Submitted:
31 July 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. FOXM1 in cancer and MPNST
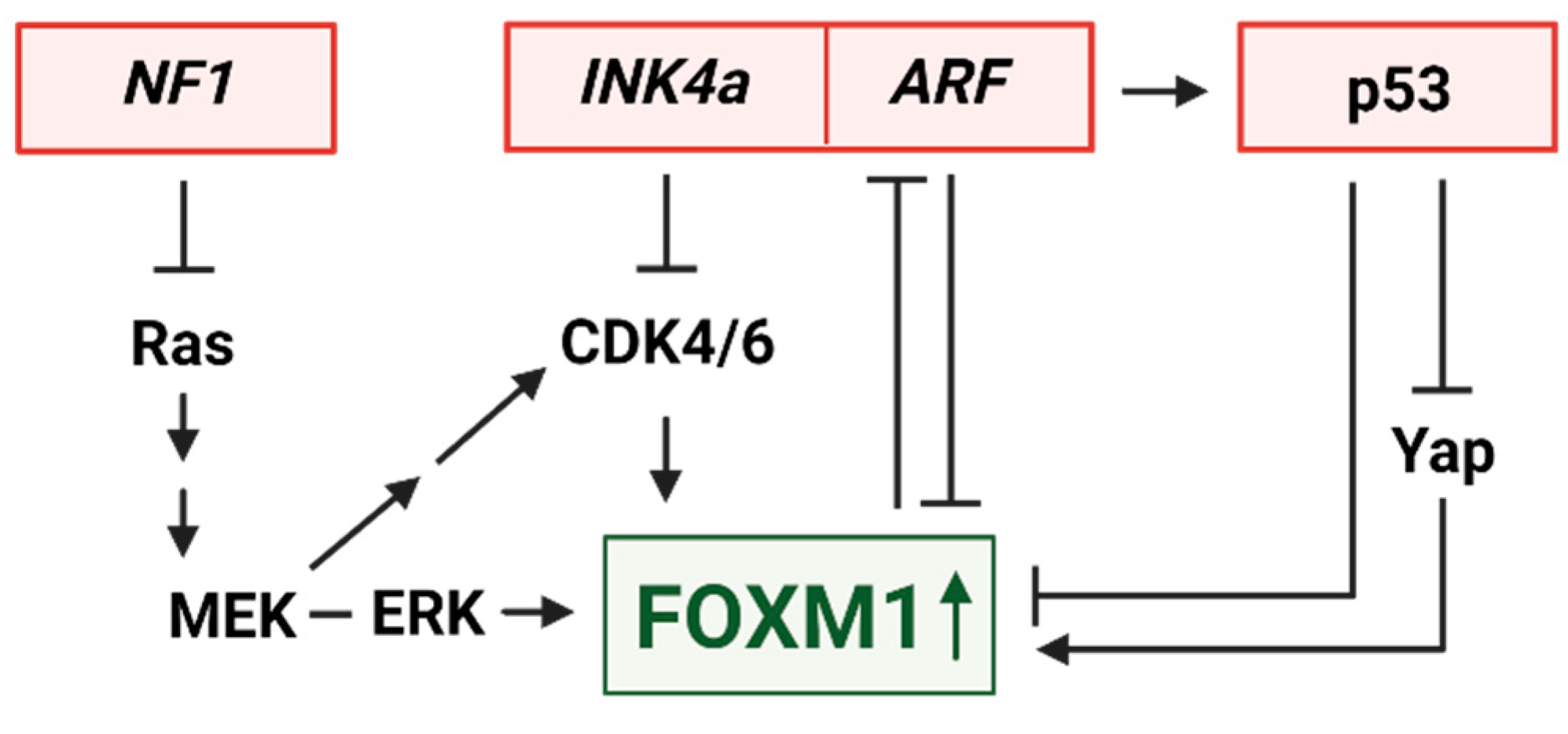
3. Upstream Regulators of FOXM1
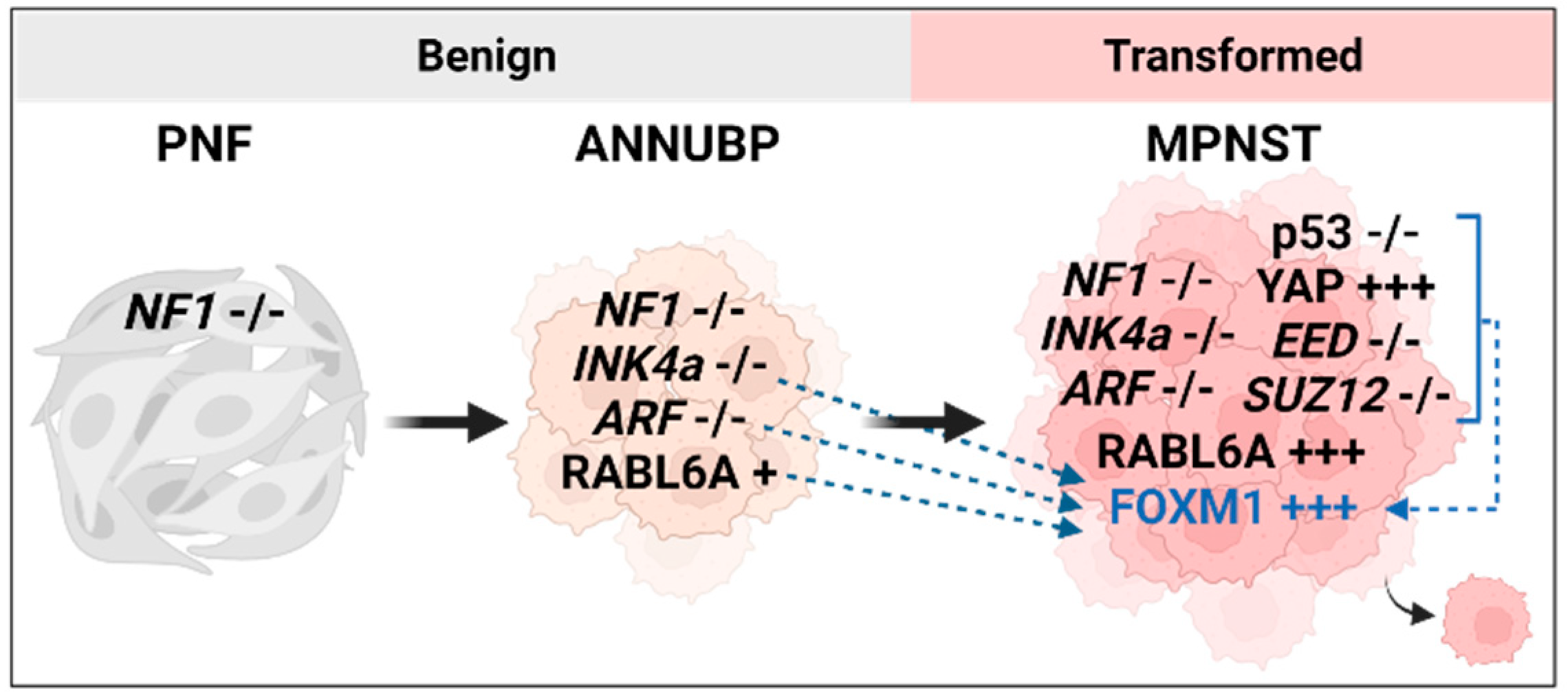
3.1. FOXM1 upregulation by INK4a/ARF loss
3.2. FOXM1 control by MEK and CDK4/6
3.3. Opposing transcriptional regulation of FOXM1 by p53 and YAP
3.4. RABL6A and FOXM1
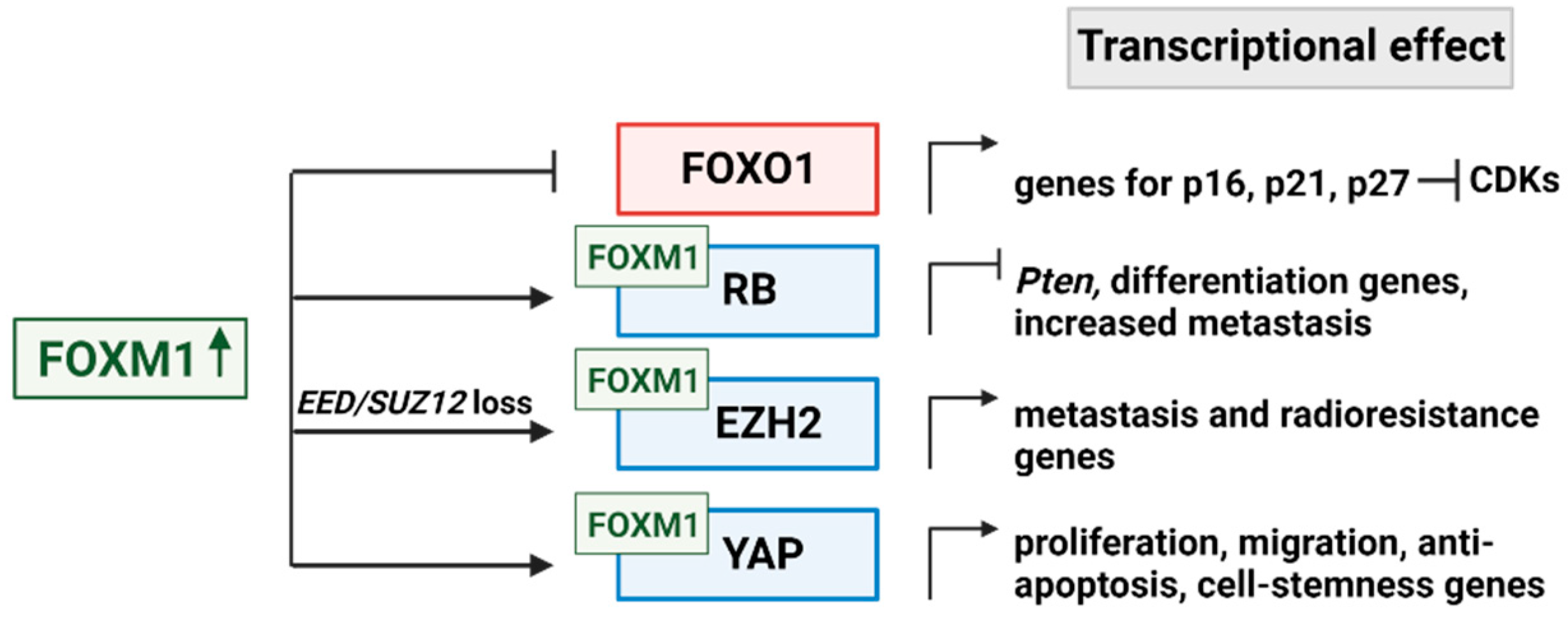
4. Downstream Targets of FOXM1
4.1. FOXO1
4.2. Multiple modes of RB1 regulation by FOXM1
4.3. EZH2 cooperation with FOXM1
4.4. YAP/ TEAD cooperation with FOXM1
5. Targeting the MEK-CDK4/6-FOXM1 axis to treat MPNST
5.1. Relevance of MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitor therapies
5.2. Targeting FOXM1 in MPNST
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, S.L. Molecular Mechanisms Promoting the Pathogenesis of Schwann Cell Neoplasms. Acta Neuropathol 2012, 123, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staedtke, V.; Bai, R.-Y.; Blakeley, J.O. Cancer of the Peripheral Nerve in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Gordon, D.J.; Tanas, M.R.; Dodd, R.D.; Monga, V.; Darbro, B.W.; Quelle, D.E. Combination Therapies for MPNSTs Targeting RABL6A-RB1 Signaling. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, M.; Høland, M.; Ågesen, T.H.; Brekke, H.R.; Liestøl, K.; Hall, K.S.; Mertens, F.; Picci, P.; Smeland, S.; Lothe, R.A. Survival Meta-Analyses for >1800 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Patients with and without Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Neuro Oncol 2013, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widemann, B.C. Current Status of Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Curr Oncol Rep 2009, 11, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, C.S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Dombi, E.; Perry, A.; Helman, L.J.; Schuetze, S.M.; Ludwig, J.A.; Staddon, A.; Milhem, M.M.; Rushing, D.; et al. SARC006: Phase II Trial of Chemotherapy in Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Associated Chemotherapy-Naive Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Sarcoma 2017, 2017, 8685638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerino, A.; Verdijk, R.M.; Nichelli, L.; Andratschke, N.H.; Idbaih, A.; Goldbrunner, R. Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral and Cranial Nerve Tumors with Expert Recommendations: An EUropean Network for RAre CANcers (EURACAN) Initiative. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Coert, J.H.; Flucke, U.E.; Slooff, W.-B.M.; Ho, V.K.Y.; van der Graaf, W.T.; van Dalen, T.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; van Houdt, W.J.; Grünhagen, D.J.; et al. A Nationwide Cohort Study on Treatment and Survival in Patients with Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. Eur J Cancer 2020, 124, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Smith, K.D.; Liu, J.; Lahat, G.; Myers, S.; Wang, W.-L.; Zhang, W.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Slopis, J.M.; Lazar, A.J.; et al. Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Variables Predictive of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Outcome. Annals of Surgery 2009, 249, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.; Gosline, S.J.C.; Stathis, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Guha, R.; Ryman, D.A.; Wallace, M.R.; Kasch-Semenza, L.; Hao, H.; et al. Pharmacological and Genomic Profiling of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Plexiform Neurofibroma-Derived Schwann Cells. Sci Data 2018, 5, 180106–180106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirbe, A.C.; Dahiya, S.; Miller, C.A.; Li, T.; Fulton, R.S.; Zhang, X.; McDonald, S.; DeSchryver, K.; Duncavage, E.J.; Walrath, J.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals the Order of Genetic Changes during Malignant Transformation and Metastasis in a Single Patient with NF1-Plexiform Neurofibroma. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 4201–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, N.; Miller, S.J. A RASopathy Gene Commonly Mutated in Cancer: The Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Tumour Suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer 2015, 15, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beert, E.; Brems, H.; Daniëls, B.; De Wever, I.; Van Calenbergh, F.; Schoenaers, J.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Gevaert, O.; De Raedt, T.; Van Den Bruel, A.; et al. Atypical Neurofibromas in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Are Premalignant Tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011, 50, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.M.; Antonescu, C.R.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Kim, A.; Lazar, A.J.; Quezado, M.M.; Reilly, K.M.