Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
2. Fundamentals of NILM Concept
2.1. Mathematical methods
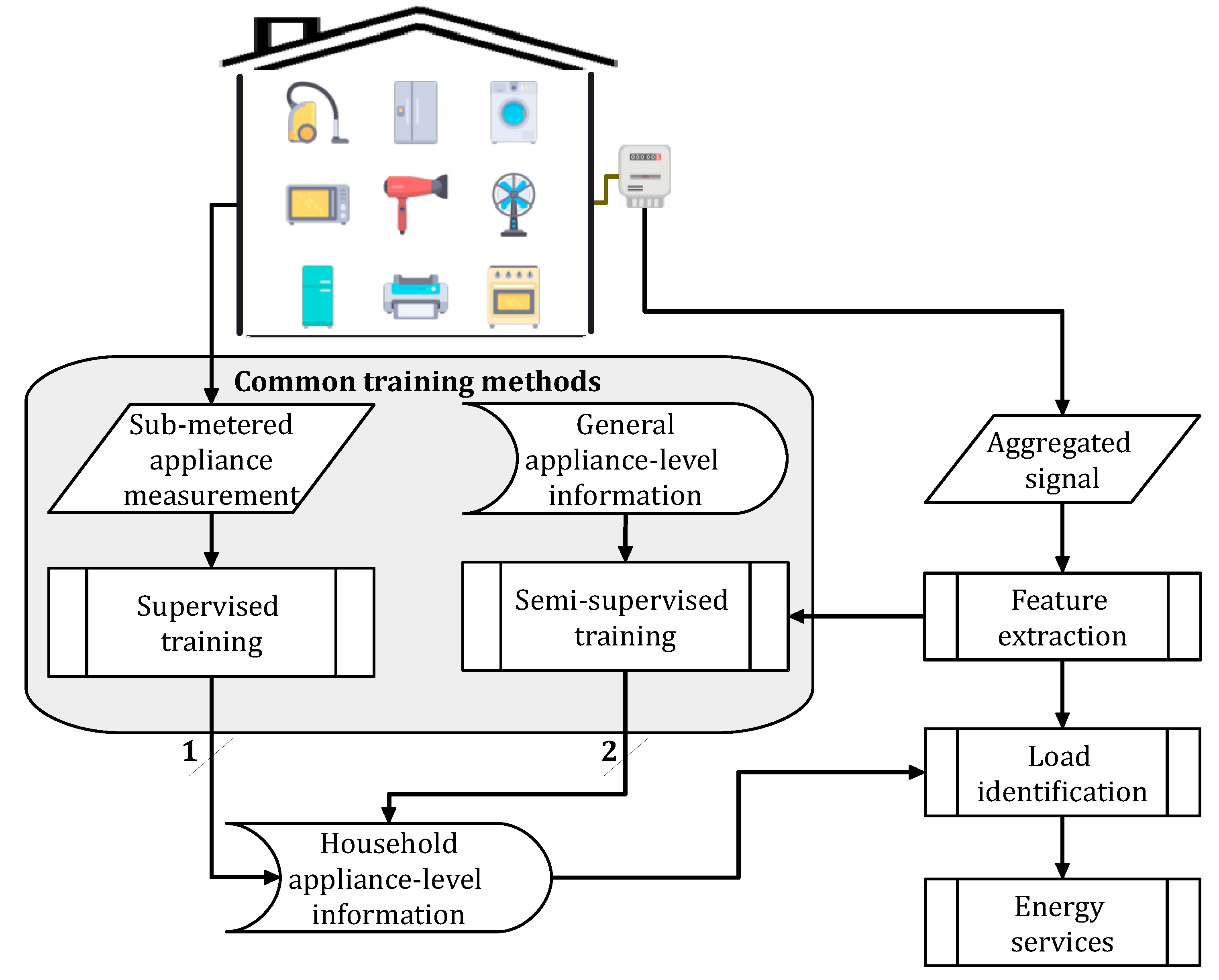
2.2. Learning procedures
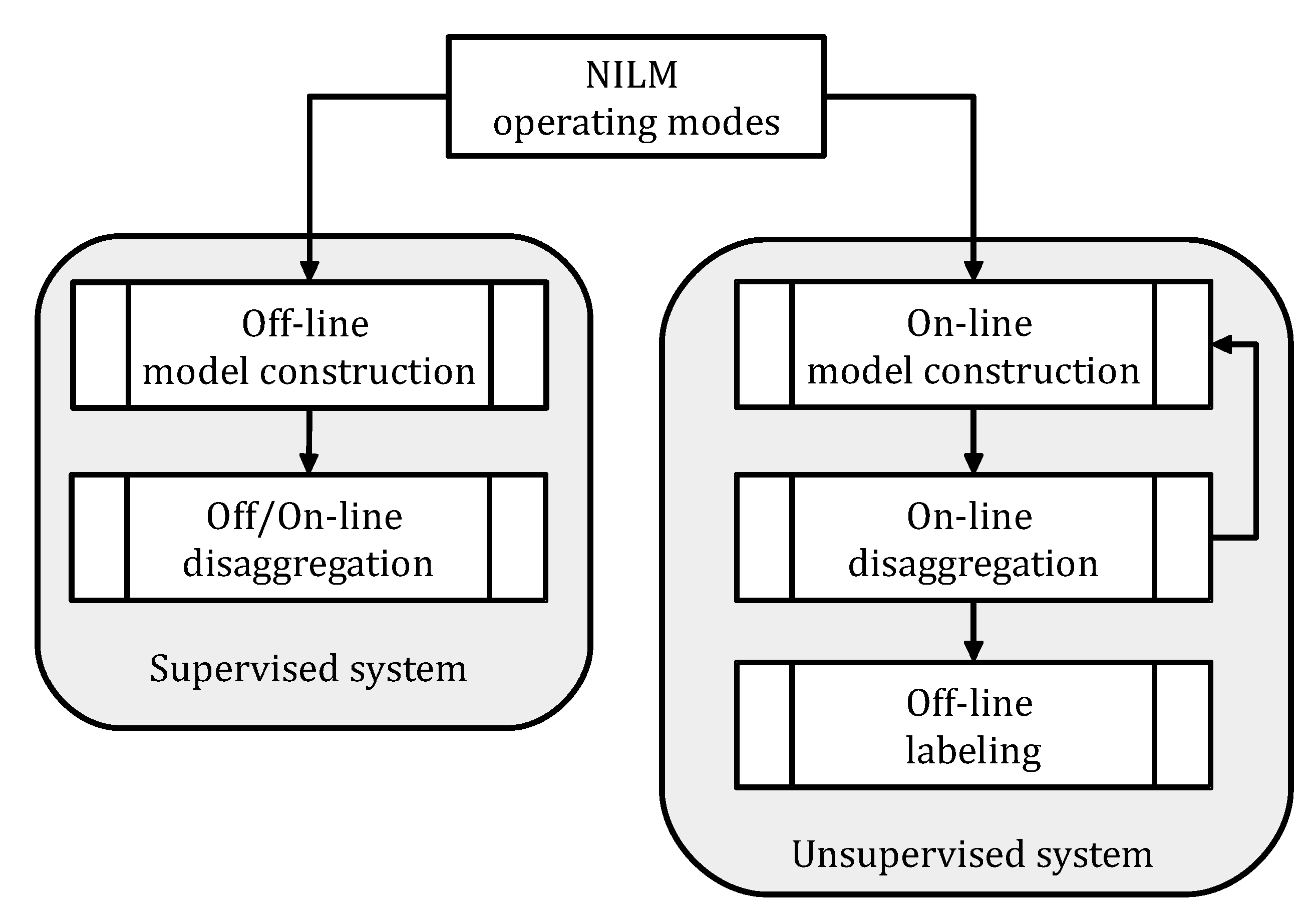
2.3. Operation modes
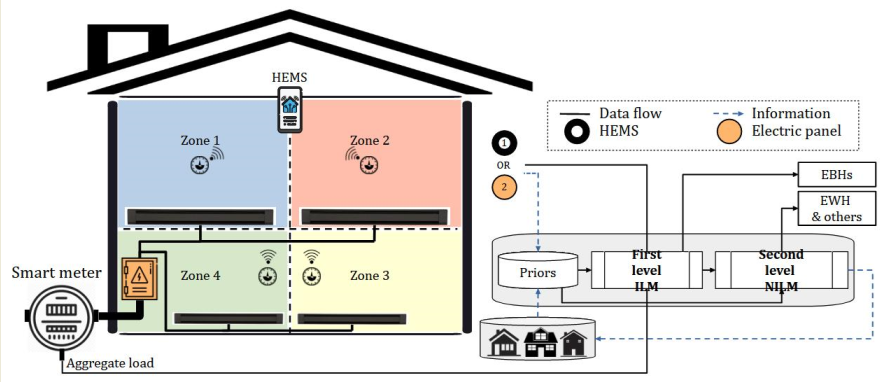
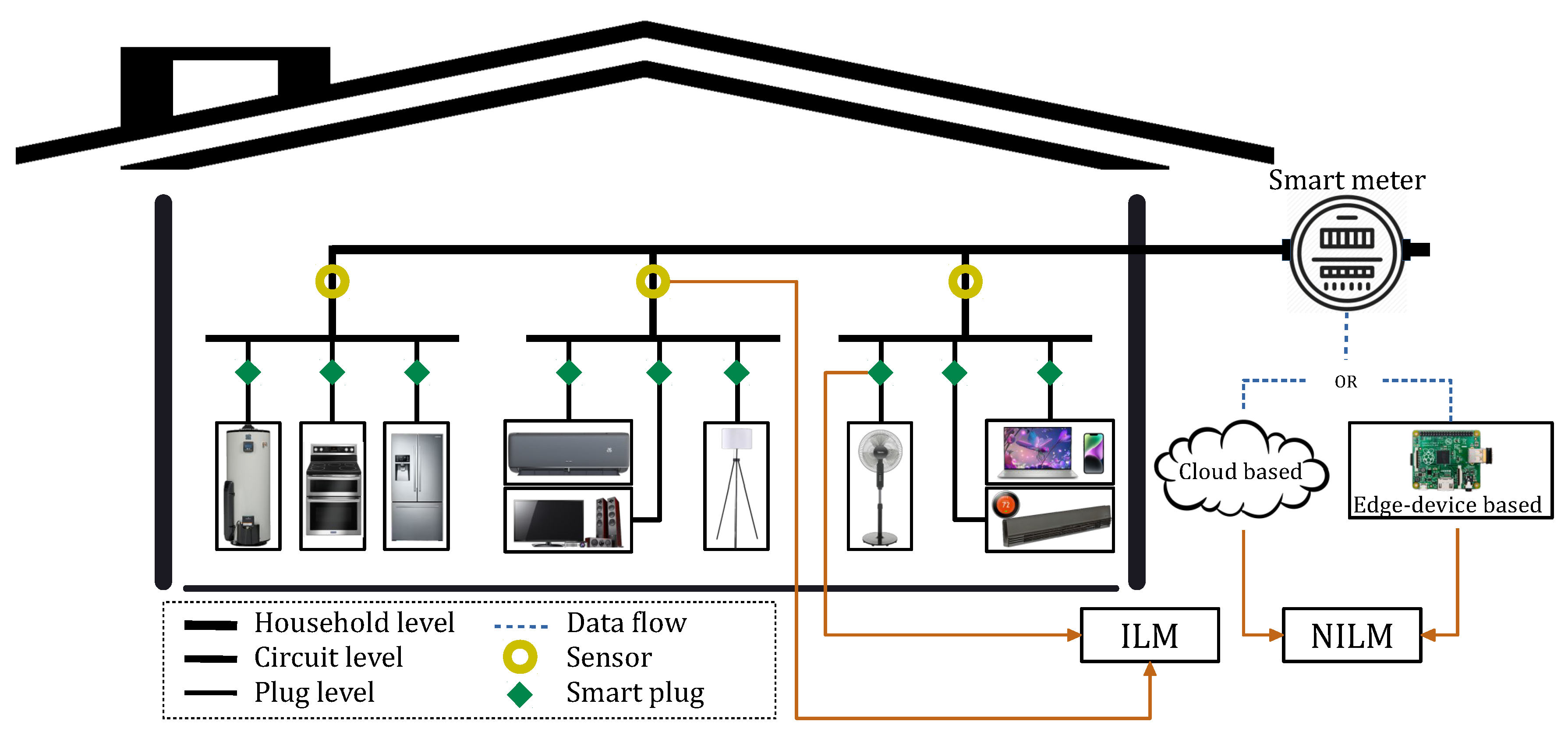
2.4. Data source
3. Quebec Residential Energy Usage Context
3.1. Quebec residential data features
3.2. Quebec comparative data statistics
4. A Disaggregation Approach to Quebec Household Power Consumption
5. An Introductory NILM Practice in Quebec residences
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hosseini, S.S.; Agbossou, K.; Kelouwani, S.; Cardenas, A. Non-intrusive load monitoring through home energy management systems: A comprehensive review, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zandi, H.; Kuruganti, P.T.V.; Vineyard, E.A.; Fugate, D.L. Home Energy Management Systems: An Overview. Proceedings of the 9th international conference on Energy Efficiency in Domestic Appliances and Lighting 2017, 2018, p 606 to 614. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Agbossou, K.; Kelouwani, S.; Cardenas, A.; Henao, N. A Practical Approach to Residential Appliances on-Line Anomaly Detection: A Case Study of Standard and Smart Refrigerators. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 57905–57922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, N.; Hossain, E.; Ahamed, S.I. A Qualitative Study on the United States Internet of Energy: A Step Towards Computational Sustainability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69003–69037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Kelouwani, S.; Agbossou, K.; Cardenas, A.; Henao, N. Adaptive on-line unsupervised appliance modeling for autonomous household database construction. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2019, 112, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. S. Hosseini. Load Monitoring and Diagnosis of Residential Electrical Appliances. PhD thesis, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, 2020.
- Oliver Parson. Disaggregated Homes: Overview of the NILM field, 2015.
- Liaqat, R.; Sajjad, I.A.; Waseem, M.; Alhelou, H.H. Appliance Level Energy Characterization of Residential Electricity Demand: Prospects, Challenges and Recommendations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 148676–148697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huchtkoetter, J.; Reinhardt, A. A study on the impact of data sampling rates on load signature event detection. Energy Informatics 2019, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Huang, B.; Cun, X.; Wang, F.; Yuan, H.; Lai, L.L.; Vaccaro, A. Classifier economics of Semi-Intrusive Load Monitoring. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2018, 103, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, G.F.; Timplalexis, C.; Krinidis, S.; Ioannidis, D.; Tzovaras, D. NILM applications: Literature review of learning approaches, recent developments and challenges. Energy and Buildings 2022, 261, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustine, A.; Pereira, L.; Bousbiat, H.; Kulkarni, S. UNet-NILM: A Deep Neural Network for Multi-tasks Appliances State Detection and Power Estimation in NILM. NILM 2020 - Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. Association for Computing Machinery, Inc, 2020, pp. 84–88. