Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
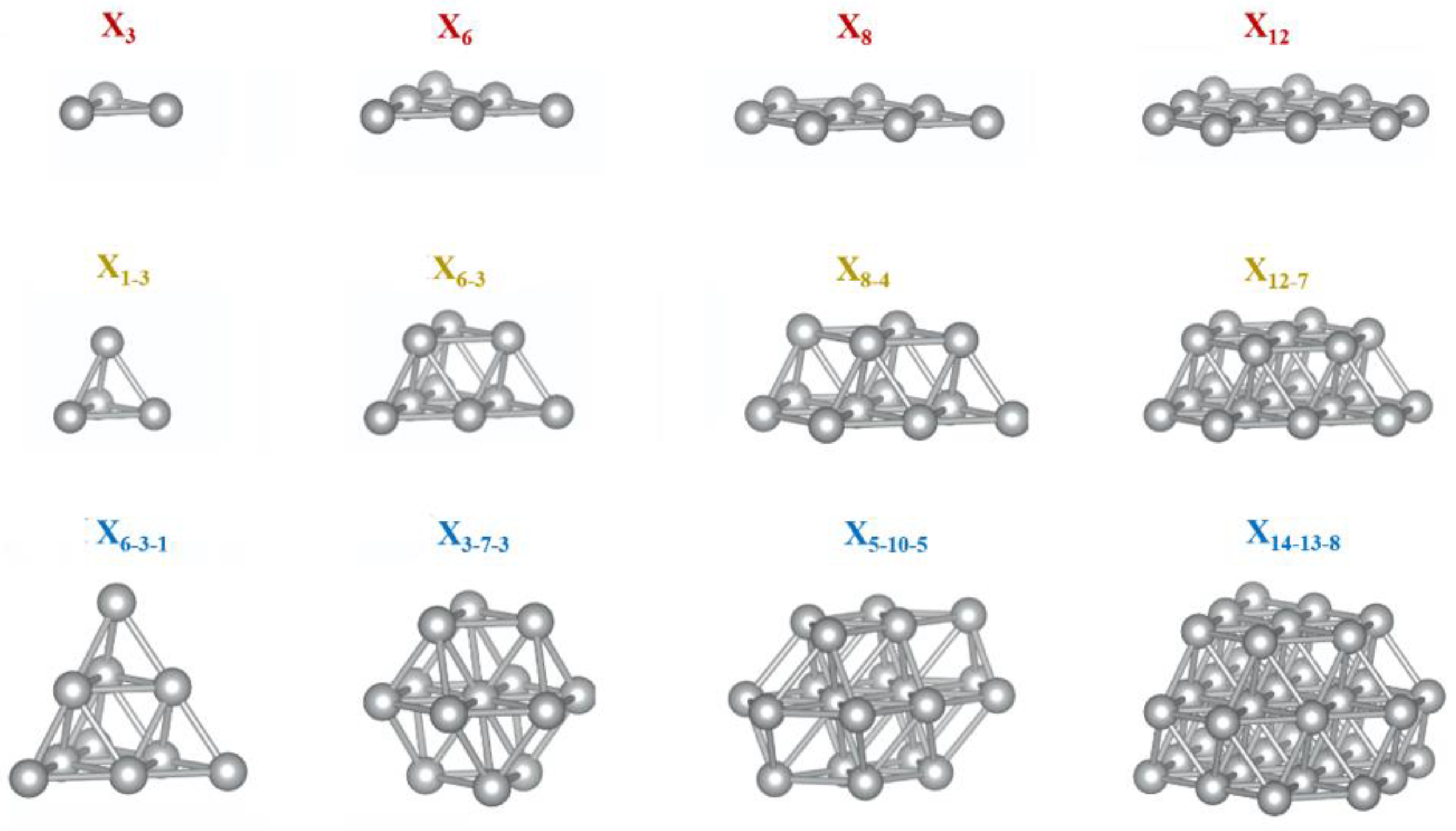
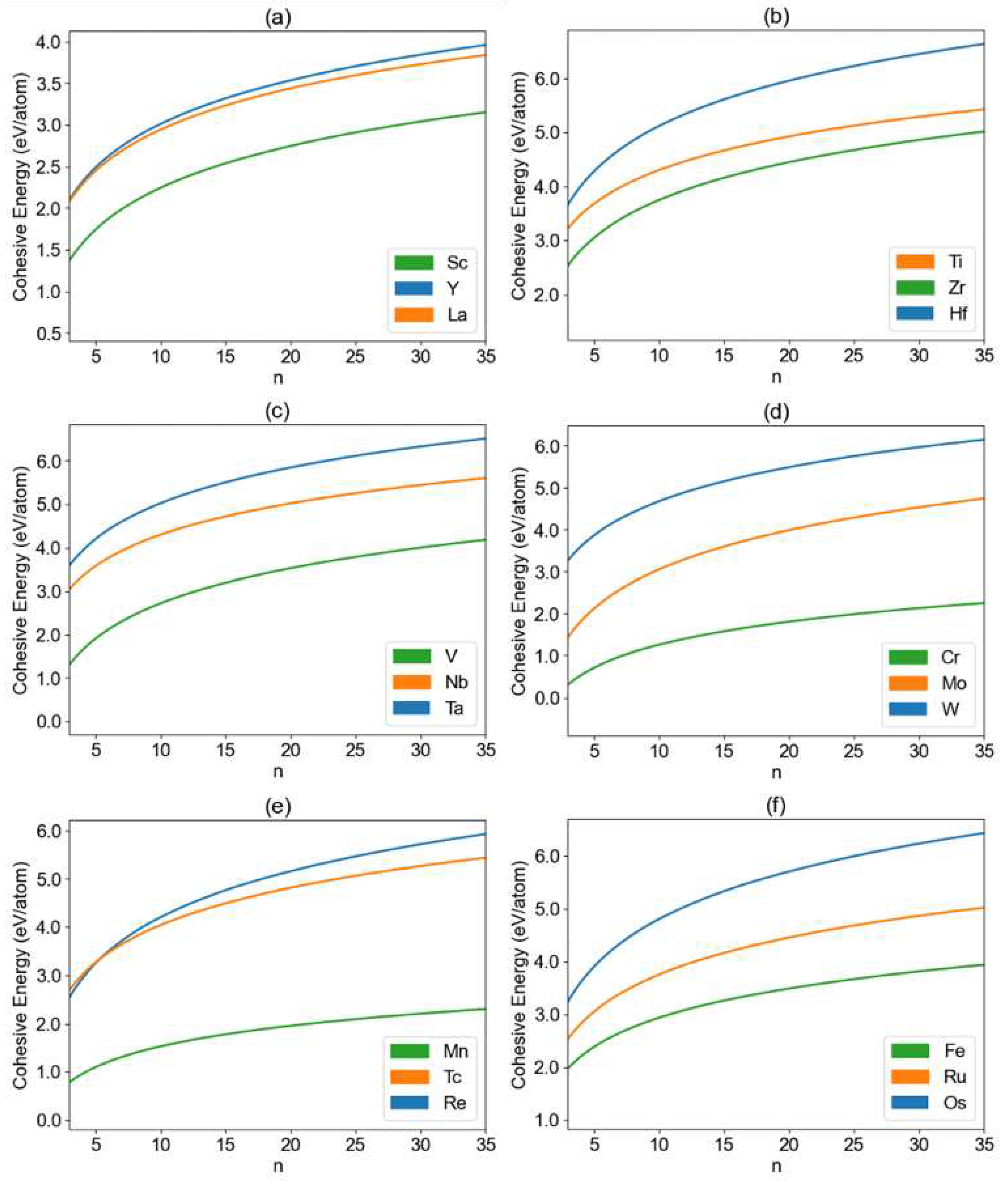
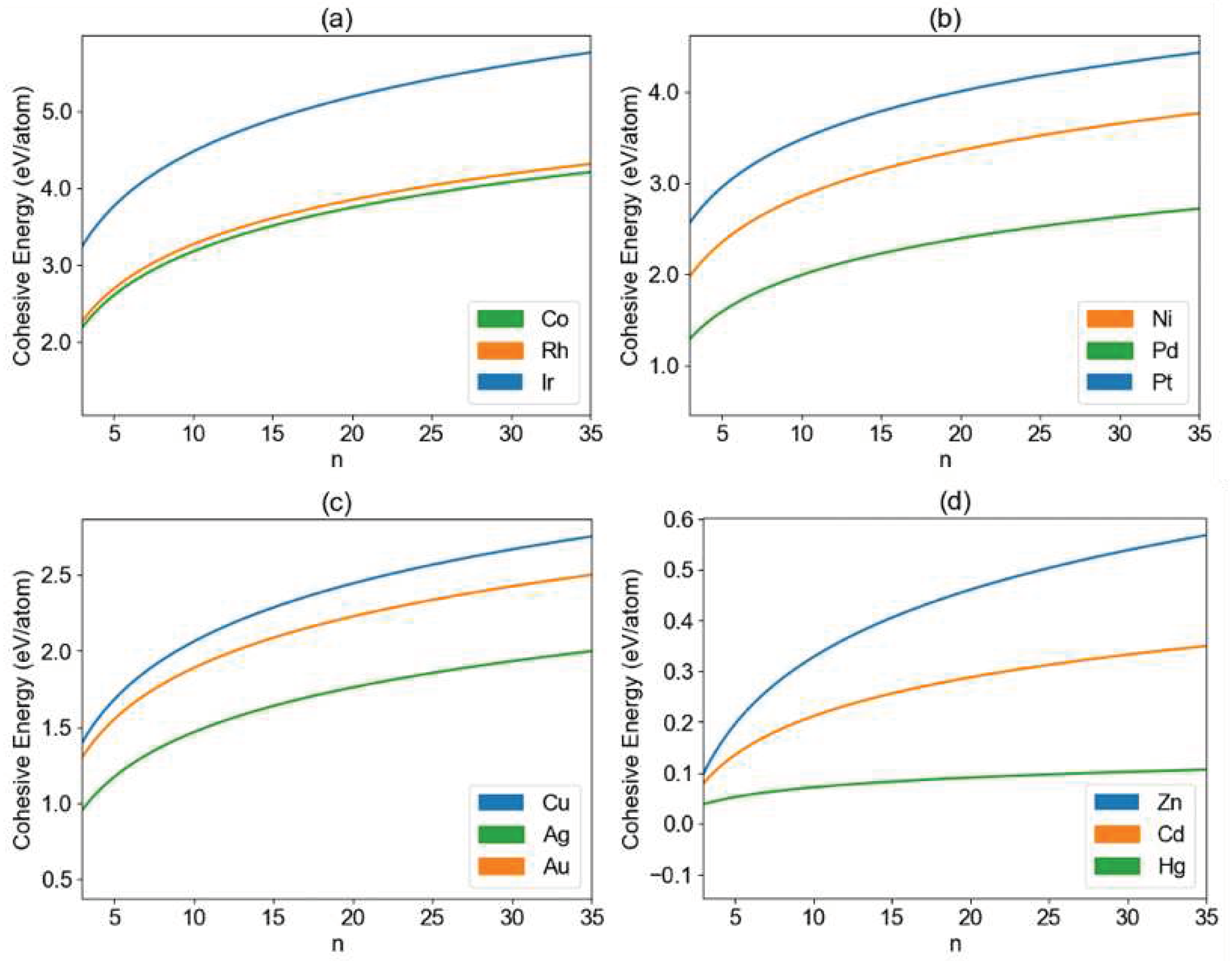
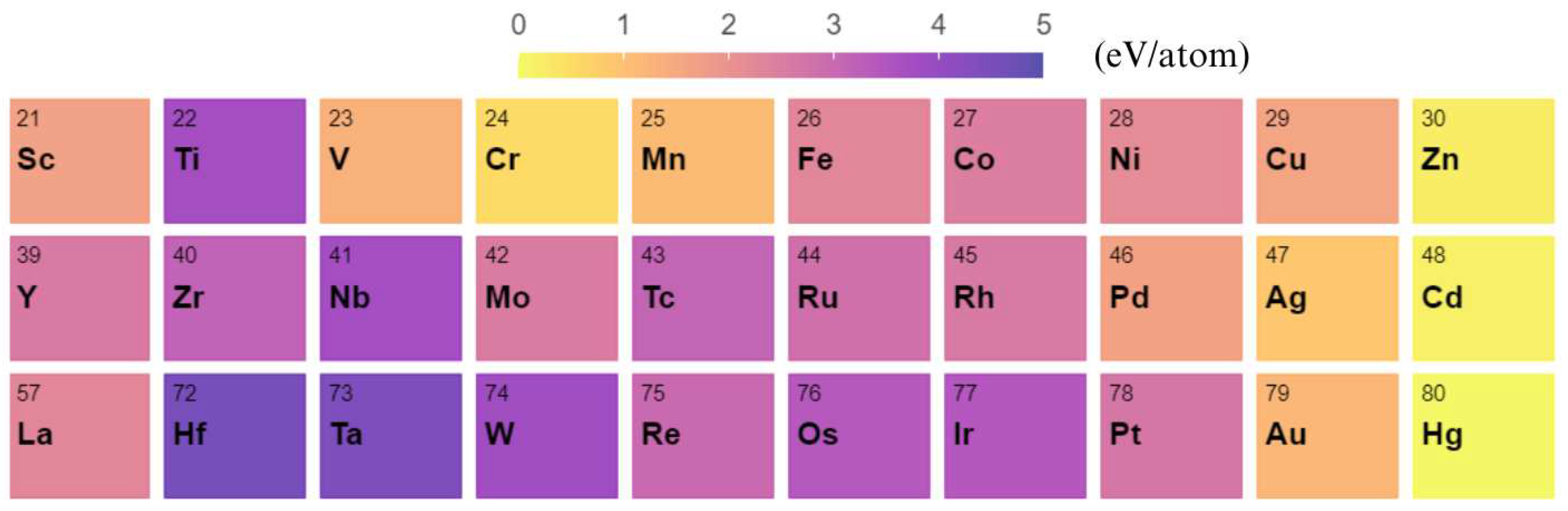
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Neugebauer, N.; Wang, Y.; Elm, M.T.; Hofmann, D.M.; Heiliger, C.; Ye, X.; Klar, P.J. Distance and size dependence of the interactions within highly ordered magnetic nanoparticle mesocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 184410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, E.C.; Vajda, S. Catalysis by clusters with precise numbers of atoms. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver-Meseguer, J.; Cabrero-Antonino, J.R.; Domínguez, I.; Leyva-Pérez, A.; Corma, A. Small Gold Clusters Formed in Solution Give Reaction Turnover Numbers of 10 7 at Room Temperature. Science 2012, 338, 1452–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Xin, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, Q.; Cai, W.; Peng, X.; Yang, F.; Xin, H. Nanoparticles advanced from preclinical studies to clinical trials for lung cancer therapy. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Significance and implications of nanoparticle–biological corona fingerprints in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics for diverse disorders. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 11422–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Kuttoth, H.; Nair, R.V.; Sandhyarani, N. Electrochemical Approach for the Synthesis of Ultrasmall Cu13 Clusters and Their Application in the Detection of Endotoxin. Langmuir 2023, 39, 10011–10020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, P.S.; Hu, P. Understanding supported noble metal catalysts using first-principles calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 180902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Qu, K.; Cheng, S.-B.; Wang, A.-L.; Lu, Q. Filling Mesopores of Conductive Metal–Organic Frameworks with Cu Clusters for Selective Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32176–32182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, R.; Huang, B.; Luo, Z. On the Nature of Three-Atom Metal Cluster Catalysis for N2 Reduction to Ammonia. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 14964–14975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Jakobsen, J.G.; Shim, S.S.; Kleis, J.; Andersson, M.P.; Rossmeisl, J.; Abildpedersen, F.; Bligaard, T.; Helveg, S.; Hinnemann, B.; et al. First principles calculations and experimental insight into methane steam reforming over transition metal catalysts. J. Catal. 2008, 259, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.; Halim, H.H.; Khairudin, N.F.; Pham, T.N.; Putra, S.E.M.; Hamamoto, Y.; Inagaki, K.; Hamada, I.; Mohamed, A.R.; Morikawa, Y. Dry Reforming of Methane on Cobalt Catalysts: DFT-Based Insights into Carbon Deposition