Submitted:
30 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and equipments
2.2. Preparation of samples
2.3. Adsorption isotherms
2.3.1. Langmuir type isotherm
2.3.2. Freundlich type isotherm
3. Result
3.1. ZTC Adsorbant characterisation
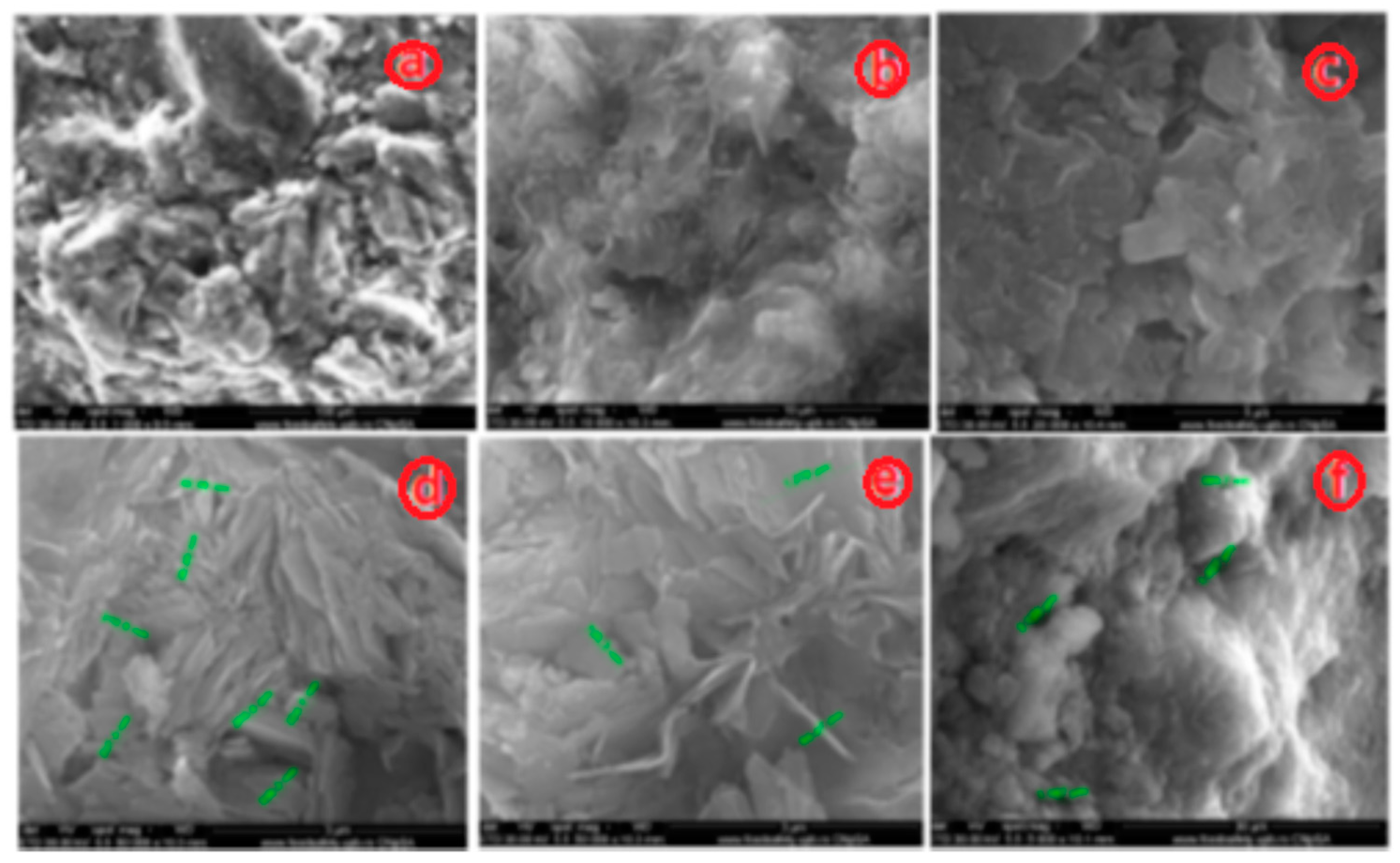
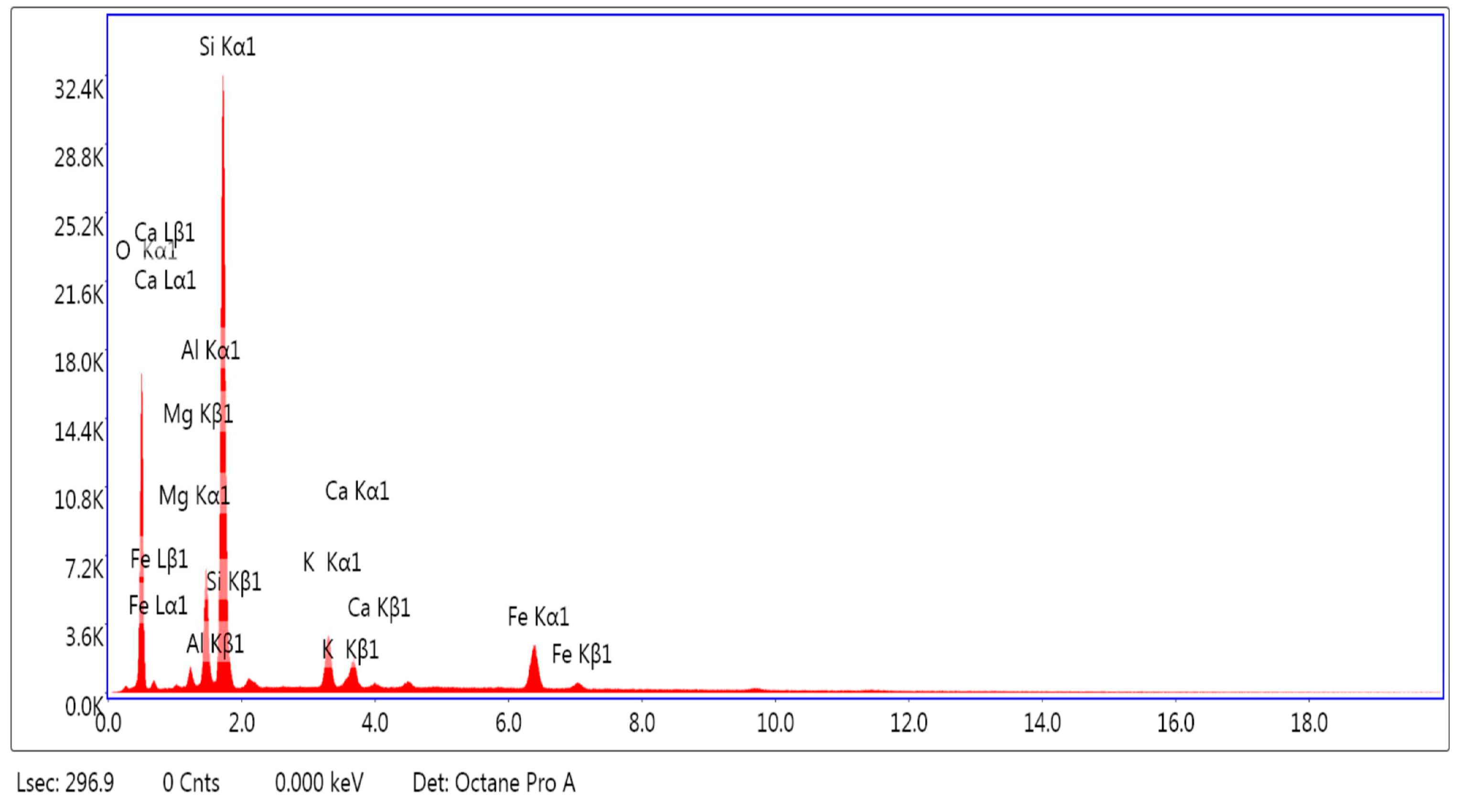
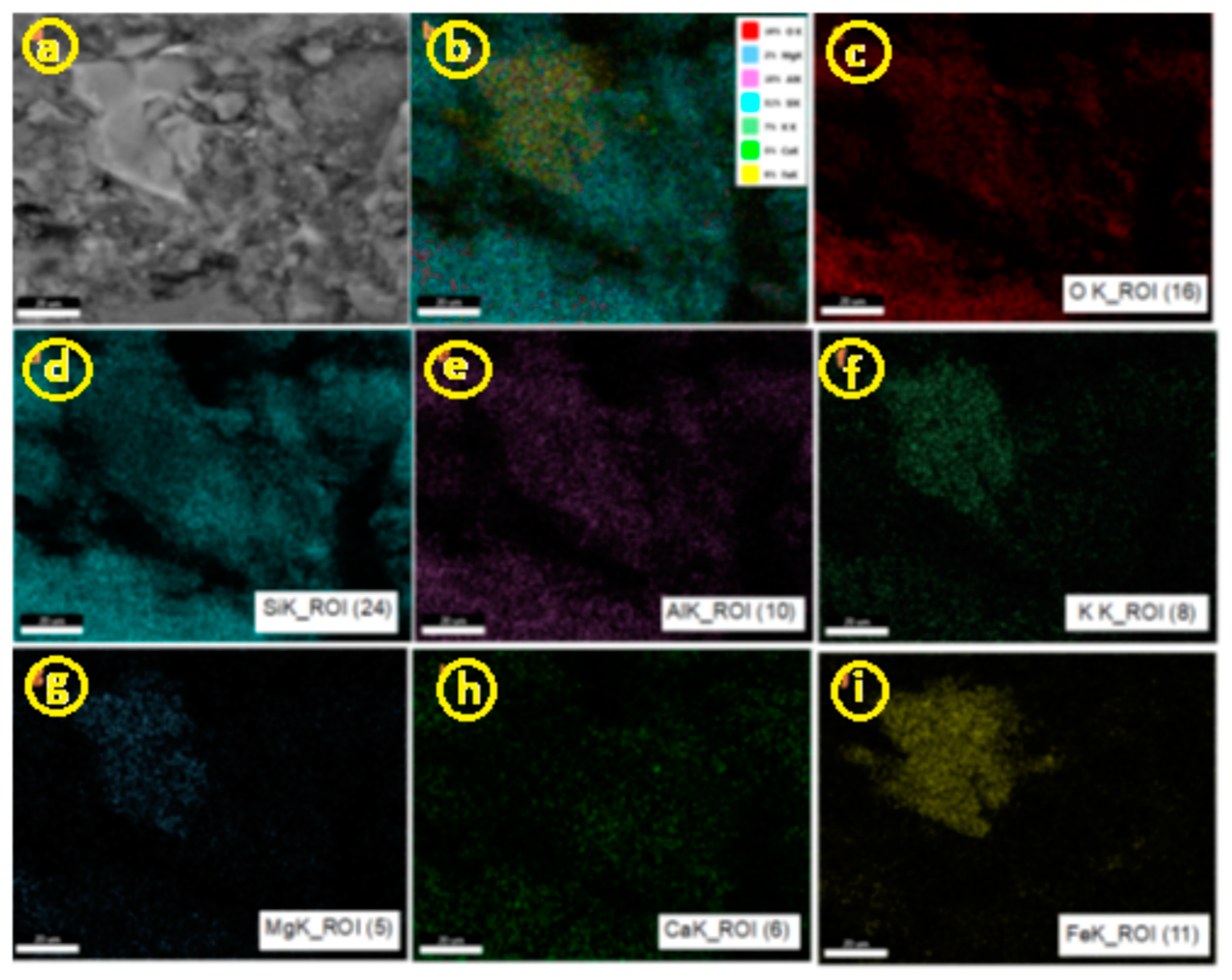
3.1.1. SEM and EDAX Analysis for ZTC
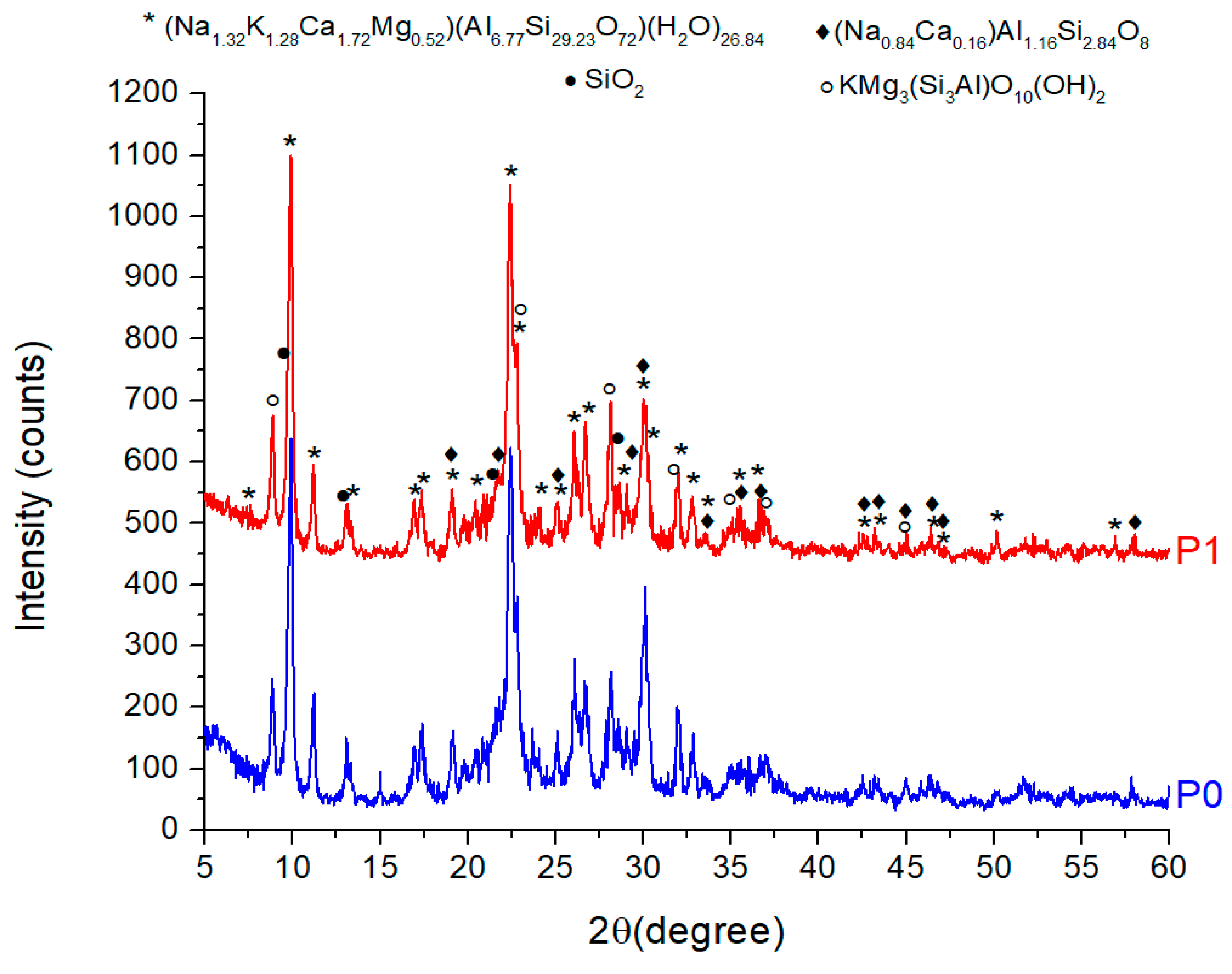
3.1.2. XRD Analysis of ZTC
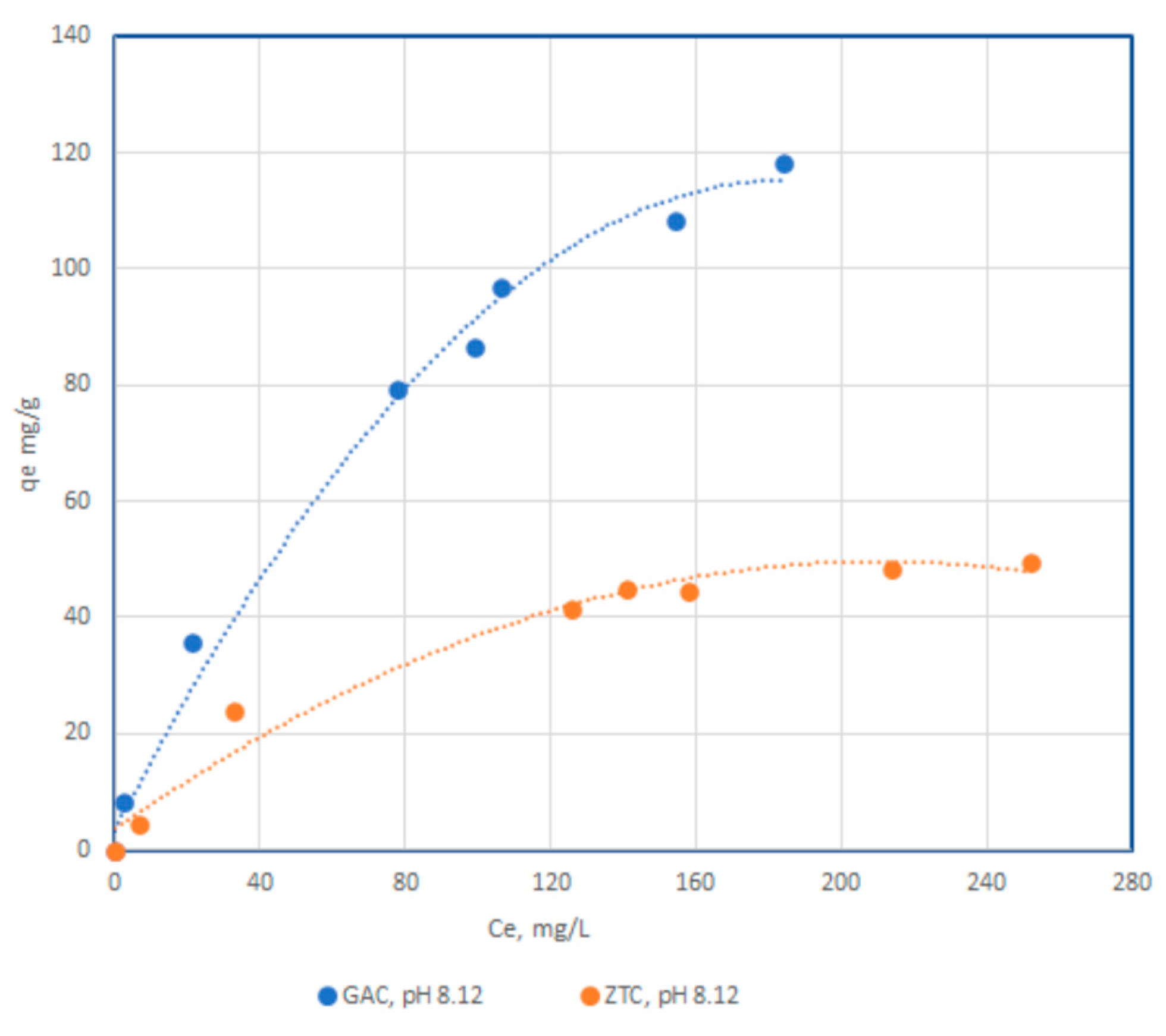
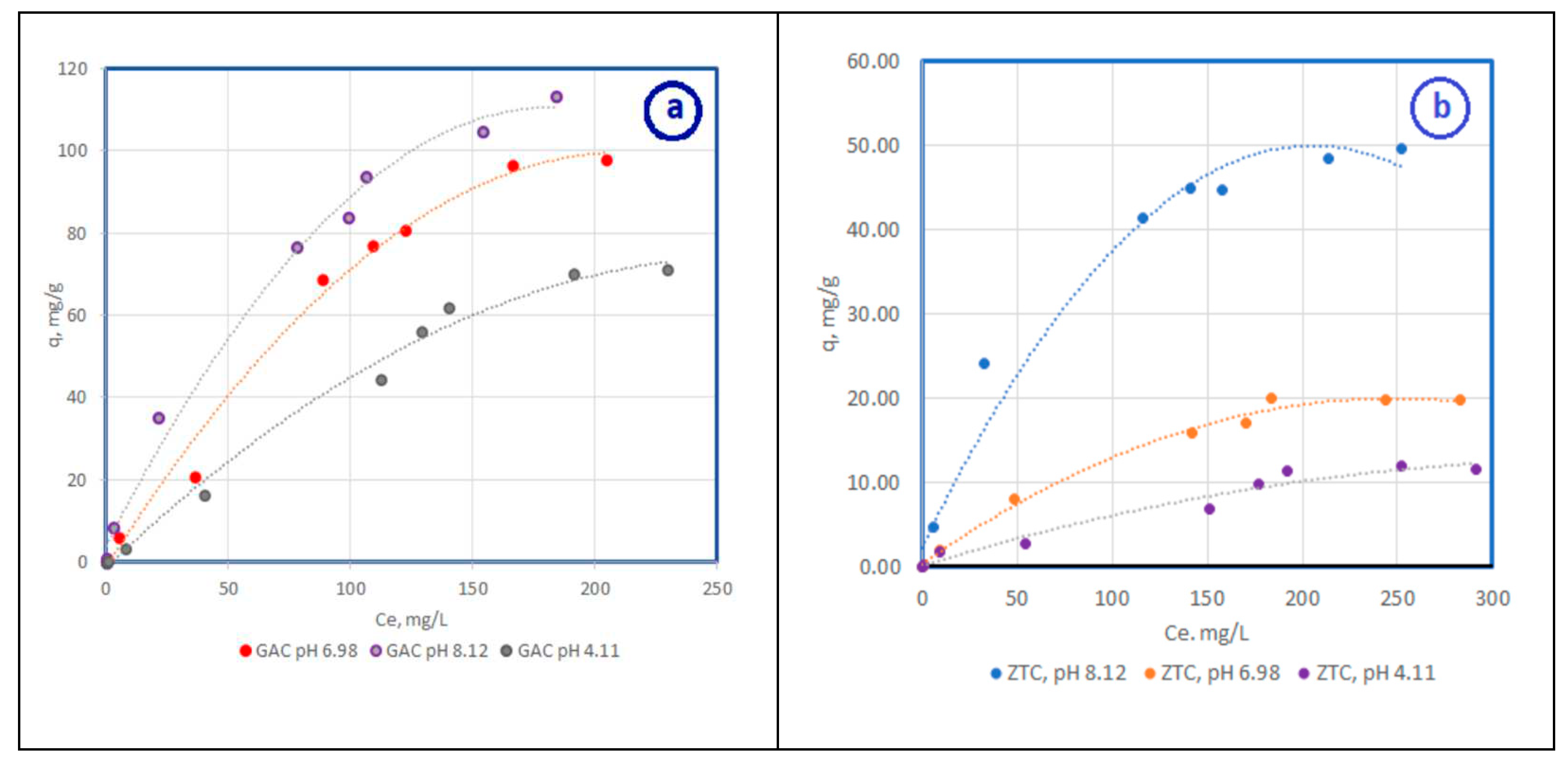
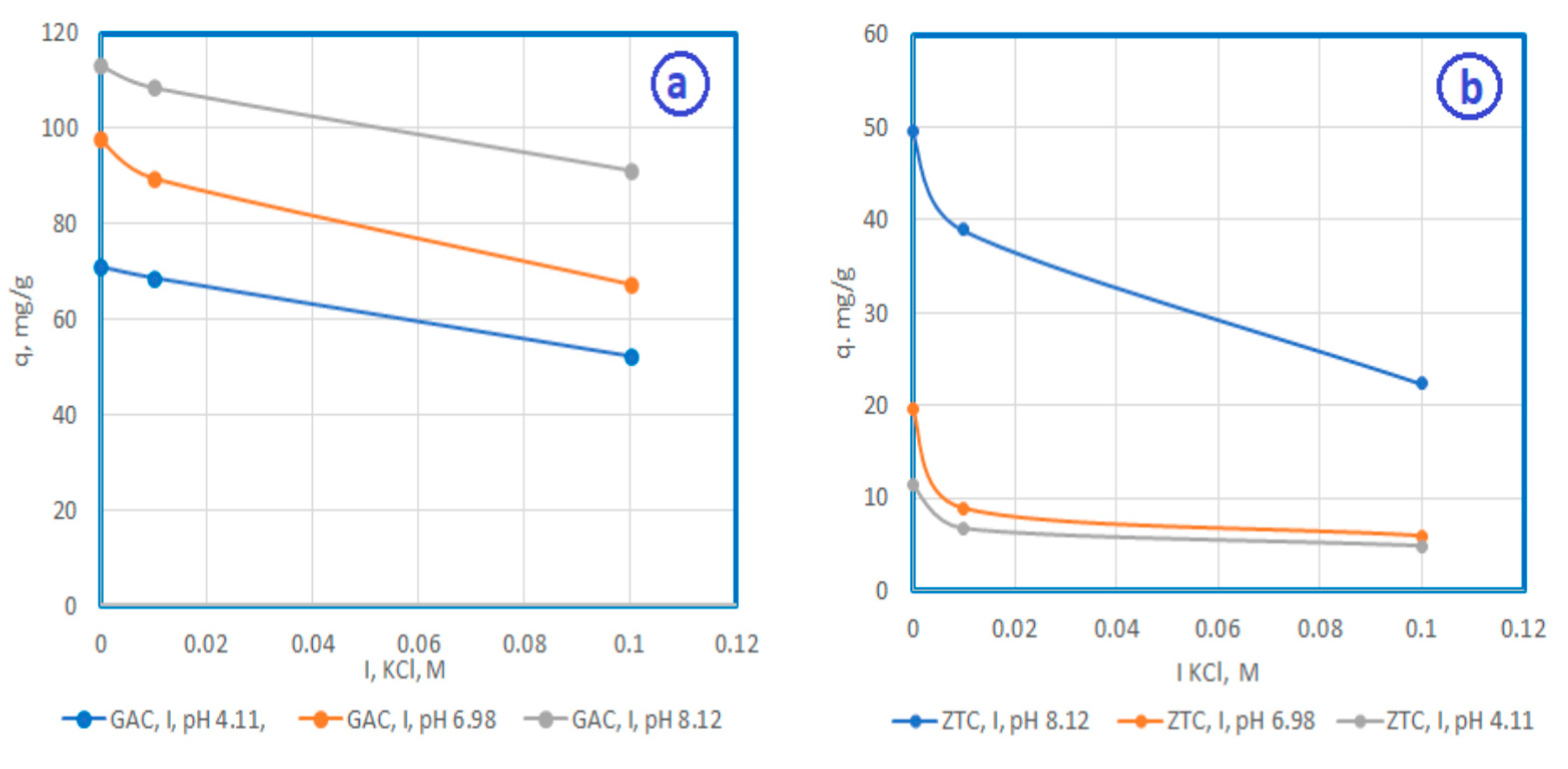
3.2. Adsorption Equilibrium
3.2.1. Adsorbtion isotherm for differents pH values
3.2.2. The influence of ionic strength on the adsorption process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hoekstra, E.; Simoneau, C. Release of bisphenol A frompolycarbonate—a review. Critic. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 386–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiljevic, T.; Harner, T. Bisphenol A and its analogues in outdoor and indoor air: Properties, sources and global levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148013, Bibcode: 2021ScTEn.789n8013V. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michałowicz, J. Bisphenol A – Sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 738–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zeng, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Li, L.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhou, J. Bisphenol A biodegradation by Sphingonomas sp. YK5 is regulated by acyl-homoserine lactone signaling molecules. Sci. Total Environ 2021, 802, 149898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dura-Pahontu, A.M.; Draganescu, R.; Stefan, D.S.; Stefan, M. Preliminary study regarding the influence of bfa on some microorganisms. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Series B 2022, 84, 4, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A Review. Chemosphere 2016, 168, 885–902, 1e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ramón, M.V.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Bautista-Toledo, M.I.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Moreno-Castilla, C.; Sánchez-Polo, M. Removal of bisphenols A and S by adsorption on activated carbon clothes enhanced by the presence of bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Mishra, I.; Kumar, V. Degradation and mineralization of Bisphenol A (BPA) in aqueous solution using advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2 and oxidation systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 266e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, Y. Removal of phenolic endocrine disrupting compounds from waste activated sludge using UV, H2O2, and UV/H2O2 oxidation processes: effects of reaction conditions and sludge matrix. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 307e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Yang, R.; Zhou, G.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Chi, Y.; Chi, J.; Li, X.; Fang, H.; Li, H.; Li, W. New progress in photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A as representative endocrine disrupting chemicals. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Shi, A.; Lu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Z. Optimized fabrication of Cu-doped ZnO/calcined CoFe‒LDH composite for efficient degradation of bisphenol a through synergistic visible-light photocatalysis and persulfate activation: Performance and mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Chu, W.; Gao, N. An expected formation of TCNM from chlorination of bisphenol A with ultrasonic pretreatment: A new nitrogen source for N-DBP from N2 in air. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 429(1), 132326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Gan, L.; Gong, H.; Su, J.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Chu, W.; Xu, L. Efficient degradation of bisphenol A using High-Frequency Ultrasound: Analysis of influencing factors and mechanistic investigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.M.P.; Almeida, K.J.C.; Conceição, M. V. S.; Pereira, D.H.; Botelho, G. Photodegradation of bisphenol A by ZnS combined with H2O2: Evaluation of photocatalytic activity, reaction parameters, and DFT calculations. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 371, 121096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Gao, K.; Xia, H.; Luo, M.; Wang, X.; Ye, L.; Shi, Y.; Lu, B. Monitoring bisphenol A and its biodegradation in water using a fluorescent molecularly imprinted chemosensor. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Shrivastava, V.; Dixit, L.; Pritam, A. Ultrasonic cavitation tailored wastewater purification and desalination using thick sand of highly permeable deep aquifer, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Ehg. Asp. 2020, 585, 124107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirag Batukbhai Godiya, B. J. Removal of bisphenol A from wastewater by physical, chemical. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1801–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare EN, M. A. Water decontamination usingbio-based, chemically functionalized, doped, and ionic