Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
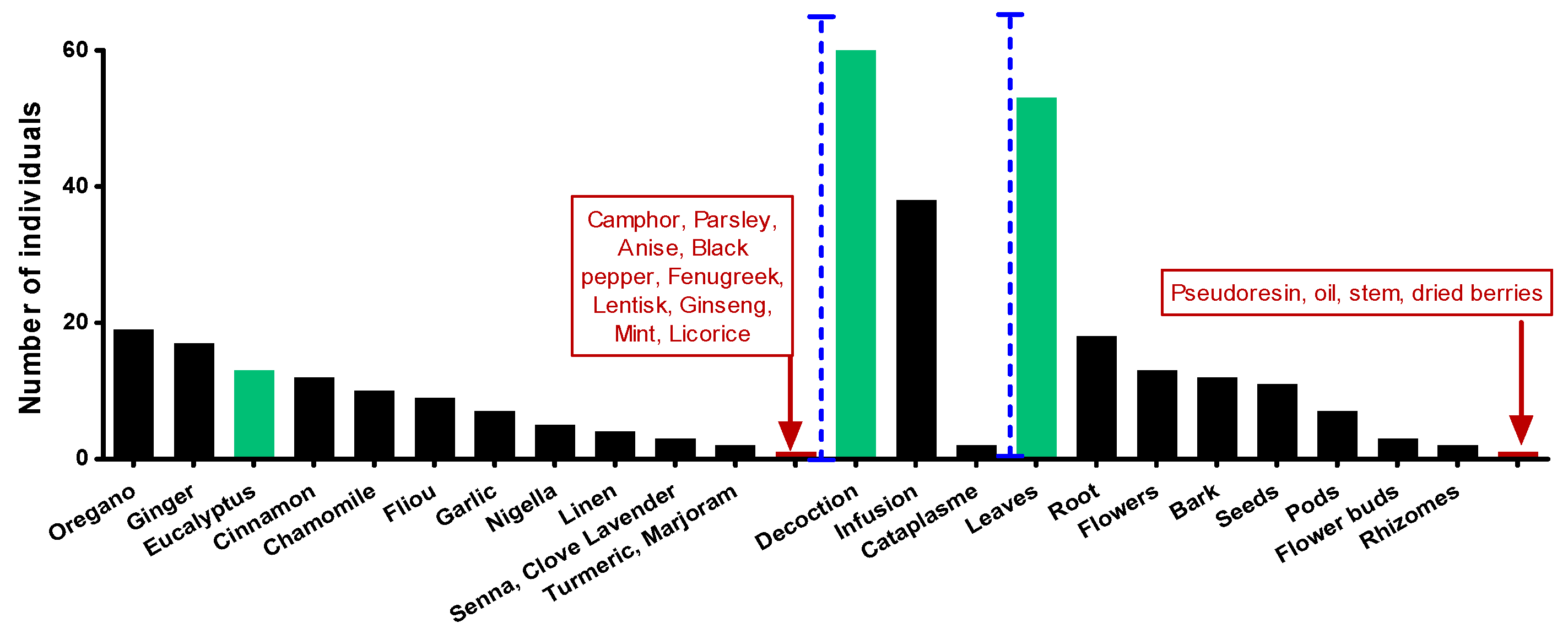
2.1. The choice of plants
2.2. Antibacterial activity
2.3. Antioxidant activity
2.4. In-vitro anti-inflammatory test
2.5. Molecular docking
Phyto-compounds
2.6. Docking analysis and protein preparation
2.7. Drug likeness, ADME/toxicity prediction
3. Results
3.1. Extraction Yield
Antibacterial activity
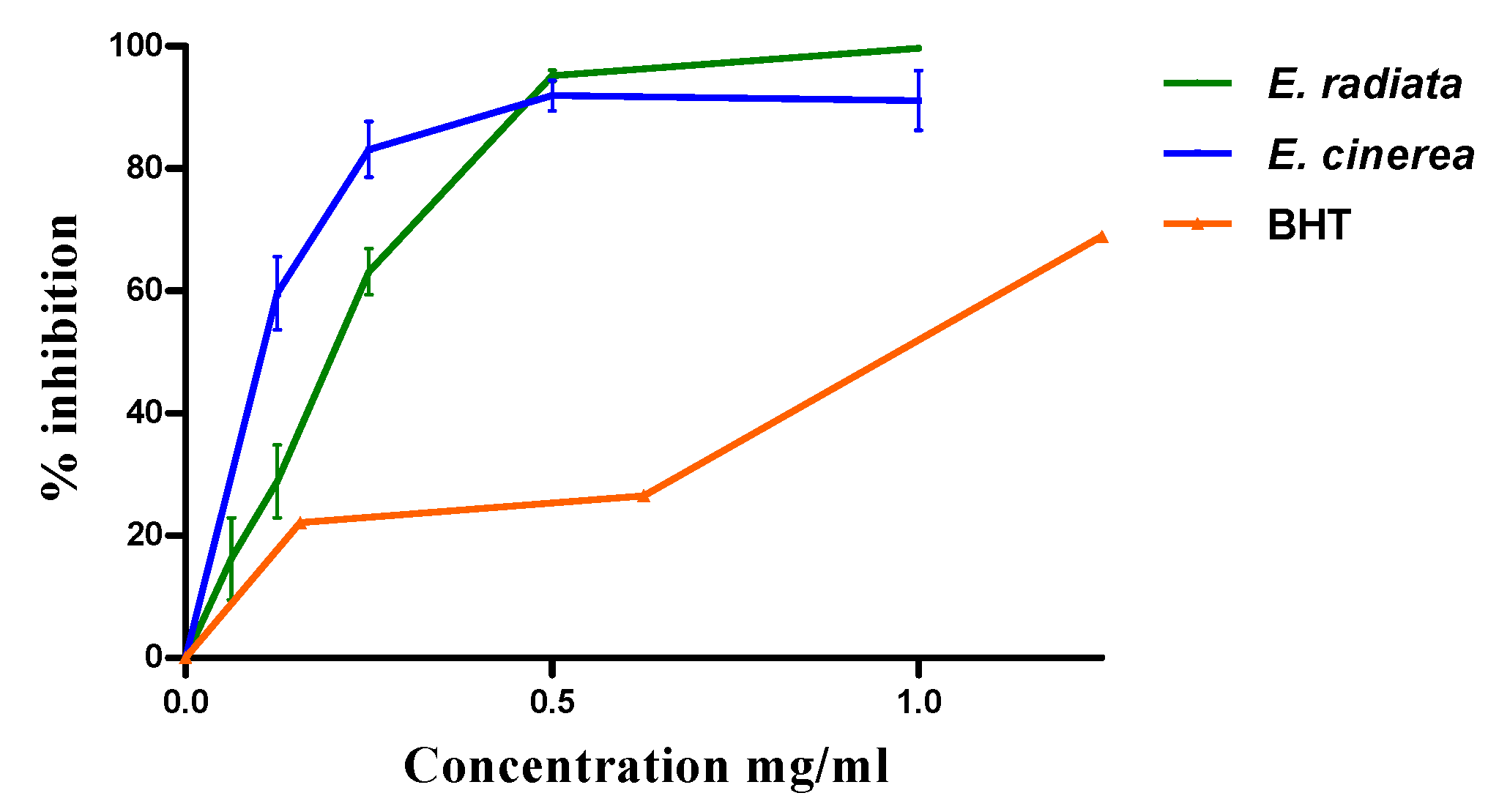
3.2. Antioxidant activity
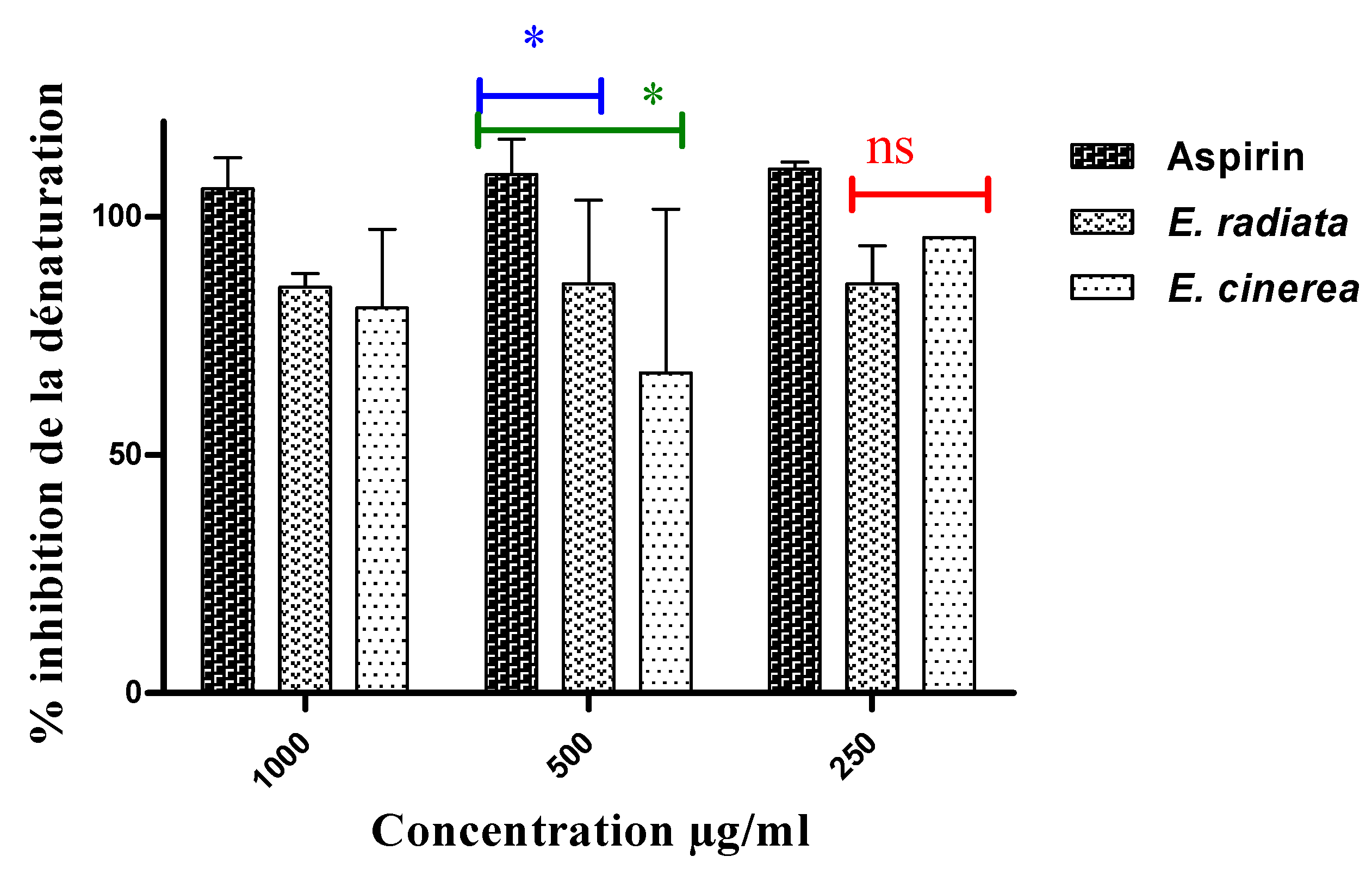
3.3. Anti-inflammatory test
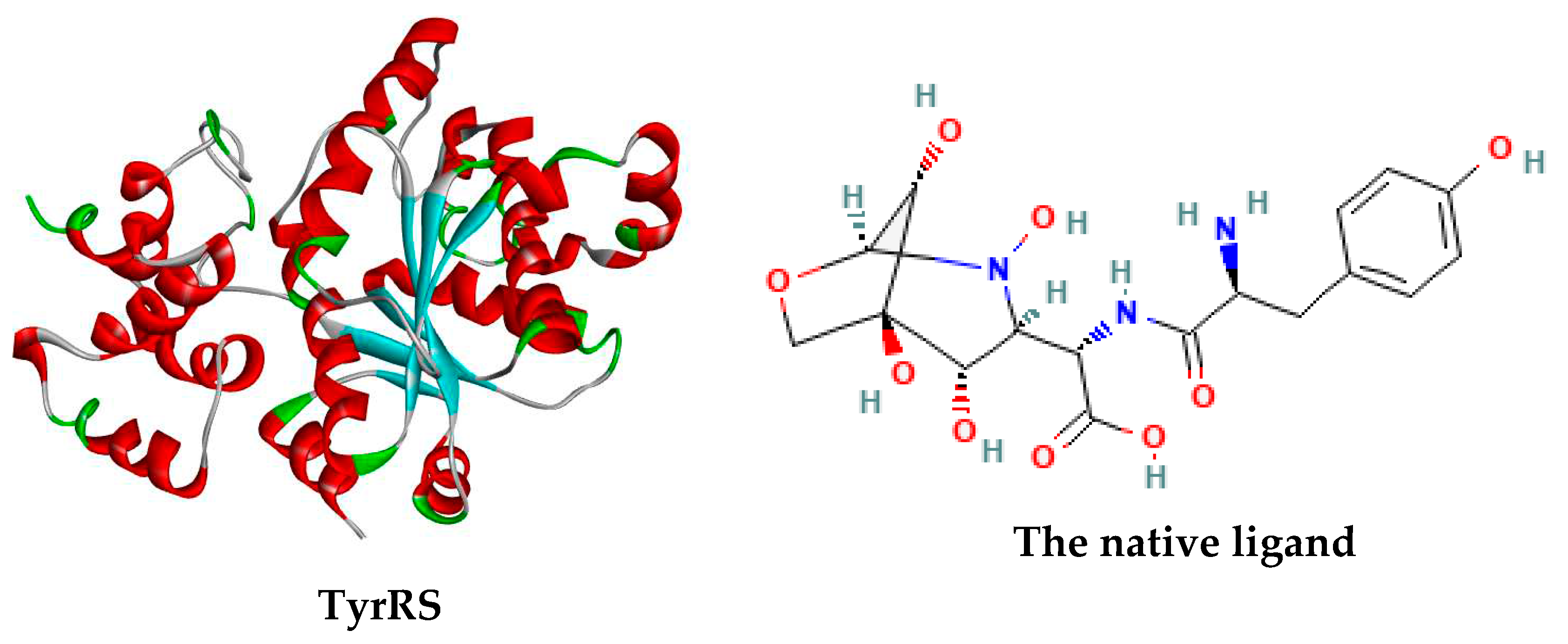
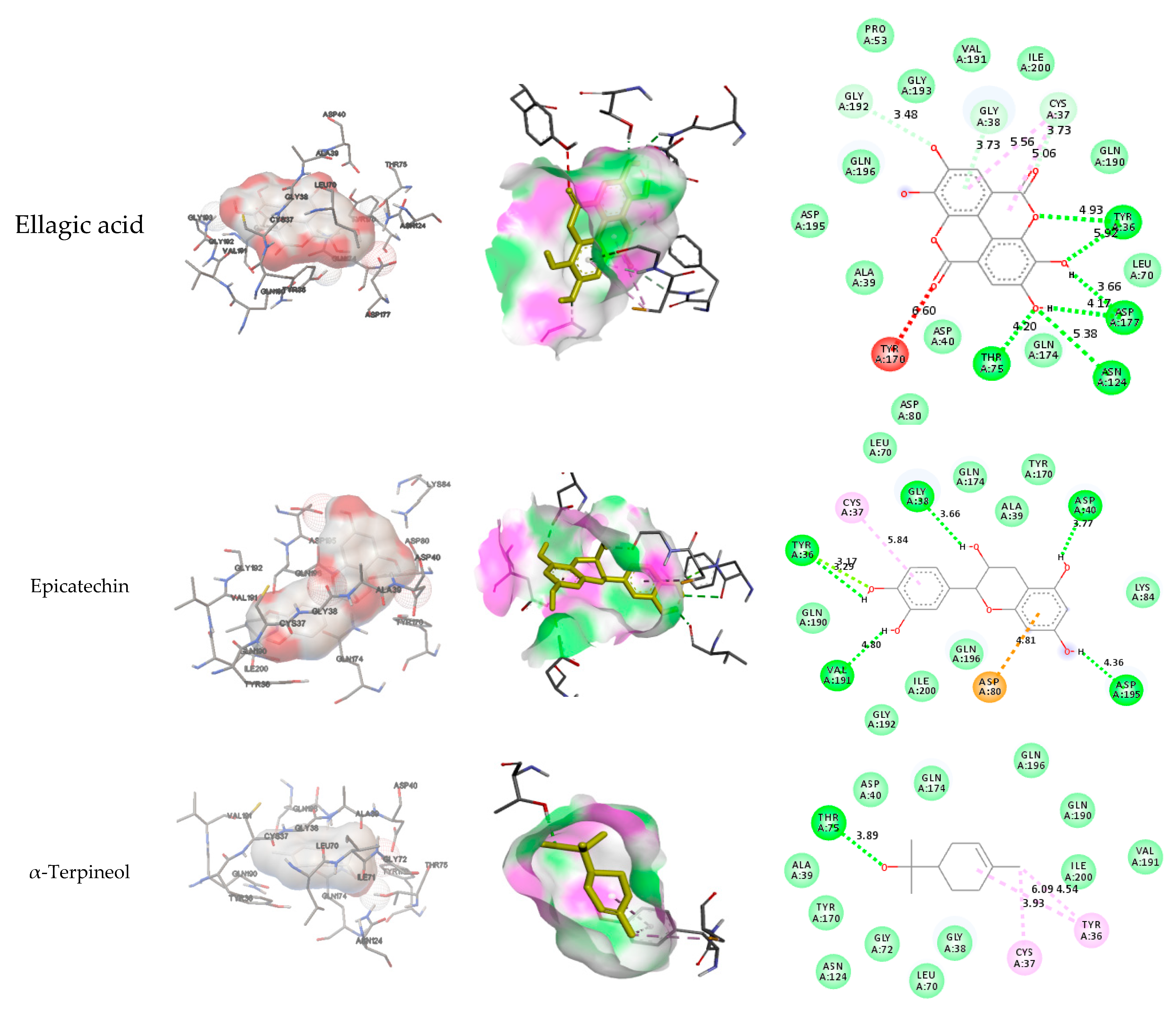
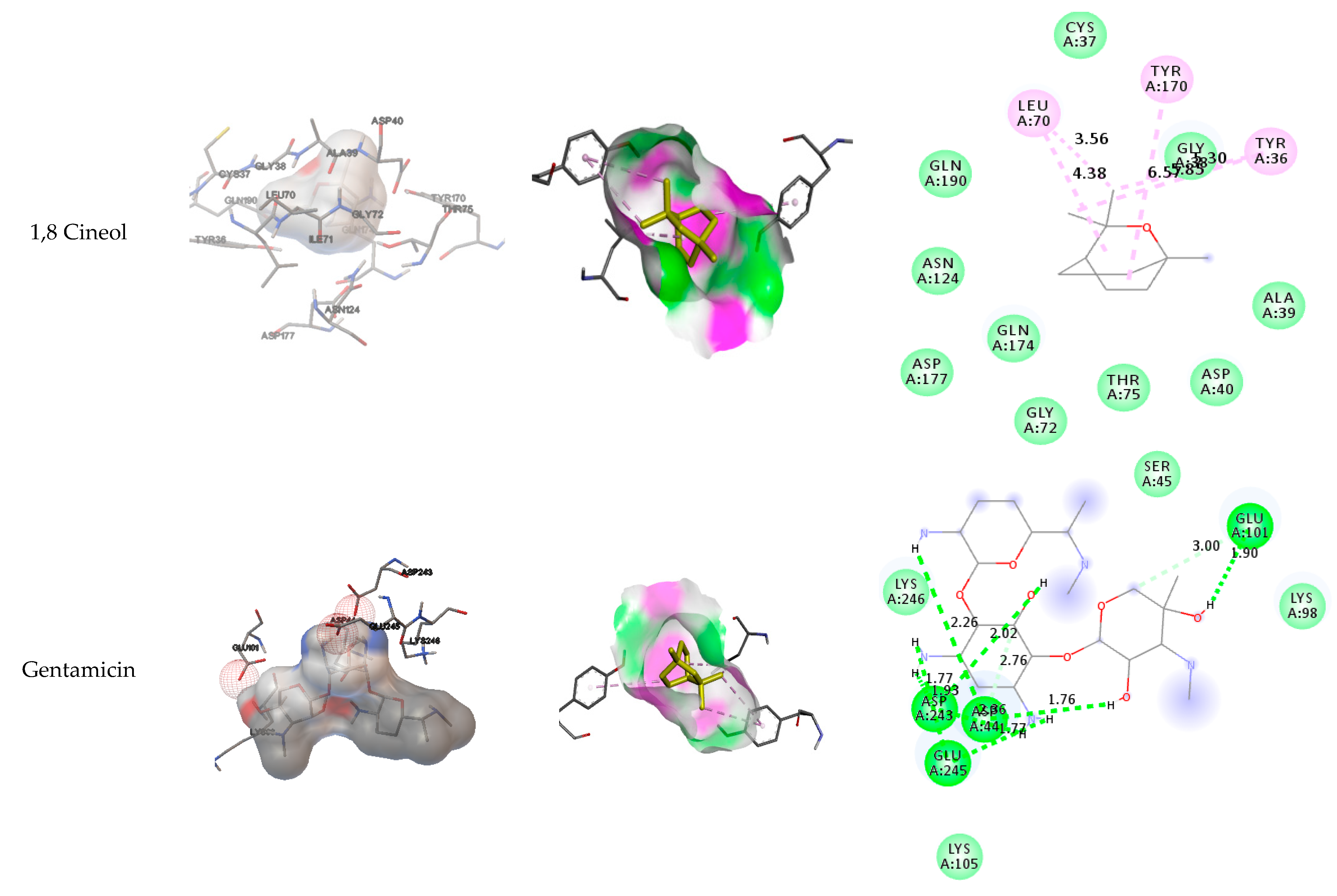
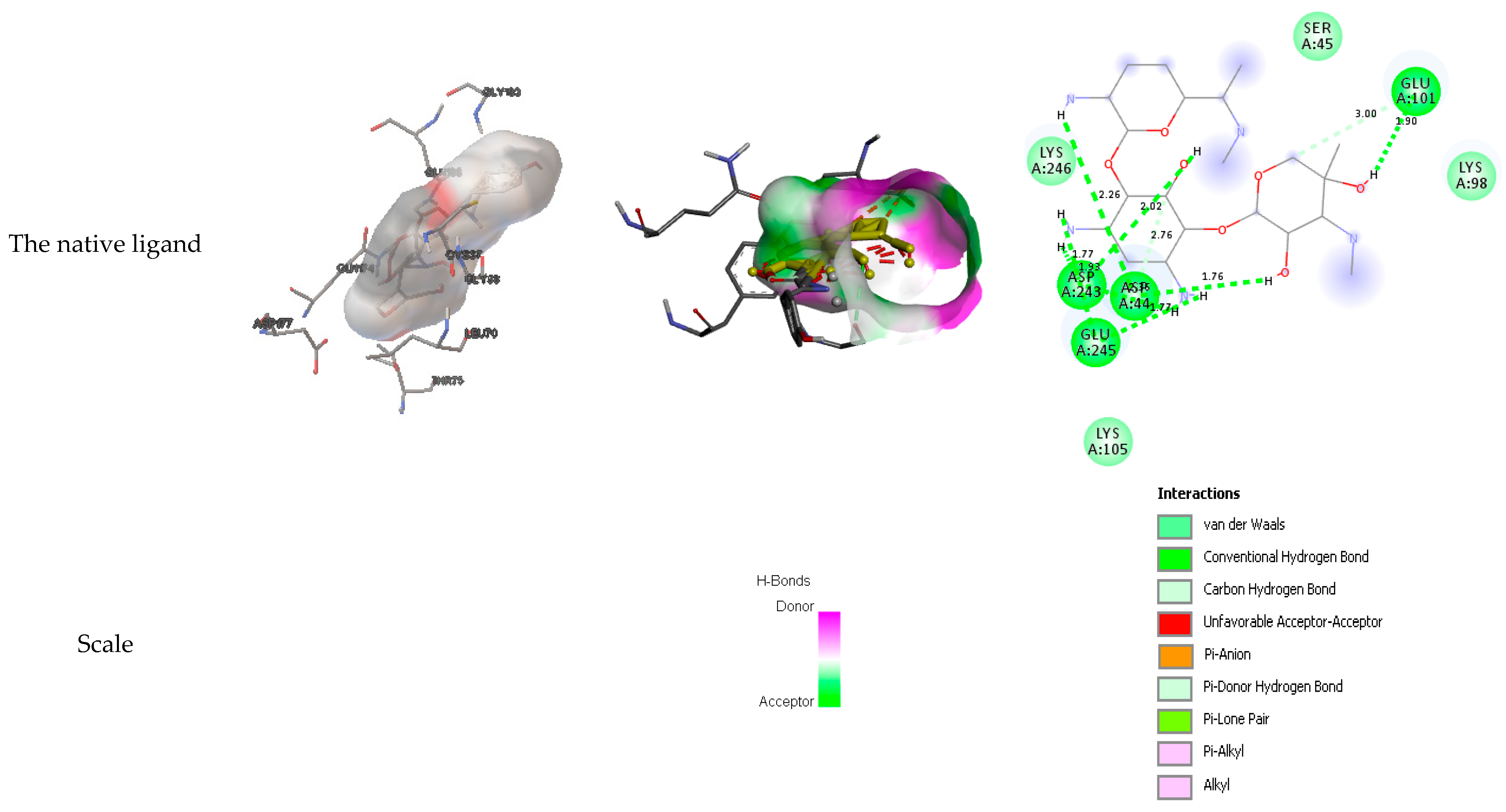
3.4. Docking results
| H bonds | VdW | C-H bond | Pi-Alkyl bonds | Alkyl bonds | Pi-anion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ellagic acid-1TYA | Asp 243, Asp 244, Glu101, Glu 245 | Ser45, Lys98, Lys246 | Lys 105 | |||
| Epicatechin | Asp 40, Asp 195, Gly38, Tyr 36, Val 191 | Leu70, Gln174, Ala39, Tyr170, Lys84, Gln196, Ile200, Gly192, Gln190 | Cys 37 | Asp 80 | ||
