1. Introduction
Real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (rt-qPCR) is nowadays a reference for the detection and quantification of fish viruses, including the viral nervous necrosis virus (VNNV). These viruses, corresponding to the genus Betanodavirus within the family Nodaviridae, produce a neurological disease with serious consequences on certain species of worldwide farmed fish [
1]. It is a small (25-30 nm), unenveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus, whose genome is bisegmented. The largest segment (RNA 1) codifies the RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase, and the other one (RNA 2) codifies the capsid protein.
The World Organization of Animal Health has recently removed this virus from its list of risk aquatic viruses. However, in a previous version of its Manual of Diagnostic Test of Aquatic Diseases [
2] they considered that, together with the traditional gold standard diagnostic test (isolation in cell culture followed by immunological or molecular confirmation), highly sensitive molecular techniques could be employed but require a previous validation. They placed special emphasis on the use of certain real time PCR (rtPCR) protocols, and mainly focused on the only truly validated technique (including a ring test) at that time, the one developed by the OIE Reference Laboratory for Viral Encephalopathy and Retinopathy [
3].
More recently, Olveira et al. [
4] reported the development and validation of a procedure not only for the detection and identification but also for the quantification of all types of the virus, in cell culture supernatants and in fish tissues. In addition to the high sensitivity of that protocol (higher than any precursor), another advantage was that, after validation, quantification was demonstrated to be highly reliable with any of the standards used, which allows for the comparison between different laboratories.
With a view to improving our capacity to detect this virus is field samples, and for its precise quantification, we explored a related emerging technology, the droplet-digital PCR (ddPCR), which is widely used for the early detection of cancer [
5,
6] and human viruses [
7,
8]. Digital PCR (dPCR) is a novel and promising technology which will probably replace qPCR due to its advantages. In reality, it is not that new, because it was first described in the late 1980s as a method for the detection of a single nucleic acid molecule, and in the early 1990s for the quantification of viruses [
9]. However, the term ‘digital PCR’ was introduced in late 90s.
The advantages of dPCR over qPCR have been described [
7,
10]: i) higher sensitivity, due to the template concentration effect of the partitioning; ii) direct absolute nucleic acid quantification, without the need use standard curves, and with higher precision, and iii) less susceptibility to impaired efficiencies due to PCR inhibitors. The technology is based on the distribution of the templates into microscopical partitions, following a Poisson distribution, and on PCR amplifications individually performed within each partition. There are two types of methods, depending on the partitioning system: the chip-based method, where the partitions are solid-microcells, and the oil-emulsion partitions, called droplets, corresponding to the ddPCR technology.
Based on the reported advantages of ddPCR over chip-based PCR due to the larger number of partitions involved, which provides a larger dynamic range [
10], we chose ddPCR to develop a new protocol to improve our capability to detect, identify and quantify VNNV isolated in cell culture, and directly from fish tissues. The new procedure has been demonstrated to be more sensitive and reliable for the detection and quantification of this virus, which confirms it as a future substitute for qPCR, improving our capabilities to control this disease.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viral Strains, Cell Culture and Viral Titration
For reference, in the present study, we selected the SJNag93 and SGWAK97 VNNV strains, corresponding to types SJNNV and RGNNV (respectively), the two VNNV types most frequently detected in Mediterranean countries and worldwide. For their propagation, E-11 cells (ECACC #01110916) were employed using L-15 (Leibovitz; Lonza, Vigo, Spain) culture medium supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Lonza). Cell culture was carried out at 25°C, and inoculated cells were incubated at 20°C. After extensive cytopathic effect (CPE), cell debris from the culture fluids was removed at 3,000 x g for 15 min at 4°C. Viral titration was performed in 96-well plates using the endpoint dilution method as described by [
4].
2.2. Optimization of the Procedure
Since the aim of this study was to compare the performance and reliability of the designed RT-ddPCR procedure against the RT-qPCR test routinely employed in our laboratory, the latter was used as reference. This RT-qPCR protocol is based on a study partially published in 2021 by Olveira et al. [
4], where many more primer sets than reported had been tested, and some probes were also evaluated. In that study, a set of primers specific for RNA 1 were selected because it provided the best results for detection and quantification of the four VNNV type strains (SJ, RG, TP and BF). Another set of primers and a probe (Pr/Pb), specific for RNA 2, had also been tested, providing optimal results only with types SJ and RG. Those results were not published, however that Pr/Pb set is the one used in the RT-qPCR procedure we routinely use for diagnosis and quantification of VNNV in isolated virus and field samples, given that SJ and RG types have been demonstrated for years to be the only types detected in the samples received from companies.
In the present study, said Pr/Pb set (
Table 1) was used for both, RT-qPCR and RT-ddPCR, and the concentrations and the annealing temperatures were the parameters optimized for ddPCR. To this end, Pr/Pb concentrations of 500/250, 500/500, 750/250, 750/500, 950/500 and 950/750 nM were tested, at an annealing temperature of 57°C (the reference from the routine RT-qPCR procedure). In another set of tests, six annealing temperatures (52, 54, 56, 57, 58 and 60°C) were tested using the Pr/Pb set at 500/500 nM.
After the ddPCR amplification, the optimal parameters were selected considering the amplitude (separation between negative and positive droplets populations), the rain (droplets falling between both populations), and the repeatability of the counting of the reference templates.
2.3. Reference Templates
For the evaluation of the RT-ddPCR procedure, and for comparison with RT-qPCR, two types of templates were used.
Titrated crude virus and extracted RNA.- SJ and RG strains were produced and titrated as described above, and viral RNA extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Madrid, Spain) following the procedure described by the manufacturer. Quantification and quality of the RNA were determined as described by Olveira et al. [
4].
Plasmid DNA (pDNA).- For each strain, a different pDNA was designed and constructed as described by Olveira et al. (2021): plasmid PGEMT, with an insert of 1421 bp corresponding to RNA 2 of SJNNV (total length 3990 bp), and plasmid BPST7, with an insert of 1430 bp, corresponding to RNA 2 of RGNNV (total length 4435 bp).
2.4. cDNA Synthesis
For amplification by qPCR and ddPCR, cDNA was synthetized as previously described [
4]. Briefly: 9µl of extracted RNA (around 1ng/µl) were mixed with 2.5 ng/µl of random primers (Promega, Madrid, Spain), and then subjected to 95°C, 5 min, and 4°C for more than 1 min. For reverse transcription (RT), the Superscript III reverse transcriptase (10U/ml; Invitrogen, Madrid, Spain), 0.5 mM dNTPs and 0.05 M DTT in First Strand buffer (Invitrogen) were added to a final volume of 20µl and incubated 10 min at 25°C and then 50 min at 50°C, in a My Cycler thermal cycler (Bio-Rad, Madrid, Spain). Immediately after cDNA synthesis, the RT enzyme was inactivated at 85°C for 5 min, and the cDNA samples conserved at -20°C until use.
