Submitted:
31 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis
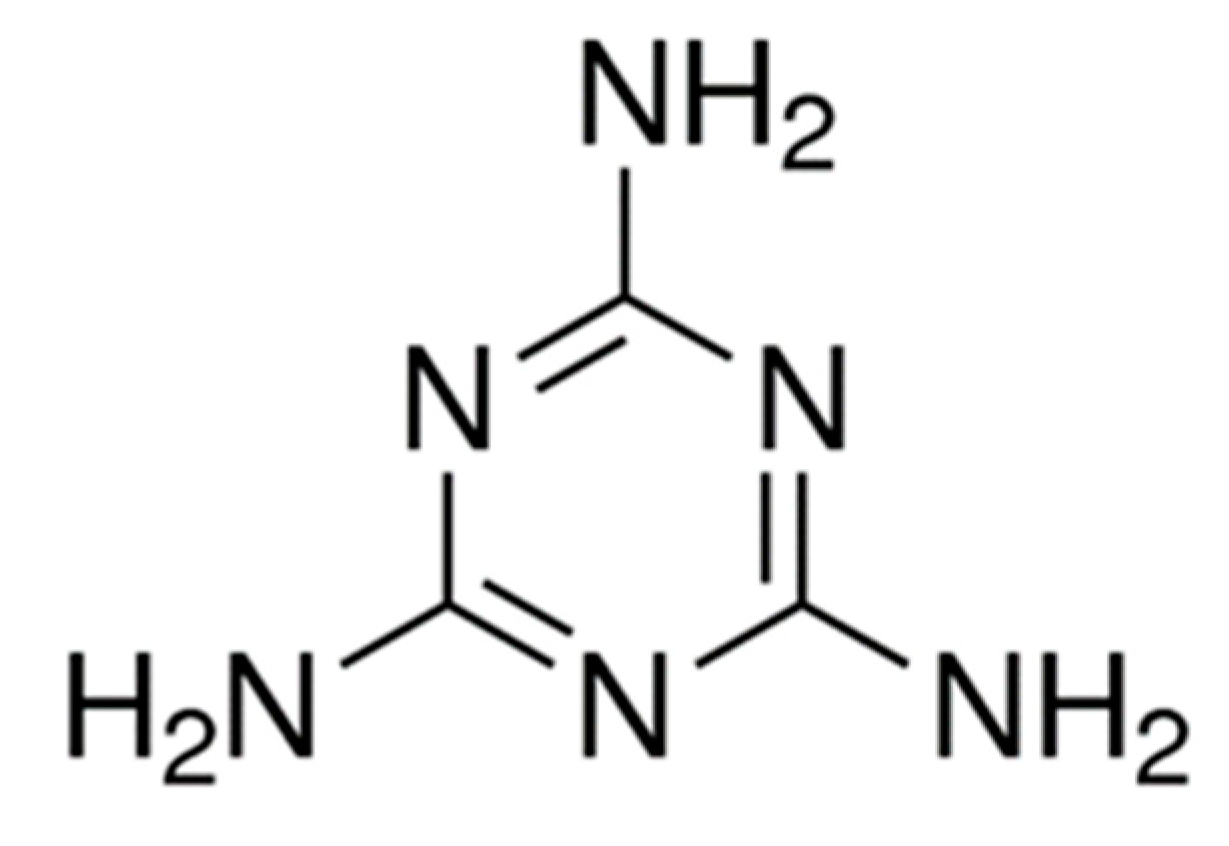
2.1.1. Synthesis of g–C3N4
2.1.2. Synthesis of CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 nanoparticles using the polyol method
2.1.3. Synthesis of Ag nanocubes
2.1.4. Ag/CoFe2O4/g–C3N4
2.3. Electrochemical Measurements
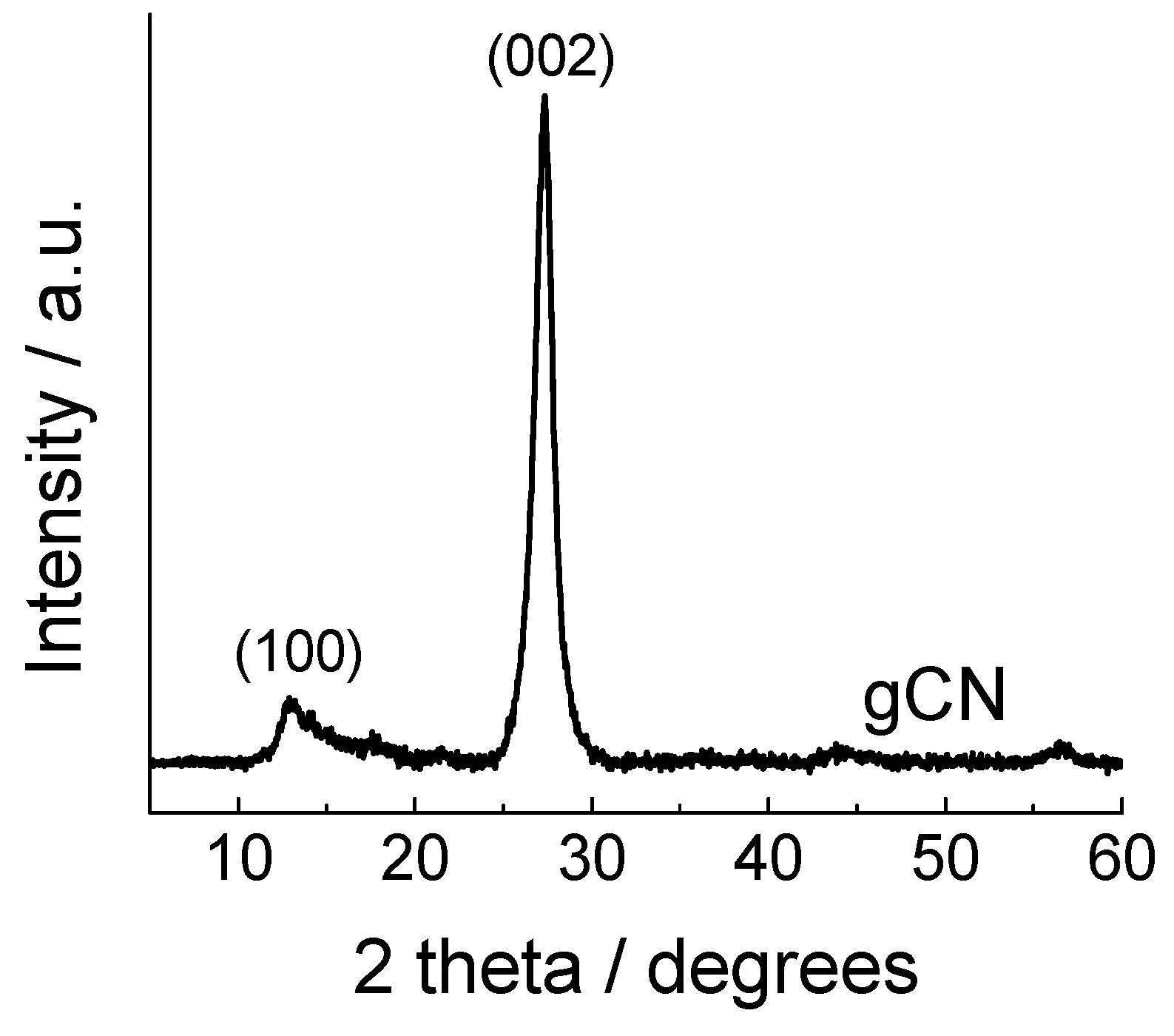
3. Results
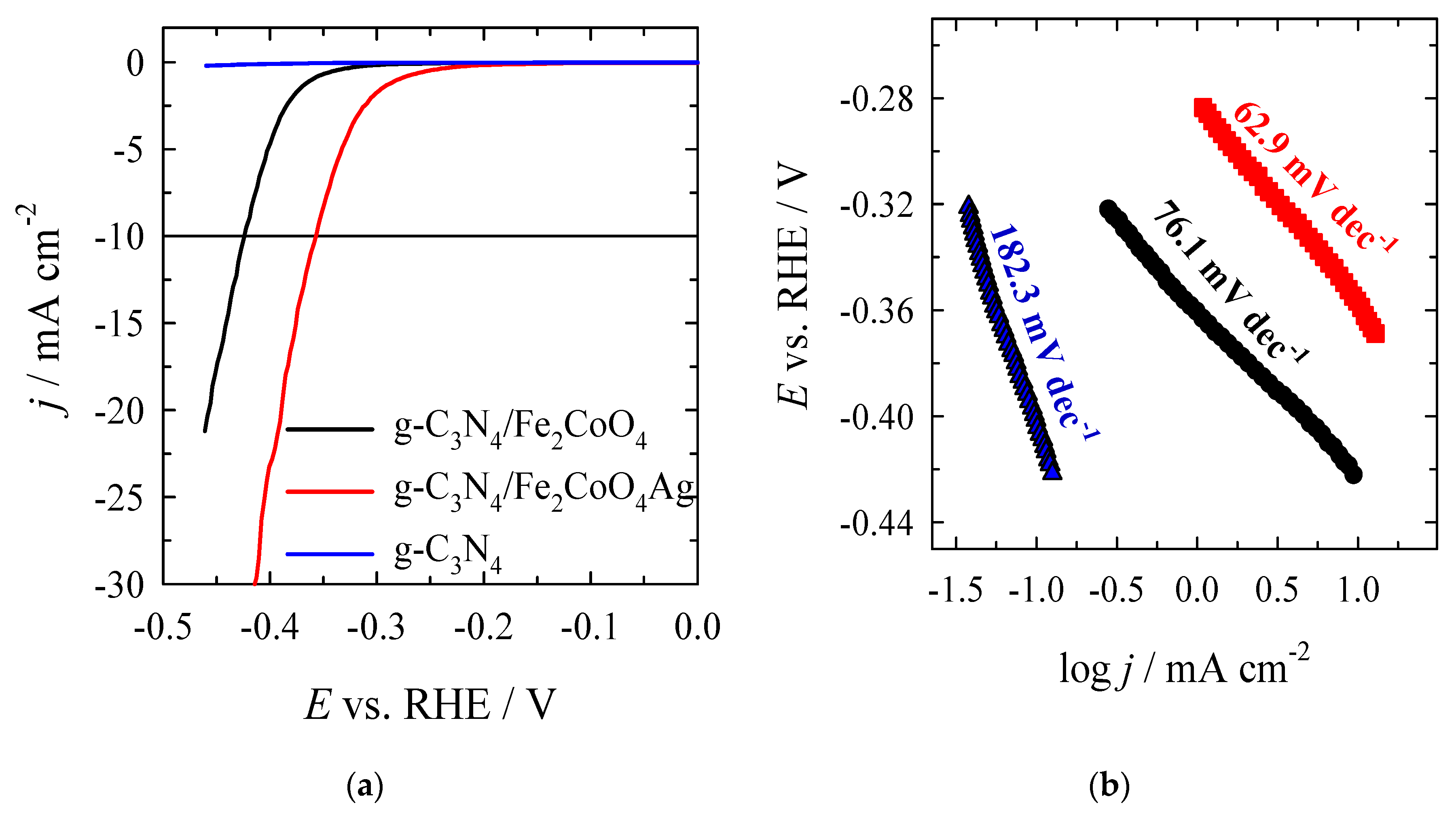
3.3. Investigation of Electrocatalysts Activity for OER
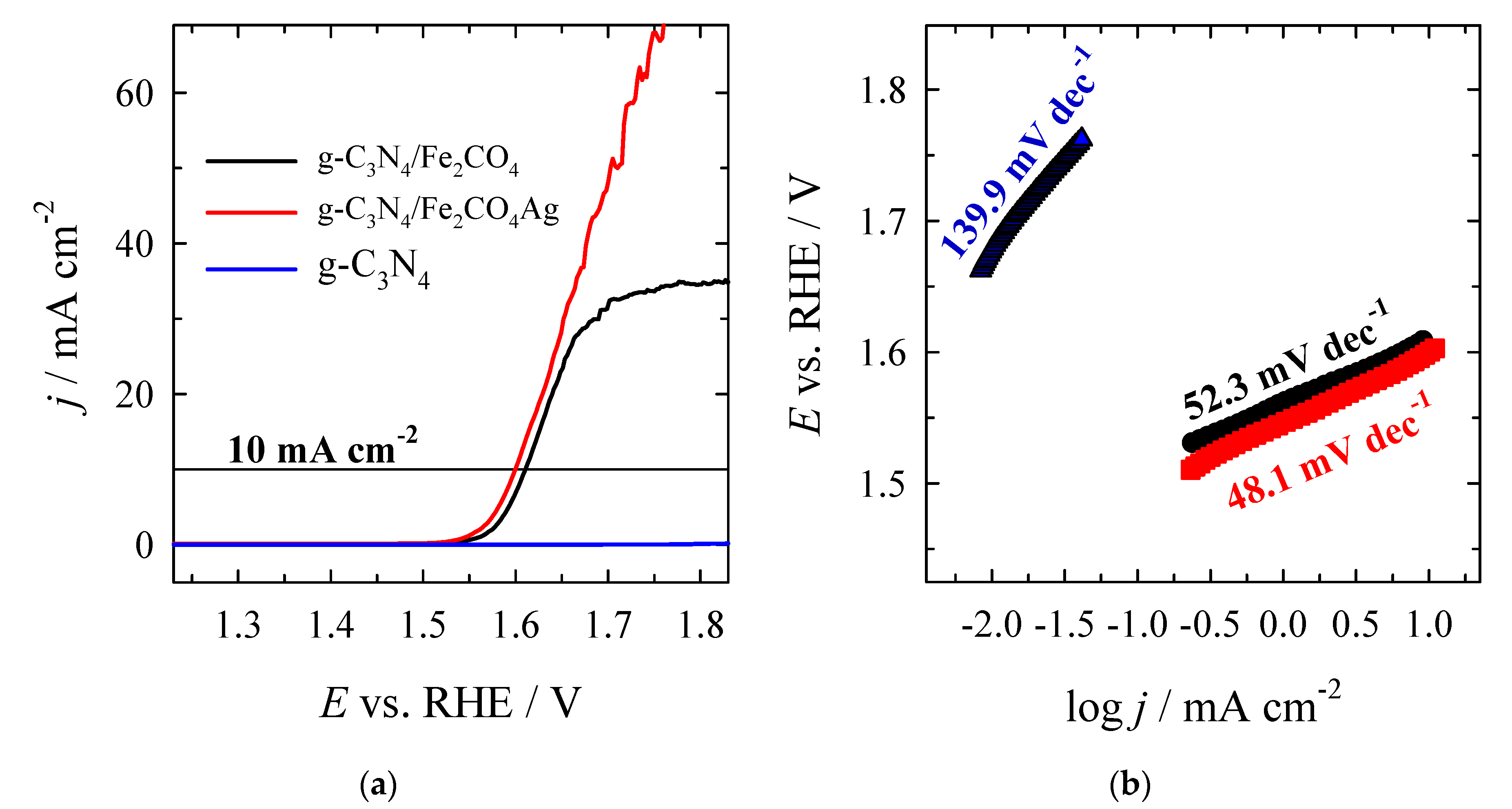
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Y.; Yao, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xu, C. Perspective of hydrogen energy and recent progress in electrocatalytic water splitting. Chin. J. Chem. Engineer. 2022, 43, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-Y.; Duan, Y.; Feng, X.-Y.; Yu, X.G.; Gao, M.-R.; Yu, S.-H. Clean and affordable hydrogen fuel from alkaline water splitting: past, recent progress, and future prospects. Adv. Mater 2007, 2007100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, X.; Meng, X. Recent advances on electrocatalytic and photocatalytic seawater splitting for hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 469087–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Wang, P.T.; Shao, Q.; Huang, X.Q. Metallic nanostructures with low dimensionality for electrochemical water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3072–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.; Sun, Y. Innovative strategies for electrocatalytic water splitting. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, A.; Shu, D.; Aftab, U.; Cao, D.; Laghari, A.J.; Solangi, M.Y.; Abro, M.I.; Nafady, A.; Vigolo, B.; Tahira, A.; Ibupoto, Z. H. Co2FeO4@rGO composite: Towards trifunctional water splitting in alkaline media. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 33919–33937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Meng, J.; Jiao, L.; et al. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 760–10. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Fischer, A.; Goettmann, F.; Antonietti, M.; Müller, J.