1. Introduction
Climate change and global warming have been the biggest topics of interest in the current decade. The global electricity demand is expected to reach 30,621 TWh in 2030 and 43,762 TWh in 2050, from 24,700 TWh, which was in 2021, with major part of consumption in buildings and an expected increasing demand from EVs and hybrid industries [
1]. Additionally, the invasion of Russia on Ukraine caused energy crisis in many countries. The skyrocketing prices for energy in Europe induced a major burden on consumers, and had a big impact on the economy which was recovering from the COVID pandemic [
2]. The net zero emissions and sustainable energy can be achieved with the implementation of different types of Renewables (such as, e.g., Solar Photovoltaics (PV), Wind, Hydropower, Geothermal power, Ocean power, Bioenergy). The total Renewable Energy capacity by the end of 2020 was 2,802 GW [
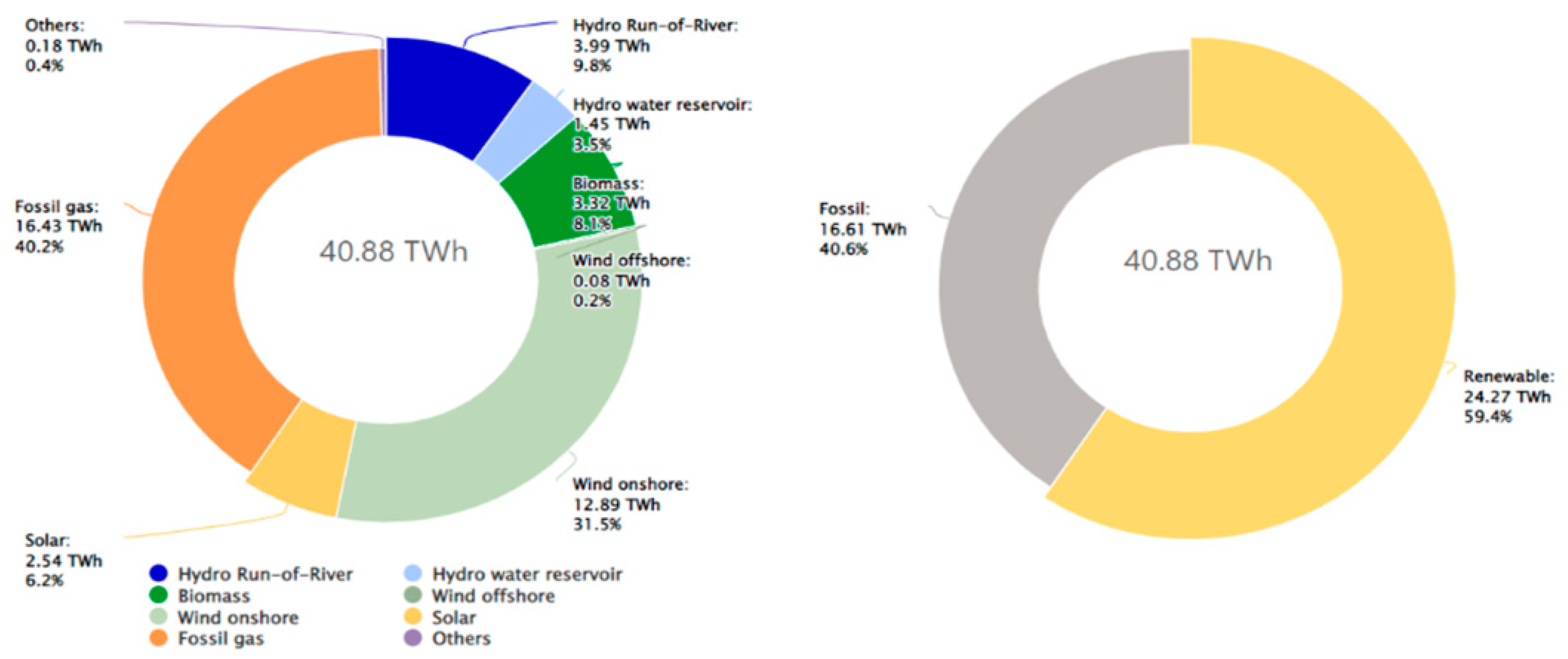
3]. Portugal generated 24.27 TWh of Energy in 2022, accounting for 59.4 % of the total electricity production as shown in
Figure 1 which is the distribution of different sources of electricity generation [
4].
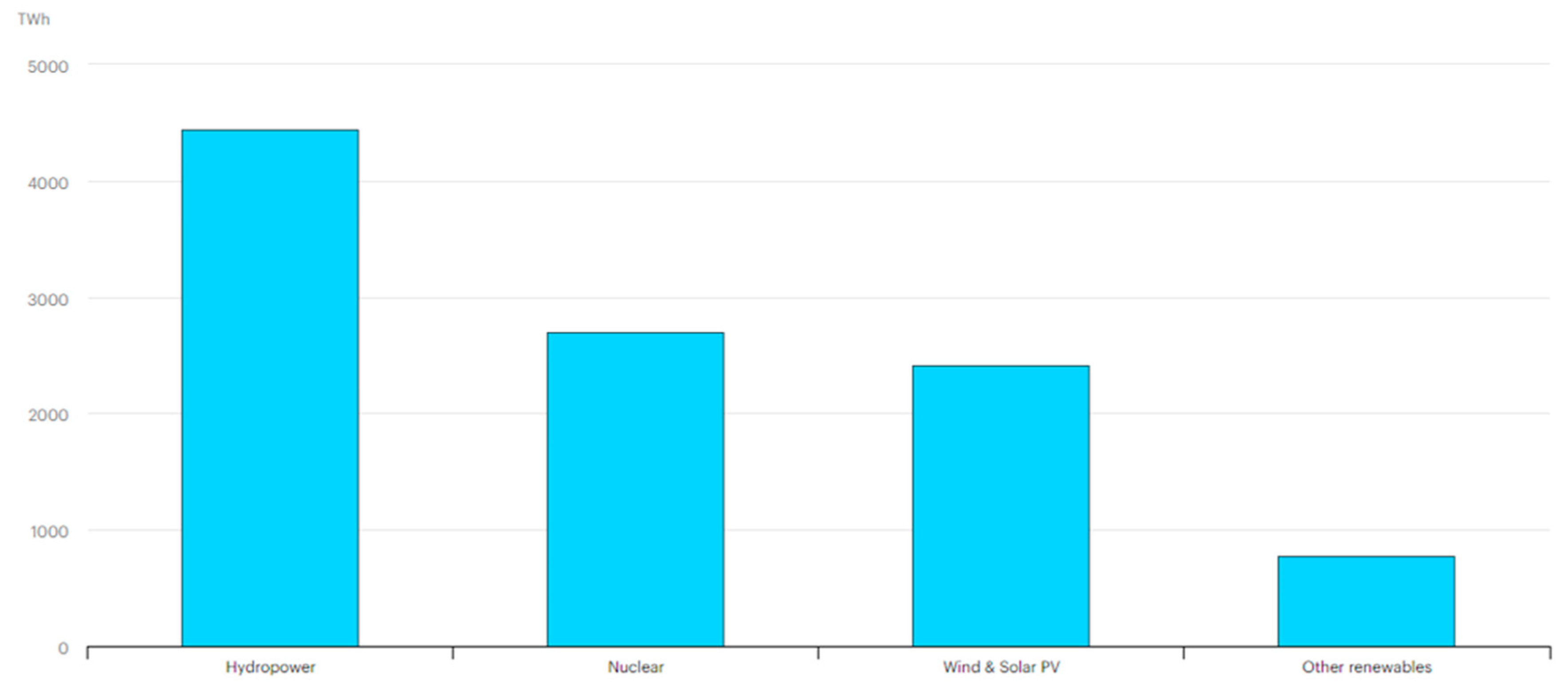
Hydropower has the highest contribution among all renewable energies. Its capacity is more than the rest of renewable energy technologies combined. 17% of the global electricity was produced by Hydropower in 2020.
Figure 2 shows the statistics of the low carbon electricity generating technologies in 2020 [
5]. This ability of Hydropower with low carbon electricity and very high generation capacity will be very critical in the journey of the energy transition. Hydropower can be produced in both large and small scales. The large or medium scales typically include the construction of dams and reservoirs to convert potential and kinetic energy into electrical energy, while small scale hydropower can also include energy extraction from water distribution systems and irrigation systems, using existent infrastructures and so adhering to the circular economy concept. Hydropower can also be exploited with the water hammer and PSH technology combined with other renewables such as Solar PV and Wind Energy.[
6]
Decentralized power systems which use only renewable energy systems as energy sources encounter the problem of intermittent energy production from solar and wind and this can be overcome using storage systems. Batteries are one of the excellent energy storage systems which store energy chemically. Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) is another storage technology which can be used to store energy mechanically. Within this context, this research tries to address the problem of an efficient energy storage technology for mini-grids at remote places and islands. This is a very relevant topic, especially in the European Union. The European Commission is indeed supporting a just and sustainable transition, which means ensuring that regions are not left behind in the clean energy transformation. Besides, the European Commission is committed to ensuring that rural areas benefit from the new economic opportunities from renewable energies. Renewables are well suited for decentralized and local generation by increasing the number of small-scale energy projects to promote sustainable energy production.
The paper’s objective is to find the optimum storage technology and have a comparison between Batteries and PSH with respect to their economic evaluation. The economic analysis between PSH and Batteries in Microgrids is done using HOMER software which gives an optimum result with lowest Net Present Cost (NPC) for Microgrids, for a given load scenario of a particular location. PSH uses water resources to store it physically and is run by a turbine to generate electricity. The water is pumped to an upper reservoir when there is excess of electricity production from other renewable resources. The batteries store the energy chemically and Li-ion batteries are efficient battery technologies which are used in current days. The economic scenario of PSH is chosen and a technical analysis is done by separating the result data into different seasons using Python data analysis and the role of PSH as storage is explained. This research further analyzes the sensitivity cases considering different capital cost of solar PV, wind turbine and PSH.
1.1. Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) for medium and large-scale energy storage and production
PSH can be considered as a big battery bank which stores water at higher elevation with respect to a lower reservoir or water body. Whenever there is a demand for electricity, water is discharged from upper reservoir to the lower reservoir. The water discharged from the upper reservoir runs a hydro turbine that generates electricity. Whenever there is a surplus of electricity produced from renewables such as wind or solar or when the electricity demand is low, the water is pumped back from the lower reservoir to the upper one. This method of energy storage becomes very critical in off-grid energy systems when there is a dearth of power production from renewables in a low sunshine or a low-speed wind condition which cannot satisfy the demand of electricity. The electricity produced can be controlled by varying the flow to the turbine according to the electricity demand.
The world’s largest battery technology is pumped storage hydropower, which accounts for more than 94% of installed global energy storage capacity [
8].There are two ways in which PSH can be effectively used for storage. In open loop PSH, the water from a natural body is used to fill one of the two reservoirs and an upper reservoir is used to store the pumped water. In the closed loop, PSH does not have any connection to natural water body and has connection between two reservoirs (upper and lower) only. The environmental impact of an open loop PSH towards the aquatic and terrestrial habitat is more than that of the closed loop PSH, because also the natural river is affected [
7]. Closed loop PSH is used in the current research for HOMER simulations.
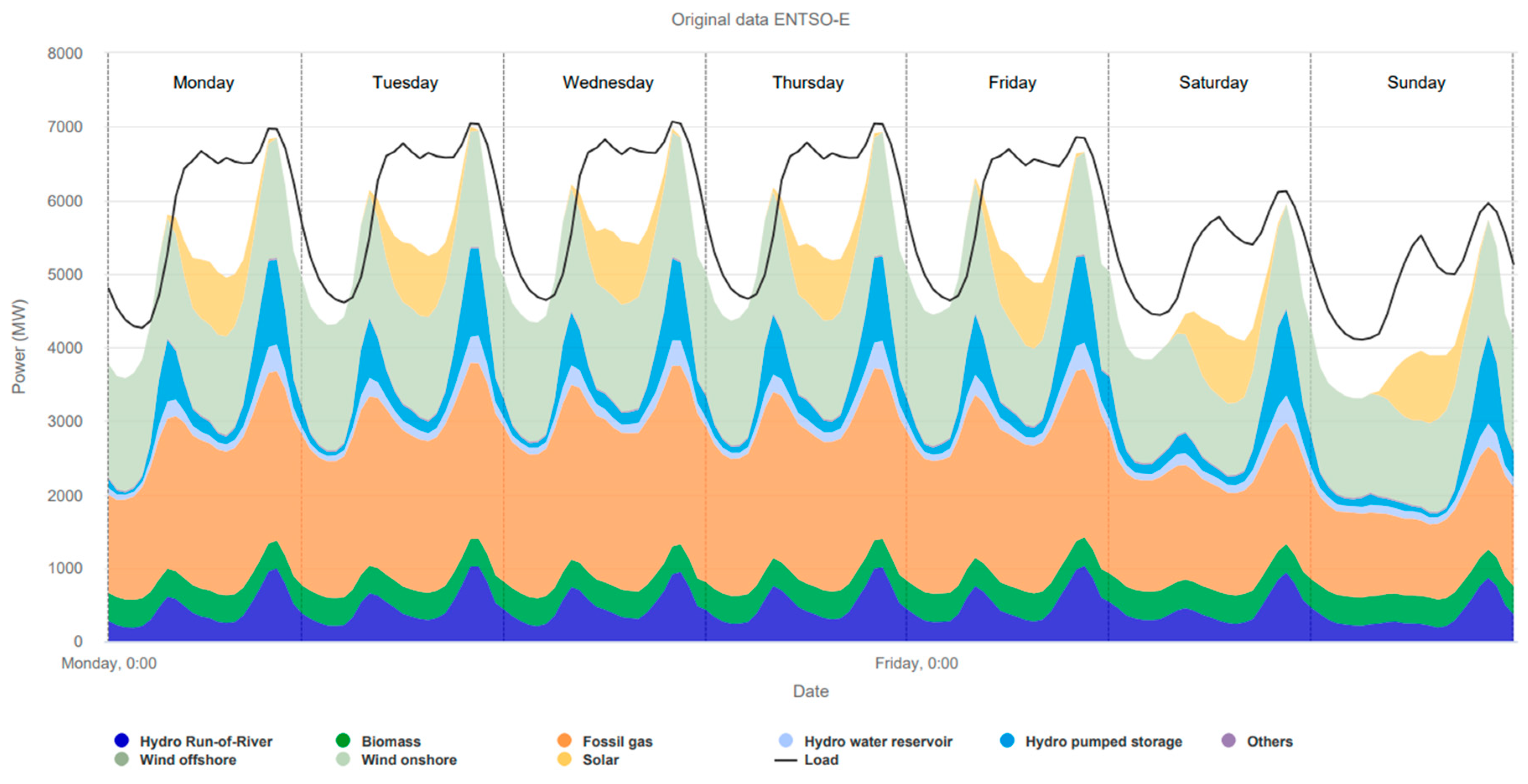
In 2022, the total installed turbine power capacity from PSH in Portugal was 3.71 GW, and
Figure 3 shows the weekly average electricity production in Portugal using different resources and shows the contribution of PSH in the total electricity generation [
9].