liquid enhance-denhanced adsorbents: review. Environ Chem Lett 2021, 19, 3075–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawna, J. BNanoporous Carbon Materials for Energy Harvesting, Storage, and Conversion; Springer Link, 2023; pp. 41–63. [Google Scholar]
- Fatemeh Fazeli Zafar, B. B. Adsorption kinetics analysis and optimization of Bisphenol A onto magnetic activated carbon with shrimp shell based precursor. Biomass and Bioenergy 2022, 166, 106604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastavaa, A.; Singha, M.; Karsauliyaa, K.; Mondalb, D.P.; Kharec, P.; Singhb, S.; Singha, S.P. Effective elimination of endocrine disrupting bisphenol A and S from drinking water using phenolic resin-based activated carbon fiber: adsorption, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, F.; Xia, L.; Dai, J.; Meng, D. The dealuminated zeolites via acid leaching and followed calcination method for removal of hydrophobic bisphenol A. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 305, 122640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmad, A.; Zango, Z.U.; Noh, T.U.; Usman, F.; Aldaghiri, O. A.; Ibnaouf, K.H.; Shaharun, M.S. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network for prediction and validation of bisphenol a adsorption onto zeolite imidazole framework. Groundw. Sustain Dev. 2023, 21, 100925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhym, A.B.; Seilkhanova, G.A.; Mastai, Y. Physicochemical evaluation of the effect of natural zeolite modification with didodecyldimethylammonium bromide on the adsorption of Bisphenol-A and Propranolol Hydrochloride. Microprous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 318, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, L.; Bialoszewska, M.; Malinowski, S.; Franus, W. Adsorptive performance of fly ash-derived zeolite modified by β-cyclodextrin for ibuprofen, bisphenol A and caffeine removal from aqueous solutions – equilibrium and kinetic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norit Gac 830 W: Datasheet | PDF | Specification (Technical Standard) | Carbon (scribd.com).