2.5. Real Time Quantitative PCR (rt-qPCR)
For the rt-qPCR reaction, a mixture containing 2 µl of cDNA, 500nM of each primer and probe in PremixTM Ex Taq (Takara bio INC, Shiga, Japan) was prepared to a final volume of 20µl. For the amplification, after an initial 30 sec denaturation/activation step at 95°C, 45 amplification cycles were applied in a CFX Connect™ Thermal Cycler (Bio- Rad, Madrid, Spain) as follows: denaturation for 15 s at 95 ◦C; annealing and extension for 20 s at 57 °C. For each run, the threshold cycle value (Ct) was established as the cycle number at which fluorescence was detectable over the threshold value determined by the equipment’s software (CFX Maestro; Bio-Rad) for cycles 2–10.
2.6. Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
The ddPCR reactions were carried out into a final volume of 20µl containing 500nM of primers and probe and 2µl of cDNA in ddPCRTM Supermix for Probes (No dUTP) (Bio-Rad). A QX200TM Droplet Generator (Bio-Rad) was used to generate the partitions. Following an initial 10 min denaturation/activation step at 95°C, the mixture was subjected to 40 cycles of amplification (20 sec denaturation at 95°C, followed by 30 sec at 58°C of annealing and extension) in a C1000TM thermal cycler (Bio-Rad), and the droplets were individually read using a QX200TM Droplet Reader (Bio-Rad). Only reactions with a total number of droplets higher that 10,000 were considered. The results were analyzed by Quanta SoftTM Pro vs 1.0.
2.7. Limit of Detection and Quantification, and Dynamic Range
Serial dilutions (10-fold) of reference templates were subjected to amplification by RT-qPCR or RT-ddPCR when using viral RNA as template, and qPCR or ddPCR when pDNA was employed.
Crude virus.- Crude virus stocks of 5.6 x 107 TCID50/ml and 1.0 x 106 TCID50/ml of SJNNV and RGNNV strains, respectively, were employed. Dilutions from 0 to 10-10 were used to determine the limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) in terms of viral concentration. To determine the LOD and LOQ values in terms of viral copies, RNA extraction was applied from 100µl of crude virus, and the RNA concentration measured as described above. The number of copies was calculated from the formula γ = n/N x GL x ncMW, where is the RNA weight in gr, n the number of copies, N the Avogadro number (6.022 x 1023 copies/mol), GL the total genome length (4528 and 4539 nc, for SJ and RG types, respectively), and ncMW is the nucleic acid molecular weight (average values: 350.5 and 328.0 gr/mol, SJ and RG, respectively).
To determine the viral titer and number of copies per reaction, the procedure followed to obtain the two microliters of cDNA for the ddPCR mix was taken into account: RNA extracted from 100µl of crude virus was concentrated into a volume of 70µl, from which 9µl were used for cDNA synthesis to a final volume of 20µl, from which 2µl were used for ddPCR to a final volume of 20µl.
pDNA.- In the case of using pDNA as reference template, 45ng/µl or 23 ng/µl stock solutions (SJ and RG, respectively) were employed, and 2µl used for the ddPCR 20µl total reaction volume. To calculate the number of copies, the same formula for γ was employed, using a ncMW average value of 620 or 660 gr/ml (SJ and RG, respectively), and the plasmid sizes described above.
To determine the LOD, the highest dilution providing positive results in a minimum of 1/3 of the replicas, and with an acceptable CV value (CV≤25%) was considered. For the LOQ, the lowest concentration within the dynamic range (DR) was contemplated. The DR was determined as the range of dilutions (or concentrations) providing reliable quantification (correlation coefficient of the curves [R2] ≥ 0.95).
2.8. Reliability of the Procedure
Repeatability and reproducibility (R&R) were measured to evaluate the procedure’s reliability. For that purpose, each assay was performed with a minimum of three replicas (repeatability), and on consecutive days (reproducibility). R&R were determined from the magnitude of the deviation from the averaged template concentrations, using the ‘coefficient of variation’ (CV; or RSD, ‘relative standard deviation’), calculated as the percentage of standard deviation with respect to the average. Values ≤ 25% were indicative of acceptable reliability [
11].
In addition, standard curves were drawn with the data obtained using the serial dilutions of the reference templates, and their reliability determined from the calculated correlation coefficient (R2). Curves with R2 ≥ 0.95 were considered reliable.
2.9. Performance of the Procedure with Field Samples
The procedure was tested on fish samples, in collaboration with a
Solea senegalensis fish farm in the Iberian Peninsula, as part of a program to select VNNV-free breeders. Twenty four fish were anesthetized with MS-222 (Tricaine Methanesulfonate) prior to puncturing the caudal vein, and the blood samples (maximum volume 500 µl) immediately heparinized. Nucleic acid extraction was performed as previously described [
12].
To evaluate the clinical reliability of the diagnostic test, the following parameters were calculated, as described [
13], always in reference to a gold standard test:
Clinical sensitivity (cSs).- Calculated as the relation (in terms of frequency or percentage) between the observed (with the test under evaluation) and the expected (with the gold standard) positive results. The higher the frequency (maximum value 1), the higher the cSs, defined as the capacity to detect diseased fish, and this is directly related to the analytical Ss.
Clinical specificity (cSp).- This is a different concept from analytical Sp, since it is not related to the capacity to detect any viral type, and no other viral groups, but to the capacity to detect true uninfected fish (the need to avoid false negatives). This parameter is calculated from the relation between the number of negatives obtained with the evaluated test, and the total expected from the gold standard.
Positive predictive value (PPV).- This parameter provides a measurement of the reliability of the positive results, and is calculated as the relation between the observed true positives (results that are positive with both tests) and the total number of positives with the test under evaluation.
Negative predictive value (NPV).- which gives the reliability of the negative results. It is calculated from the relation between true negatives (results that are negative with both tests) and total number of negatives with the evaluated test.
In all four cases, the higher the value (1 or 100, frequency or percentage, respectively), the better the procedure. In the present study, two approaches were contemplated: using qPCR and ddPCR, alternatively, as gold standard.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
To compare the quantification data obtained by both procedures (qPCR and ddPCR), three tests were consecutively applied using Prism vs 10.0 (GraphPad): a Student’s t test, an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (not assuming equal SDs), and a Wilcoxon test. Values of P ≤ 0.05 mean significative differences between results.
