1. Introduction
The microbial infections constitute one of the most important global public health challenges of the 21st century. The misuse and abuse of antibiotics in medicine, food production and the environment as a whole have sadly further amplified this problem [
1]. Many leading international scientific, political and social organizations have warned that the rise of antimicrobial resistance could cost the lives of millions of people if it is not tackled on a global scale [
2]. There is a pressing need to develop new and effective antimicrobial agents that can overcome the intrinsic resistance developed against currently used biocides.
In this respect, compounds containing metal ions are promising substitutes [
3] and, among them, porous coordination polymers, also known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are attracting growing interest [
4]. MOFs possess favorable structures of large-surface crystalline networks with regular porosity and good structural rigidity, and since their first developments have been largely investigated in many applications in gas storage, separation of gases, purification of water, sensors, heterogeneous catalysis and drug storage and release [
5,
6,
7]. Investigation of MOFs as antimicrobial agents is more recent, and the attention has been mainly paid to MOFs with Ag(I), Cu(II), Zn(II), Co(II) and Fe(III) ions. One reason for the interest in MOFs for antimicrobial applications lies in their poor or very low solubility in water and organic solvents, which allows their use in solid composite materials for a wide variety of applications [
8]. Furthermore, the advantage of MOFs over other antimicrobial agents is that they can use different mechanisms of action, from simple surface contact with microbes through the so-called “chelation effect”, or the slow and controlled release of metal ions with antimicrobial activity and / or bioactive linkers, or also by photocatalytic production of reactive organic species (ROS) that kill microbes and finally, thanks to their porosity, they can also act as carriers for the controlled release of biocides [
9]. However, most studies on antimicrobial MOFs are generally related to a limited number of well-known MOFs such as metal carboxylates and imidazolates and in the case of the essential elements Cu and Zn, despite the large number of MOFs already synthesized with these metal ions and used for other applications, those investigated for their potential antimicrobial activities are still relatively few [
4]. We have previously synthesized and characterized several Zn(II) and Cu(II) MOFs with bipyrazole linkers [
10], which have been investigated as potential catalysts in the peroxidative oxidation of alcohols and cyclohexane [
11] and also as efficient carbon dioxide adsorbents [
12,
13]. Here we report a new synthetic protocol based on the use of MW condition which was found suitable to improve the yield of products and a detailed study of their antimicrobial activity against typical gram positive (
S. aureus) and gram negative (
E. coli) bacterial strains. An in-dept study of their possible mechanism of action is also discussed.
2. Results and Discussion
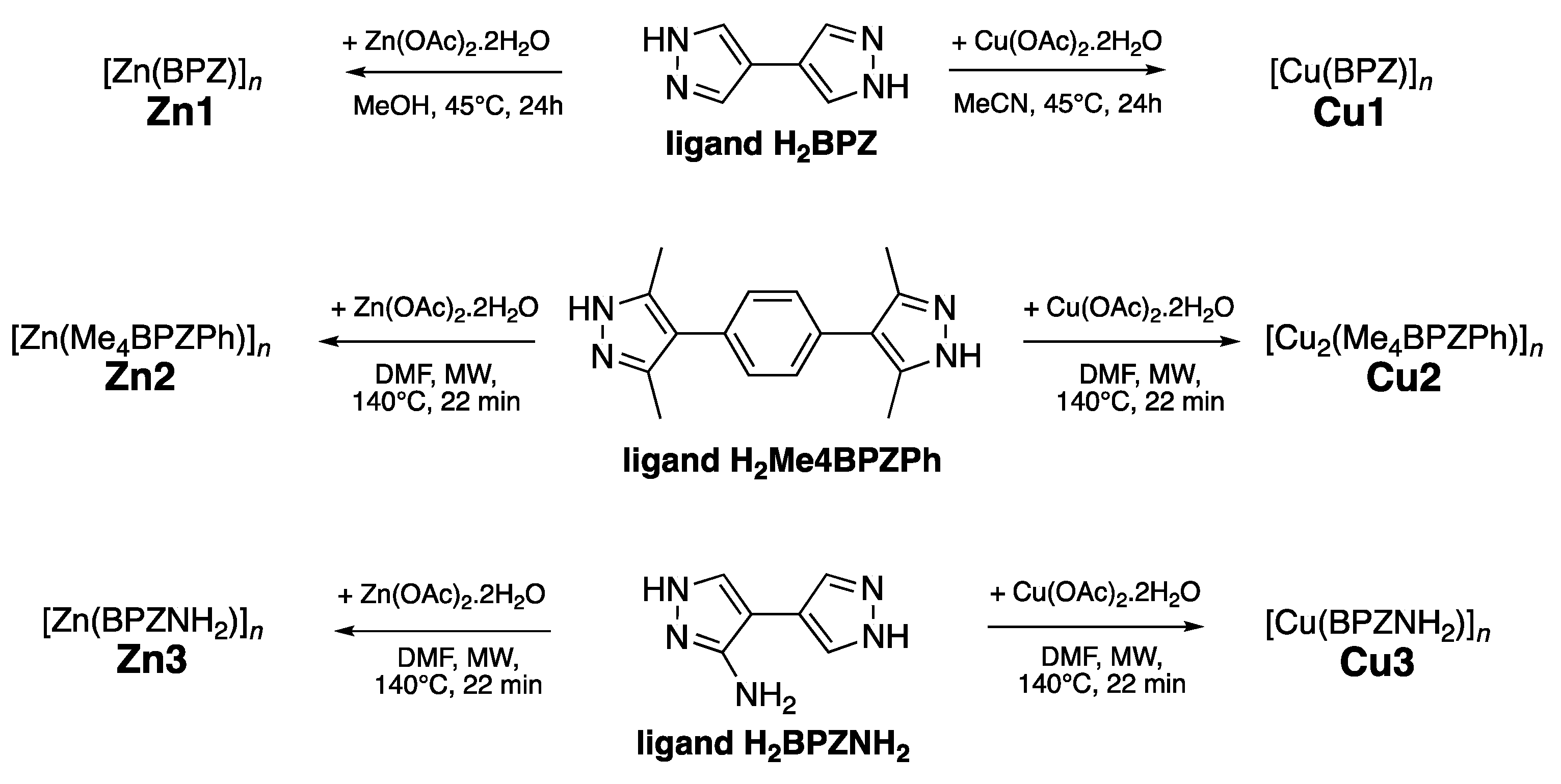
The selected Zn(II) MOFs
Zn1-
Zn3 and Cu(II) MOFs
Cu1-
Cu3 were synthesized according to previously published methods[
10,
11,
12,
13] and, for
Zn2-
Zn3 and
Cu2-
Cu3, also by Microwave-Assisted Synthesis (
Scheme 1), with the aim of reducing reaction times, obtaining more crystalline products and higher yields.
