Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila melanogaster strains
2.2. Preparation of keto-enol insecticide yeast paste
2.3. Treatment scheme for keto-enol insecticides Movento® 240SC and Envidor® 240SC
2.4. Dissection of ovaries
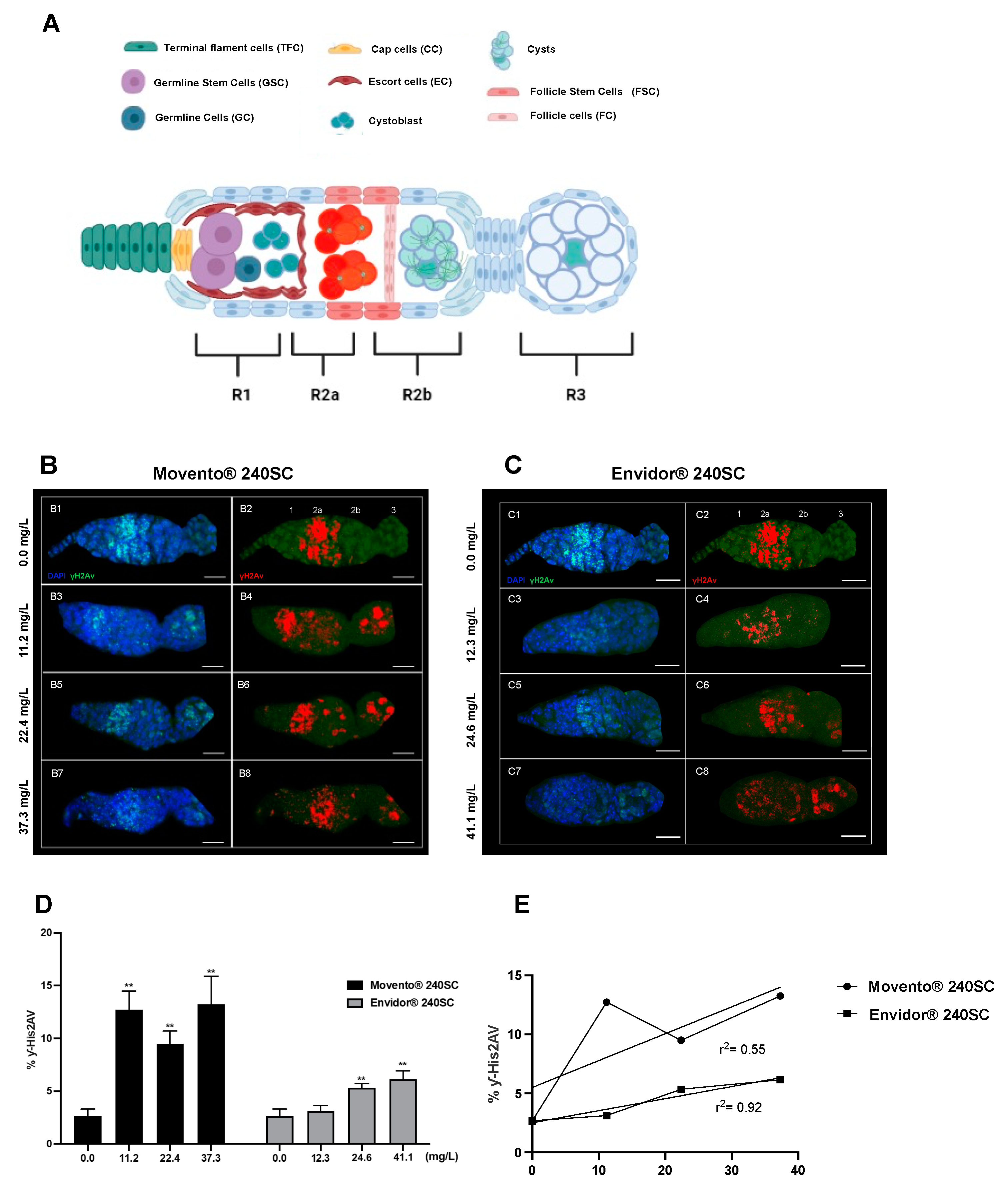
2.5. Expression of γH2AV in the ovary germarium of mutant and wild-type D. melanogaster strains exposed and unexposed to keto-enol insecticides by confocal immunofluorescence.
2.6. Image processing
2.7. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Induction of DNA damage in the germarium in the wild-type strain of Drosophila melanogaster (Oregon R) by keto-enol insecticides Movento® 240SC and Envidor® 240SC.