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.K.; Malik, F.H.; Muhammad, A.; Qureshi, M.A.; Abbasi, M.N.; Chishti, A.R. A critical review of state-of-the-art non-intrusive load monitoring datasets. Electric Power Systems Research 2021, 192, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völker, B.; Pfeifer, M.; Scholl, P.M.; Becker, B. Annoticity: A Smart Annotation Tool and Data Browser for Electricity Datasets. Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ma, J.; Zhu, J.; Liang, H. Deep Domain Adaptation for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Based on a Knowledge Transfer Learning Network. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. Sequence-to-Sequence Load Disaggregation Using Multiscale Residual Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2021, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, M.; Squartini, S.; Zhong, M. Transfer Learning for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Ochani, M.K.; Shah, A.A. Generalizability improvement of deep learning-based non-intrusive load monitoring system using data augmentation. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, B.; Luan, W.; Yu, Y. Estimation of Target Appliance Electricity Consumption Using Background Filtering. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 5920–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzalan, M.; Jazizadeh, F. Residential loads flexibility potential for demand response using energy consumption patterns and user segments. Applied Energy 2019, 254, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Gomes, �. ; Antunes, C.H. Categorization of residential electricity consumption as a basis for the assessment of the impacts of demand response actions. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2014, 30, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Kelouwani, S.; Agbossou, K.; Cardenas, A.; Henao, N. A semi-synthetic dataset development tool for household energy consumption analysis. IEEE Int. Conf. Ind. Tech. (ICIT), 2017, pp. 564–569. [CrossRef]
- Hart, G. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 1870–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.F.; Ahmet Sekercioglu, Y.; Drummond, T.; Wong, V.S. Recent approaches to non-intrusive load monitoring techniques in residential settings. 2013 IEEE Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid (CIASG). IEEE, 2013, pp. 73–79. [CrossRef]
- Kaselimi, M.; Protopapadakis, E.; Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A. Towards Trustworthy Energy Disaggregation: A Review of Challenges, Methods, and Perspectives for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub - nilmtk/nilmtk: Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Toolkit (nilmtk).
