Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
28 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
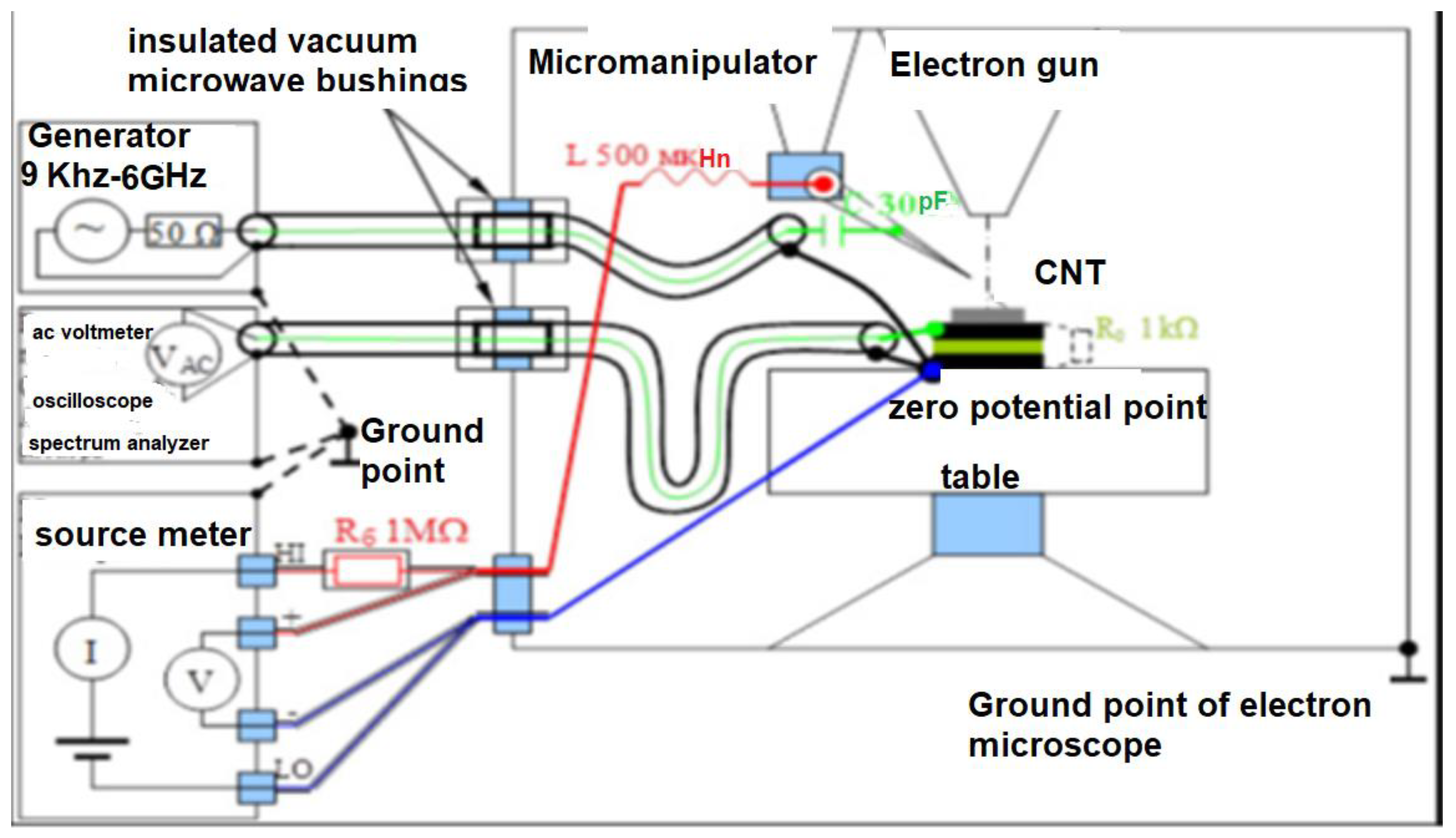
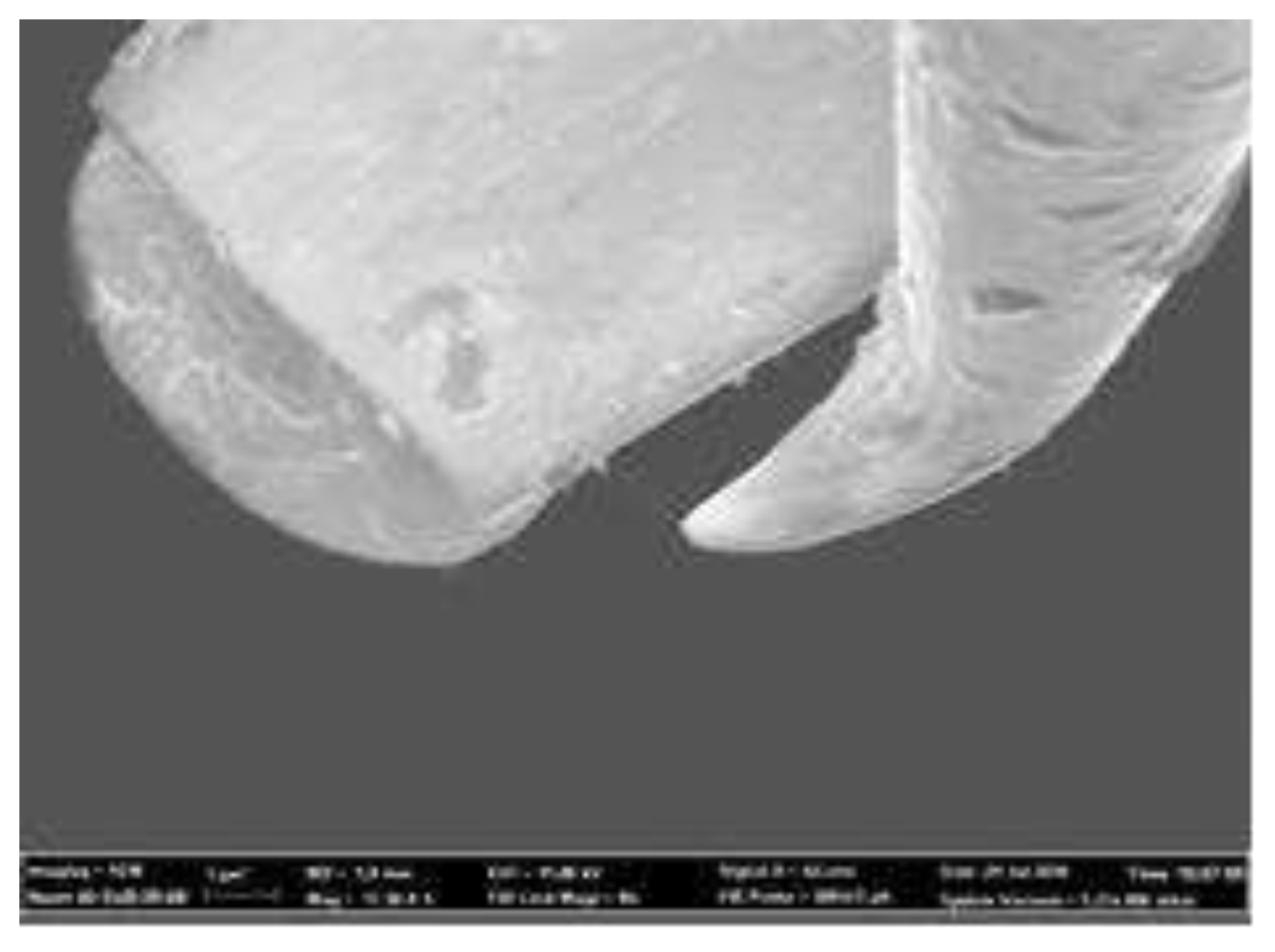
2. Materials and Methods
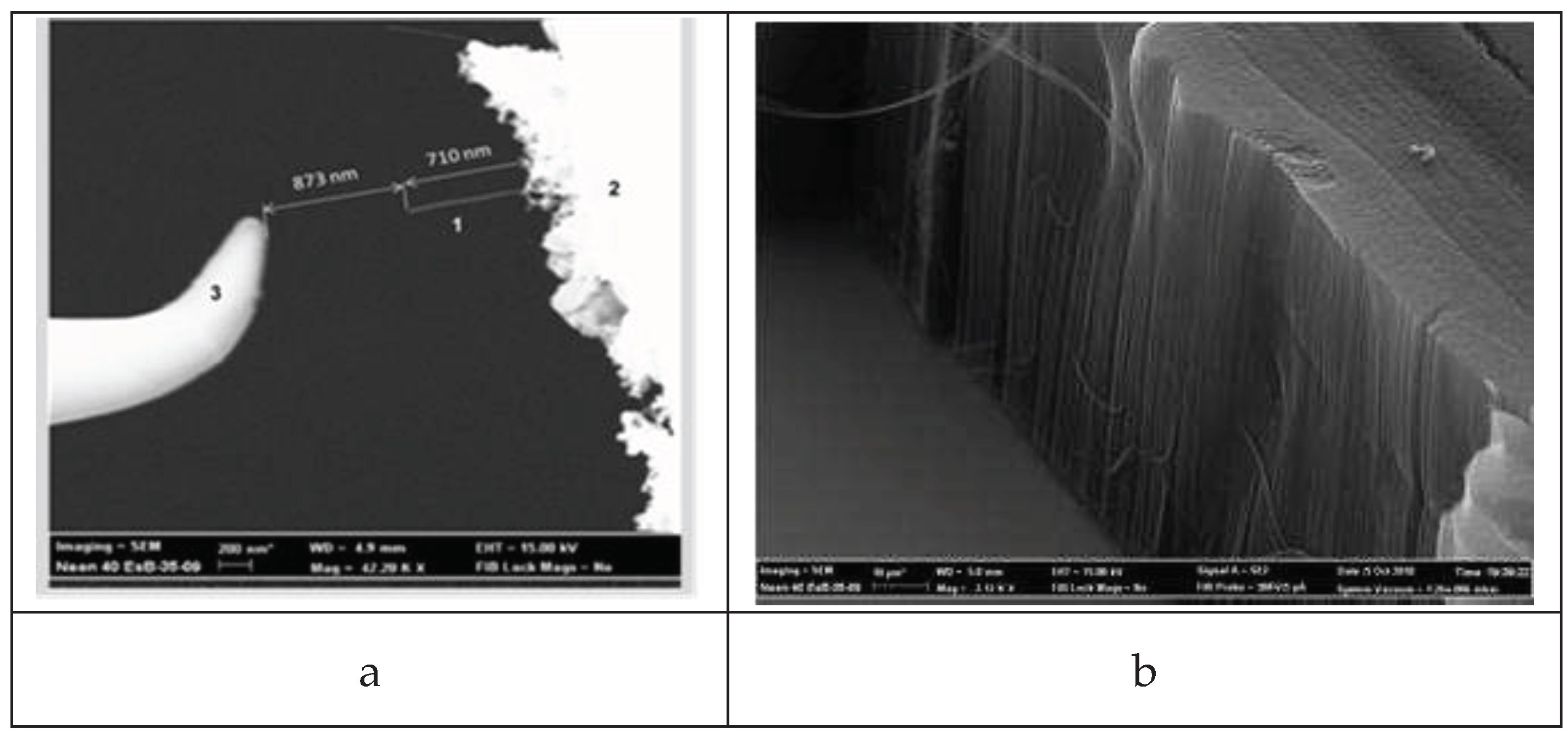
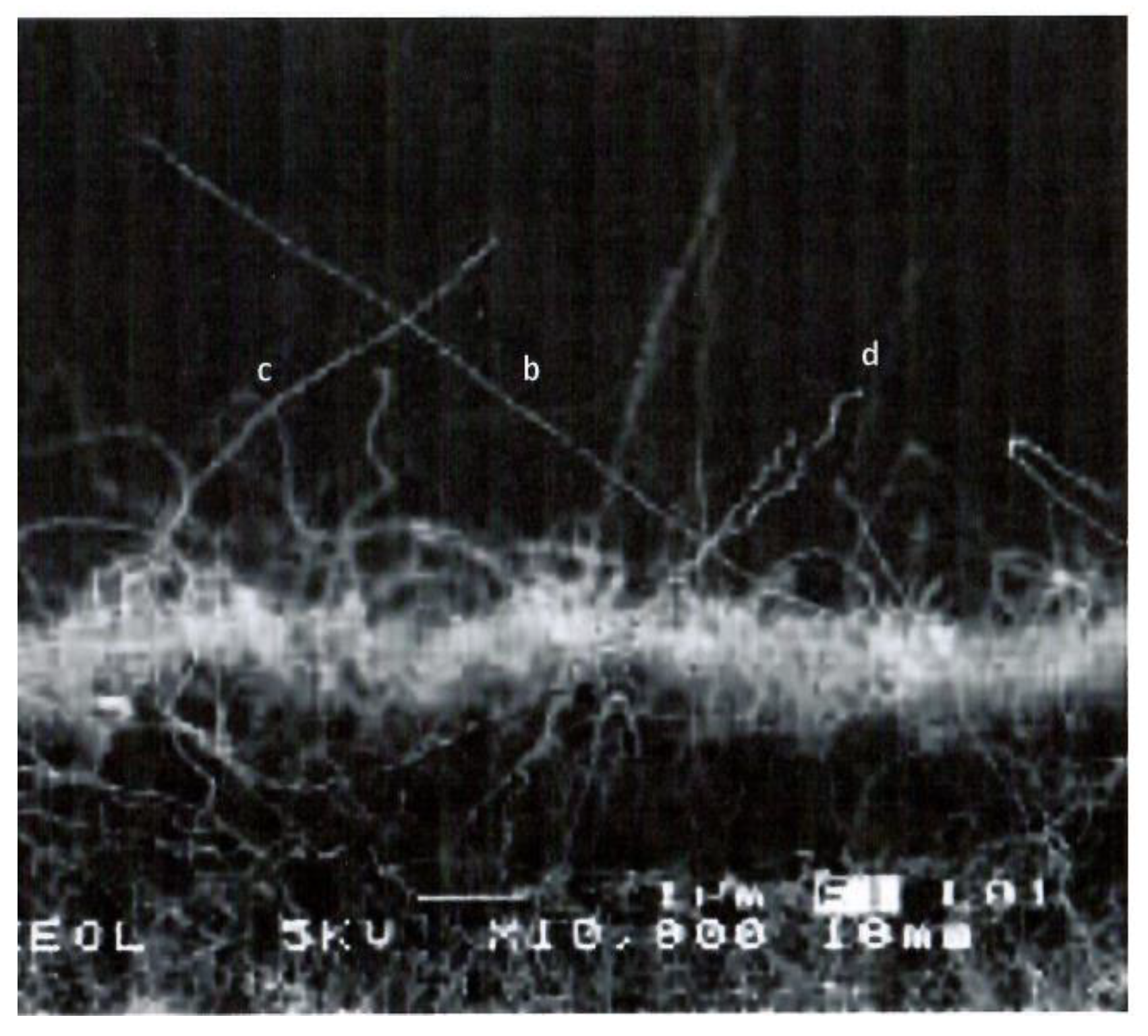
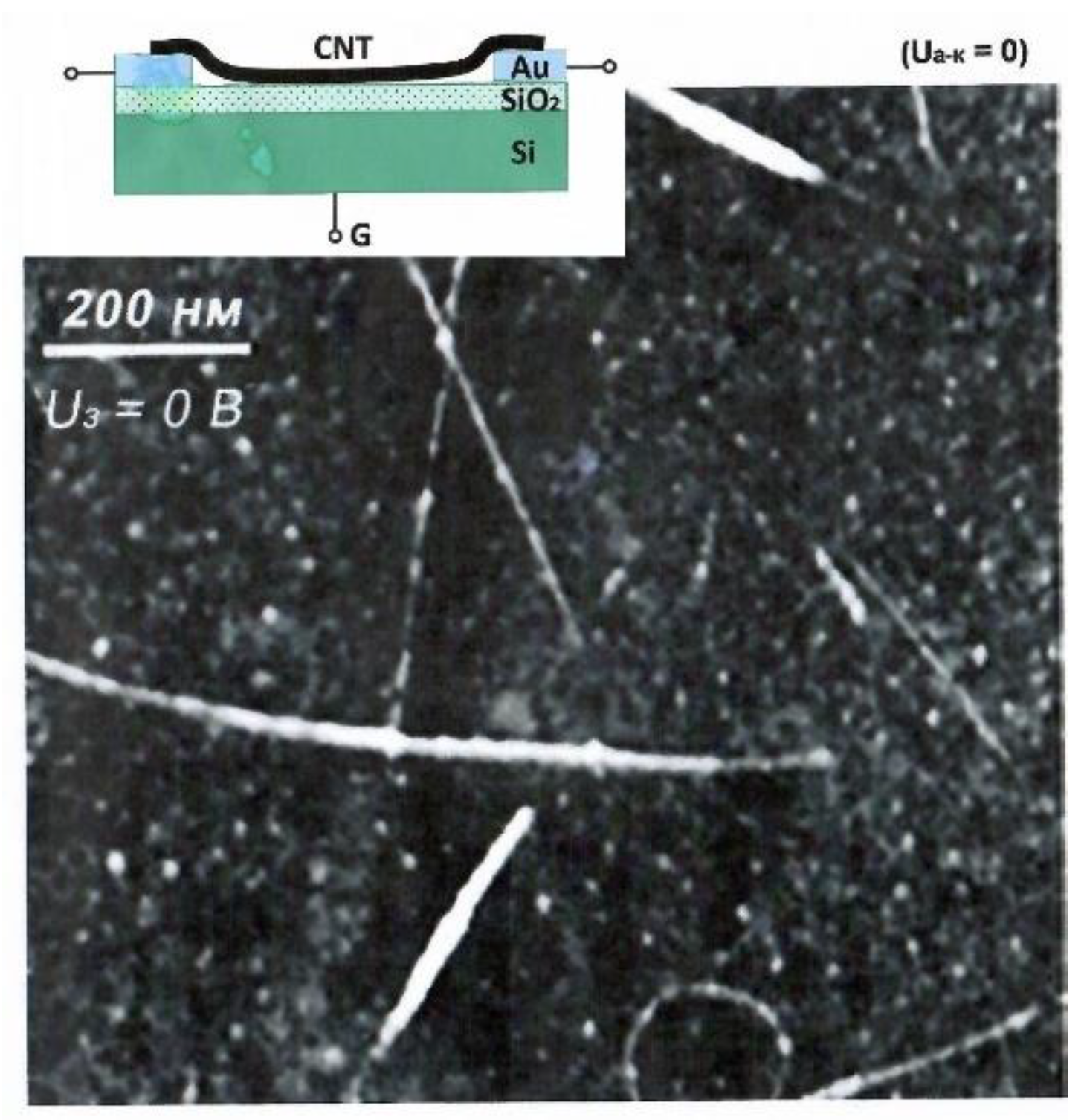
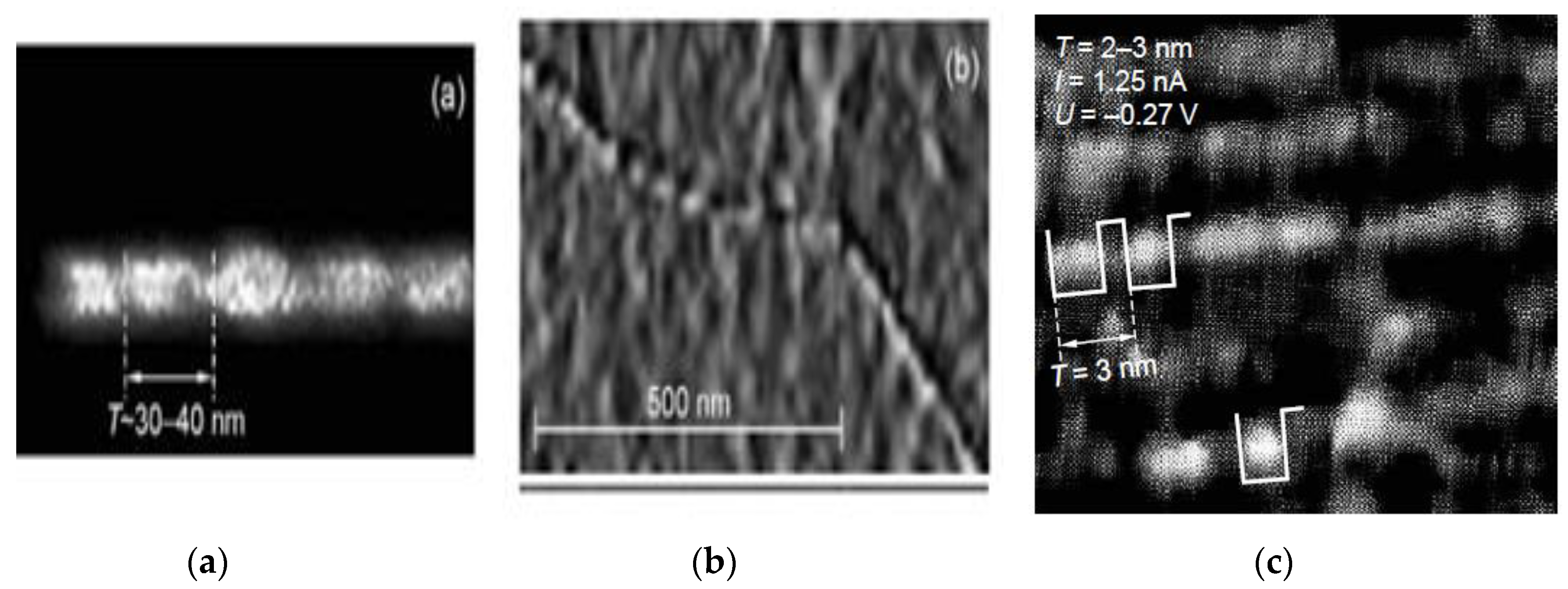
3. Experimental studies of the structure of closed CNTs.
4. Experimental results
4.1. Experimental studies of the structure of closed CNTs
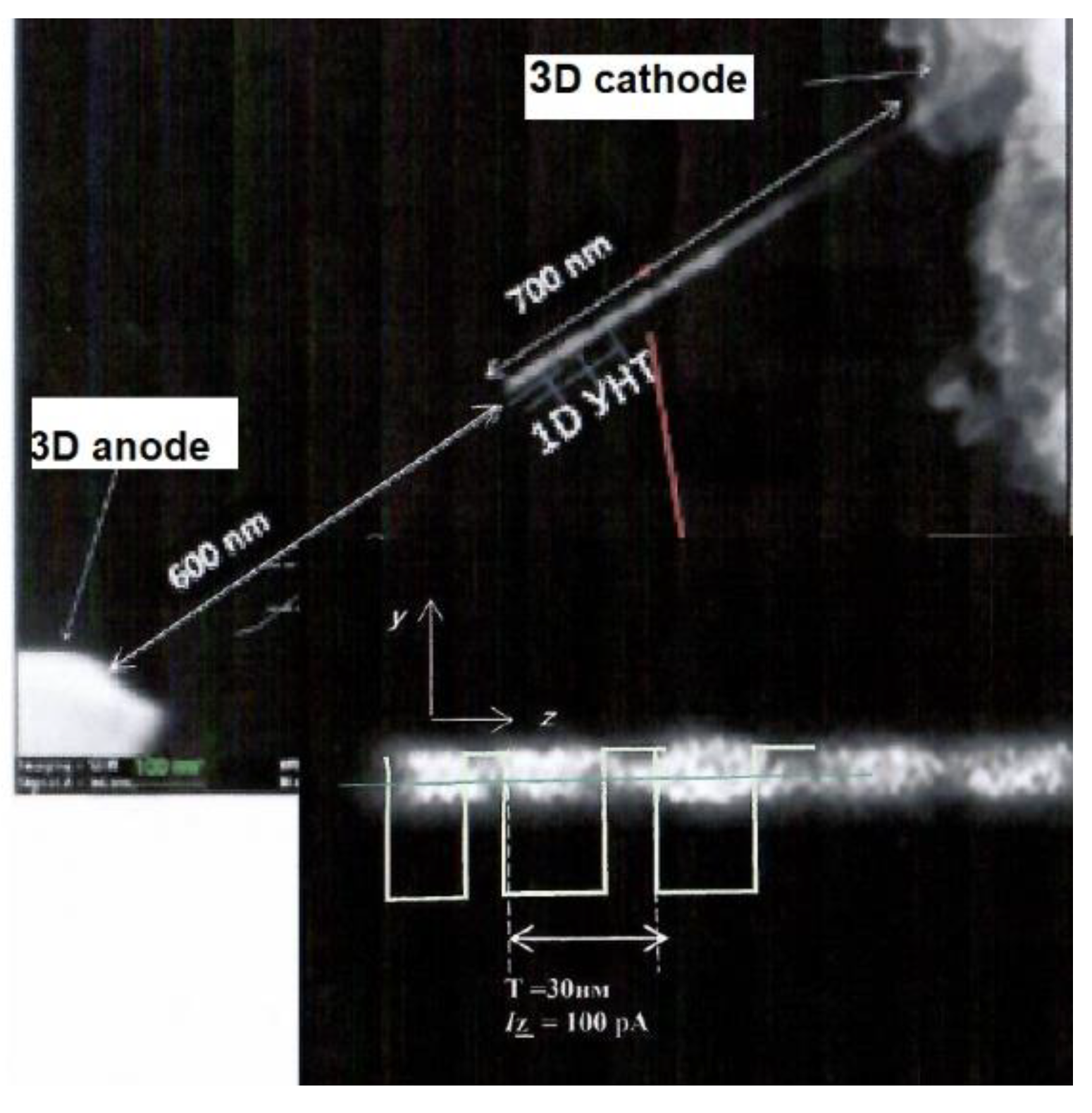
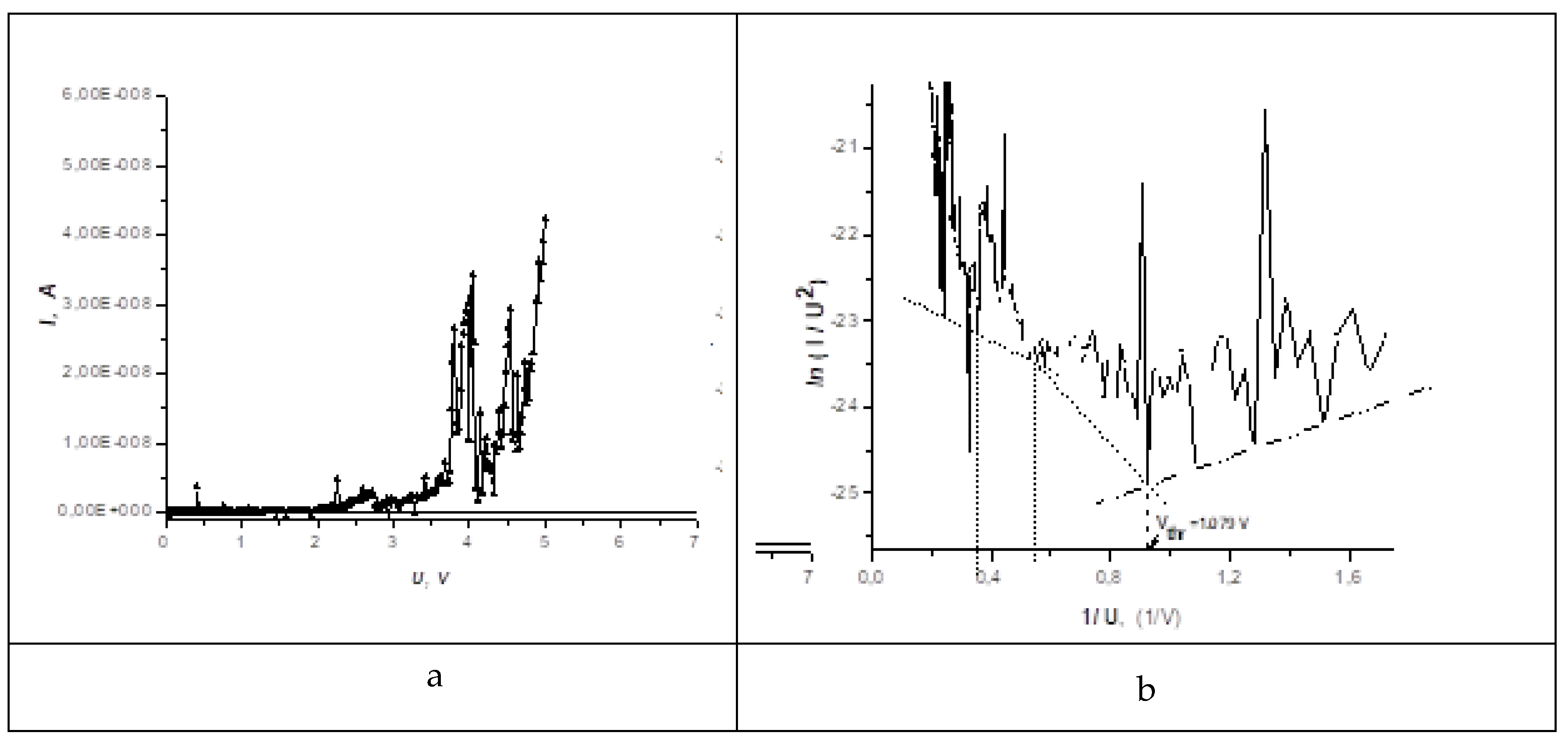
4.2. Experimental studies of the features of charge transfer in the circuit of a nanotube emitter
5. Discussion
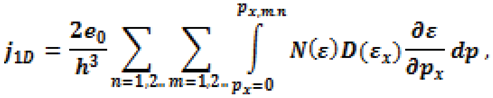
6. Conclusion
Funding