1.2. Batteries as storage in Microgrids or off-grids
Batteries are the chemical energy storage technologies that have been revolutionizing the world with their storage capabilities in grids, mobility, electronic gadgets, and many more. The critical factors to consider in a battery are its efficiency, its life cycle time, the temperature of the operation, depth of discharge (DOD), density of energy and self-discharge [
10]
. There are different classifications of technologies based on the chemistry of the battery such as Lead Acid batteries, Li-ion, Nickel Cadmium, Sodium-Sulphur, Vanadium redox, and much more. The study in
[11] analyses the different types of batteries for energy storage and concludes by saying that sodium-sulfur batteries are used in large-scale storage systems, and the production cost of Li-ion and sodium-sulfur batteries are very high in comparison with other battery technologies. However Li-ion batteries have a high efficiency, high energy density and also a longer life cycle which makes them a potential energy storage system for grid application (both off-grid and on-grid) [
12]
. Lead acid batteries are also the potential competitors for energy storage in off- grids and microgrids due to their low cost. When Lead acid batteries are compared with Li-ion batteries, Li-ion batteries show a longer life cycle, greater efficiency, a better charging and discharging cycles, although the upfront cost of Lead acid batteries seems to be lesser than Li-ion batteries but over the lifetime of the batteries, Li-ion batteries come out to be the economic option [
13].
1.3. Microgrids or Decentralized Power Production
There are several constraints in extending energy access to remote places and islands as this will be a problem economically and will also cause environmental impacts. Decentralized power production with distributed energy resources is a promising system where power generation and consumption exist at the same place. This system can have zero emissions by using renewable sources only. Wind and Solar can be the major resources for the production of electricity, however, the problem of intermittency of power production in Solar PV and Wind Energy is a major problem to use only renewables as a source for satisfying the demand. Therefore, the usage of Energy storage technologies such as Batteries and PSH becomes inevitable to satisfy the continuous demand for electricity. Batteries and PSH come with their pros and cons when used as storage technology. Reference [
14] gives an overview of the different software that can be used for the design of hybrid energy systems. A hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) is one where there is a combination of more than one energy source [
15]. The HOMER is a software tool that is used to design power systems which is developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory of the US. The software can be used to design microgrid systems using various energy generation technologies with the resources that can be taken from a specific geographic location. The software performs simulation, optimization and sensitivity analysis. The simulation is done to consider the technical aspects and life cycle costs and the optimization of HOMER selects the scenario that satisfies the technical aspects with least cost over the period of project. The sensitivity analysis takes care of the uncertainties and performs a range of simulations and optimization considering the variability in inputs [
16].
Table 1 shows the different researches that are studied on HOMER software.
1.4. Data Preparation and Cleaning of the obtained load data
The load data is obtained for each hour from the REN website source [
23] of Portugal country and is scaled down to obtain the load suitable for the analyzed microgrid. The load data obtained from the website are further used in the simulations of the HOMER software. The quality of data is enhanced by identifying and clearing the error and data that are not consistent [
24]. There can be different types of data, but quantitative data are the data that can measure the topic of interest with numbers such as integers or decimals, and consistent data will result in a reliable analysis of data [
25]. To avoid any sort of unwanted results where there is a usage of data, the data has to be cleaned first before using it. With the use of Python language for data analysis, the load data that is obtained from the REN website is prepared. The zero and missing value of power is replaced by the average value of power consumption. The duplicate values from the collected data are removed in the data preparing process. Outliers are the data that are significantly deviating from the normal value or the pattern in the obtained data.
4. Conclusions
In an ever-increasing demand for energy in the foregoing world, due to climate change and global warming issues, the need for energy transition has become critical. The rise in Solar PV and Wind Energy renewables have given rise to potential problems for variability in power production. The storage of energy is necessary for the problem of intermittent power production from renewables. Batteries and Pumped Storage Hydropower are some of the storage technologies that are being used.
This research discussed the analysis of two scenarios using HOMER and Phyton softwares. The HOMER model finds an economic solution for the microgrid which satisfies the demand of the load. Scenario 1 used batteries as storage with solar PV and wind turbine as renewable sources of power generation. An inverter is used to convert DC to AC. Scenario 2 used PSH with the same renewable sources as Scenario 1 and from same manufacturers. The simulations resulted in a NPC of 95.2 M € and a LCOE of 0.786 €/kWh for Scenario 1, whereas Scenario 2 resulted in a NPC of 45.8 M€ and a LCOE of 0.379 €/kWh, clearly indicating that Scenario 2 with PSH is the most economical solution. The real projects should be chosen based on the location and the batteries have a small lifetime in comparison with PSH which result in replacement costs. Even though the cost of batteries is getting reduced over time, it is still difficult to compete with PSH economically. The technical analysis of Scenario 2 indicates the need for the storage of the data obtained from the HOMER. Data analysis with Python is done to separate data into different seasons and was plotted to understand the role of PSH in winter and autumn seasons where the power from PV is less. Sensitivity analysis gives an advantage to analyzing projects by varying important variables. The most optimal solutions with different capital cost multipliers for Solar PV - SG-340P and Wind Turbine - Enercon E-48 resulted from the combination of Solar PV, Wind Turbine, and PSH.
The topic further has scope with machine learning techniques to forecast energy demand and weather data. Modern digital technologies are used to develop smart solutions and smart grids with the Internet of Things (IoT) where the lowest cost of energy is inserted into the grid automatically and the PSH started based on the power demand and weather forecast conditions.
The other advantages that are worth mentioning of hydropower as a storage solution against batteries are that i) Hydropower is a huge “water battery” where the size between battery and hydropower, the flexibility, renewable energies integration can be made in a complementary way allowing to better face to climate changes and local climate weather harmonization, fighting against water scarcity, social and environmental impacts creating a water reserve to fight fires and for drinking and irrigation water uses. ii) Hydropower multi-purposes hybrid water-energy solution is more and more of utmost importance in near future. iii) The lifetime of PSH is comparably higher than Batteries, guaranteeing a long-life solution. iv) The number of cycles of charging and discharging can be high for PSH without losing the lifespan of the system, when compared with batteries. These advantages and the economic analysis suggest that PSH can be a better solution as storage for microgrid and off-grid systems in comparison with batteries. However, with the trends for future solid batteries maybe in the future, a solution will incorporate both components, but PSH presents always more technical, environmental and social benefits for the population welfare.
Figure 1.
Share of electricity production in Portugal for the year 2022.
Figure 1.
Share of electricity production in Portugal for the year 2022.
Figure 2.
Different technology for electricity generation worldwide with low carbon emissions in 2020.
Figure 2.
Different technology for electricity generation worldwide with low carbon emissions in 2020.
Figure 3.
Average total net electricity generation during one week in Portugal in 2022.
Figure 3.
Average total net electricity generation during one week in Portugal in 2022.
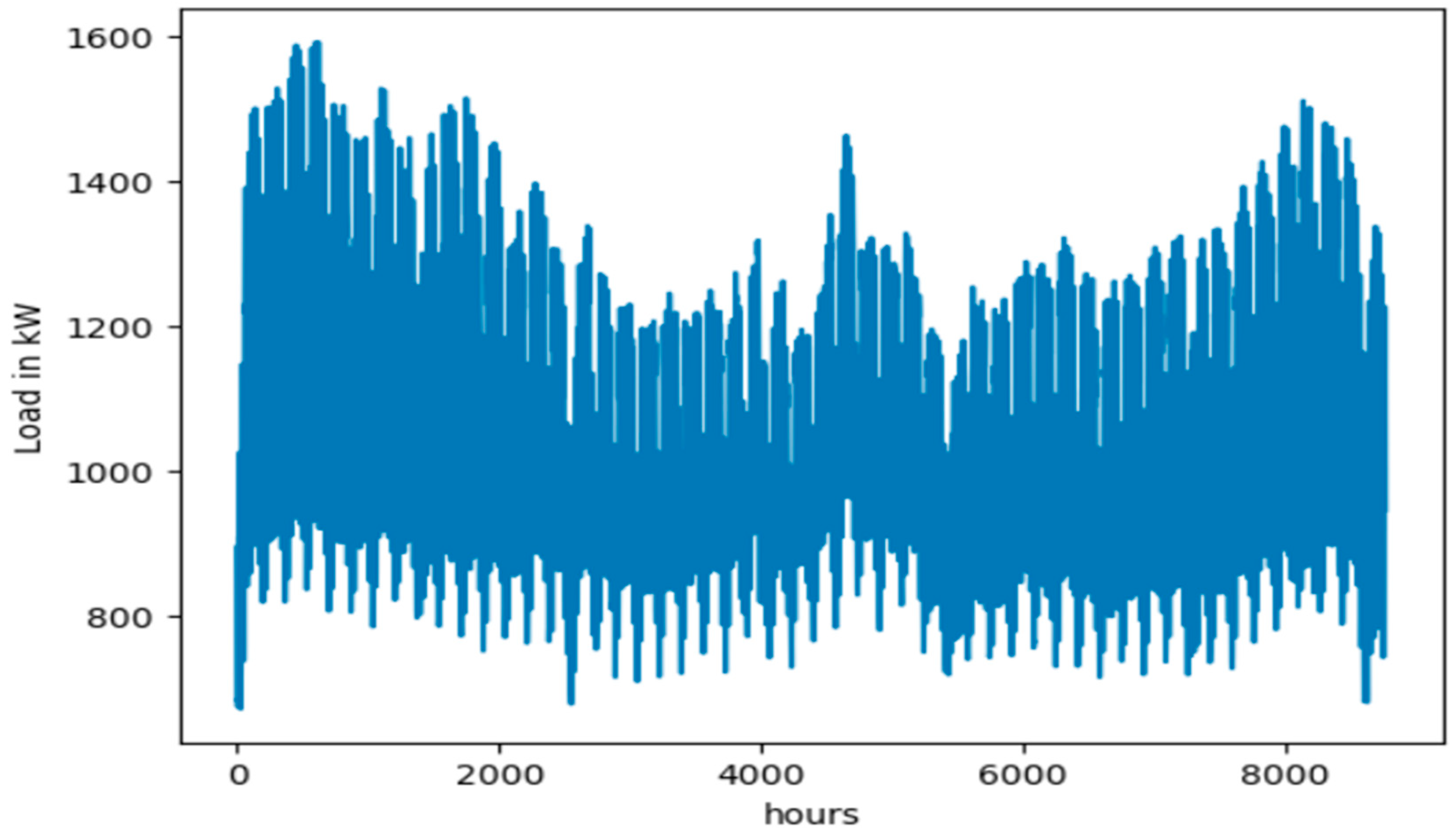
Figure 4.
Hourly load distribution in kW throughout the year 2022.
Figure 4.
Hourly load distribution in kW throughout the year 2022.
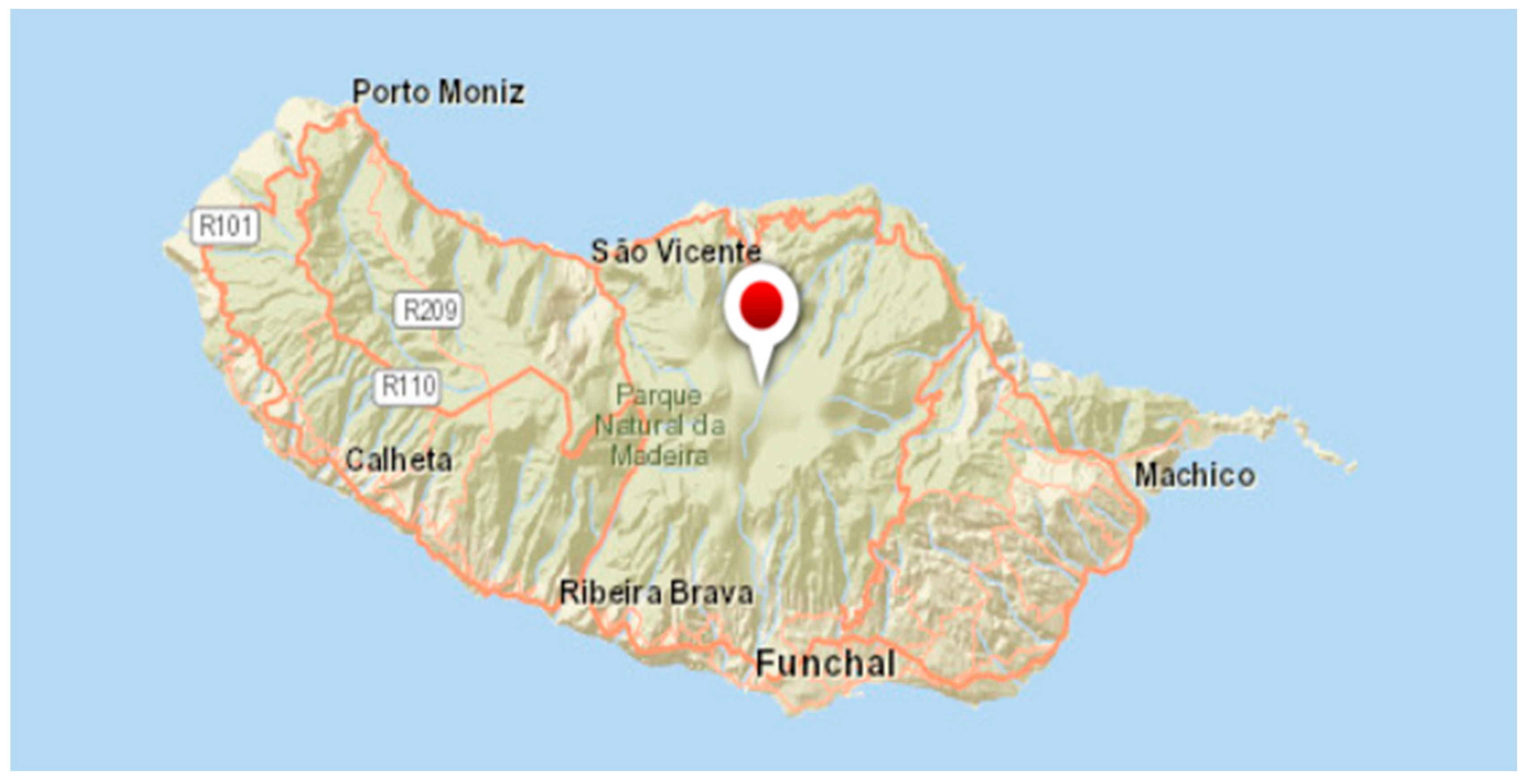
Figure 5.
Map of the location for simulations.
Figure 5.
Map of the location for simulations.