Prior their use in microbiological tests, all the samples were carefully activated through repeated washings with dichloromethane and prolonged heating at 353 K, to eliminate all traces of solvents incorporated in the pores of the MOFs.
2.1. Antibacterial Activity
The activity of
Zn1-Zn3 and
Cu1-Cu3 against
E. coli and
S. aureus, chosen as models of Gram- and Gram+ bacterial strains, was assessed by enumerating the total colony forming units (CFUs) after incubation for 24 h at 335 K. A preliminary investigation was carried out on our MOFs to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for each of them, against the selected bacterial strains. In general, the MIC values for all compounds have been observed to be in the range of 10-30 μg/mL for both bacteria (
Table 1), thus revealing a bacterial inhibition comparable to that of commonly used chemical disinfectants [
14]. Furthermore, the values obtained are lower than those of the corresponding copper and zinc ions released by the corresponding metal salts [
15].
The bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects against
E. coli and
S. aureus were verified by evaluating the temporal evolution of the antibacterial activity of the MOFs in the MICs, through the growth inhibition assay. Bactericidal activity is defined as the reduction of bacterial growth ≥ 99.9% within 18-24 hours of inoculation, whereas bacteriostatic activity is associated with the reduction of bacterial growth maintained stable between 90 and 99 % within 18-24 hours from inoculation [
16].
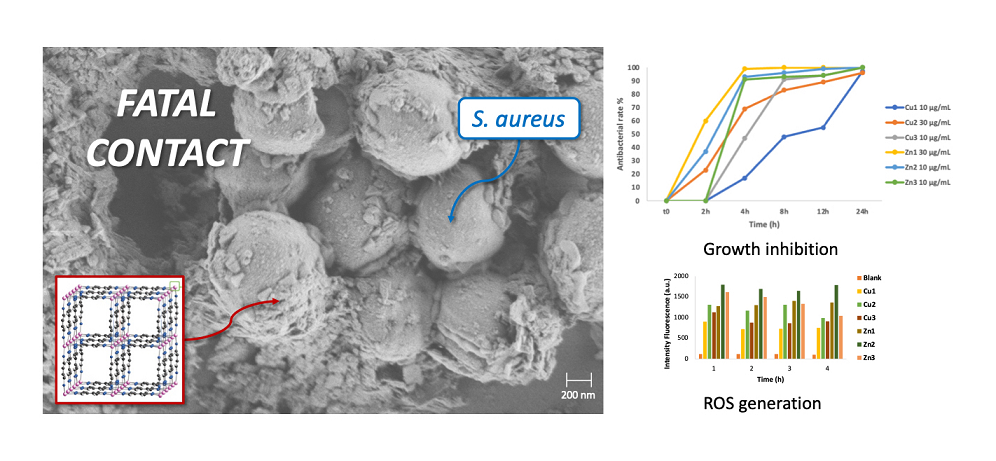
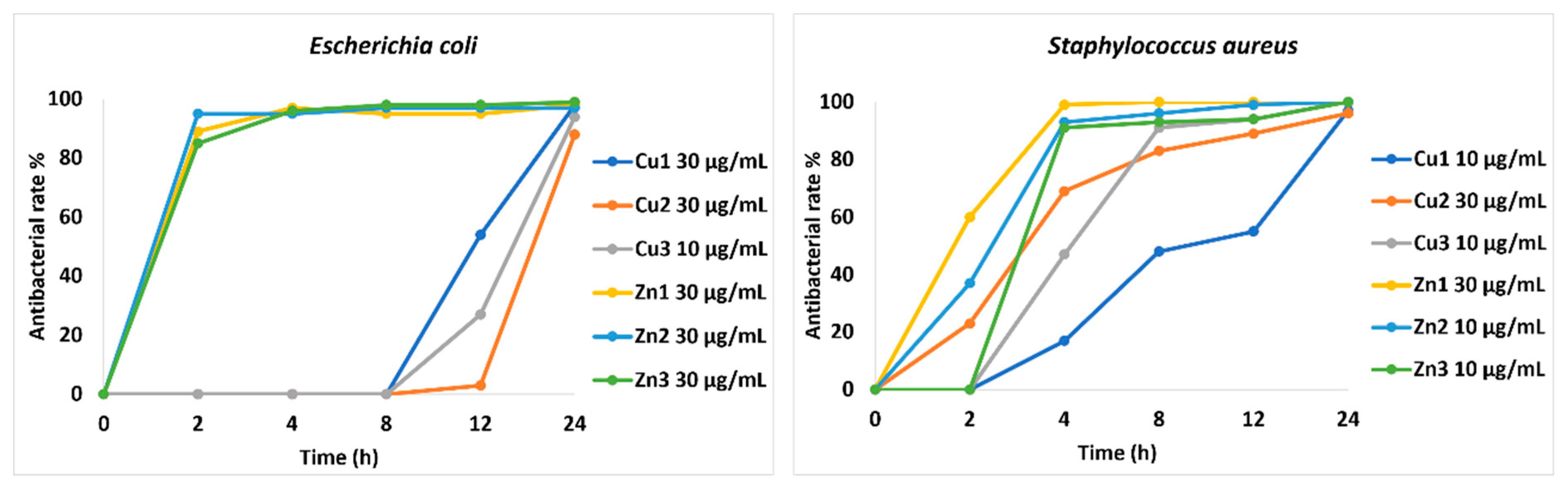
Figure 1 shows the trend of growth inhibition of MOFs against the two bacterial strains, represented as a percentage of antibacterial rate over time. In general, the results show a good activity for all compounds at the defined concentrations against both strains. In detail, all the compounds are bacteriostatic after 24 hours against
E. coli, except for
Cu2. On the other hand,
Cu1 and
Cu2, are bacteriostatic within 24 hours against
S. aureus, while the remaining compounds show not only a bacteriostatic action, but also a bactericidal one within 24 hours of the experiment.