- Henao, N.; Agbossou, K.; Kelouwani, S.; Dube, Y.; Fournier, M. Approach in Nonintrusive Type I Load Monitoring Using Subtractive Clustering. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 8, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V. On a Training-Less Solution for Non-Intrusive Appliance Load Monitoring Using Graph Signal Processing. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1784–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammig, F.; Ditze, M.; Janacik, P.; Heimfarth, T.; Kerstan, T.; Oberthuer, S.; Stahl, K. Basic Concepts of Real Time Operating Systems. In Hardware-dependent Software; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2009; pp. 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Rho, S.; Lee, H.; Rhee, W. Data Requirements for Applying Machine Learning to Energy Disaggregation. Energies 2019, 12, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeifman, M.; Roth, K. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring: Review and outlook. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 2011, 57, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; Kashani, A. Home appliance load modeling from aggregated smart meter data. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, S.; Kalra, S.; Irwin, D.; Shenoy, P. Empirical Characterization, Modeling, and Analysis of Smart Meter Data. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2014, 32, 1312–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöchacker, M.; Egarter, D.; Elmenreich, W. Proficiency of power values for load disaggregation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, C.; Makonin, S.; Bajic, I.V. Incorporating time-of-day usage patterns into non-intrusive load monitoring. 2017 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1110–1114. [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.; Naranjo, F.; Barzola, J.; Otero, C.; Garcia, P. Load Identification for Smart Grid Management. 2019 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference - Latin America (ISGT Latin America). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Rahman Tito, S.; Nieuwoudt, P.; Imran, G.; Lie, T.T.; Valles, B.; Ahmad, W. Applications of Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Towards Smart and Sustainable Power Grids: A System Perspective. 