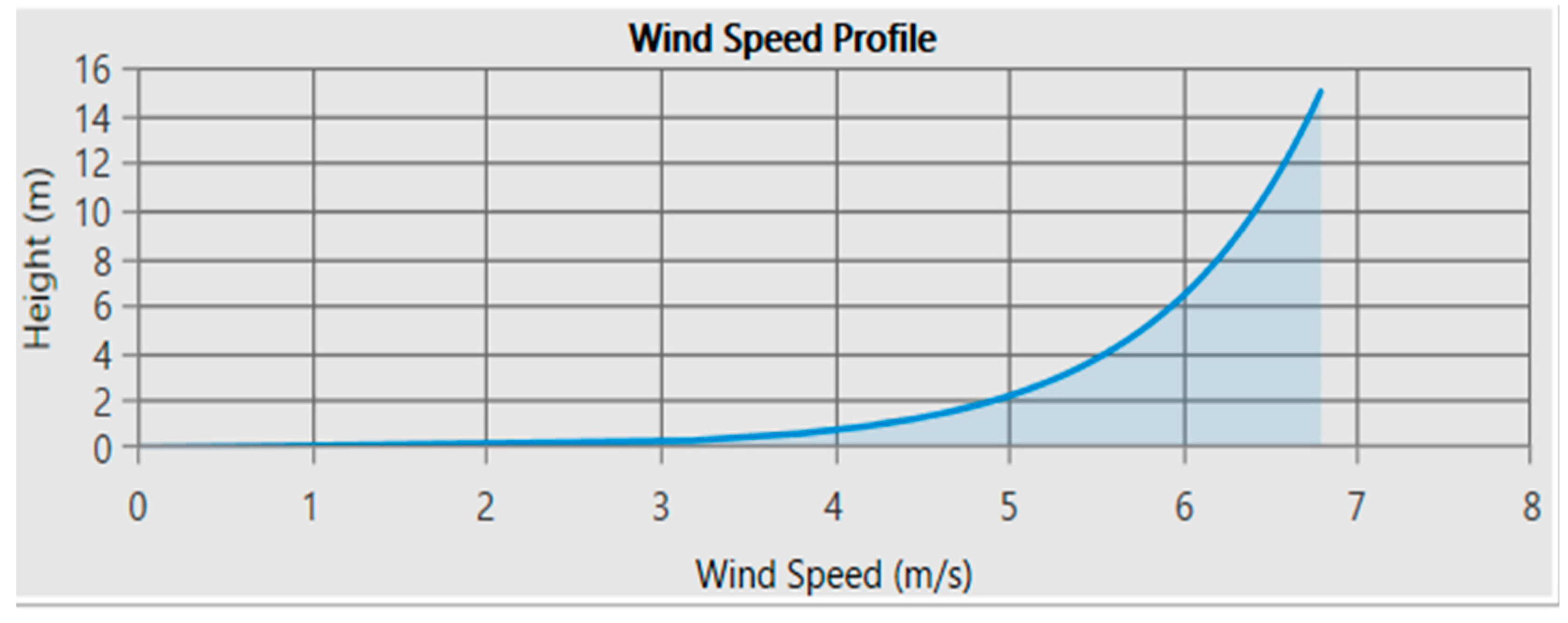
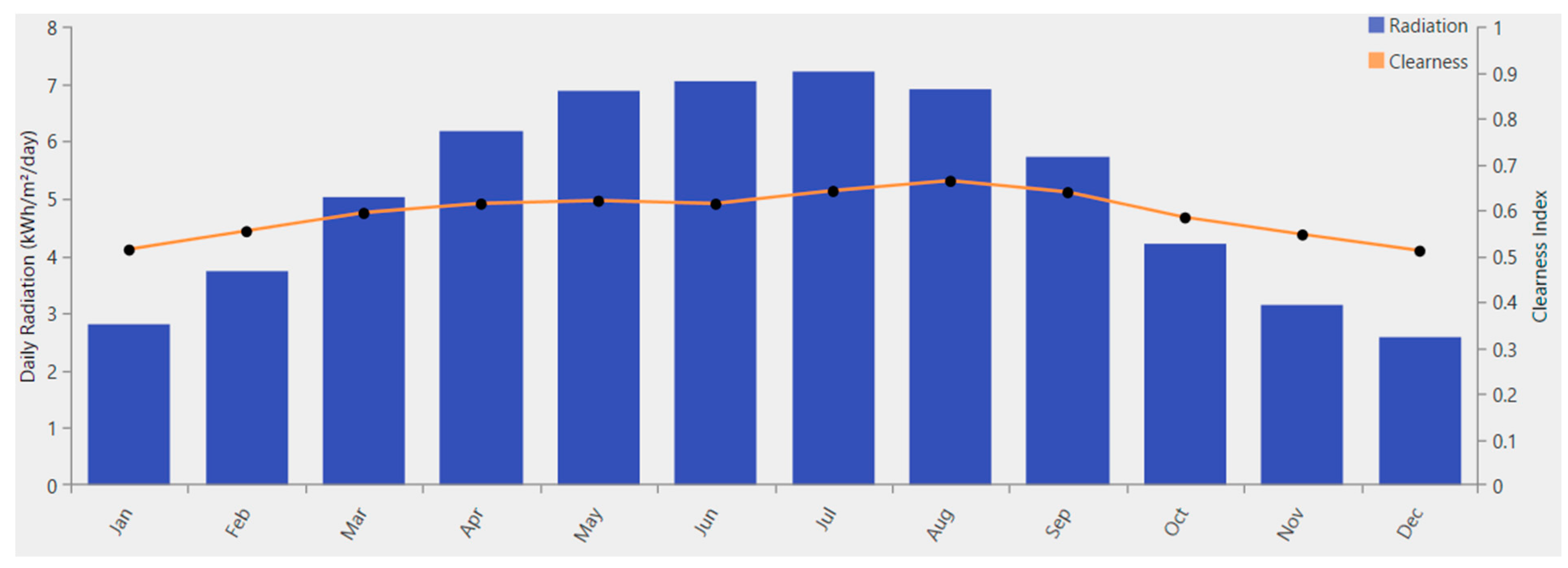
Figure 6.
Solar Radiation data of the location with radiation in kWh/ /day for different months of an average year and with the clearness index for different months.
Figure 6.
Solar Radiation data of the location with radiation in kWh/ /day for different months of an average year and with the clearness index for different months.
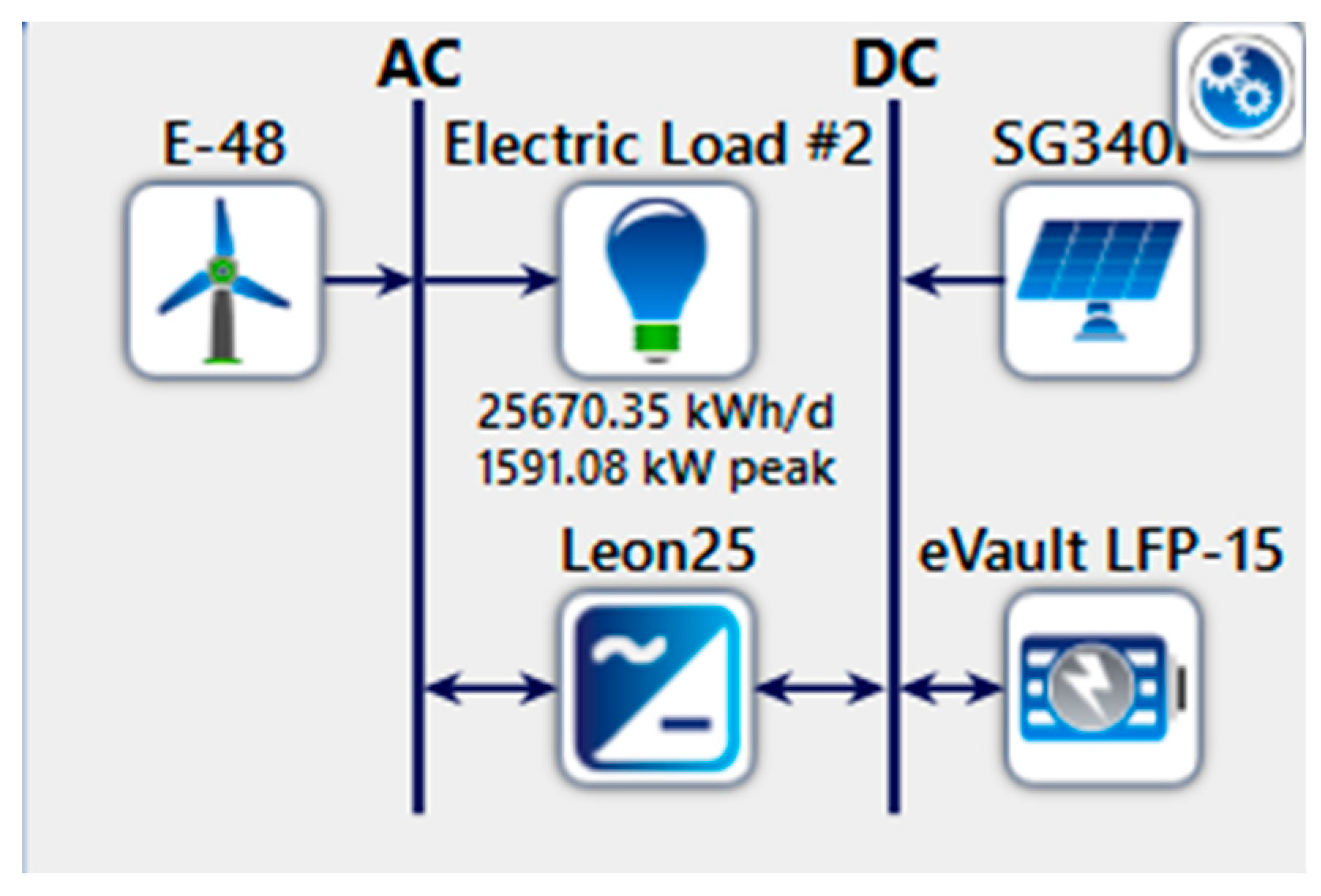
Figure 9.
Scenario 1 with Wind Turbine, Solar PV and Battery as storage.
Figure 9.
Scenario 1 with Wind Turbine, Solar PV and Battery as storage.
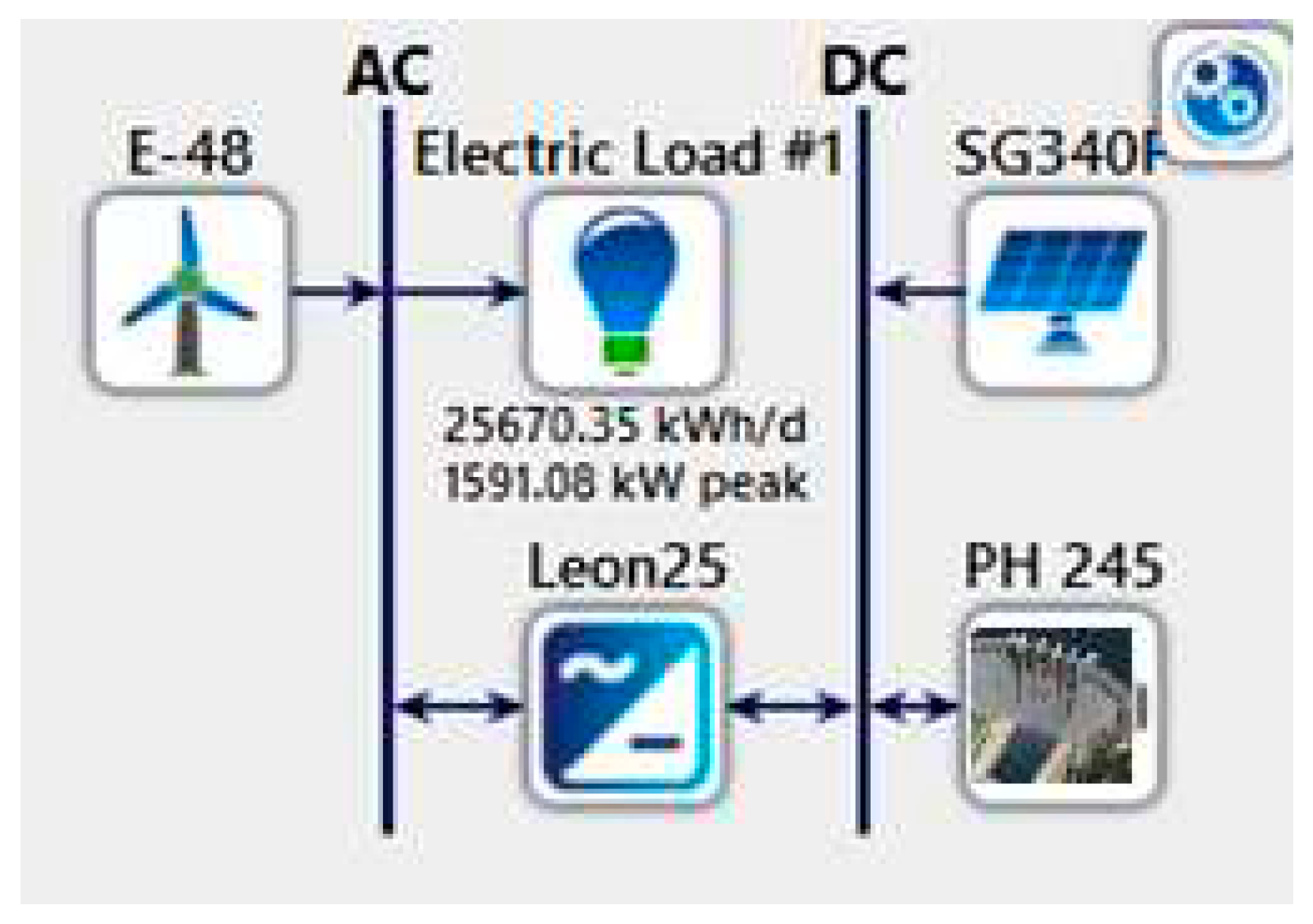
Figure 10.
Scenario 2 with Wind Turbine, Solar PV and PSH as storage.
Figure 10.
Scenario 2 with Wind Turbine, Solar PV and PSH as storage.
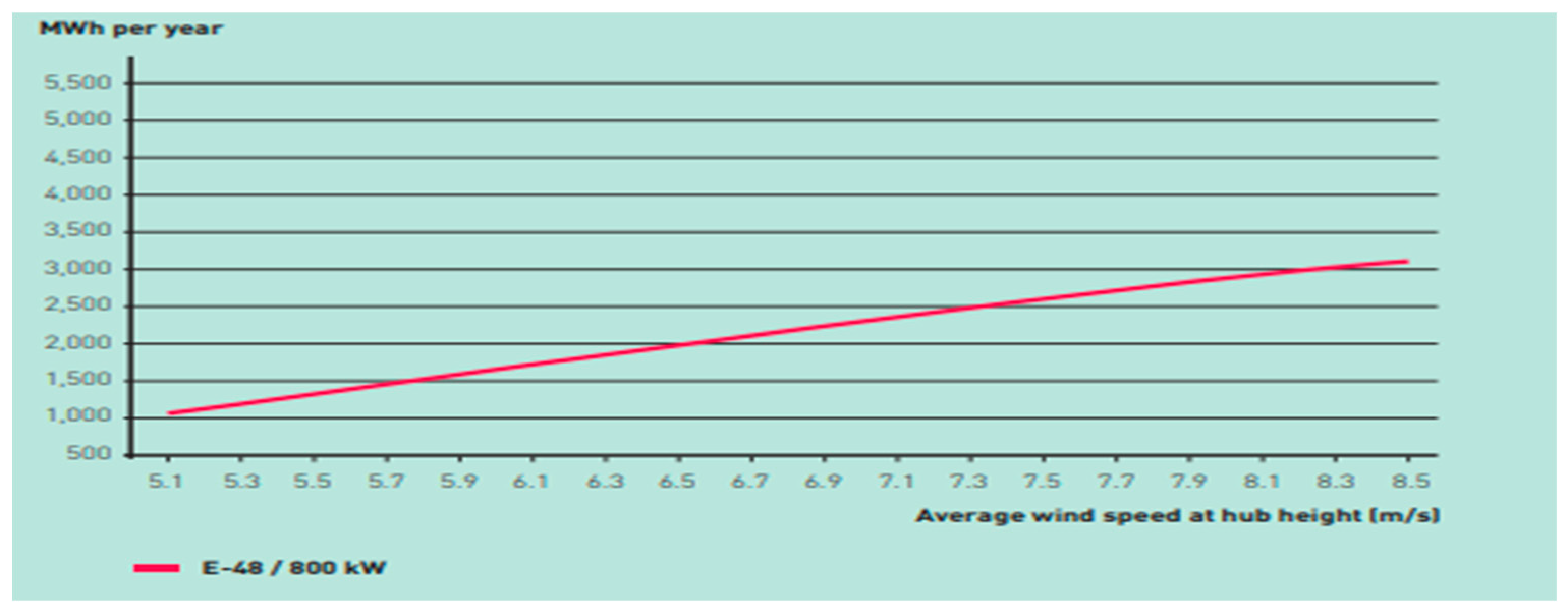
Figure 11.