-O.; Schlügl, R.; Carlsson, J. M. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hwang, S.; Yu, J.S. Novel ordered nanoporous graphitic C3N4 as a support for Pt–Ru anode catalyst in direct methanol fuel cell. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewolt, M.; Antonietti, M. Synthesis of g-C3N4 nanoparticles in mesoporous silica host matrices. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1789–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.C.; Li, Z.S.; Zou, Z.G. Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4 fabricated by directly heating melamine. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10397–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Shen, L.H.; et al. Preparation and characterization of graphitic carbon nitride through pyrolysis of melamine. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 94, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lou, Z.; Liao, Y.; Xue, C. Temperature-controlled morphology evolution of graphitic carbon nitride nanostructures and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49317–49325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, S. Noble metal-free electrocatalytic materials for water splitting in alkaline electrolyte. EnergyChem 2021, 3, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, E.; An, X.; Hao, X.; Guan, G. Transition metal-based catalysts for electrochemical water splitting at high current density: current status and perspectives. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 12788–127817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wilkinson, D.P. Non-noble metal electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution rea-ction in water electrolysis. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2021, 4, 473–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naggar, A.H.; Shinde, N.M.; Kim, J.-S.; Mane, R.S. Water splitting performance of metal and non-metal-doped transi-tion metal oxide electrocatalysts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 474, 214864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Ni, B.J. Cost-effective catalysts for renewable hydrogel production via electrochemical water splitting: Recent advances. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Eisenberg, R. Catalysts made of earth-abundant elements (Co, Ni, Fe) for water splitting: recent progress and future challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6012–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, T.; Jiao, L. Transition-metal (Fe, Co, and Ni)-based nanofiber electrocatalysts for water splitting. Adv. Fi-ber Mater. 2021, 3, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Transition-metal (Co, Ni, and Fe)-based electrocatalysts for the water oxidation reaction. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9266–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Ai, H.; Chen, M.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; et al. Multi-phase heterostructure of CoNiP/CoxP for enhanced hydrogel evolution under alkaline and seawater conditions by promoting H2O dissociation. Small 2021, 17, 2007557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Ma, A.; Abbas, S.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Choe, H.R.; Jo, S.Y.; Nam, K. M. A new synthetic approach to cobalt oxides: Designed phase transformation for electrochemical water splitting. Chem. Engineer. J. 2021, 415, 127958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraivel, M.; Nagappan, S.; Park, K.H.; Prabakar, K. Hierarchical 3D flower like cobalt hydroxide as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 411, 140071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Kang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhu, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Self-supported cobalt nitride porous nanowire arrays as bi-functional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 273, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, G.; Duan, L.; Kou, Z.; Wang, J. In situ coupled amorphous cobalt nitride with nitrogen-doped graphene aerogel as a trifunctional electrocatalyst towards Zn-air battery deriven full water splitting. Appl. Catal. B: Environm. 2019, 259, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Du, P.