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Conditions
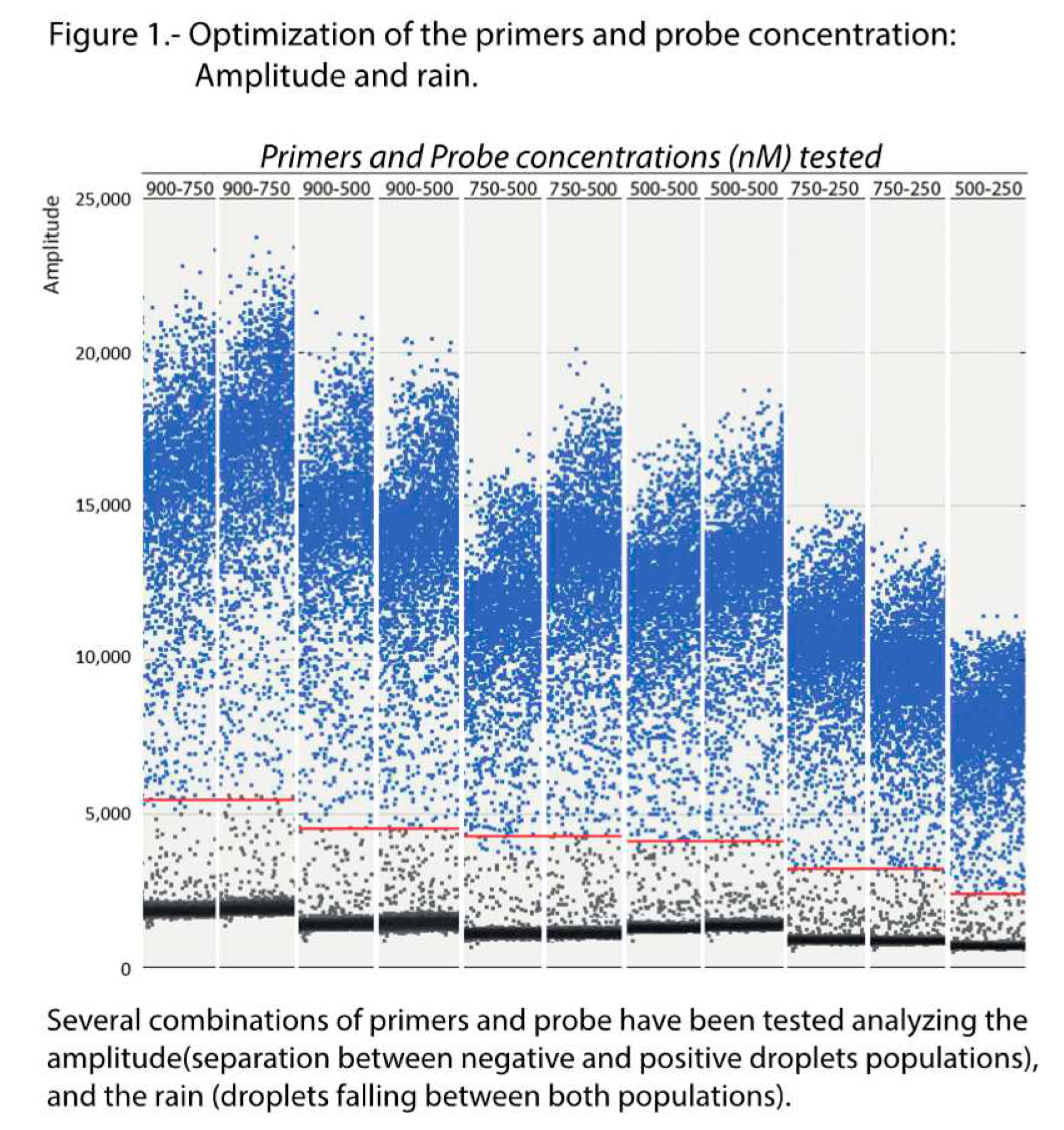
Optimization of the conditions was performed testing six annealing temperatures, from 52 to 60°C, and six combinations of Pr/Pb concentrations, from 500/250 to 900/750 nM. As shown in the scatter plot of
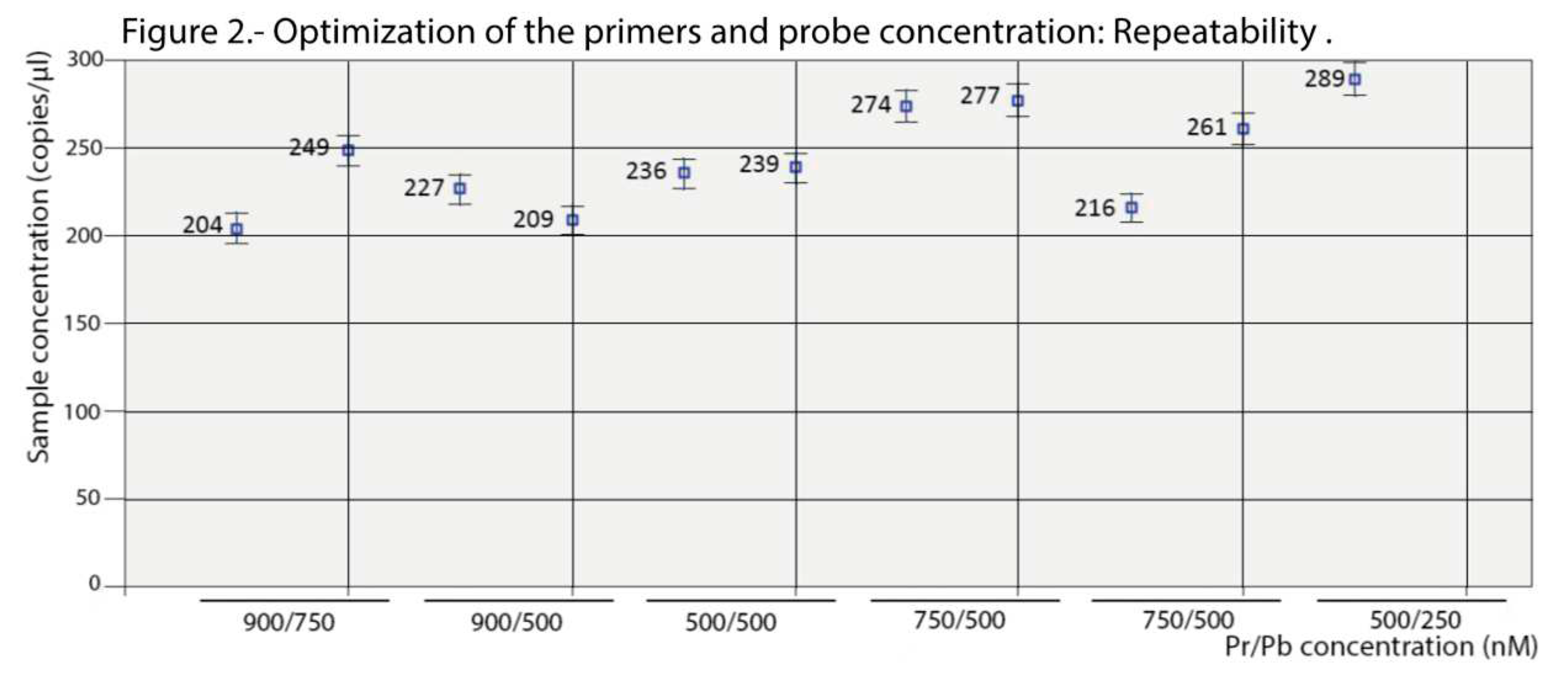
Figure 1, maximum amplitude was obtained with the highest concentration of primers (900 nM) at both probe concentrations tested (500 and 750 nM). Enough separation between the two droplet populations (positive and negative) and with a similar level of rain was also observed at the 500/500 nM combination. With the remaining concentrations, the amplitude was too low and/or the rain was excessive. Based on these results, the logical choice would be either of the first two combinations (900/500 or 900/750); however, as shown in
Figure 2, the results (using two replicas) were not repeatable at those concentrations. We must point out that deviations due to variations in the number of readable droplets between repeats, or due to low numbers of dots, were discarded (
Figure S1). Therefore, the combination 500/500 nM was chosen for the concentration of primers and probes in the ddPCR procedure.