Annual Energy yield of Enercon E-48 wind turbine.
Figure 11.
Annual Energy yield of Enercon E-48 wind turbine.
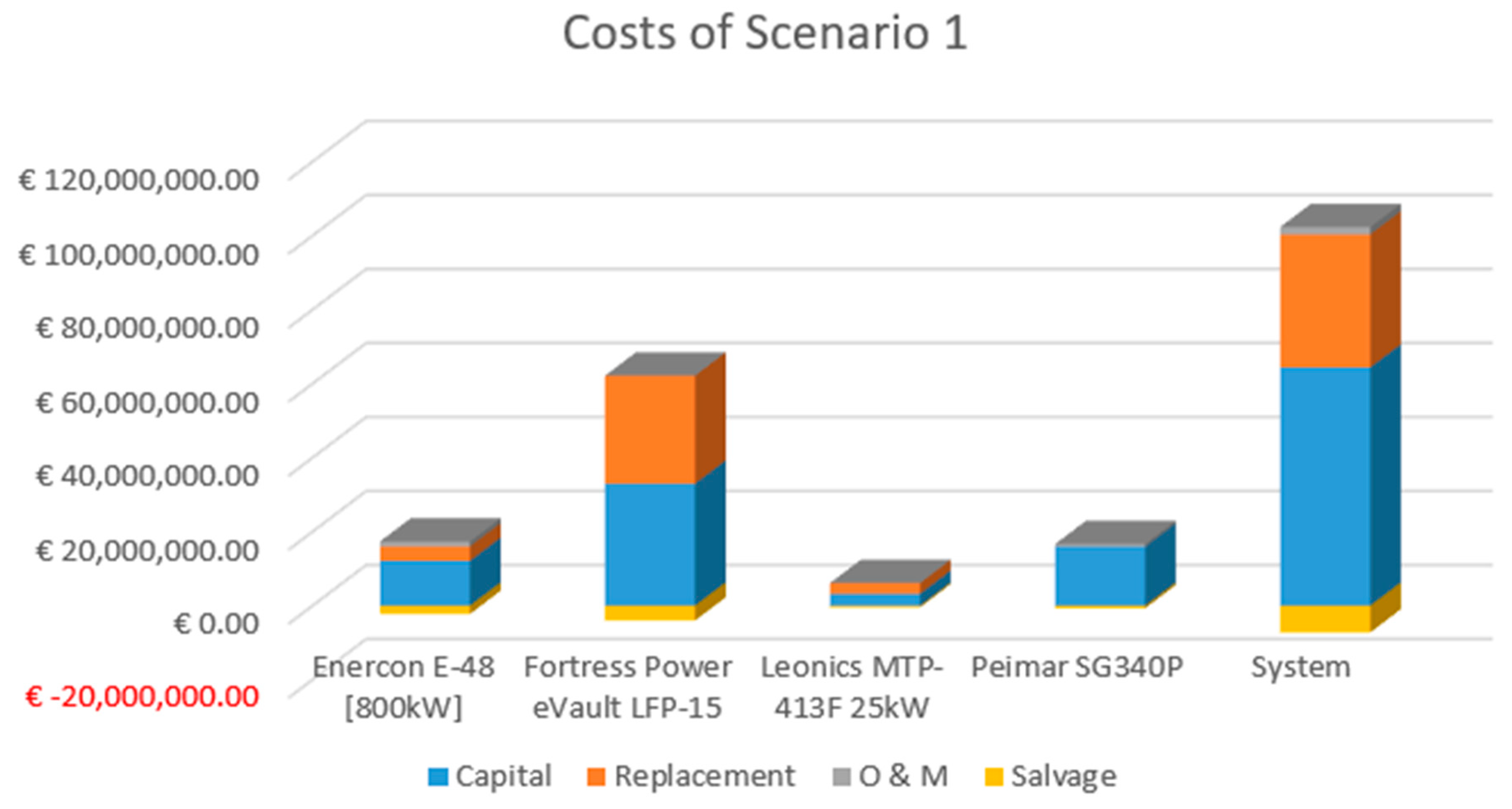
Figure 12.
Representation of Capital, Replacement, O & M and Salvage cost values of PV, Wind Turbine, Battery, Converter and the whole system for Scenario 1.
Figure 12.
Representation of Capital, Replacement, O & M and Salvage cost values of PV, Wind Turbine, Battery, Converter and the whole system for Scenario 1.
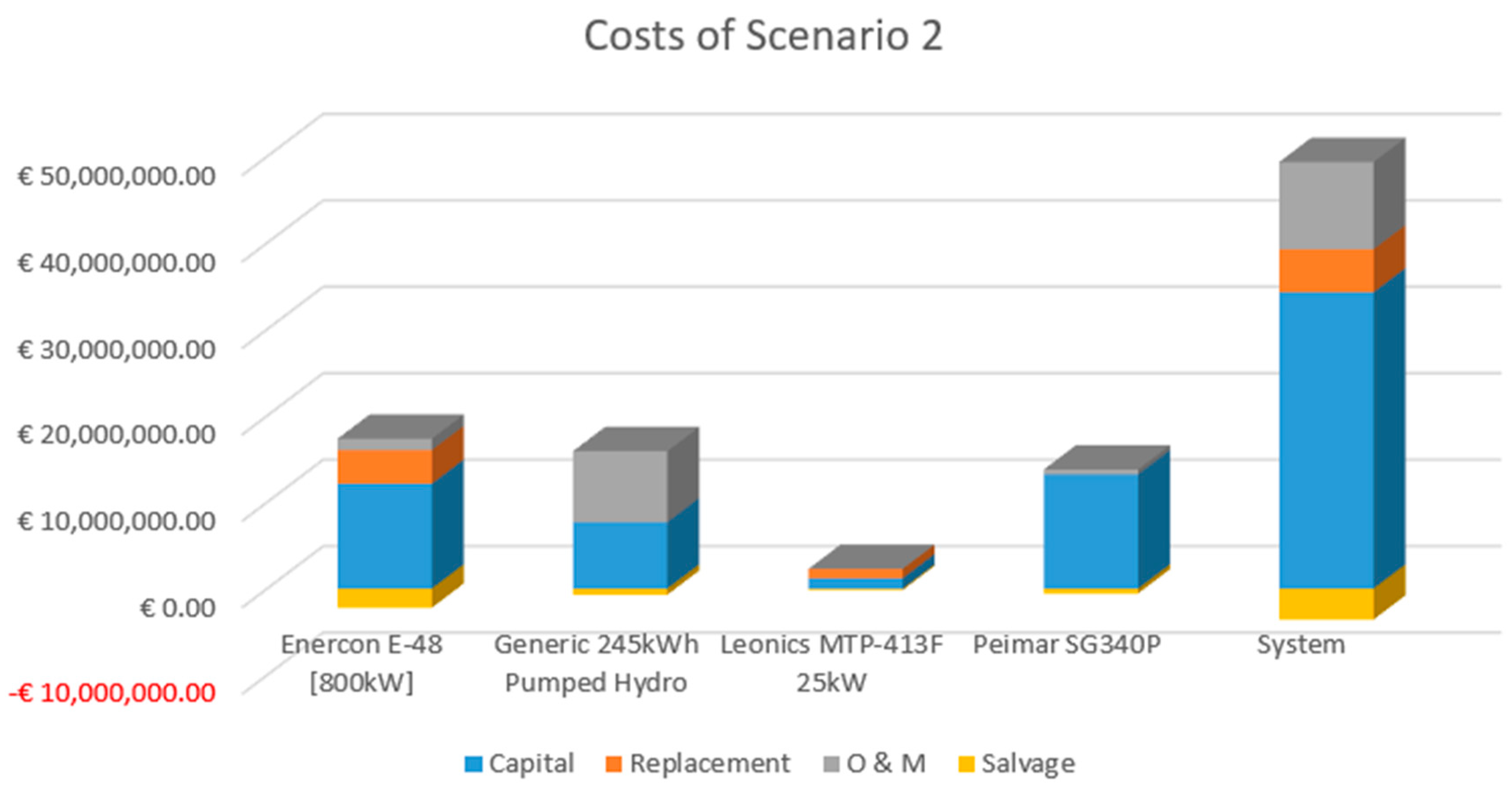
Figure 13.
Representation of Capital, Replacement, O & M and Salvage cost values of PV, Wind Turbine, PSH, Converter and the whole system for Scenario 2.
Figure 13.
Representation of Capital, Replacement, O & M and Salvage cost values of PV, Wind Turbine, PSH, Converter and the whole system for Scenario 2.
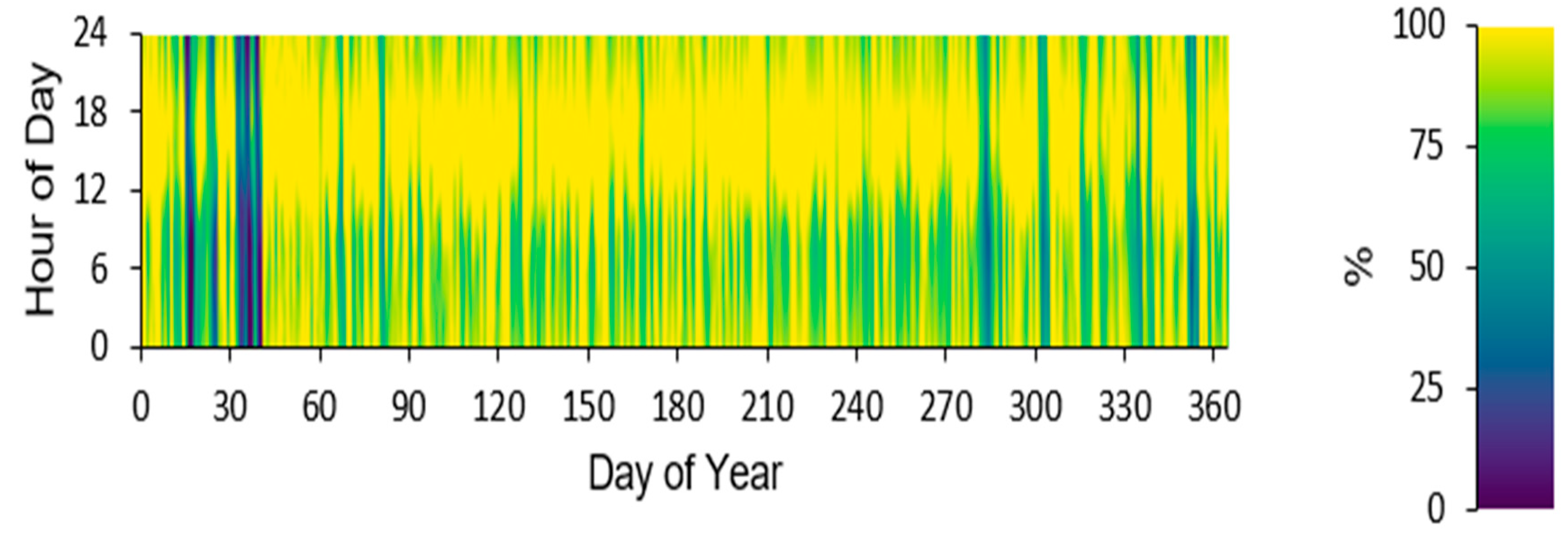
Figure 14.
State of charge of PSH for different hours of the day and different days of the year.
Figure 14.
State of charge of PSH for different hours of the day and different days of the year.
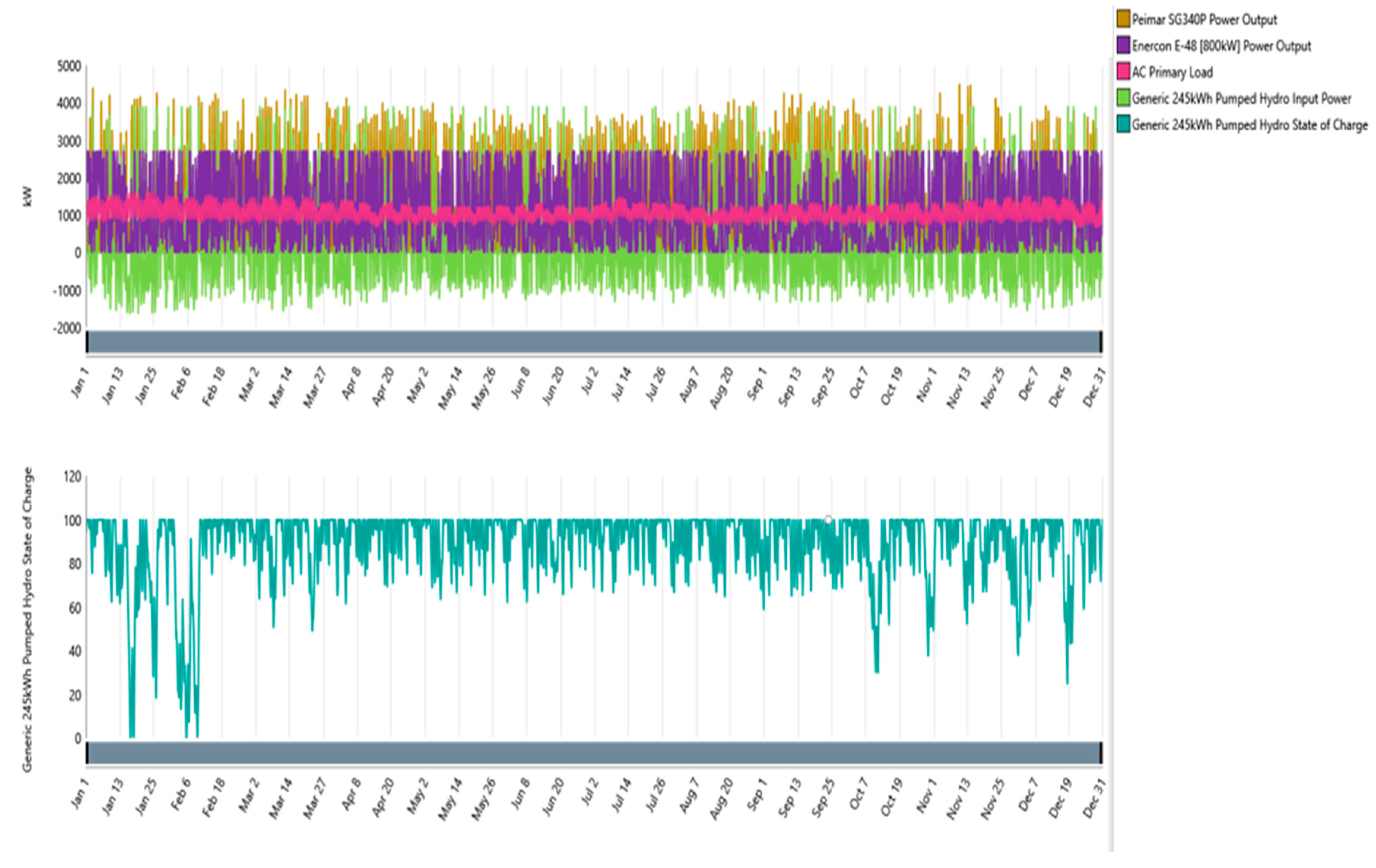
Figure 15.
