Submitted:
30 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. Theoretical Details
2.2. Cell Structure and Numerical Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
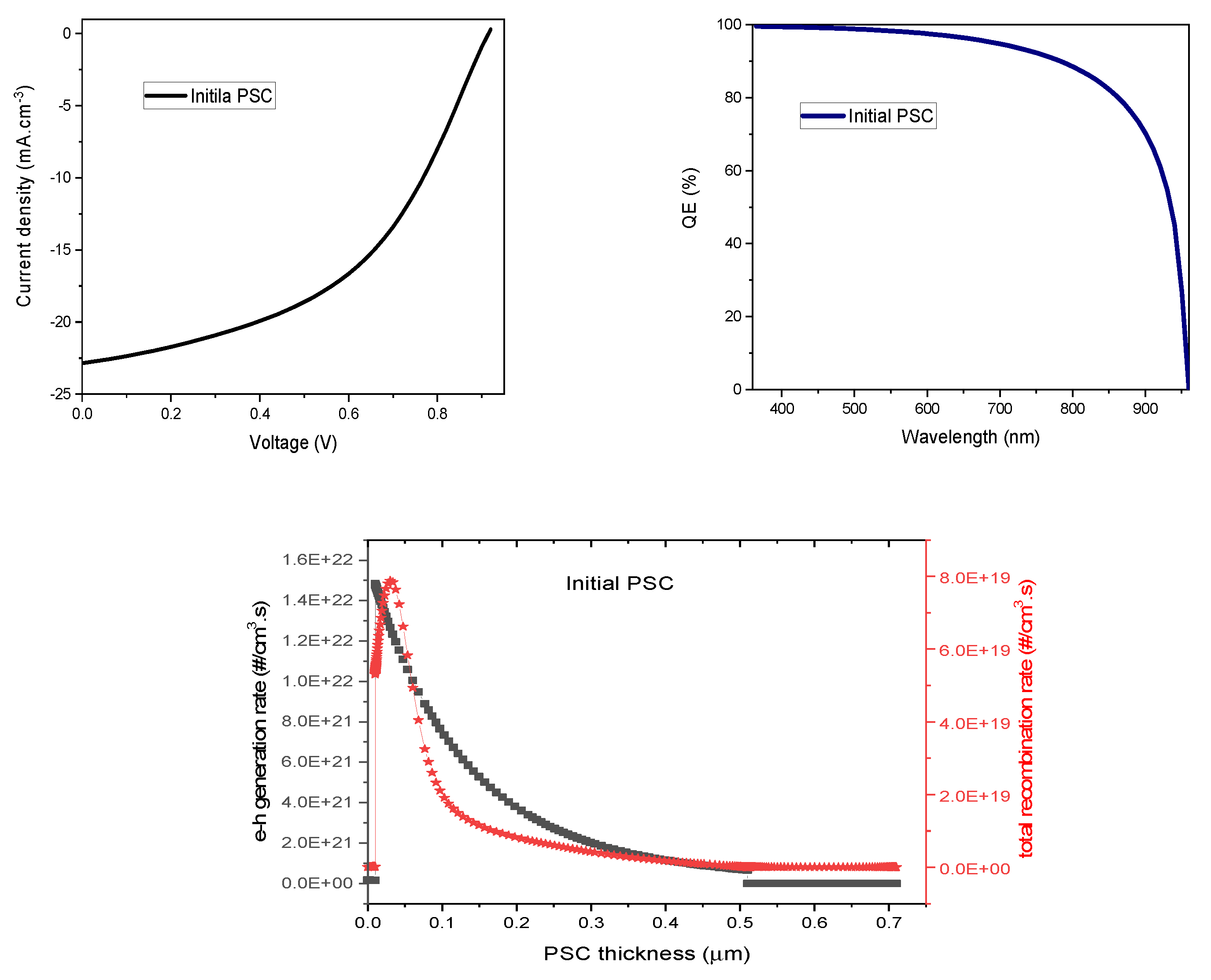
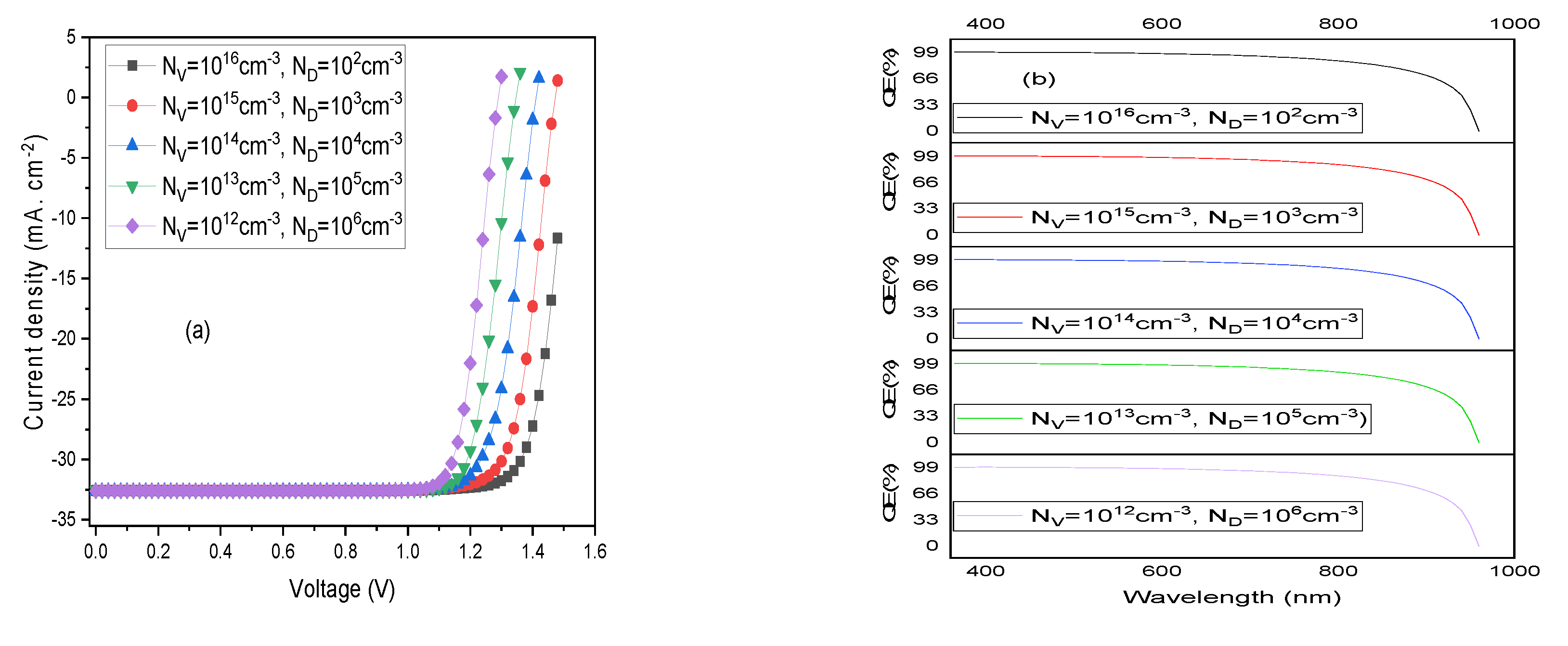
3.1. Initial PSC Simulation and Validation
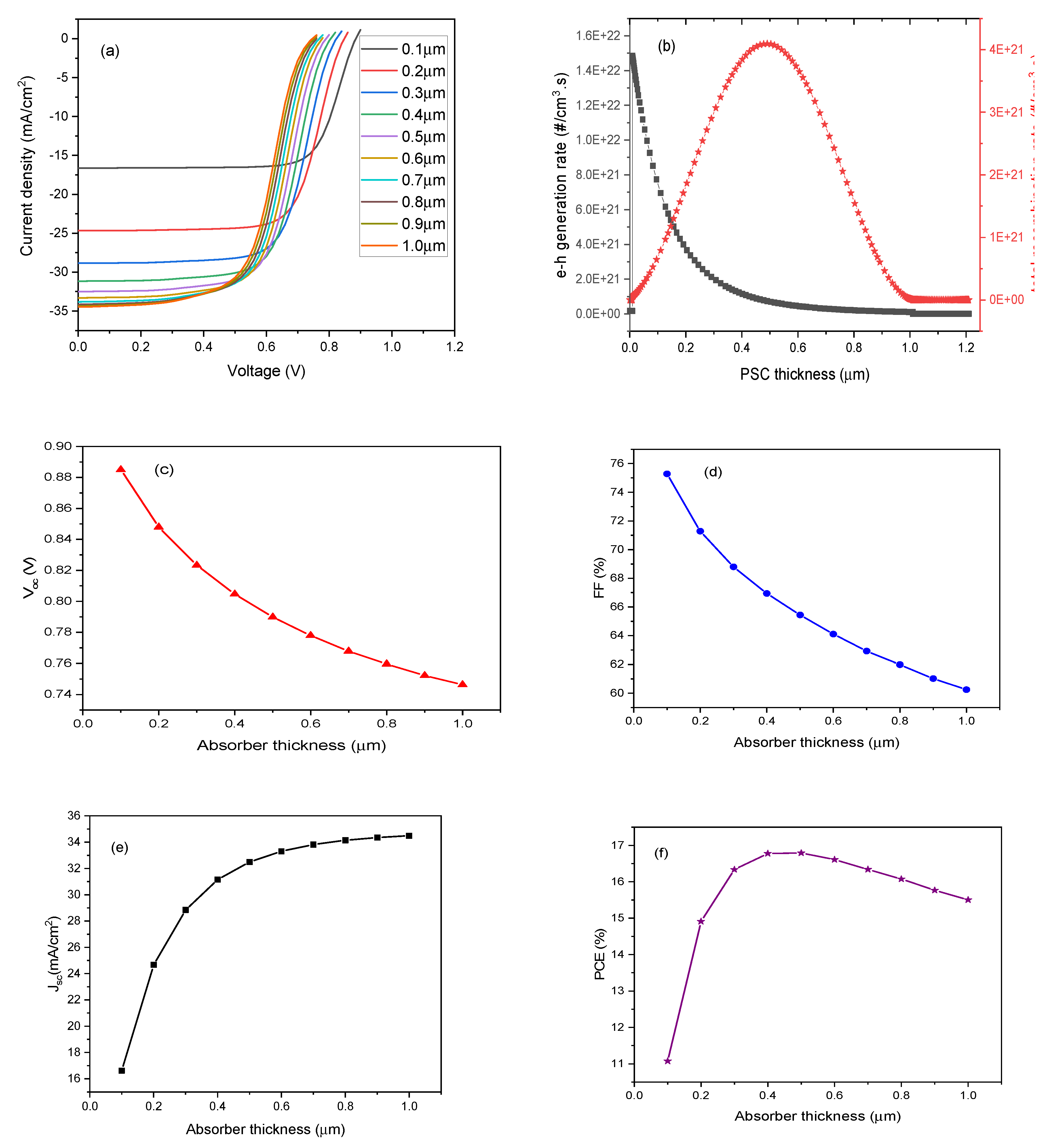
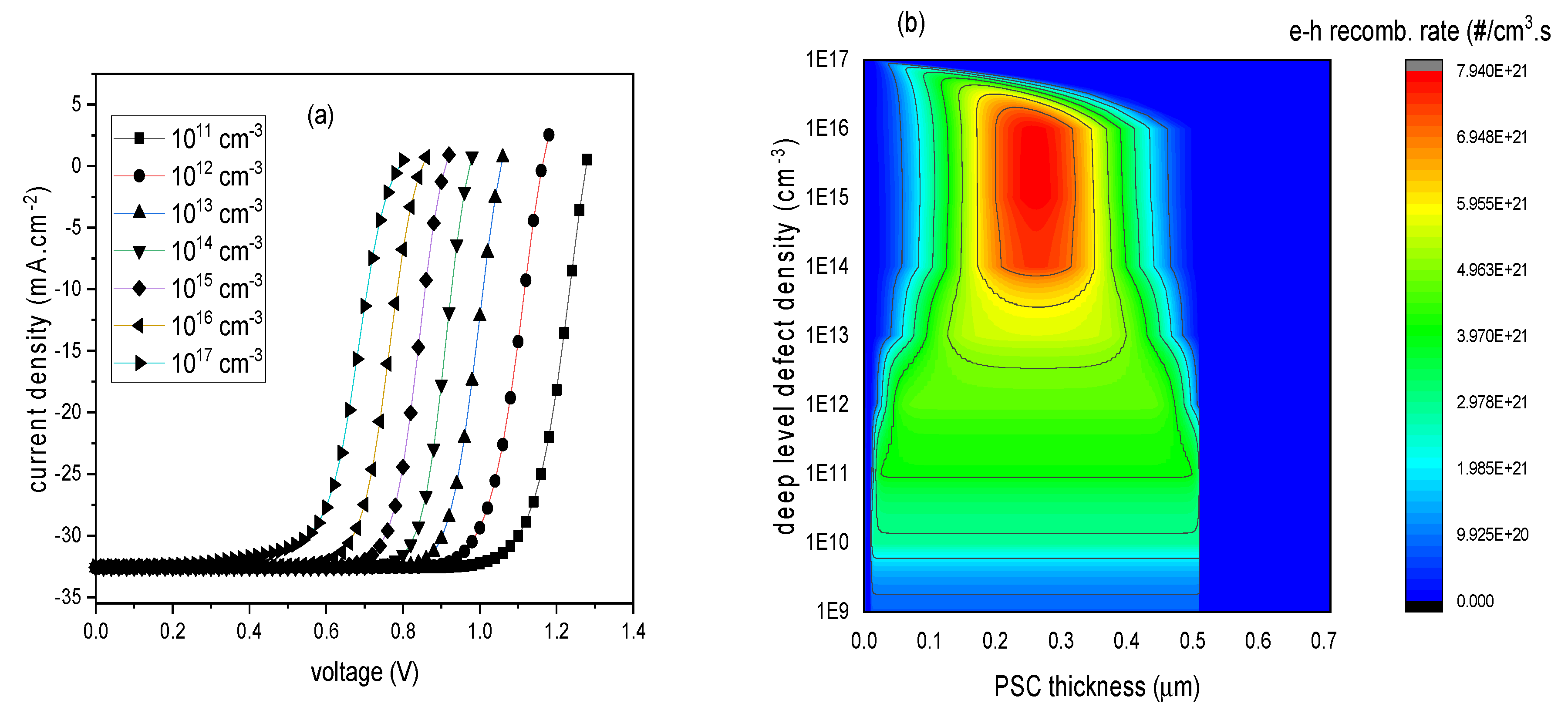
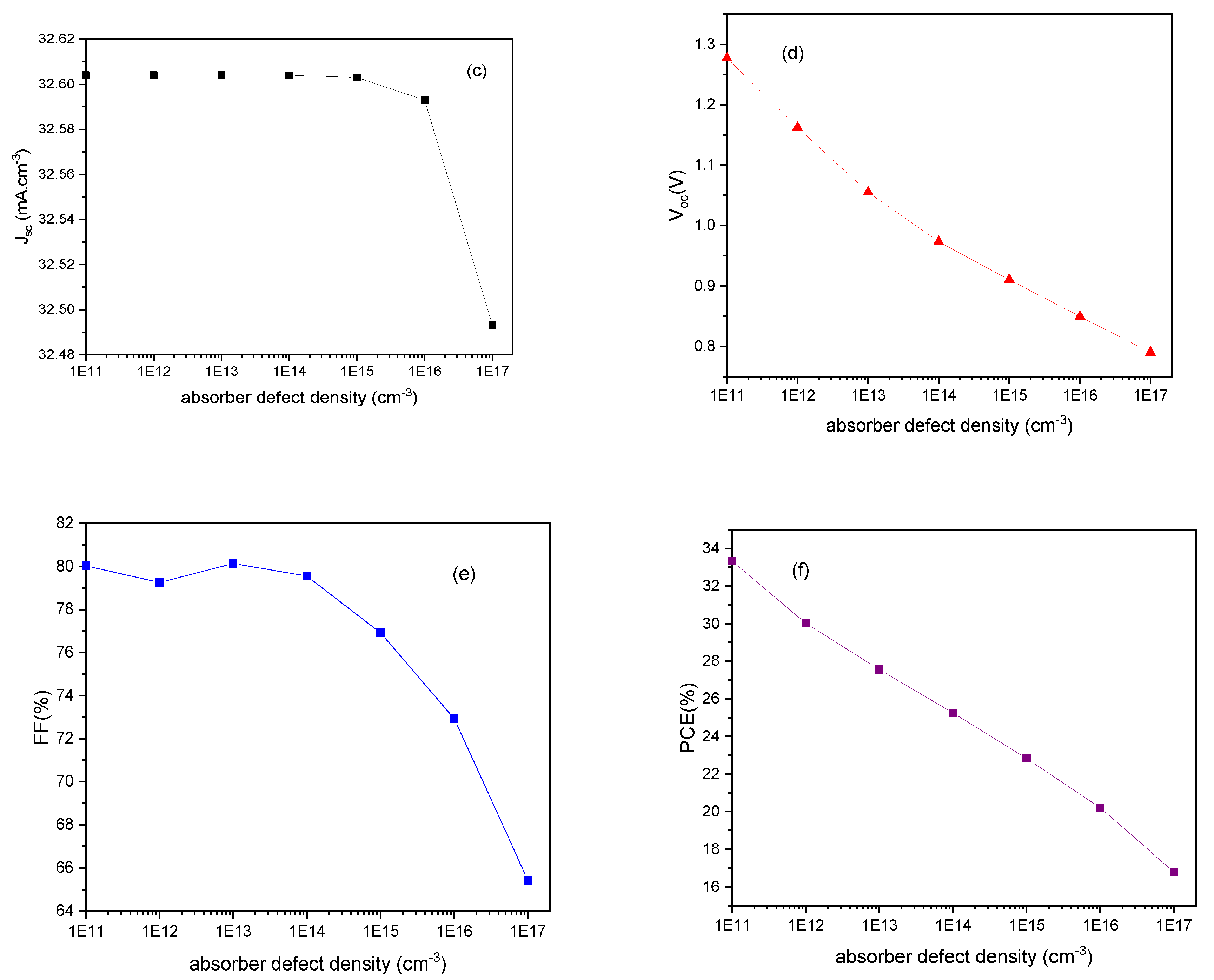
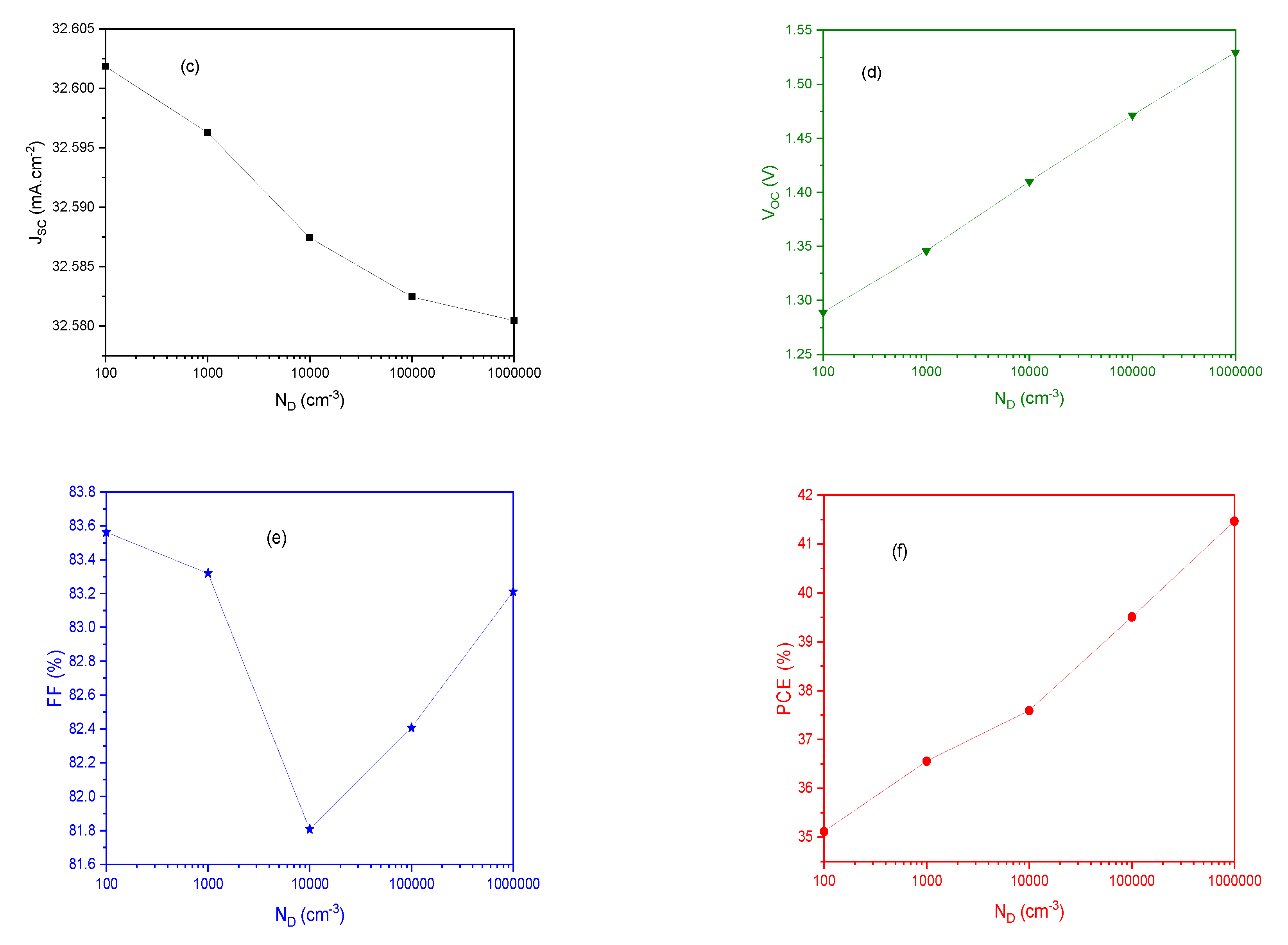
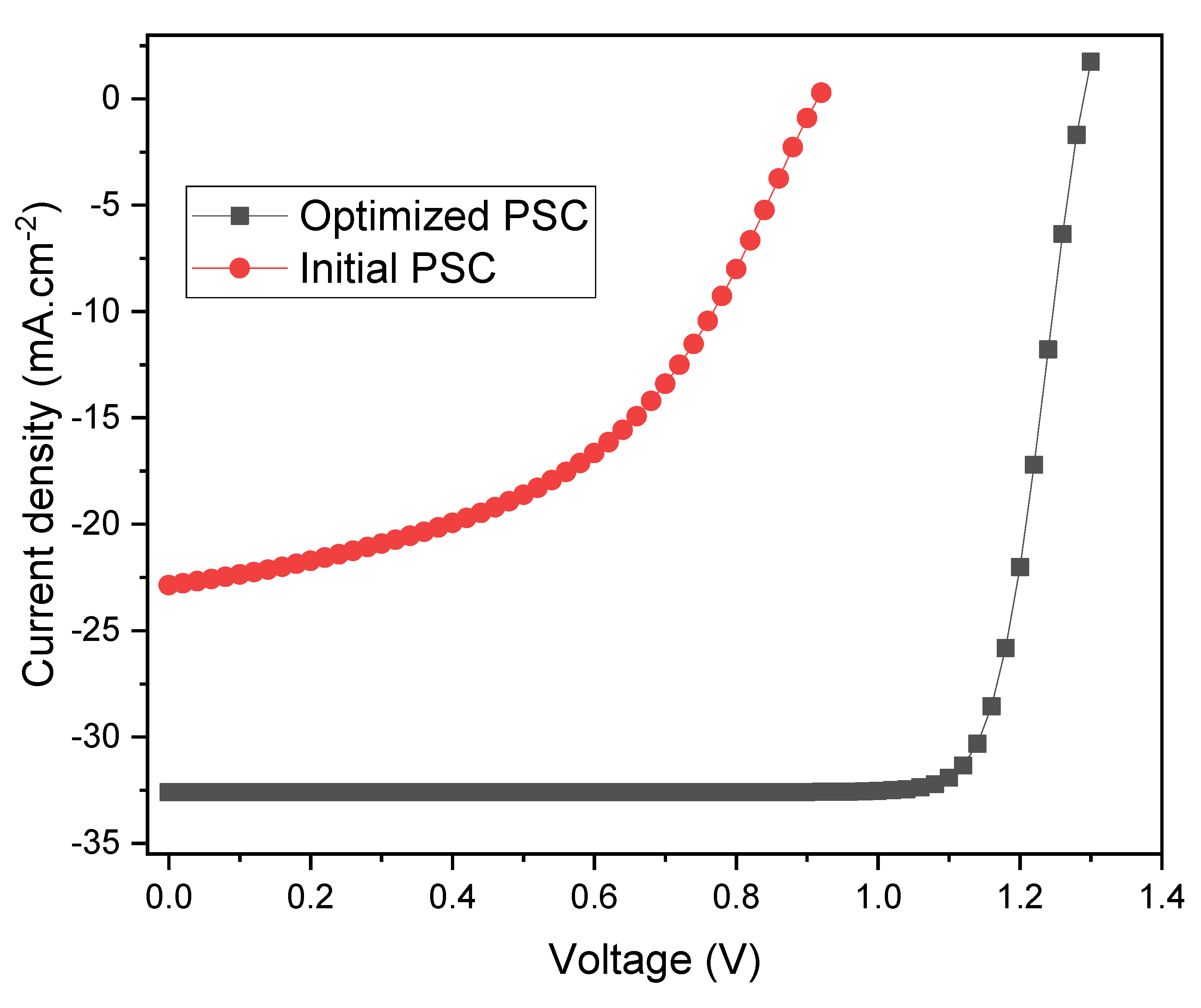
3.2. Absorber Enrichment and Device Optimization
4. Conclusions
References
- Wilson, G.M.; Al-Jassim, M.; Metzger, W.K.; Glunz, S.W.; Verlinden, P.; Xiong, G.; Mansfield, L.M.; Stanbery, B.J.; Zhu, K.; Yan, Y. The 2020 photovoltaic technologies roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 493001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Goyal, S.K.; Kumar, P. Solar PV cell materials and technologies: Analyzing the recent developments. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METGroup. Renewable and Solar Energy Vs Fossil Fuels. Available online: https://group.met.com/en/mind-the-fyouture/mindthefyouture/solar-energy-vs-fossil-fuels (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- PV Magazine. World has Installed 1 TW of Solar Capacity. Available online: https://www.pv-magazine.com/2022/03/15/humans-have-installed-1-terawatt-of-solar-capacity/ (accessed on 25 November 2022); https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/03/22/new-global-solar-capacity-additions-hit-191-gw-in-2022-says-irena/ (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Statista. Global Cumulative Installed Solar PV Capacity 2000-2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/280220/global-cumulative-installed-solar-pv-capacity/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Marques Lameirinhas, R.A.; Torres, J.P.N.; de