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Stewart, D.R.; Viskochil, D.; et al. Histopathologic Evaluation of Atypical Neurofibromatous Tumors and Their Transformation into Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor in Patients with Neurofibromatosis 1-a Consensus Overview. Hum Pathol 2017, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallón-Lorenz, M.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.; Terribas, E.; Creus-Batchiller, E.; Romagosa, C.; Estival, A.; Perez Sidelnikova, D.; Salvador, H.; Villanueva, A.; Blanco, I.; et al. Chromosomal Translocations Inactivating CDKN2A Support a Single Path for Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Initiation. Hum Genet 2021, 140, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemberg, K.M.; Wang, J.; Pratilas, C.A. From Genes to -Omics: The Evolving Molecular Landscape of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, S.D.; He, Y.; Smith, A.; Jiang, L.; Lu, Q.; Mund, J.; Li, X.; Bessler, W.; Qian, S.; Dyer, W.; et al. Cdkn2a (Arf) Loss Drives NF1-Associated Atypical Neurofibroma and Malignant Transformation. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaney, K.E.; Perrino, M.R.; Kershner, L.J.; Patel, A.V.; Wu, J.; Choi, K.; Rizvi, T.A.; Dombi, E.; Szabo, S.; Largaespada, D.A.; et al. Cdkn2a Loss in a Model of Neurofibroma Demonstrates Stepwise Tumor Progression to Atypical Neurofibroma and MPNST. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 4720–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Sharpless, N.E. The Regulation of INK4/ARF in Cancer and Aging. Cell 2006, 127, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelle, D.E.; Nteeba, J.; Darbro, B.W. The INK4a/ARF Locus. In Encyclopedia of Cell Biology; Bradshaw, R.A., Stahl, P.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, 2016; pp. 447–457. ISBN 978-0-12-394796-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reilly, K.M.; Kim, A.; Blakely, J.; Ferner, R.E.; Gutmann, D.H.; Legius, E.; Miettinen, M.M.; Randall, R.L.; Ratner, N.; Jumbé, N.L.; et al. Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated MPNST State of the Science: Outlining a Research Agenda for the Future. J Natl Cancer Inst 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Stewart, D.R.; Reilly, K.M.; Viskochil, D.; Miettinen, M.M.; Widemann, B.C. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors State of the Science: Leveraging Clinical and Biological Insights into Effective Therapies. Sarcoma 2017, 2017, 7429697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemov, A.; Li, H.; Presley, W.; Wallace, M.R.; Miller, D.T. Genetics of Human Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Neuro-Oncology Advances 2020, 2, i50–i61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathil, D.; John, S.; Nair, A.S. FOXM1 and Cancer: Faulty Cellular Signaling Derails Homeostasis. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Barger, C.J.; Karpf, A.R. FOXM1: A Multifunctional Oncoprotein and Emerging Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Deshmukh, H.; Payton, J.E.; Dunham, C.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Tihan, T.; Prayson, R.A.; Guha, A.; Bridge, J.A.; Ferner, R.E.; et al. Array-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization Identifies CDK4 and FOXM1 Alterations as Independent Predictors of Survival in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor. Clin Cancer Res 2011, 17, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Teckie, S.; Wiesner, T.; Ran, L.; Prieto Granada, C.N.; Lin, M.; Zhu, S.; Cao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Sboner, A.; et al. PRC2 Is Recurrently Inactivated through EED or SUZ12 Loss in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Nat Genet 2014, 46, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Raedt, T.; Beert, E.; Pasmant, E.; Luscan, A.; Brems, H.; Ortonne, N.; Helin, K.; Hornick, J.L.; Mautner, V.; Kehrer-Sawatzki, H.; et al. PRC2 Loss Amplifies Ras-Driven Transcription and Confers Sensitivity to BRD4-Based Therapies. Nature 2014, 514, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, F.C.; O’Sullivan, H. FOXM1 in Sarcoma: Role in Cell Cycle, Pluripotency Genes and Stem Cell Pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42792–42804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.-B.; Li, X.-Z.; Zeng, S.; Liu, C.; Yang, S.-M.; Yang, L.; Hu, C.-J.; Bai, J.-Y. Regulation of the Master Regulator FOXM1 in Cancer. Cell Communication and Signaling 2018, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.K.Y.; Ngan, A.W.L.; Leung, M.-H.; Kwok, D.C.T.; Liu, V.W.S.; Chan, D.W.; Leung, W.Y.; Yao, K.-M. FOXM1b, Which Is Present at Elevated Levels in Cancer Cells, Has a Greater Transforming Potential than FOXM1c. Front Oncol 2013, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kohashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Maekawa, A.; Kuda, M.; Furue, M.; Oda, Y. Prognostic Significance of Forkhead Box M1 (FoxM1) Expression and Antitumour Effect of FoxM1 Inhibition in Melanoma. Histopathology 2016, 69, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.