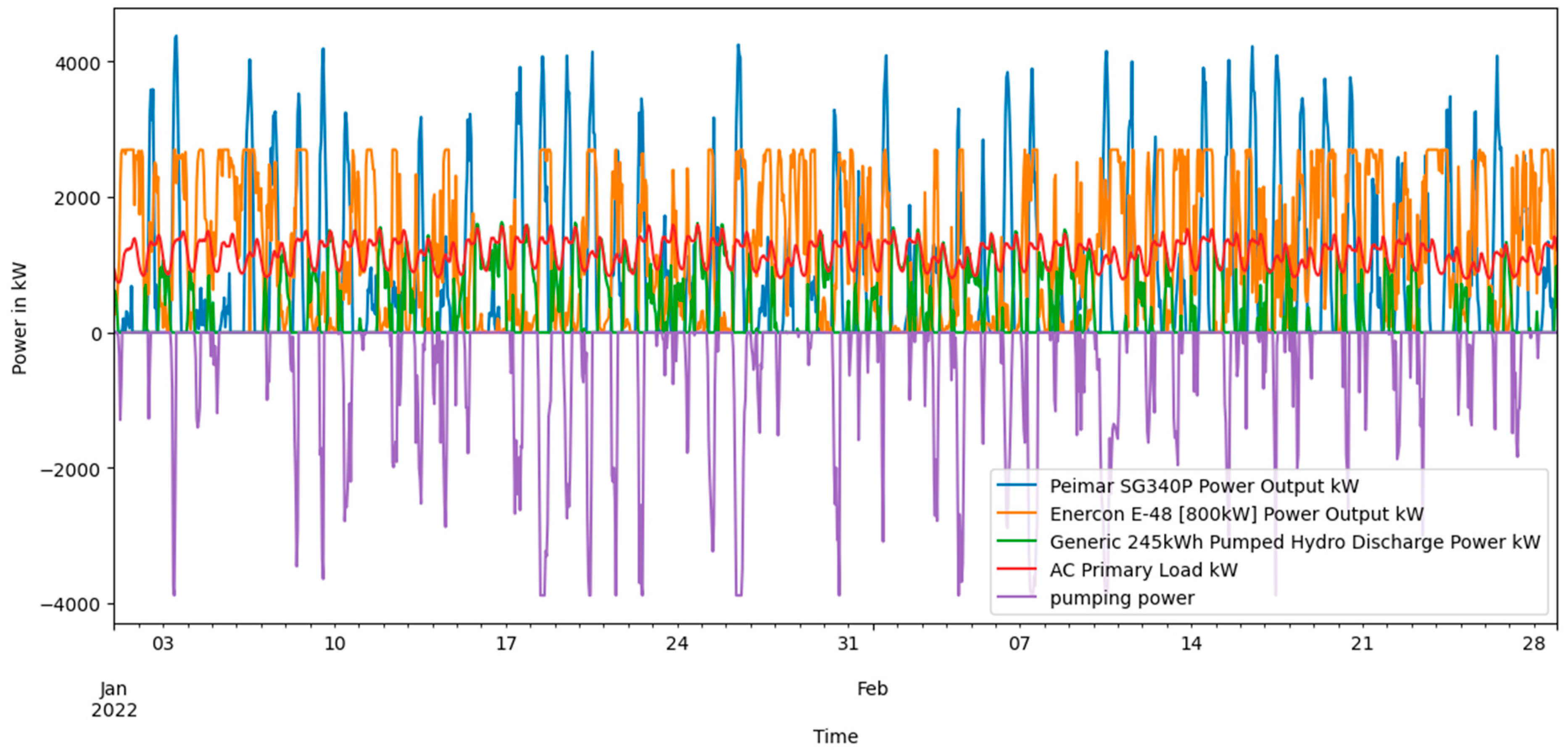
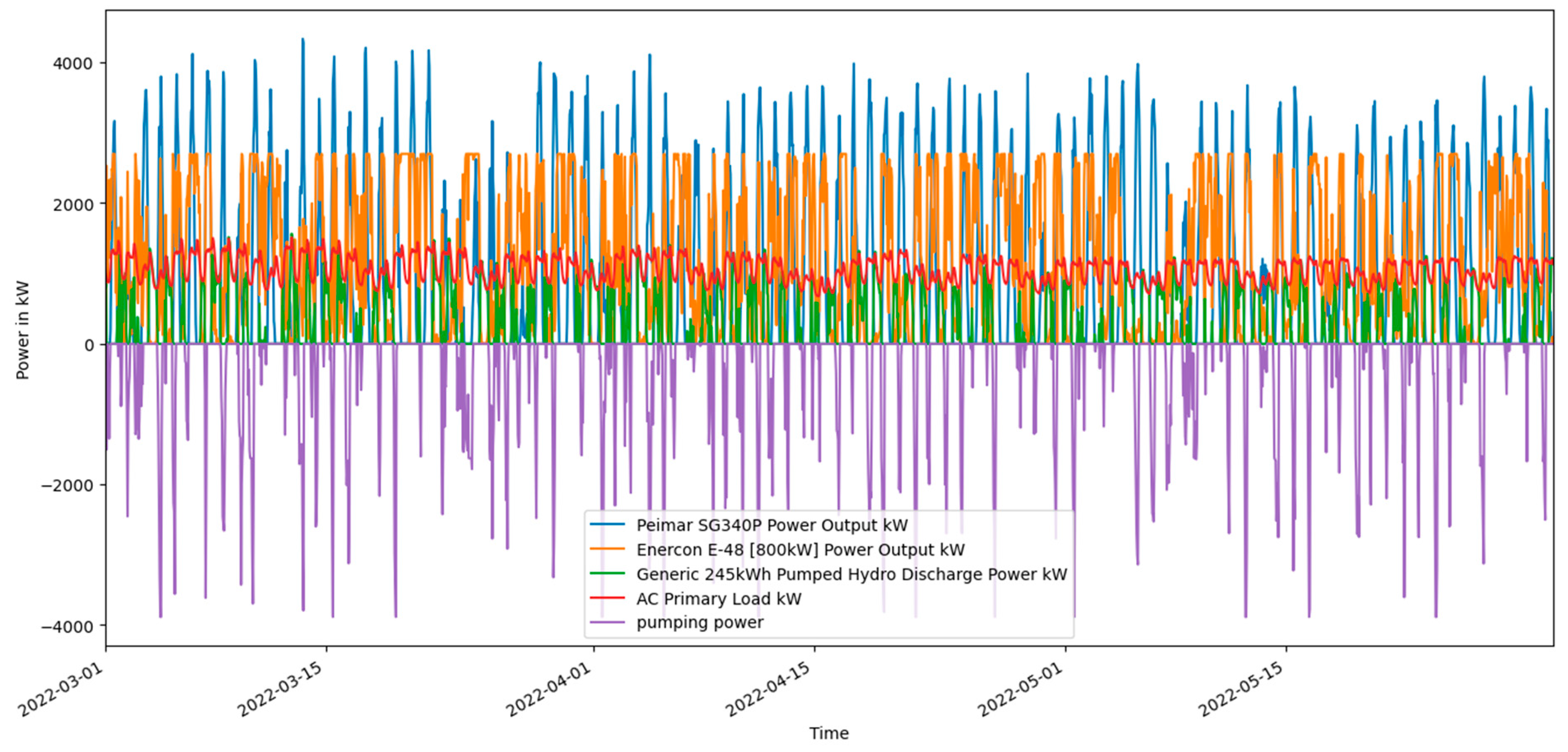
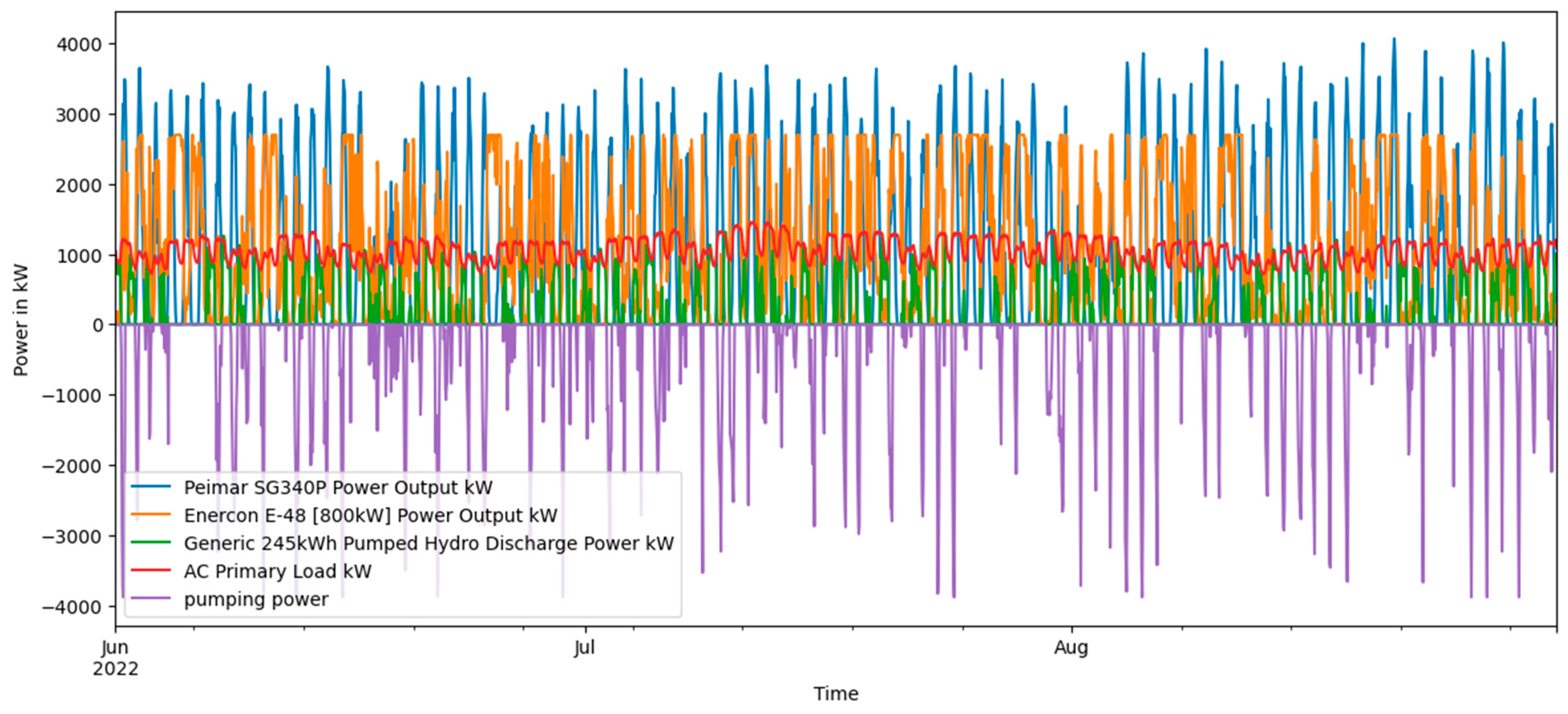
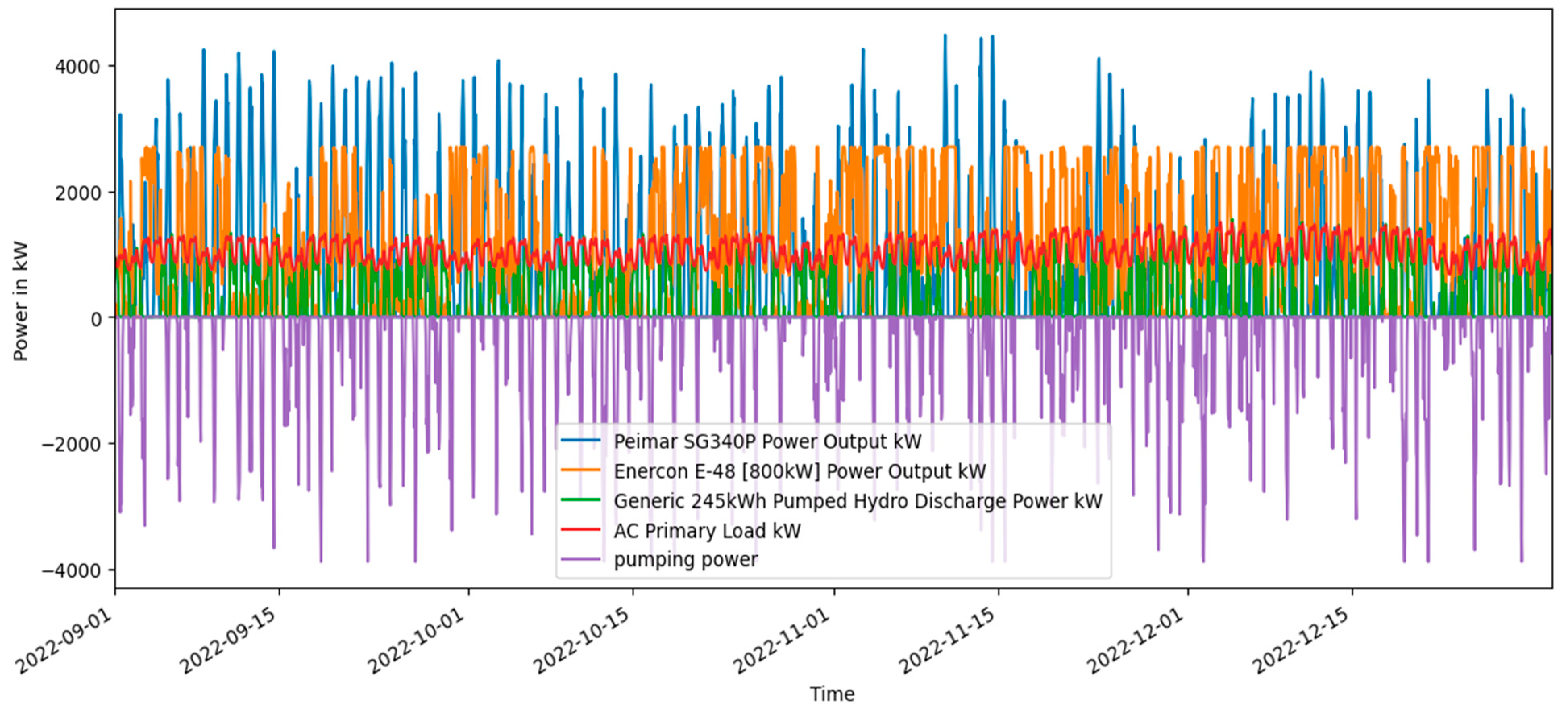
Scenario 2 Solar PV, Wind turbine and PSH power output along with the power demand and PSH state of charge.