Melo Cunha, J.P. A Photovoltaic Technology Review: History, Fundamentals and Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuszak, J.; Wegierek, P. Photovoltaic Cell Generations and Current Research Directions for Their Development. Materials 2022, 15, 5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lan, K.; Mei, A.; Sheng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Han, H. Fully printable hole-conductor-free mesoscopic perovskite solar cells based on mesoporous anatase single crystals. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Ji, L.; Liu, C.; Ahmad, W.; Chen, Z. D.; Li, S. Perovskite Solar Cells with ZnO Electron-Transporting Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Fu, W. Improved performance and stability of perovskite solar cells with bilayer electron-transporting layers. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Z. S. Enhanced interfacial electron transfer of inverted perovskite solar cells by introduction of CoSe into the electron-transporting-layer. J. Power Sources 2017, 353, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A. K.; Numata, Y.; Ikegami, M.; Miyasaka, T. Role of spiro-OMeTAD in performance deterioration of perovskite solar cells at high temperature and reuse of the perovskite films to avoid Pb-waste. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C. H.; Ripolles, T. S.; Hamada, K.; Teo, S. H.; Lim, H. N.; Bisquert, J.; Hayase, S. Tunable Open Circuit Voltage by Engineering Inorganic Cesium Lead Bromide/Iodide Perovskite Solar Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, M.; Griffiths, J.; Fraser, J.; Kirkus, M.; Chen, H.; Nielsen, C. B.; McCulloch, I. High mobility, hole transport materials for highly efficient PEDOT:PSS replacement in inverted perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NREL. Best Research-Cell Efficiency Chart. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-effienciency.html (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Sharma, P.; Goyal, P. Evolution of PV technology from conventional to nano-materials. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, J.P.C.; Abate, A.; Saliba, M.; Tress,W.; Jacobsson, J.; Grätzel, M.; Hagfeldt, A. The rapid evolution of highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 710–727. [CrossRef]
- Haider, S. Z.; Anwar, H.; Wang, M. Theoretical Device Engineering for High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells Using CuSCN as Hole Transport Material Boost the Efficiency Above 25%. Phys. Status Solidi A 2019, 216, 1900102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kima, B. and Seok, S.I. Molecular aspects of organic cations affecting the humidity stability of perovskites. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 805–820. [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, M.; Griffiths, J.; Fraser, J.; Kirkus, M.; Chen, H.; Nielsen, C. B.; McCulloch, I. High mobility, hole transport materials for highly efficient PEDOT:PSS replacement in inverted perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 4940–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Y.; Deng, L. L.; Dai, S. M.; Wang, X.; Tian, C. B.; Zhan, X. X.; Xie, S. Y.; Huang, R. B.; Zheng, L. S. Low-cost solution-processed copper iodide as an alternative to PEDOT:PSS hole transport layer for efficient and stable inverted planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19353–19359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Chu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Xin, J. Synergistic Effect to High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells with Reduced Hysteresis and Improved Stability by the Introduction of Na-Treated TiO2 and Spraying-Deposited