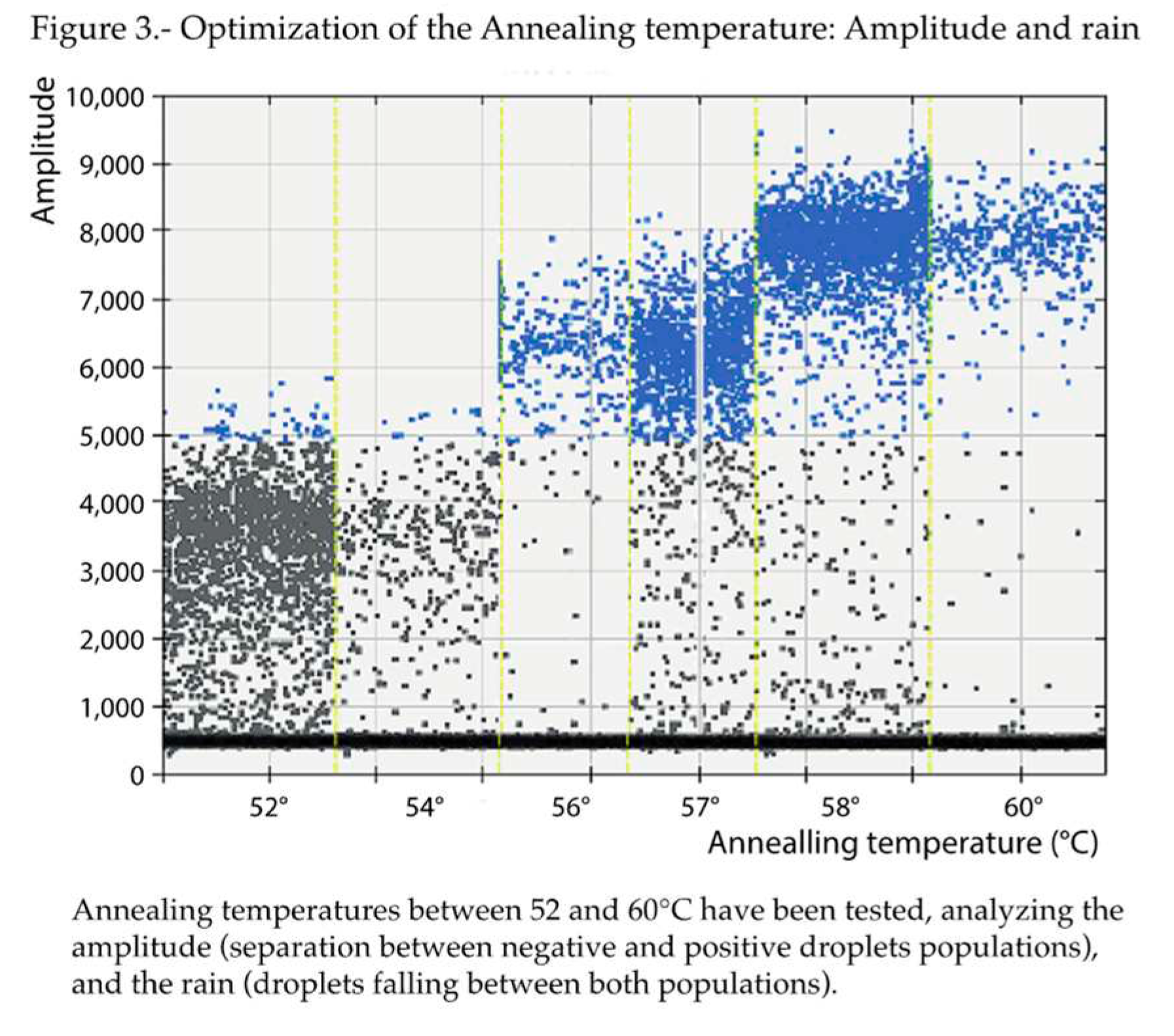
Regarding the annealing temperature (
Figure 3), based on the amplitudes, 57 and 58°C were the best options. Given that 57°C was the annealing temperature originally employed in the qPCR protocol, it was also maintained in the present study for those assays involving qPCR. But, because, less rain was obtained at 58°C, this annealing temperature was chosen for the ddPCR runs.
3.2. Repeatability, Reproducibility and Specificity
To evaluate repeatability, all the assays were carried out applying at least three replicas, with both reference templates (plasmid and crude virus) and both VNNV types (SJ and RG). There was only one exception, the fourth repeat using SJ-type pDNA (
Tables S1–S5), in which case only one replica was used as it was carried out to test the highest dilutions.
With the RG type, and within the quantification range (see below), all the repeats demonstrated to be repeatable, with CV values ≤ 25%, except in one case, namely SJ crude virus in repeat 2 at dilution 10
-8, where a CV of 28.3 was obtained (
Table S9). For all the remaining, CV data were between 0.3 and 24.95, or 9.91 and 22.65 (SJ and RG types, respectively) with pDNA, and between 2.9 and 24.2 (SJ) or 9.67 and 21.4 (RG) with crude virus (see Tables S1 to S11).
