1. Introduction
Abscisic acid is a terpenoid plant hormone also present and active in mammals, with a cross-kingdom conserved role as stress hormone, regulating cell responses to stimuli as diverse as root water availability and blood glucose levels [
1]. The origin of ABA dates back to unicellular algae and bacteria and its conservation in modern, far more complex organisms testifies to its important role in cell and species conservation, allowing adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
ABA and its mammalian receptors LANCL1 and LANCL2 have been recently shown to play a hitherto unrecognized role in the response of cardiomyocytes to hypoxia. The heart is a very well-perfused organ and the necessity to endure severe hypoxia does not occur under physiological conditions, as is instead the case with skeletal muscle, where extreme physical exertion can shift metabolism from the aerobic to the anaerobic condition. Indeed, type II skeletal myocytes are especially adapted to fast and brief bursts of contractile activity that are largely oxygen-, and mitochondria-, independent, while type I skeletal myocytes rely chiefly on oxidative metabolism for energy production during prolonged physical exercise. The cardiac muscle is not as well adaptable to hypoxia as the skeletal muscle; cardiomyocytes have an obligate aerobic metabolism and are thus exposed to the damaging effects of sudden oxygen deprivation.
One of the fundamental players in heart protection from hypoxia-derived damage is the gaseous hormone nitric oxide (NO), also an evolutionarily ancient signal molecule. Indeed, NO protects cardiomyocyte function not just after hypoxia/reoxygenation (a time-limited pathological event), but constitutively, under physiological conditions, improving electrical transmission, contractility, energy metabolism and myocyte growth [
2]. Indeed, NO deficiency is associated with heart diseases [
3] and NO replacement therapy can improve cardiac performance [
4]. In the rat cardiomyocyte cell line H9c2 hypoxia induces production of endogenous ABA and the ABA-LANCL1/2 hormone-receptors system activates a signaling pathway involving AMPK and PGC-1α, which leads to a concerted series of transcriptional and post-transcriptional events leading to an increased NO generation: expression and phosphorylation of eNOS, transcription of the enzyme GTPCH, which synthesizes the coenzyme tetrahydrobiopterin (TBH4), necessary for NO generation, and of the arginine transporter CAT-2A, required for arginine entry into the cells [
5]. Interestingly, in LANCL1/2-overexpressing H9c2 the mitochondrial proton gradient (ΔΨ) after hypoxia is conserved to a significantly higher degree compared with LANCL1/2-silenced cells and further improves after reoxygenation. Moreover, exogenous ABA increases the mitochondrial ΔΨ after reoxygenation in LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells and this effect is reduced in the double-silenced cells. These results suggest a role for the ABA-LANCL1/2 system in the maintenance of mitochondrial ΔΨ and consequently in the generation of metabolic energy in cardiomyocytes.
Mitochondrial function is of the utmost importance not only for cardiomyocyte survival to hypoxia, a condition that they do not normally experience, but for the contractile and electrical functions of cardiomyocytes under normoxic conditions. We hypothesized that the ABA/LANCL1-2 system, by increasing mitochondrial ΔΨ under normoxia, as well as after hypoxia/reoxygenation, could increase energy production in cardiomyocytes, improving the structural and metabolic features of the cells, put in a word improve cardiomyocyte “fitness”. In cardiac myocytes mitochondrial function and biogenesis are controlled by the PGC-1α/ERRα team of transcription factors [
6,
7,
8]. In skeletal myocytes, the ABA-LANCL1/2 system controls mitochondrial function, increasing mitochondrial DNA content and respiration
via a signaling pathway involving AMPK and PGC-1α [
9] and PGC-1α together with ERRα have been shown to control transcription of several genes critical for mitochondrial energy-production in cardiac and skeletal muscle
in vivo [
7]; moreover, both PGC-1α and ERRα are transcriptionally upregulated in LANCL1/2-overexpressing human brown and beige adipocytes [
10]. Starting from these observations, a role for ERRα in the mitochondrial effects of the ABA/LANCL1-2 system in cardiomyocytes can be hypothesized.
The aims of this study were two-fold: i) to compare mitochondrial number, glucose- and palmitate-dependent respiration, oxphos uncoupling, expression of cytoskeletal, contractile and ion channel proteins, cell morphology and doubling time in rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes overexpressing, or silenced for, LANCL1 and LANCL2, cultured in the presence or in the absence of nanomolar ABA; ii) to investigate whether ERRα is involved in the signaling pathway activated by the ABA/LANCL system in cardiomyocytes.
2. Materials and Methods
Cell culture
Rat embryonic cardiomyocyte H9c2 cell line was purchased from ATCC (LGC Standards s.r.l. Milan, Italy) and was cultured in DMEM high glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy), penicillin (62.5 μg/ml) and streptomycin (100 μg/ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy). Cells were kept at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2.
Lentiviral cell transduction
The lentiviral plasmids pLV[shRNA]-Puro-U6 encoding for a control scramble shRNA (SCR), for the shRNA targeting rat LANCL1 (SHL1), for the shRNA targeting rat LANCL2 (SHL2) and for the shRNA targeting rat ERRα (SHERRα) (plasmid ID: VB010000-0005mme, VB181016-1107sen, VB181016-1124zjp, VB221005-1073jxq), were purchased from Vector Builder (Chicago, IL, USA). Overexpression of hLANCL1 (OVL1) and hLANCL2 (OVL2) was obtained in rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes using pBABE vectors constructed as described in [
9], with the empty vector pBABE (Addgene) as negative control (PLV). Lentiviral transductions were performed as described in [
9].
qPCR analysis
H9c2 cells were incubated with or without 100 nM ABA or 100 μM L-NAME for 4 hours after being serum-starved for 18 hours. Total RNA was extracted from cardiomyocytes using RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was obtained from 1 μg of total RNA by using iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy) and qPCR reactions were performed in an iQ5 Real-Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy) as described in [
10]. Specific primers were designed using Beacon Designer 2.0 software (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy), and their sequences are listed in
Table S1. Values were normalized on hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase-1 (Hprt1) mRNA expression. Statistical analysis of the qPCR was performed using the iQ5 Optical System Software version 1.0 (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Milan, Italy) by 2
-△△Ct method [
9]. The dissociation curve for each cycle of amplification was analyzed to confirm the absence of nonspecific PCR products.
Western blot
H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes (1 x 10
6/well) were seeded in 6-well plates in DMEM with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. After serum deprivation for 18 hours, cells were washed once in Krebs-Ringer HEPES buffer (KRH) and then incubated in KRH with 5 mM glucose for 60 min at 37° C with or without 100 nM ABA. The supernatant was removed and cells were scraped in 200 μL of 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA and 1% NP40 containing a protease inhibitor cocktail. After brief sonication, the protein concentration was determined on an aliquot of each lysate. 25 μg of lysates were loaded on 10% polyacrylamide gel and separated by SDS-PAGE and proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy), according to standard procedures. Membranes were blocked for 1 hour with TBST containing 5% non-fat dry milk and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with primary antibodies (
Table S2). Following incubation with the appropriate secondary antibodies (
Table S2) and ECL detection (GE Healthcare, Milan, Italy), band intensity was quantified with the ChemiDoc imaging system (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy).
