Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
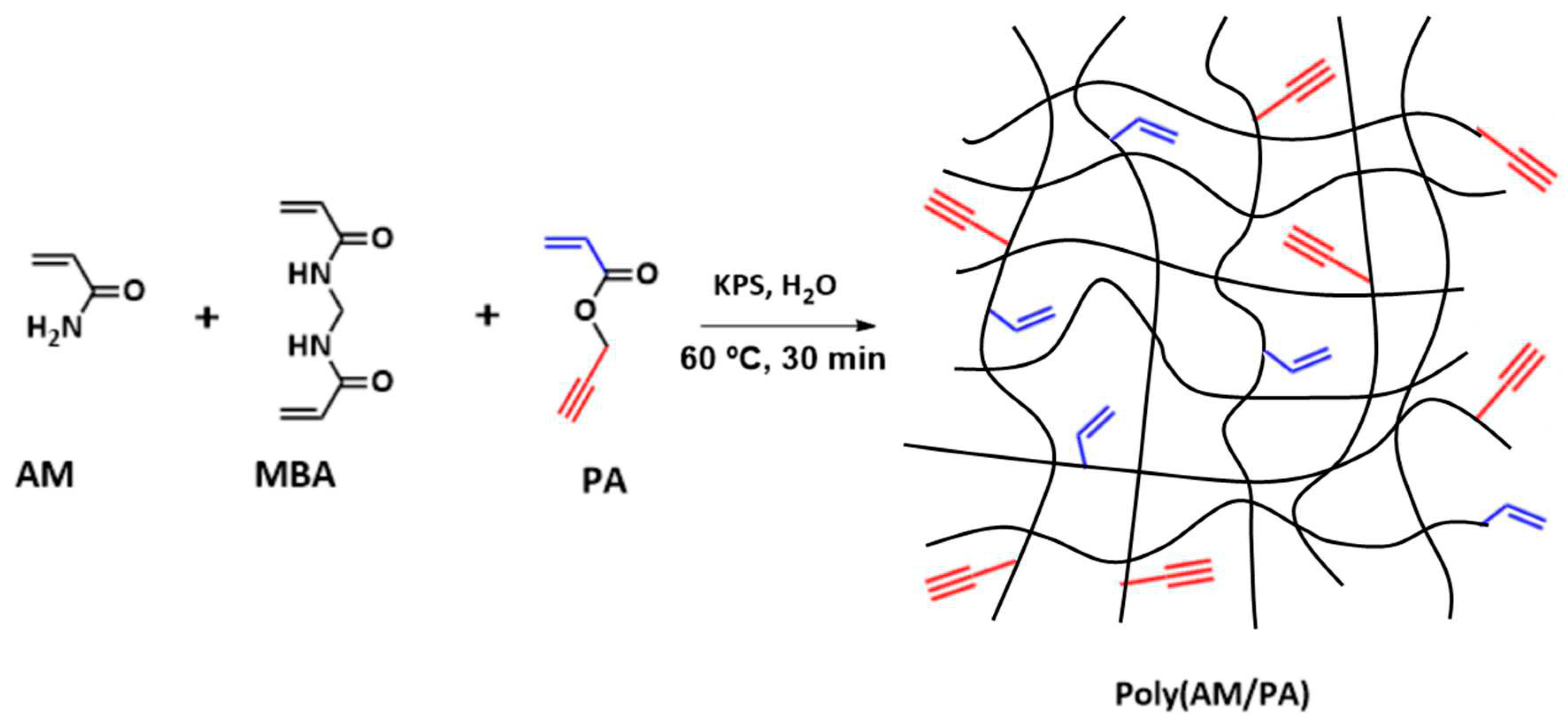
2.2. Hydrogel layers preparation
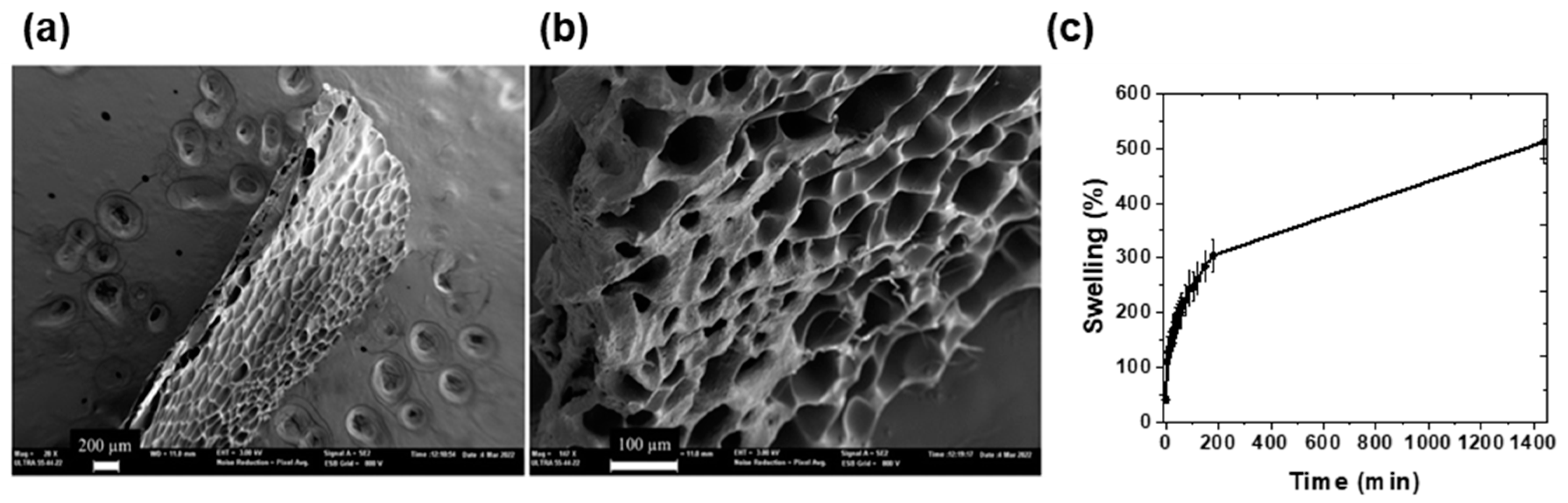
2.3. Morphology characterization
2.4. Swelling behavior studies
2.5. Incubation step before recording
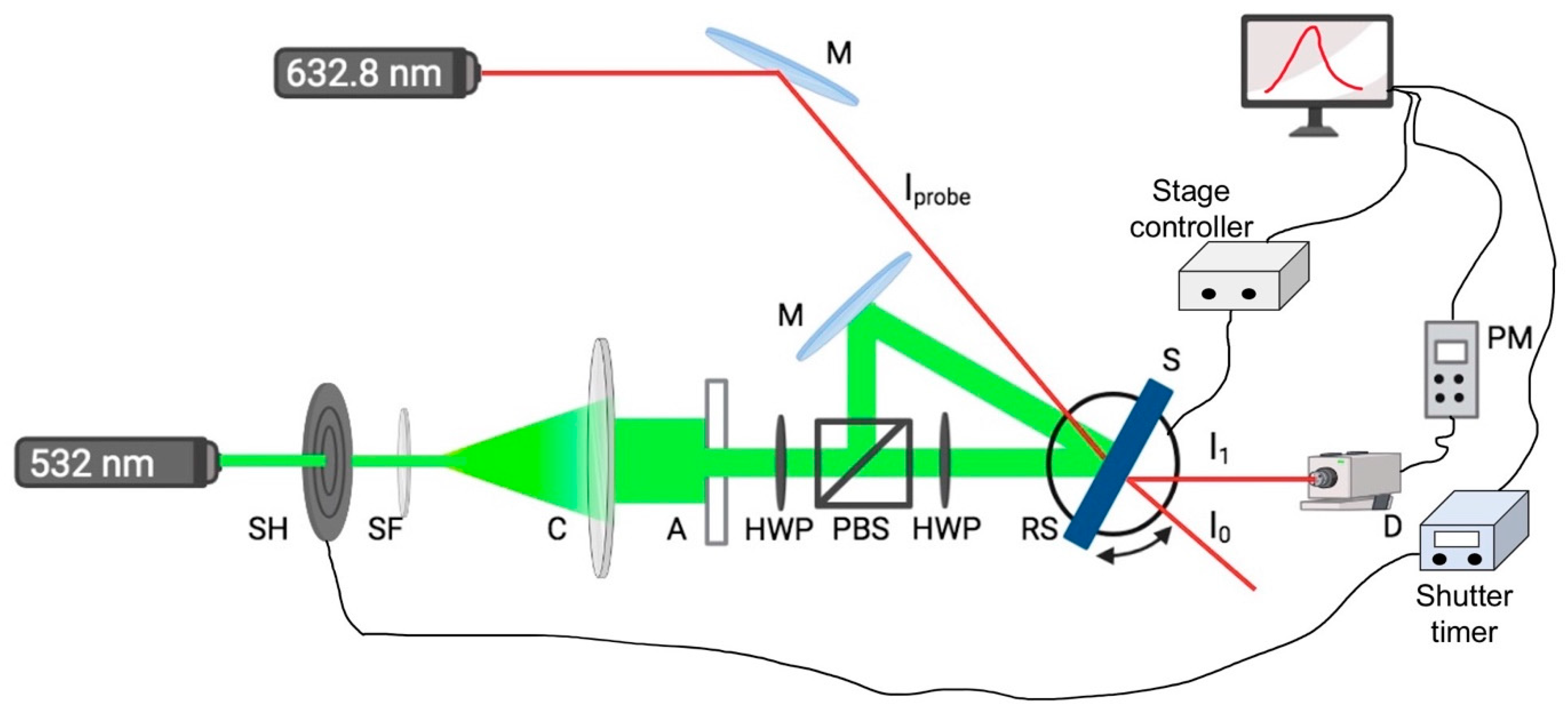
2.6. Holographic recording and probe set-up
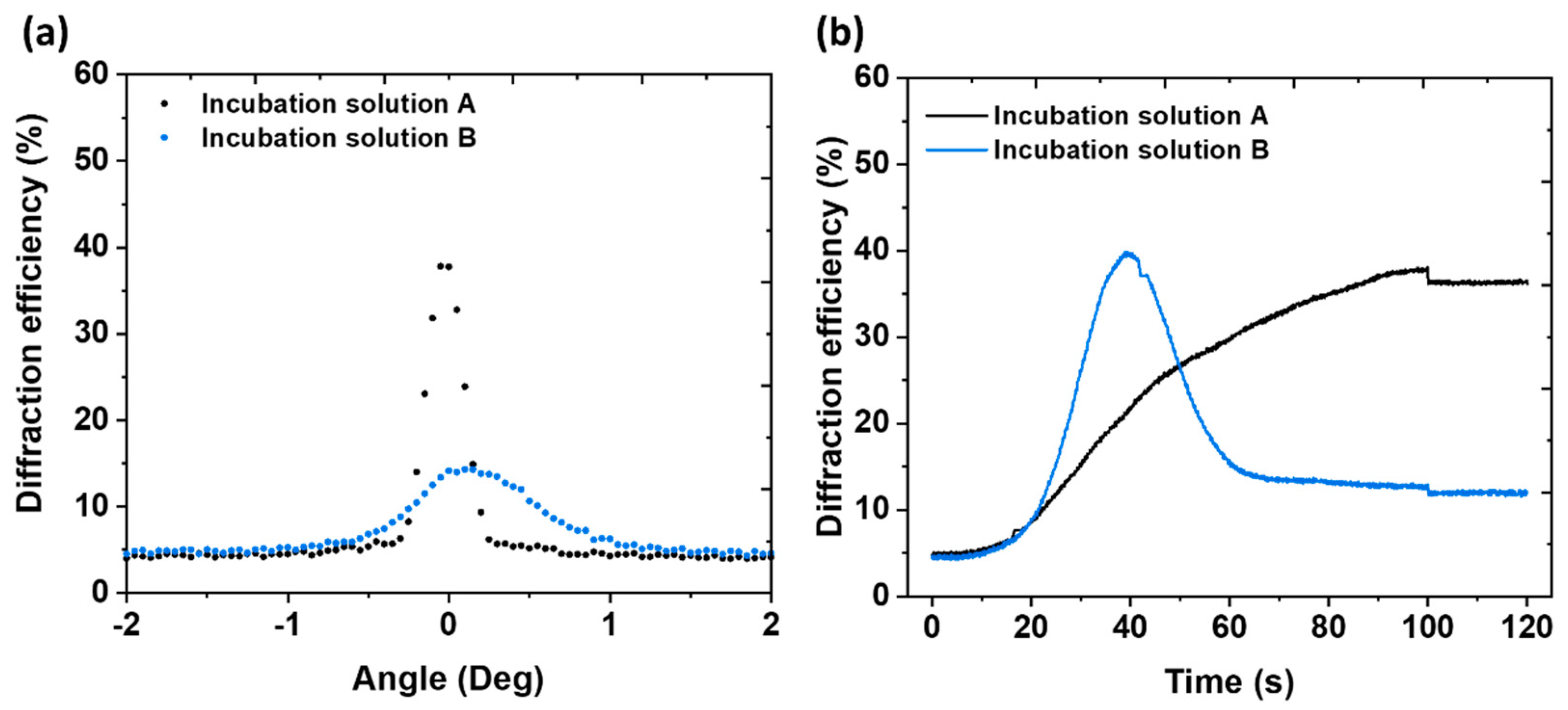
2.7. Holographic recording and characterisation of hydrogel layers
2.8. Biofuncionalization of VTGs and hybridization/dehybridization experiments
3. Results and Discussions
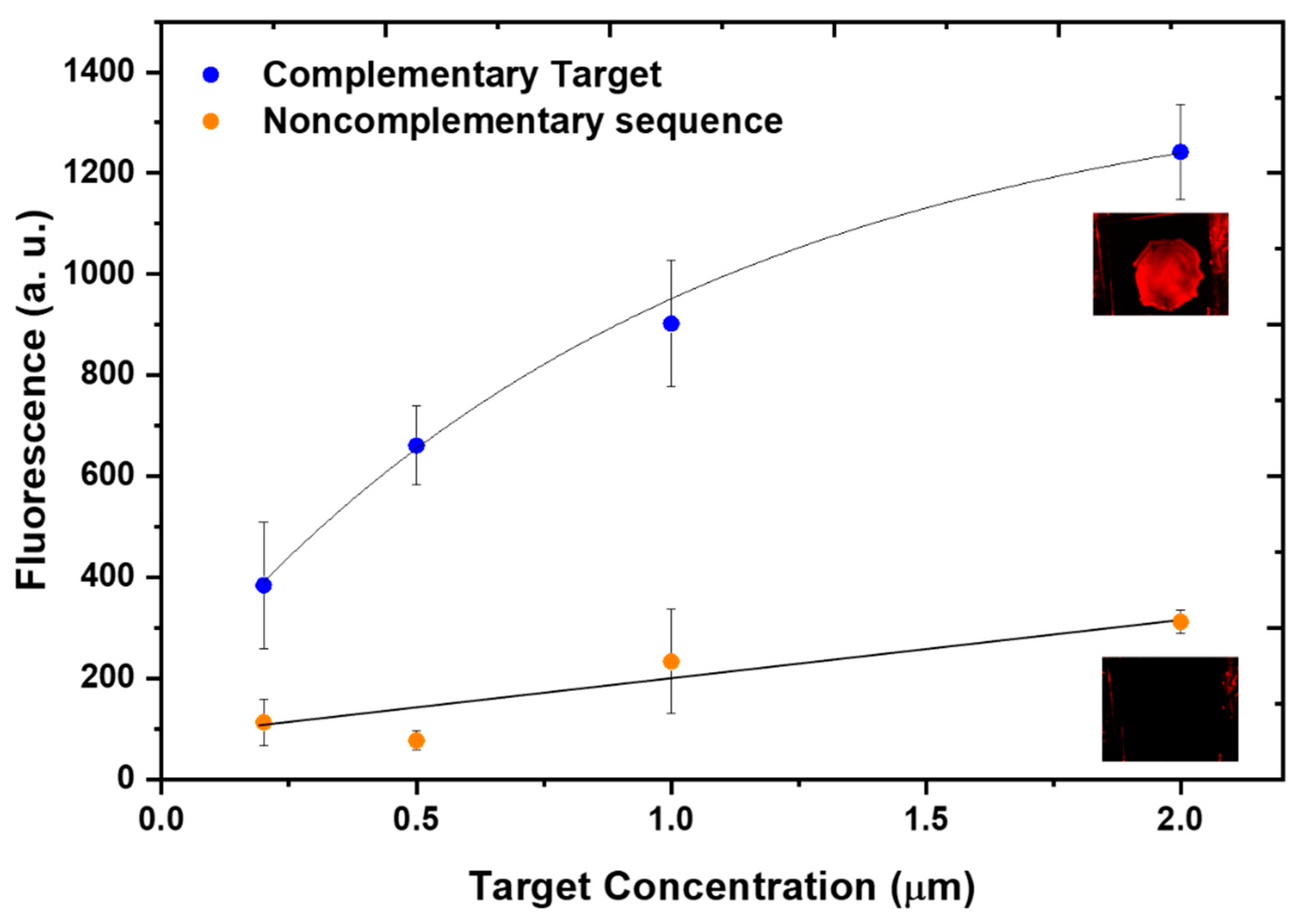
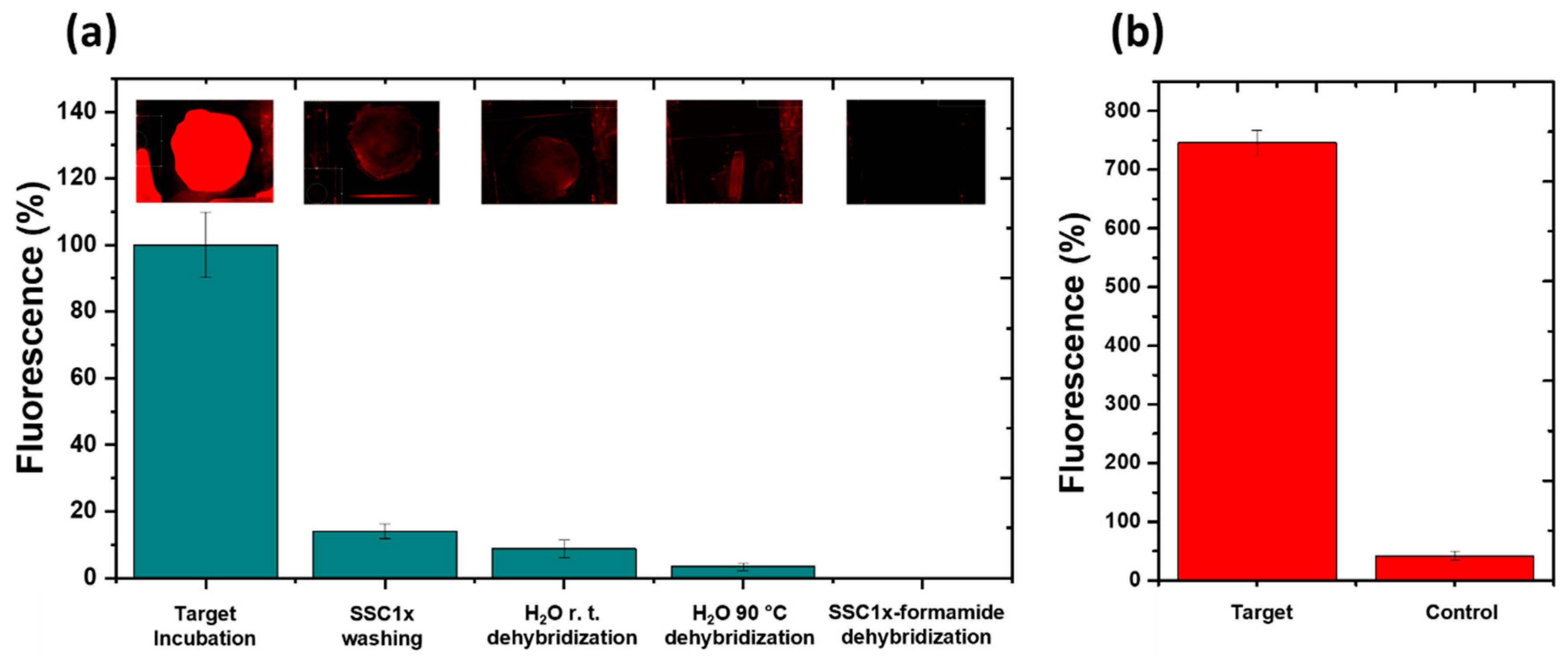
Biofunctionalization of VTGs and Hybridization assays by fluorescence detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yetisen, A.K.; Naydenova, I.; Da Cruz Vasconcellos, F.; Blyth, J.; Lowe, C.R. Holographic Sensors: Three-Dimensional Analyte-Sensitive Nanostructures and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10654–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanche, P.A. Holographic Recording Media and Devices. Encycl. Mod. Opt. 2018, 1–5, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, E.M. Water-Soluble Holographic Photopolymers for a Sustainable Future—A Review. Coatings 2022, 12, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.K.; Labella, E.; Goddard, N.J.; Gupta, R. Photofunctionalizable Hydrogel for Fabricating Volume Optical Diffractive Sensors. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Agate, S.; Salem, K.S.; Lucia, L.; Pal, L. Hydrogel-Based Sensor Networks: Compositions, Properties, and Applications - A Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madduma-Bandarage, U.S.K.; Madihally, S. V. Synthetic Hydrogels: Synthesis, Novel Trends, and Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouassier, J.P.; Allonas, X.; Burget, D. Photopolymerization Reactions under Visible Lights: Principle, Mechanisms and Examples of Applications. Prog. Org. Coatings 2003, 47, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulchyk, T.; Martin, S.; Naydenova, I. Humidity and Temperature Effect on Properties of Transmission Gratings Recorded in PVA/AA-Based Photopolymer Layers. J. Opt. 2013, 15, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toal, V. Photopolymers: Beyond the Standard Approach to Photosensitisation. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. - Rapid Publ. 2009, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, M. G.; Lucío, M. I.; Morales-Vidal, M.; Beléndez, A.; Bañusl, M.