1. Introduction
Apical lesions (AL) are a radiographic sign of a dental condition, mainly an endodontic infection [
1,
2]. These infections are discussed to have an impact on systemic health [
3] and can compromise the survival of affected teeth, which is why clinicians should detect and manage such lesions appropriately.
To optimize the diagnostics and treatment planning of AL, a priori knowledge on the baseline risk of a tooth or a patient suffering from AL is helpful, allowing to tailor diagnostic efforts and therapy. Cross-sectional studies based on different types of radiographs like panoramic radiographs (OPG), cone beam tomography (CBCT)) or periapical radiographs (PR) provide valuable information about the prevalence and the associated risk factors of AL.
In general, there is a broad variation in the reported prevalence of AL, from 0.6% in Norway [
4] to 13.6% in Greece [
5] on tooth level. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis revealed a global prevalence of 5% on tooth- and 52% on patient-level [
1].
The reasons for this variability are assumingly complex and manifold, for example depending on the characteristics, accessibility and education to dental care of each population. For example, Tiburcio-Machado et al. 2021 found that patients in developing countries had 2% more AL on tooth level compared to patients of developed countries [
1].
Factors concerning the prevalence of AL were identified by several studies. Lopez-Lopez
, et al. [
6] and Sunay
, et al. [
7] found that root-filled teeth had a significantly increased risk of AL compared with untreated teeth.
Also, an association between sex and AL has been controversially discussed in the literature, Lopez-Lopez et al. 2012 found a significant more AL in male than in female (42.3% vs. 26.1%, OR = 2.4; 95% CI (1.5, 3.7)) whereby Bürklein et al. 2020 indicated no statically significant difference (47.6% vs. 39.8%, p>0.05).
Maxillary and more posterior teeth also showed a higher risk of AL compared to mandibular and more anterior teeth, respectively [
8,
9].
Additionally, Tiburcio-Machado et al. 2021 demonstrated that patients with a systemic health condition had a higher prevalence on AL compared to healthy patients (48% (95% CI 43%–53%; I2 = 98.3% vs. 63%; 95% CI 56%–69%; I2 = 89.7%).
Most of these prevalence studies used conventional statistics and logistic regression to analyze and explain datasets and provide valuable associations between distinct variables within the respective dataset/cohort. In recent years, machine learning algorithms (ML) are gaining strongly more popularity in the field of oral medicine [
10]. With their focus on prediction rather on explanation, ML learn intrinsic statistical structures within datasets to eventually perform predictions on unseen data.
So far, little is known about the predictive capacity, and, in consequence, the clinical relevance of the reported associations identified by conventional statistics and association analyses. Those predictors may help clinicians to identify important risk factors and assist the diagnostic process. Additionally, it is crucial whether the found associations were relevant and generalizable for clinical practice or if they are constrained to the internal pattern of the restricted dataset.
Therefore, we first aimed to estimate the prevalence of AL in a cohort of a German university hospital and to identify associations with a range of variables on patient and tooth level, respectively, using conventional statistics, logistic regression and more sophisticated ML (k-nearest neighbor, decision tree, random forest, support vector machine as well as adaptive and gradient boosting).
Second, we yielded to utilize logistic regression and the aforementioned ML for evaluating the predictive capacity of the found associations on the occurrence of AL on panoramic views. Hence we tested the following hypotheses:
1) Different ML show no statistically significant differences with regards to their predictive performance.
2) There is no statistically significant difference between using ML and simply guessing the majority class of the dependent variable.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study design and source of data
Reporting of this study follows the TRIPOD [
11] and STROBE [
12] guidelines as well as the checklist for artificial intelligence in dental research [
13]. Using the retrospective, cross-sectional study design, we assessed the patient records and the dental panoramic radiographs (Orthopantomogram; OPG) from the patients who presented themselves at the dental clinic of Charité University Medicine Berlin between January 1
st, 2015 and December 31
st, 2018. The device used was Sirona Orthophos XG 3 (Dentsply Sirona, York, Pennsylvania, USA) and indications for taking the OPG were widely spread and were not relevant for our analyses. A formal sample size calculation was not performed, but a general rule of thumb states that the estimated sample size for logistic regression is 100 + (50 x number of independent variables in the final model) [
14]. Because our study had six independent variables, the minimum sample size according to this formula was 400. All patients from pre-adolescent age with permanent teeth and over with a well conducted OPG were included in the study. The exclusion criteria for the study were patients with primary or mixed dentition, completely edentulous patients, incomplete arches and OPGs with distorted images or poor quality. In case of multiple OPGs were present in a patient, the latest one was used for the analyses. This resulted in having 1071 patients each with an OPG for the final analyses. The study sample had a mean age of 50.6 years ± 19.7 and ranged between 11 and 93 years.