Glucose transport assays
Rat H9c2 cells infected with the empty vector (PLV), overexpressing hLANCL1 and hLANCL2 (OVL1+2), infected with a scramble shRNA (SCR) or silenced for the expression of both rLANCL1 and rLANCL2 (SHL1+2) were cultured overnight at 1 x 10
4/well in a 96-well plate in DMEM (5 mM glucose) without serum. Cells were washed once with DMEM and then incubated for 30 min at 37°C in DMEM without (controls) or with 100 nM ABA. At the end of incubation, cells were washed with KRH at 37°C. The fluorescently labeled deoxyglucose analog 2-NBDG (50 μM) was added to each well, and after 10 min, the supernatant was removed, wells were washed once with ice-cold KRH, 50 μL KRH was added to each well, and the mean fluorescence (excitation at 480 nm and emission at 540 nm) from 9 acquisitions/well was calculated. Each experimental condition was assayed in at least 6 wells. Unspecific 2-NBDG uptake was subtracted from each experimental value as reported in [
11].
JC-1 analysis
Cardiomyocytes were stained with the cationic dye JC-1 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), with the same method already described in [
5]. Briefly, H9c2 cells were seeded at 3 x 10
4 onto µ-slide wells, treated or not with 4 µM CsA for 2 hours, stained with JC-1 (2,5 µg/ml) for 20 min at 37°C in a 5% CO
2 incubator and then imaged live. The red/green ratio, expression of the mitochondrial proton gradient [
12], was analyzed after a background subtraction with the ImageJ software (v1.8.0, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), using a quantitative analysis based on an intensity measurement of specific selected ROIs.
Mitochondrial and cytoskeletal staining
H9c2 cardiomyocytes overexpressing or silenced for the expression of both LANCL proteins were plated on glass coverslips and then stained with MitoTracker
TM Deep Red FM (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA). After preparing the solution as previously described in [
10], H9c2 cells were stained for 40 min at 37°C in a 5% CO
2 incubator and then imaged live. Moreover, the actin cytoskeleton (F-actin) was visualized using Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 488 (diluted 1:20, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA). Rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes, cultured as mentioned above, were also set in 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy). Detection of cytoskeleton staining was performed with the following antibodies: mouse anti-α-tubulin (diluted 1:1000 in PBS, Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy), rabbit anti β-catenin (diluted 1:100 in PBS, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), mouse anti-MYH7 (diluted 1:50, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., California) and mouse anti-Cx43 (diluted 1:100, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., California). The slides were rinsed in PBS and mounted with a ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). Images were acquired on a Leica TCS SP confocal laser scanning microscope, equipped with 476, 488, 543 and 633 excitation lines with a 60X Plan Apo oil objective. Fluorescence signals were then analyzed, after background subtraction, by ImageJ software (v1.8.0, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) using a semi-manual method based on the delimitation of the cells. Three fields were chosen at random in two slide preparations for each sample.
Seahorse analysis
Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) were determined using a Seahorse XFp Extracellular Flux Analyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). H9c2 cells were replated in XF plates at a density of 6000 cells/well. After 24 hours, cells were incubated at 37°C for 45 min in no-CO2 incubator with Agilent Seahorse DMEM pH 7.4, enriched with glucose (25 mM), glutamine (2 mM) and pyruvate (1 mM). The bioenergetic profile was measured using the Cell Mito Stress Test Kit (Cat. #103010-100) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Three measurements of OCR and ECAR were taken initially without additions to the cells (basal respiration and basal ECAR) and then after sequential injections of oligomycin (1.5 µM, ATP synthase inhibitor), carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP, 2.0 µM, proton gradient dissipator) and rotenone (0.5 µM, respiratory Complex I inhibitor) plus antimycin A (0.5 µM, respiratory Complex III inhibitor). OCR and ECAR were normalized to total cell number determined directly in the plate, immediately after each experimental run and reported as pmolO2/min and mpH/min, respectively. To determine the intrinsic rate and capacity of cells to oxidize palmitate in the absence or limitation of other exogenous substrates, XF Palmitate Oxidation Stress Test Kit (Cat. #103693-100) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, H9c2 cardiomyocytes were incubated at 37°C for 45 min in no-CO2 incubator with Agilent Seahorse DMEM pH 7.4, enriched with 1mM Sodium Palmitate/0.17 mM BSA solution (Palm-BSA), 25 mM glucose, 2 mM glutamine and 1 mM pyruvate. The OCR was monitored upon serial injections of etomoxir (4 μM, an inhibitor of long chain fatty acid oxidation) or DMEM, oligomycin (2 μM), FCCP (1 μM) and a rotenone/antimycin A mixture (1 μM). Whole-cell OCR was normalized to the final cell number as determined by manual cell counting.
Determination of intracellular NAD+ and ATP levels
To determine the content of ATP and NAD
+, H9c2 were seeded in 6-well plates in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS. At confluence, the cells were washed in PBS buffer, harvested and deproteinized with 5% TCA. After centrifugation (700xg for 30 sec), the supernatants were neutralized by removing TCA with diethyl ether and were analyzed by HPLC [
13]. NAD
+ and ATP values were normalized to protein concentrations [
14].
Cell volume measurement
To determine cell volume, H9c2 cardiomyocytes overexpressing or silenced for the expression of both LANCL proteins were treated with a solution of 1.25 μg/mL calcein-AM (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy) in isotonic PBS for 30 min at 37°C and then imaged live. Z-stack imaging series were acquired using a Leica TCS SP2 confocal microscope and a 60X oil objective with a numerical aperture of 1.4 and a pinhole size of 1 Airy unit. To reduce the time for acquiring and to minimize photobleaching, scanning was performed at the fastest scan speed possible. Imaging emission and detection settings were adjusted to an optimal level, minimizing pixel saturation for each channel. The offset and gain of the system were also utilized to minimize background signal. Once imported as TIFF images in FIJI ImageJ, image stacks were then separated into the independent channels, filtered to emphasize the borders and thresholded automatically using the Otsu method from the automatic threshold dropdown box. A region of interest was then selected around each cell and an open-source plugin integrated in FIJI ImageJ (
https://visikol.com/blog/2018/11/29/blog-post-loading-and-measurement-of-volumes-in-3d-confocal-image-stacks-with-imagej) was used to calculate the number of voxels in the ROI in the image stack [
15,
16]. Briefly, the plugin calculates the area of each individual ROI of each section, then sums the areas and multiplies the sum by the depth of each individual section, then showing the outcome.
DNA extraction and determination of mitochondrial levels by qPCR analysis
Total DNA was extracted from cardiomyocytes (1 x 10
6 cells on 6-cm plates) with the QIAamp DNA Micro Kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The purity and quantity of DNA were evaluated with the NanoDrop 1000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). The mitochondrial/genomic DNA ratio was determined using specific primers listed in
Table S1 for mitochondrial ND1 (MT-ND1) and genomic/nuclear Hprt1 by qPCR analysis as described in [
10].