-F.; Qu, Z.-Q.; Yuan, H.-H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Y.-H.; Shi, J.; Gong, X.-D.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Liu, F.; et al. Overexpression of FOXM1 Is Associated with EMT and Is a Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol Rep 2014, 31, 2660–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassi, R.A.; Todeschini, P.; Siegel, E.R.; Calza, S.; Cappella, P.; Ardighieri, L.; Cadei, M.; Bugatti, M.; Romani, C.; Bandiera, E.; et al. FOXM1 Expression Is Significantly Associated with Chemotherapy Resistance and Adverse Prognosis in Non-Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2017, 36, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanja, D.; Chand, V.; O’Brien, E.; Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Zappia, M.P.; Islam, A.B.M.M.K.; Frolov, M.V.; Merrill, B.J.; Raychaudhuri, P. Transcriptional Repression by FoxM1 Suppresses Tumor Differentiation and Promotes Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Cancer Res 2022, 82, 2458–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Yin, L.; Peng, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhou, W.; Gong, Z.; Liu, J.; He, L.; et al. FOXM1 Promotes the Progression of Prostate Cancer by Regulating PSA Gene Transcription. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17027–17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichenko, V.V.; Major, M.L.; Wang, X.; Petrovic, V.; Kuechle, J.; Yoder, H.M.; Dennewitz, M.B.; Shin, B.; Datta, A.; Raychaudhuri, P.; et al. Foxm1b Transcription Factor Is Essential for Development of Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Is Negatively Regulated by the P19ARF Tumor Suppressor. Genes Dev 2004, 18, 830–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanja, D.; Pandey, A.; Kiefer, M.; Wang, Z.; Chandan, N.; Carr, J.R.; Franks, R.; Yu, D.-Y.; Guzman, G.; Maker, A.; et al. Essential Roles of FoxM1 in Ras-Induced Liver Cancer Progression and in Cancer Cells with Stem Cell Features. J Hepatol 2015, 63, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Ogura, S.; Kurahashi, T.; Kizu, T.; Furuta, K.; Kamada, Y.; Chatani, N.; Hamano, M.; Kiso, S.; et al. Increased Expression of Forkhead Box M1 Transcription Factor Is Associated with Clinicopathological Features and Confers a Poor Prognosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatol Res 2017, 47, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhong, H.; Li, L.; Ji, W.; Zhang, X. Overexpressed Transcription Factor FOXM1 Contributes to the Progression of Colorectal Cancer. Mol Med Rep 2016, 13, 2696–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Quan, M.; Gao, Y. The FOXM1/ATX Signaling Contributes to Pancreatic Cancer Development. Am J Transl Res 2020, 12, 4478–4487. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Z.; Le, X.; Dai, B.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; Tan, D.; Xie, K. Critical Role and Regulation of Transcription Factor FoxM1 in Human Gastric Cancer Angiogenesis and Progression. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Dai, B.; Liu, M.; Sawaya, R.; Xie, K.; Huang, S. FoxM1B Transcriptionally Regulates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Promotes the Angiogenesis and Growth of Glioma Cells. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 8733–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Gusarova, G.; Wang, Z.; Carr, J.R.; Li, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Qiu, J.; Park, Y.-D.; Williamson, P.R.; Hay, N.; et al. Deregulation of FoxM1b Leads to Tumour Metastasis. EMBO Mol Med 2011, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, P.; Park, H.J. FoxM1: A Master Regulator of Tumor Metastasis. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 4329–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Wang, A.; Ziegler, Y.; Kim, S.H.; El-Ashry, D.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Suppression of Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Signaling Pathways by Reducing FOXM1 Activity in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Tan, G.; Ding, M.; Dong, D.; Chen, T.; Meng, X.; Huang, X.; Tan, Y. Foxm1 Transcription Factor Is Required for Maintenance of Pluripotency of P19 Embryonal Carcinoma Cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, 8027–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Snyder, J.; Sutherland, M.J.; Burhans, M.S.; Shannon, J.M.; Park, H.J.; Whitsett, J.A.; Kalinichenko, V.V. Increased Expression of FoxM1 Transcription Factor in Respiratory Epithelium Inhibits Lung Sacculation and Causes Clara Cell Hyperplasia. Developmental Biology 2010, 347, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Raychaudhuri, P.; Costa, R.H. Chk2 Mediates Stabilization of the FoxM1 Transcription Factor to Stimulate Expression of DNA Repair Genes. Mol Cell Biol 2007, 27, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, J.M.