2.2. Image processing and assessment
All image data were processed in an established online annotation tool [
15]. Every anatomical structure was marked pixelwise by four experienced dental radiologists. One dental radiologist reviewed all annotated OPG and evaluated each diagnosis and decided in cases of disagreement. Then, the final vote was the consensus of all annotated pixels of the radiograph. So, each OPG was seen by five independent dentists eventually. Every tooth was radiologically classified by the FDI schema, restorative (fillings, crowns and root canal treatment) and apical status. Following this, the periapical status was evaluated according to the periapical index score [
16]. We defined a score of at least 3 as an AL in our analysis. Based on this, we were able to calculate the prevalence of AL on tooth- and patient-level within subgroups.
2.3. Variables
The covariates were divided into patient-level and tooth-level for presentation purposes. The patient-related information was gained from the DICOM-dataset, whereas the tooth-related information was acquired from the OPG analysis. Patients’ age (continuous variable) and gender (male or female) were patient-related variables; whereas the jaw type (upper or lower), type of the tooth (incisor, canine, premolar, or molar) and restorative status of the tooth (non-restored, filled, crown or root canal treatment) were defined as tooth-related variables.
2.4. Sources of Bias
The annotation process of any anatomical and pathological structure was identified as a potential source of bias. Due to the high number of examiners and a consecutive majority voting for each finding, we reduced the risk of bias in the stage of OPG analysis.
We obtained all available radiographic data for a multivariate approach to minimize the risk of selection bias. But we did not include clinical data, because we just focused on the radiographical appearance of AL. Additionally, we were aware of methodological information bias resulting from the use of OPG for prevalence analysis.
2.5. Statistical analysis
First, the descriptive statistics such as number (percentage) for categorical variables and mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables for all covariates and the category-wise prevalence of apical lesions were calculated (
Table 1). Second, simple bivariate comparisons of AL prevalence between the categories of the covariates were performed. Continuous and categorical variables were compared using Student’s t-test and Chi-square test, respectively. Third, a logistic regression model was constructed by regressing the patient- and tooth-level covariates on the presence (binary: present/not present) of AL. The adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) and p-values were calculated and tabulated (
