Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. One glance, three spans
1.2. Written word recognition between phonology and semantics
1.3. Higher order processing between syntax and semantics
1.4. Written word recognition between sequential and parallel processing
2. Methodology
2.1. Participants
2.2. Design and Materials
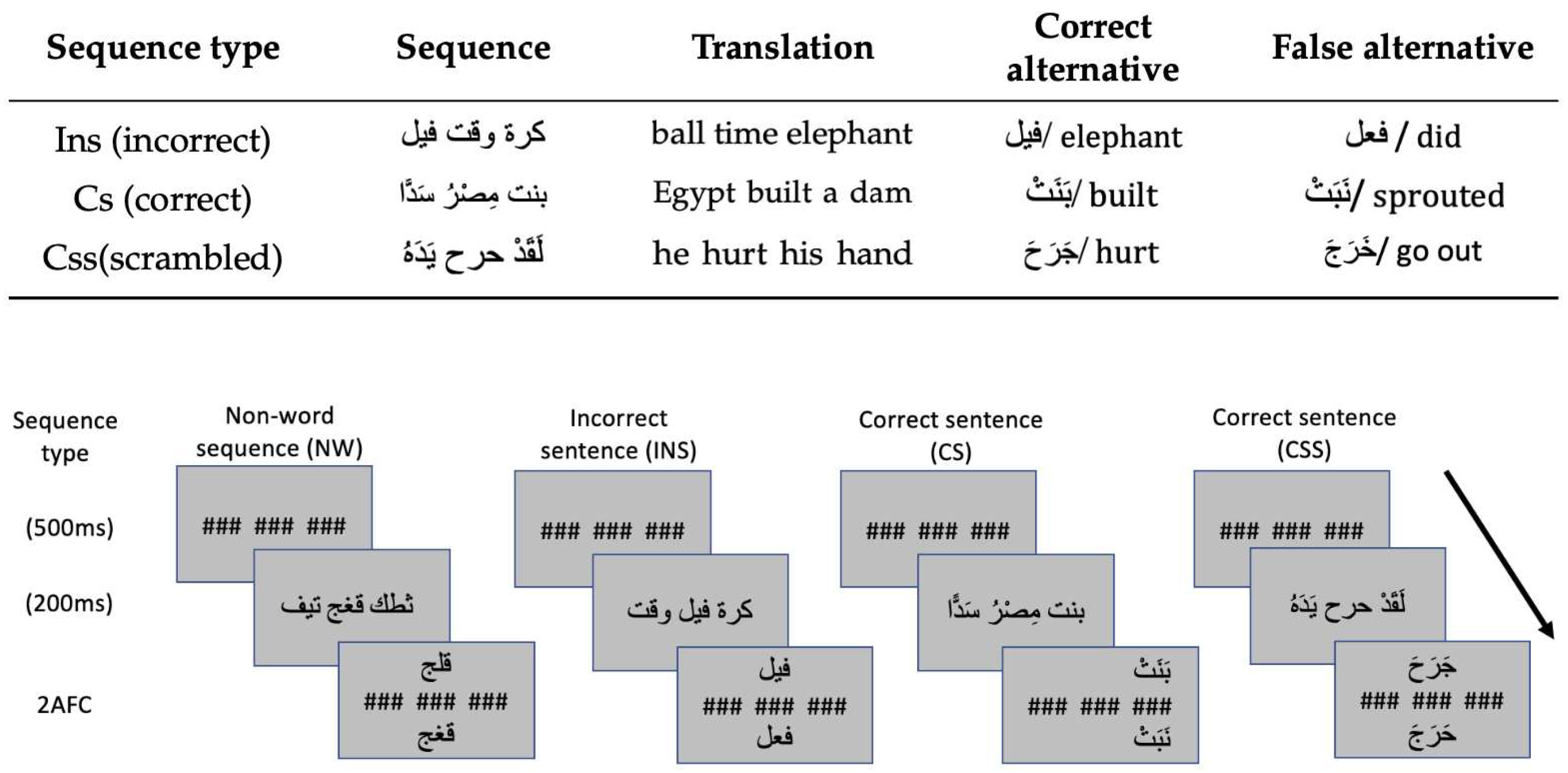
2.3. Appartus and Procedure
2.4. Data analysis
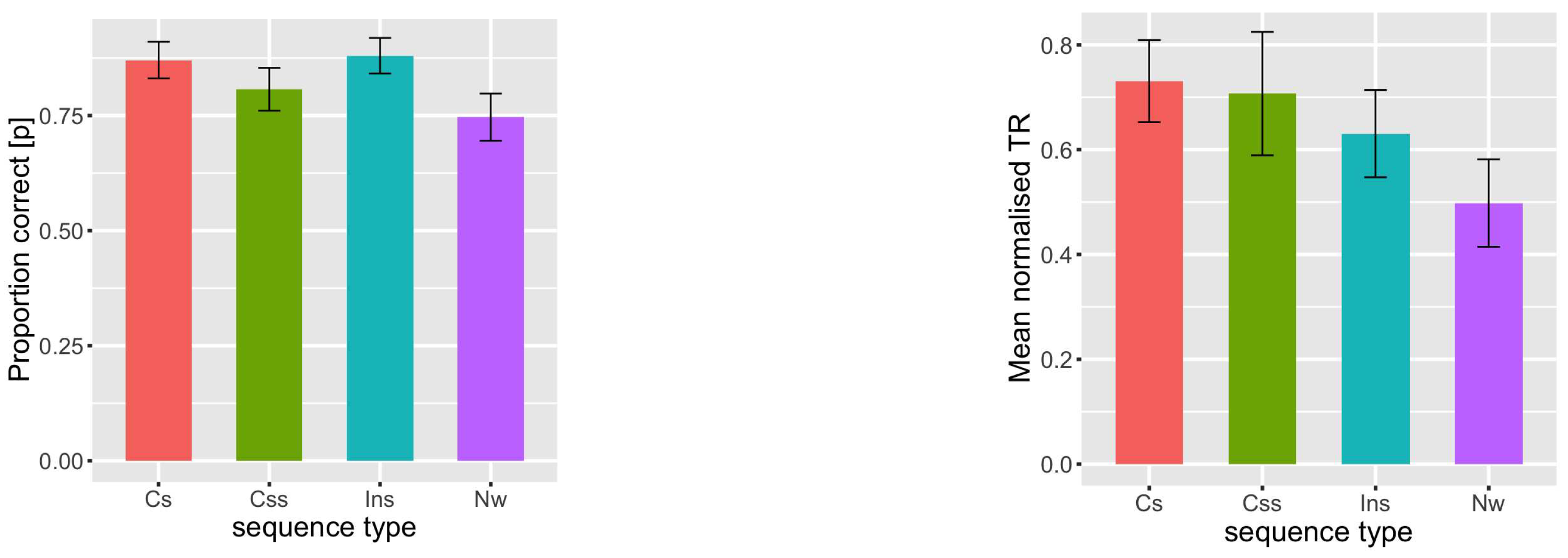
3. Results
| Proportion Correct | Normalized RT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | Estimate | SE | z | Estimate | SE | z |
| (Intercept) | 1.372 | 0.110 | 12.413 | 0.649 | 0.034 | 19.050 |
| Median | 0.710 | 0.122 | 5.799 | -0.050 | 0.018 | -2.706 |
| Final | -0.452 | 0.106 | -4.227 | -0.023 | 0.020 | -1.133 |
| Incorrect | -0.232 | 0.120 | -1.922 | 0.030 | 0.018 | 1.657 |
| Non-word | -1.011 | 0.114 | -8.843 | -0.074 | 0.019 | -3.777 |
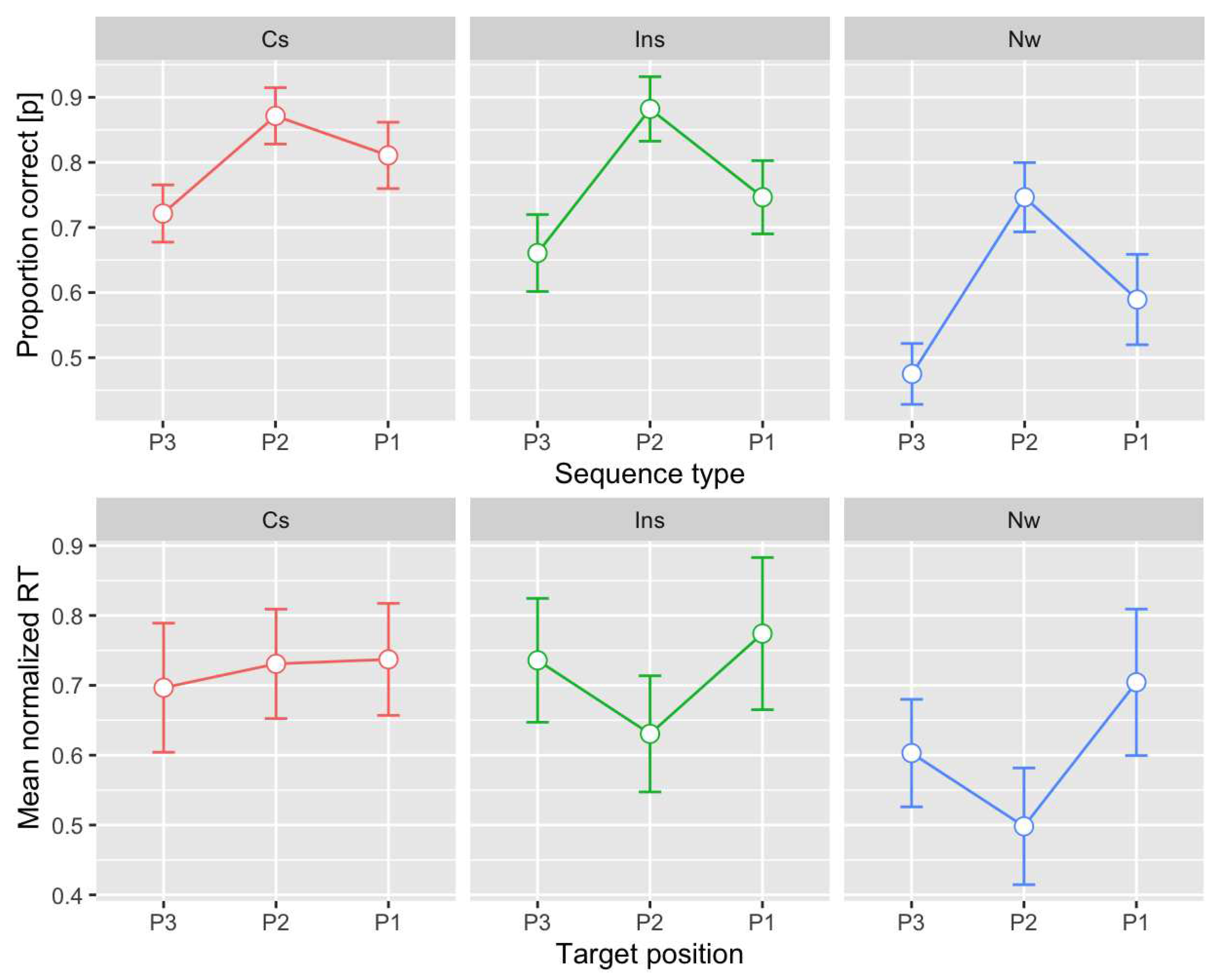
4. Discussion
 / could be expressed in the Schrödinger sense as:
/ could be expressed in the Schrödinger sense as:
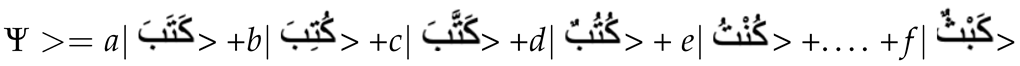
5. Conclusion
References
- Legge, G.E.; Mansfield, J.S.; Chung, S.T. Psychophysics of reading: XX. Linking letter recognition to reading speed in central and peripheral vision. Vis. Res. 2001, 41, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.; Bosse, M.L. Perceptual span, visual span, and visual attention span: Three potential ways to quantify limits on visual processing during reading. Vis. Cogn. 2018, 26, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadh, F.H.; Phénix, T.; Antzaka, A.; Lallier, M.; Carreiras, M.; Valdois, S. Cross-language modulation of visual attention span: an Arabic-French-Spanish comparison in skilled adult readers. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, G. The information available in brief visual presentations. Psychol. Monogr. Gen. Appl. 1960, 74, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbach, E.; Coriell, A.S. Short-term memory in vision. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1961, 40, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConkie, G.W.; Rayner, K. The span of the effective stimulus during a fixation in reading. Percept. Psychophys. 1975, 17, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; McConkie, G.W. What guides a reader’s eye movements? Vis. Res. 1976, 16, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Bertera, J.H. Reading without a fovea. Science 1979, 206, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Well, A. Pollatsek a. Asymmetry Eff. Vis. Field Reading. Percept Psychophys 1980, 27, 537–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.R.; Almabruk, A.A.; Gadalla, E.A.; McGowan, V.A.; White, S.J.; Abedipour, L.; Paterson, K.B. Reading direction and the central perceptual span: Evidence from Arabic and English. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2014, 21, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatsek, A.; Bolozky, S.; Well, A.D.; Rayner, K. Asymmetries in the perceptual span for Israeli readers. Brain Lang. 1981, 14, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, K.B.; McGowan, V.A.; White, S.J.; Malik, S.; Abedipour, L.; Jordan, T.R. Reading direction and the central perceptual span in Urdu and English. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e88358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatsek, A.; Lesch, M.; Morris, R.K.; Rayner, K. Phonological codes are used in integrating information across saccades in word identification and reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 1992, 18, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Well, A.D.; Pollatsek, A.; Bertera, J.H. The availability of useful information to the right of fixation in reading. Percept. Psychophys. 1982, 31, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.L.; Perea, M.; Rayner, K. Transposed-letter effects in reading: evidence from eye movements and parafoveal preview. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2007, 33, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenstein, S.; Kliegl, R. Semantic preview benefit during reading. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2014, 40, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, H.; Lewis, S.S.; Rubenstein, M.A. Evidence for phonemic recoding in visual word recognition. J. Verbal Learn. Verbal Behav. 1971, 10, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfetti, C.A.; Zhang, S. Phonological processes in reading Chinese characters. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 1991, 17, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Orden, G.C. A ROWS is a ROSE: Spelling, sound, and reading. Mem. Cogn. 1987, 15, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K.; Pollatsek, A.; Schotter, E.R. Reading: Word identification and eye movements. 2013.