-M.; Peck, B.; Monteiro, L.J.; Schwenen, H.D.C.; Millour, J.; Coombes, R.C.; Myatt, S.S.; Lam, E.W.-F. FOXM1 Confers Acquired Cisplatin Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol Cancer Res 2010, 8, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.-G.; Mun, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K.; Park, W.; Jeong, M.-S.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, W.-T.; Choi, Y.H.; Chu, I.-S.; Leem, S.-H. Fanconi Anemia Pathway Activation by FOXM1 Is Critical to Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Anticancer Drug Resistance. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-N.; Chu, I.-S. A Gene Expression Signature of FOXM1 Predicts the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp Mol Med 2018, 50, e418–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Roh, Y.-G.; Park, K.; Kang, T.-H.; Kim, W.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Leem, S.-H.; Chu, I.-S. Expression Signature Defined by FOXM1–CCNB1 Activation Predicts Disease Recurrence in Non–Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 2014, 20, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Kaemmer, C.A.; Lingo, J.J.; Voigt, E.; Leidinger, M.R.; McGivney, G.R.; Scherer, A.; Koppenhafer, S.L.; Gordon, D.J.; Breheny, P.; et al. Oncogenic RABL6A Promotes NF1-Associated MPNST Progression in Vivo. Neuro-Oncology Advances 2022, vdac047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quelle, D.E.; Zindy, F.; Ashmun, R.A.; Sherr, C.J. Alternative Reading Frames of the INK4a Tumor Suppressor Gene Encode Two Unrelated Proteins Capable of Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest. Cell 1995, 83, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.; Hannon, G.J.; Beach, D. A New Regulatory Motif in Cell-Cycle Control Causing Specific Inhibition of Cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 1993, 366, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J. Divorcing ARF and P53: An Unsettled Case. Nat Rev Cancer 2006, 6, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.H.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Major, M.L.; Raychaudhuri, P. New and Unexpected: Forkhead Meets ARF. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 2005, 15, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarova, G.A.; Wang, I.-C.; Major, M.L.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Ackerson, T.; Petrovic, V.; Costa, R.H. A Cell-Penetrating ARF Peptide Inhibitor of FoxM1 in Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.M.; Quelle, D.E. P53 Acetylation: Regulation and Consequences. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 7, 30–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.K.M.; Smith, D.K.; Leung, W.Y.; Cheung, A.M.S.; Lam, E.W.F.; Dimri, G.P.; Yao, K.-M. FoxM1c Counteracts Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Stimulates Bmi-1 Expression. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 16545–16553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, V.; Liao, X.; Guzman, G.; Benevolenskaya, E.; Raychaudhuri, P. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Evades RB1-Induced Senescence by Activating the FOXM1–FOXO1 Axis. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3778–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, C.H.; Charles, N.J.; Gilks, C.B.; Kalloger, S.E.; Argenta, P.A.; Lange, C.A. Progesterone Receptors Induce FOXO1-Dependent Senescence in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 64. M., R.Y.; Tong, T.H.K.; Alice M. S. Cheung; Alice M. S. Cheung; Cheung, A.M.S.; Tsang, A.C.C.; Leung, W.Y.; Yao, K.-M. Raf/MEK/MAPK Signaling Stimulates the Nuclear Translocation and Transactivating Activity of FOXM1c. Journal of Cell Science 2005, 118, 795–806. [CrossRef]
- Kruiswijk, F.; Hasenfuss, S.C.; Sivapatham, R.; Baar, M.P.; Putavet, D.; Naipal, K. a. T.; van den Broek, N.J.F.; Kruit, W.; van der Spek, P.J.; van Gent, D.C.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of Metastatic Melanoma through Interference with Pin1-FOXM1 Signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, L.; Ke, N.; Hydbring, P.; Choi, Y.J.; Widlund, H.R.; Chick, J.M.; Zhai, H.; Vidal, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Braun, P.; et al. A Systematic Screen for CDK4/6 Substrates Links FOXM1 Phosphorylation to Senescence Suppression in Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Qu, K.; Tao, J.; Yin, G.; Han, S.; Liu, Q.; Sun, H. Inhibition of CIP2A Attenuates Tumor Progression by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Promoting Cellular Senescence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018, 495, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, A.H.; Brison, C.M.; Nerli, S.; Arsenault, H.E.; McShan, A.C.; Chen, E.; Lee, H.