Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Location and Environmental Conditions
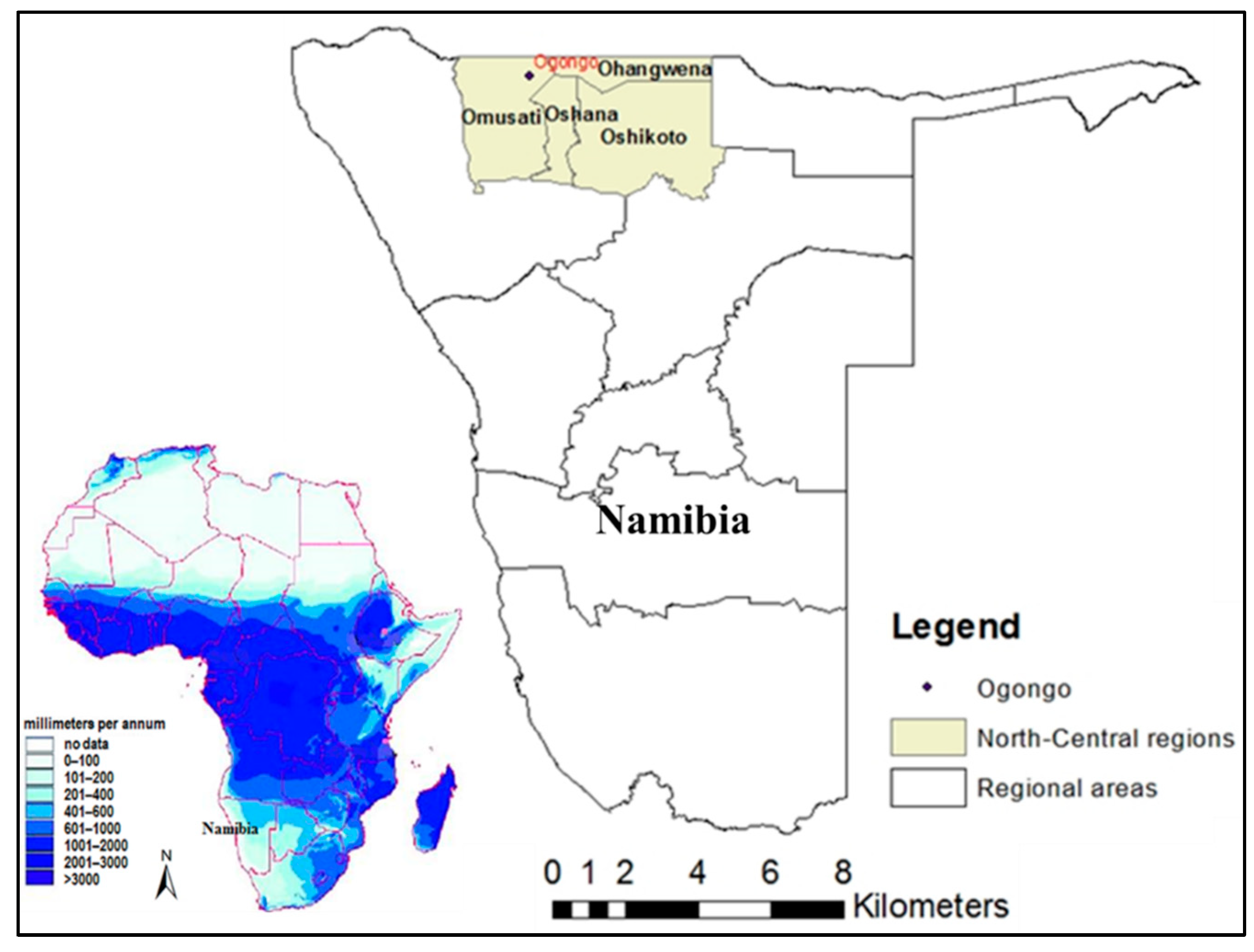
2.2. Rainfall Analysis
2.2.1. Standard Deviation and Mean
2.2.2. Mann-Kendall (MK) Test