Table 2).
Fourth, we trained multiple machine learning classifier models such as logistic regression, k-nearest neighbor, decision tree, random forest, support vector machine and GradientBoost, AdaBoost (
Table 3) on the full dataset and evaluated the predictive performance during the 10-fold cross validation. Due to the imbalanced nature of the outcome variable, oversampling and removal of noisy data was performed with Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique (SMOTE) and Edited Nearest Neighbor (ENN) for each model. During cross validation, each real sample and their synthetic correspondents as well teeth from the same radiograph were assigned to the same split for avoiding data leakage. Balanced accuracy, precision, specificity, F1 weighted and ROC-AUC scores and their corresponding 95% CI from all machine learning models were presented (
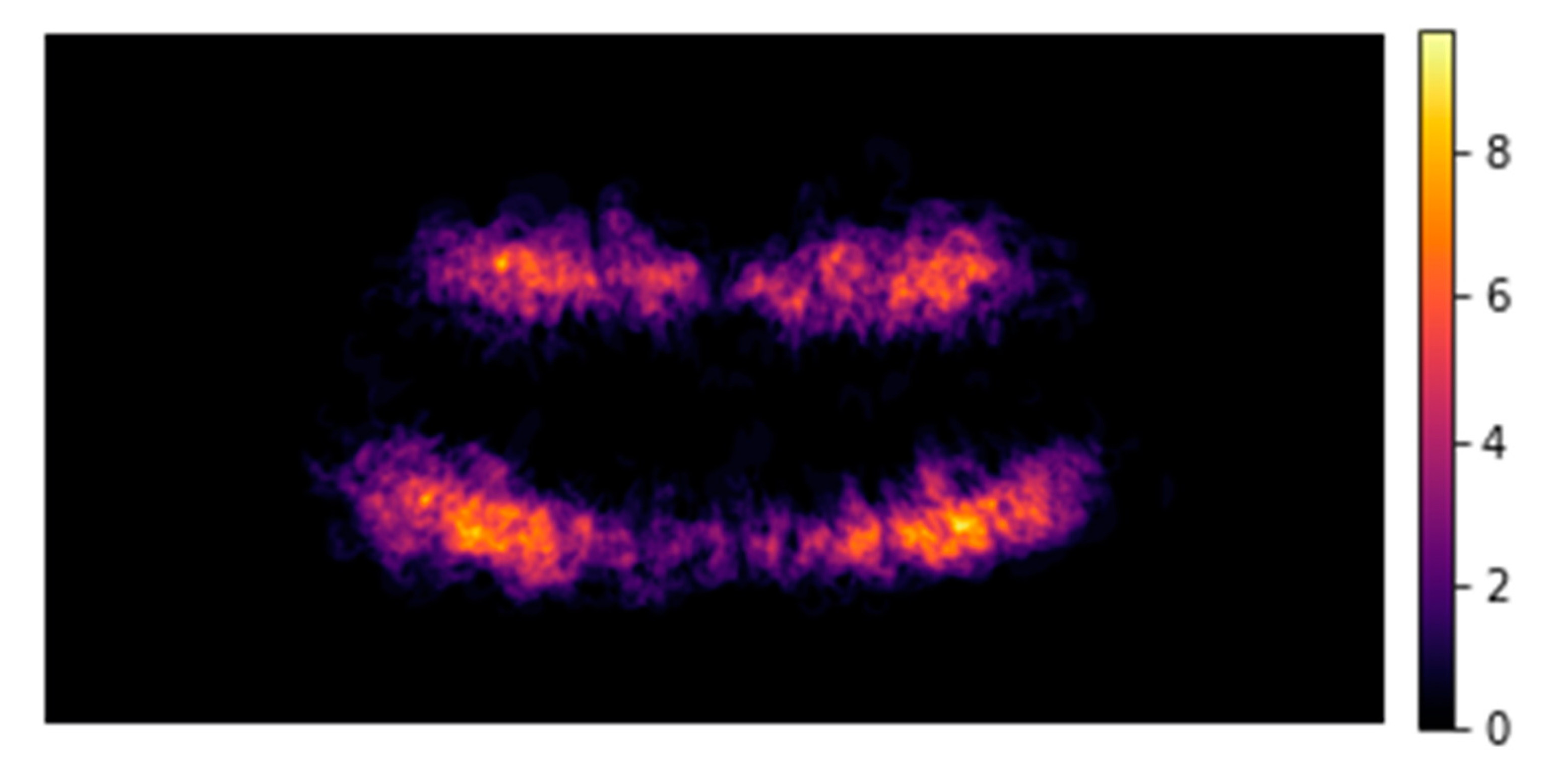
Table 4). Fifth, no-Information rate was calculated and compared with the majority class of the dependent variable AL (‘present’/’not present’) via 1-sided binomial hypothesis testing. Finally, mean rank values of the covariates based on their relative importance (based on decision tree, GradientBoost and AdaBoost models) were presented (Table 5) along with a heat map fashioned distribution of AL lesions along the dentition (
Figure 1). All statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.2.2 (R Core Team 2022, Vienna, Austria); and all machine learning models were performed in Python (Version: 3.10.5).
3. Results
Our study had a total of 1071 patients (male/female 51.6%/48.4%) which had 27,532 teeth with an average of 25.7 ± 6.2 teeth per patient the mean age in our study was 50.6 ± 19.7 years, which ranged between 11 and 93 years. 522 of 1071 patients and 1133 of 27,532 teeth showed an AL, resulting in a prevalence of 48.7% on the patient level and 4.1% on the tooth level (
Table 1).
3.1. Statistical analysis
We found that AL was significantly more prevalent in the patients aged ≥ 40 years than in the age group of 10 - 39 years; whereby men (52.5%; 95% CI: 48.4-56.7 ) demonstrated significantly more AL than women (44.8%; 40.5-49.1). On a tooth level, there was no significant difference between the lower (4.1%; 3.7-4.4) and upper jaw (4.2%; 3.8-4.5). Anterior teeth (incisors: 2.1%; 1.8-2.4) and canines: 2.0%; 1.6-2.5) had a significantly lower prevalence than premolars (3.7%; 3.2-4.1) and molars (7.6%; 7.0-8.2).