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosakovskaia, Z.I.; Chernozatonskii, L.A.; Fedorov, E.A. Nanofiber carbon structure. JETP Lett. 1992, 56, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Barrelenes, C.L.A. Tubelenes—A new class of cage carbon molecules and its solids. Physics Letters A 1992, 166, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Bethune, D.S.; Kiang, C.H.; De Vries, M.S.; Gorman, G.; Savoy, R.; Vazquez, J.; Beyers, R. Cobalt-catalysed growth of carbon nanotubes with single-atomic-layer walls. Nature 1993, 363, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernozatonskii, L.A.; Gulyaev, Y.V.; Kosakovskaja, Z.J.; Sinitsyn, N.I.; Torgashov, G.V.; Zakharchenko, Y.F.; Val'chuk, V.P. Electron field emission from nanofilament carbon films. Chemical Physics Letters 1995, 233, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Electron field emitters based on carbon nanotubes. Uspekhi Fizicheskikh Nauk 2010, 180, 897–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidelman, E.D.; Arkhipov, A.V. Field emission from carbon nanostructures: Models and experiment. Physics-Uspekhi 2020, 63, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, O. Electron field emission from carbon nanotubes. Comptes Rendus Physique 2003, 4, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, W.I.; Teo KB, K.; Mann, M.; Bu IY, Y.; Amaratunga GA, J.; De Jonge, N.; El-Gomati, M. Carbon nanotubes as electron sources. physica status solidi (a) 2006, 203, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.R.; Hwang, O.J.; Cho, B.; Park, K.C. Scanning electron imaging with vertically aligned carbon nanotube (CNT) based cold cathode electron beam (C-beam). Vacuum 2020, 182, 109696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Ren, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Ballistic