2.2.3. Sen’s Slope Estimate
2.3. Agronomic Evaluation
2.3.1. Experimental Treatments, Design, and Management
2.3.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Weather Conditions
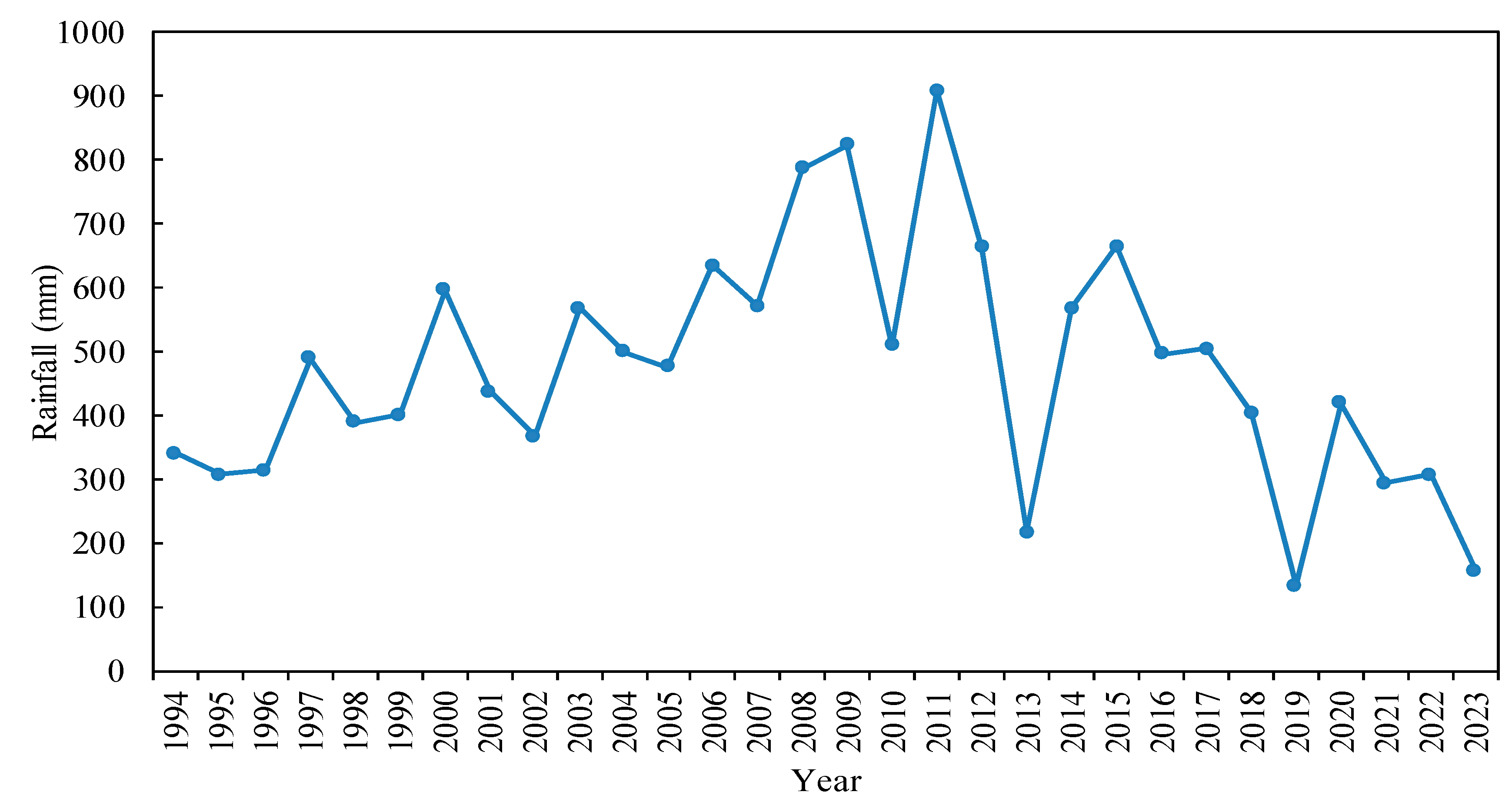