Figure 1 shows in a heat map the distribution of AL among all OPG. We also found that non-restored teeth (1.4%; 1.2-1.6) were significantly associated with lower AL prevalence than teeth with a filling (3.3%; 2.9-3.8), a crown (4.2%; 3.6-4.8) or a root canal treatment (24.6%; 22.8-26.4) (
Table 1).
The logistic regression analysis showed that at the patient level ‘male’ (aOR 1.43; 95% CI: 1.26-1.62) have higher odds to develop AL than female. In addition, it could be shown that AL occur significantly more frequently with increasing years of life (1.01; 1.0-1.01). With respect to the tooth level covariates, the lower jaw (1.21; 1.06-1.37), molars (2.54; 2.1-3.08), teeth with fillings (1.76; 1.44-2.16), crowns (2.10; 1.67-2.63) or a root canal treatment (16.89; 13.98-20.41) had significantly higher risk to present AL (
Table 2).
3.2. Machine learning models
The unbalanced tooth-level dataset (26032 healthy surfaces vs. 1129 apical lesions) was resampled using SMOTE and ENN to arrive at a balanced dataset (22347 healthy surfaces vs. 20130 apical lesions). Decision tree model had the highest accuracy (0,9; 95% CI: 0.89-0.9) followed by GradientBoost (0.88; 0.87-0.88), random forest (0.87; 0.87-0.87) and k-nearest neighbor (0.87; 0.87-0.87); while logistic regression showed an accuracy of 0.83 (0.82-0.83) Compared to other models, the decision tree showed a high precision (0.9; 0.89-0.9), specificity (0.92; 0.91-0.92) and F1 score (0.9; 0.89-0.9); however, with the lowest ROC-AUC value (0.67; 0.65-0.68).
Comparing the ROC-AUC score, logistic regression, GradientBoost, support vector machine showed statistically significant higher values compared to k-nearest neighbor, decision tree and random forest. With regards to the F1 score, support vector machine (0.81; 0.8-0.82) significantly underperformed all other models while the decision tree offered the highest F1 score with 0.9 (0.89-0.9). A summary of all used machine learning classifier models is given in
Table 3.
Notably, none of the model performance parameters were higher than the NIR (95.9%, p>0.05). Decision tree, AdaBoost and GradientBoost assigned a score (relative importance) to each input covariate, so we calculated mean rank values for the six most important covariates (
Table 4). Age was the covariate with the highest relative importance with a mean rank value of 1.7, followed by teeth restored with root canal treatments (2.3), tooth type (2.3), crowns (4.7), and sex (5.0).
4. Discussion
Radiographic examinations are essential for diagnostics and treatment planning. Knowing about the prevalence and the associated risk factors of AL is helpful for evaluating the respective radiograph and sensitizes the operator to pay attention to certain regions with higher risks for AL. Our analysis aimed first to figure out which independent patient- and tooth-related variables had an influence on the dependent variable AL and second to predict the occurrence of AL based on the identified risk factors.
4.1. Key results
In our study, prevalence was similar to other studies [
7,
17,
18,
19]. One recent CBCT study from Münster/Germany found a similar prevalence of AL on tooth level as we did [
20]. A recent study from Finland indicated a lower prevalence (27%) on patient level but confirmed our findings that 1) AL is significantly more prevalent in men than in women and 2) teeth with a root canal filling are more likely associated with AL than teeth without previous endodontic treatment [
21]. In our study, root filled teeth showed a 17-times higher probability in having an AL compared to non-treated teeth. This general finding is in line with other studies [
5,
6] indicating a significantly higher prevalence of AL for root canal treated teeth.
The bivariate analysis showed no statistically significant difference between maxilla and mandible in prevalence in the prevalence of AL. In the multivariate analysis, it became clear that allocation to the upper or lower jaw had a significant influence on the prevalence of AL. These at a first glance contradictory results can be explained by the different utilized statistical approaches. With multivariate logistic regression analysis, we were able to examine several dependent variables for their influence on the outcome. Thus, the significance of the multivariate model exceeds that of the bivariate analysis.