| α-Terpineol -1TYA | Thr 75 | Asp40, Gln174, Gln196, Gln190, Ile200, Val191, Gly38, Leu70, Gly72, Asn124, Tyr170, Ala39 | Tyr 36, Cys 37 | Tyr 36, Cys 37 | ||
| 1,8-Cineol -1TYA | Cys37, Gly38, Ala39, Asp40, Thr75, Gly72, Gln174, Asp177, Asn124, Gln190. | Tyr 36, Tyr 170, Leu 70 | Tyr 36, Tyr 170, Leu 70 | |||
| Gentamicin -1TYA | Glu 101, Asp 243, Asp 44, Glu 245 | Lys246, Ser45, Lys98 | Lys 105 | |||
| The native ligand | Glu 101, Asp 243, Asp 44, Glu 245 | Ser 45, Lys 98, Lys 246 | Lys 105 |
3.5. Drug likeness and ADME prediction
4. Discussion
Efficacy against bacteria
Results in reducing inflammation
Investigation of Docking
Prediction of ADME/toxicity and similarity to existing drugs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahla, Y.; Zouari-Bouassida, K.; Rezgui, F.; Trigui, M.; Tounsi, S. Efficacy of Eucalyptus cinerea as a Source of Bioactive Compounds for Curative Biocontrol of Crown Gall Caused by Agrobacterium Tumefaciens Strain B6. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, B. Genome-Wide Identification of MicroRNAs Involved in the Somatic Embryogenesis of Eucalyptus. G3 GenesGenomesGenetics 2021, 11, jkab070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, F.M.; Fathy, MM; Salama, M. M.; Saber, F.R. Chemical Composition and Bioactivity of the Volatile Oil from Leaves and Stems of Eucalyptus cinerea. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzkhar, F.A.; Yangui, I.; Messaoud, C.; Ben Jamâa, M.L. Eucalyptus Leaf Diseases Associated with Neofusicoccum spp. in North Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2022, 197, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeno, D.; Silva, R.F.; Almeida, H.S.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Vanzan, M.; Andreazza, R. Influence of Eucalyptus Development under Soil Fauna. Braz. J. Biol. 2020, 80, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penín, L.; López, M.; Santos, V.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J.C. Technologies for Eucalyptus Wood Processing in the Scope of Biorefineries: A Comprehensive Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, D.J.; Vuong, Q.V.; Chalmers, A.C.; van Altena, IA; Bowyer, M. C.; Scarlett, C.J. Phytochemical, Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of an Aqueous Extract of Eucalyptus microcorys Leaves. South Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 112, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwabor, O.F.; Singh, S.; Syukri, D.M.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Bioactive Fractions of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Inhibit Important Foodborne Pathogens, Reduce Listeriolysin O-Induced Haemolysis, and Ameliorate Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress on Human Embryonic Colon Cells. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; DaCunha, D.C.; Barros, L.; Caires, H.R.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Eucalyptus globulus Labill. Decoction Extract Inhibits the Growth of NCI-H460 Cells by Increasing the P53 Levels and Altering the Cell Cycle Profile. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetni, S.; Bertella, N. In Vitro Study of Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Methanolic Extract Fruits from Rosa Canina L. (Rosaceae). Nutr. Santé 2020, 09, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugbodi, J.O.; Tincho, M.B.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Olaleye, M.T.; Akinmoladun, A.C. Glyphaea brevis – In Vitro Antioxidant and in Silico Biological Activity of Major Constituents and Molecular Docking Analyses. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 59, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI M02-A11: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility, Tests; Approved Standard—Eleventh Edition. 2012, 76. CLSI M02-A11: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard—Eleventh Edition. 2012, 76.
- Singh, G.; Marimuthu, P.; de Heluani, C.S.; Catalan, C.A.N. Antioxidant and Biocidal Activities of Carum nigrum (Seed) Essential Oil, Oleoresin, and Their Selected Components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma; BRINDHA, P. ; ARUN KP In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant And Nephroprotective Studies On Leaves Of Aegle marmelos And Ocimum sanctum. 2014, 7, 9.