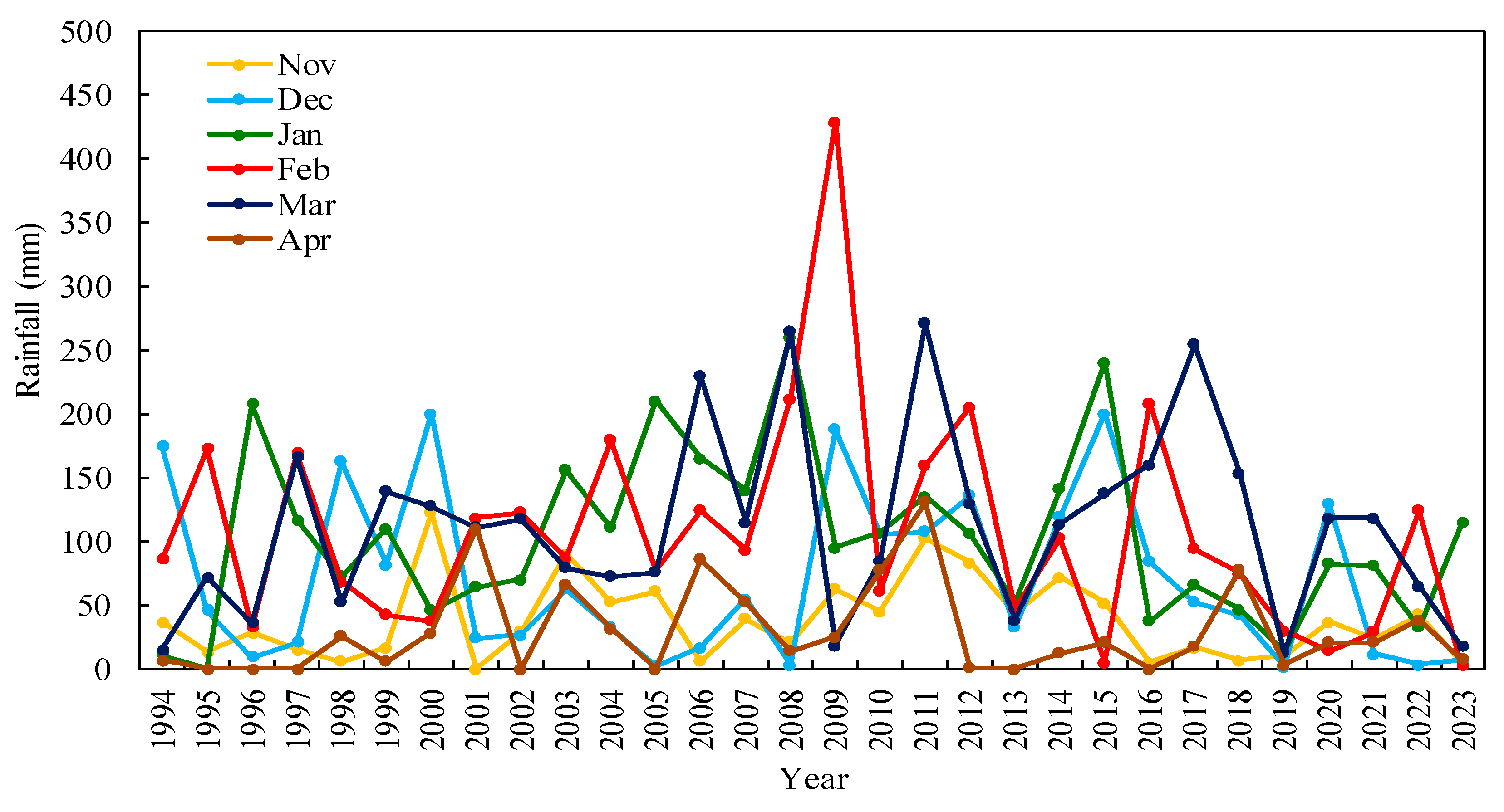
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics for Annual and Monthly Rainfall
3.1.2. Annual and Monthly Rainfall Trends
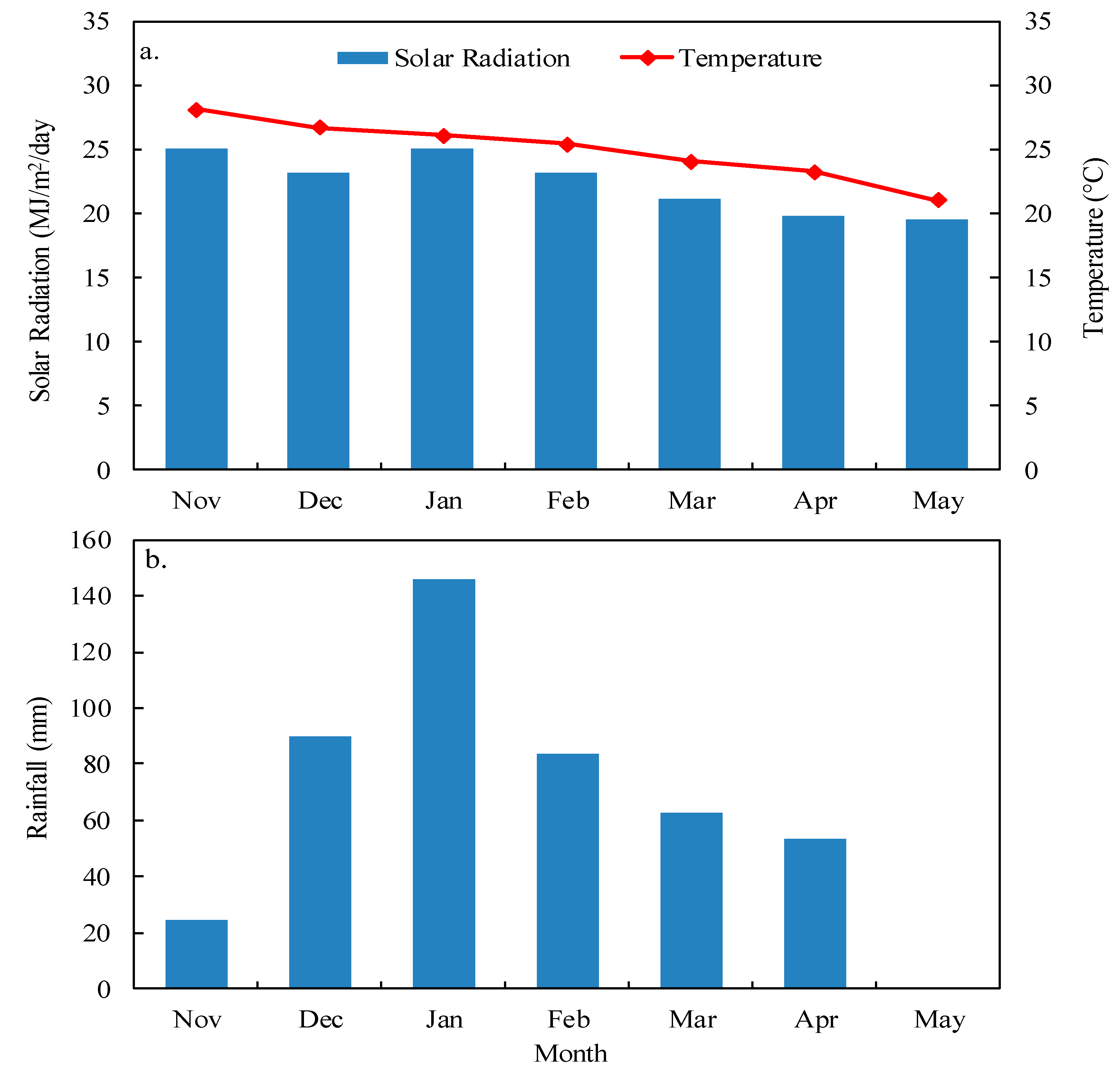