-J.; Maquieira, Á.; Pascual, I. Holographic Transmission Gratings Stored in a Hydrogel Matrix. Photosensit. Mater. their Appl. 2020, SPIE 11367, 113670B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berramdane, K.; Ramírez, M.G.; Zezza, P.; Lucío, M.I.; Bañuls, M.J.; Maquieira, Á.; Morales-Vidal, M.; Beléndez, A.; Pascual, I. Processing of Holographic Hydrogels in Liquid Media: A Study by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Diffraction Efficiency. Polymers. 2022, 14, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, I.; Jallapuram, R.; Howard, R.; Martin, S.; Toal, V. Investigation of the Diffusion Processes in a Self-Processing Acrylamide-Based Photopolymer System. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2900–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.R.; Sheridan, J.T. A Review of the Modelling of Free-Radical Photopolymerization in the Formation of Holographic Gratings. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2009, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Blyth, J.; Kaminska, M.; Liu, Y.; Yetisen, A.K. Holographic Sensors in Biotechnology. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucío, M.I.; Cubells-Gómez, A.; Maquieira, Á.; Bañuls, M.J. Hydrogel-Based Holographic Sensors and Biosensors: Past, Present, and Future. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 993–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.J.; Young, D.S.; Blyth, J.; Kabilan, S.; Lowe, C.R. Metabolite-Sensitive Holographic Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulchyk, T.; Walshe, J.; Cody, D.; Martin, S.; Naydenova, I. Humidity and Temperature Induced Changes in the Diffraction Efficiency and the Bragg Angle of Slanted Photopolymer-Based Holographic Gratings. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2017, 239, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Martin, S.; Naydenova, I. Temperature-Sensitive Holograms with Switchable Memory. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2100062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Ferrara, M.A.; Borbone, F.; Zuppardi, F.; Roviello, A.; Striano, V.; Coppola, G. Volume Holographic Gratings as Optical Sensor for Heavy Metal in Bathing Waters. Opt. Sensors 2015 2015, 9506, 95062B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Qasim, M.M.; Nosheen, S.; Wilkinson, T.D.; Lowe, C.R. Pulsed Laser Writing of Holographic Nanosensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3569–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Wearable Contact Lens Biosensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Using Smartphones. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5452–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.; Hu, Y.; Blyth, J.; Jiang, N.; Yetisen, A.K. Reusable Dual-Photopolymerized Holographic Glucose Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezza, P.; Lucío, M. I.; Fernández, E.; Maquieira, Á.; Bañuls, M.-J. Surface Micro-Patterned Biofunctionalized Hydrogel for Direct Nucleic Acid Hybridization Detection. 2023, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, I. Holographic Sensors; Elsevier Inc., 2019; ISBN 9780128154670. [Google Scholar]
- Kogelnik, H. Coupled Wave Theory for Thick Hologram Gratings. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1969, 48(9), 2909–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, D.; Llorente, R.; Morais, S.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A.; Marti, J. High-Throughput Screening of Surface-Enhanced Fluorescence on Industrial Standard Digital Recording Media. Opt. Based Biol. Chem. Sens. Def. 2004, 5617, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