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, C. One-step synthesis of mesoporous cobalt sulfides (CoSx) on the metal substrate as an efficient bifunctional electrode for overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Ke, N.; Dong, B.; Huang, A.; Tan, C.; Yin, L.; Xu, X.; Hao, L.; Xian, Y.; Agathopoulos, S. Self-supported co-balt/cobalt selenide heterojunction for highly efficient overall water splitting. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 925, 166683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, R.; Yang, F.; Tian, X.; Sui, H.; Feng, L. An overview of heteroatom doped cobalt phosphide for efficient elec-trochemical water splitting. Chem. Engineer. J. 2023, 456, 141056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghunath, B.S.; Rajasekaran, S.; KR, S.D.; Pinheiro, D.; UC, J.R.J. N-doped graphene quantum dots incorporated cobalt ferrite/graphitic carbon nitride ternary composite for electrochemical overall water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 2906–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, F.T.; Rabe, A.; Schmidt, F.-P.; Herzog, A.; Jeon, H.S.; Frandsen, W.; Narangoda, P.V.; Spanos, I.; Ortega, K.F.; Timoshenko, J.; Lunkenbein, T.; Behrens, M.; Bergmann, A.; Schlögl, R.; Cuenya, B. R. Role of nanoscale inhomogeneities in Co2FeO4 catalysts during the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12007–12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Qin, P.; Luo, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, R.; Chu, P.K. Recent progress and perspective of cobalt-based catalysts for water splitting: design and nanoarchitectonics. Mat. Today Energy 2022, 23, 10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Liu, J. Recent advances in cobalt-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lou, Z.; Liao, Y.; Xue, C. Temperature-controlled morphology evolution of graphitic carbon nitride nanostructures and their photocatalytic activities under visible light. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49317–49325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chu, Y.-C.; Wang, M.