Figure 15.
Scenario 2 Solar PV, Wind turbine and PSH power output along with the power demand and PSH state of charge.
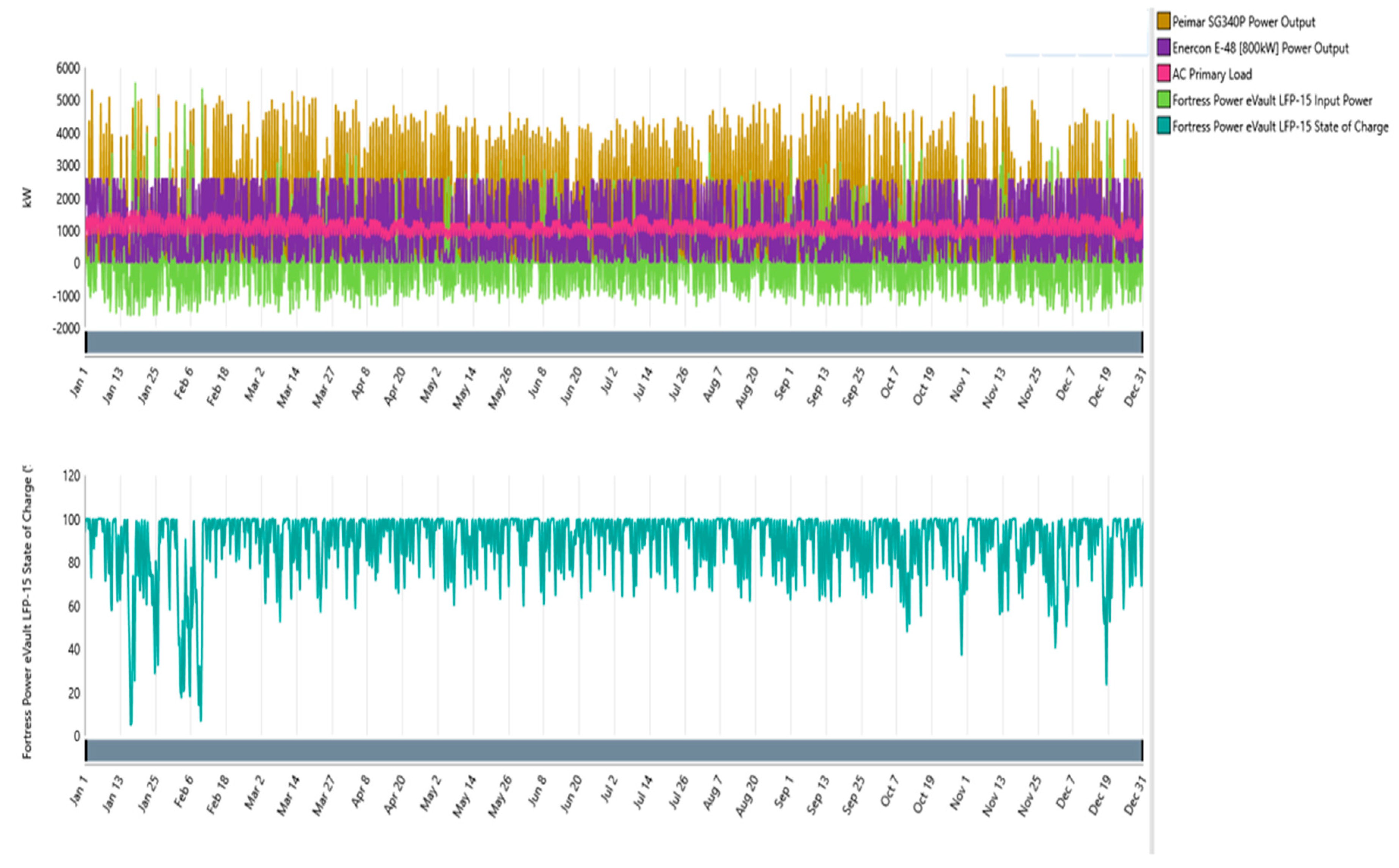
Figure 16.
Scenario 1 Solar PV, Wind turbine and Battery power output along with the power demand and Battery state of charge.
Figure 16.
Scenario 1 Solar PV, Wind turbine and Battery power output along with the power demand and Battery state of charge.
Figure 17.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Winter.
Figure 17.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Winter.
Figure 18.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped Storage Hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Spring.
Figure 18.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped Storage Hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Spring.
Figure 19.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Summer.
Figure 19.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Summer.
Figure 20.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Autumn.
Figure 20.
Power production from Solar PV, Wind Turbine, Pumped storage hydropower charge and discharge power along with the load demand for the season of Autumn.
Figure 21.
Power production of Solar PV, Wind Turbine and PSH along with load demand of hourly data averaged to months of the analyzed year.
Figure 21.
Power production of Solar PV, Wind Turbine and PSH along with load demand of hourly data averaged to months of the analyzed year.
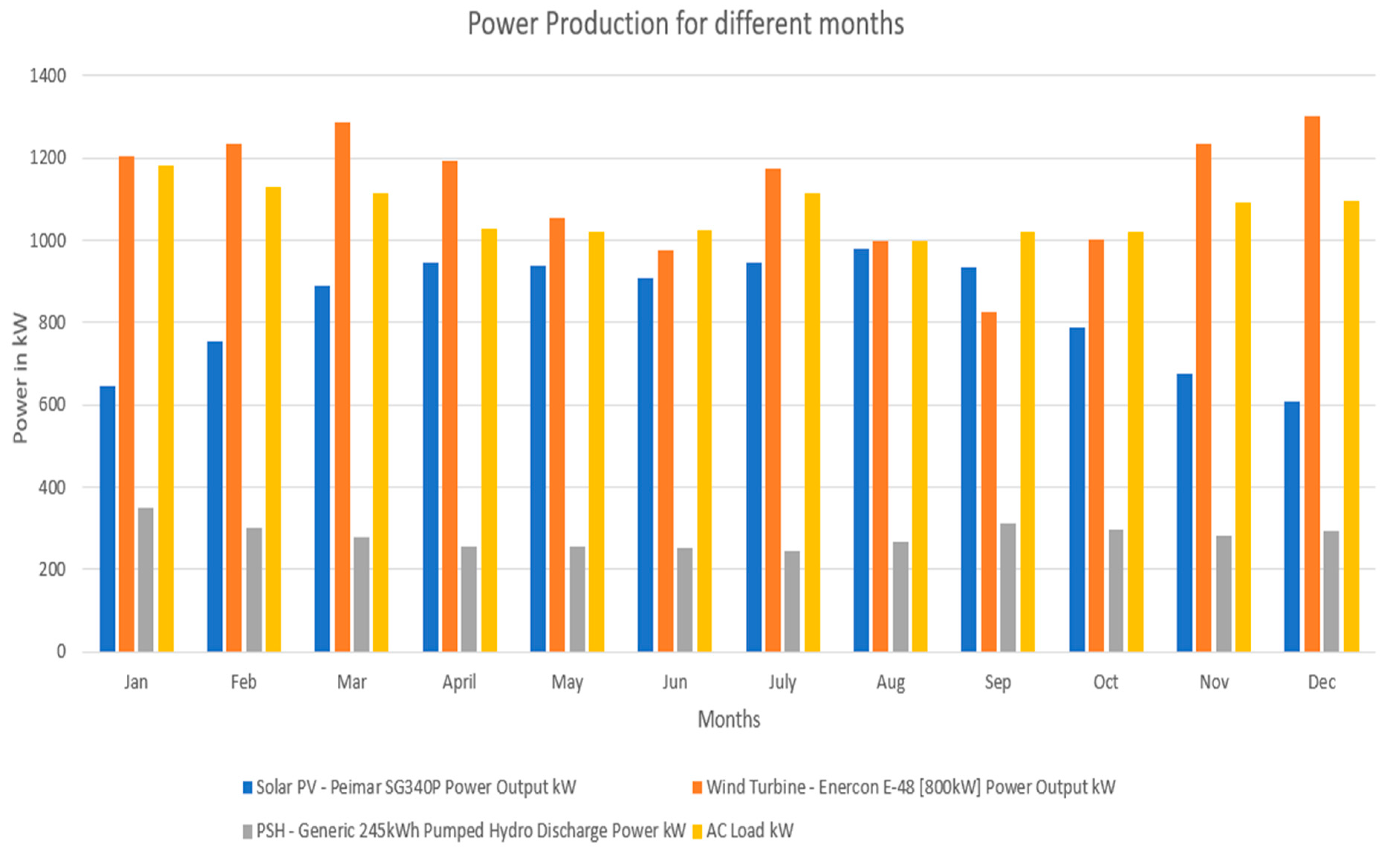
Figure 22.
Power production on 2nd-3rd of January 2022 with solar PV, wind turbine, PSH charge and discharge power along with the demand for power.
Figure 22.
Power production on 2nd-3rd of January 2022 with solar PV, wind turbine, PSH charge and discharge power along with the demand for power.
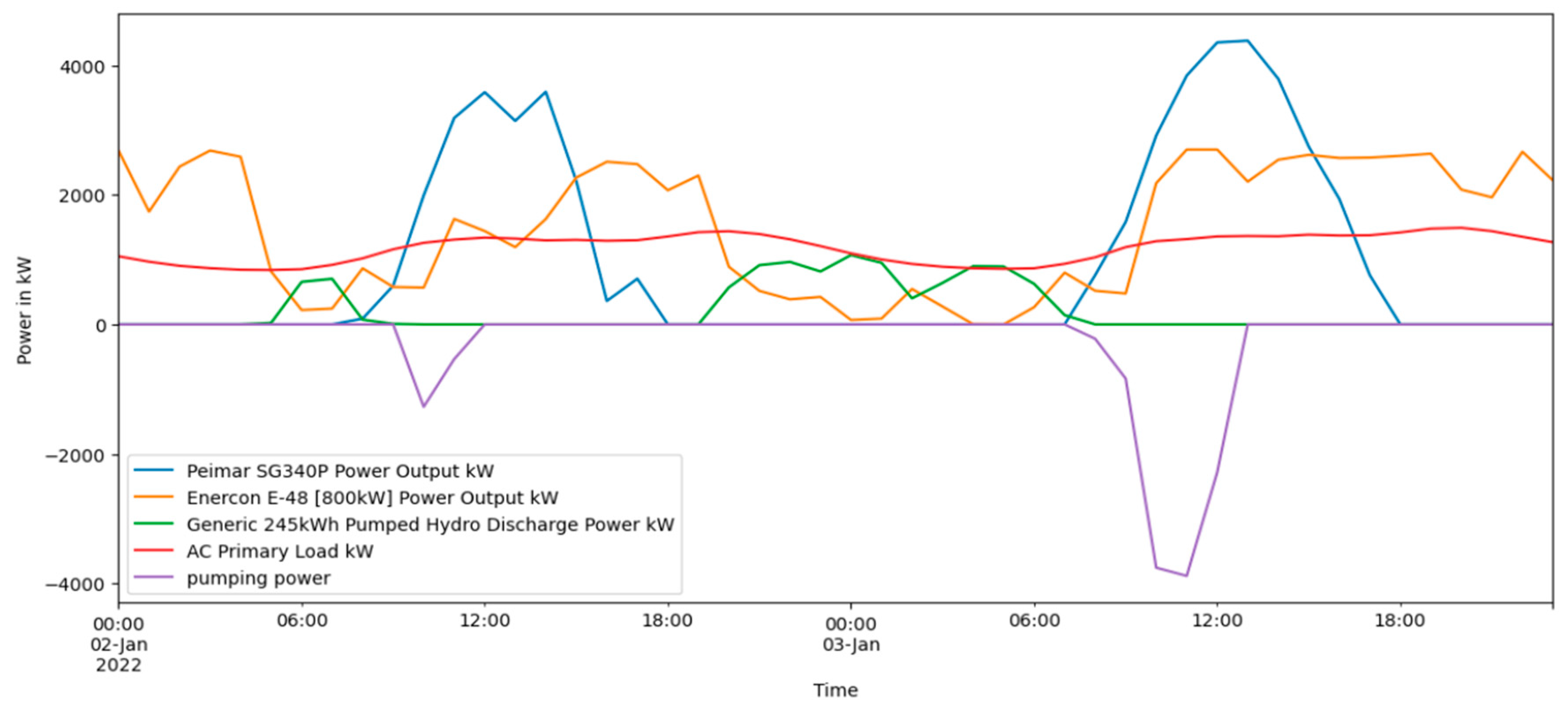
Figure 23.
Average daily profile of solar PV output for different months of the year 2022.
Figure 23.
Average daily profile of solar PV output for different months of the year 2022.