- Haddad, M.; Herent, M.-F.; Tilquin, B.; Quetin-Leclercq, J. Effect of Gamma and E-Beam Radiation on the Essential Oils of Thymus Vulgaris Thymoliferum, Eucalyptus Radiata, and Lavandula Angustifolia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 6082–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capetti, F.; Cagliero, C.; Marengo, A.; Bicchi, C.; Rubiolo, P.; Sgorbini, B. Bio-Guided Fractionation Driven by In Vitro α-Amylase Inhibition Assays of Essential Oils Bearing Specialized Metabolites with Potential Hypoglycemic Activity. Plants 2020, 9, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppen, J.J.W. Eucalyptus: The Genus Eucalyptus; Taylor and Francis: London, 2002; ISBN 0-415-27879-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.; Ahmed, B.; Ansari, S.M.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Dwivedi, S.; Alshaeri, M.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. Comparative in Situ ROS Mediated Killing of Bacteria with Bulk Analogue, Eucalyptus Leaf Extract (ELE)-Capped and Bare Surface Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, I.F.; Fernandes, E.; Lima, JLFC; Valentão, P. ; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M.; Costa, P.C.; Bahia, MF Oxygen and Nitrogen Reactive Species Are Effectively Scavenged by Eucalyptus globulus Leaf Water Extract. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevanandam, J.; Chan, Y.S.; Ku, Y.H. Aqueous Eucalyptus globulus Leaf Extract-Mediated Biosynthesis of MgO Nanorods. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, P.; Sousa, F.J.; Matos, P.; Brites, GS; Gonçalves, M. J.; Cavaleiro, C.; Figueirinha, A.; Salgueiro, L.; Batista, M.T.; Branco, P.C.; et al. Chemical Composition and Effect against Skin Alterations of Bioactive Extracts Obtained by the Hydrodistillation of Eucalyptus globulus Leaves. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, C.G.; Reigosa, M.J.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Pedrol, N. Unravelling the Bioherbicide Potential of Eucalyptus globulus Labill: Biochemistry and Effects of Its Aqueous Extract. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0192872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Q.V.; Hirun, S.; Chuen, TLK; Goldsmith, C. D.; Munro, B.; Bowyer, M.C.; Chalmers, A.C.; Sakoff, J.A.; Phillips, P.A.; Scarlett, C.J. Physicochemical, Antioxidant and Anti-Cancer Activity of a Eucalyptus robusta (Sm.) Leaf Aqueous Extract. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 64, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, D.J.; Vuong, Q.V.; Bond, D.R.; Chalmers, A.C.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J. Eucalyptus microcorys Leaf Extract Derived HPLC-Fraction Reduces the Viability of MIA PaCa-2 Cells by Inducing Apoptosis and Arresting Cell Cycle. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; An, M.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.L.; Stanton, R. Phytotoxic Activity and Chemical Composition of Aqueous Volatile Fractions from Eucalyptus Species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaria, D.; Rolta, R.; Patel, C.N.; Dev, K.; Sourirajan, A.; Kumar, V. In Vitro and in Silico Analysis of Thymus serpyllum Essential Oil as Bioactivity Enhancer of Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and Drug-like Compounds: The Rule-of-Five Revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjissi, L.; Chafai, N.; Benbouguerra, K.; Kirouani, I.; Hellal, A.; Layaida, H.; Elkolli, M.; Bensouici, C.; Chafaa, S. Synthesis, Characterization, DFT, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Pharmacokinetics and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease of Some Heterocyclic Hydrazones. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1270, 134005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarba, B. Medicinal Plants Used by Traditional Healers from South-West Algeria: An Ethnobotanical Study. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhouala, K.; Benarba, B. Medicinal Plants Used by Traditional Healers in Algeria: A Multiregional Ethnobotanical Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 760492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouafia, M.; Amamou, F.; Gherib, M.; Benaissa, M.; Azzi, R.; Nemmiche, S. Ethnobotanical and Ethnomedicinal Analysis of Wild Medicinal Plants Traditionally Used in Naâma, Southwest Algeria. Vegetos 2021, 34, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, D.J.; Van Vuong, Q.; Chalmers, A.C.; van Altena, IA; Bowyer, M. C.; Scarlett, C.J. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Eucalyptus robusta Leaf for the Optimal Yield of Total Phenolic Compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneria, M.; Kanani, B.; Chanda, S. Assessment of Effect of Hydroalcoholic and Decoction Methods on Extraction of Antioxidants from Selected Indian Medicinal Plants. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïbi, K.; Aït Abderrahim, L.; Boussaid, M.; Taibi, F.; Achir, M.; Souana, K.; Benaissa, T.; Farhi, K.H.; Naamani, F.Z.; Nait Said, K. Unraveling the Ethnopharmacological Potential of Medicinal Plants Used in Algerian Traditional Medicine for Urinary Diseases. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 44, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periche, A.; Castelló, M.L.; Heredia, A.; Escriche, I. Influence of Extraction Methods on the Yield of Steviol Glycosides and Antioxidants in Stevia rebaudiana Extracts. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoraibi, I.; Soukkarieh, Ch.; Zein, R.; Alahmad, A.; Walter, J.-G.; Daghestani, M. Aqueous Extract of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Leaves as Reducing and Capping Agent in Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2020, 50, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anigbo, A.A.; Avwioroko, O.J.; Cholu, C.O. Phytochemical Constituents, Antimalarial Efficacy, and Protective Effect of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Aqueous Leaf Extract in Plasmodium Berghei-Infected Mice. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 25, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.; Palmer, A.; Nixon, R. Eucalyptus Oil: Contact Allergy and Safety: Eucalyptus Oil Contact Allergy And Safety. Contact Dermatitis 2015, 72, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, A.K.; Pandey, V.V.; Beg, S.; Rawat, J.M.; Singh, A. Biological, Medicinal and Toxicological Significance of Eucalyptus Leaf Essential Oil: A Review: Biological, Medicinal and Toxicological Significance of Eucalyptus Leaf Essential Oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X. Repellent, Insecticidal and Antimicrobial Activities of Leaf Essential Oils from Three Eucalyptus Species. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juergens, L.J.; Worth, H.; Juergens, U.R. New Perspectives for Mucolytic, Anti-Inflammatory and Adjunctive Therapy with 1,8-Cineole in COPD and Asthma: Review on the New Therapeutic Approach. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivekanandhan, P.; Usha-Raja-Nanthini, A.; Valli, G.; Subramanian Shivakumar, M. Comparative Efficacy of Eucalyptus globulus (Labill) Hydrodistilled Essential Oil and Temephos as Mosquito Larvicide. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2626–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danna, C.; Cornara, L.; Smeriglio, A.; Trombetta, D.; Amato, G.; Aicardi, P.; De Martino, L.; De Feo, V.; Caputo, L. Eucalyptus gunnii and Eucalyptus oulverulenta' Baby Blue' Essential Oils as Potential Natural Herbicides. Molecules 2021, 26, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeizi, Z.; Benbouzid, H.; Ouchenane, S.; Yılmaz, D.; Culha, M.; Bououdina, M. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Essential Oil of Eucalyptus globulus with Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Activities. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najda, A.; Bains, A.; Chawla, P.; Kumar, A.; Balant, S.; Walasek-Janusz, M.; Wach, D.; Kaushik, R. Assessment of Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Potential of Ethanolic Extract of Woodfordia Fruticosa Flowers: GC-MS Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, T.A.; Chretien, L.D.; Olive Vivien, N.E.; Djaouda, M.; Aoudou, Y.; Roger, T.; Moïse, N. Use of the Aqueous Extract of Eucalyptus Microcorys for the Treatment in Microcosm, of Water Containing Enterococcus faecalis: Hierarchisation of Cells' Inhibition Factors. H2Open J. 2018, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Nur, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Berto, F. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties of Herbal Materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breidenstein, E.B.M.; de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Hancock, R.E.W. Pseudomonas Aeruginosa: All Roads Lead to Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, S.; Bouffartigues, E.; Bodilis, J.; Maillot, O.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Orange, N.; Dufour, A.; Cornelis, P. Structure, Function and Regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Porins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 698–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, A.; Haenni, M.; Madec, J.-Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in Acinetobacter Spp. and Pseudomonas Spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 6–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, N.G.; Evans-Roberts, K.; Maxwell, A. DNA Topoisomerases. EcoSal Plus 2015, 6, ecosalplus.ESP–0010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, E.; Wright, G.D. Bacterial Proteases, Untapped Antimicrobial Drug Targets. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traversier, M.; Gaslonde, T.; Lecso, M.; Michel, S.; Delannay, E. Comparison of Extraction Methods for Chemical Composition, Antibacterial, Depigmenting and Antioxidant Activities of Eryngium maritimum. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabolsi, C.; Takash Chamoun, W.; Hijazi, A.; Nicoletti, C.; Maresca, M.; Nasser, M. Study of Neuroprotection by a Combination of the Biological Antioxidant (Eucalyptus Extract) and the Antihypertensive Drug Candesartan against Chronic Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Molecules 2021, 26, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.P.; Oliveira, M.S.; Fernandes, D.A.; Ferreira, M.D.L.; Cordeiro, L.V.; Souza, M.F.V.; Fernandes, L.M.D.; Souza, H.D.S.; Oliveira Filho, AA; Pessoa, H. L.F.; et al. In Silico, in Vitro, and Ex Vivo Studies of the Toxicological and Pharmacological Properties of the Flavonoid 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,8,4’-Trimethoxy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratianni, F.; d’Acierno, A.; Ombra, M.N.; Amato, G.; De Feo, V.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Coppola, R.; Nazzaro, F. Fatty Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and in Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Five Cold-Pressed Prunus Seed Oils, and Their Anti-Biofilm Effect Against Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 775751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, M.; Akhtar, S.; Ismail, T.; Yuan, Y.; Ahmad, N.; Tawab, A.; Ismail, A.; Barnard, R.T.; Cooper, M.A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; et al. Syzygium cumini(L.),Skeels Fruit Extracts: In Vitro and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modak, D.; Paul, S.; Sarkar, S.; Thakur, S.; Bhattacharjee, S. Validating Potent Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Rheumatoid Properties of Drynaria quercifolia Rhizome Methanolic Extract through in Vitro, in Vivo, in Silico and GC-MS-Based Profiling. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiya, P.; Senarat, S.; Phaechamud, T.; Narakornwit, W. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity Using Thermally Inhibiting Protein Denaturation of Egg Albumin and Antimicrobial Activities of Some Organic Solvents. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sava, A.; Buron, F.; Routier, S.; Panainte, A.; Bibire, N.; Constantin, S.M.; Lupașcu, F.G.; Focșa, A.V.; Profire, L. Design, Synthesis, In Silico and In Vitro Studies for New Nitric Oxide-Releasing Indomethacin Derivatives with 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-2-Thiol Scaffold. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babar, Z.M.; Jaswir, I.; Tareq, A.M.; Ali Reza, A.S.M.; Azizi, W.M.; Hafidz, M.; Ahfter, F.; Hasan, M.; Farhad, S.; Uddin, M.M.R.; et al. In Vivo Anxiolytic and in Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Water-Soluble Extract (WSE) of Nigella sativa (L.) Seeds. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Chow, A.; Fang, M. Metabolomics and In Silico Docking-Directed Discovery of Small-Molecule Enzyme Targets. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3072–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, A.; Azam, M.; Allemailem, K.S.; Alrumaihi, F.; Almatroudi, A.; A. Alhumaydhi, F.; Azam, F.; Khan, S.H.; Zofair, S.F.F.; et al. Liposomal Ellagic Acid Alleviates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Toxicity and Eliminates the Systemic Cryptococcus neoformans Infection in Leukopenic Mice. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aishwarya, V.; Solaipriya, S.; Sivaramakrishnan, V. Role of Ellagic Acid for the Prevention and Treatment of Liver Diseases. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 2925–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesar, P.H.S.; Trento, M.V.C.; Konig, I.F.M.; Marcussi, S. Catechin, and Epicatechin as an Adjuvant in the Therapy of Hemostasis Disorders Induced by Snake Venoms. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-N.; Lim, Y.K.; Freire, M.O.; Cho, E.; Jin, D.; Kook, J.-K. Antimicrobial Effect of Linalool and α-Terpineol against Periodontopathic and Cariogenic Bacteria. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Zhang, L.; An, P.; Qi, J.; Yu, X.; Lu, J.; Ren, X. Antifungal Mechanisms of α-Terpineol and Terpene-4-Alcohol as the Critical Components of Melaleuca alternifolia Oil in the Inhibition of Rot Disease Caused by Aspergillus Ochraceus in Postharvest Grapes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1161–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.N.; Csehi, B.; József, S.; Ferenc, H.; Kiskó, G.; Dalmadi, I.; Friedrich, L. Effect of α-Terpineol on Chicken Meat Quality during Refrigerated Conditions. Foods 2021, 10, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moo, C.-L.; Osman, M.A.; Yang, S.-K.; Yap, W.-S.; Ismail, S.; Lim, S.-H.-E.; Chong, C.-M.; Lai, K.-S. Antimicrobial Activity and Mode of Action of 1,8-Cineol against Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mączka, W.; Duda-Madej, A.; Górny, A.; Grabarczyk, M.; Wińska, K. Can Eucalyptol Replace Antibiotics? Molecules 2021, 26, 4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juergens, U. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Monoterpene 1.8-Cineole: Current Evidence for Co-Medication in Inflammatory Airway Diseases. Drug Res. 2014, 64, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, R.; Aliahmadi, A.; Rafati, H. Ultrasonic Nanoemulsification of Food Grade Trans-Cinnamaldehyde: 1,8-Cineol and investigation of the Mechanism of Antibacterial Activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa-Benítez, Á.; Medina-Romero, Y.M.; Sánchez-Fernández, R.E.; Lappe-Oliveras, P.; Roque-Flores, G.; Duarte Lisci, G.; Herrera Suárez, T.; Macías-Rubalcava, M.L. Phytotoxic and Antimicrobial Activity of Volatile and Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds from the Endophyte Hypoxylon anthochroum Strain Blaci Isolated from Bursera Lancifolia (Burseraceae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviani, G.; Gosling, D.J.; Patissier, C.; Rodde, S.; Zhou, L.; Faller, B. What Is Modulating Solubility in Simulated Intestinal Fluids? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 41, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, I.J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Murray, J.E.; Porter, R.; Langat, MK; Sadgrove, N. J.; Barker, J.; Zhang, G.; Delgoda, R. Potential Chemopreventive, Anticancer and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of a Refined Artocarpin-Rich Wood Extract of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Tanaka, K.; Takenaka, S.; Murayama, N.; Martin, M.V.; Foroozesh, M.K.; Yamazaki, H.; Guengerich, F.P.; Komori, M. Structure-Function Relationships of Inhibition of Human Cytochromes P450 1A1, 1A2, 1B1, 2C9, and 3A4 by 33 Flavonoid Derivatives. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodek, P.; Trefil, P.; Stiborová, M. Flavonoids-Potent and Versatile Biologically Active Compounds Interacting with Cytochromes P450. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 139, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | Compound | Extract | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. radiata | 1,8-Cineol | The main compound in EOs of most species | [15,16] |
| E. cinerea | Ellagic acid Sideroxylonal B Macrocarpal A | Aqueous extract | [17] |
| Aqueous extract | [3] | ||
| E. camaldulensis | Ellagic acid Gallic acid | Aqueous soluble fraction | [8] |
| E. globulus | 1,8 Cineol α-Terpineol | Aqueous extract | [18] |
| Ellagic acid Quercetin | Aqueous extract | [19] | |
| 1,8-cineol Epicatechin | Aqueous extract | [20] | |
| Ellagic acid | Hydrodistillation residual water | [21] | |
| Ellagic acid | Aqueous extract | [22] | |
| E. robusta | Epicatechin Quercetin | Aqueous extract | [23] |
| E. microcorys | Ellagic acid Epicatechin | Aqueous extract | [24] |
| Different species | 1,8-Cineol α-Terpineol | Aqueous Volatile Fractions | [25] |
| Plant | E. radiata | E. cinerea | GM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 200 | 150 | 100 | 50 | 10 µg/disc |
| E. coli | 20 ±7,07 | 14 ±1,00 | 13 ±0 | 9 ±00 | 19 ±2,64 | 20 ±0 | 20 ±0 | 19 ±1,73 | 40 |
| S. aureus | 18 ±2 | 15,5 ±0,70 | 16 ±1,41 | - | 23,5 | 22,6 ±2,51 | 18 ±0 | 18,6±1,15 | 40 |
| P. aeruginosa | 11,66 ±1,52 | 12 ±00 | - | - | 15,33 ±0,57 | 12 | - | - | 27 |
| Compound | Best run | Free energy of binding (kcal/mol) | Inhibition Constant, Ki (uM) | vdW + H-bond + desolv energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ellagic acid | 8 | -7.53 | 3.03 | -8.48 |
| Epicatechin | 7 | -6.75 | 11.31 | -7.88 |
| α-Terpineol | 3 | -6.43 | 19.31 | -6.92 |
| 1,8-Cineol | 7 | -5.59 | 79.89 | -5.55 |
| Gentamicin | 8 | -10.04 | 44.00 | -5.40 |
| The native ligand | 2 | -10.42 | 23.10 nM | -10.88 |
| Compound | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ellagic acid | Epicatechin | α-Terpineol | 1-8-Cineol | GM | |||
| Physicochemical and pharmacokinetic parameters (Molinspiration Cheminformatics) | |||||||
| miLogP < 5 | 0.94 | 1.37 | 2.60 | 2.72 | -4.21 | ||
| TPSA (oA) < 500 | 141.33 | 110.37 | 20.23 | 9.23 | 199.74 | ||
| MW < 500 (g/mol) | 302.19 | 290.27 | 154.25 | 154.25 | 477.60 | ||
| MV | 221.78 | 244.14 | 170.65 | 166.66 | 450.66 | ||
| nON < 10 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 12 (vio) | ||
| nOHNH < 5 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 11 (vio) | ||
| Lipinski's violation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Solubility and pharmacokinetics properties (SwissADME) | |||||||
| Water solubility | Soluble | Soluble | Soluble | Soluble | Highly soluble | ||
| Lipophilicity | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Gastrointestinal absorption | High | High | High | High | Low | ||
| Log Kp (skin permeation:cm/s) | -7.36 | -7.82 | -4.83 | -5.30 | -12.12 | ||
| Cytochromes inhibitors | CYP1A2 | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2C19 | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| CYP2C9 | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| CYP2D6 | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| CYP3A4 | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| Toxicity risks (OSIRIS Property Explorer) | |||||||
| Mutagenic | No | No | No | Yes | No | ||
| Tumorigenic | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| Irritant | No | No | MR | No | No | ||
| Reproductive effective | No | No | No | Yes | No | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