Statistical analysis
Results were expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using the GraphPad Prism 7 Software (GraphPad Software Inc). Comparisons were drawn by an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test, if not otherwise indicated. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
4. Discussion
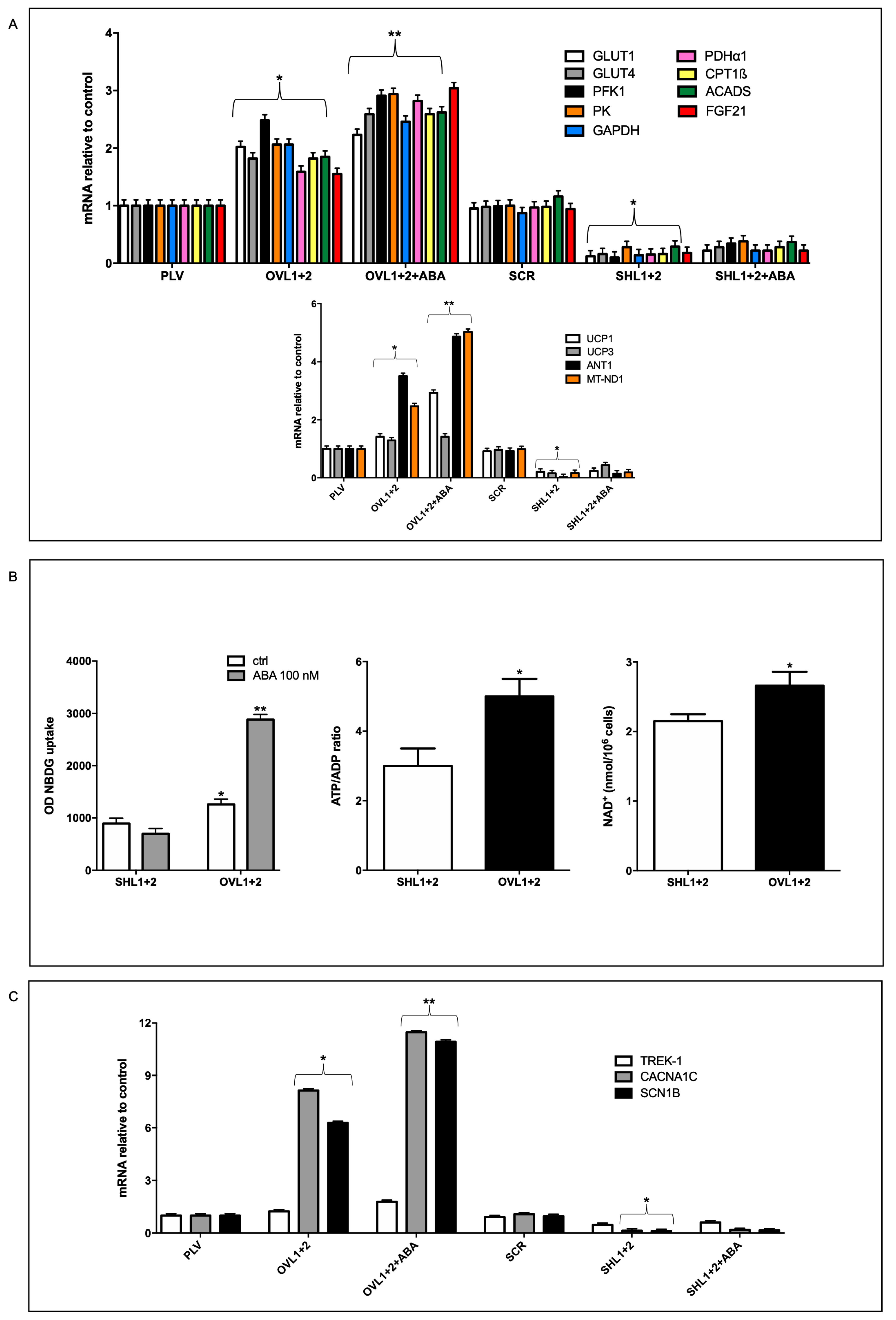
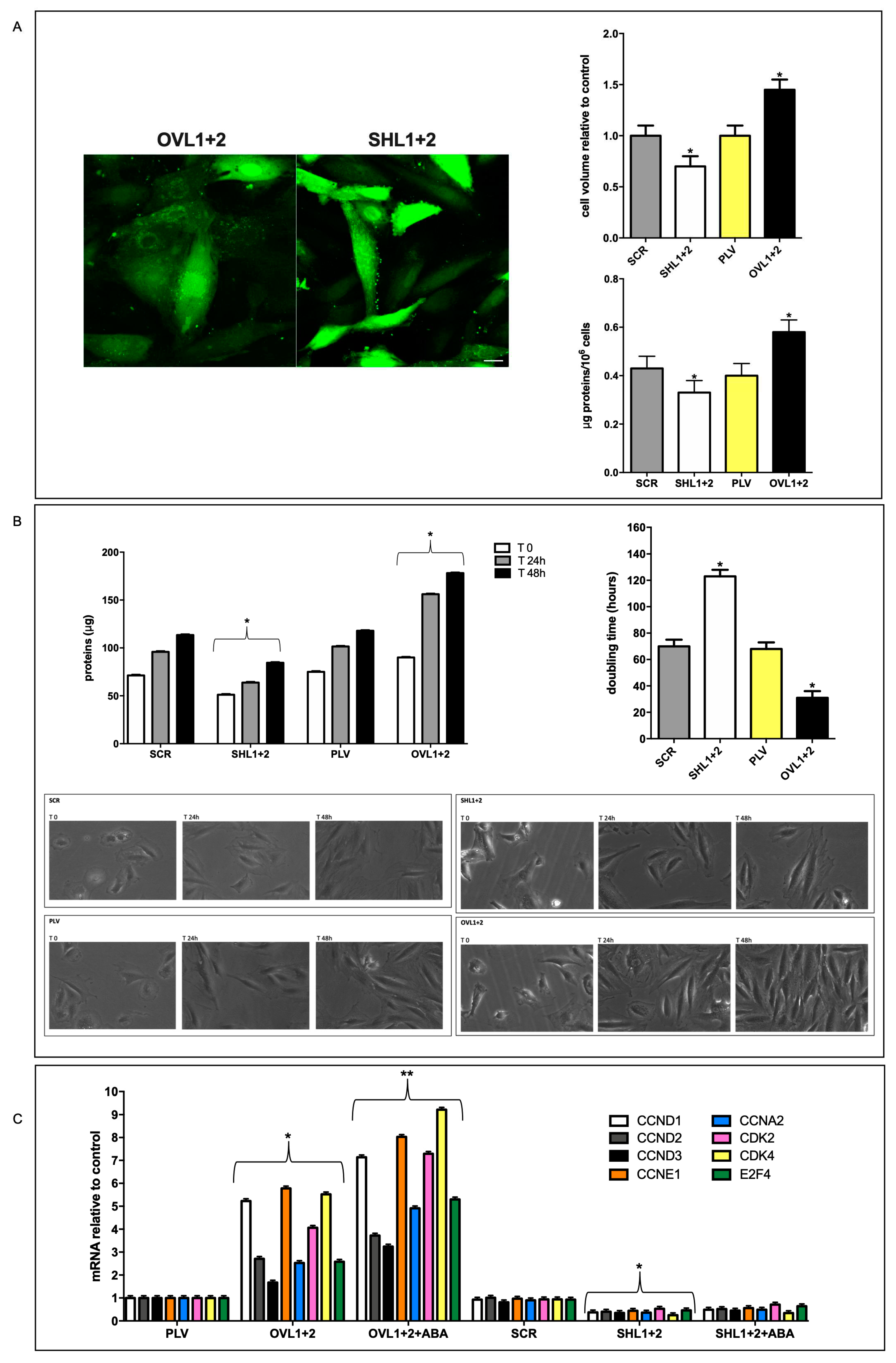
Taken together, results reported in this study allow us to conclude that overexpression of LANCL1/2 significantly improves, while their combined silencing dramatically reduces several key functional features of rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes (
Figure 7).