Normally, to be effective, a biocide must bind to the bacterial cell wall, which is different in Gram+ and Gram- bacteria. Gram- bacteria (
E. coli) have a membrane barrier outside the cell wall, formed by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and proteins, while Gram+ bacteria (
S. aureus) have a less complex cellular structure [
17]. Based on this, the slightly lower performance observed against
E. coli compared to
S. aureus could be explained by considering the cell structure of the bacteria.
2.2. Antibacterial Mechanisms and Morphological Study
To further investigate the antimicrobial effect, studies focused on understanding the mechanism of action of
Zn/Cu-MOFs against selected bacteria were conducted. In detail, the assay for the detection of reactive oxygen species and the analysis of the membrane permeabilization of the treated bacterial cells were performed. Moreover, to analyse morphological changes in both bacterial strains after the treatment with our
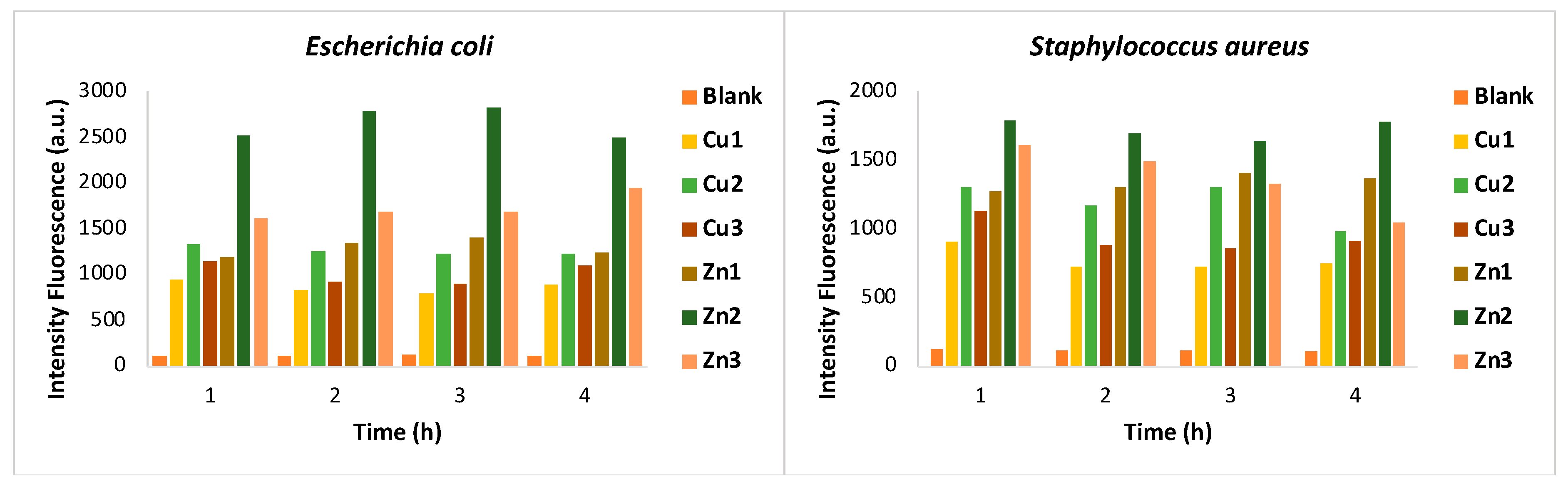
Zn/Cu-MOFs, SEM was employed. One of the antibacterial mechanisms could be related to the oxidative stress of cells in contact with MOFs. Thus, the resulting cell damage is quantified by measuring ROS generation through the DCFH-DA probe. Initial diacylation of DCFH-DA by cellular esterase, followed by oxidation by ROS, leads to the formation of DCF, which is highly fluorescent and is detected by excitation/emission fluorescence spectroscopy at 485 nm/535 nm.
Figure 2 shows the quantification of ROS generated after incubation of the bacterial strains with
Zn1-Zn3 and
Cu1-Cu3 for different time intervals (1-4 hours). The amount of ROS was estimated by measuring the fluorescence emission at 528 nm. The results confirm the generation of free radicals in both bacterial strains, while the fluorescence emission of the untreated bacterial suspension (blank) is negligible. In general, all zinc MOFs show greater activity than copper MOFs against both bacterial strains, confirming the growth inhibition data. Particularly, a very rapid antibacterial activity of
Zn2 was confirmed for both bacteria by the fluorescence intensity measured after only one hour of treatment.
