yaguchi, S.; Kiyama, T.; Liang, S.; Mu, X.; Agca, C.; Klein, W.; et al. A Genomic View of the Sea Urchin Nervous System. Developmental Biology 2006, 300, 434–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raible, F.; Tessmar-Raible, K.; Arboleda, E.; Kaller, T.; Bork, P.; Arendt, D.; Arnone, M.I. Opsins and Clusters of Sensory G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in the Sea Urchin Genome. Developmental Biology 2006, 300, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganos, P.; Ullrich-Lüter, E.; Caccavale, F.; Zakrzewski, A.; Voronov, D.; Fournon-Berodia, I.; Cocurullo, M.; Lüter, C.; Arnone, M.I. A New Model Organism to Investigate Extraocular Photoreception: Opsin and Retinal Gene Expression in the Sea Urchin Paracentrotus Lividus. Cells 2022, 11, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich-Lüter, E.M.; D’Aniello, S.; Arnone, M.I. C-Opsin Expressing Photoreceptors in Echinoderms. Integrative and Comparative Biology 2013, 53, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero-Gracia, A.; Petrone, L.; Oliveri, P.; Nilsson, D.-E.; Arnone, M.I. Non-Directional Photoreceptors in the Pluteus of Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 2016, 4, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, J.; Yaguchi, S. Sea Urchin Larvae Utilize Light for Regulating the Pyloric Opening. BMC Biology 2021, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaguchi, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kamata, M.; Yaguchi, J. Planktonic Sea Urchin Larvae Change Their Swimming Direction in Response to Strong Photoirradiation. PLOS Genetics 2022, 18, e1010033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Oulhen, N.; Wessel, G. A Single Cell RNA Sequencing Resource for Early Sea Urchin Development. Development (Cambridge) 2020, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massri, A.J.; Greenstreet, L.; Afanassiev, A.; Berrio, A.; Wray, G.A.; Schiebinger, G.; McClay, D.R. Developmental Single-Cell Transcriptomics in the Lytechinus Variegatus Sea Urchin Embryo. Development (Cambridge) 2021, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganos, P.; Voronov, D.; Musser, J.; Arendt, D.; Arnone, M.I. Single Cell Rna Sequencing of the Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus Larva Reveals the Blueprint of Major Cell Types and Nervous System of a Nonchordate Deuterostome. eLife 2021, 10, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, L. Circadian Clock and Light Input System in the Sea Urchin Larva; UCL (University College London), 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Paganos, P.; Caccavale, F.; La Vecchia, C.; D’Aniello, E.; D’Aniello, S.; Arnone, M.I. FISH for All: A Fast and Efficient Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Protocol for Marine Embryos and Larvae. Frontiers in Physiology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, M.; Paganos, P.; Spurrell, M.; Arnone, M.I.; Wessel, G.M. Methodology for Whole Mount and Fluorescent RNA In Situ Hybridization in Echinoderms: Single, Double, and Beyond. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc., 2021; Volume 2219, pp. 195–216. [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann, M.; Jékely, G. Antibodies against Conserved Amidated Neuropeptide Epitopes Enrich the Comparative Neurobiology Toolbox. EvoDevo 2012, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, N.J. Investigating the Roles of Neuropeptides in the Development of the Sea Urchin, Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Doctoral, UCL (University College London), 2020; pp. 1–349. [Google Scholar]
- Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.M.; Davidson, E.H.; Cameron, R.A.; Gibbs, R.A.; Angerer, R.C.; Angerer, L.M.; Arnone, M.I.; Burgess, D.R.; Burke, R.D.; et al. The Genome of the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Science 2006, 314, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudtarkar, P.; Cameron, R.A. Echinobase: An Expanding Resource for Echinoderm Genomic Information. Database 2017, 2017, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Smibert, P.; Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data across Different Conditions, Technologies, and Species. Nat Biotechnol 2018, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganos, P.; Ronchi, P.; Carl, J.; Mizzon, G.; Martinez, P.; Benvenuto, G.; Arnone, M.I. Integrating Single Cell Transcriptomics and Volume Electron Microscopy Confirms the Presence of Pancreatic Acinar-like Cells in Sea Urchins. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 991664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, Sensitive and Accurate Integration of Single-Cell Data with Harmony. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Chee, F.C.; Burke, R.D. Apical Organs in Echinoderm Larvae: Insights into Larval Evolution in the Ambulacraria. Evolution and Development 2007, 9, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, M.; Meleshkevitch, E.; Boudko, D. The Apical Sensory Organ of a Gastropod Veliger Is a Receptor for Settlement Cues. The Biological Bulletin 2016, 198, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinigaglia, C.; Busengdal, H.; Lerner, A.; Oliveri, P.; Rentzsch, F. Molecular Characterization of the Apical Organ of the Anthozoan Nematostella Vectensis. Developmental Biology 2015, 398, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgrove, B.W.; Burke, R.D. Development of Serotonergic Neurons in Embryos of the Sea Urchin, Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Development Growth and Differentiation 1986, 28, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, N.J.; Mattiello, T.; Rowe, M.L.; Ward, L.; Perillo, M.; Arnone, M.I.; Elphick, M.R.; Oliveri, P. Neuropeptidergic Systems in Pluteus Larvae of the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus: Neurochemical Complexity in a “Simple” Nervous System-Supplementary. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2018, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocurullo, M.; Paganos, P.; Wood, N.J.; Arnone, M.I.; Oliveri, P. Molecular and Cellular Characterization of the TH Pathway in the Sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus. Cells 2023, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Tan, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Sancar, A.; Zhong, D. Dynamics and Mechanism of Repair of Ultraviolet-Induced (6-4) Photoproduct by Photolyase. Nature 2010, 466, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paganos, P.; Voronov, D.; Musser, J.; Arendt, D.; Arnone, M.I. Single Cell Rna Sequencing of the Strongylocentrotus Purpuratus Larva Reveals the Blueprint of Major Cell Types and Nervous System of a Nonchordate Deuterostome. eLife 2021, 10, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angerer, L.M.; Yaguchi, S.; Angerer, R.C.; Burke, R.D. The Evolution of Nervous System Patterning: Insights from Sea Urchin Development. Development 2011, 138, 3613–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartenstein, V. The Neuroendocrine System of Invertebrates: A Developmental and Evolutionary Perspective. Journal of Endocrinology 2006, 190, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessmar-Raible, K.; Raible, F.; Christodoulou, F.; Guy, K.; Rembold, M.; Hausen, H.; Arendt, D. Conserved Sensory-Neurosecretory Cell Types in Annelid and Fish Forebrain: Insights into Hypothalamus Evolution. Cell 2007, 129, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, C.Y.; Kitahashi, T.; Parhar, I.S. Localization and Characterization of Val-Opsin Isoform-Expressing Cells in the Brain of Adult Zebrafish. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2014, 522, 3847–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jékely, G.; Colombelli, J.; Hausen, H.; Guy, K.; Stelzer, E.; Nédélec, F.; Arendt, D. Mechanism of Phototaxis in Marine Zooplankton. Nature 2008, 456, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, K.M.; Schuh, N.W.; Heyland, A.; Rast, J.P. Analysis of Immune Response in the Sea Urchin Larva. In Methods in Cell Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 150, pp. 333–355. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, K.M.; Rast, J.P. Immune Activity at the Gut Epithelium in the Larval Sea Urchin. Cell and Tissue Research 2019, 377, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leech, D.; Johnsen, S. Behavioral Responses–UVR Avoidance and Vision. In UV Effects in Aquatic Organisms and Ecosystems; Helbling, W., Z.H., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry, 2003; pp. 457–481. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.K.; Sewell, M.A.; Angerer, R.C.; Angerer, L.M. Rapid Adaptation to Food Availability by a Dopamine-Mediated Morphogenetic Response. Nature Communications 2011, 2, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