2019 29th Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Henao, N.; Agbossou, K.; Kelouwani, S.; Hosseini, S.; Fournier, M. Power Estimation of Multiple Two-State Loads Using A Probabilistic Non-Intrusive Approach. Energies 2018, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CleverGuard - Invisible protection for pensioners based on energy data - CLEMAP Blog, 2023.
- Rafiq, H.; Manandhar, P.; Rodriguez-Ubinas, E.; Barbosa, J.D.; Qureshi, O.A. Analysis of residential electricity consumption patterns utilizing smart-meter data: Dubai as a case study. Energy and Buildings 2023, 291, 113103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dab, K.; Agbossou, K.; Henao, N.; Dubé, Y.; Kelouwani, S.; Hosseini, S.S. A compositional kernel based gaussian process approach to day-ahead residential load forecasting. Energy and Buildings 2022, 254, 111459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Disaggregation - Bidgely Utility AI - Energy Analytics, 2022.
- Culière, F.; Leduc, L.; Belikov, A. Bayesian model of electrical heating disaggregation. Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Vol. 197, pp. 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, C.; Frei, M.; Hofer, J.; Schlueter, A. Automated load disaggregation for residences with electrical resistance heating. Energy and Buildings 2019, 182, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
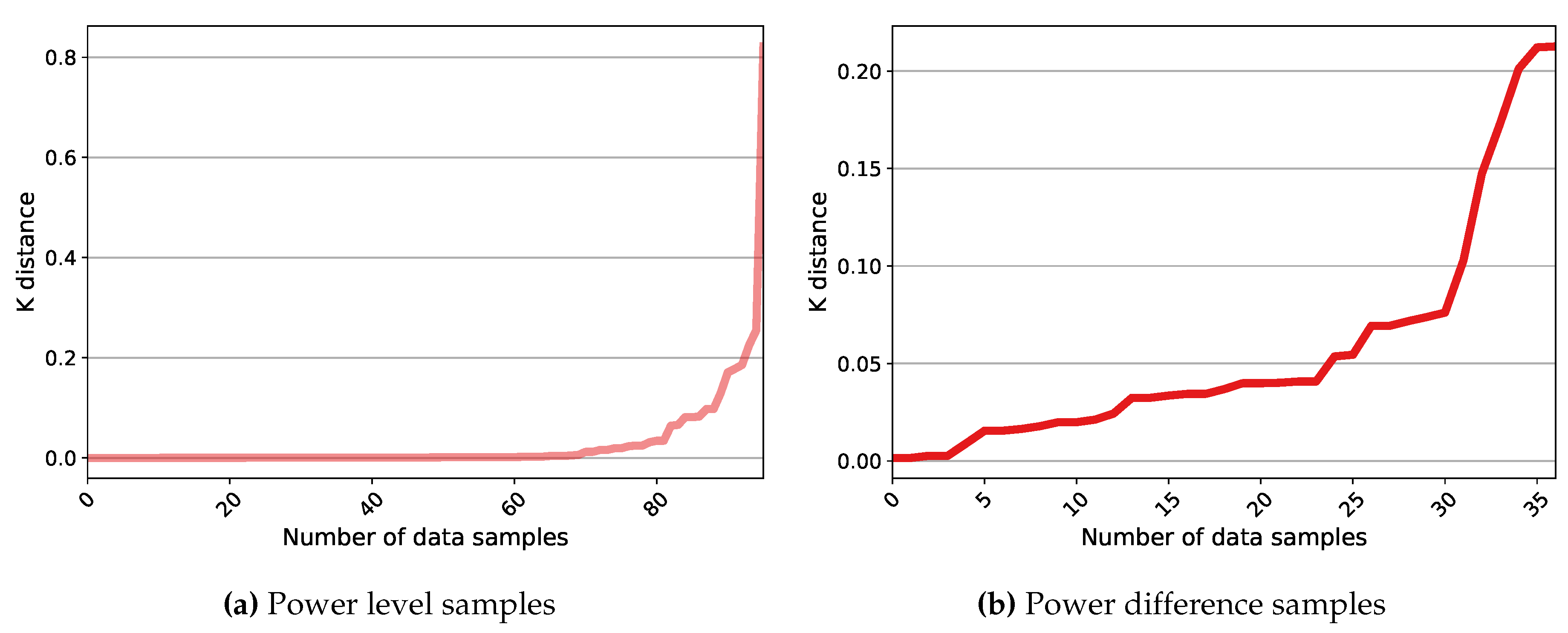