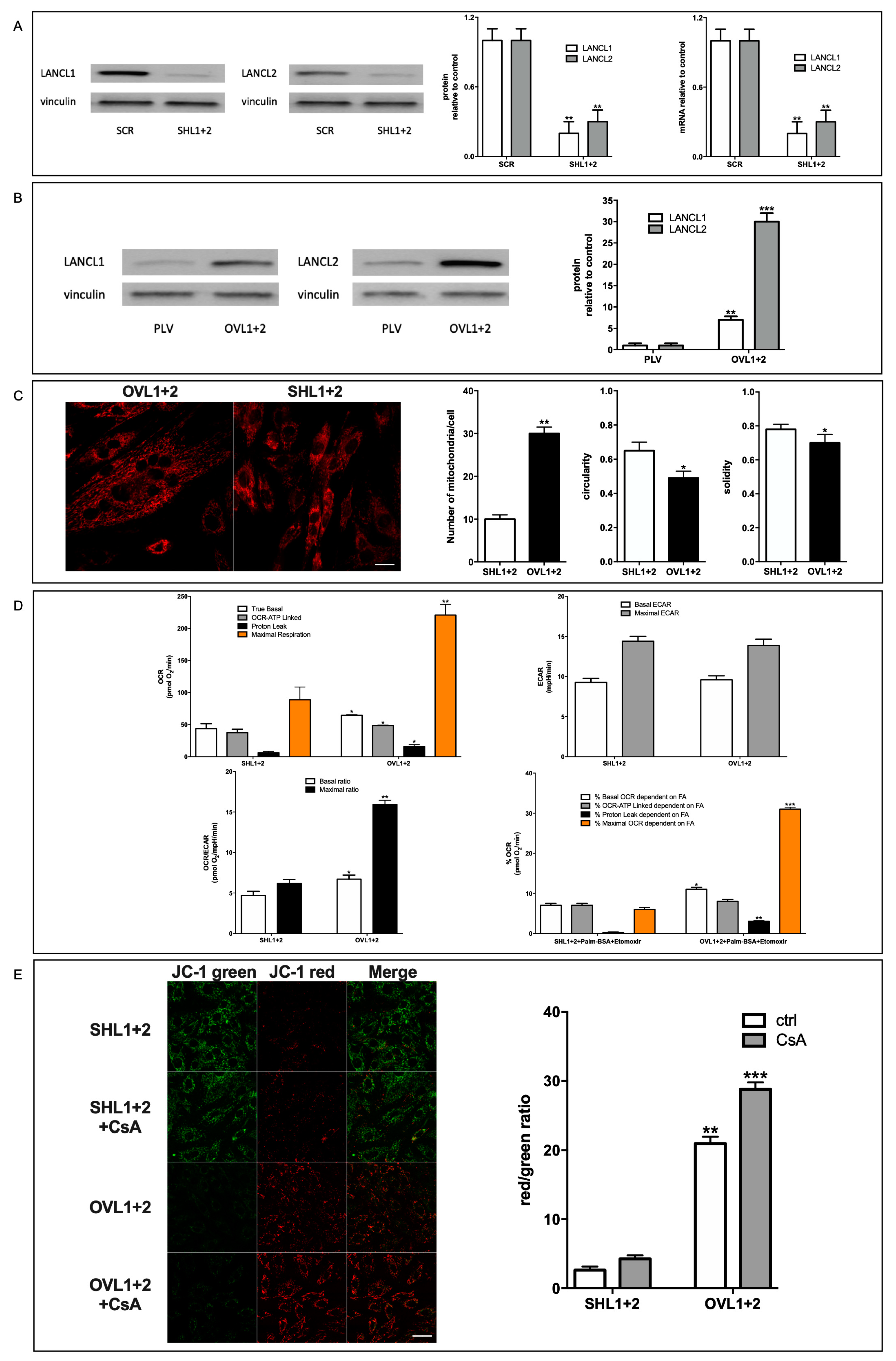
As compared with double-silenced cells, LANCL1/2-overexpressing H9c2 show: i) increased mitochondrial respiration, with higher basal and maximal respiration rates, a doubling of the spare respiratory capacity and a steeper proton gradient (ΔΨ) (
Figure 1D, E); ii) increased fatty acid-fueled respiration rate (
Figure 1D); iii) increased NO generation [
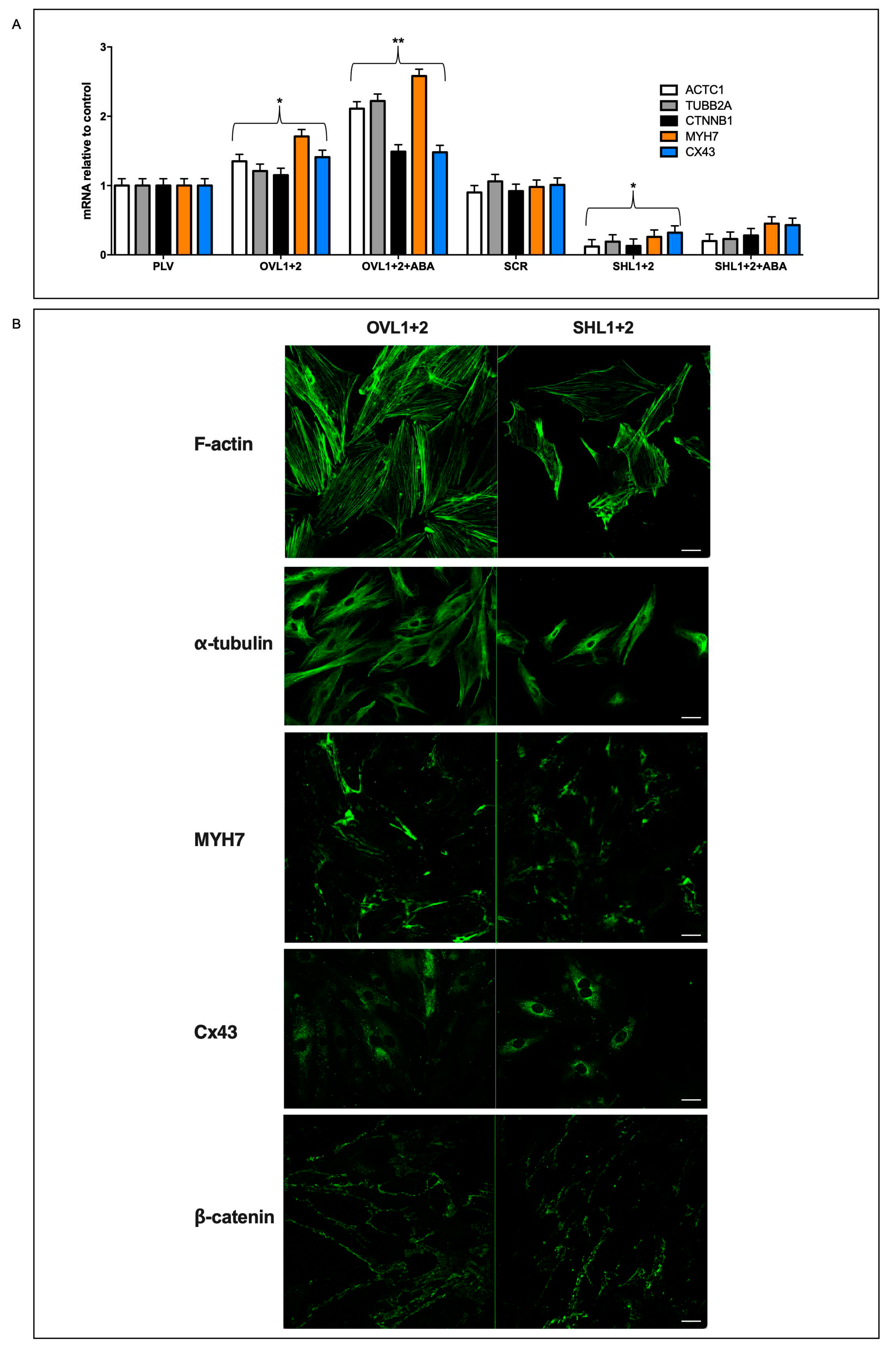
5]; iv) reduced mitochondrial ROS content, higher expression levels of ROS-scavenging and lower levels of ROS-producing enzymes [Spinelli S. et al. submitted]; v) increased transcription and expression of contractile and ion channel proteins (
Figure 4); vi) improved resistance to hypoxia/reoxygenation [
10]; vii) increased proliferation rate (
Figure 3). In short, LANCL1/2 overexpression, and their targeted stimulation by treatment of the cells with ABA, transforms H9c2 cardiomyoblasts into “super-cells”. How are such pleiotropic effects orchestrated?