Predicting AL based on the identified risk factors was possible with differences among the selected models. Assuming that the relevance of identifying the true positive cases (AL present) is more important than the true negative class (AL not present), the F1 score is more informative for our analysis than the ROC-AUC; the F1 score is more sensitive to changes in predicting the positive class whereas the ROC-AUC balances the true negatives and the true positives [
22]. Decision tree revealed the highest F1 score and outperformed the more complex models like random forest or GradientBoost. This can be explained by the straightforward associations between the identified risk factors and the presence of an AL; more complex models are intended to identify complex patterns in data structures but are more likely to fail in situations with non-complex patterns. Consequently, the identified risk factors in the logistic regression modelling offered some predictive value. When it comes to prediction accuracy, no model outperformed simply guessing the majority/negative class (“AL not present”). One reason is the high prevalence of healthy units (95.9%) on tooth level. Overall, we had to reject the first hypothesis due to statistically significant differences in the performance of the models (F1 score/ROC-AUC) and to accept the second hypothesis, because all models did not outperform simply guessing the majority class.
There is a difference with regards to the importance ranking of the risk factors: Multivariate analysis with logistic regression found that the presence of a root canal filling was the most important risk factor while mean rank values indicated that the patients age was most relevant. This difference might be explained by the different types of measurement scales across the models. During predictive modeling, the age was categorized into nine defined age groups (
Table 1) and in the multivariate analysis, age was implemented as a continuous variable. As a consequence, belonging a distinct “age group” seems to more significant than the gradual increase of years.
4.2. Limitations and generalizability
The use of OPG for screening AL leads to information-bias, because it is known that OPG are less accurate in detecting AL than periapical radiographs (PR) or cone beam tomography (CBCT). One study found a sensitivity of 0.28 and 0.58 for OPG and PR respectively, considering CBCT as the reference tool [
23]. Also, despite of technical improvements, especially front teeth are difficult to assess in OPG, due to superimposition of anatomical structures like the cervical spine and the mental fossa area [
24]. Within these limitations, OPG is still a good method in detecting AL [
25]: It delivers data of the whole dentition of a patient, whereby PR and CBCT are just focusing a particular region of interest, and only a small group of patients obtain PR of all teeth, e.g., for periodontal treatment planning and we would generate an indication bias. Also, the indication for a CBCT of both jaws is rare, whereas the indication for OPG is more commonly given. Hence, the group of patients obtaining a OPG is more representable than that for CBCT and full-mouth PR status. For this reason, OPG are the most common method in cross-sectional studies [
26].
In general, there is still a problem regarding the manual labeling of specialists as the ground truth for ML training [
27]. For evaluating AL, histological data were still the gold standard but not available in large, so we tried to reduce the obsever bias through a gradual majority process for labelling the AL. Every entry of each examiner was checked twice by an experienced supervisor and in case of disagreement, the experienced supervisor decided. One major advantage of this procedure is, that every annotated structure and decision of PAI was transparent and saved.
The generalizability of this study is limited due to the study design. We analyzed a local cohort from Berlin, Germany. However, based on such retrospective prevalence studies, only prevalence estimates for the entire population can be made. As mentioned before, a very recent study from another local cohort in Germany found similar prevalence values to ours [
20], so the true prevalence could be in the range of our data. In general, our findings concerning the risk factors were comparable to other international studies, while they differ in the magnitude of the associations .
5. Conclusions
On tooth level, posterior and restored teeth and those root canal fillings showed the highest prevalence of AL. Predicting the occurrence of AL was possible, even though no model performed better than guessing “AL not present”. Simpler ML models outperformed more sophisticated algorithms with regards to the F1 score.