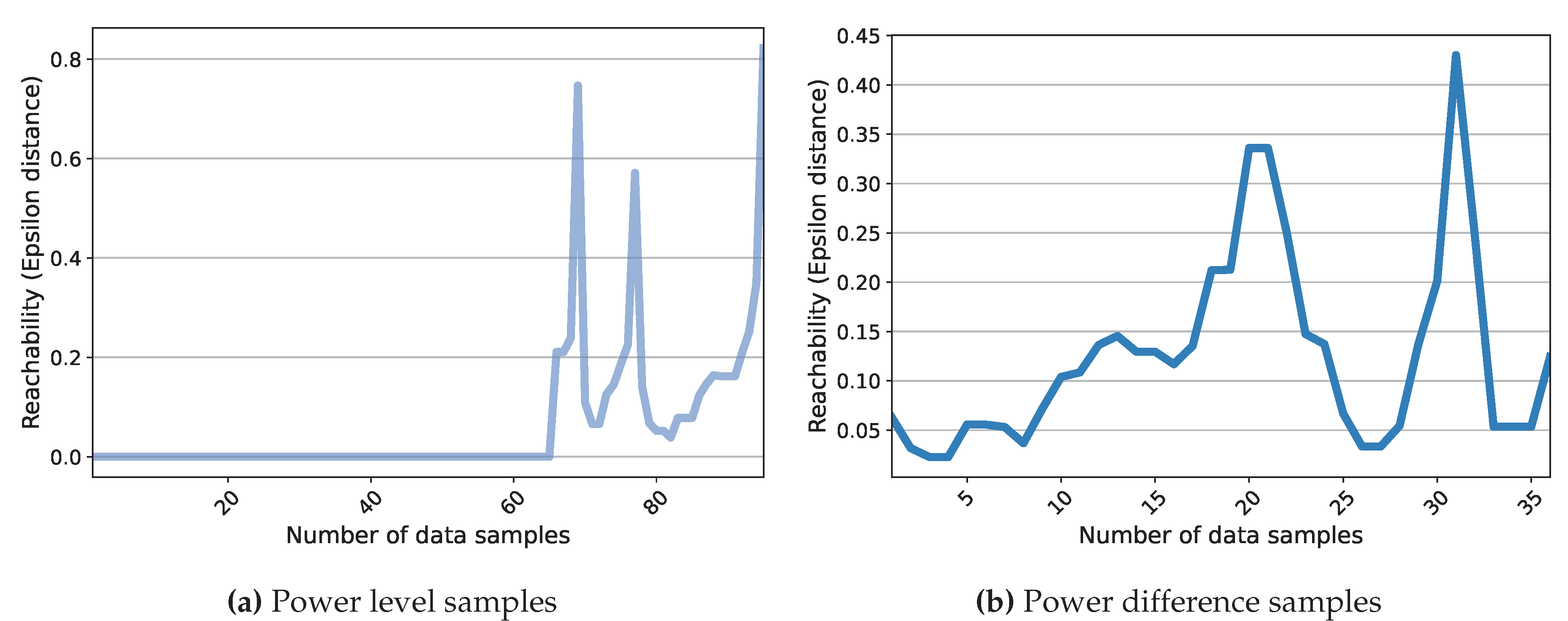
- Sander, J.; Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Xu, X. Density-based clustering in spatial databases: The algorithm GDBSCAN and its applications. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 1998, 2, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmah, N.; Sitanggang, I.S. Determination of Optimal Epsilon (Eps) Value on DBSCAN Algorithm to Clustering Data on Peatland Hotspots in Sumatra. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2016, 31, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | "CleverGuard - ICT solution based on energy data for protecting elderly at home, staying safe and independently" an EU funded AALJP project, 2021 - 2023, contact: Pascal Kienast, pascal@clemap.ch |
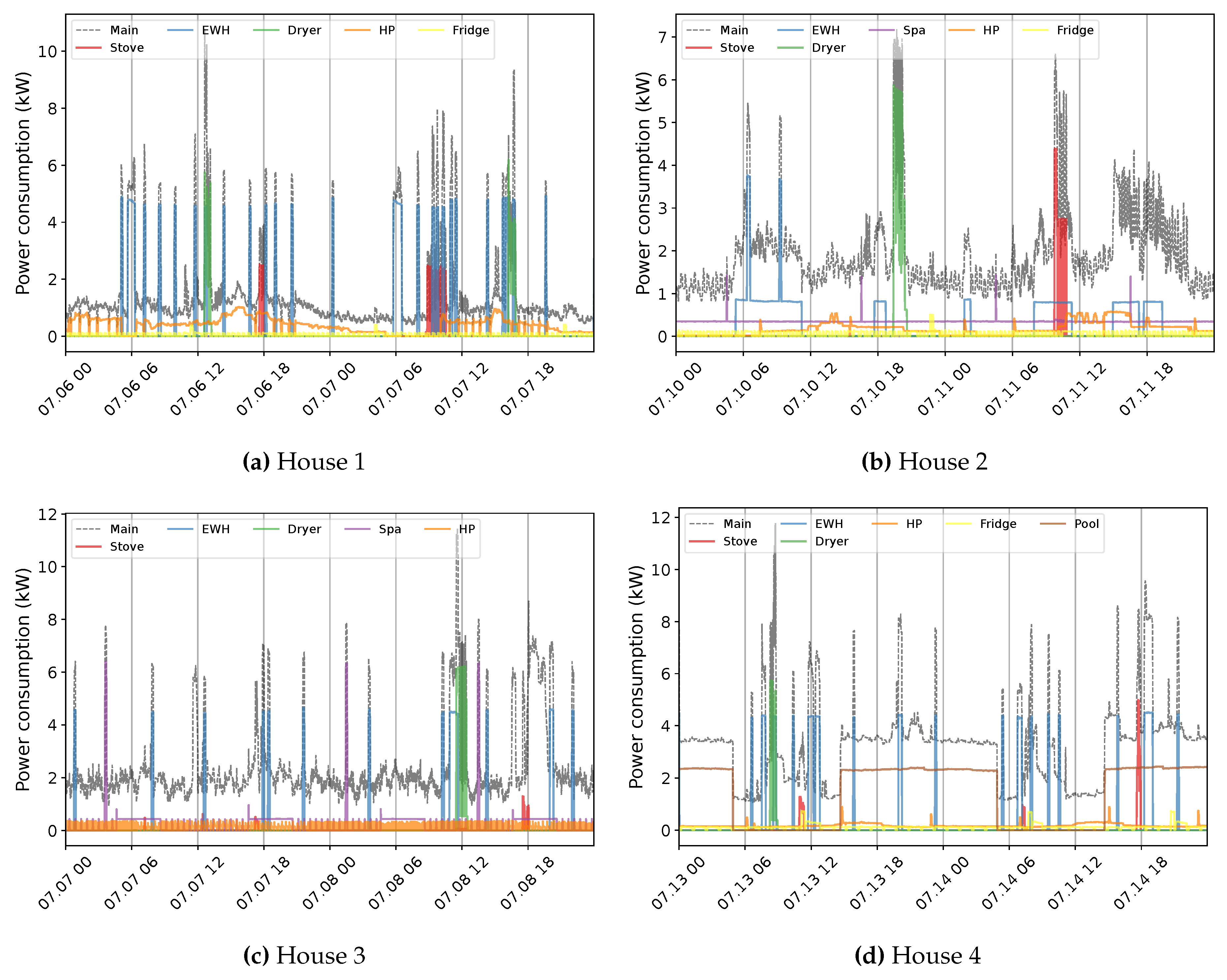
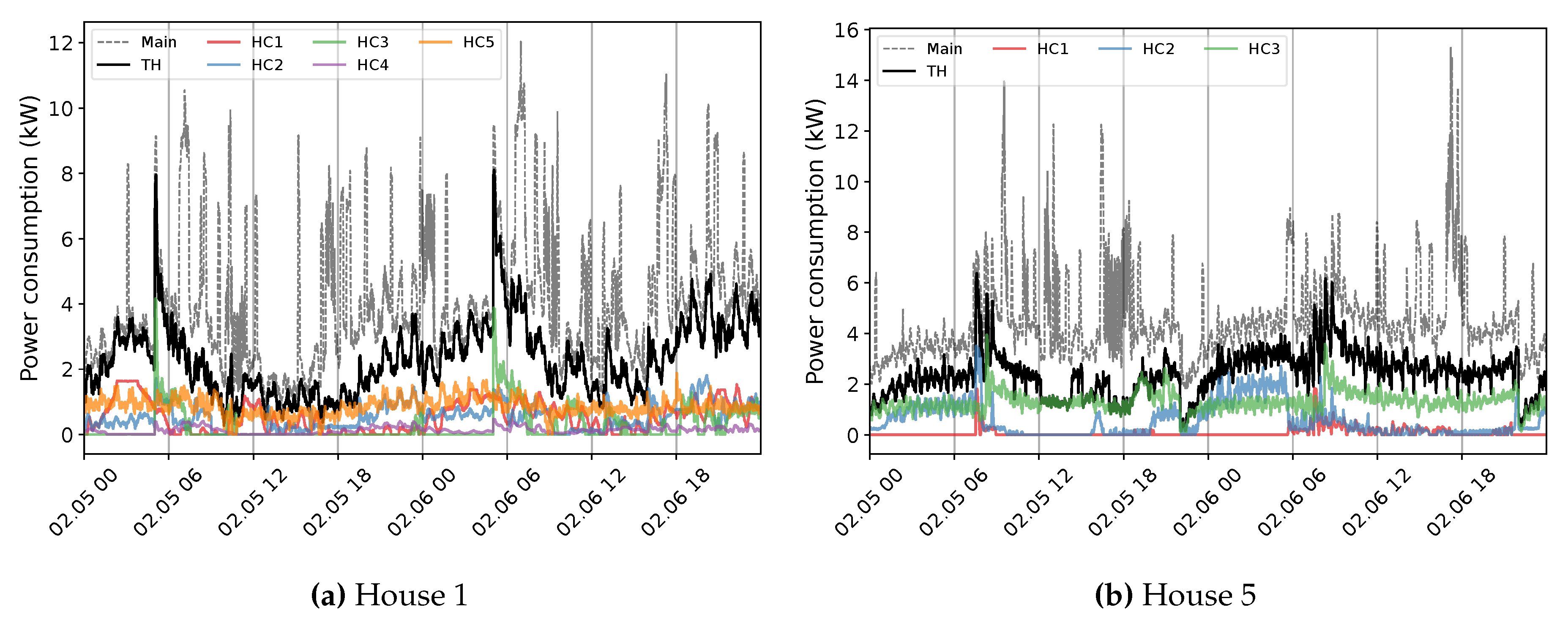
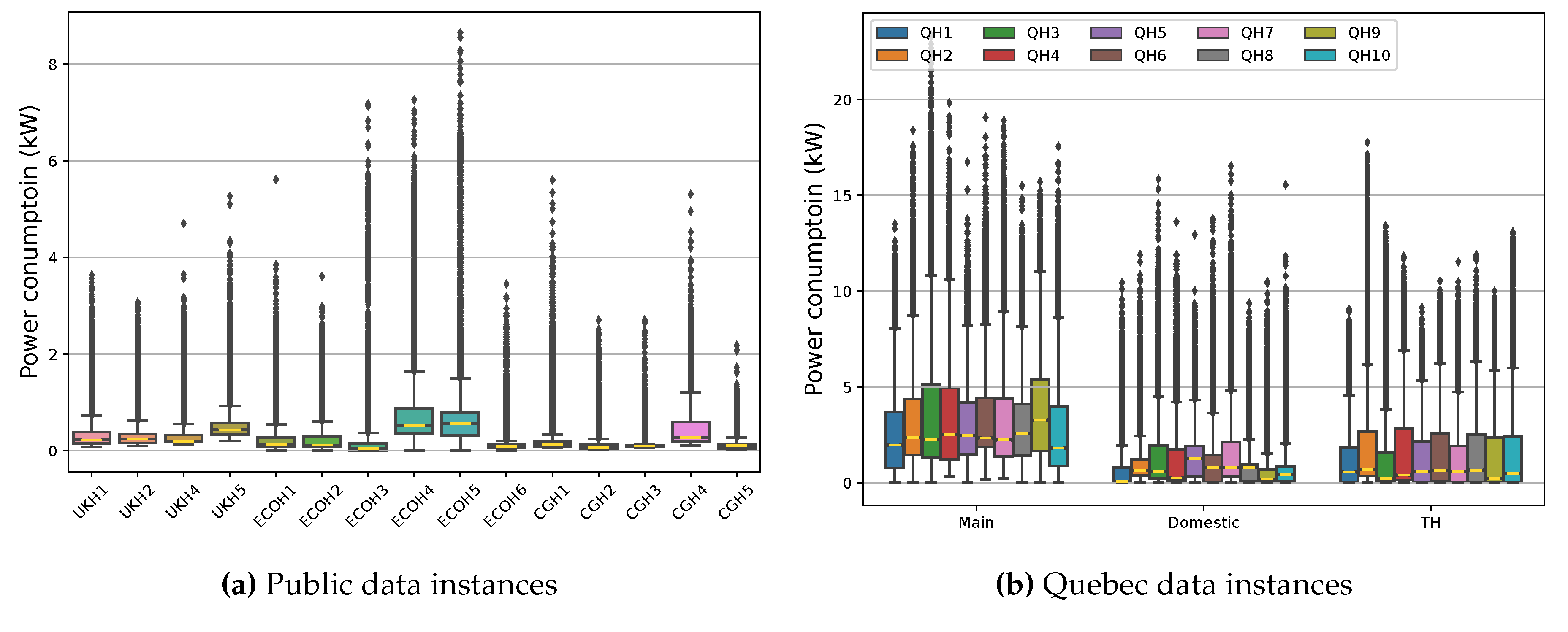
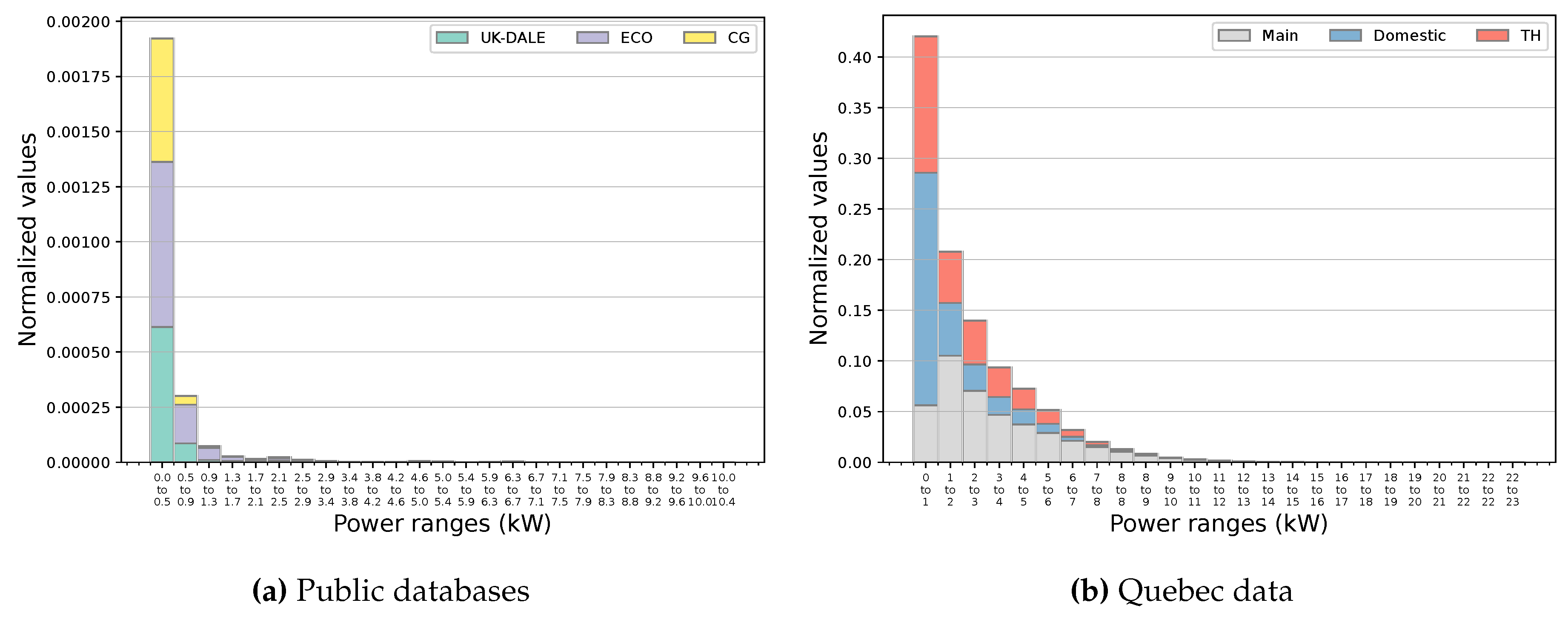
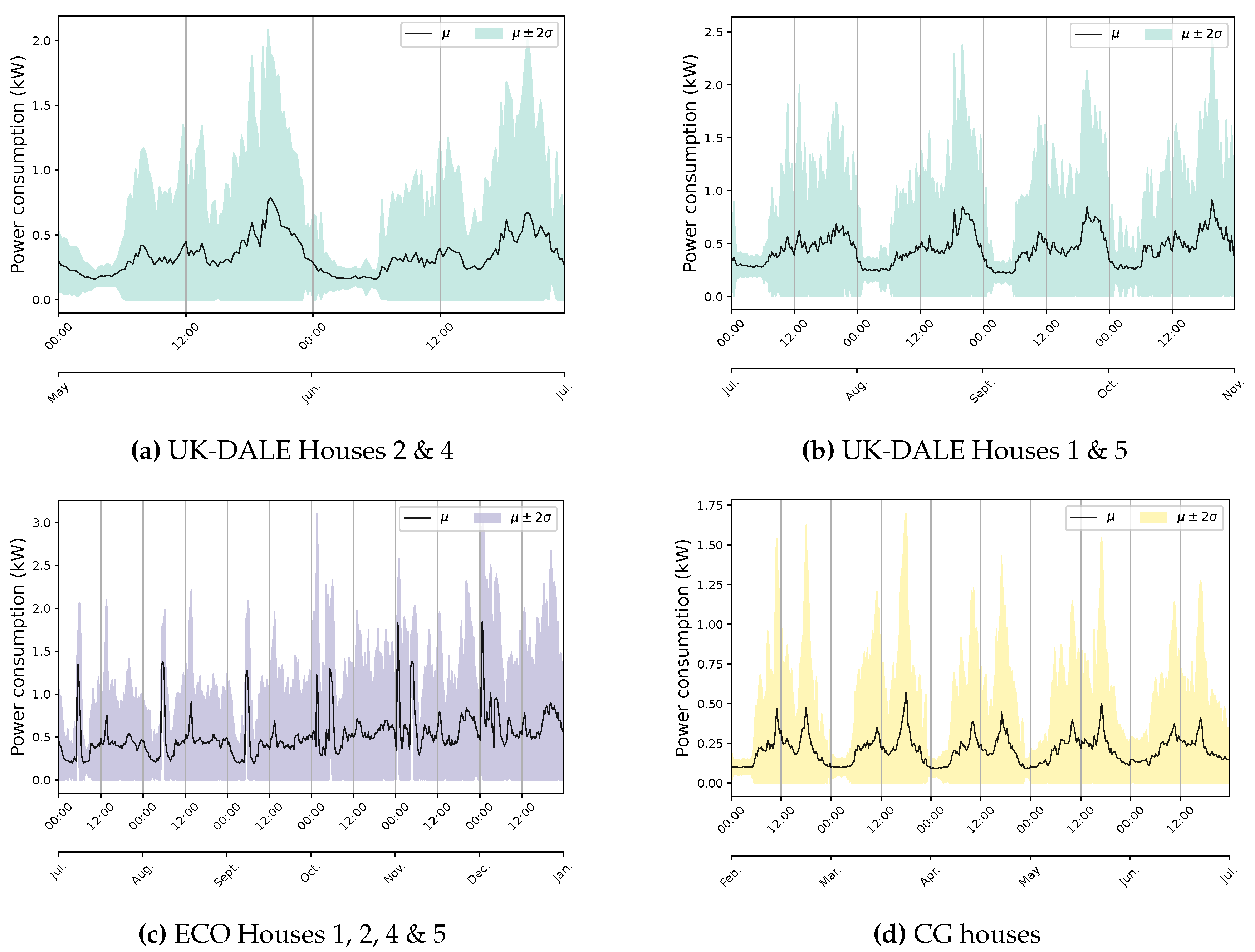
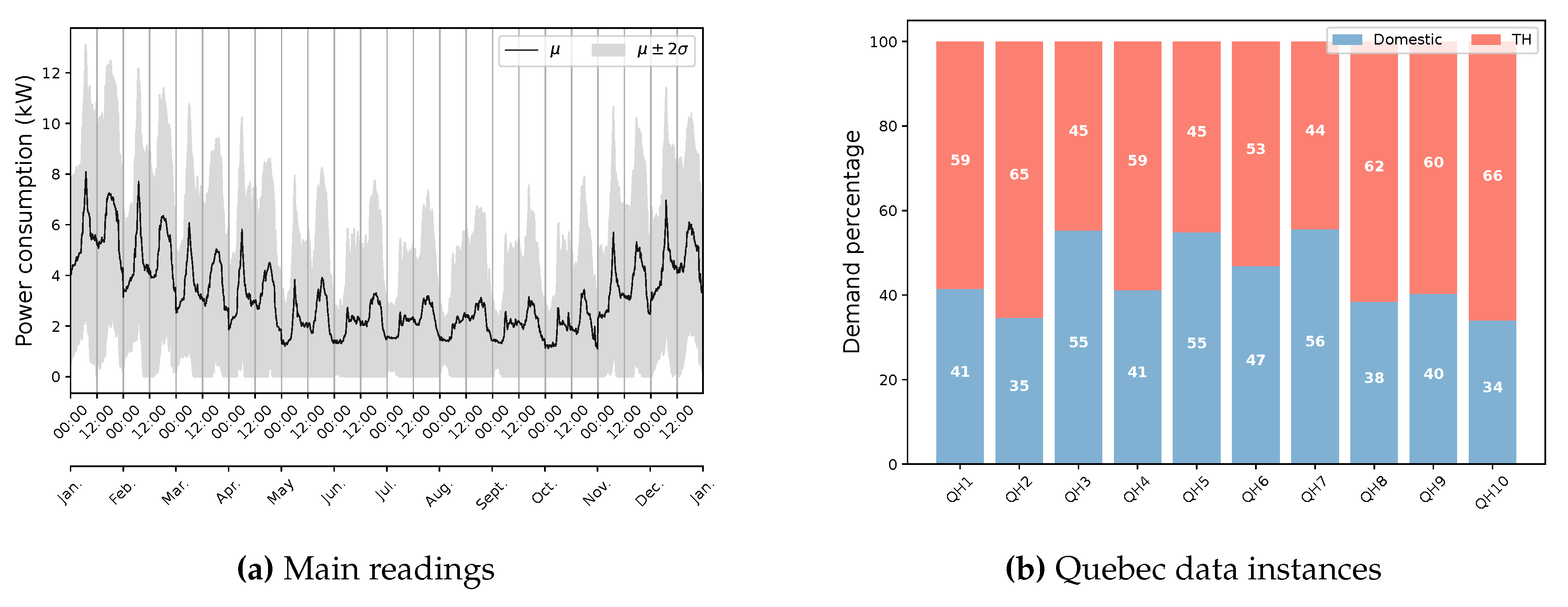
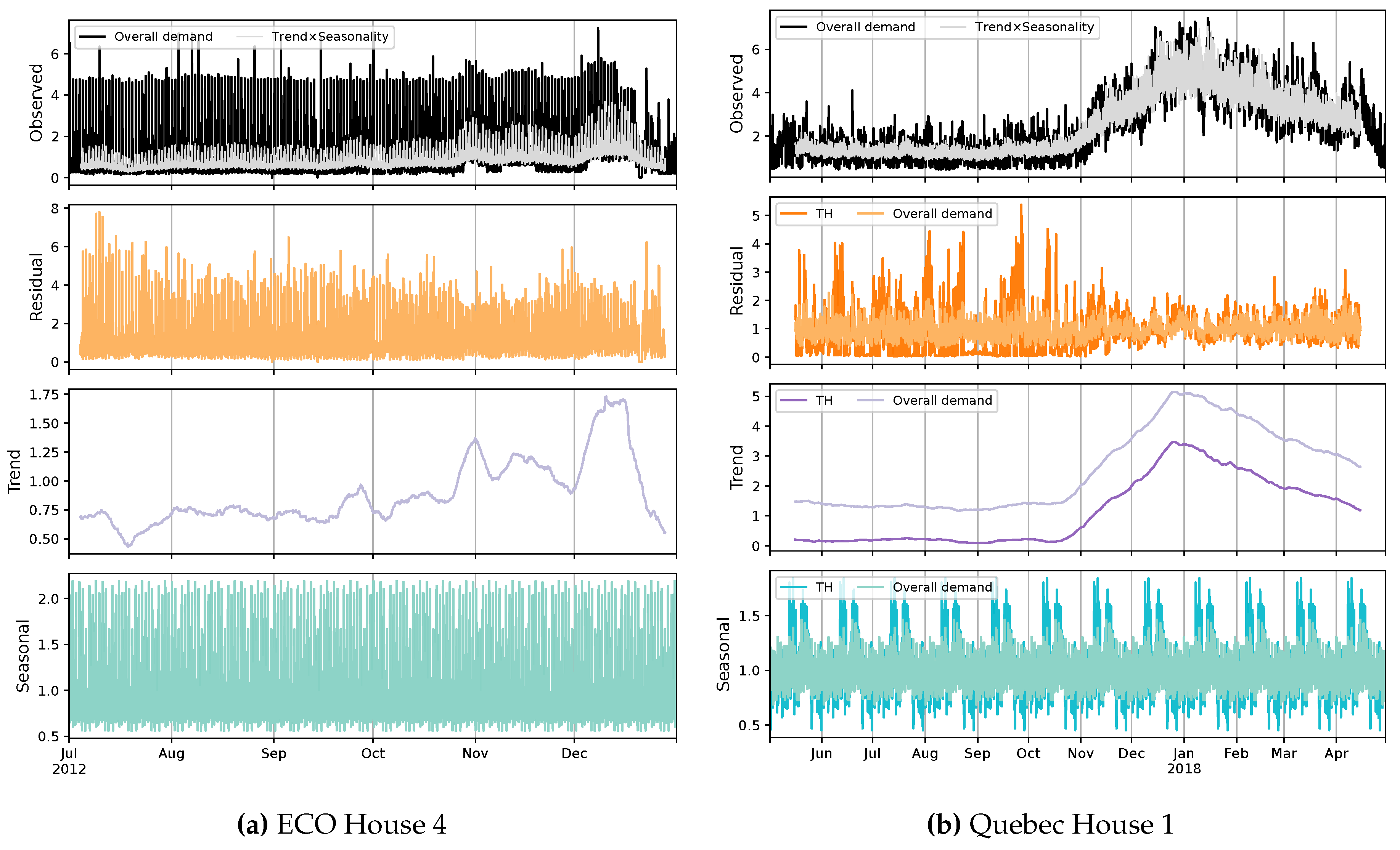
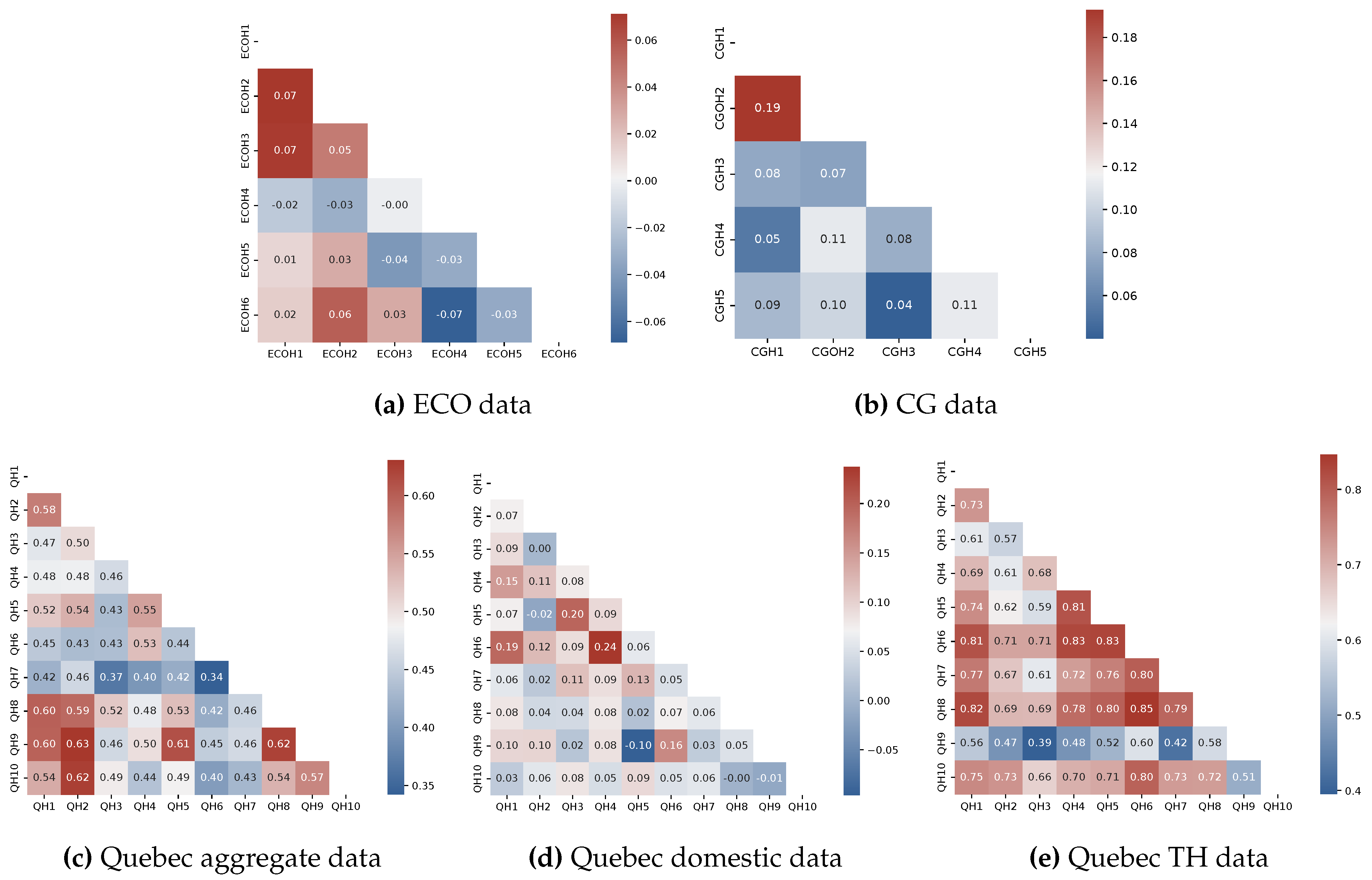
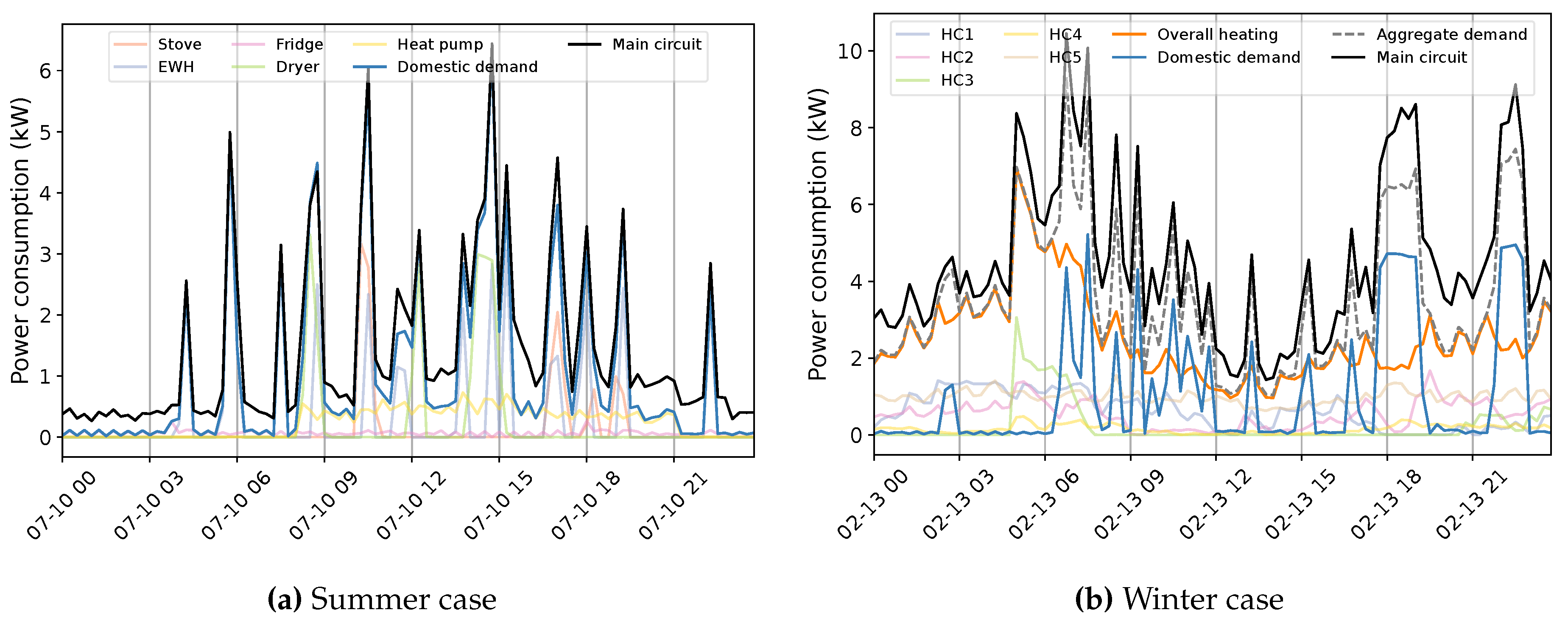
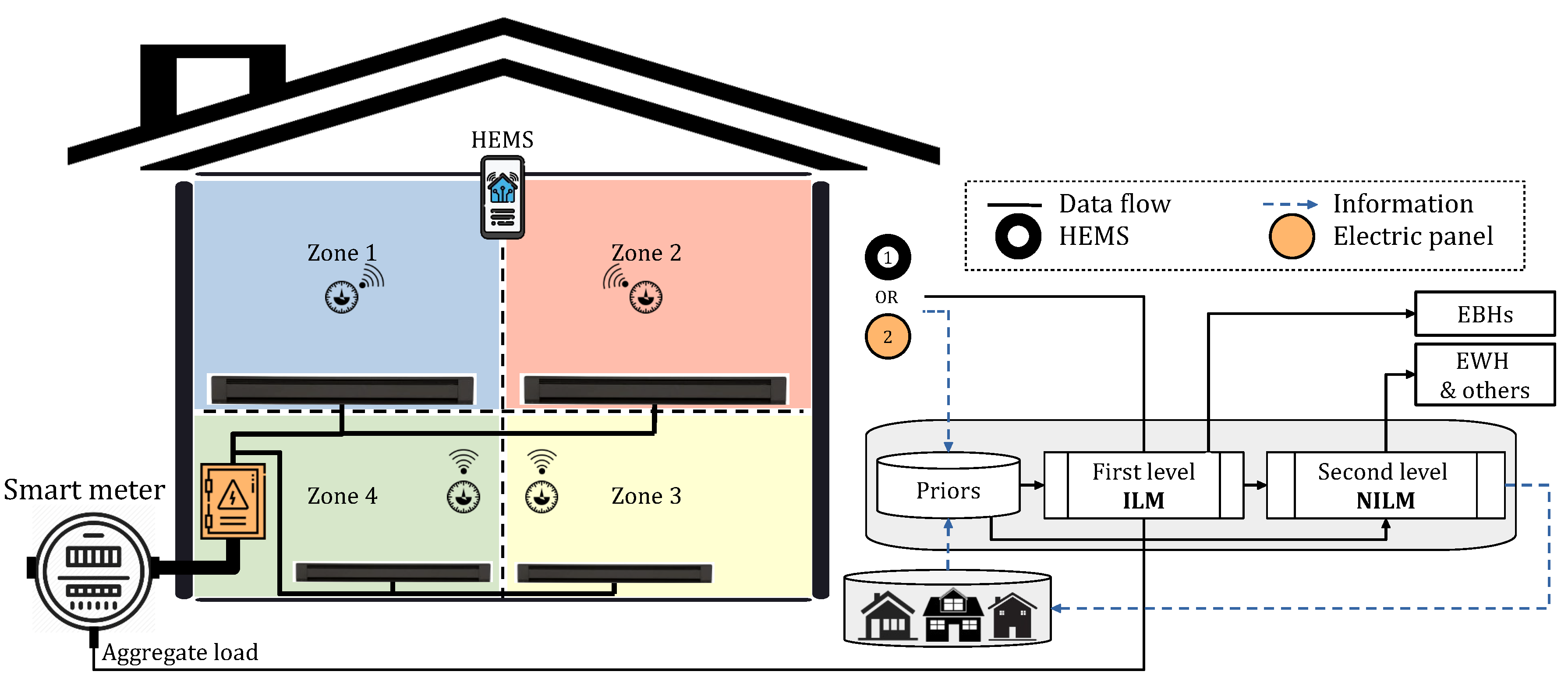
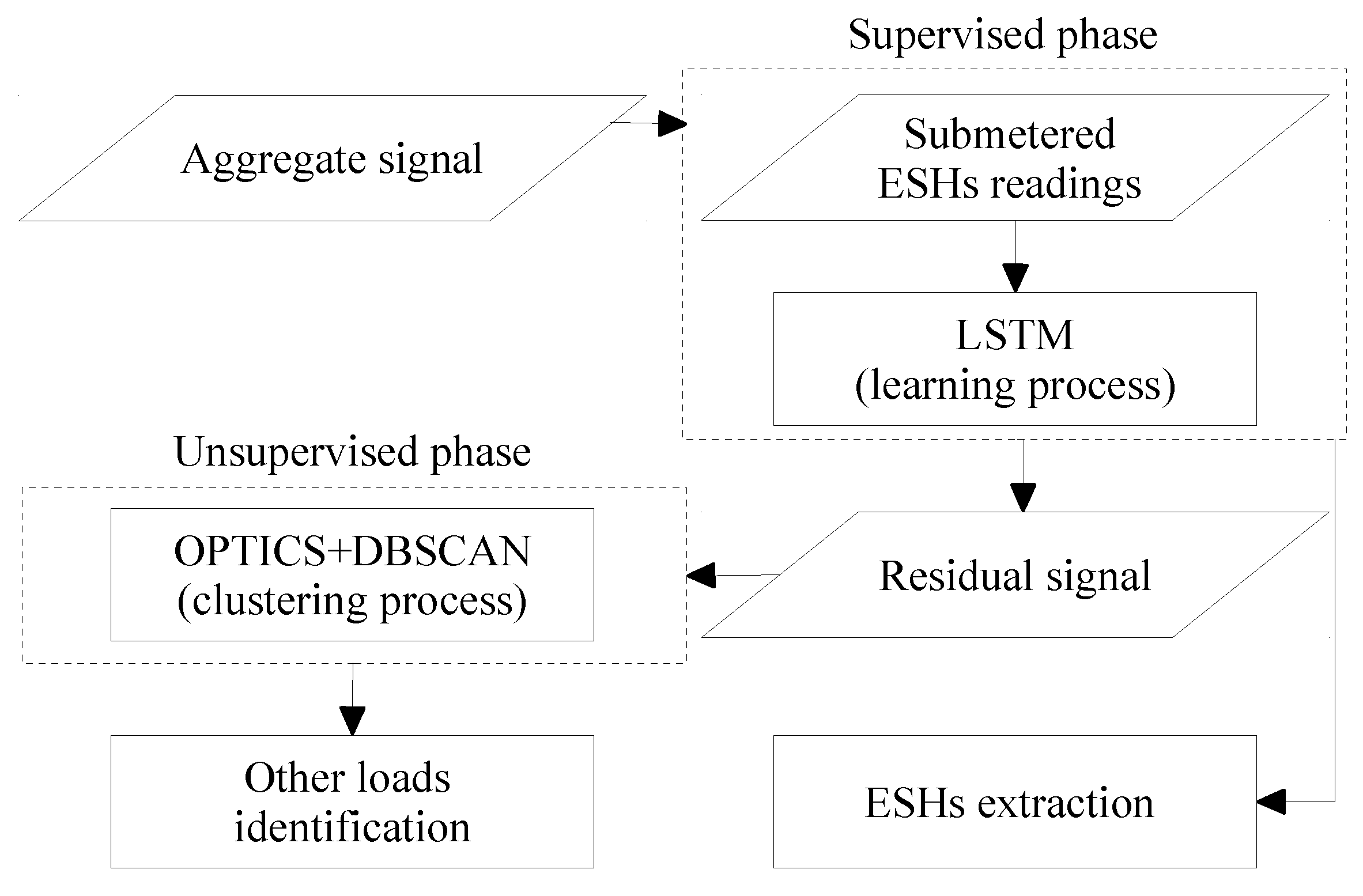
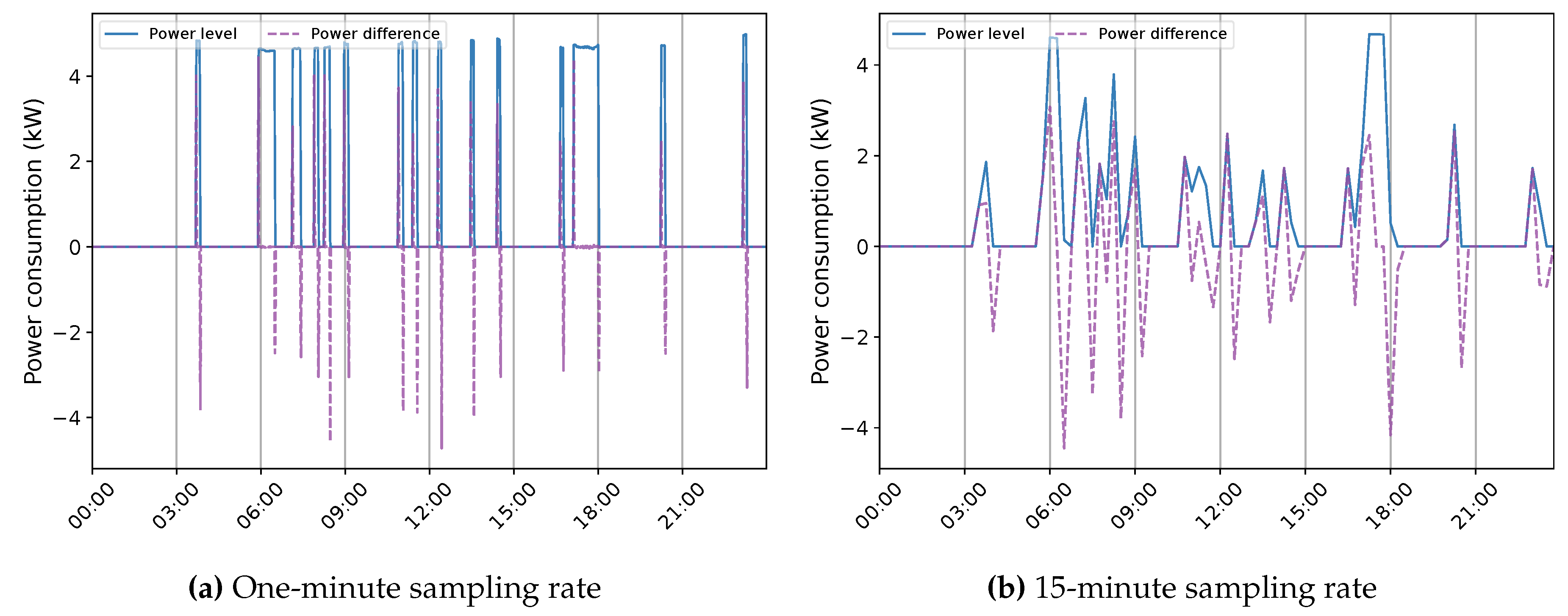