CuI as Transport Layers ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 41354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumara, G.R.R.A.; Konno, A.; Senadeera, G.K.R.; Jayaweera, P.V.V.; De Silva, D.B.R.A.; Tennakone, K. Dye-Sensitized solar cell with the hole collector p-CuSCN deposited from a solution in n-Propyl sulphide. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 69, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Yum, J.-H.; Moon, S.-J.; Chen, P. Inorganic p-Type Semiconductors: Their Applications and Progress in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells and Perovskite Solar Cells. Energies 2016, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehl, R.; Thiele, G. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Me3NHCu2(SCN)3, Me2C=NMe2Cu2(SCN)3, and Me2C=NMe2Ag2(SCN)3. Three-dimensional Networks of Thiocyanatometallates(I). Zeitschrift für Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie 2000, 626, 2167–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrov, B.; Hagfeldt, A.; Lenzmann, F.; Boschloo, G. Comparison of charge accumulation and transport in nanostructured dye-Sensitized solar cells with electrolyte or CuSCN as hole conductor. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 88, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanasattayavong, P.; Ndjawa, G. O. N.; Zhao, K.; Chou, K. W.; Yaacobi-Gross, N.; O’Regan, B. C.; Amassian, A.; Anthopoulos, T. D. Electric field-induced hole transport in copper(i) thiocyanate (CuSCN) thin-films processed from solution at room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4154–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I. S.; Sohn, M. R.; Do Sung, S.; Kim, Y. J.; Yoo, Y. J.; Kim, J.; Lee, W. I. Formation of pristine CuSCN layer by spray deposition method for efficient perovskite solar cell with extended stability. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Tanaka, S.; Ito, S.; Tetreault, N.; Manabe, K.; Nishino, H.; Nazeeruddin, M. K.; Gratzel, M. Inorganic hole conductor-based lead halide perovskite solar cells with 12.4% conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Kim, Y. C.; Jeon, N. J.; Yang, W. S.; Seo, J.; Noh, J. H.; Seok, S. I. Thermal Stability of CuSCN Hole Conductor-Based Perovskite Solar Cells. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttu, N. Shockley–Queisser Detailed Balance Efficiency Limit for Nanowire Solar Cells. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W. E. I.; Ren, X.; Chen, L.; Choy, W. C. H. The efficiency limit of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostefaoui, M.; Mazari, H.; Khelifi, S.; Bouraiou, A.; Dabou, R. Simulation of High Efficiency CIGS Solar Cells with SCAPS-1D Software. Energy Procedia 2015, 74, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshniwal, A.; Jariwala, A.; Kheraj, V.; Opanasyuk, A. S.; Panchal, C. J. Numerical Simulation of Tin Based Perovskite Solar Cell: Effects of Absorber Parameters and Hole Transport Materials. jnep 2017, 9, 03038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S. Z.; Anwar, H.; Wang, M. A comparative study of interface engineering with different hole transport materials for high-performance perovskite solar cells. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2018, 33, 35001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Mahbub, R.; Satter, S. S.; Ullah, S. M. Effect of Different HTM Layers and Electrical Parameters on ZnO Nanorod-Based Lead-Free Perovskite Solar Cell for High-Efficiency Performance. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayigit, A.; Duy Thanh, D.; Ethirajan, A.; Manca, J.; Muller, M.; Boyen, H.G.; Conings, B. Assessing the toxicity of Pb- and Sn-based perovskite solar cells in model organism Danio rerio. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, H. L.; Jiao, W. B.; Wang, Q.; Wei, M.; Cantone, I.; Lü, J.; Abate, A. Biological impact of lead from halide perovskites reveals the risk of introducing a safe threshold. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 1–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. T.; Jani, M. R.; Al Amin, S. M.; Sami, M. S. U.; Shorowordi, K. M.; Hossain, M. I.; Devgun, M.; Chowdhury, A. S.; Bernajee, S.; Ahmed, S. Numerical simulation studies of a fully inorganic Cs2AgBiBr6 perovskite solar device. Optical Materials 2020, 105, 109957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K. Meng, W., Wang, X., Yan, Y. & Mitzi, D. B. Bandgap Engineering of Lead-Free Double Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 through Trivalent Metal Alloying. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8158–8162.
- Ju, M.-G.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Garces, H. F.; Dai, J.; Ma, L.; Padture, N. P.; Zeng, X. C. Earth-Abundant Nontoxic Titanium(IV)-based Vacancy-Ordered Double Perovskite Halides with Tunable 1.0 to 1.8 eV Bandgaps for Photovoltaic Applications. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Ju, M-G.; Garces, H. F.; Ding, T.; Pang, S.; Zeng, X. C.; Padture, N. P.; Sun, X. W. Heterojunction-Depleted Lead-Free Perovskite Solar Cells with Coarse-Grained B-γ-CsSnI3 Thin Films. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 01, 130.
- Canil, L.; Salunke, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Köbler, H.; Flatken, M.; Gregori, L.; Meggiolaro, D.; Ricciarelli, D.; De Angelis, F.; Stolterfoht, M.; Neher, D.; Priimagi, A.; Vivo, P.; Abate, A. Halogen-Bonded Hole-Transport Material Suppresses Charge Recombination and Enhances Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 01, 553.