References
- Ramachandran Nair, P.N.; Pajarola, G.; Schroeder, H.E. Types and incidence of human periapical lesions obtained with extracted teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1996, 81, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakehashi, S.; Stanley, H.R.; Fitzgerald, R.J. The Effects of Surgical Exposures of Dental Pulps in Germ-Free and Conventional Laboratory Rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1965, 20, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Egea, J.J.; Martin-Gonzalez, J.; Castellanos-Cosano, L. Endodontic medicine: connections between apical periodontitis and systemic diseases. Int Endod J 2015, 48, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, H.M. Endodontology--epidemiologic considerations. Endod Dent Traumatol 1991, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, M.K.; Spanaki-Voreadi, A.P.; Pantazis, N.; Kontakiotis, E.G. Frequency and distribution of root filled teeth and apical periodontitis in a Greek population. Int Endod J 2005, 38, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Lopez, J.; Jane-Salas, E.; Estrugo-Devesa, A.; Castellanos-Cosano, L.; Martin-Gonzalez, J.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Segura-Egea, J.J. Frequency and distribution of root-filled teeth and apical periodontitis in an adult population of Barcelona, Spain. Int Dent J 2012, 62, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunay, H.; Tanalp, J.; Dikbas, I.; Bayirli, G. Cross-sectional evaluation of the periapical status and quality of root canal treatment in a selected population of urban Turkish adults. Int Endod J 2007, 40, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes da Silva Ramos Fernandes, L.M.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Hungaro Duarte, M.A.; Alvares Capelozza, A.L. Prevalence of apical periodontitis detected in cone beam CT images of a Brazilian subpopulation. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2013, 42, 80179163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirinhos, J.; Martins, J.N.R.; Pereira, B.; Baruwa, A.; Gouveia, J.; Quaresma, S.A.; Monroe, A.; Ginjeira, A. Prevalence of apical periodontitis and its association with previous root canal treatment, root canal filling length and type of coronal restoration - a cross-sectional study. Int Endod J 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Tay, F.R.; Gu, L. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry. J Dent Res 2020, 22034520969115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 2015, 162, W1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendicke, F.; Singh, T.; Lee, J.H.; Gaudin, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Uribe, S.; Krois, J.; network, I.e.-o.h.; the, I.T.U.W.H.O.f.g.A.I.f.H. Artificial intelligence in dental research: Checklist for authors, reviewers, readers. J Dent 2021, 107, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujang, M.A.; Sa'at, N.; Sidik, T.; Joo, L.C. Sample Size Guidelines for Logistic Regression from Observational Studies with Large Population: Emphasis on the Accuracy Between Statistics and Parameters Based on Real Life Clinical Data. Malays J Med Sci 2018, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekert, T.; Krois, J.; Meinhold, L.; Elhennawy, K.; Emara, R.; Golla, T.; Schwendicke, F. Deep Learning for the Radiographic Detection of Apical Lesions. J Endod 2019, 45, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orstavik, D.; Kerekes, K.; Eriksen, H.M. The periapical index: a scoring system for radiographic assessment of apical periodontitis. Endod Dent Traumatol 1986, 2, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pak, J.G.; Fayazi, S.; White, S.N. Prevalence of periapical radiolucency and root canal treatment: a systematic review of cross-sectional studies. J Endod 2012, 38, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, H.M.; Bjertness, E. Prevalence of apical periodontitis and results of endodontic treatment in middle-aged adults in Norway. Endod Dent Traumatol 1991, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, M.; Spangberg, L.S. The prevalence and technical quality of endodontic treatment in an American subpopulation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1995, 79, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burklein, S.; Schafer, E.; Johren, H.P.; Donnermeyer, D. Quality of root canal fillings and prevalence of apical radiolucencies in a German population: a CBCT analysis. Clin Oral Investig 2020, 24, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huumonen, S.; Suominen, A.L.; Vehkalahti, M.M. Prevalence of apical periodontitis in root filled teeth: findings from a nationwide survey in Finland. Int Endod J 2017, 50, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks. Inform Process Manag 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Bueno, M.R.; Leles, C.R.; Azevedo, B.; Azevedo, J.R. Accuracy of cone beam computed tomography and panoramic and periapical radiography for detection of apical periodontitis. J Endod 2008, 34, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.; Thomson, D.; McKenna, G. Case study: limitations of panoramic radiography in the anterior mandible. Dent Update 2009, 36, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, C.; Calistri, L.; Grazzini, G.; Desideri, I.; Lorini, C.; Occhipinti, M.; Mungai, F.; Colagrande, S. Is Panoramic Radiography an Accurate Imaging Technique for the Detection of Endodontically Treated Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis? J Endod 2018, 44, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persoon, I.F.; Ozok, A.R. Definitions and Epidemiology of Endodontic Infections. Curr Oral Health Rep 2017, 4, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Fu, Y.; Ren, G.; Yang, X.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q. Micro-Computed Tomography-Guided Artificial Intelligence for Pulp Cavity and Tooth Segmentation on Cone-beam Computed Tomography. J Endod 2021, 47, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).