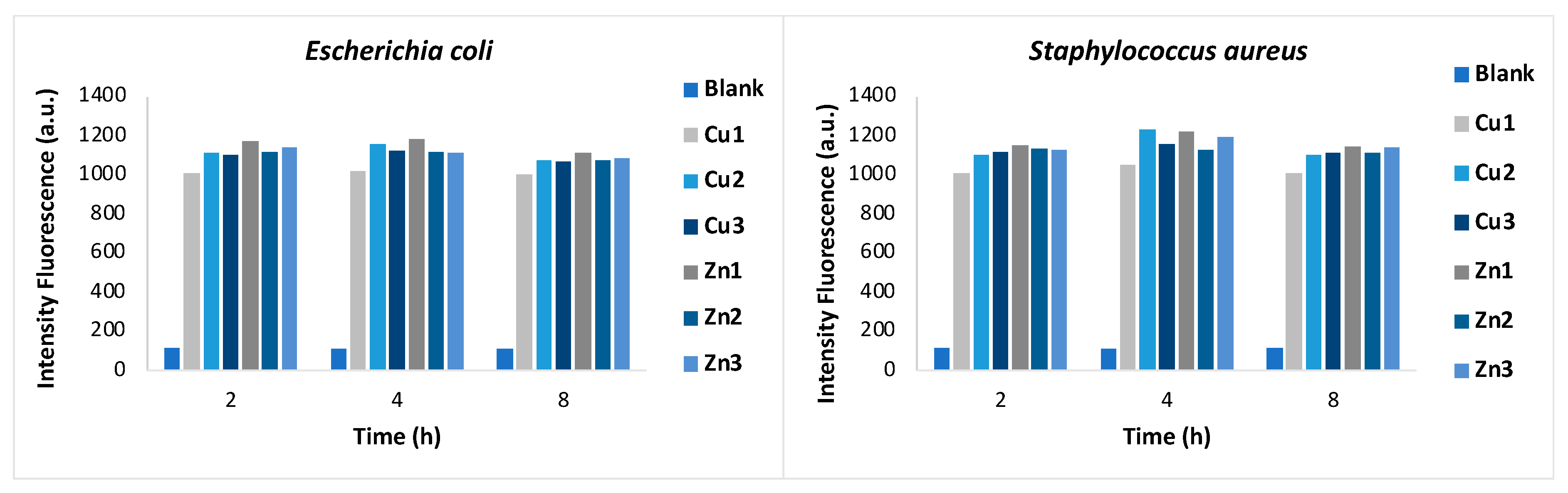
To evaluate the level of damage related to membrane permeability, the fluorescent PI staining assay was carried out. PI is an appropriate probe to assess membrane integrity, as it penetrates only the cells with damaged membrane. Once inside the cell, PI binds to DNA by intercalating between the bases with no preference. After binding, the fluorescence is enhanced and excited at 488 nm, resulting in emission maximum at 635 nm. The red fluorescence emission of bacterial cells exposed to
Zn1-Zn3 and
Cu1-Cu3 and stained with PI, was measured against untreated bacterial suspensions placed in contact with PI. As shown in
Figure 3, all MOFs tested at MIC concentration, show after 2 hours of treatment a statistically significant damage in comparison with the control (blank) against both bacterial cultures. The fluorescence intensity remains higher than the blank even after 8 hours of treatment against both bacteria. The results obtained verify the previous data, highlighting the ability of our MOFs to modify the permeability of the cell membrane, disorganizing it and leading to cell death. To further determine the overall viability of the bacterial cells, CLSM was performed by double fluorescence staining with Syto 9 and PI dyes. Based on the principle of staining, Syto 9 stain live and dead bacteria, which results in the production of green fluorescence. Similarly, dead bacteria emit red fluorescence upon staining with PI.
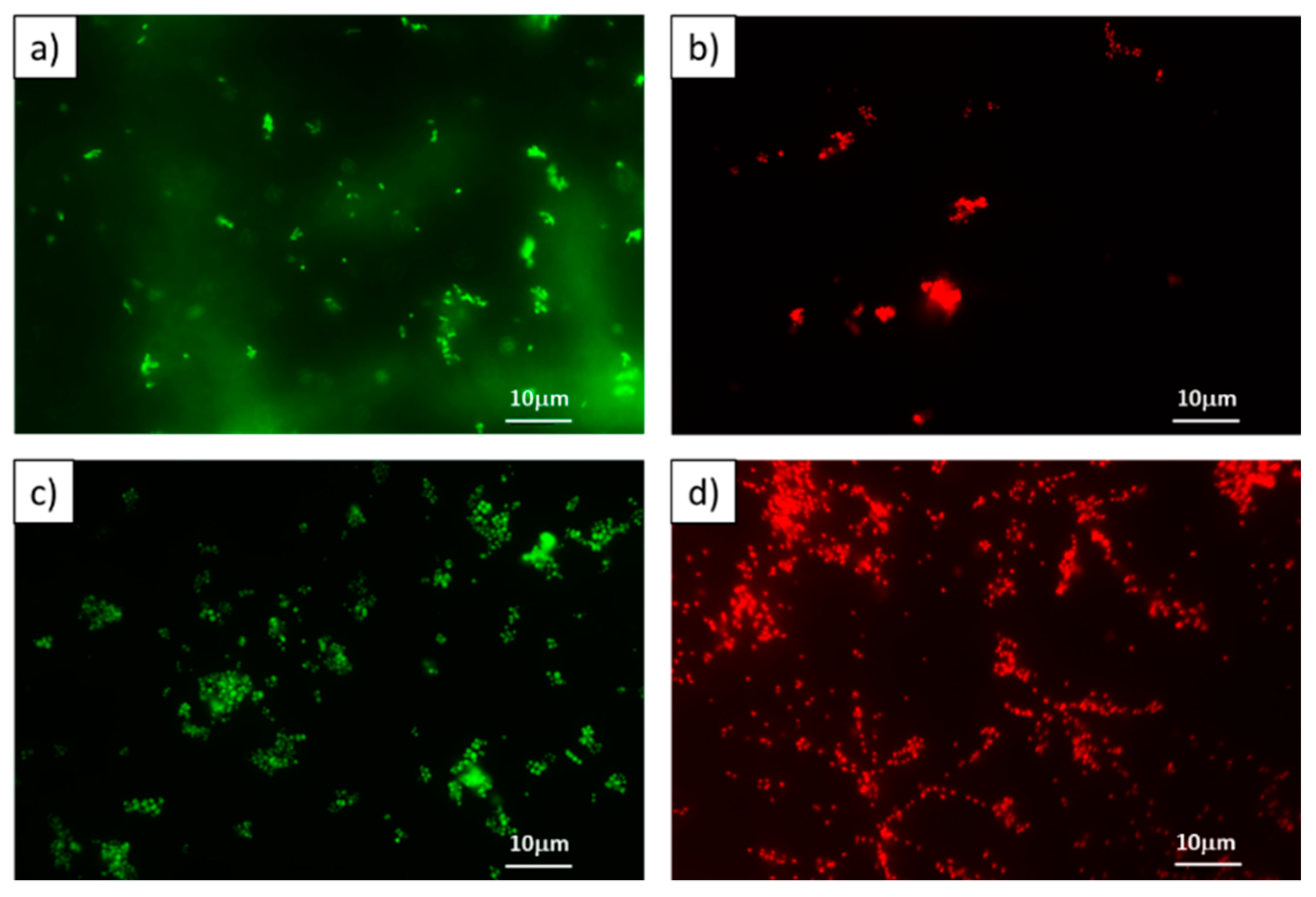
The CLSM images in
Figure 4 revealed that the untreated cells produced only sharp green light (4a and 4c), representing that the cells were alive and intact. On the other hand, the portion of cells tagged with red fluorescence was observed with
Zn1 and
Cu1 at MIC (4b and 4d). This could be due to the increased permeability of the cell membrane after treatment. These results revealed that most of the cell membranes of
S. aureus and
E. coli were severely destroyed following
Zn1 and
Cu1 treatment at the MIC, which was in agreement with previous results.