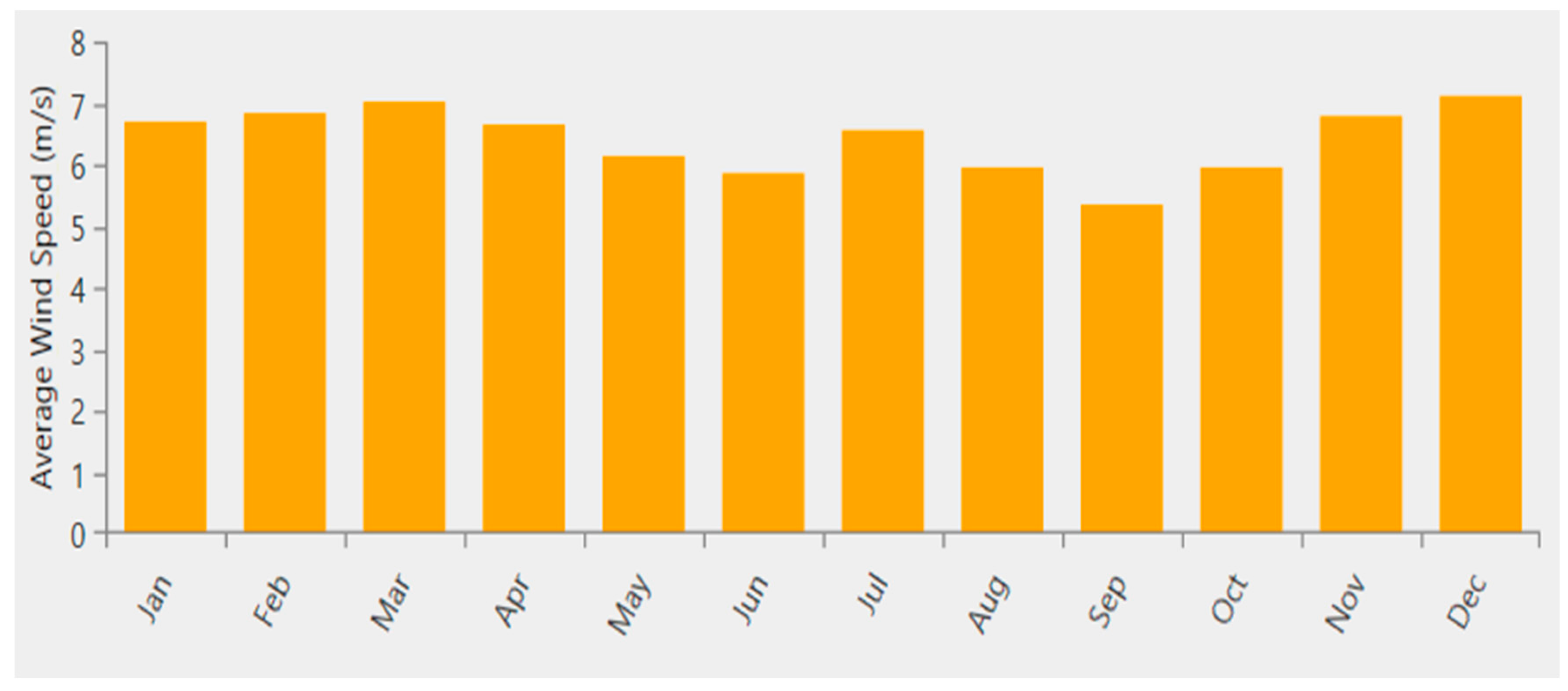
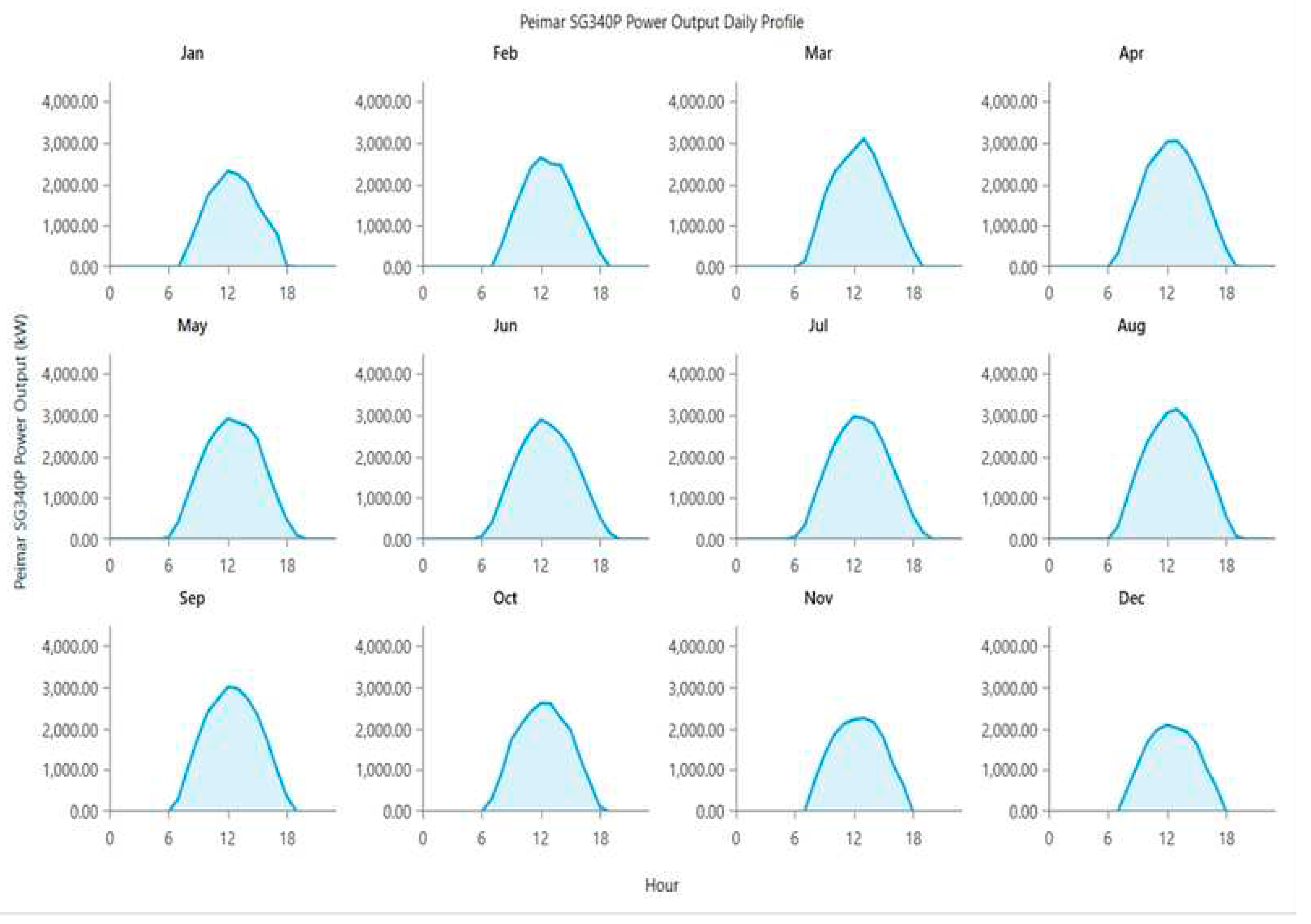
Figure 24.
Average daily profile of wind turbine Enercon E-48 output for different months of the year 2022 which shows the variability of power generation.
Figure 24.
Average daily profile of wind turbine Enercon E-48 output for different months of the year 2022 which shows the variability of power generation.
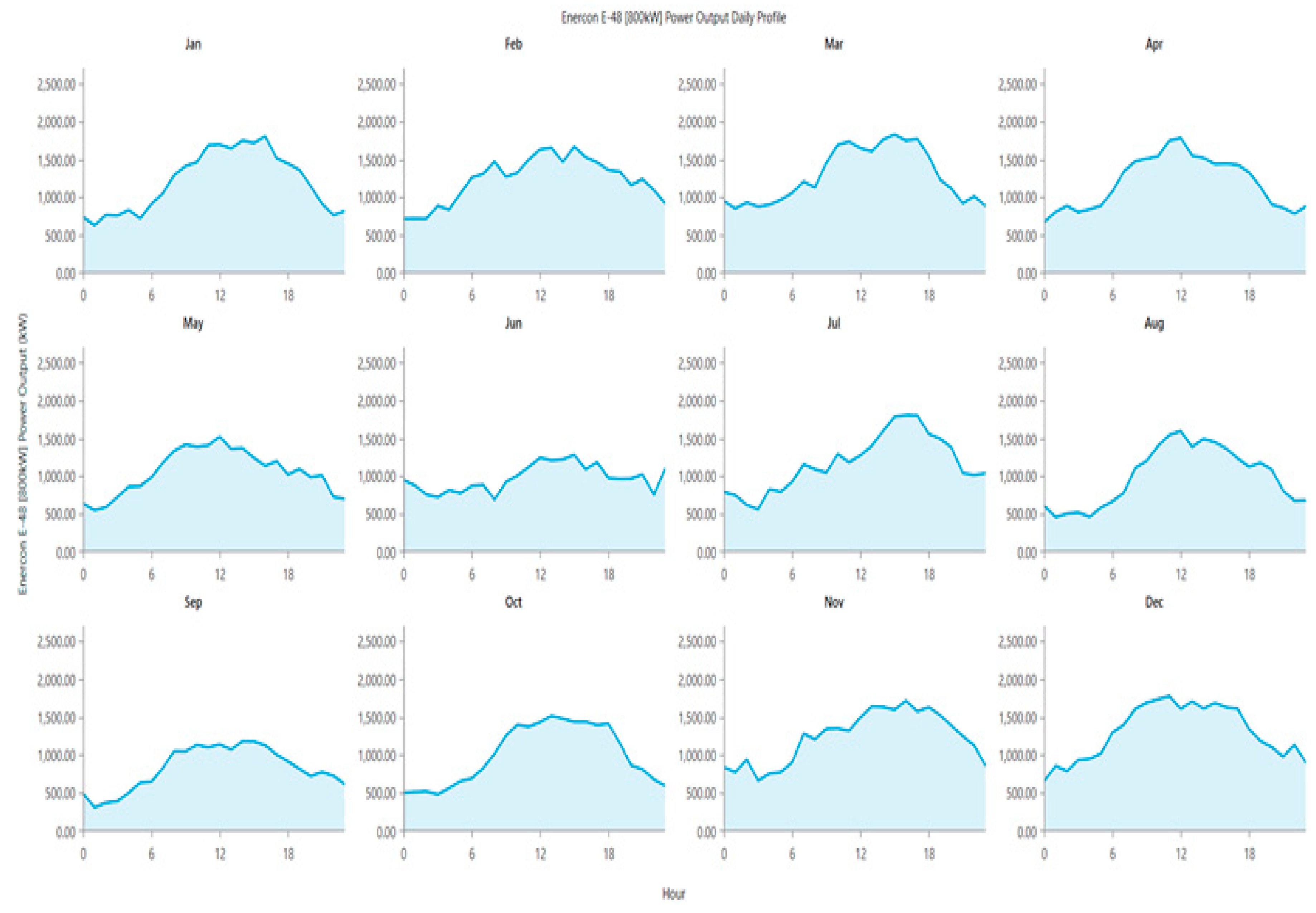
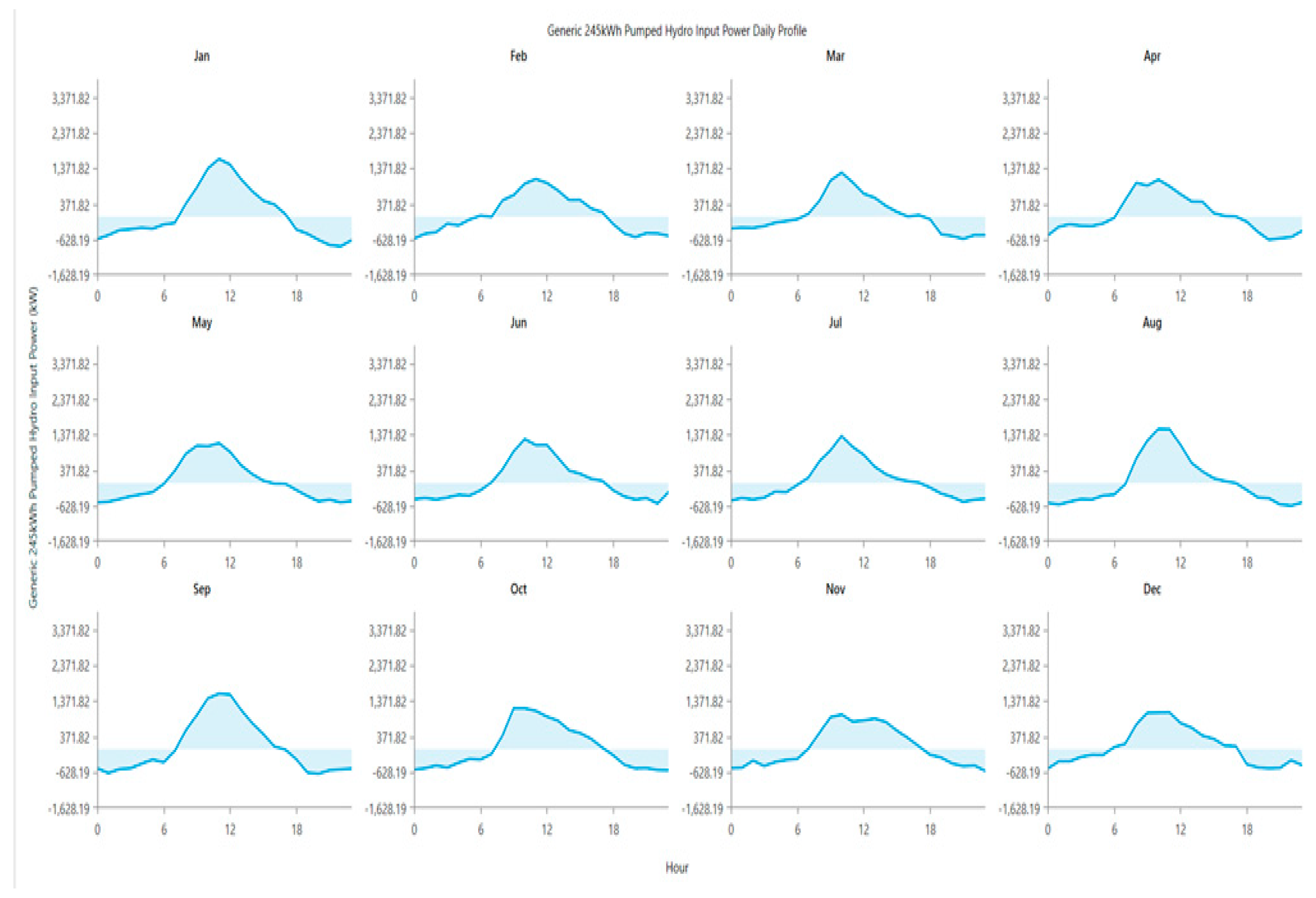
Figure 25.
Average daily profile of PSH input and output power for different months of the year 2022.
Figure 25.
Average daily profile of PSH input and output power for different months of the year 2022.
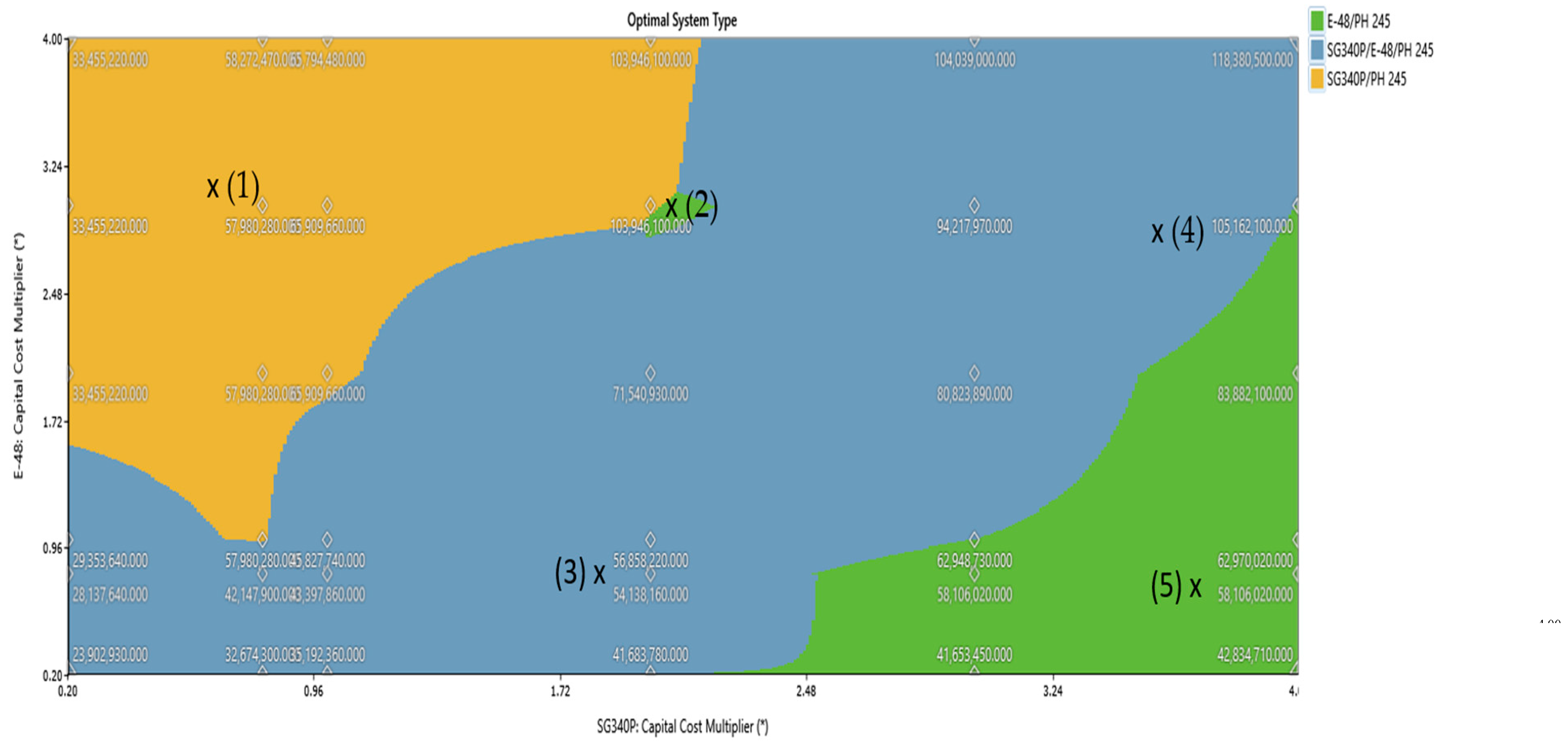
Figure 26.