-S.; Xiao-Han, W. Rapid synthesis of g-C3N4 spheres using microwave-assisted solvothermal method for enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2017, 348, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, Y.; Xu, H.; Cui, D.; Xue, C.; Zhang, W. A facile and green microwave hydrothermal method for fabricating g-C3N4 nanosheets with improved hydrogen evolution performance. J. Alloys Compn. 2021, 863, 158448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, A.; Sinsermsuksakul, P.; Yang, P. Polyhedral silver nanocrystals with distinct scattering signatures. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4597–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.X.; Lu, T.L.; Han, L.; Zhan, Y. Z. Graphitic carbon nitride (g–C3N4) as an efficient metal-free Fenton-like catalyst for degrading organic pollutants: the overlooked non-photocatalytic activity. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, H.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Du, P.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, C. One-step synthesis of mesoporous cobalt sulfides (CoSx) on the metal substrate as an efficient bifunctional electrode for overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevová, M.; Hnát, J.; Bouzek, K. Electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline and neutral media. A comparative review. J. Power Sources 2021, 507, 230072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanan, A.; Lakhan, M.N.; Shu, D.; Hussain, A.; Ahmed, M.; Soomro, I.A.; Kumar, V.; Cao, D. An efficient and durable bifunctional electrocatalysts based on PdO and Co2FeO4 for HER and OER. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 19494–19508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, R.; Pervaiz, E.; Baig, M.M.; Rabi, O. Three-dimensional hierarchical flowers-like cobalt-nickel sulfide constructed on graphitic carbon nitride: bifunctional non-noble electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 418, 140346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.