- Spinelli, E. Psychologie du langage: l’écrit et le parlé, du signal à la signification; Armand Colin, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, H. The role of semantic activation during word recognition in Arabic. Cogn. Process. 2019, 20, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, J.; Grainger, J. The sentence superiority effect revisited. Cognition 2017, 168, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snell, J.; Meeter, M.; Grainger, J. Evidence for simultaneous syntactic processing of multiple words during reading. PloS One 2017, 12, e0173720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massol, S.; Grainger, J. The sentence superiority effect in young readers. Dev. Sci. 2021, 24, e13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, M.; Yokosawa, K. Rapid extraction of gist from visual text and its influence on word recognition. J. Gen. Psychol. 2011, 138, 127–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichle, E.; Pollatsek, A. & Rayner, K. E–Z Reader: A cognitive-control, serial-attention model of eye-movement behavior during reading. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engbert, R.; Nuthmann, A.; Richter, E.M.; Kliegl, R. SWIFT: a dynamical model of saccade generation during reading. Psychol. Rev. 2005, 112, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A. Parafoveal processing in word recognition. The Quarterly J. Exp. Psychol. Sect. A 2000, 53, 429–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, W.S. Parafoveal pragmatics. In Eye guidance in reading and scene perception; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 181–199. [Google Scholar]
- Reicher, G.M. Perceptual recognition as a function of meaningfulness of stimulus material. J. Exp. Psychol. 1969, 81, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.D. Processes in word recognition. Cogn. Psychol. 1970, 1, 59–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baayen, R. Analyzing Linguistic Data: A Practical Introduction to Statistics Using R. Cambridge University Press, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, S. Les conceptions" système unique" de la mémoire: aspects théoriques. Rev. De Neuropsychol. 2000, 10, 27–51. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Martínez, G.A.; Castillo-Parra, H. Bistable perception: neural bases and usefulness in psychological research. Int. J. Psychol. Res. 2018, 11, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintzman, D.L. MINERVA 2: A simulation model of human memory. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1984, 16, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzman, D.L. " Schema abstraction" in a multiple-trace memory model. Psychol. Rev. 1986, 93, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, R.; Vallet, G.T.; Riou, B.; Lesourd, M.; Labeye, É.; Brunel, L. Act-In: An integrated view of memory mechanisms. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2014, 26, 280–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, K.C.; Brascamp, J.; Tadin, D.; Blake, R. Does visual attention drive the dynamics of bistable perception? Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2016, 78, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadh, F.H.R. Caractérisation et rôle de l’empan visuo-attentionnel chez les lecteurs arabophones adultes et enfants (experts et dyslexiques développementales). Theses, Université Grenoble Alpes, 2016.
- Abu-Rabia, S. Reading in Arabic orthography: The effect of vowels and context on reading accuracy of poor and skilled native Arabic readers. Read. Writ. 1997, 9, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.R.; Paterson, K.B.; Almabruk, A.A. Revealing the superior perceptibility of words in Arabic. Perception 2010, 39, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, J.; Declerck, M.; Grainger, J. Parallel semantic processing in reading revisited: Effects of translation equivalents in bilingual readers. Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrand, L. Psychologie cognitive de la lecture (De Boeck ed.), 2007.
- Davis, C.J. The spatial coding model of visual word identification. Psychol. Rev. 2010, 117, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltheart, M.; Rastle, K.; Perry, C.; Langdon, R.; Ziegler, J. DRC: a dual route cascaded model of visual word recognition and reading aloud. Psychol. Rev. 2001, 108, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.; Ziegler, J.C.; Zorzi, M. Beyond single syllables: Large-scale modeling of reading aloud with the Connectionist Dual Process (CDP++) model. Cogn. Psychol. 2010, 61, 106–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintsch, W.; Mangalath, P. The construction of meaning. Top. Cogn. Sci. 2011, 3, 346–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