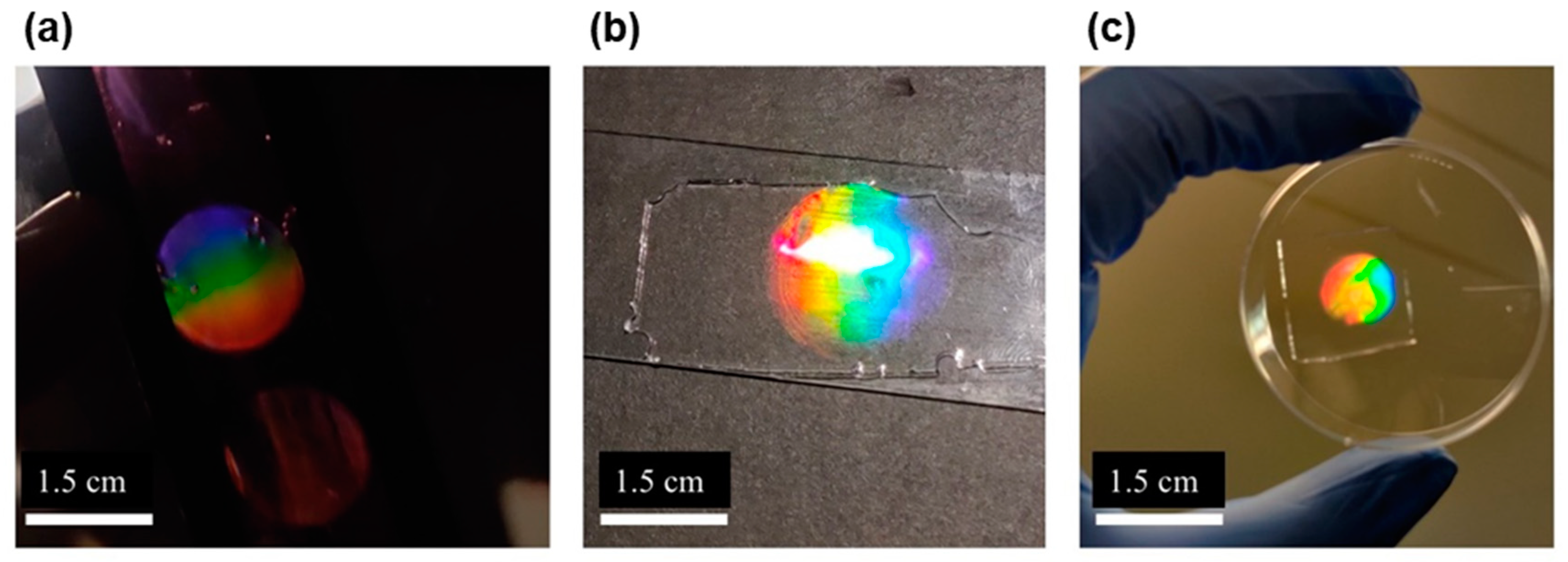
| Incubation solution | AM (g) | MBA (g) | TEA (mL) | EB (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 4 |
| B | 2 | 0.4 | 1 | 4 |
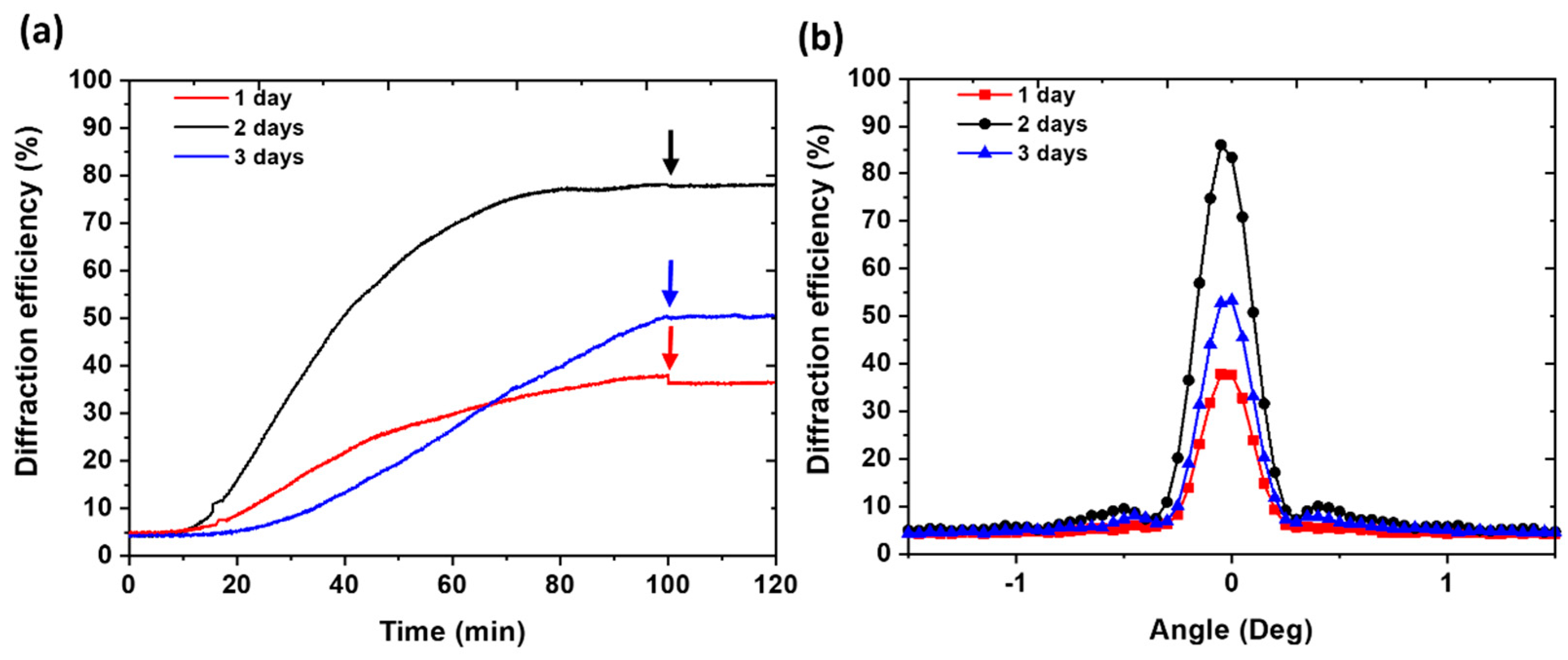
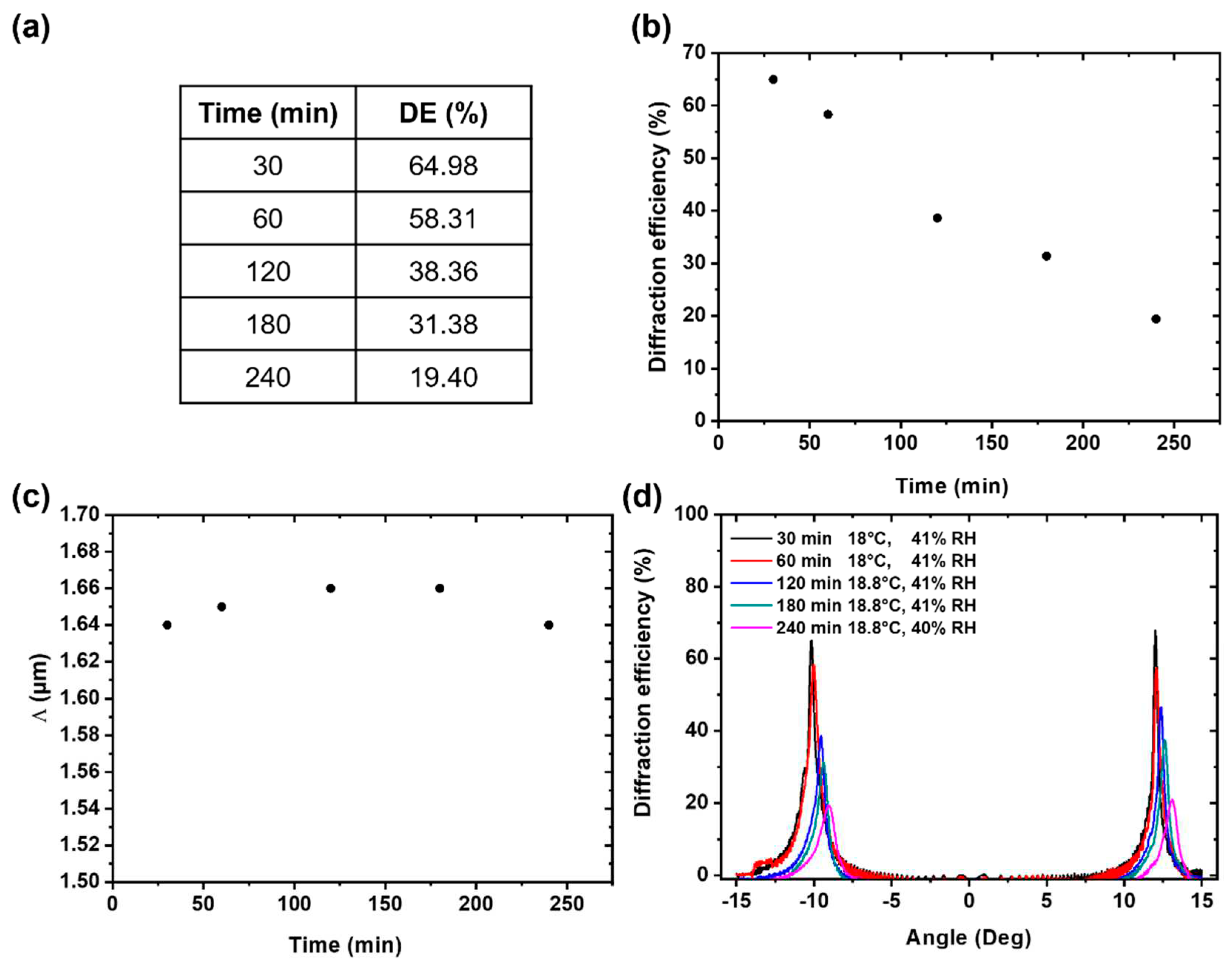
| Incubation time (days) |
Layer thickness (µm) |
Recording beams intensity (mW/cm2) | Recording exposure time (s) | Maximum DE achieved (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 | 7.5 | 100 | 40 |
| 2 | 300 | 7.5 | 100 | 80 |
| 3 | 300 | 7.5 | 100 | 50 |
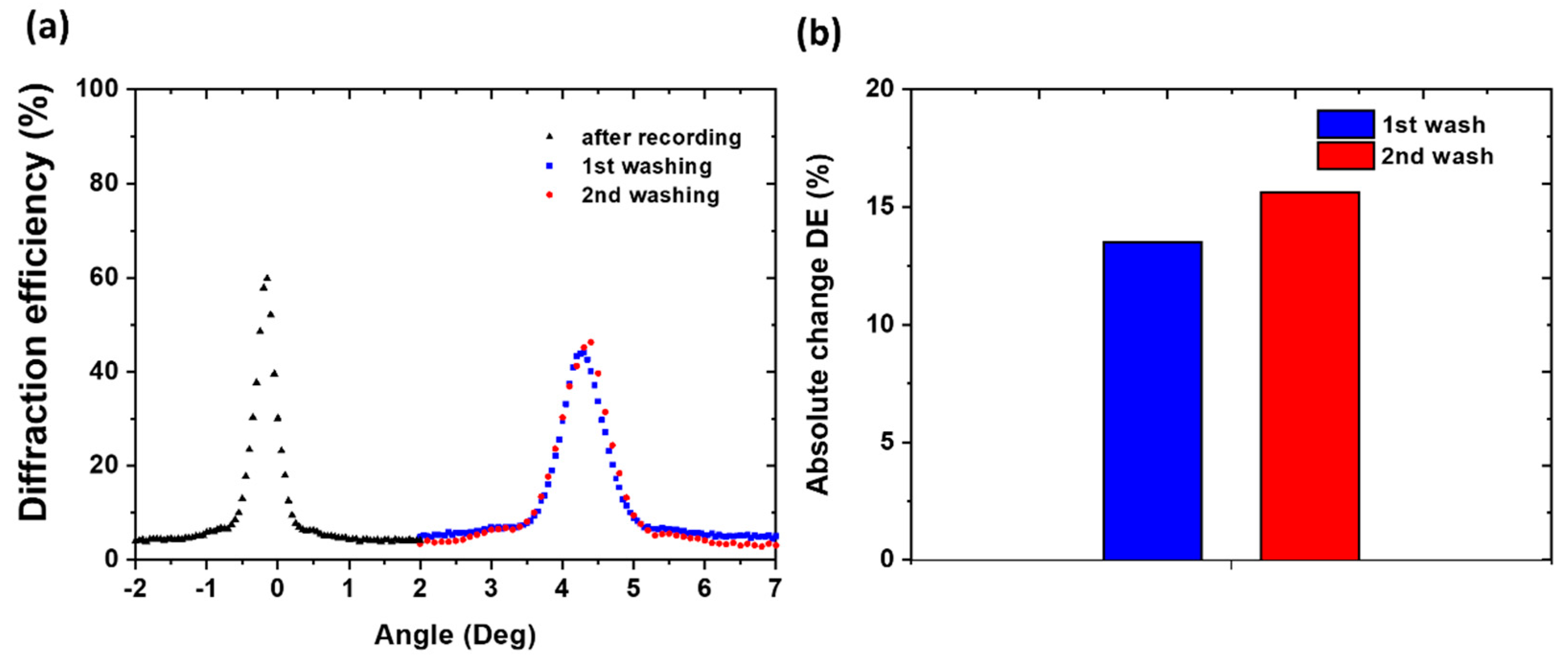
| VTG thickness (µm) | Refractive index modulation (RIM) | |
|---|---|---|
| after recording | 190 | 0.0010 |
| 1st washing | 60 | 0.0015 |
| 2nd washing | 62 | 0.0017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