-K.; Moru, S.; Tonda, S. Cobalt-coordinated sulfur-doped graphitic carbon nitride on reduced graphene oxide: an efficient metal−(N,S)−C-class bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting in alkaline media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15373–15384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Biswas, R. A.; Patil, K. K.; Halder, H.; Singh, B.; Banerjee, B.; Kumar, Y.-R.; Ma, K. K.; Haldar, *!!! REPLACE !!!*. Graphitic carbon nitride composites with MoO3-decorated Co3O4 nanorods as catalysts for oxygen and hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl. Nano Mat. 2021, 4, 12672–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Eonset, V at j = −0.1 mA cm−2 | η10*, mV | Tafel slope, mV dec−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| g–C3N4 | −0.40 | − | 182.3 |
| CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | −0.280 | −424.6 | 76.1 |
| Ag/CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | −0.161 | −259.0 | 62.9 |
| Catalysts | Eonset, V at j = 0.1 mA cm−2 | ηonset, mV | E, V at j = 10 mA cm−2 | η10*, mV | Tafel slope, mV dec−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g–C3N4 | 1.6404 | 410.4 | – | – | 139.9 |
| CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | 1.5056 | 275.6 | 1.6127 | 382.7 | 52.3 |
| Ag/CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | 1.4855 | 255.5 | 1.6000 | 370.2 | 48.1 |
| Catalyst | Electrolyte | HER | OER | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| η10*, mV | Tafel slope, mV dec−1 | η10*, mV | Tafel slope, mV dec−1 | |||
| CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | 1 M KOH | 424.6 | 76.1 | 382.7 | 52.3 | This study |
| Ag/CoFe2O4/g–C3N4 | 1 M KOH | 259.0 | 62.9 | 370.2 | 48.1 | This study |
| CoFe2O4/gCN/NGQDs | 1 M KOH | 287 | 96 | 445 | 69 | [30] |
| Co2FeO4@rGO (CFG-10) | 1 M KOH | 320 | 48 | 240at 20mA cm−2 | 51 | [6] |
| Co2FeO4@PdO | 1 M KOH | 269 | 49 | 259at 20mA cm−2 | 59 | [41] |
| CoNi2S4/gCN | 1 M KOH | 160 | 90.76 | 310at 30mA cm−2 | 49.86 | [42] |
| Co-SCN/RGO | 1 M KOH | 150 | 94 | 250 | 96 | [43] |
| Co3O4/g–C3N4 | 1 M KOH | 313 | 169 | 315 | 67 | [44] |
| Co3O4MoO3/g-C3N4 | 1 M KOH | 125 | 94 | 206 | 60 | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