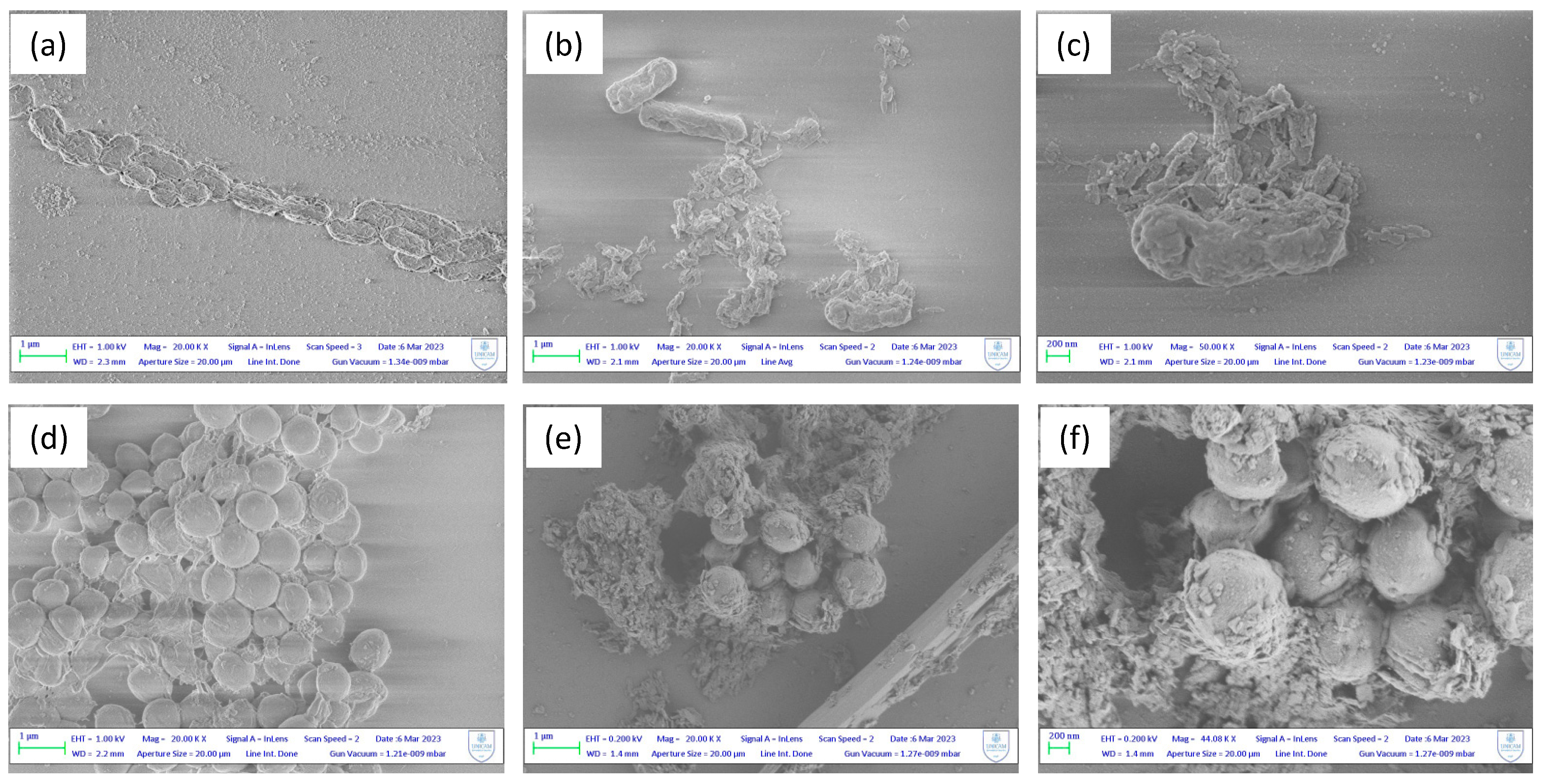
The structural alterations following the treatment of bacterial cells with MOFs was confirmed by SEM images.
Figure 5 demonstrates the destructive impact towards the treatment of
E. coli and
S. aureus with
Zn1, compared to the untreated cells. The contact between the bacterial membrane and the unsaturated metal nodes of the MOFs surface is favoured by the presence of nanometric MOFs particles, ranging from 50 to 100 nm. These are attracted to the negatively charged membrane, affecting its potential resulting in membrane disorganization and cell death. In 5a, a control sample of
E. coli exhibit regular rod-shaped morphology with smooth and regular surface, and the cells are uniform in size and distribution. In contrast, MOF-treated cells showed an irregular and wrinkled outer surface, with a notable change also in cell size likely due to agglomeration of MOF nanoparticles. In 5d, a control sample of
S. aureus show a rigid and smooth cell wall with a round appearance and a regular size (so called “bald cell”). The clear presence of biofilm-matrix is interesting, which is typically formed by the
S. aureus to ensure its survival. In 5e and 5f instead,
S. aureus show loss of the regular shape and dimensions after contact with the MOFs particles, which again have the tendency to agglomerate around the bacterial membrane. Even with SEM images it is therefore possible to confirm the previous results, thanks to the clear presence of the damage that occurs on the cell wall of the bacteria.