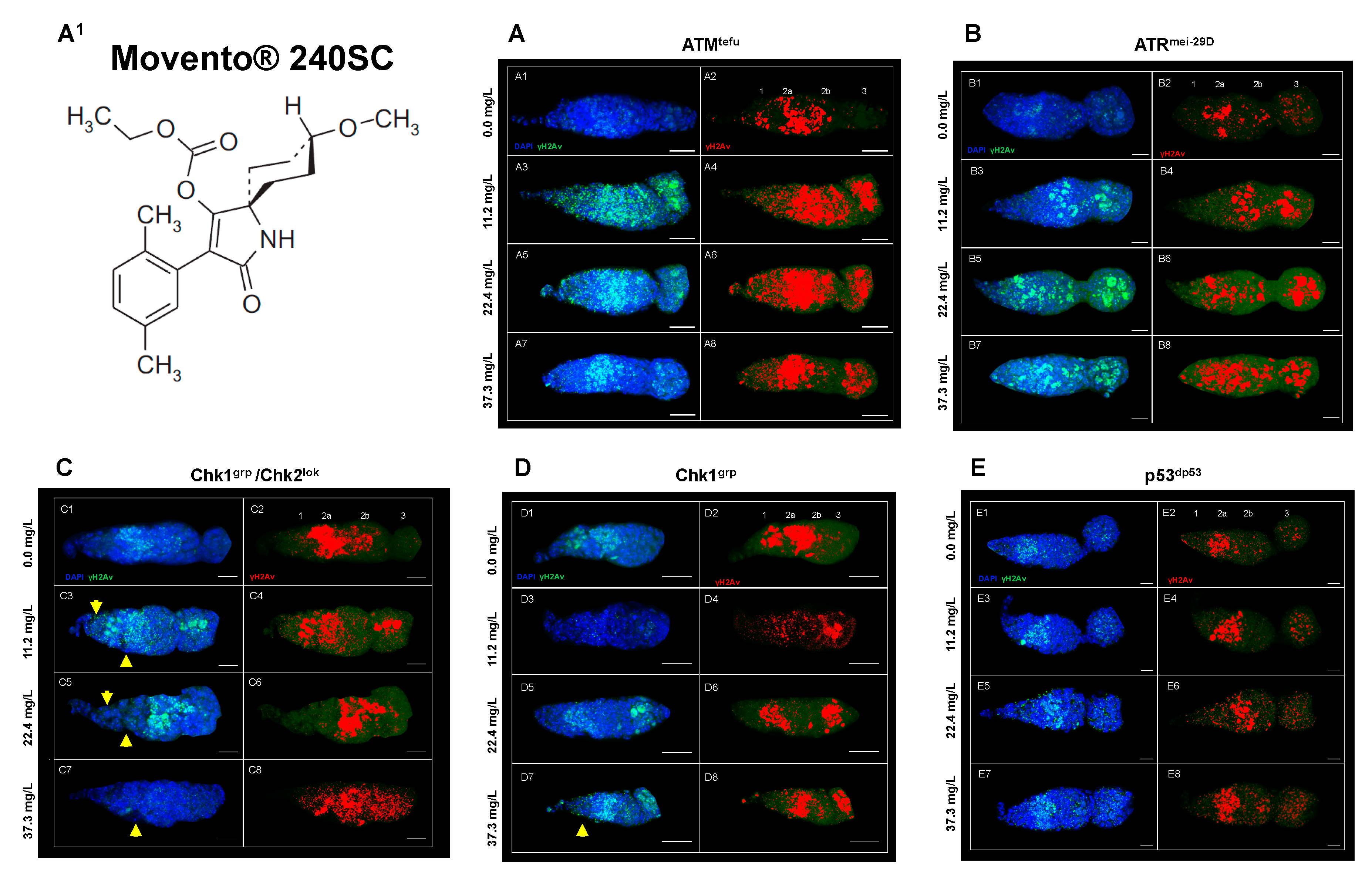
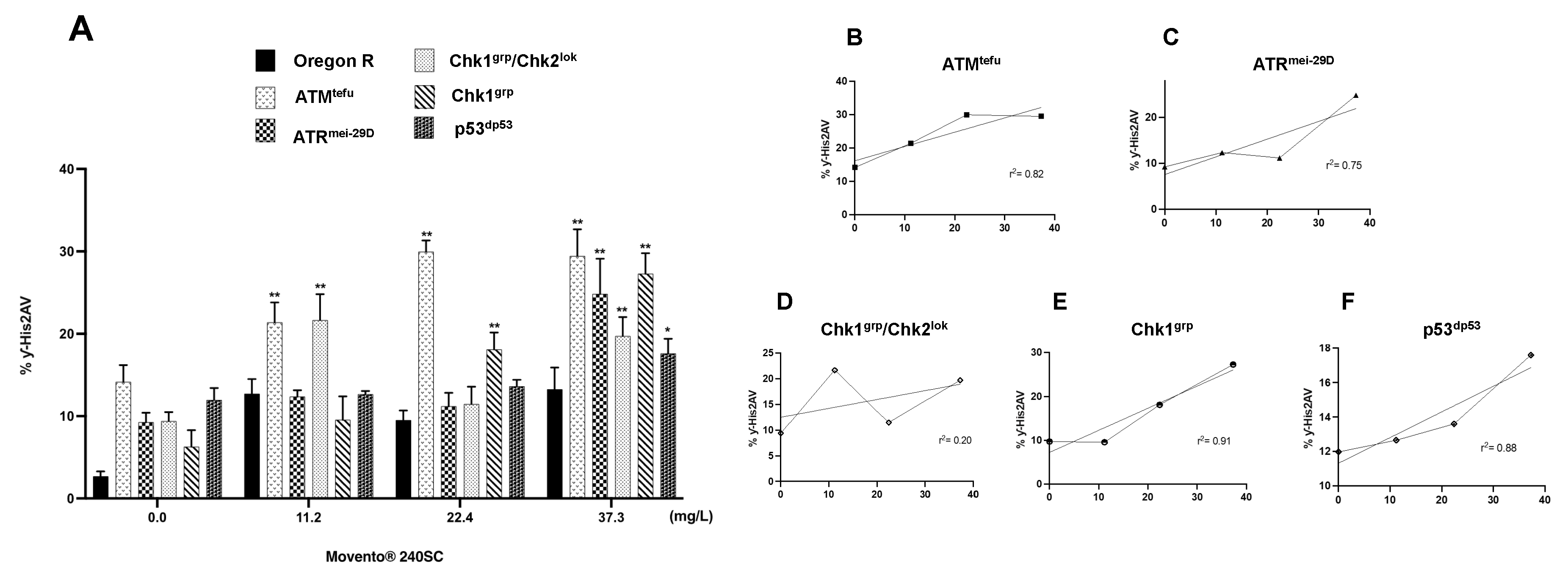
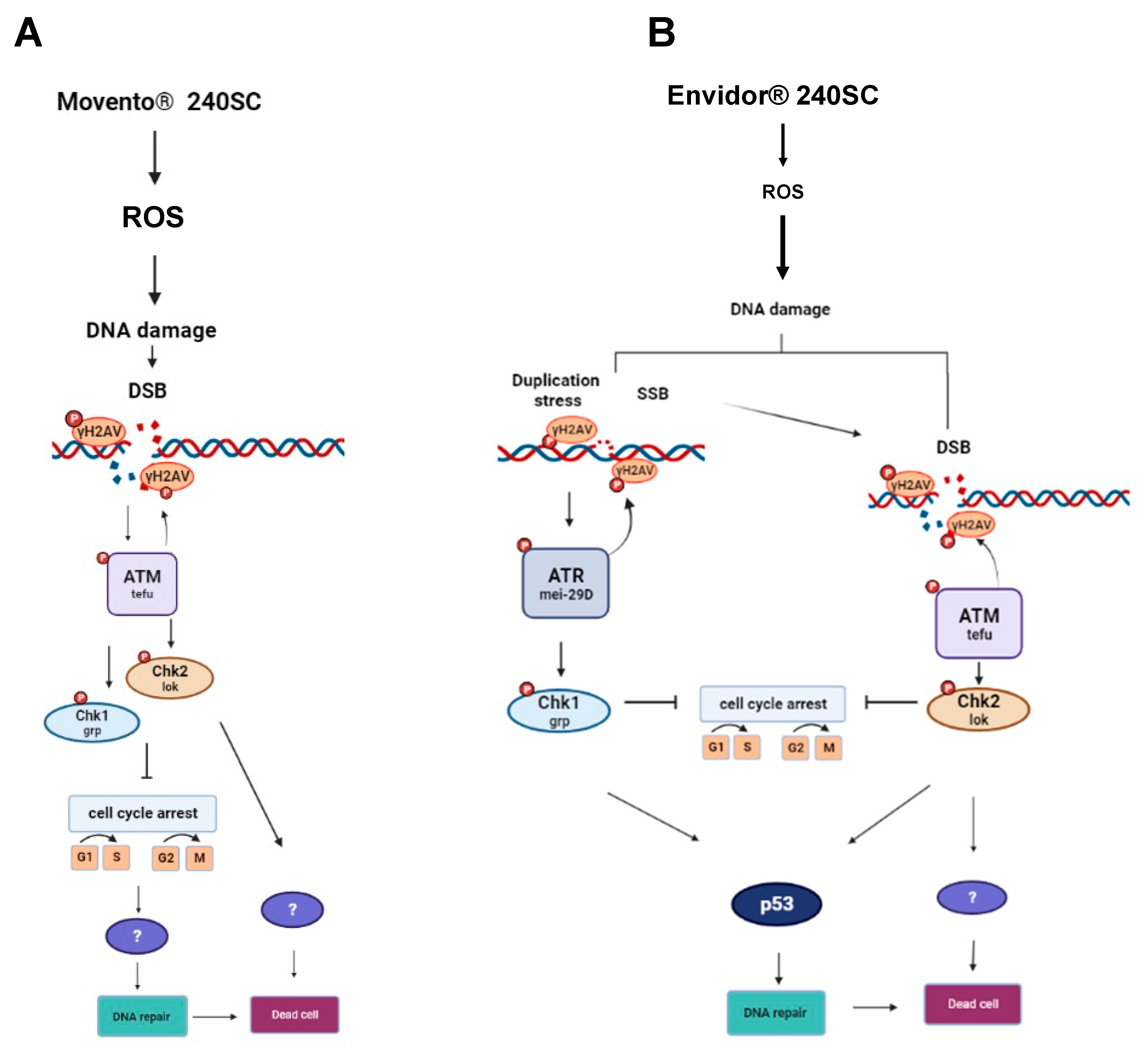
3.2. Response of ATM, Chk1 and Chk2 in the germarium with DNA damage induced by the keto-enol insecticide Movento® 240SC.