3.1.3. Solar Radiation, Temperature, and Rainfall during the Experiment
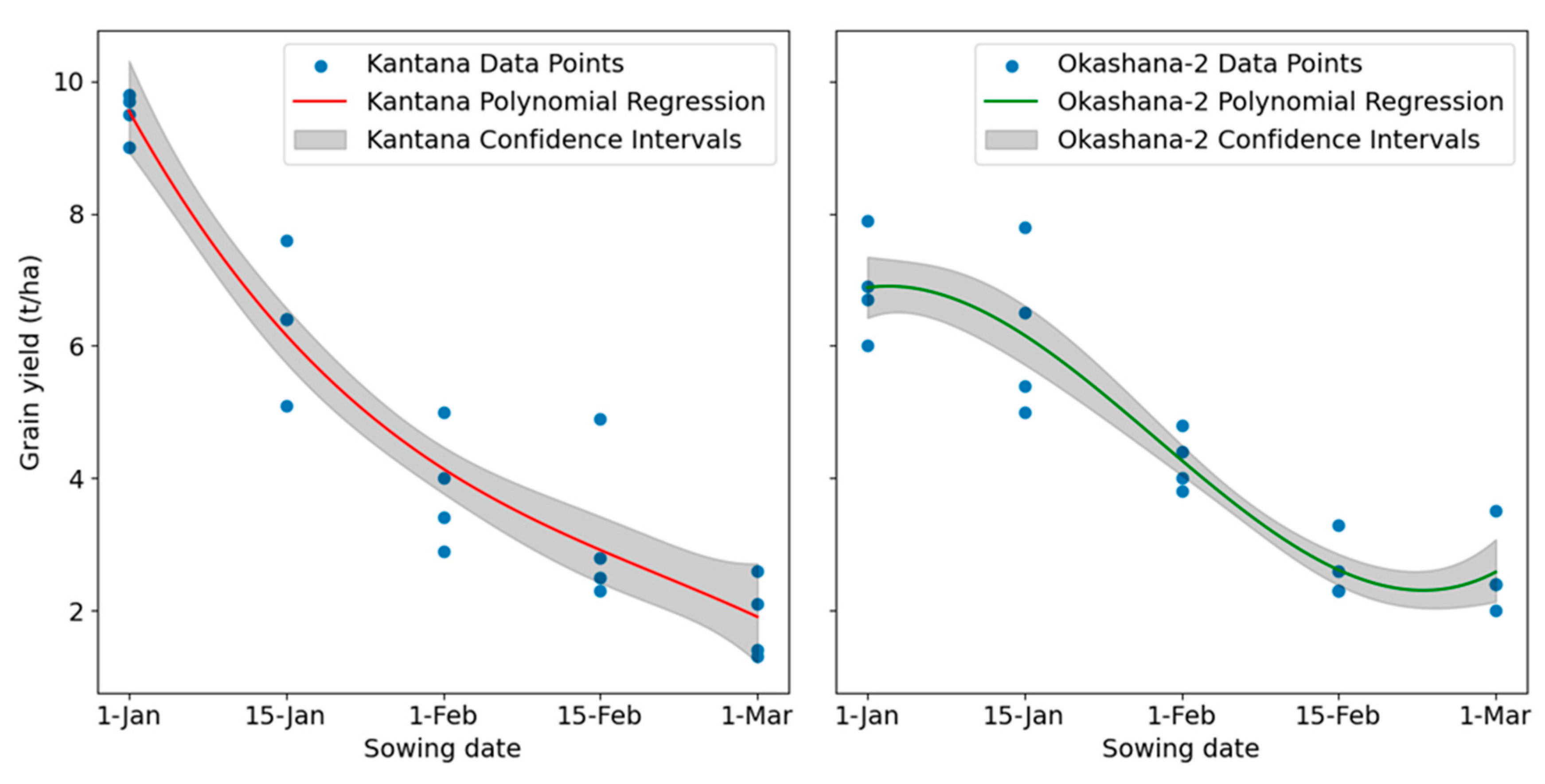
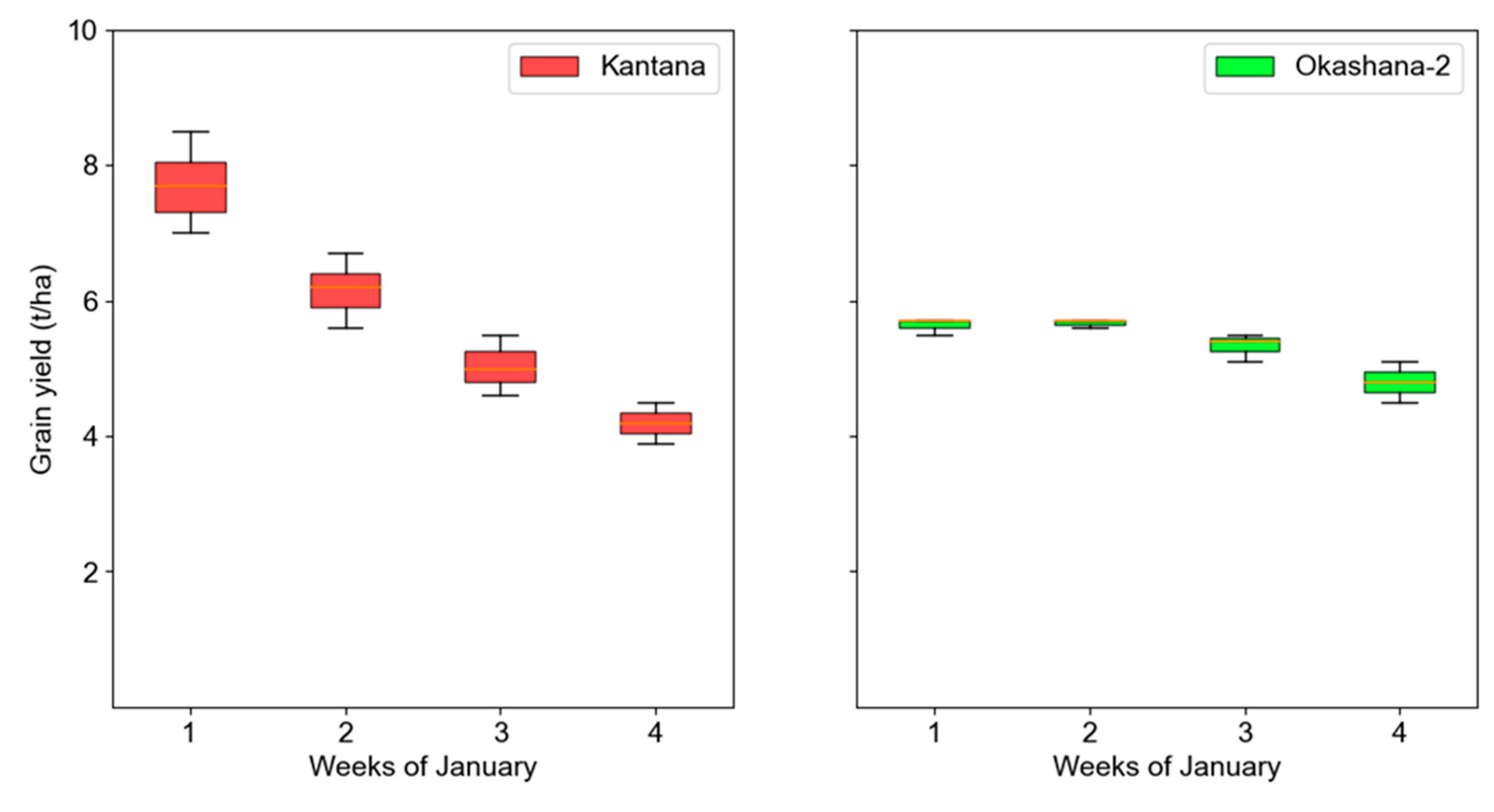
3.2. Grain-yield Dynamics
3.3. Variety Optimal Sowing Windows
4. Discussion
4.1. Weather conditions
4.2. Crop Performance
4.3. Optimal Sowing Window for the NCR
4.4. Agronomic Significance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namibia Statistics Agency Namibia 2011 Population & Housing Census - Main Report; Windhoek, 2013.