Versus Removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 21902–21913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachin; Pandey, B. K.; Jaiswal, R.L. Dimensional effect on cohesive energy, melting temperature and Debye temperature of metallic nanoparticles. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 2023, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-F.; Wang, A.; Qiao, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T. Single-Atom Catalysts: A New Frontier in Heterogeneous Catalysis. Accounts Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.D.; Liang, X.L.; Kong, X.Q.; Zhang, W.J. Size-dependent cohesive energy, melting temperature, and Debye temperature of spherical metallic nanoparticles. Phys. Met. Met. 2017, 118, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeriniemi, J.; Melander, M.; Lipasti, S.; Hatz, R.; Laasonen, K. Fe–Ni Nanoparticles: A Multiscale First-Principles Study to Predict Geometry, Structure, and Catalytic Activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Kuang, X.Y.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.R. Geometries, stabilities, and electronic properties of Pt-group-doped gold clusters, their relationship to cluster size, and comparison with pure gold clusters. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 10119–10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.; Chattopadhyay, A.P. Dissociation of methane on Ni 4 cluster-A DFT study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2017, 1106, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes forab initiototal-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtarolo, S.; Setyawan, W.; Hart, G.L.; Jahnatek, M.; Chepulskii, R.V.; Taylor, R.H.; Wang, S.; Xue, J.; Yang, K.; Levy, O.; et al. AFLOW: An automatic framework for high-throughput materials discovery. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2012, 58, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, G.F.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, J.I.; Harvey, D.; Jang, S.S. Interactions of Pt nanoparticles with molecular components in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: multi-scale modeling approach. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69670–69676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, U.; Inukai, M.; Sato, H.; Zijlstra, E. S. In Physical Metallurgy; Laughlin, D. E. , Hono, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Glasser, L.; Sheppard, D.A. Cohesive Energies and Enthalpies: Complexities, Confusions, and Corrections. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 7103–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambie, S.; Steenbergen, K.G.; Gaston, N. Modulating the thermal and structural stability of galleneneviavariation of atomistic thickness. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 3, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