The AMPK/PGC-1α/Sirt1 axis is known to control energy metabolism and mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle [
29,
30], adipose tissue [
31,
32] and heart [
33,
34,
35]; thus, the fact that LANCL1/2 overexpression induces the activation of this signaling axis (
via transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms) in adipocytes [
10], skeletal muscle cells [
9] and cardiomyocytes [
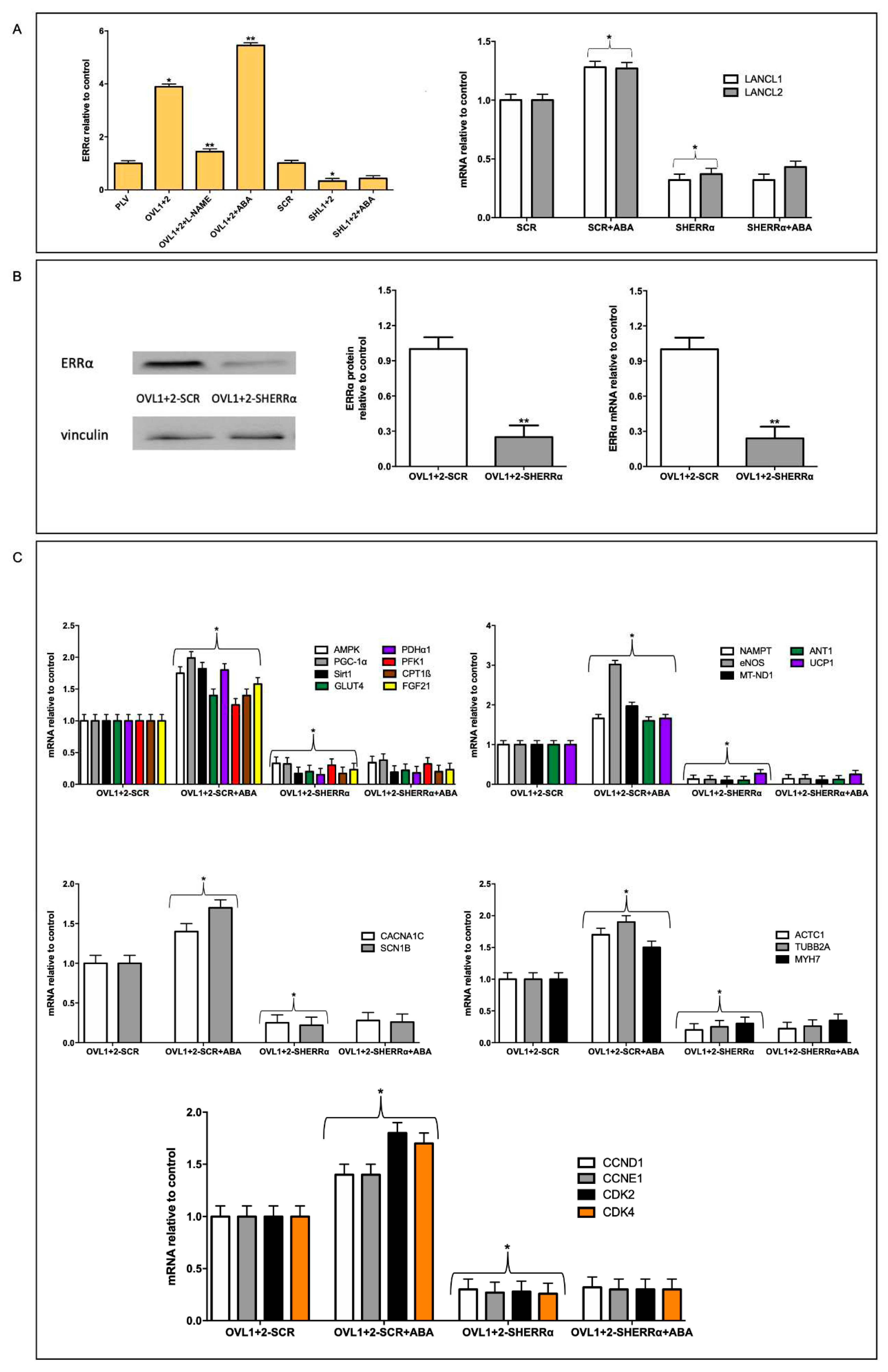
5] is expected to underlie most of the functional effects observed in overexpressing H9c2. A significant new piece of information added in this study is that the transcription factor ERRα is directly responsible for all transcriptional effects observed in LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells and is functionally linked to the LANCL proteins, with a reciprocal feed-forward mechanism of transcriptional stimulation (
Figure 7).