- Hirooka, Y.; Masuda, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Inai, H.; Awala, S.K.; Iijima, M. Agronomic and Socio-Economic Assessment of the Introduction of a Rice-Based Mixed Cropping System to Cuvelai Seasonal Wetland System in Northern Namibia. Agrekon 2021, 60, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Weber, B. Cuvelai: The Cuvelai Basin, Its Water and People in Angola and Namibia; Development Workshop Angola: Luanda, 2011; ISBN 978-99916-780-7-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Jarvis, A.; Roberts, C.; Robertson, T. Atlas of Namibia: A Portrait of the Land and Its People; David Philip Publishers: Cape Town, 2002; ISBN 1435-1935. [Google Scholar]
- Hove, K.; Johannes, J.; Hatutale, G.; Awala, S.K.; Ausiku, P. Growth and Yield Response of Swiss Chard (Beta Vulgaris (L.) to Media Mixture Ratios of Sand, Acacia Soil, and Goat Manure. Magna Sci. Adv. Biol. Pharm. 2020, 1, 018–024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, J.F.; Hillyer, A.E.M. Grain Legumes in Pearl Millet Systems in Northern Namibia: An Assessment of Potential Nitrogen Contributions. Exp. Agric. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Jarvis, A.; Robertson, T. A Profile and Atlas of the Cuvela - Etosha Basin; RAISON: Windhoek, 2013; ISBN 9991678077. [Google Scholar]
- Awala, S.K.; Hove, K.; Wanga, M.A.; Valombola, J.S.; Mwandemele, O.D. Rainfall Trend and Variability in Semi-Arid Northern Namibia: Implications for Smallholder Agricultural Production. Welwitschai Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.E. Coefficient of Variation. In Applied multivariate statistics in geohydrology and related sciences; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1998; pp. 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics, Vol. 2: Inference and Relationship.; Waffler Publishing: New York, 1967; ISBN 0852640110. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques of Trend Analysis for Monthly Water Quality Data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarres, R.; de Paulo Rodrigues da Silva, V. Rainfall Trends in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions of Iran. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 70, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, G.C. The Mann-Kendall Test: The Need to Consider the Interaction between Serial Correlation and Trend. Acta Sci. Agron. 2013, 35, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monyo, E.S.; Gupta, S.C.; Muuka, F.; Ipinge, S.A.; Chambo, H.; Mpofu, L.; Chintu, E.; Mogorosi, M.; Mutaliano, J. Pearl Millet Cultivars Released in the SADC Region. ICRISAT, Bulawayo 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mgonja, M.A.; Monyo, E.S.; Chandra, S. Enhancing Crop Breeding Programmes: The Case of Sorghum and Pearl Millet in Southern Africa. African Crop Sci. J. 2005, 13, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ipinge, S.A. The Effects of Dates of Planting on Yield and Yield Components of Pearl Millet. Agricola 2001, 12, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Monyo, E.S. 15 Years of Pearl Millet Improvement in the SADC Region. Int. Sorghum Millet Newsl. 1998, 39, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Traore, B.; Corbeels, M.; van Wijk, M.T.; Rufino, M.C.; Giller, K.E. Effects of Climate Variability and Climate Change on Crop Production in Southern Mali. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, F.D.; Soderberg, K.; Coop, L.J.; Muller, A.A.; Vickery, K.J.; Grandin, R.D.; Jack, C.; Kapalanga, T.S.; Henschel, J. The Nature of Moisture at Gobabeb, in the Central Namib Desert. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 93, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Pan, M.; Kaseke, K.F.; Li, B. A Multi-Scale Analysis of Namibian Rainfall over the Recent Decade – Comparing TMPA Satellite Estimates and Ground Observations. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 8, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongi, H.; Majule, A.E.; Lyimo, J.G. Vulnerability and Adaptation of Rain Fed Agriculture to Climate Change and Variability in Semi-Arid Tanzania. African J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangalawe, R.Y.M.; Lyimo, J.G. Climate Change, Adaptive Strategies and Rural Livelihoods in Semiarid Tanzania. Nat. Resour. 