transport in bent-shaped carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2019, 149, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lu, W.G.; Li, J.J.; Bai, X.D.; Gu, C.Z. Multichannel ballistic transport in multiwall carbon nanotubes. Physical review letters 2005, 95, 086601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletskii, A.V. Transport properties of carbon nanotubes. Physics-Uspekhi 2009, 52, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Xu, X.; Cole, M.T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, Y. Design and simulation of a multi-sheet beam terahertz radiation source based on carbon-nanotube cold cathode. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, W.I.; Teo KB, K.; Amaratunga GA, J.; Legagneux, P.; Gangloff, L.; Schnell, J.P.; Groening, O. Carbon nanotubes as field emission sources. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2004, 14, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Hu, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z. Carbon nanotubes as field emitter. Journal of Nanoscience and nanotechnology 2010, 10, 7876–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Q.; Cole, M.T.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yan, Y. A low-voltage, premodulation terahertz oscillator based on a carbon nanotube cold cathode. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 2020, 67, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Xu, X.; Cole, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y. A high-current-density terahertz electron-optical system based on carbon nanotube cold cathode. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 2020, 67, 5760–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Liang, F.; Sun, A.B. Review on development of carbon nanotube field emission cathode for space propulsion systems. High Voltage 2020, 5, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Amlani, I.; Orlov, A.O.; Snider, G.L.; Fay, P.J. Operation of single-walled carbon nanotube as a radio-frequency single-electron transistor. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 445203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatov, E.S.; Kolesov, V.V. The single electronics: Past, present, future. RENSIT 2012, 4, 71–90e. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Dai, Q. Ultra Coherent Single Electron Emission of Carbon Nanotubes. Advanced Materials 2023, 2300185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, H.; Tanemura, M.; Filip, V.; Iwata, K.; Takahashi, K.; Okuyama, F. Carbon nanotubes as electron source in an x-ray tube. Applied physics letters 2001, 78, 2578–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musatov, A.L.; Gulyaev, Y.V.; Izrael’yants, K.R.; Kukovitskii, E.F.; Kiselev, N.A.; Maslennikov, O.Y.; Chirkova, E.G. A compact X-ray tube with a field emitter based on carbon nanotubes. Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics 2007, 52, 714–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmee, R.J.; Collins, C.M.; Milne, W.I.; Cole, M.T. X-ray generation using carbon nanotubes. Nano Convergence 2015, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psuja, P.; Hreniak, D.; Strek, W. (2009, February). The concept of a new simple low-voltage cathodoluminescence set-up with CNT field emission cathodes. In Reliability, Packaging, Testing, and Characterization of MEMS/MOEMS and Nanodevices VIII (Vol. 7206, pp. 132–137). SPIE.