ERRα activity is known to be important for cardiomyocyte mitochondrial function. The critical role of ERRα in cardiomyocyte function starts during myocyte maturation [
36] and continues in adult cardiomyocytes, in combination with PGC-1α, with which it shares a reciprocal transcriptional positive regulation [
6,
37]. Thus, ERRα/PGC-1α control cardiac energy metabolism, metabolic flexibility, mitochondrial respiration and biogenesis. Indeed, pharmacologic targeting of AMPK, which activates ERRα transcription and promoter activity [
38] and/or of the ERRα/PGC-1α system [
39,
40] has been proposed to improve cardiac function in the ailing heart.
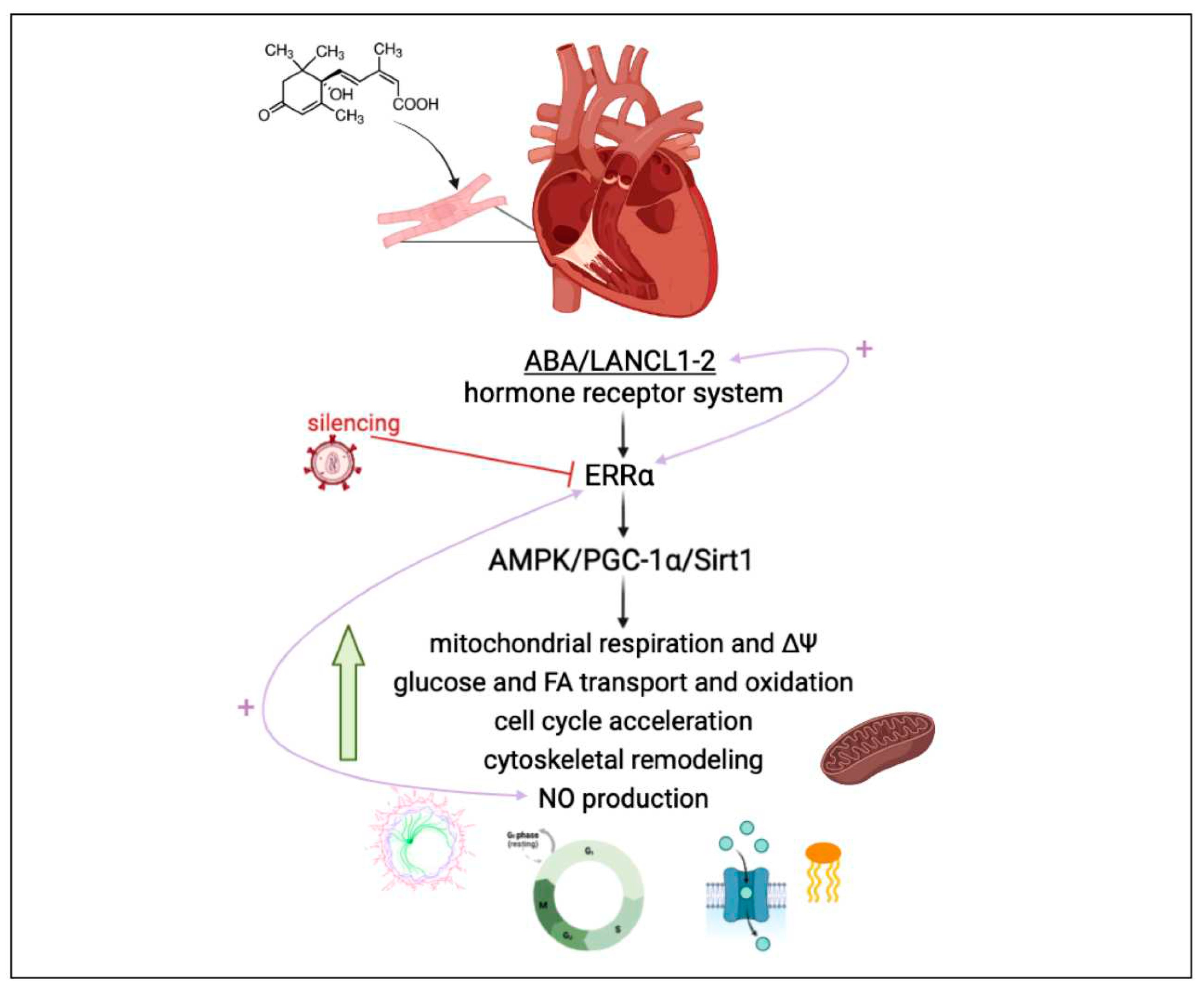
Figure 7.
The ABA/LANCL1-2 hormone-receptors system controls cardiomyocyte fitness via NO and ERRα. LANCL1/2 overexpression activates the AMPK/PCG-1α/Sirt1 axis in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes [5-Spinelli Cells 2022], via the orphan-receptor/transcription factor ERRα. A reciprocal transcriptional stimulation links LANCL1/2 and ERRα (right pink arrow). Downstream of this signaling axis several key functional features of H9c2 are stimulated, resulting in a higher energy availability and increased NO production, which in turn activates ERRα transcription (left pink arrow) providing a positive feedback which tends to maintain cells in this energy-proficient state.
Figure 7.
The ABA/LANCL1-2 hormone-receptors system controls cardiomyocyte fitness via NO and ERRα. LANCL1/2 overexpression activates the AMPK/PCG-1α/Sirt1 axis in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes [5-Spinelli Cells 2022], via the orphan-receptor/transcription factor ERRα. A reciprocal transcriptional stimulation links LANCL1/2 and ERRα (right pink arrow). Downstream of this signaling axis several key functional features of H9c2 are stimulated, resulting in a higher energy availability and increased NO production, which in turn activates ERRα transcription (left pink arrow) providing a positive feedback which tends to maintain cells in this energy-proficient state.