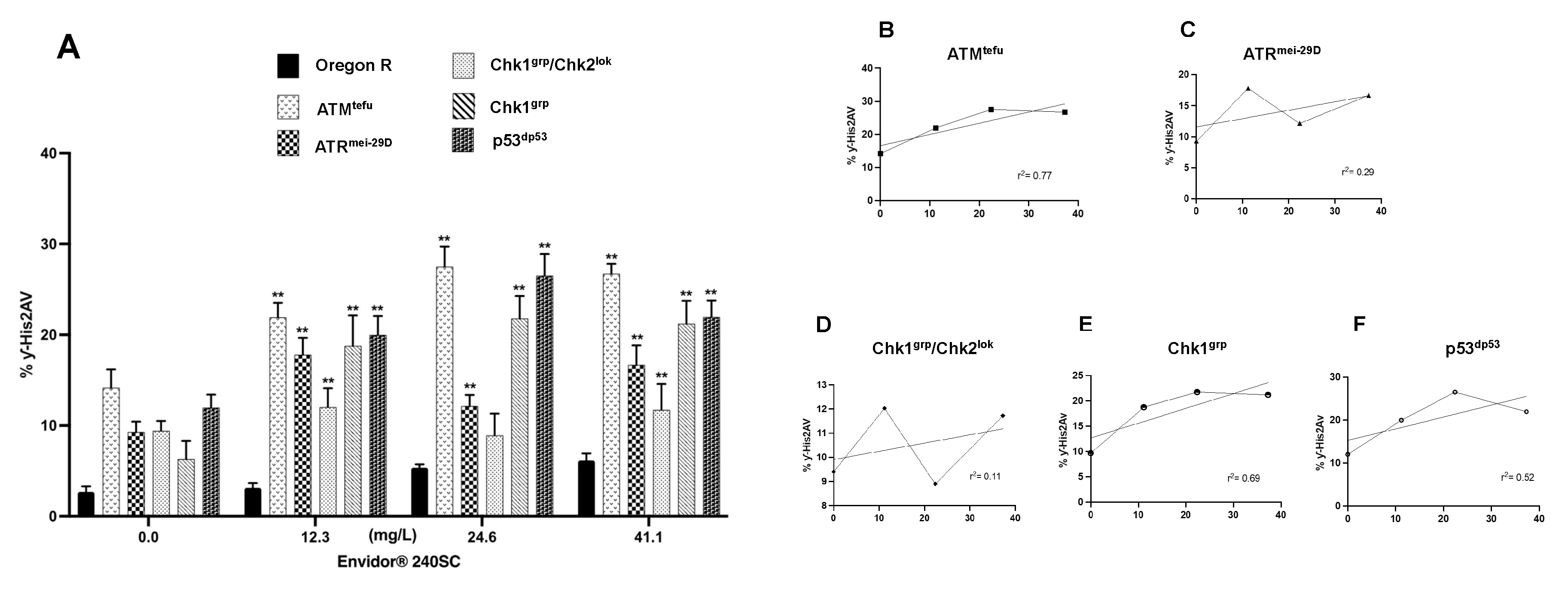
3.3. Response of ATM, ATR, Chk1, Chk1 and p53 in the germarium of D. melanogaster with DNA damage induced by the keto-enol insecticide Envidor® 240 SC.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gundogan, K.; Donmez-Altuntas, H.; Hamurcu, Z.; Akbudak, I.H.; Sungur, M.; Bitgen, N.; Baskol, G.; Bayram, F. Evaluation of chromosomal DNA damage, cytotoxicity, cytostasis, oxidative DNA damage and their relationship with endocrine hormones in patients with acute organophosphate poisoning. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2018, 825, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen-Pereira, C.H.; dos Santos, C.R.; Maraslis, F.T.; Pimentel, L.; Feijó, A.J.L.; Silva, C.I.; Medeiros, G.d.S.d.; Zeferino, R.C.; Pedrosa, R.C.; Maluf, S.W. Markers of genotoxicity and oxidative stress in farmers exposed to pesticides. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabarwal, A.; Kumar, K.; Singh, R.P. Hazardous effects of chemical pesticides on human health–Cancer and other associated disorders. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 63, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Bretschneider, T.; Elbert, A.; Fischer, R.; Tieman, R. Spirodiclofen and Spiromesifen. Pestic. Outlook 2003, 14, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Montez, G.H.; Liu, L.; E Grafton-Cardwell, E. Spirodiclofen and spirotetramat bioassays for monitoring resistance in citrus red mite, Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 68, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.C.; Nauen, R. IRAC: Mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretschneider, T.; Benet-Buchholz, J.; Fischer, R.; Nauen, R. Spirodiclofen and Spiromesifen – Novel Acaricidal and Insecticidal Tetronic Acid Derivatives with a New Mode of Action. Chimia 2003, 57, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lümmen, P.; Khajehali, J.; Luther, K.; Van Leeuwen, T. The cyclic keto-enol insecticide spirotetramat inhibits insect and spider mite acetyl-CoA carboxylases by interfering with the carboxyltransferase partial reaction. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Inoue, K.; Takahashi, M. Predictive modes of action of pesticides in uterine adenocarcinoma development in rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 28, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. (2019). Food and Agriculture Organization, Pesticides-Spirodiklofen Report No: 09. Available at: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/agphome/documents/Pests_Pesticides/JMPR/Report09/Spirodiclofen.pdf. Retrieved Feb 2023.
- Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Teng, M.; Mu, X.; Qi, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Pang, S.; Li, X.; et al. The lipid metabolism alteration of three spirocyclic tetramic acids on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuşoğlu, D.; Yalçin, E.; Çavuşoğlu, K.; Acar, A.; Yapar, K. Molecular docking and toxicity assessment of spirodiclofen: protective role of lycopene. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 57372–57385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbohessi, P.T.; Toko, I.I.; Houndji, A.; Gillardin, V.; Mandiki, S.N.M.; Kestemont, P. Acute Toxicity of Agricultural Pesticides to Embryo-Larval and Juvenile African Catfish Clarias gariepinus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 64, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, G.; Wu, H.; Mao, C. Effects of spirotetramat on the acute toxicity, oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation in Chinese toad (Bufo bufo gargarizans) tadpoles. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yin, P.; Lv, Y.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, C. Toxicological effects of soil contaminated with spirotetramat to the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Chemosphere 2015, 139, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafshgiri, S.K.; Parivar, K.; Baharara, J.; Kerachian, M.A.; Roodbari, N.H. Movento influences development of granulosa cells and ovarian follicles and FoxO1 and Vnn1 gene expression in BALB/c mice. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2016, 19, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Rao, Q.; Gu, D.; Wu, H. Acute and chronic toxicities of spirotetramat to Daphnia magna. J Pest Sci. 2018, 20, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Houssou, A., Cocan, D., Bonou, C., Vioara, M., Montchowui, E. (2018). Survival and reproduction of Cyclops abyssorum (freshwater copepod) exposed to spirotetramat and 2,4-D. Romanian Biotechnological Letters. 23. 13761–13770. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Rao, Q.; Zheng, J.; Mao, C.; Sun, Y.; Gu, D.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. Biochemical and histological alterations in adult zebrafish(Danio rerio)ovary following exposure to the tetronic acid insecticide spirotetramat. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Wang, C.; Teng, M.; Duan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Bo, R.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Dysregulation of endocrine disruption, apoptosis and the transgenerational toxicity induced by spirotetramat. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Wang, C.; Teng, M.; Duan, M.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C. UPLC-TOF-MS/MS metabolomics analysis of zebrafish metabolism by spirotetramat. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Marín, B.; Calderón-Segura, M.E.; Pérez, A.K.G.; Ciénega, L.G.M. Movento® 240SC (Spirotetramat) and Envidor® 240SC (Spirodiclofen) keto-enol insecticides induce DNA damage in Drosophila melanogaster ovaries. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 8, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku-Centurión, M.; González-Marín, B.; Calderón-Ezquerro, M.C.; Martínez-Valenzuela, M.C.; Maldonado, E.; Calderón-Segura, M.E. DNA Damage Assessment in Zebrafish Embryos Exposed to Monceren® 250 SC Fungicide Using the Alkaline Comet Assay. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E.; Derbes, R.S.; Ade, C.M.; Ortego, J.C.; Stark, J.; Deininger, P.L.; Roy-Engel, A.M. Heavy Metal Exposure Influences Double Strand Break DNA Repair Outcomes. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0151367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santivasi, W.L.; Xia, F. Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Damage, Response, and Repair. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Anjum, N.A.; Gill, R.; Jha, M.; Tuteja, N. DNA Damage and Repair in Plants under Ultraviolet and Ionizing Radiations. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, J. Progress in the epidemiological understanding of gene–environment interactions in major diseases: cancer. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2007, 330, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guanggang, X.; Diqiu, L.; Jianzhong, Y.; Jingmin, G.; Huifeng, Z.; Mingan, S.; Liming, T. Carbamate insecticide methomyl confers cytotoxicity through DNA damage induction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Ünsal-Kaçmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Mammalian DNA Repair and the DNA Damage Checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA Double-stranded Breaks Induce Histone H2AX Phosphorylation on Serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Boon, C.; Redon, C.; Bonner, W.M. Megabase Chromatin Domains Involved in DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Vivo. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, J.P.; Chotkowski, H.L.; Glaser, R.L. DNA double-strand break-induced phosphorylation of Drosophila histone variant H2Av helps prevent radiation-induced apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Traganos, F.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. DNA damage induced by DNA topoisomerase I- and topoisomerase II-inhibitors detected by histone H2AX phosphorylation in relation to the cell cycle phase and apoptosis. Cell Cycle 2003, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Horikawa, I.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Popescu, N.C.; Bonner, W.M.; Barrett, J.C. Senescing human cells and ageing mice accumulate DNA lesions with unrepairable double-strand breaks. Nature 2004, 6, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costes, S.; Chiolo, I.; Pluth, J.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.; Jakob, B. Spatiotemporal characterization of ionizing radiation induced DNA damage foci and their relation to chromatin organization. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2010, 704, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Z.; Diao, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Dai, Y.; Chen, F.F.; Yang, J. DNA damage evaluated by γH2AX foci formation by a selective group of chemical/physical stressors. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2006, 604, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, G.P.; Smart, D.J.; Harvey, J.S.; Austin, C.A. H2AX phosphorylation as a genotoxicity endpoint. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2009, 679, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershman, J.M.; France, B.; Hon, K.; Damoiseaux, R. Direct quantification of gamma H2AX by cell-based high throughput screening for evaluation of genotoxicity of pesticides in a human thyroid cell lines. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.-H.; Mirey, G.; Betson, M.; A Haber, D.; Settleman, J. The Drosophila ATM Ortholog, dATM, Mediates the Response to Ionizing Radiation and to Spontaneous DNA Damage during Development. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, A.; Zou, L. DNA Damage Sensing by the ATM and ATR Kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, M.H.; Weinert, B.T.; Tsang, G.; Rong, Y.S.; McGinnis, N.M.; Golic, K.G.; Rio, D.C.; Rubin, G.M. Drosophila melanogaster MNK/Chk2 and p53 Regulate Multiple DNA Repair and Apoptotic Pathways following DNA Damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, H.I.; Uyetake, L.; Lemstra, W.; Brunsting, J.F.; Su, T.T.; Kampinga, H.H.; Sibon, O.C.M. Grp/DChk1 is required for G2-M checkpoint activation inDrosophilaS2 cells, whereas Dmnk/DChk2 is dispensable. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, C.; Muliyil, S.; Rao, B. Genome Damage Sensing Leads to Tissue Homeostasis in Drosophila. International review of cell and molecular biology 2019, 345, 173–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Khadpe, J.; Hu, B.; Iliakis, G.; Wang, Y. An Overactivated ATR/CHK1 Pathway Is Responsible for the Prolonged G2 Accumulation in Irradiated AT Cells. PEDIATRICS 2003, 278, 30869–30874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiloh, Y.; Ziv, Y. The ATM protein: The importance of being active. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiloh, Y.; Ziv, Y. The ATM protein kinase: regulating the cellular response to genotoxic stress, and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, M.H.; Nordstrom, W.; Tsang, G.; Kwan, E.; Rubin, G.M.; Abrams, J.M. Drosophila p53 Binds a Damage Response Element at the reaper Locus. Cell 2000, 101, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollmann, M.; Young, L.M.; Di Como, C.J.; Karim, F.; Belvin, M.; Robertson, S.; Whittaker, K.; Demsky, M.; Fisher, W.W.; Buchman, A.; et al. Drosophila p53 Is a Structural and Functional Homolog of the Tumor Suppressor p53. Cell 2000, 101, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, P.; Dutta, M.; Roy, S. Altered differential hemocyte count in 3rd instar larvae of Drosophila melanogaster as a response to chronic exposure of Acephate. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyan, Z.; Sollazzo, M.; Allocca, M.; Valenza, A.M.; Grifoni, D.; Bellosta, P. Drosophila melanogaster: A Model Organism to Study Cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.M.; Beck, B.D.; Rhomberg, L.R. Historical perspective on the role of cell proliferation in carcinogenesis for DNA-reactive and non-DNA-reactive carcinogens: Arsenic as an example. Toxicology 2021, 456, 152783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekelsky, J.J.; Brodsky, M.H.; Burtis, K.C. DNA Repair in Drosophila. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, F31–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekelsky, J. DNA Repair inDrosophila: Mutagens, Models, and Missing Genes. Genetics 2017, 205, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baonza, A.; Tur-Gracia, S.; Pérez-Aguilera, M.; Estella, C. Regulation and coordination of the different DNA damage responses in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 993257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Sherizen, D.E.; Bhagat, R.; Manheim, E.A.; McKim, K.S. Relationship of DNA double-strand breaks to synapsis in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. Insulin signals control the competence of the Drosophila female germline stem cell niche to respond to Notch ligands. Dev. Biol. 2011, 350, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatkevich, T.; E Miller, D.; A Turcotte, C.; Miller, M.C.; Sekelsky, J. A pathway for error-free non-homologous end joining of resected meiotic double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, S.L.; Bergstralh, D.T.; Kohl, K.P.; LaRocque, J.R.; Moore, C.B.; Sekelsky, J. Drosophila MUS312 and the Vertebrate Ortholog BTBD12 Interact with DNA Structure-Specific Endonucleases in DNA Repair and Recombination. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, J.; Álvarez, L.; A Ferreiro, J.; Sancho, I.; A Comendador, M.; Sierra, L. Female germ cell mutagenicity of model chemicals in Drosophila melanogaster: mechanistic information and analysis of repair systems. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2004, 545, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRocque, J.R.; Jaklevic, B.; Su, T.T.; Sekelsky, J. Drosophila ATR in Double-Strand Break Repair. Genetics 2007, 175, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurençon, A.; Purdy, A.; Sekelsky, J.; Hawley, R.S.; Su, T.T. Phenotypic Analysis of Separation-of-Function Alleles of MEI-41, Drosophila ATM/ATR. Genetics 2003, 164, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zong, M.; Tao, L. The organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos confers its genotoxic effects by inducing DNA damage and cell apoptosis. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, H.R.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, S.C.; Murthy, R.C.; Dhawan, A.; Saxena, D.K.; Chowdhuri, D.K. DNA damage induced by industrial solid waste leachates inDrosophila melanogaster: A mechanistic approach. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2008, 49, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Huang, X.; Halicka, H.D.; Zhao, H.; Traganos, F.; Albino, A.P.; Dai, W.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Cytometry of ATM activation and histone H2AX phosphorylation to estimate extent of DNA damage induced by exogenous agents. Cytom. Part A 2007, 71A, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, E.B.; Parra, A.S.; Johnston, C.A. Loss of the spectraplakin gene Short stop induces a DNA damage response in Drosophila epithelia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, M.M.; Romeijn, R.J.; Eeken, J.C.; de Jong, A.W.; van Veen, B.L.; Szuhai, K.; Mullenders, L.H.; Ferro, W.; Pastink, A. Disruption of Drosophila Rad50 causes pupal lethality, the accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks and the induction of apoptosis in third instar larvae. DNA Repair 2004, 3, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaschler, M.M.; Stockwell, B.R. Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiloh, Y. ATM and ATR: networking cellular responses to DNA damage. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, R.T. Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2177–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. DNA damage checkpoints: from initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Raychaudhuri, P.; Costa, R.H. Chk2 Mediates Stabilization of the FoxM1 Transcription Factor To Stimulate Expression of DNA Repair Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Anderson, H.J.; Alfieri, C.M.; Yutzey, K.E. Regulation of Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Myocardial Growth During Development by FOXO Transcription Factors. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.-H.; Kollipara, R.; Chu, G.; Ji, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Miao, L.; Tothova, Z.; Horner, J.W.; Carrasco, D.R.; et al. FoxOs Are Lineage-Restricted Redundant Tumor Suppressors and Regulate Endothelial Cell Homeostasis. Cell 2007, 128, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Molkentin, J.D.; Paik, J.-H.; DePinho, R.A.; Yutzey, K.E. FoxO Transcription Factors Promote Cardiomyocyte Survival upon Induction of Oxidative Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7468–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar, J.C.; Cortez, D.; Cimprich, K.A. The essential kinase ATR: ensuring faithful duplication of a challenging genome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, T.S.; Pacek, M.; Yee, M.-C.; Walter, J.C.; Cimprich, K.A. Functional uncoupling of MCM helicase and DNA polymerase activities activates the ATR-dependent checkpoint. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Elledge, S.J. Sensing DNA Damage Through ATRIP Recognition of RPA-ssDNA Complexes. Science 2003, 300, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Powell, S.N.; Iliakis, G.; Wang, Y. ATR Affecting Cell Radiosensitivity Is Dependent on Homologous Recombination Repair but Independent of Nonhomologous End Joining. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 7139–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, W.P.; Kaina, B. DNA damage-induced cell death: From specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastan, M.B.; Bartek, J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 2004, 432, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Tho, L.M.; Xu, N.; Gillespie, D.A. The ATM–Chk2 and ATR–Chk1 Pathways in DNA Damage Signaling and Cancer. Advances in cancer research 2010, 108, 73–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehab, N.H.; Malikzay, A.; Appel, M.; Halazonetis, T.D. Chk2/hCds1 functions as a DNA damage checkpoint in G(1) by stabilizing p53. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, S.-Y.; Ahn, J.; Tamai, K.; Taya, Y.; Prives, C. The human homologs of checkpoint kinases Chk1 and Cds1 (Chk2) phosphorylate p53 at multiple DNA damage-inducible sites. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2000, 14, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Trotman, L.C.; Shaffer, D.; Lin, H.-K.; Dotan, Z.A.; Niki, M.; Koutcher, J.A.; Scher, H.I.; Ludwig, T.; Gerald, W.; et al. Crucial role of p53-dependent cellular senescence in suppression of Pten-deficient tumorigenesis. Nature 2005, 436, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.; Smith, L.; La Thangue, N.B. Chk2 activates E2F-1 in response to DNA damage. Nature 2003, 5, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
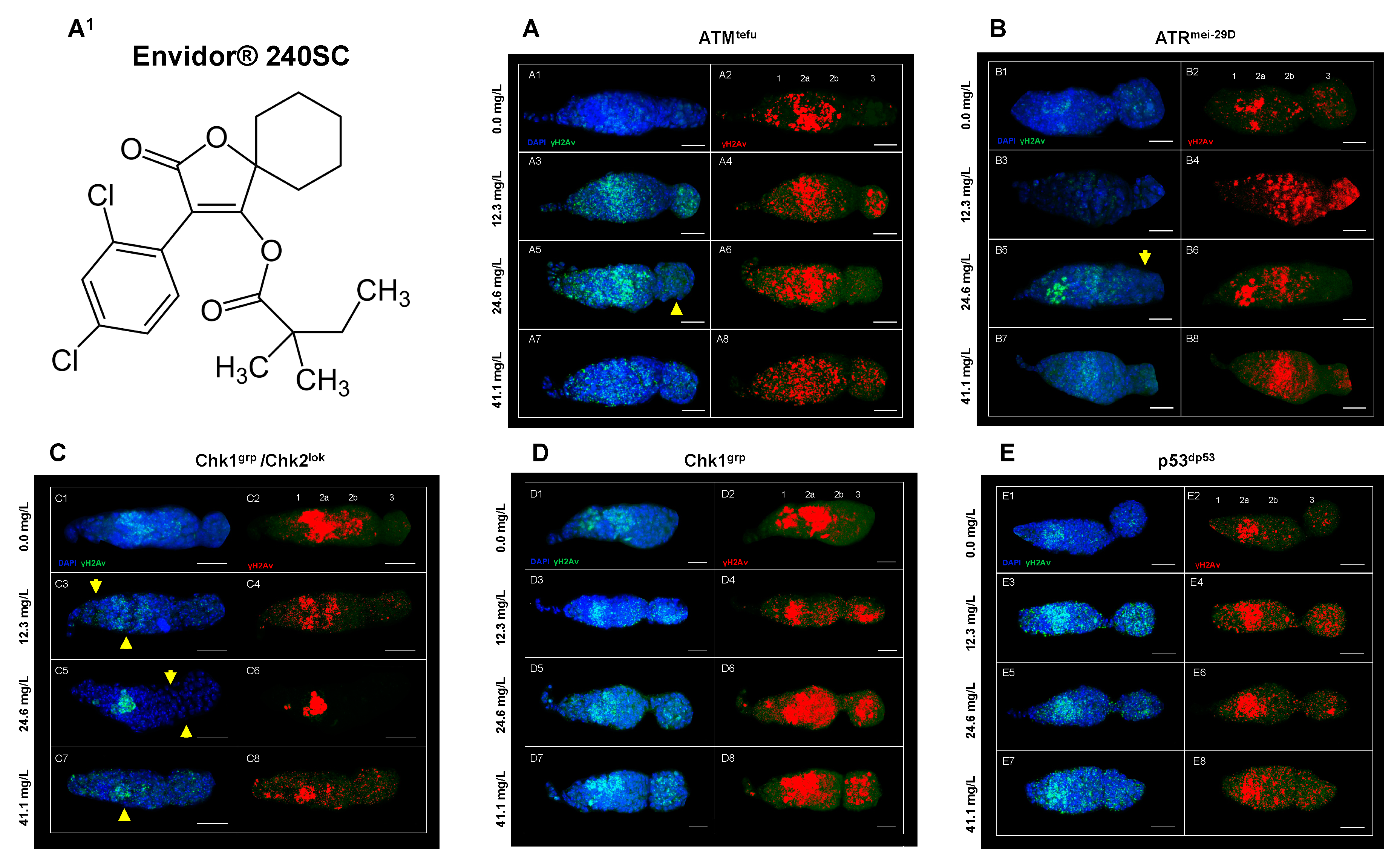
| Genotype in writing | Genotype1 | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| ATMtefu | +/+/+ | Wild strain competent in all DNA damage response mechanisms. |
| ATRmei-29D | w; mei-4129D/y{UASp41} mei-4129D; p{mtα}/+ | Mutant deficient in the protein kinase mei-41 (meiotic 41), ortholog of ATR in mammals. |
| Chk1grp/Chk2lok | w/+; grp209 lok30/grpZ5170 lok30 | Mutant deficient in the protein kinases: grp (grappes) and lok (localized ovarian kinase), respectively orthologs of Chk1 and Chk2 in mammals. |
| Chk1grp | w/+; grp209/grpZ5170 | Mutant deficient in the protein kinase grp (grapes), ortholog of Chk1 in mammals. |
| p53dp53 | y1 w1118; p535A-1-4 | Mutant deficient in the dp53 protein (tumor suppressor), ortholog of p53 in mammals. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