| Dataset | Number of houses |
Measuring duration per house |
Sampling frequency | Site | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appliance | Aggregate | ||||
| REDD | 6 | 3-19 days | 3 sec | 1 sec & 15 kHz | USA |
| UMass Smart | 3 | 3 months | 1 sec | 1 sec | USA |
| UK-DALE | 5 | 3-17 months | 6 sec | 1-6 sec & 16 kHz | UK |
| BLUED | 1 | 8 days | event label | 12 kHz | USA |
| AMPDs | 1 | 1 year | 1 min | 1 min | CDN |
| ECO | 6 | 8 months | 1 sec | 1 sec | CH |
| Tracebase | 15 | N/A | 1-10 sec | N/A | DE |
| HES | 251 | 1-12 months | 2-10 min | 2-10 min | UK |
| iAWE | 1 | 73 days | 1-6 sec | 1 sec | IND |
| GreenD | 9 | 1 year | 1 sec | 1 sec | AT/IT |
| Data | MAE (kW) | MSE | RMSE (kW) | sMAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| House 1 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.64 | 46 |
| House 2 | 1.03 | 2.68 | 1.65 | 88 |
| House 3 | 0.72 | 1.71 | 1.31 | 56 |
| House 4 | 0.97 | 2.26 | 1.50 | 76 |
| House 5 | 0.48 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 46 |
| House 6 | 0.79 | 1.37 | 1.17 | 58 |
| House 7 | 0.67 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 69 |
| House 8 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.83 | 54 |