To evaluate reproducibility, all the data were set together (see Tables S12 to S15) and again the CV values were maintained ≤ 25%, except for the aforementioned high dilution of SJ crude virus (
Table S12), which suggests a certain deviation (not too high: CV=32.2) at the lowest concentrations with one of the type strains.
Analyzing the results of reproducibility with RT-qPCR, whereas with the RG type all CV values were below 25% (
Tables S14 and S15), with SJ they were extremely high at all dilutions, from 49.25 to 167.99% (
Table S12). As expected, the CV values were reduced below 10 in most cases when the decimal logarithm of the quantification data were used instead of the absolute values.
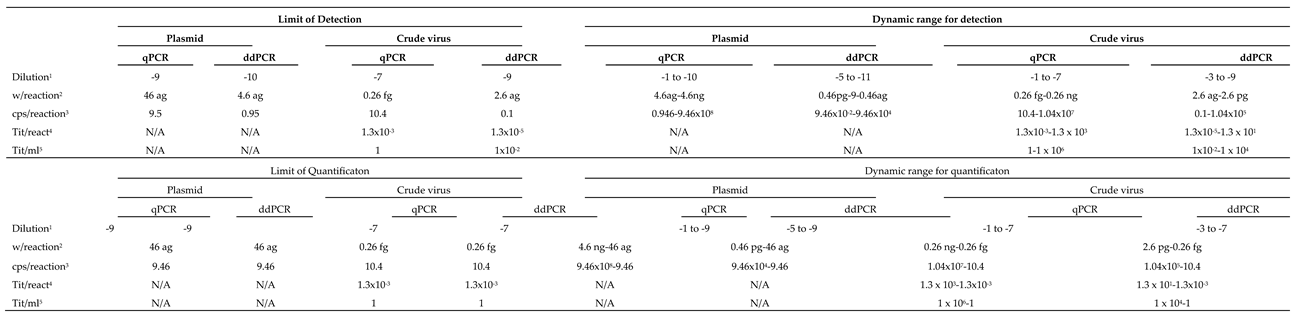
3.3. Dynamic Range (DR); Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
Both, detection and quantification DR were generally lower with ddPCR than with qPCR (
Table 2 and
Table 3). For quantification, the DR with ddPCR was always of 5 Log
10, in a range between attograms (ag) and femtograms (fg) with plasmid, and ag and picograms (pg) with crude virus. The DR was always higher with qPCR, between 6 and 9 Log
10, depending on the template and the viral strain. The DR for detection increased up to 2 Log
10, with the RG type strain, or a maximum of 1, with SJ.
The LOD per reaction (rctn) using pDNA as reference was in the order of ag: 0.9 ag (equivalent to 0.22 copies/rctn) with SJ, and 4.6 ag (0.95 cps/rctn) with RG (
Table 2 and 3), 10 times lower than with qPCR. With crude virus, the LOD per rctn was 18 ag with SJ and 2.6 ag with RG. This corresponds to 6.8 and 0.1 genome copies/rctn or 7.2 x 10
-4 and 1.3 x 10
-5 TCID
50/rctn, (SJ and RG, respectively), and represents a much higher sensitivity than with qPCR (between 1 and 2 Log
10 lower LOD). It is interesting to note that with crude virus there is a 1/10
-4 ratio between RNA cps/rctn (calculated based on the weight of extracted RNA and the Avogadro formula) and the viral titers/rctn.
3.4. Reliability of the Quantification
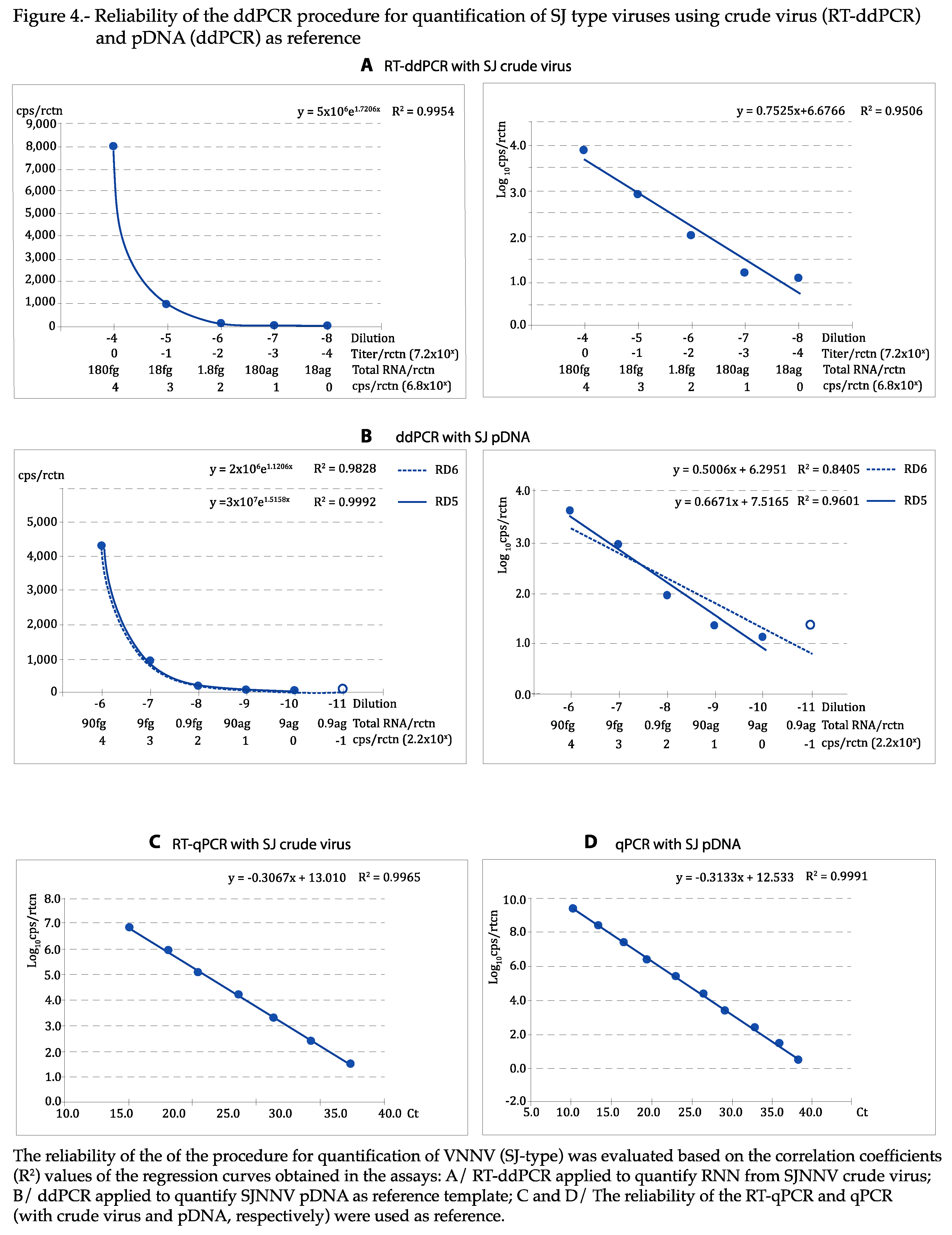
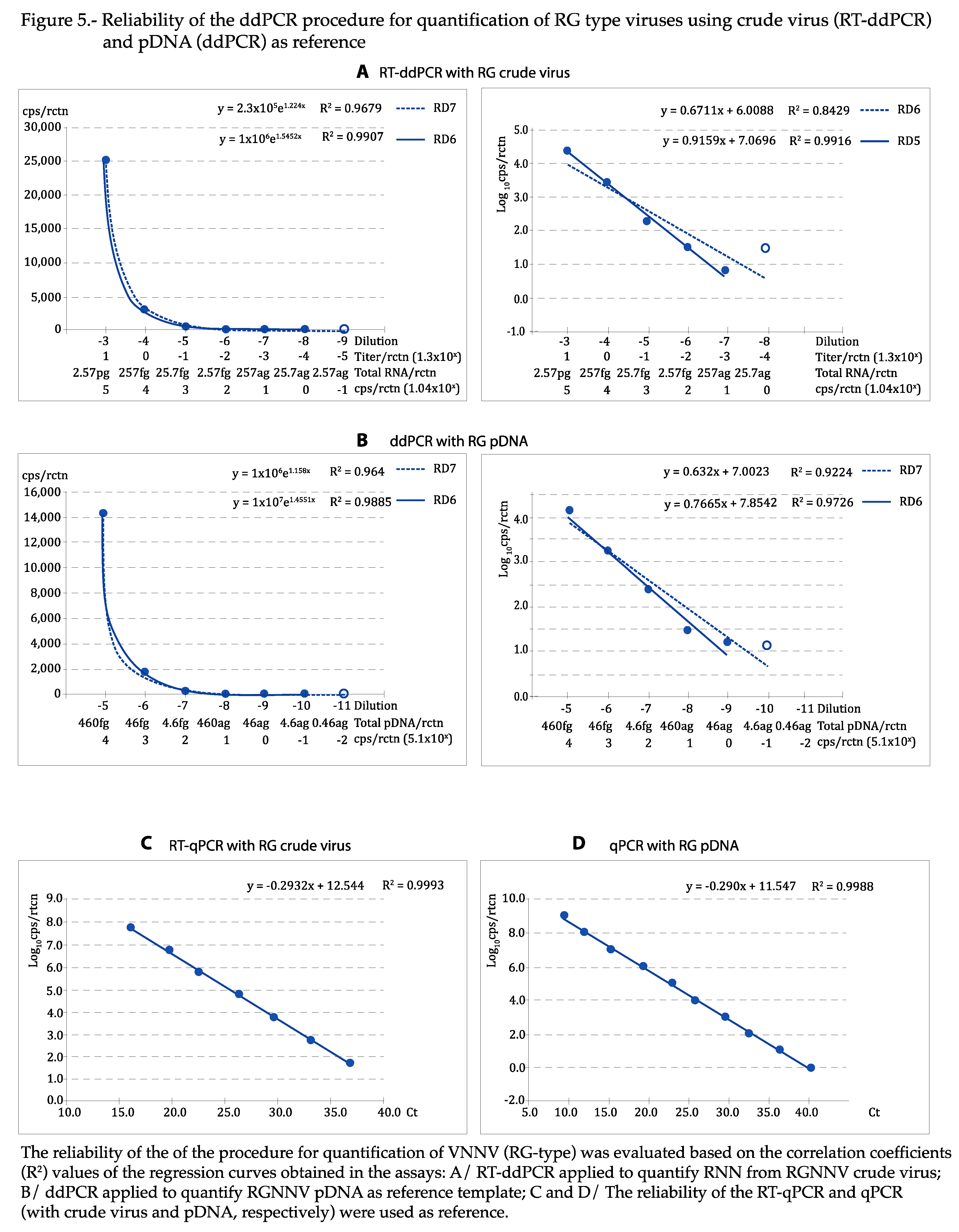
As shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, the regression curves were highly reliable, with at least the expected DR of 5 Log