- Zeeshan, M.; Shah, J.; Rasul, J.M.; Iqbal, M. Removal of Bisphenol-A from Aqueous Samples Using Graphene Oxide Assimilated Magnetic Silica Polyaniline Composite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibor, S.T.; Grande, C.A. Industrial production of activated carbon using circular bioeconomy principles: Case study from a Romanian company. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No Crt. | Specification | Active charcoal Norit GAC 830 W |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Particle size >2.36 mm | Max 15 % in mass unit |
| 2 | Particle size <0.6 mm | Max 5 % in mass unit |
| 3 | Moisture | Max 5 % |
| 4. | Iodine number | 957 |
| 5 | Methylene blue adsorption | 20 g/100g |
| 6 | Ash content | 12 % |
| 7 | Total surface area, BET analises | 1100 m2/g |
| 8 | Apparent density | 500 kg/m3 |
| Element | Weight % | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|
| O K | 50.40 | 65.81 |
| MgK | 1.37 | 1.18 |
| AlK | 6.77 | 5.24 |
| SiK | 30.85 | 22.95 |
| K K | 3.45 | 1.84 |
| CaK | 2.11 | 1.10 |
| FeK | 5.05 | 1.89 |
| No. | Compound | Chemical formula | PDF file | Quantity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | P1 | ||||
| 1 | Clinoptilolite Ca | (Na1.32K1.28Ca1.72Mg0.52)(Al6.77Si29.23O72)(H2O)26.84 | 00-089-7535 | 80.3 | 80.8 |
| 2 | Phlogopite-1M | (KMg3Si3AlO10(OH)2) | 00-010-0495 | 9.7 | 11.7 |
| 3 | Albite | (Na0.84Ca0.16)Al1.16Si2.84O8 | 01-076-0927 | 8.3 | 5.2 |
| 4 | Quartz | SiO2 | 04-020-9990 | 1.7 | 2.3 |
| pH | Liniar Langmuir equations | Liniar Freudlinch equations |
|---|---|---|
| 4.11 | = 2.0223 + 2.6403 | log qe = 0.5830 log Ce + 1.0567 |
| 6.98 | =1.196 + 2.3293 | log qe = 0.5582 log Ce + 0.9144 |
| 8.12 | = 0.29 + 2.0039 | log qe = 0.5852 log Ce + 0.4713 |
| pH | Liniar Langmuir equations | Liniar Freudlinch equations |
|---|---|---|
| 4.11 | =4.181 +19.253 | log qe = 0.7661 log Ce +1.3215 |
| 6.98 | = 1.8256 +10.045 | log qe = 0.9063 log Ce +1.0016 |
| 8.12 | = 1.2897 +3.4878 | log qe = 1.0309 log Ce +0.4886 |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir isotherm | Freundlich isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm, mg/g | b | R2 | K | n | R2 | |
| CA pH 4,11 | 84.5 | 1.3 | 0.9996 | 11.37 | 1.71 | 0.9064 |
| CA pH 6,98 | 95.78 | 1.94 | 0.9996 | 8.21 | 1.79 | 0.9588 |
| CA pH 8,12 | 111.34 | 6.91 | 0.9965 | 2.96 | 1.70 | 0.9392 |
| Zeolite pH 4,11 | 11.60 | 4.6 | 0.9961 | 20.96 | 1.3 | 0.9701 |
| Zeolite pH 6,98 | 22.21 | 5.5 | 0.9992 | 10.04 | 1.1 | 0.9711 |
| Zeolite pH 8,12 | 63.9 | 2.7 | 0.9995 | 10.73 | 0.97 | 0.9147 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