ICP-OES was used to determine the copper and zinc ions release-ability for the investigated MOFs. It was found that the concentrations of copper(II) and zinc(II) ions, released respectively from Cu1 and Zn1, were 0.008 and 0.010 ppm. From the values obtained it is possible to exclude the possibility that cellular damage may derive from the release of copper and zinc ions, since these are clearly lower than the MIC values found in the literature for both investigated ions. We can therefore hypothesize that the antibacterial mechanism is mainly due to the electrostatic interactions with the positive charges of the unsaturated metal nodes present on the surface of the MOFs, also known as the "chelation theory". These interactions lead to cell membrane disorganization resulting in cell disruption. Furthermore, Zn1-Zn3 and Cu1-Cu3 seem able to induce the production of ROS leading to the breakdown of cellular integrity.
3. Materials and Methods
All reagents were purchased (Merck) and used without further purification. All solvents were purified by conventional methods and stored under nitrogen. All reactions and manipulations for the syntheses of proligands H2Ln and their interactions with zinc and copper acetate dihydrate were carried out in the air. The solvothermal syntheses were carried out with flexiWAVE (Advanced Flexible Microwave Synthesis Platform) of the “MILESTONE”. The samples for microanalyses were dried in vacuo to constant weight (293 K, ca. 0.1 Torr). Elemental analyses (C, H, N) were performed in-house with a Fisons Instruments 1108 CHNS-O Elemental Analyser. Melting points are uncorrected and were recorded on a STMP3 Stuart scientific instrument and on a capillary apparatus. IR spectra were recorded from 4000 to 200 cm−1 with a PerkinElmer Spectrum 100 FT-IR instrument. 1H, NMR spectra of ligands were recorded with a 500 Bruker AscendTM (500 MHz for 1H) instrument operating at room temperature relative to TMS. Thermogravimetric analyses (TGA) were carried out in a N2 stream with a PerkinElmer STA 6000 simultaneous thermal analyser. The samples were heated from 303 to 923 K at a heating rate of 10 K min−1 under a nitrogen flow (20 mL min−1) Viability assays on bacterial and fungal cultures were performed with a confocal microscope Nikon ECLIPSE Ti. The Optical Density of the bacterial suspensions (OD600) was determined by using a BioTek mQuant MQX200 Microplate Spectrophotometer at 600 nm.
3.1. Synthetic Procedures
The ligands 4,4′-bipyrazole (H
2BPZ), 1,4-bis-4′-(3′,5′-dimethyl)-pyrazolylbenzene (H
2Me
4BPZPh) and 3-amino-4,4’-bipyrazole (H
2BPZNH
2) were synthesized by following the methods reported in the literature [
13,
18,
19].
General Procedure for Synthesis of Ligands and MOFs Zn1-Zn3 and Cu1-Cu3
MOFs
Zn2-Zn3 and
Cu2-Cu3 were initially synthesized according to previously published procedures through a solvothermal synthesis (in a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave under autogenous pressure) in DMF at 393 K for 48 h [
11,
13]. Whereas,
Zn1 and
Cu1 were prepared by mixing the metal acetate and H
2BPZ in methanol or acetonitrile, respectively, in the presence of sodium methoxide and, after 1/2 h of gentle warming at 318 K, the solution was left under stirring at room temperature for 24 h. The precipitate obtained was filtered off, washed twice with methanol or acetonitrile, and, after repeated washings with dichloromethane, it was outgassed in high vacuum (0.005 mbar) at 353 K overnight [
10].
Zn2-Zn3 and
Cu2-Cu3 were also prepared following a MAS procedure. In detail, zinc or copper acetate (0,4 mmol) was added to a solution of 1,4-bis(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)benzene (0,106 g, 0,4 mmol) or 3-amino-4,4’-bipyrazole (0,060 g, 0,4 mmol) in DMF (20 mL). The resulting clear solution was poured into a 100 mL Teflon vessel. The reaction mixture was heated at 413 K, 800 W, under stirring for 20 minutes, then it was cooled down to room temperature in 14 hours at 600 W. The resulting precipitate was filtered off, washed with hot DMF, solvent-exchanged with CH
2Cl
2 and air dired. The yield was significantly improved, resulting in a total yield of 82% (
Cu2), 91% (
Cu3), 79% (
Zn2) and 94% (
Zn3), with respect to previoulsy reported yields of 50%, 78%, 64%, and 86%, respectively. It is interesting to note that despite a different synthesis methodology, the BET values still remain high for both MOFs.
3.2. Antibacterial Studies
3.2.1. Bacterial Culture
The antibacterial activity of Zn1-Zn3 and Cu1-Cu3 was investigated against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) ATCC 25923 (PBI International) and Gram-negative, Escherichia coli (E. coli) ATCC 25922 (PBI International). Bacterial inocula were prepared with a monocolonies of E. coli or S. aureus grown aerobically at 335 K overnight using Tryptone Soya Broth (TSB) as the growth medium. For sterilization of the tubes, an Alfa-10-plus autoclave (PBI International) was used, operating at 394 K for 15 min. Bacteria proliferation was monitored by measuring the increase of optical density in the culture determined by using a BioTek mQuant MQX200 Microplate Spectrophotometer suspension at 600 nm (OD600). The enriched culture (log phase) obtained was further diluted to 106 CFUs/mL concentration.
3.2.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) were defined as the lowest concentration of the compound able to inhibit the growth of the microorganisms. The MIC determination of
Zn1-Zn3 and
Cu1-Cu3 was done by broth dilution method with slight modifications [
20] against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative, Escherichia coli. Briefly, each compound (10 mg) was dissolved in physiological solution (10 mL), then sonicated, to obtain a dispersed homogeneous stock solution. Serial dilutions were performed to test different concentrations (5, 10, 30, 50, 100, 500, 1000) μg/mL for the determination of MIC values. An equal concentration of bacterial inoculum (10
6 CFUs/mL), obtained by a direct colony suspension of an overnight culture in tryptone soya broth (TSB), was added to each sample. After incubation for 18−24 h at 335 K, the final solution was included uniformly into Petri dishes containing Plate Count Agar (OXOID).