10, with both viral types and reference templates: using the absolute values, the exponential regression curves showed P>0.99 in all cases, and P was at least 0.95 in linear regression when the logarithmic values were used. The curves calculated for each repeat of all tests can be visualized in
Figures S2–S5. With qPCR, DR was of 7 Log
10 with crude virus and 10 with pDNA (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5C,D).
4. Correlation between ddPCR and qPCR Quantification Methods
Correlation between the measurements obtained with both procedures seemed to be demonstrated by the correlation coefficients in all cases (Figure 6). However, because in many cases the data looked really different to the naked eye, a Student’s t test was applied, obtaining p values always higher than 0.05. Then, we tried the Welch correction, with similar results; and finally, the Wilcoxon test was applied, with no differences either.
5. Performance of the RT-ddPCR Procedure in Field Samples
To validate the procedure for diagnosis, it was tested in field samples of –expected– extremely low viral loads: blood samples from breeders. It was carried out as part of a program for the selection of VNNV-free breeders, and for which our RT-qPCR protocol is routinely employed. As shown in
Table 4, some of the fish considered VNNV-free by RT-qPCR (Ct≥40) were confirmed positive by RT-ddPCR. On the other hand, two cases of Ct>3.95, considered weak positives by RT-qPCR (but enough to reject the specimens as breeders) are actually virus-free as determined by RT-ddPCR.
To evaluate the clinical parameters, the results with both methods were compared in a contingency table, alternating both methods as the gold standard, and comparing the results obtained changing the threshold Ct for positives (Ct<40 or ≤39.5). As shown in
Table 5, the clinical sensitivity of the ddPCR procedure was extremely high (cSs = 1) when the threshold for positive results was lowered just 0.5, and the reliability of negatives (NPV) was also maximum.
6. Discussion
Digital PCR (dPCR) is an accurate technology for the detection and quantification of nucleic acid templates, which has proven important advantages over rtPCR, such as higher sensitivity and not needing standard curves to quantify [
10]. Furthermore, among the dPCR variants, ddPCR outperforms digital chip PCR [
14]. For this reason, we chose ddPCR technology to adapt our laboratory to the future of diagnosis of viral pathologies in aquaculture.