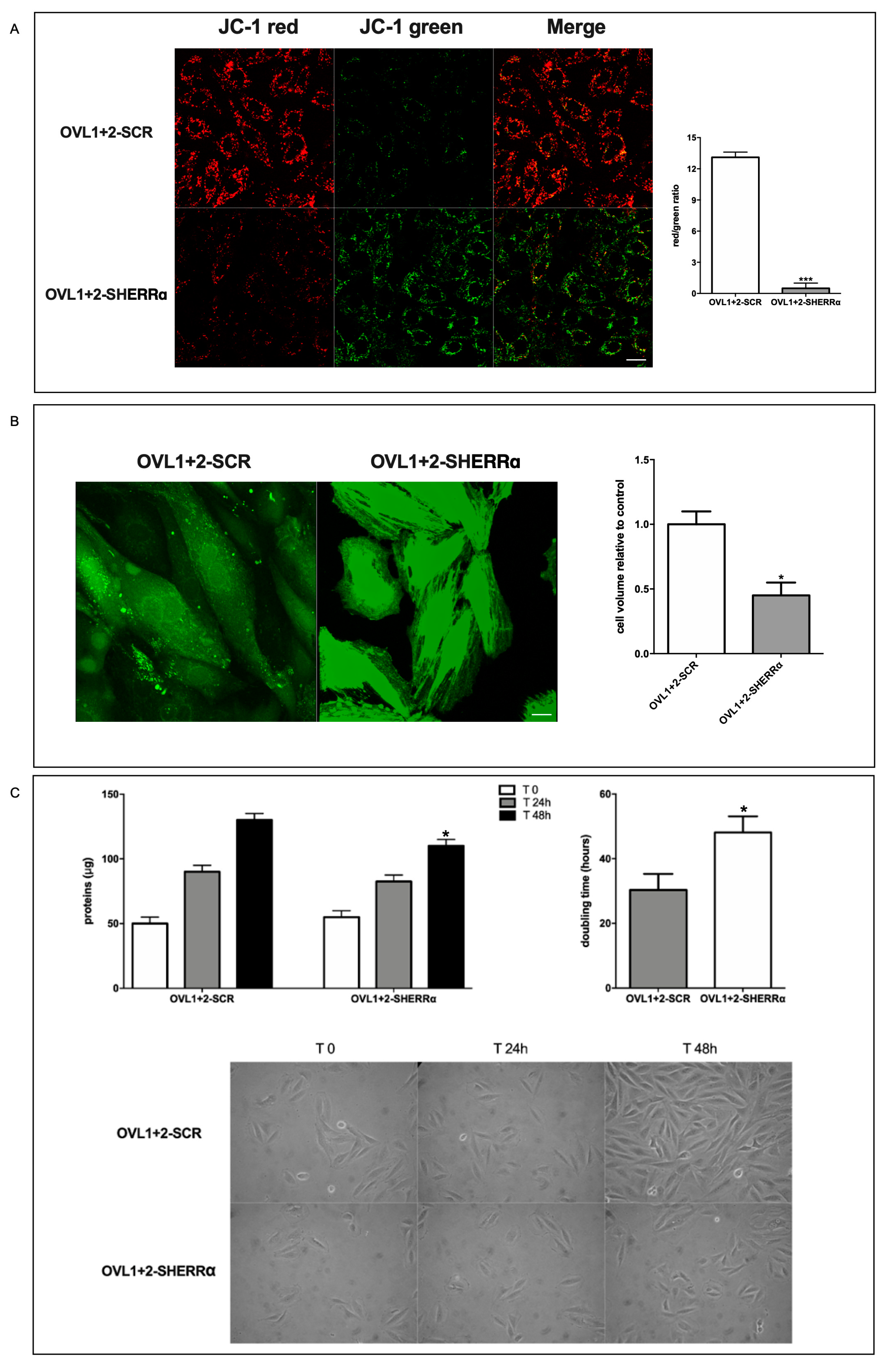
Here we show that LANCL1/2 overexpression increases, and their double silencing conversely significantly reduces ERRα transcription and expression. In turn, silencing of ERRα reduces endogenous LANCL1/2 mRNA levels in H9c2 and significantly reduces or abrogates all transcriptional and functional effects induced by LANCL1/2-overexpression (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). In particular, ERRα silencing abrogates the mitochondrial effects of LANCL1/2 overexpression, reducing the proton gradient (
Figure 6A), increasing mitochondrial ROS [Spinelli S. et al submitted] and reducing expression of ROS-scavenging enzymes [Spinelli S. et al submitted]. It may be surprising that silencing just one transcription factor (ERRα) should have such wide-ranging effects on cardiomyocyte physiology; however, one should consider that all transcriptional and functional effects studied here are closely related: an increased oxidative metabolism is needed to allow higher rates of ATP production, in turn allowing increased protein synthesis and accelerated cell proliferation. Indeed, cyclin levels control transcription of several metabolism-related genes, whose enzyme products are necessary for energy production to allow cell duplication [
41].
A role for ERRα in the control of cell proliferation has been previously described in lung cancer cells [
42]. However, to our knowledge the result reported here (
Figure 5C) is the first direct evidence that silencing of ERRα significantly reduces the transcriptional levels of several cyclins and negatively affects cardiomyocyte proliferation (
Figure 6).
Although adult cardiomyocytes have lost their proliferative potential, specific cyclin (CCN)/cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complexes have been shown to be able to re-start proliferation when overexpressed in adult cardiomyocytes: CDK4/CCND and CDK2/CCND complexes promote entry into G1-S phase [
25]; overexpression of CCNA2 induces a proliferative response in adult porcine cardiomyocytes
in vivo and
in vitro [
24]; the targeted expression of cyclin D2 induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and infarct regression in mice [
22]. These cell cycle-controlling genes are among the ones whose transcription increases in LANCL1/2-overexpressing, and decreases in double-silenced H9c2 (
Figure 3C), indicating a transcriptional control by the LANCL proteins on these cell cycle regulators.
Cell cycle-controlling cyclins, kinases and transcription factors, in particular CCNDs and E2Fs, besides being essential for cell cycle progression, also play important roles in the regulation of energy metabolism [
41]: indeed, nutrient availability, metabolic energy production, mitochondrial activity and cell division are tightly linked processes, which need a coordinated regulation. The fact that overexpression of LANCL1/2 significantly increases transcription of several cell cycle- and metabolism-controlling cyclins
via ERRα, and that conversely their combined silencing dramatically reduces mRNA levels, identifies the ABA/LANCL1-2/ERRα system as a new regulator of this complex gene system, warranting further studies to deepen our understanding of the role of this hitherto unknown relationship in heart pathological conditions, which may benefit from its pharmacologic stimulation.
An increased mitochondrial respiratory activity is generally considered conducive to an increased ROS production, as all respiratory complexes (RC) can produce ROS when electron flow is excessive, causing an electron “overflow” at the reduced RC, or hampered by a limitation of the terminal electron acceptor, O
2. Instead, we observe a higher respiratory capacity in LANCL1/2-overexpressing vs. double-silenced cells, coupled with a reduced mitochondrial ROS production [Spinelli S. et al submitted]. The marked reduction of the mitochondrial proton gradient observed in ERRα-silenced, LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells (
Figure 6A) is accompanied by a significant increase of ROS production, as compared with control LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells transfected with the scrambled sequences for ERRα [Spinelli S. et al submitted]. Together, these observations indicate that ERRα is necessary to mediate the beneficial effect of LANCL1/2 on the mitochondrial proton gradient (which increases) and on ROS production (which is instead reduced).
The reduced ROS generation observed in LANCL1/2-overexpressing vs. double-silenced H9c2 may be due at least in part to the increased expression of ROS-scavenging and the reduced expression of ROS-generating enzymes in the overexpressing cells [Spinelli S. et al submitted]. However, other mechanisms may contribute to reducing ROS generation in the face of an increased mitochondrial respiratory activity.