2013, 04, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, P.; Ramachandran, R. Farmers’ Perceptions of Climate Change and the Proposed Agriculture Adaptation Strategies in a Semi Arid Region of South India. J. Integr. Environ. Sci. 2016, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschakert, P.; Sagoe, R.; Ofori-Darko, G.; Codjoe, S.N. Floods in the Sahel: An Analysis of Anomalies, Memory, and Anticipatory Learning. Clim. Change 2010, 103, 471–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonj, C.; Nkongolo, O.T.; Schmitz, P.; Hango, J.N.; Kistemann, T. The Impact of Flooding on People Living with HIV: A Case Study from the Ohangwena Region, Namibia. Glob. Health Action 2015, 8, 26441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, J. ; Obeid, el S.; Roberts, C. A Profile of North-Central Namibia, Ed.; Gamsberg Macmillan Publishers: Windhoek, 2000; ISBN 99916-0-215-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yamusa, A.M.; Abubakar, I.U.; Falaki, A.M. Rainfall Variability and Crop Production in the North-Western Semi-Arid Zone of Nigeria. J. Soil Sci. Environ. Manag. 2015, 6, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarr, B. Present and Future Climate Change in the Semi-arid Region of West Africa: A Crucial Input for Practical Adaptation in Agriculture. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2012, 13, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Cabello, D.; Tomás-Burguera, M.; Martín-Hernández, N.; Beguería, S.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Kenawy, A. El Drought Variability and Land Degradation in Semiarid Regions: Assessment Using Remote Sensing Data and Drought Indices (1982-2011). Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4391–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihupi, N.I.; Tarimo, A.K.P.R.; Masika, R.J.; Boman, B.; Dick, W.A. Trend of Growing Season Characteristics of Semi-Arid Arusha District in Tanzania. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persendt, F.C.; Gomez, C.; Zawar-Reza, P. Identifying Hydro-Meteorological Events from Precipitation Extremes Indices and Other Sources over Northern Namibia, Cuvelai Basin. Jàmbá J. Disaster Risk Stud. 2015, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphale, K.M.; Dash, S.K.; Adedoyin, A.; Panda, S.K. Rainfall Regime Changes and Trends in Botswana Kalahari Transect’s Late Summer Precipitation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 116, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batisani, N.; Yarnal, B. Rainfall Variability and Trends in Semi-Arid Botswana: Implications for Climate Change Adaptation Policy. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikodzi, D.; Murwendo, T.; Simba, F.M. Climate Change and Variability in Southeast Zimbabwe: Scenarios and Societal Opportunities. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2013, 02, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiros, G.; Shetty, A.; Nandagiri, L. Extreme Rainfall Signatures under Changing Climate in Semi-Arid Northern Highlands of Ethiopia. Cogent Geosci. 2017, 3, 1353719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addisu, S.; Selassie, Y.G.; Fissha, G.; Gedif, B. Time Series Trend Analysis of Temperature and Rainfall in Lake Tana Sub-Basin, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2015, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwajei, S.E.; Omoregie, A.U.; Ogedegbe, F.O. Effects of Planting Dates on the Growth and Grain Yield of Two Indigenous Varieties of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum Glaucum (L.) R.Br.) in a Forest-Savanna Transition Zone of Edo State, Nigeria. Acta Agric. Slov. 2019, 114, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwajei, S.E. Effects of Planting Dates on the Crude Protein and Nutrient Uptake of Two Varieties of Millet ( Pennisetum Typhoides ( Burm. f.)) Stapf & Hubbard in a Forest-Savanna Transition Zone of Edo State. Sustain. Agri, Food Environ. Res. 2023, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoregie, A.U.; Nwajei, S.E.; Iredia, B.E. Effects of Planting Density on the Growth and Forage Yield of Two Varieties of Millet (Pennisetum Typhoides Burm. F.) Grown in Ekpoma, Nigeria. Sustain. Agri, Food Environ. Res. 2020, 8, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerioli, T.; Gentimis, T.; Linscombe, S.D.; Famoso, A.N. Effect of Rice Planting Date and Optimal Planting Window for Southwest Louisiana. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaton, N.A.; Linscombe, S.D.; Norman, R.J.; Gbur, E.E. Seeding Date Effect on Rice Grain Yields in Arkansas and Louisiana. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation Statistics Available online:. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- 2018.