- Wilson, N.R.; Macpherson, J.V. Carbon nanotube tips for atomic force microscopy. Nature nanotechnology 2009, 4, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingaya, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Aono, M. Carbon nanotube tip for scanning tunneling microscopy. Physica B: Condensed Matter 2002, 323, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, W. Scanning tunneling microscopy of carbon nanotubes. Applied Physics A 1999, 69, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, L.P.; Thiry, P.A.; Lambin, P.; Journet, C.; Bernier, P.; Lucas, A.A. Influence of tunneling voltage on the imaging of carbon nanotube rafts by scanning tunneling microscopy. Applied physics letters 1998, 73, 3680–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Hafner, J.H.; Rinzler, A.G.; Colbert, D.T.; Smalley, R.E. Nanotubes as nanoprobes in scanning probe microscopy. Nature 1996, 384, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J. Vacuum gauges with emitters based on carbon nanotubes. Technical physics letters 2005, 31, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, R.H.; Nordheim, L. Electron emission in intense electric fields. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character 1928, 119, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, R.G. Field emission: New theory for the derivation of emission area from a Fowler–Nordheim plot. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B: Microelectronics and Nanometer Structures Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena 1999, 17, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.D.; Chen, L. Generalized Fowler-Nordheim theory of field emission of carbon nanotubes. Physical Review Letters 2008, 101, 027602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.L. Electron emission theory and its application: Fowler–Nordheim equation and beyond. Journal of vacuum science & technology B: Microelectronics and nanometer structures processing, measurement, and phenomena 2003, 21, 1528–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, B. Electronic field emission models beyond the Fowler-Nordheim one. Journal of Applied Physics 2017, 122, 215105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vul, A.; Reich, K.; Eidelman, E.; Terranova, M.L.; Ciorba, A.; Orlanducci, S.; Rossi, M. A model of field emission from carbon nanotubes decorated by nanodiamonds. Advanced Science Letters 2010, 3, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkov, V.L.; Osipov, V.A. Energy distributions of field emitted electrons from carbon nanosheets: Manifestation of the quantum size effect. JETP letters, 2009, 90, P. 278-283. 41. Xie, S.S., Li, W.Z., Qian, L.X., Chang, B.H., Fu, C.S., Zhao, R.A., Wang, G. (1996). Equilibrium shape equation and possible shapes of carbon nanotubes. Physical Review B, 54, 16436. 90.
- Kibis, O.V.; Parfitt DG, W.; Portnoi, M.E. Superlattice properties of carbon nanotubes in a transverse electric field. Physical Review B 2005, 71, 035411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuela, A.; Chico, L.; Jaskólski, W. Electronic band structure of carbon nanotube superlattices from first-principles calculations. Physical Review B 2008, 77, 085435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, A.A.; Khoeini, F. Electron localization in superlattice-carbon nanotubes. The European Physical Journal B 2010, 78, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, J.W.; Venema, L.C.; Rinzler, A.G.; Smalley, R.E.; Dekker, C. Electronic structure of atomically resolved carbon nanotubes. Nature 1998, 391, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Nshimiyimana, J.P.; Deng, Y.; Hu, X.; Chi, X.; Sun, L. Observation of van Hove singularities and temperature dependence of electrical characteristics in suspended carbon nanotube Schottky barrier transistors. Nano-Micro Letters 2018, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fedorov, G.; Shafranjuk, S.E.; Klapwijk, T.M.; Cooper, B.K.; Lewis, R.M.; Barbara, P. Electronic transport and possible superconductivity at van hove singularities in carbon nanotubes. Nano letters 2015, 15, 7859–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskólski, W.; Stachow, A.; Chico, L. Band structure and quantum conductance of metallic carbon nanotube superlattices. Acta Physica Polonica-Series A General Physics 2005, 108, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuela, A.; Chico, L.; Jaskólski, W. Electronic band structure of carbon nanotube superlattices from first-principles calculations. Physical Review B 2008, 77, 085435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.M. (2002). Nanowire superlattices.
- Lambin, P.; Loiseau, A.; Culot, C.; Biro, L.P. Structure of carbon nanotubes probed by local and global probes. Carbon 2002, 40, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, M.V.; Dadidchik, F.I.; Kovalevsky, S.A. Ordered adsorption of carbon nanotubes on pyrolytic graphite Surface. X-ray, synchrotron neutron research. 2001. N. 7. C. 103. In Russian.
- Dalidchik, F.I.; Grishin, M.V.; Kovalevsky, S.A. Features of the electronic structure of interacting nanocarbon particles. Microsystem Engineering 2004, (5), 29-33. In Russian.
- Dalidchik, F.I.; Balashov, E.M.; Grishin, M.V. Scanning tunneling spectroscopy of interacting nanocarbon sp2 structures. Russian Chemical Journal 2005, 159, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Dalidchik, F.I.; Shub, B.R. Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy of imperfect and interacting nanoparticles (metal oxides and carbon). Russian Nanotechnologies, 2006, 1. Jg., Nr. 1-2, S. 82-96. In Russian.
- Bower, C.; Zhu, W.; Shalom, D.; Lopez, D.; Chen, L.H.; Gammel, P.L.; Jin, S. On-chip vacuum microtriode using carbon nanotube field emitters. Applied physics letters 2002, 80, 3820–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohara, H.; Dang, W.L.; Siegel, P.H.; Hoenk, M.; Husain, A.; Scherer, A. (2003, December). Field emission testing of carbon nanotubes for THz frequency vacuum microtube sources. In Reliability, Testing, and Characterization of MEMS/MOEMS III (Vol. 5343, pp. 227–234). SPIE.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