- Chen, M.; Ju, M-G.; Garces, H. F.; Carl, A. D.; Ono, L. K.; Hawash, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, T.; Qi, Y.; Grimm, R. L.; Pacifici, D.; Zeng, X. C.; Zhou, Y.; Padture, N. P. Highly stable and efficient all-inorganic lead-free perovskite solar cells with native-oxide passivation. Nature Commun. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liu, J.; Portale, G.; Fang, H-H.; Blake, G. R.; Brink, G. H.; L. Jan Anton Koster, J. A.; Loi, M. A. Highly Reproducible Sn-Based Hybrid Perovskite Solar Cells with 9% Efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targhi, F. F.; Jalili, Y. S.; Kanjouri, F. MAPbI3 and FAPbI3 perovskites as solar cells: Case study on structural, electrical and optical properties. Results in Physics 2018, 10, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K. P.; Walker, M.; Walton, R. I.; Hatton, R. A. Enhanced stability and efficiency in hole-transport-layer-free CsSnI3 perovskite photovoltaics. Nature Energy 2016, 1, 16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Lee, B.; He, J.; Chang, R.P.H.; Kanatzidis, M.G. All-Solid-State Dye-Sensitized solar cells with high efficiency. Nature 2012, 485, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lan, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, M.; Huang, Y.; Fan, L.; Luo, G. Electrolytes in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2136–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, U.; Daeneke, T. A Solid Advancement for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10451–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallouk, T.E. Applied chemistry: Molecules meet materials. Nature 2012, 485, 450–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.J.; Ren, Y.; Yu, C.; Shum, K. Schottky solar cells based on CsSnI3 thin-films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, K.; Chen, Z.; Qureshi, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, J.J.; Pfenninger, W.; Vockic, N.; Midgley, J.; Kenney, J.T. Synthesis and characterization of CsSnI3 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 221903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Z.J.; Wang, J.; Pfenninger, W.; Vockic, N.; Kenney, J.T.; Shum, K. Temperature dependence of the band gap of perovskite semiconductor compound CsSnI3. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 063526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, C.; Shum, K.; Wang, J.J.; Pfenninger, W.; Vockic, N.; Midgley, J.; Kenney, J.T. Photoluminescence study of polycrystalline CsSnI3 thin films: Determination of exciton binding energy. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Funabiki, S.; Horimoto, H.; Matsui, T.; Okuda, T.; Ichiba, S. Structural Phase Transitions of the Polymorphs of CsSnI3 by Means of Rietveld Analysis of the X-Ray Di_raction. Chem. Lett. 1991, 20, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Song, J.-H.; Im, J.; Androulakis, J.; Malliakas, C.D.; Li, H.; Freeman, A.J.; Kenney, J.T.; Kanatzidis, M.G. CsSnI3: Semiconductor or Metal? High Electrical Conductivity and Strong Near-Infrared Photoluminescence from a Single Material. High Hole Mobility and Phase-Transitions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8579–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Garces, H.F.; Senturk, B.S.; Ortiz, A.L.; Padture, N.P. Room temperature “one-Pot” solution synthesis of nanoscale CsSnI3 orthorhombic perovskite thin films and particles. Mater. Lett. 2013, 110, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Lee, B. H.; He, J.; Chang, R.; Kanatzidis, M.G. All-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with high efficiency. Nature 2012, 485, 486–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sze, S.M.; Ng, K. Physics of Semiconductor Devices; John Wiley & Sons:, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M. H.; Dharani, S.; Leong, W. L. , Boix, P. P.; Prabhakar, R. R.; Baikie, T.; Shi, C.; Ding, H.; Ramesh, R.; Asta, M.; Graetzel M.; Mhaisalkar, S. G.; Mathews, N. Lead-free halide perovskite solar cells with high photocurrents realized through vacancy modulation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7122–7127. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, G.; Xu, Q.; Garces, H. F.; Solanki, A.; Goh, T. W.; Padture, N. P.; Sum, T. C. Long minority-carrier diffusion length and low surface-recombination velocity in inorganic lead-free CsSnI3 perovskite crystal for solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, V.; Erhart, P.; Li, S.; Rachut, K.; Morasch, J.; Brötz, J.; Reckers, P.; Mayer, T.; Rühle, S.; Zaban, A.; Mora Sero, I.; Bisquert, J.; Jaegermann, W.; Klein, A. Klein, Energy Band Alignment between Anatase and Rutile TiO2. J Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 4182–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyasinghe, N.; Regoutz, A.; Eisner, F.; Du, T.; Tsetseris, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Faber, H.; Pattanasattayavong, P.; Li, J.; Yan, F.; McLachlan, M.A.; Payne, D.J.; Heeney, M.; Anthopoulos, T.D. Copper(I) Thiocyanate (CuSCN) Hole-Transport Layers Processed from Aqueous Precursor Solutions and Their Application in Thin-Film Transistors and Highly Efficient Organic and Organometal Halide Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, F. H.; Sheini, N. A.; . Lajvardi, M. M. Oxygen adsorption at noble metal/TiO2 junctions. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2016, 108, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Moddel, G. Metal Single-Insulator and Multi-Insulator Diodes for Rectenna Solar Cells; Springer, 2013; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lajvardi, M. M.; Jahangiri, M. Ni/TiO2 ultraviolet detector IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 108, 012031. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilov, S. A.; Zheleznyakova, A. V.; Dronov, A. A.; Dittrich, T. Efficiency Enhancement of Eta-cells Fabricated by SILAR Deposition. Phy. Chem. Appl. Nanostructures 2009, 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Boschloo, G.; Edvinsson, T.; Hagfeldt, A. Nanostructured Materials for Solar Energy Conversion, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, J. E.; Kaspar, T. C.; Droubay, T. C.; Varga, T.; Bowden, M. E.; Exarhos, G. J. Electronic and Defect Structures of CuSCN. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9111–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shi, W.; Xi, J.; Wang, D.; Shuai, Z. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Charge Transport in CH3NH3PbI3 Perovskites Predicted from First-Principles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M. I.; Alharbi, F. H.; Tabet, N. Copper oxide as inorganic hole transport material for lead halide perovskite based solar cells. Sol. Energy 2015, 120, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dandeneau, C. S.; Zhou, X.; Cao, G. ZnO nanostructures for dye-sensitized solar cells Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4087. [Google Scholar]
- Pattanasattayavong, P.; Promarak, V.; Anthopoulos, T. D. Electronic Properties of Copper(I) Thiocyanate (CuSCN). Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1600378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tu, J.; Li, T.; Tao, C.; Deng, X.; Li, Z. Convenient preparation of CsSnI3 quantum dots, excellent stability, and the highest performance of lead-free inorganic perovskite solar cells so far. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 7683–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Gu, X.; Kyaw, A. K.; Wang, D. H.; Priya, S.; Ye, T. Fully Inorganic CsSnI3-based solar cells with>6% efficiency and enhanced stability enabled by mixed electron transport layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Di, H.; Chang, B.; Yin, R.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, L. Efficient passivation strategy on Sn related defects for high performance all-inorganic CsSnI3 perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Ma, S.; Yang, D.; Hou, Y.; Yoon, J.; Wang, K.; Priya, S. Localized electron density engineering for stabilized B-γ CsSnI3-based perovskite solar cells with efficiencies >10%. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuo, L., Baoping Z., Tie-Yu L., Jin-Cheng Z., Huaqing P., Huanting C., Chuanjin L., Xirong L., Jinrong Z. Inorganic Lead-Free B-γ-CsSnI3 Perovskite Solar Cells Using Diverse Electron-Transporting Materials: A Simulation Study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 26689–26698. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T-B.; Yokoyama, T.; Stoumpos, C. C.; Logsdon, J.; Cao, D. H.; Wasielewski, M. R.; Aramaki, S.; Kanatzidis, M. G. Importance of reducing vapor atmosphere in the fabrication of Tin-based perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T-B.; Yokoyama, T.; Aramaki, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Performance enhancement of lead-free tin-based perovskite solar cells with reducing atmosphere-assisted dispersible additive. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Chen, C.; Gu, S.; Lin, R.; Zhu, J. CsSnI3 Solar Cells via an Evaporation- Assisted Solution Method. Sol. RRL. 2018, 2, 1700224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Moon, S.H.; Im, S.H.; Hong, K.H. Roles of SnX2 (X=F, Cl, Br) additives in tin-based halide perovskites toward highly efficient and stable lead-free perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 6024–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, H.; Zhang, T.; Gong, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.-L.; Pootrakulchote, N.; Shen, Y.; Wang, M. Fully inorganic CsSnI3 mesoporous perovskite solar cells with high efficiency and stability via coadditive engineering, Sol. RRL. 2021, 5, 2100069. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T.; Wang, K.; Hou, Y.; Yang, D.; Smith, N.; Magill, B.; Yoon, J.; Mudiyanselage, R. H. H.; Khodaparast, G. A.; Wang, K.; Priya, S. Ambient-air-stable lead-free CsSnI3 Solar cells with greater than 7.5% efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4319–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, H.; Nakajima, T.; Liu, Z.; Yu, H.; Sun, Q.; Dai, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X-L; Zhu, J.; Chen, P.; Mingkui Wang, M. Over 8% efficient CsSnI3-based mesoporous perovskite solar cells enabled by two-step thermal annealing and surface cationic coordination dual treatment. J. Mater. Chem. 2022, 10, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
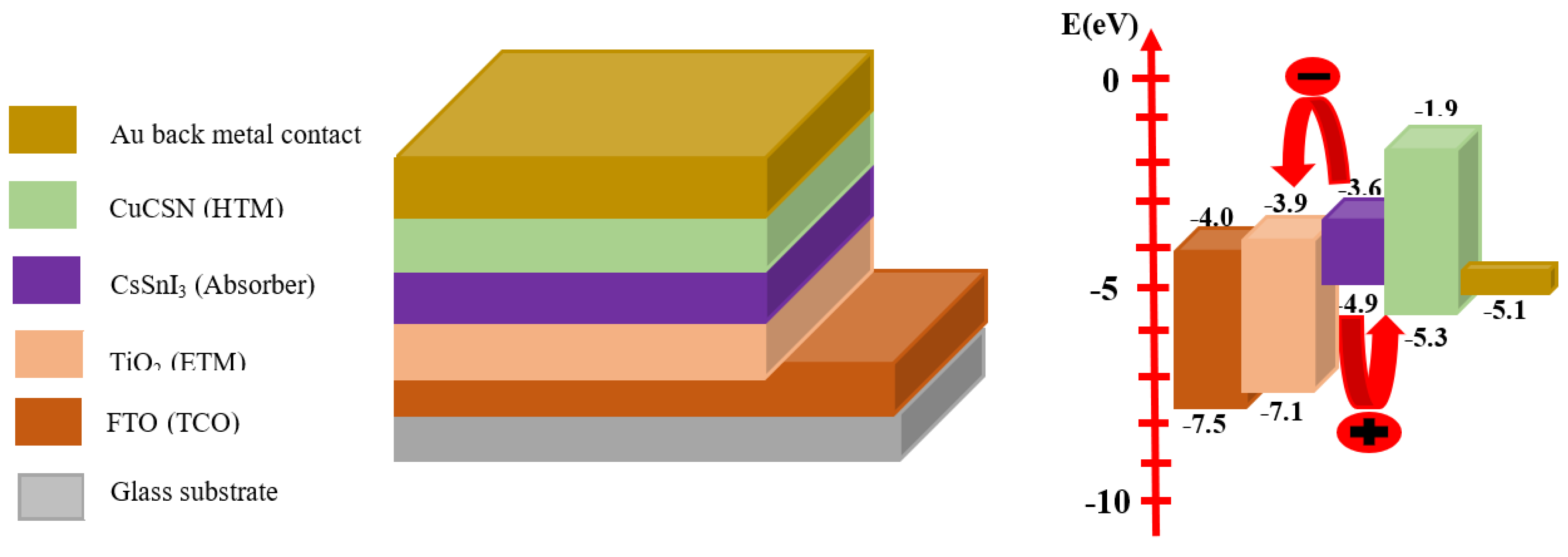
| Parameters | FTO | TiO2 | CsSnI3 | CuSCN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (µm) Band-gap energy Eg (eV) Electron affinity χ (eV) Relative Permittivity εr Effective conduction band density Nc (cm-3) Effective valence band density Nv (cm-3) Electron mobility µn (cm2V-1 s-1) Hole mobility µp (cm2V-1 s-1) Donor concentration ND (cm-3) Acceptor concentration NA (cm-3) Defect density Nt (cm-3) |
0.500 3.5 4.0 9 2.2x1018 1.8x1019 20 10 2x1019 0 1x1015 |
0.010 3.2[63] 3.9-4.8[65,66,67] 38-108[69] 2.2x1018 [71] 1.8x1019 [71] 20[73] 10[73] 1x1016 0 1x1017 |
0.200 1.3[57] 3.6[59] 28[62] 1.57x1019[53] 1.47x1018[53] 50[62] 585[57] 0 1x1017[62] 1x1017[53] |
0.100 3.40[64] 1.9[68] 9[70] 2.2x1018 [72] 2.9x1019 [72] 1x10-4 [74] 1x10-2[74] 0 1x1018 1x1017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