-W.; Benanti, J.A.; Sgourakis, N.G.; Rubin, S.M. An Order-to-Disorder Structural Switch Activates the FoxM1 Transcription Factor. Elife 2019, 8, e46131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, M.L.; Lepe, R.; Costa, R.H. Forkhead Box M1B Transcriptional Activity Requires Binding of Cdk-Cyclin Complexes for Phosphorylation-Dependent Recruitment of P300/CBP Coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 2649–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laoukili, J.; Alvarez, M.; Meijer, L.A.T.; Stahl, M.; Mohammed, S.; Kleij, L.; Heck, A.J.R.; Medema, R.H. Activation of FoxM1 during G2 Requires Cyclin A/Cdk-Dependent Relief of Autorepression by the FoxM1 N-Terminal Domain. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 3076–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Malureanu, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; van Deursen, J.M.; Tindall, D.J.; Chen, J. Plk1-Dependent Phosphorylation of FoxM1 Regulates a Transcriptional Programme Required for Mitotic Progression. Nat Cell Biol 2008, 10, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher-Firzlaff, J.M.; Lilischkis, R.; Lüscher, B. Regulation of the Transcription Factor FOXM1c by Cyclin E/CDK2. FEBS Lett 2006, 580, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The First 30 Years of P53: Growing Ever More Complex. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Kluwe, L.; Spurlock, G.; Monem, B.; Majounie, E.; Mantripragada, K.; Ruggieri, M.; Chuzhanova, N.; Evans, D.G.; Ferner, R.; et al. Germline and Somatic NF1 Gene Mutation Spectrum in NF1-Associated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNSTs). Hum Mutat 2008, 29, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdijk, R.M.; den Bakker, M.A.; Dubbink, H.J.; Hop, W.C.J.; Dinjens, W.N.M.; Kros, J.M. TP53 Mutation Analysis of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2010, 69, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Mautner, V.-F.; Cooper, D.N.; Upadhyaya, M. Molecular Heterogeneity in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Human Genomics 2012, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Janke, L.J.; Gudenas, B.L.; Jin, H.; Fan, Y.; Paré, J.; Clay, M.R.; Northcott, P.A.; Hirbe, A.C.; Cao, X. A Genetic Mouse Model with Postnatal Nf1 and P53 Loss Recapitulates the Histology and Transcriptome of Human Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor. Neurooncol Adv 2021, 3, vdab129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millour, J.; de Olano, N.; Horimoto, Y.; Monteiro, L.J.; Langer, J.K.; Aligue, R.; Hajji, N.; Lam, E.W.F. ATM and P53 Regulate FOXM1 Expression via E2F in Breast Cancer Epirubicin Treatment and Resistance. Mol Cancer Ther 2011, 10, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, B.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. P53 Negatively Regulates Expression of FoxM1. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3425–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurinna, S.; Stratton, S.A.; Coban, Z.; Schumacher, J.M.; Grompe, M.; Duncan, A.W.; Barton, M.C. P53 Regulates a Mitotic Transcription Program and Determines Ploidy in Normal Mouse Liver. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, A.M.; Prives, C. Pro-Proliferative FoxM1 Is a Target of P53-Mediated Repression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 4295–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cheng, Y.; Kalra, A.; Ma, K.; Zheng, Y.; Ziman, B.; Tressler, C.; Glunde, K.; Shin, E.J.; Ngamruengphong, S.; et al. Generation and Multiomic Profiling of a TP53/CDKN2A Double-Knockout Gastroesophageal Junction Organoid Model. Science Translational Medicine 2022, 14, eabq6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Bam, R. Reciprocal Crosstalk Between YAP1/Hippo Pathway and the P53 Family Proteins: Mechanisms and Outcomes in Cancer. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furth, N.; Aylon, Y.; Oren, M. P53 Shades of Hippo. Cell Death Differ 2018, 25, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Murakami, H.; Fujii, M.; Ishiguro, F.; Tanaka, I.; Kondo, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Toyokuni, S.; Yokoi, K.; Osada, H.; et al. YAP Induces Malignant Mesothelioma Cell Proliferation by Upregulating Transcription of Cell Cycle-Promoting Genes. Oncogene 2012, 31, 5117–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermeking, H.; Lengauer, C.; Polyak, K.; He, T.C.; Zhang, L.; Thiagalingam, S.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. 