- Awala, S.K.; Hove, K.; Shivute, V.; Valombola, J.S.; Nanhapo, P.I.; Hirooka, Y.; Mwandemele, O.D.; Iijima, M. Growth and Productivity Assessment of Short-Duration Rice (Oryza Sativa L. and Upland NERICA) Genotypes in Semiarid North-Central Namibia. Adv. Agric. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Awala, S.K.; Watanabe, Y.; Kawato, Y.; Fujioka, Y.; Yamane, K.; Wada, K.C. Mixed Cropping Has the Potential to Enhance Flood Tolerance of Drought-Adapted Grain Crops. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 192, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awala, S.K.; Yamane, K.; Izumi, Y.; Fujioka, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Wada, K.C.; Kawato, Y.; Mwandemele, O.D.; Iijima, M. Field Evaluation of Mixed-Seedlings with Rice to Alleviate Flood Stress for Semi-Arid Cereals. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 80, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirooka, Y.; Shoji, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Awala, S.K.; Iijima, M. Ridge Formation with Strip Tillage Alleviates Excess Moisture Stress for Drought-Tolerant Crops. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Awala, S.K.; Nanhapo, P.I.; Wanga, A.; Mwandemele, O.D. Development of Flood-and Drought-Adaptive Cropping Systems in Namibia. In Crop Production under Stressful Conditions; Springer, 2018; pp. 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Siyambango, N.; Togarepi, C.; Mudamburi, B.; Mupambwa, H.A.; Awala, S. Climate-Smart Agriculture: Perspectives for Subsistence Crop Farming in Namibia. In Food Security for African Smallholder Farmers; Springer, 2022; pp. 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Mudamburi, B.; Ogunmokun, A.A.; Kachigunda, B. A Comparison of the Effects of Conventional and Namibia Specific Conservation Tillage Methods Used in Ogongo, Namibia on Root Development and Yield of Pearl Millet. Volume 1. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2018, 40, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeigbe, H.A.; Akinseye, F.M.; Kunihya, A.; Abdullahi, I.; Kamara, A.Y. Response of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum Glaucum L.) to Plant Population in the Semi-Arid Environments of Nigeria. Net J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 7, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausiku, A.P.; Annandale, J.G.; Steyn, J.M.; Sanewe, A.J. Improving Pearl Millet (Pennisetum Glaucum) Productivity through Adaptive Management of Water and Nitrogen. Water 2020, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.B.P.; Madhuri, K.V.N.; Venkaiah, K.; Prathima, T. Effect of Nitrogen and Potassium on Yield and Quality of Pearl Millet ( Pennisetum Glaucum L.). Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. Vol. 2016, 4, 678–681. [Google Scholar]
| Statistic | Annual | Month | |||||||||||
| May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | ||
| Mean (mm) | 475.1 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 10.3 | 38.5 | 71.6 | 103.4 | 107.3 | 112.6 | 29.7 |
| SD | 185.4 | 5.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 18.5 | 31.6 | 65.3 | 66.4 | 86.8 | 72.4 | 35.6 |
| Statistic | Annual | Dry season | Rainy season | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | |||
| ZMK | -0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.116 | -0.094 | -0.011 | -0.097 | -0.062 | -0.140 | 0.083 | 0.102 | |
| P-value | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.488 | 0.498 | 0.943 | 0.464 | 0.643 | 0.284 | 0.532 | 0.442 | |
| Sen's slope (mm/year) | -0.036 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.033 | -0.800 | -0.833 | -1.727 | 0.763 | 0.194 | |
| Day of the year | Calendar date | Relative yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kantana | Okashana-2 | ||
| 1 | 1-Jan | 100 | 64 |
| 7 | 7-Jan | 82 | 67 |
| 14 | 14-Jan | 66 | 67 |
| 21 | 21-Jan | 55 | 63 |
| 28 | 28-Jan | 47 | 57 |
| 35 | 4-Feb | 43 | 50 |
| 42 | 11-Feb | 40 | 44 |
| 49 | 18-Feb | 38 | 40 |
| 56 | 27-Feb | 36 | 38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