Diagnosis by ddPCR has been extensivelly introduced in human viral diseases and for a wide range of viruses, such as influenza, leukemia, encephalitis, hepatitis (A and B), norovirus, papilloma and polyoma, SARS and Zika [
14]. However, few reports on the use of ddPCR for the diagnosis and quantification of fish viruses have been published, and even less have addressed the evaluation (and none the complete validation) of the reported procedure. A first approach by Jia et al. [
15] developed and validated (just from an analytical point of view) a ddPCR procedure for the detection and quantification of the infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV). They reported a LOD of 2.2 pfu/µl, surprisingly higher that the data they got with qPCR. Assuming an equivalence of 4.4 pfu/rctn, it would be much higher that the LOD that we obtained in terms of titer: in the order of 10
-4 (with SJ) and 10
-5 (with RG) TCID
50/rctn. However, as indicated in Results, we have observed a 1/10
-4 ratio between copies and crude virus titer. Therefore, the LOD reported by those authors would be between the LOD values we observed with RGNNV (0.1 cps/rctn) and SJNNV (6.8 cps/rctn). Similar LOD values have been reported by other authors, for infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (3 cps/rctn; [
16]), carp edema virus (2.2 cps/rctn; [
17]), largemouth bass ranavirus (2.0 cps/rctn; [
18]) or tilapia lake virus (3.3 cps/rtcn; [
19]). A lower LOD, 0.07 cps/µl, has been reported for a method developed for tilapia parvovirus [
20]; assuming a volume of 2µl of template per ddRNA reaction mixture, that LOD would be equivalent to 0.14 cps/rctn, quite similar to what we obtained for the RG type with our protocol. Similar analytical sensitivities, but also higher LOD values, have been reported by other authors, as reviewed by Lei et al. [
14] and Chen et al. [
8].
The LOQ is expected to be higher than the LOD; this is because, to accept a dynamic range for quantification, the linearity between the measurements of serial diluted samples usually fails at the lower concentrations providing acceptable numbers of positive droplets. And, as expected, the LOQ obtained with the RG type strain was 10 times higher (LOQ=10.4 cps/rctn) than the LOD (0.1 cps/rctn); however, this was not the case with the SJ type, which provided a value of 6.8 cps/rctn for both LOD and LOQ. We must note that the reliability of the quantification was ensured by the linearity of all the curves, with R2 values always >0.95. These values are below those reported by other authors, like Han et al. [
21], who reported a LOQ of 20 or 25 cps/rctn, depending on the virus (hepatitis A or norovirus g.I or g.II), or Mairiang et al. [
22], who obtained a LOQ of 2.337, but in terms of Loq
10cps/rctn, actually corresponds to 217 cps/rctn.
LOQ and LOD define the lowest limit of the DR, but in ddPCR it clearly depends on the saturation of positive droplets, which makes the Poisson distribution invalid at template concentrations over 10
5 [
17,
23,
24]. Therefore, the 5 Log
10 DR values observed in the present study were within those expected and reported in most cases, although others have been able to reach DRs of 6 Log
10 [
25,
26].
Although this limit in DR looks like a disadvantage of ddPCR with respect to qPCR (which can easily reach DR values of 10 Log
10) because failures can occur if high concentrated viruses are measured, it is compensated by its higher precision [
10]. To this regard, the evaluation of repeatability and reproducibility of the RT-ddPCR developed here has provided CV values within the limit of 25% for both VNNV types. On the contrary, the deviations reached with RT-qPCR were extremely high with one of the viral types. We must mention that this is not unusual, although rarely shown in qPCR validation procedures, given that R&R are always evaluated in terms of Ct values, and not template quantities.
To ensure the validation of a procedure for the diagnosis of fish viral diseases, the analytical point of view is only a first step, and the clinical –or diagnostic– approach is also mandatory [
27]. Therefore, we chose a type of sample which is extremely complicated, due to the type of tissue itself (blood), and also due to the expected viral load (very low, since it is from asymptomatic breeder fish). The designed RT-ddPCR procedure has demonstrated to be more reliable that RT-qPCR for detecting VNNV in field samples, because it provided higher clinical sensitivity and NPV values, reaching the maximum when false positives by RT-qPCR were avoided by reducing the threshold Ct for positive reactions.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, we have designed and formally validated a RT-ddPCR procedure for the diagnosis and quantification of the nervous necrosis virus VNNV. The procedure has demonstrated higher reliability and performance that RT-qPCR and represents the first protocol available for the control of an important disease in Europe and worldwide.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1.- Optimization of the primers and probe concentration: Total events and positive events. Figure S2.- Reliability of the RT-ddPCR procedure for quantification of SJ crude virus. Results obtained from each repeat. Figure S3.- Reliability of the ddPCR procedure for quantification of SJ pDNA. Results obtained from each repeat. Figure S4.- Reliability of the RT-ddPCR procedure for quantification of RG crude virus. Results obtained from each repeat. Figure S5.- Reliability of the ddPCR procedure for quantification of RG pDNA. Results obtained from each repeat. Table S1.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ pDNA – Repeat 1. Table S2.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ pDNA – Repeat 2. Table S3.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ pDNA – Repeat 3. Table S4.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ pDNA – Repeat 4. Table S5.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ pDNA – Repeat 5, Table S6.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on RG pDNA – Repeat 1. Table S7.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on RG pDNA – Repeat 2. Table S8.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ crude virus – Repeat 1. Table S9.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on SJ crude virus – Repeat 2. Table S10.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on RG crude virus – Repeat 1. Table S11.- Results obtained with ddPCR applied on RG crude virus – Repeat 2. Table S12.- Detection of SJNNV crude virus by RT-ddPCR and RT-qPCR. Table S13.- Detection of SJNNV pDNA by ddPCR and qPCR. Table S14.- Detection of RGNNV crude virus by RT-ddPCR and RT-qPCR. Table S15.- Detection of RGNNV pDNA by ddPCR and qPCR
Author Contributions
In the present study, the contribution of the authors has been distributed as follows: “Conceptualization, S.S. and C.P.D.; methodology, J.G.O., C.L.V. and C.P.D.; software, J.G.O. and C.L.V.; validation, S.S. and C.P.D.; formal analysis, S.S., I.B. and C.P.D.; investigation, S.S., J.G.O. and C.L.V.; resources, J.G.O., I.B. and C.P.D.; data curation, J.G.O. and C.P.D.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S. and J.G.O; writing—review and editing, I.B. and C.P.D.; visualization, S.S., I.B. and C.P.D.; supervision, I.B. and C.P.D.; project administration, I.B. and C.P.D.; funding acquisition, I.B. and C.P.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study has been partially supported by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación and Xunta de Galicia with funding from European Union NextGenerationEU (PRTR-C17.I1) and European Maritime and Fisheries Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
“Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to blood samples were not taken by our laboratory, but by by those responsible for the fish farm.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Crude data will be available at “Dopazo, C. P., Bandín, I., Olveira, J. G., López-Vázquez, C., & Pereira, S. S. (2023, July 29). Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) for diagnosis of VNNV. Retrieved from osf.io/ch4rn”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bandín, I.; Souto, S. Betanodavirus and VER Disease: A 30-year Research Review. Pathogens 2020, 9, 106. [CrossRef]
- World Organization of Animal Health (WOAH, 2019). Viral encephalopathy and retinopathy. In: “Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals”· Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/aahm/current/chapitre_viral_encephalopathy_retinopathy.pdf (Accessed on July 9th, 2023).