Mild proton leak across the inner mitochondrial membrane has been recently acknowledged as a means to improve respiratory chain function, while at the same time reducing ROS generation [
43]. The general consensus is that, by reducing the ΔG for proton pumping, a mild proton leak facilitates electron transport and reduces ROS generation at the RC, at the expense of some ATP. However, we observe both a higher proton leak and an increased ATP-dependent respiration in LANCL1/2-overexpressing vs. double silenced cells (
Figure 1D), indicating that the “fine-tuning” of the respiratory chain works better in overexpressing vs. silenced cells, allowing a higher respiration rate and ATP-production and a reduction of mitochondrial ROS content in the face of an increased ΔΨ. Proton transport associated with fatty acid (FA) translocation by ANT1 and with the activity of ATP-synthase have been identified as mechanisms responsible for partial dissipation of the ΔΨ [
19,
20].
ANT1, whose main function is to translocate ATP and ADP across the inner mitochondrial membrane, also allows a FA-dependent “proton leak” through the inner mitochondrial membrane [
20,
44]. ANT1 and ATP-synthase are both inhibited by CsA [
19] and indeed a quantitatively marked increase of the ΔΨ occurs in CsA-treated LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells, further increasing their already high gradient (
Figure 1E). This conspicuous CsA-sensitive proton leak in LANCL1/2-overexpressing cells (
Figure 1E) may play a role in “easing” the work of the proton pumps of the respiratory chain. Indeed, overexpressing cells show a significantly higher FA-dependent percentage of proton leak and of maximal OCR than double-silenced cells, while the percentage of FA-dependent ATP-linked OCR is similar in the two cell types (
Figure 1D), suggesting that the primary function of FA mitochondrial utilization in overexpressing cells is not to produce ATP. Beside ANT1, transcription of UCP1 and UCP3 is also significantly increased in overexpressing compared with double-silenced cells (approx. 7 and 8- times higher), likely indicating a role also for these proton leakers in the higher oxphos efficiency in overexpressing vs. silenced cells.
Mechanisms allowing an unconstrained and regular flow of electrons from NADH (and FADH
2) to oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor (TEA) are also important to prevent ROS production during electron transfer at the RC, since they all can become sites of ROS production through retrograde electron transport, typically under limited oxygen availability [
45,
46,
47]; however, it is reasonable to assume that an increased oxidative metabolic rate may also “overflow” RC with electrons, exceeding their ability of electron transport and resulting in ROS generation. A mechanism “easing” electron flow through RC is availability of other TEAs that can prevent the retrograde electron transport from reduced respiratory complexes, reducing ROS production, while at the same time allowing coenzyme re-oxidation. Fumarate reduction to succinate has long been known as a mechanism capable of alleviating electron “overflow” at the succinate dehydrogenase-coenzyme Q site of the respiratory chain [
48] and fumarate has recently been rediscovered as a TEA and an important means to allow complex I proton pumping under conditions of limited O
2 availability [
49]. By providing an electron “leak” from the respiratory chain, fumarate also prevents ROS production at the RCs while at the same time allowing some proton pumping to occur via complex I. Whether this mechanism of electron leak is more active in LANCL1/2-overexpressing vs. double-silenced cells remains to be investigated.
To sum up, both a proton “leak” from the intermembrane space and an electron “leak” from the respiratory chain flow are mechanisms of oxphos fine tuning, which can be activated in mitochondria to adapt to quantitative changes in the flow of charges in order to maximize energy production and limit ROS generation. The ABA/LANCL system, via ERRα, appears to take advantage of, or to regulate, some of these oxphos fine-tuning mechanisms, as it allows an increased mitochondrial respiration, proton gradient formation, ATP-dependent respiration to occur in H9c2 cardiomyocytes (
Figure 1) in the face of a reduced ROS generation [Spinelli S. et al submitted]. Indeed, despite a 2-fold increase of the proton leak in overexpressing cells, the spare respiratory capacity of these cells is approximately twice that of double-silenced cells (
Figure 1D).
The term “mitohormesis” is used to describe a complex and so far incompletely understood mitochondrial response to “stress”, such as oxygen deprivation, excess ROS production or nutrient deficiency [
50]. Interestingly, several of the transcriptional and functional effects observed in LANCL1/2-overexpressing H9c2 fall within this concerted response. Mild oxphos uncoupling
via increased transcription of several H
+ transporters (UCP1, UCP3, ANT1,
Figure 2A), leading to an increased proton leak (
Figure 1D), increased mitokine production (FGF21,
Figure 2A), exerting mitochondrial and nuclear autocrine and paracrine effects, are among the keynote features of mitohormesis. This multifaceted response is orchestrated through the activation of AMPK, PGC-1α and Sirt1, which is indeed the main signaling axis activated by the ABA/LANCL system, not only in H9c2 cardiomyocytes [
5], but also in human brown adipocytes, where a similar increase of mitochondrial respiration rate and ΔΨ were observed in overexpressing cells [
10]. The fact that several keynote mitochondrial responses typical of mitohormesis are among those activated by the ABA/LANCL system allows to hypothesize that this hormone/receptors system controls mitohormesis, whose function may not be limited to the response to mitochondrial “stress” conditions, such as hypoxia, but could more generally serve the purpose of optimizing mitochondrial function under conditions of changing oxygen availability, electron flow intensity and ATP requirement. Indeed, some of these mitochondrial adaptations to increased oxidative metabolism occur in the skeletal muscle and in the heart under conditions of physical exercise, arguably a “physiological” condition.
Several questions arise from the results described in this and in the previous reports [5 and Spinelli S. et al submitted].
Can we use ABA to activate the LANCL1/2-ERRα signaling pathway and improve cardiomyocyte function or resilience to stress conditions? Targeting the PGC-1α/Sirt1/ERRα axis has been proposed as a means to improve cardiomyocyte function in diabetic cardiomyopathy [
39]; identification of the ABA/LANCL1-2 system as an essential part of the ERRα activating pathway may provide a new pharmacological agonist (ABA) and new molecular targets (the LANCL proteins) to this end.
Another open question regards the molecular signal that activates endogenous LANCL1/2 transcription in cardiomyocytes. NO may indeed be the first signal initiating the functional responses downstream of the LANCL1/2-ERRα signaling pathway, as it is normally produced by the beating heart and cardiac NO levels are affected by conditions of cardiomyocyte “stress” [
51]. NO is apparently involved in a positive feedback mechanism linking eNOS transcription and activity to the expression levels of LANCL1/2 and ERRα. Thus, once activated, a reciprocal feed-forward mechanism maintains a transcriptional activation of LANCL1/2 and ERRα and NO generation in cardiomyocytes (
Figure S2, supplementary data).
It is noteworthy that LANCL1/2 overexpression and ABA-treatment in H9c2 also significantly increase transcription of GPTCH [5-Spinelli 2022], the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of TBH4, the coenzyme needed to prevent “uncoupling” of NOS, resulting in ROS instead of NO generation [
52]. In addition, TBH4 also stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and cardiac contractility via PGC-1α [
53], possibly participating in the LANCL-ERRα-coordinated improvement of mitochondrial performance.