Sensitivity analysis superimposed with total net present cost for cost multipliers of Solar PV and Wind Turbine.
Figure 26.
Sensitivity analysis superimposed with total net present cost for cost multipliers of Solar PV and Wind Turbine.
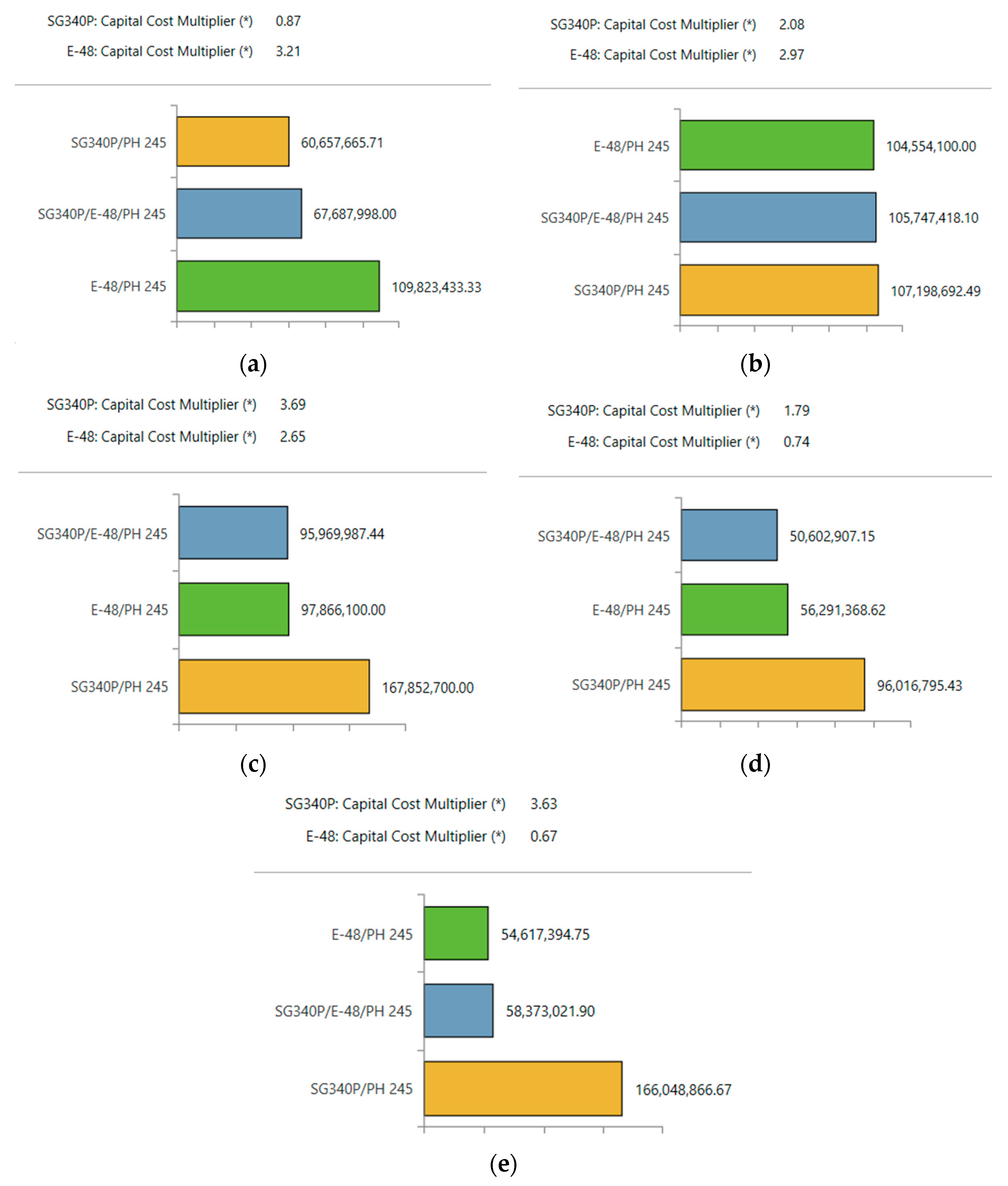
Figure 27.
Interpolated values of capital cost multipliers for Solar PV and Wind Turbine in the developed sensitivity analysis at: a) point 1; b) point 2; c) point 3; d) point 4; e) point 5.
Figure 27.
Interpolated values of capital cost multipliers for Solar PV and Wind Turbine in the developed sensitivity analysis at: a) point 1; b) point 2; c) point 3; d) point 4; e) point 5.
Table 1.
Different research on microgrids using HOMER software at different locations.
Table 1.
Different research on microgrids using HOMER software at different locations.
| Paper |
Optimal Energy System |
Location |
Economics |
| Demiroren and Yilmaz (2010) [17] |
Wind Energy System (PV/Battery) |
Gokceada, Turkey |
NPC : 32, 537, 056 $
LCOE : 0.174 $/kWh |
| Yimen et al. (2018) [18] |
PV/Biogas/PSH |
Djoundé, Cameroon |
NPC : 370,426 €
LCOE : 0.256 €/kWh |
| Dalton et al. (2009) [19] |
Wind Energy System with Battery |
Coastal area of Queensland, Australia |
NPC : 19.1 M$
|
| Ioakimidis et al. (2016) [20] |
Scenario 1 : Generator/ wind energy/
Battery
Sceanrio 2 : Wind/Solar PV/
generator/Battery
Scenario 3 : Wind/PV/Battery |
An Island in Greece |
NPC : 1,834,996 €
LCOE: 0.1658 €/kWh
NPC : 2,249,666 €
LCOE: 0.2047 €/kWh
NPC : 6.5 million €
LCOE: 0.61 €/kWh |
| He et al. (2018) [21] |
Stand alone: Solar PV/Wind Energy/ Battery/Diesel Generator
Grid Connected : Solar PV/Wind Energy/ Battery/ Grid |
Beijing, China |
NPC : 16,806,238 $
LCOE: 0.133 $/kWh
NPC : 9034,966 $
LCOE : 0.055 $/kWh |
| Sen and Bhattacharyya (2014) [22] |
Solar PV/Wind Energy/Battery/Bio-Diesel Generator/Hydropower |
Chhattisgarh, India |
NPC: 673,147 $
LCOE : 0.420 $/kWh |
Table 3.
Costs of different components used in Scenario 1.
Table 3.
Costs of different components used in Scenario 1.
| Component |
Capital |
Replacement |
O & M |
Salvage |
Total |
| Enercon E-48 [800kW] |
€ 12,160,000.00 |
€ 3,876,697.38 |
€ 1,323,777.69 |
€ -2,184,767.59 |
€ 15,175,707.48 |
| Fortress Power eVault LFP-15 |
€ 33,012,000.00 |
€ 29,164,042.96 |
€ 0.00 |
€ -3,954,141.87 |
€ 58,221,901.08 |
| Leonics MTP-413F 25kW |
€ 3,260,278.43 |
€ 2,880,252.64 |
€ 0.00 |
€ -390,512.65 |
€ 5,750,018.43 |
| Peimar SG340P |
€ 15,993,758.47 |
€ 0.00 |
€ 689,198.61 |
€ -638,571.73 |
€ 16,044,385.35 |
| System |
€ 64,426,036.90 |
€ 35,920,992.98 |
€ 2,012,976.31 |
€ -7,167,993.84 |
€ 95,192,012.34 |
Table 4.
Electrical Specifications of Scenario 1.
Table 4.
Electrical Specifications of Scenario 1.
| Quantity |
kWh/yr |
Percentage % |
| Peimar SG340P |
8,841,858 |
48.7 |
| Enercon E-48 [800kW] |
9,299,602 |
51.3 |
| AC Primary Load |
9,362,509 |
100 |
| Excess Electricity |
8,540,931 |
47.1 |
| Unmet Electric Load |
7,169 |
0.0765 |
| Capacity Shortage |
9,355 |
0.0998 |
Table 5.
Technical Specifications of Battery for results of Scenario 1.
Table 5.
Technical Specifications of Battery for results of Scenario 1.
| Quantity |
Value |
Units |
| Batteries |
2,358 |
qty. |
| String Size |
1 |
batteries |
| Strings in Parallel |
2,358 |
strings |
| Bus Voltage |
48 |
V |
| Autonomy |
30.2 |
hr |
| Storage Wear Cost |
0.236 |
€/kWh |
| Nominal Capacity |
33,955 |
kWh |
| Usable Nominal Capacity |
32,257 |
kWh |
| Lifetime Throughput |
25,136,156 |
kWh |
| Expected Life |
10 |
yr |
| Average Energy Cost |
0 |
€/kWh |
| Energy In |
2,538,404 |
kWh/yr |
| Energy Out |
2,488,352 |
kWh/yr |
| Storage Depletion |
724 |
kWh/yr |
| Losses |
50,775 |
kWh/yr |
| Annual Throughput |
2,513,616 |
kWh/yr |
Table 6.
Technical specifications of Solar PV and Wind Turbine for results of Scenario 1.
Table 6.
Technical specifications of Solar PV and Wind Turbine for results of Scenario 1.
| Peimar SG340P. |
|
Enercon E-48 [800 kW] |
| Quantity |
Value |
Units |
|
Quantity |
Value |
Units |
| Rated Capacity |
5,331 |
kW |
|
Total Rated Capacity |
3,200 |
kW |
| Mean Output |
1,009 |
kW |
|
Mean Output |
1,062 |
kW |
| Mean Output |
24,224 |
kWh/d |
|
Capacity Factor |
33.2 |
% |
| Capacity Factor |
18.9 |
% |
|
Total Production |
9,299,602 |
kWh/yr |
| Total Production |
8,841,858 |
kWh/yr |
|
Minimum Output |
0 |
kW |
| Minimum Output |
0 |
kW |
|
Maximum Output |
2,573 |
kW |
| Maximum Output |
5,410 |
kW |
|
Wind Penetration |
99.3 |
% |
| PV Penetration |
94.4 |
% |
|
Hours of Operation |
8,339 |
hrs/yr |
| Hours of Operation |
4,385 |
hrs/yr |
|
Levelized Cost |
0.126 |
€/kWh |
| Levelized Cost |
0.14 |
€/kWh |
|
|
|
|
| Clipped production |
0 |
kWh |
|
|
|
|
Table 7.
Costs of different components used in Scenario 2.
Table 7.
Costs of different components used in Scenario 2.
| Component |
Capital |
Replacement |
O & M |
Salvage |
Total |
| Enercon E-48 [800kW] |
€ 12,160,000.00 |
€ 3,876,697.38 |
€ 1,323,777.69 |
€ -2,184,767.59 |
€ 15,175,707.48 |
| Generic 245kWh Pumped Hydro |
€ 7,695,600.00 |
€ 0.00 |
€ 8,221,900.52 |
€ -691,328.02 |
€ 15,226,172.50 |
| Leonics MTP-413F 25kW |
€ 1,220,369.05 |
€ 1,078,119.94 |
€ 0.00 |
€ -146,174.49 |
€ 2,152,314.50 |
| Peimar SG340P |
€ 13,231,667.72 |
€ 0.00 |
€ 570,175.36 |
€ -528,291.65 |
€ 13,273,551.43 |
| System |
€ 34,307,636.77 |
€ 4,954,817.32 |
€ 10,115,853.58 |
€ -3,550,561.75 |
€ 45,827,745.91 |
Table 8.
Electrical Specifications of Scenario 2.
Table 8.
Electrical Specifications of Scenario 2.
| Quantity |
kWh/yr |
Percentage % |
| Peimar SG340P |
7,314,886 |
42.6 |
| Enercon E-48 [800kW] |
9,841,470 |
57.4 |
| AC Primary Load |
9,361,602 |
100 |
| Excess Electricity |
7,006,065 |
40.8 |
| Unmet Electric Load |
8,077 |
0.0862 |
| Capacity Shortage |
9,365 |
0.0999 |
Table 9.
Technical Specifications of PSH for results of Scenario 2.
Table 9.
Technical Specifications of PSH for results of Scenario 2.
| Quantity |
Value |
Units |
| Bus Voltage |
240 |
V |
| Autonomy |
37.8 |
hr |
| Storage Wear Cost |
0 |
€/kWh |
| Nominal Capacity |
40,411 |
kWh |
| Usable Nominal Capacity |
40,411 |
kWh |
| Lifetime Throughput |
109,828,332 |
kWh |
| Expected Life |
40 |
yr |
| Average Energy Cost |
0 |
€/kWh |
| Energy In |
3,050,767 |
kWh/yr |
| Energy Out |
2,471,137 |
kWh/yr |
| Storage Depletion |
18.3 |
kWh/yr |
| Losses |
579,647 |
kWh/yr |
| Annual Throughput |
2,745,708 |
kWh/yr |
Table 10.
Technical specifications of Solar PV and Wind Turbine for results of Scenario 2.
Table 10.
Technical specifications of Solar PV and Wind Turbine for results of Scenario 2.
| Solar PV - Peimar SG340P |
|
Wind Turbine - Enercon E-48 [800 kW] |
| Quantity |
Value |
Units |
|
Quantity |
Value |
Units |
| Rated Capacity |
4,411 |
kW |
|
Total Rated Capacity |
3,200 |
kW |
| Mean Output |
835 |
kW |
|
Mean Output |
1,123 |
kW |
| Mean Output |
20,041 |
kWh/d |
|
Capacity Factor |
35.1 |
% |
| Capacity Factor |
18.9 |
% |
|
Total Production |
9,841,470 |
kWh/yr |
| Total Production |
7,314,886 |
kWh/yr |
|
Minimum Output |
0 |
kW |
| Minimum Output |
0 |
kW |
|
Maximum Output |
2,699 |
kW |
| Maximum Output |
4,476 |
kW |
|
Wind Penetration |
105 |
% |
| PV Penetration |
78.1 |
% |
|
Hours of Operation |
8,339 |
hrs/yr |
| Hours of Operation |
4,385 |
hrs/yr |
|
Levelized Cost |
0.119 |
€/kWh |
| Levelized Cost |
0.14 |
€/kWh |
|
|
|
|
| Clipped production |
0 |
kWh |
|
|
|
|
Table 11.
Capital cost multiplier for Sensitivity analysis.
Table 11.
Capital cost multiplier for Sensitivity analysis.
| SG 340P solar PV |
Enercon E-48 wind turbine |
| 0.2 |
0.2 |
| 0.8 |
0.8 |
| 1 |
1 |
| 2 |
2 |
| 3 |
3 |
| 4 |
4 |