- Panzarin, V.; Patarnello, P.; Mori, A.; Rampazzo, E.; Cappellozza, E.; Bovo, G.; Cattoli, G. Development and validation of a real-time TaqMan PCR assay for the detection of Betanodavirus in clinical specimens. Arch Virol 2010, 155: 1193-1203. [CrossRef]
- Olveira, J.G.; Souto, S.; Bandín, I.; Dopazo, C.P. Development and validation of a SYBR Green real time PCR protocol for detection and quantification of nervous necrosis virus (NNV) using different standards. Animals 2021, 11, 1100. [CrossRef]
- Gezer, U.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Holdenrieder, S. The Clinical Utility of Droplet Digital PCR for Profiling Circulating Tumor DNA in Breast Cancer Patients. (Special Issue Cell-Free Nucleic Acids—New Insights into Physico-Chemical Properties, Analytical Considerations, and Clinical Applications). Diagnostics 2022, 12(12), 3042. [CrossRef]
- Huerta, M.; Roselló, S.; Sabater, L.; Ferrer, A.; Tarazona, N.; Roda, D.; Gambardella, V.; Alfaro-Cervelló, C.; Garcés-Albir, M.; Cervantes, A.; Ibarrola-Villava, M. Circulating Tumor DNA Detection by Digital-Droplet PCR in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Systematic Review. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13(5): 994. [CrossRef]
- Salipante, S.J.; Jerome, K.R. Digital PCR—An Emerging Technology with Broad Applications in Microbiology. Clin Chemist 2020, 66(1): 117-123. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, N.; Shi, D. Droplet digital PCR as an emerging tool in detecting pathogens nucleic acids in infectious diseases. Clin Chim Acta 2021, 517: 156–161. [CrossRef]
- Morley, A.A. Digital PCR: A brief history. Biomol Detect Quantif 2014, 1: 1-2. [CrossRef]
- 10. Huggett, JF; Foy, C.A.; Benes, V.; Emslie, K.; Garson, J.A.; Haynes, R.; Hellemans, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.D.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; Vandesompele, J.; Wittwer, C.T.; Bustin, S.A. The Digital MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Digital PCR Experiments. Clin Chemist 2013, 59(6): 892-902. [CrossRef]
- 11. European Network of GMO Laboratories (ENGL, 2015). Definition of Minimum Performance Requirements for Analytical Methods of GMO Testing. Available on line: https://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/doc/Min_Perf_Requirements_Analytical_methods.pdf. (Accessed on July 9th, 2023).
- Olveira, J.G.; Soares, F.; Engrola, S.; Dopazo, C.P.; Bandín, I. Antemortem versus postmortem methods for detection of betanodavirus in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). J Vet Diagn Invest 2008, 20:215–219. [CrossRef]
- Dopazo, C.P.; Moreno, P.; Olveira, J.G.; Borrego, J.J. The theoretical reliability of PCRbased fish viral diagnostic methods is critically affected when they are applied to fish populations with low prevalence and virus loads. J Appl Microbiol 2017, 124, 977-989. [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Chen, S.; Zhong, Q. Digital PCR for accurate quantification of pathogens: Principles, applications, challenges and future prospects. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 184: 750–759. [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Purcell, M.K.; Pan, G.; Wang, J.; Kan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shi, X.; He, J.; Yu, L.; Hua, Q.; Lu, T.; Lan, W.; Winton, J.R.; Jin, R.; Liu, H. Analytical validation of a reverse transcriptase droplet digital PCR (RTddPCR) for quantitative detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. J Virol Methods 2017, 245: 73–80. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Fu, X.; Liu, L.; Liang, H.; Niu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, N. Development and application of a sensitive droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) for the detection of infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735697. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Zhang, M.; Wu, S.; Lin, X. Development of a novel droplet digital PCR assay for the sensitive detection of carp edema virus. Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737162. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, M.; Xu, C.; Fan, Y. Development of a droplet digital PCR method for the sensitive detection and quantification of largemouth bass ranavirus. J Fish Dis 2022, 46: 91-98. [CrossRef]
- Shahi, N.; Prasartset, T.; Surachetpong, W. A specific and sensitive droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of tilapia lake virus in fish tissue and environmental samples. J Fish Dis 2023, 00: 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, N.; Meng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, M.; Xu, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, W. Development and application of a sensitive droplet digital PCR-based method to detect tilapia parvovirus. J Fish Dis 2023, 46(3):239-245. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xu, X. Simultaneous quantification of hepatitis A virus and norovirus genogroup I and II by triplex droplet digital PCR. Food Microbiol 2022, 103 (2022) 103933. [CrossRef]
- Mairiang, D.; Songjaeng, A.; Hansuealueang, P.; Malila, Y.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Silapong, S.; Poolpanichupatam, Y.; Klungthong, C.; Chin-Inmanu, C.; Thiemmeca, S.; Tangthawornchaikul, N.; Sriraksa, K.; Limpitikul, W.; Vasanawathana, S.; Ellison, D.W; Malasit, P.; Suriyaphol, P.; Avirutnan, P. Application of One-Step Reverse Transcription Droplet Digital PCR for Dengue Virus Detection and Quantification in Clinical Specimens. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 639. [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, L.B.; Coleman, V.A.; Hindson, C.M.; Herrmann, J.; Hindson, B.J.; Bhat, S.; Emslie, K.R. Evaluation of a droplet digital polymerase chain reaction format for DNA copy number quantification. Anal Chem 2012, 84, 1003–1011. [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xi, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, S.; Chen, N.; Qiao, S.; Wan, S.; Bao, D. The development of a sensitive droplet digital PCR for quantitative detection of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Int J Bio Manromol 2017, 104: 1223-1228. [CrossRef]
- Rački, R.; Morisset, D.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Ravnikar, M. One-step RT-droplet digital PCR: a breakthrough in the quantification of waterborne RNA viruses. Anal Bioanal Chem 2014, 406:661–667. [CrossRef]
- World Organization of Animal Health (WOAH; 2023). Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/aquatic-manual-online-access/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).