3.4.3. Growth Inhibition Assay
To evaluate the antibacterial rate over time, the colony-forming units were measured by using the Agar diffusion method (Bauer et al., 1966). The test was performed using the MIC concentrations of each compound, which were dispersed in autoclaved physiological solution and to which 1 μL of the enriched culture (10
6 CFUs/mL) was then added. All the Eppendorf tubes were kept on an IKA KS 130 BASIC platform shaker for 24 h at a speed of 160 rpm. To obtain the bacterial colony count, the final solutions were diluted and included into Petri dishes containing Plate Count Agar (PCA). Maintaining the same procedure, an untreated sample strain was used as a control (blank). The tests were carried out at different time intervals (0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 hours) for mortality measurements over time. The growth inhibition was reported as Antibacterial Rate (%) using Equation 1:
where t
0 is the zero time at the beginning of the experiment and t
k is the specific time in hours of the rate withdrawal during the experiment.
3.3. Antibacterial Mechanism and Morphology Study
3.3.1. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection Assay
The production of ROS was evaluated using a fluorescent-dependent method where the oxidant sensitive probe, 2',7'-dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA), enhanced fluorescence under the condition of oxidative stress generation. Briefly, cells grown aerobically in TSB overnight and diluted to a concentration of 106 CFUs/mL were incubated for 30 minutes with DCFH-DA at 335K. 10 μL of bacterial suspension were then added to the Eppendorf containing 10 μg or 30 μg of Cu1-Cu3 and Zn1-Zn3, suspended in 1 mL of physiological solution. At the end of the treatment time, 100 μL of the suspension from each Eppendorf tube were transferred into 96 well plates, in triplicate, in the dark. The treatment is performed to evaluate the production of ROS after 1, 2, 3, 4 hours. Adopting the same procedure, an untreated sample strain was used as a control (blank). Fluorescence from each sample well was read using the FLUOstar Omega fluorescence cytometer from BMG LABTECH at 485/20 nm and 528/20 nm wavelengths for excitation and emission respectively. The average of the triplicate was calculated and reported as the intensity of fluorescence in arbitrary unit (a.u).
3.3.2. Propidium Iodide Uptake
Bacterial viability staining treated with compounds Cu1-Cu3 and Zn1-Zn3, was assessed using Propidium Iodide (PI) as a red-fluorescent dye, which penetrates only damaged cellular membranes. A suspension (106 CFUs/mL) of E. coli and S. aureus, treated with 10 μg or 30 μg of Cu1-Cu3 and Zn1-Zn3, were incubated for a period of 24 h at 335 K. After 4, 8, 12 hours, 100 μL of the content were transferred in triplicate into 96-well plate in the dark and 1,5 μL of Propidium Iodide (PI) were added in each well. Maintaining the same procedure, an untreated sample strain was used as a control (blank). Fluorescence emitted by the cells was read using the FLUOstar Omega fluorescence cytometer from BMG LABTECH at 485/20 nm and 528/20 nm wavelengths for excitation and emission respectively. The average of the triplicate was calculated and reported as the intensity of fluorescence in arbitrary unit (a.u).
3.3.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) Study
To evaluate the level of damage related to cell membrane permeability caused by
Zn1 and
Cu1 (arbitrary chosen), CLSM analysis was performed with LIVE/DEAD® BacLight™ Bacterial Viability Kits (Invitrogen). BacLight is composed of two nucleic acid-binding stains: SYTO 9™ which penetrates all bacterial membranes and stains the cells green, and PI which penetrates cells with damaged membranes, and stains the cells red [
21]. A bacterial suspension in the range of 1x10
8 CFUs/mL (0.3 OD
670) for E. coli and 1x10
7 CFUs/mL (0.15 OD
670) for S. aureus, were treated with 10 μg of
Zn1 and
Cu1, during the logarithmic growth phase for 4 h. Then suspensions were centrifugated at 10.000 rpm for 15 minutes. The supernatant was removed, and the pellet was resuspended in 0.85 % NaCl solution. After the procedure was repeated three times, a mixture of Syto 9 and PI was prepared and added to all samples in the dark. They were incubated for 15 min in the absence of light and finally 10 μL of each sample were fixed between a slide and an 18 mm square coverslip to observe the fluorescence under confocal microscope (Nikon ECLIPSE Ti). The control assay was conducted without treatment. The excitation/emission for these dyes are 480/500 nm for SYTO 9 and 490/635 nm for PI.
3.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Study
SEM was performed to study the physical and morphological variations in bacterial cells after their treatment with
Zn1 and
Cu1 MOFs, arbitrary chosen. Bacterial strains were processed according to a previously described procedure [
22]. Briefly, log phase cells of E. coli and S. aureus (10
6 CFUs/mL) were incubated with 1 mg of
Zn1 and
Cu1, for 4 hours at 335 K. After the incubation, bacterial cells were centrifuged, washed thrice with fresh physiological solution, followed by glutaraldehyde (2.5%, v/v) fixation for 2 h on silicon plates. The latter were dehydrated in ethanol (10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, 90%, 100%, v/v). Finally, the silicon plates were placed on aluminium stubs using self-adhesive carbon conductive tab, and they were chrome coated. The bacterial cells were studied on SEM operating at 1-5 kV. The unprocessed bacterial cells were chosen as control samples.
3.3.5. Copper and Zinc Ion Release Test
The concentrations of released copper and zinc ions were measured under conditions amenable to biological testing, by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES). The samples Zn1 and Cu1 were arbitrarily selected and 1 mg of each was suspended in 10 mL of physiological solution for 72 hours at 335 K. Finally, the suspensions were filtered through a pad of Celite due to the small grain size of the samples, and the maximum quantity of released ions was evaluated.
4. Conclusions
The present work demonstrated that it is possible to use Zn(II) and Cu(II) bis(pyrazolyl)-based MOFs as antibacterial agents due to their significant antibacterial activity. Particularly, Zn-MOFs achieve within the first hours of exposure a great viable cells reduction. The antibacterial mechanism of Cu1-Cu3 and Zn1-Zn3 was suggested to be the disruption of the integrity of bacterial cell membrane and generation of ROS through stress induced by contact with MOFs’ surface. This hypothesis was also confirmed by the significant morphological alterations observed in the SEM images, where a change in the regular shape of the bacteria is clearly visible, due to the agglomeration of the MOFs particles around the cell membrane and to the established electrostatic interactions. Damage to the cell membrane permeability occurs without the release of metal ions. Finally, the total yield for Cu1-Cu2 and Zn1-Zn2 has been increased by exploiting the microwave-assisted synthesis, also improving their reaction times.