14-3-3sigma Is a P53-Regulated Inhibitor of G2/M Progression. Mol Cell 1997, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, S.S.; Valente, L.J.; Raj, N.; Seoane, J.A.; Flowers, B.M.; McClendon, J.; Bieging-Rolett, K.T.; Lee, J.; Ivanochko, D.; Kozak, M.M.; et al. A P53 Super-Tumor Suppressor Reveals a Tumor Suppressive P53-Ptpn14-Yap Axis in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 460–473.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Feng, W.; Yu, Y.; Jeong, K.; Guo, W.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B. Verteporfin Inhibits YAP Function through Up-Regulating 14-3-3σ Sequestering YAP in the Cytoplasm. Am J Cancer Res 2016, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weiler, S.M.E.; Pinna, F.; Wolf, T.; Lutz, T.; Geldiyev, A.; Sticht, C.; Knaub, M.; Thomann, S.; Bissinger, M.; Wan, S.; et al. Induction of Chromosome Instability by Activation of Yes-Associated Protein and Forkhead Box M1 in Liver Cancer. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 2037–2051.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisinger-Mathason, T.S.K.; Mucaj, V.; Biju, K.M.; Nakazawa, M.S.; Gohil, M.; Cash, T.P.; Yoon, S.S.; Skuli, N.; Park, K.M.; Gerecht, S.; et al. Deregulation of the Hippo Pathway in Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Promotes FOXM1 Expression and Tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, E3402–E3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, C.; Thomason, J.; Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Reisetter, A.C.; Ahirwar, P.; Jahanseir, K.; Leidinger, M.; Ofori-Amanfo, G.; Fritchie, K.; Velu, S.E.; et al. Prognostic and Therapeutic Value of the Hippo Pathway, RABL6A, and P53-MDM2 Axes in Sarcomas. Oncotarget 2021, 12, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Kaemmer, C.A.; Pulliam, C.; Maharjan, C.K.; Samayoa, A.M.; Major, H.J.; Cornick, K.E.; Knepper-Adrian, V.; Khanna, R.; Sieren, J.C.; et al. RABL6A Is an Essential Driver of MPNSTs That Negatively Regulates the RB1 Pathway and Sensitizes Tumor Cells to CDK4/6 Inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 2997–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, J.; Jin, W.; Sheikh, M.S.; Huang, Y. RBEL1 Is a Novel Gene That Encodes a Nucleocytoplasmic Ras Superfamily GTP-Binding Protein and Is Overexpressed in Breast Cancer. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 37640–37649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, V.; Hagen, J.; Zediak, V.P.; Quelle, D.E. Identification of Novel ARF Binding Proteins by Two-Hybrid Screening. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Kaemmer, C.A.; Umesalma, S.; Gourronc, F.A.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Quelle, D.E. RABL6A Regulates Schwann Cell Senescence in an RB1-Dependent Manner. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yan, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, F.; Lei, Y. High Expression of RABL6 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, J.; Muniz, V.P.; Falls, K.C.; Reed, S.M.; Taghiyev, A.F.; Quelle, F.W.; Gourronc, F.A.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; Major, H.J.; Askeland, R.W.; et al. RABL6A Promotes G1-S Phase Progression and Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Cell Proliferation in an Rb1-Dependent Manner. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 6661–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, V.P.; Askeland, R.W.; Zhang, X.; Reed, S.M.; Tompkins, V.S.; Hagen, J.; McDowell, B.D.; Button, A.; Smith, B.J.; Weydert, J.A.; et al. RABL6A Promotes Oxaliplatin Resistance in Tumor Cells and Is a New Marker of Survival for Resected Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Patients. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.-P.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zeng, M.-S.; Shao, J.-Y. Down-Regulation of C9orf86 in Human Breast Cancer Cells Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Tumor Growth and Correlates with Survival of Breast Cancer Patients. PLoS One 2013, 8, e71764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Osman, M.; Inoue, Y.; Suda, T.; Sugimura, H. A Novel Prognostic Marker of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Chromosome 9 Open Reading Frame 86 (C9orf86). J Thorac Dis 2016, 8, 2284–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Ji, F.; Sun, J.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yue, H. RBEL1 Is Required for Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation via Inhibiting Retinoblastoma 1. Mol Med Rep 2016, 13, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Gordon, D.J.; Tanas, M.R.; Monga, V.; Dodd, R.D.; Quelle, D.E. CDKs in Sarcoma: Mediators of Disease and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbano, J.; Lui, K.; Sheikh, M.S.; Huang, Y. Identification and Characterization of RBEL1 Subfamily of GTPases in the Ras Superfamily Involved in Cell Growth Regulation. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 18129–18142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlmeyer, J.L.; Lingo, J.J.; Kaemmer, C.A.; Scherer, A.; Warrier, A.; Voigt, E.; Raygoza Garay, J.A.; McGivney, G.R.; Brockman, Q.R.; Tang, A.; et al. CDK4/6-MEK Inhibition in MPNSTs Causes Plasma Cell Infiltration, Sensitization to PD-L1 Blockade, and Tumor Regression. Clin Cancer Res 2023, CCR-23-0749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Targeting Forkhead Box Transcription Factors FOXM1 and FOXO in Leukemia (Review). Oncology Reports 2014, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calissi, G.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Link, W. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting FOXO Transcription Factors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021, 20, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomans de Brachène, A.; Demoulin, J.-B. FOXO Transcription Factors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; An, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhu, W.; Yang, X. FOXO1 Inhibits the Invasion and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Reversing ZEB2-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda, M.; den Hollander, P.; Mani, S.A. Forkhead Box Transcription Factors: Double-Edged Swords in Cancer. Cancer Res 2022, 82, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M.; Weinberg, R.A. The Role of RB in Cell Cycle Control. Prog Cell Cycle Res 1995, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierstra, I. The Transcription Factor FOXM1 (Forkhead Box M1): Proliferation-Specific Expression, Transcription Factor Function, Target Genes, Mouse Models, and Normal Biological Roles. Advances in Cancer Research 2013, 118, 97–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorian, C.; Nakashima, J.; Dry, S.M.; Nghiemphu, P.L.; Smith, K.B.; Ao, Y.; Dang, J.; Lawson, G.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Mischel, P.S.; et al. PTEN Dosage Is Essential for Neurofibroma Development and Malignant Transformation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, 19479–19484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradtmöller, M.; Hartmann, C.; Zietsch, J.; Jäschke, S.; Mautner, V.-F.; Kurtz, A.; Park, S.-J.; Baier, M.; Harder, A.; Reuss, D.; et al. Impaired Pten Expression in Human Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. PLoS One 2012, 7, e47595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Yang, R.; Malik, R.; Qiao, Y.; Poliakov, A.; Yocum, A.K.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; et al. The Central Role of EED in the Orchestration of Polycomb Group Complexes. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comet, I.; Riising, E.M.; Leblanc, B.; Helin, K. Maintaining Cell Identity: PRC2-Mediated Regulation of Transcription and Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2016, 16, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, Q.R.; Scherer, A.; McGivney, G.R.; Gutierrez, W.R.; Voigt, A.P.; Isaacson, A.L.; Laverty, E.A.; Roughton, G.; Knepper-Adrian, V.; Darbro, B.; et al. PRC2 Loss Drives MPNST Metastasis and Matrix Remodeling. JCI Insight 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, J.B.; Marchione, D.M.; Sidoli, S.; Djedid, A.; Lisby, A.; Majewski, J.; Garcia, B.A. Epigenomic Reordering Induced by Polycomb Loss Drives Oncogenesis but Leads to Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.-H.; Mu, L.-J.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zeng, J.; Long, Q.-Z. ; Bin-Guan, null; Wang, W. ; Jiang, Y.-M.; Bai, X.-J.; Du, Y.-F. FOXM1-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation of EZH2 Induces Proliferation and Progression in Prostate Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2021, 21, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Joshi, K.; Ezhilarasan, R.; Myers, T.R.; Siu, J.; Gu, C.; Nakano-Okuno, M.; Taylor, D.; Minata, M.; Sulman, E.P.; et al. EZH2 Protects Glioma Stem Cells from Radiation-Induced Cell Death in a MELK/FOXM1-Dependent Manner. Stem Cell Reports 2015, 4, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, S.; Lee, P.L.; Feng, M.; Tergaonkar, V.; Chng, W.J.; Yu, Q. HIFI-α Activation Underlies a Functional Switch in the Paradoxical Role of Ezh2/PRC2 in Breast Cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, E3735–E3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-L.; Men, J.-R.; Liu, H.-Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhang, H.-S. FOXM1 Facilitates Breast Cancer Cell Stemness and Migration in YAP1-Dependent Manner. Arch Biochem Biophys 2020, 685, 108349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.B.; Sun, H.; Robichaux, J.; Pfeifer, M.; McDermott, U.; Travers, J.; Diao, L.; Xi, Y.; Tong, P.; Shen, L.; et al. A YAP/FOXM1 Axis Mediates EMT-Associated EGFR Inhibitor Resistance and Increased Expression of Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Components. Sci Transl Med 2020, 12, eaaz4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Reyes, G.L.; Koes, N.; Ryu, J.H.; Kaufmann, G.; Berner, M.; Weg, M.T.; Wolf, N.K.; Rathe, S.K.; Ratner, N.; Moriarity, B.S.; et al. Transposon Mutagenesis-Guided CRISPR/Cas9 Screening Strongly Implicates Dysregulation of Hippo/YAP Signaling in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Development. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiu, W.; Liu, B.; Yao, R.; Liu, S.; Yao, Y.; Liang, J. Forkhead Box Transcription Factor 1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: FOXM1 Is a Poor Prognostic Factor and Mediates Resistance to Docetaxel. J Transl Med 2013, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, A.; Huang, Z.; Huang, S. FoxM1 Inhibition Sensitizes Resistant Glioblastoma Cells to Temozolomide by Downregulating the Expression of DNA-Repair Gene Rad51. Clinical Cancer Research 2012, 18, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, S.; Wright, A.J.; D’Santos, P.; Hu, D.; Hesketh, R.L.; Lubling, Y.; Georgopoulou, D.; Lerda, G.; Couturier, D.-L.; Razavi, P.; et al. Metabolic Imaging Detects Resistance to PI3Kα Inhibition Mediated by Persistent FOXM1 Expression in ER+ Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 516–533.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Fernández, M.; Malumbres, M. Mechanisms of Sensitivity and Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.; Martínez-Fernández, M.; Segovia, C.; Lodewijk, I.; Suarez-Cabrera, C.; Segrelles, C.; López-Calderón, F.; Munera-Maravilla, E.; Santos, M.; Bernardini, A.; et al. CDK4/6 Inhibitor as a Novel Therapeutic Approach for Advanced Bladder Cancer Independently of RB1 Status. Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 25, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, R.; Watson, A.L.; Largaespada, D.A.; Ratner, N.; Osum, S.; Moertel, C.L. Neurofibromatosis in the Era of Precision Medicine: Development of MEK Inhibitors and Recent Successes with Selumetinib. Curr Oncol Rep 2021, 23, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Blank, P.M.K.; Gross, A.M.; Akshintala, S.; Blakeley, J.O.; Bollag, G.; Cannon, A.; Dombi, E.; Fangusaro, J.; Gelb, B.D.; Hargrave, D.; et al. MEK Inhibitors for Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Manifestations: Clinical Evidence and Consensus. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayle, S.S.; Castellino, R.C.; Buss, M.C.; Nahta, R. MEK Inhibition Increases Lapatinib Sensitivity via Modulation of FOXM1. Curr Med Chem 2013, 20, 2486–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, V.S.; Ziegler, Y.; Gopinath, C.; Kumar, S.; Dey, P.; Plotner, B.N.; Dawson, N.Z.; Kim, S.H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Effective Combination Treatments for Breast Cancer Inhibition by FOXM1 Inhibitors with Other Targeted Cancer Drugs. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2023, 198, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, A.; Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lu, H.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. The Forkhead Transcription Factor FOXM1 Promotes Endocrine Resistance and Invasiveness in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer by Expansion of Stem-like Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Research 2014, 16, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushweller, J.H. Targeting Transcription Factors in Cancer — from Undruggable to Reality. Nat Rev Cancer 2019, 19, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; Bhat, U.G.; Hughes, D.E.; Wang, I.-C.; Costa, R.H.; Gartel, A.L. Identification of a Chemical Inhibitor of the Oncogenic Transcription Factor Forkhead Box M1. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 9731–9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, U.G.; Zipfel, P.A.; Tyler, D.S.; Gartel, A.L. Novel Anticancer Compounds Induce Apoptosis in Melanoma Cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, U.G.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Thiazole Antibiotics Target FoxM1 and Induce Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.S.; Sanders, D.A.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. The Transcription Factor FOXM1 Is a Cellular Target of the Natural Product Thiostrepton. Nat Chem 2011, 3, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas Korkmaz, F.; Dogan Turacli, I.; Esendagli, G.; Ekmekci, A. Effects of Thiostrepton Alone or in Combination with Selumetinib on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis. Mol Biol Rep 2022, 49, 10387–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, Y.; Laws, M.J.; Sanabria Guillen, V.; Kim, S.H.; Dey, P.; Smith, B.P.; Gong, P.; Bindman, N.; Zhao, Y.; Carlson, K.; et al. Suppression of FOXM1 Activities and Breast Cancer Growth in Vitro and in Vivo by a New Class of Compounds. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