| House 9 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 0.81 | 45 |
| House 10 | 0.72 | 1.62 | 1.27 | 72 |
| Day | TECA (%) | MAE (kW) | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 86 | 0.48 | 0.57 |
| 2nd | 86 | 0.41 | 0.52 |
| 3rd | 86 | 0.47 | 0.37 |
| 4th | 84 | 0.53 | 0.58 |
| 5th | 84 | 0.47 | 0.73 |
| 6th | 85 | 0.37 | 0.36 |
| 7th | 85 | 0.38 | 0.33 |
| Day | Detected load (kW) and related device | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2st | 3rd | 4th | 5th | Energy (%) | |
| 1st | 0.92 |
3.8 EWH |
2.3 EWH Stove |
1.9 EWH Stove |
4.6 EWH |
30 |
| 2nd | 0.75 |
2.9 EWH |
2.5 EWH |
1.8 EWH |
- | 37 |
| 3rd | 0.89 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 4th | 0.93 | 2.9 EWH Stove Dryer |
4.4 EWH Stove |
3.7 EWH Stove |
- | 38 |
| 5th | 0.82 | 3.8 EWH Stove |
3.2 EWH Stove Dryer |
- | - | 23 |
| 6th | 0.81 |
3.1 EWH |
- | - | - | 34 |
| 7th | 0.87 |
2.9 EWH Stove |
4.9 EWH |
- | - | 35 |
| Day | Load (kW) | F1-score (%) | TECA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 3.8 4.6 |
25 25 |
54 55 |
| Total | 44 | - | |
| 2nd | 2.9 2.5 1.8 |
30 21 39 |
54 55 59 |
| Total | 62 | - | |
| 6th | 3.1 | 69 | 66 |
| 7th | 2.9 4.9 |
47 39 |
57 59 |
| Total | 70 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