Author Contributions
S. Xhafa – synthesis and characterization of copper MOFs and antimicrobial investigation – writing – original draft; L. Olivieri – antimicrobial and biological investigation –data curation; C. Di Nicola – synthesis and characterization of ligands – formal analysis; R. Pettinari – resources and writing – review & editing; C. Pettinari – project administration and ligands and MOFs synthesis supervision; A. Tombesi – synthesis and characterization of zinc MOFs - invstigation; F. Marchetti – conceptualization, funding acquisition and writing – review & editing.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to the University of Camerino (Italy) for financial support. The research grant of Dr. Laura Olivieri and doctoral scholarship of Dr. Sonila Xhafa were funded under the frame of the project Nano4-Fresh – Nanomaterials for an environmentally friendly and sustainable handling of perishable products (PRIMA19_00246), which is part of the Partnership on Research and Innovation in the Mediterranean Area (PRIMA) Programme supported by the European Union and funded by the national funding bodies of Participating States (MUR in Italy is gratefully acknowledged). The University of Camerino is also acknowledged for partial funding through the Research Project FAR 2022 PNR “Development of Innovative Antimicrobial Biodegradable Food Packaging” (ActiveFoodPack).
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
References
- Friedman, N.D.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The Negative Impact of Antibiotic Resistance. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2016, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxminarayan, R.; Matsoso, P.; Pant, S.; Brower, C.; Røttingen, J.-A.; Klugman, K.; Davies, S. Access to Effective Antimicrobials: A Worldwide Challenge. The Lancet 2016, 387, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, A.; Elliott, A.G.; Kan, A.; Dinh, H.; Bräse, S.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.; Chen, F.; Humaidy, D.; Jung, N.; et al. Metal Complexes as Antifungals? From a Crowd-Sourced Compound Library to the First In Vivo Experiments. JACS Au 2022, 2, 2277–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Di Nicola, C.; Tombesi, A.; Scuri, S.; Marchetti, F. Antimicrobial MOFs. Coord Chem Rev 2021, 446, 214121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, C.; Marchetti, F.; Mosca, N.; Tosi, G.; Drozdov, A. Application of Metal − Organic Frameworks. Polym Int 2017, 66, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C. “Joe”; Kitagawa, S. Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5415–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem Rev 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Chen, T.; Pan, X. Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Materials for Antimicrobial Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3808–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Liu, X.; Wu, S. Metal Organic Framework-Based Antibacterial Agents and Their Underlying Mechanisms. Chem Soc Rev 2022, 51, 7138–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinari, C.; Tăbăcaru, A.; Boldog, I.; Domasevitch, K. V.; Galli, S.; Masciocchi, N. Novel Coordination Frameworks Incorporating the 4,4′-Bipyrazolyl Ditopic Ligand. Inorg Chem 2012, 51, 5235–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timokhin, I.; Pettinari, C.; Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, R.; Condello, F.; Galli, S.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Novel Coordination Polymers with (Pyrazolato)-Based Tectons: Catalytic Activity in the Peroxidative Oxidation of Alcohols and Cyclohexane. Cryst Growth Des 2015, 15, 2303–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismara, R.; Tuci, G.; Tombesi, A.; Domasevitch, K. V.; Di Nicola, C.; Giambastiani, G.; Chierotti, M.R.; Bordignon, S.; Gobetto, R.; Pettinari, C.; et al. Tuning Carbon Dioxide Adsorption Affinity of Zinc(II) MOFs by Mixing Bis(Pyrazolate) Ligands with N-Containing Tags. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 26956–26969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismara, R.; Tuci, G.; Mosca, N.; Domasevitch, K. V.; Di Nicola, C.; Pettinari, C.; Giambastiani, G.; Galli, S.; Rossin, A. Amino-Decorated Bis(Pyrazolate) Metal–Organic Frameworks for Carbon Dioxide Capture and Green Conversion into Cyclic Carbonates. Inorg Chem Front 2019, 6, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ye, J.; Sun, Y.; Bogale, R.F.; Zhao, L.; Tian, P.; Ning, G. Ligand Effects on the Structural Dimensionality and Antibacterial Activities of Silver-Based Coordination Polymers. Dalton Transactions 2014, 43, 10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, L.; Engqvist, H.; Öhman-Mägi, C. Effect of Copper Ion Concentration on Bacteria and Cells. Materials 2019, 12, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankey, G.A.; Sabath, L.D. Clinical Relevance of Bacteriostatic versus Bactericidal Mechanisms of Action in the Treatment of Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004, 38, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamakura, K.; Perez-Ballestero, R.; Luo, Z.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J. Comparison of Bactericidal Activities of Silver Nanoparticles with Common Chemical Disinfectants. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldog, I.; Sieler, J.; Chernega, A.N.; Domasevitch, K. V 4,4′-Bipyrazolyl: New Bitopic Connector for Construction of Coordination Networks. Inorganica Chim Acta 2002, 338, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-H.; Huang, H.-P.; Yu, S.-Y.; Li, X.-P. Design and Synthesis of Polypyrazolyl Compounds as a New Type of Versatile Building Blocks†. Chin J Chem 2006, 24, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and Broth Dilution Methods to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Substances. Nat Protoc 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, L.; Prévost, M.; Barbeau, B.; Coallier, J.; Desjardins, R. LIVE/DEAD® BacLightTM: Application of a New Rapid Staining Method for Direct Enumeration of Viable and Total Bacteria in Drinking Water. J Microbiol Methods 1999, 37, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nicola, C.; Marchetti, F.; Tombesi, A.; Xhafa, S.; Campitelli, P.; Moroni, M.; Galli, S.; Pettinari, R.; Pettinari, C. Antibacterial Activity of Copper Pyrazolate Coordination Polymers. New J. Chem. Submitted.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).