1. Introduction
Lipid droplets (LDs) are cytoplasmic organelles coated by structural proteins, perilipins and phospholipids, which covering a hydrophobic core composed by triacylglycerol and cholesteryl esters, and a variable content of proteins [
1]. The accumulation of LDs within non-adipocyte cells, such as leukocytes, epithelial and endothelial cells, hepatocytes, and cancer, has been reported. According to the current knowledge, LDs are not only fat storing intracellular structures but also players in cell signaling, lipid metabolism, membrane trafficking, and in the production of inflammatory mediators [
2]. LDs have also been linked to protein storage, for instance a temporal storage of unfolded membrane proteins before proteasomal degradation [
3].
Lipid droplet biogenesis is a regulated process that involves various cellular and molecular mechanisms, like increased lipid uptake, de novo lipid synthesis and lipolysis. Nevertheless, mechanisms involved in LD formation are still not completely understood [
4]. Various pathogen-associated molecular patterns, including lipopolysaccharide (LPS), can induce LDs. For example, LPS triggers LD formation in macrophages [
5] and endothelial cell [
6]. Recent studies demonstrate that type II pneumocytes and monocytes from COVID-19 patients are characterized by the pronounced accumulation of LDs [
7], and that in multiple cell lines severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) induces LD accumulation to benefit viral replication [
8,
9]. However, how SARS-CoV-2 triggers LD accumulation remains unknown.
SARS-CoV-2 virus contains four structural proteins namely the spike, membrane, envelope, and nucleocapsid proteins. The trimer spike (S) glycoprotein is a sole SARS-CoV-2 viral membrane protein that binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor on the target cell and mediates virus-cell fusion [
10,
11]. Typically, virions are decorated with 25-50 spike trimers although others can contain more than 90 trimers [
12] which are very immunogenic [
13]. As spike is the most immunogenic of coronaviruses proteins, it is in a major focus for vaccine, therapeutic and diagnostic development. New study reported that spike protein interferes with metabolic and autophagic pathways in host cells [
14,
15], and thus might affect LD formation. Herein, we aimed to investigate whether recombinant trimeric spike glycoproteins can induce LDs in human total peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and/or in lung microvascular endothelial cells (HPMEC).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spike proteins
The widely spread SARS-CoV-2 variants were designated as Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), Delta (B.1.617.2), and Omicron (B.1.1.529). We employed highly purified and endotoxin-free trimeric SARS-CoV-2 spike variants engineered for a high-yield production by ExcellGene, to be used for research hand the development of novel vaccines [
16]. Secreted forms of a trimeric spike protein variants were produced in CHO cells based on the CHO-vector pXLG-6 by ExcellGene SA as described previously [
17]. LAL (limulus amebocyte lysate) assay was used to detect bacterial endotoxins in proteins (Pierce™ chromogenes Endotoxin Quant Kit, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, USA).
2.2. PBMC isolation, treatments, and cytokine/chemokine analyses
PBMCs were isolated from fresh peripheral human donor blood by using Lymphosep (PL-15-M, c.c.pro, Oberdorla, Germany) discontinuous gradient centrifugation according to the protocol of the manufacturer. Isolated total PBMCs were suspended in serum-free RPMI Medium 1640 (Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific, Paisley, UK), and were incubated for 6 or 18 h alone or with spikes (12 µg/mL each) in multiwell plates with cell-repellent surface (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, Frickenhausen, Germany) at 37°C with 5% CO2. Cell supernatants were used for ELISA-based quantitative analysis of IL-1β (DY201, sensitivity: 3.91-250 pg/mL), TNF-α (DY210, sensitivity: 15.6-1000 pg/mL), IL-6 (DY206, sensitivity: 9.38-600 pg/mL), IL-8 (DY208, sensitivity: 31.2-2000 pg/mL), and CCL2/MCP-1 (DY279, Sensitivity: 15.6-1000 pg/mL). ELISA kits were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, US). Microplate reader Tecan Infinite M200 (Männedorf, Switzerland).
2.3. Primary human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell culture
Human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMEC; Promocell, Heidelberg, Germany) were cultured in MV-2 endothelial cell growth medium (Promocell) at 37°C with 5% CO2. HPMEC (passages 4–6, at 70–90% confluence) were incubated for 6 or 18 h alone or with spikes (12 µg/mL). Experiments were performed in serum-free cell growth medium.
2.4. Oil red O staining
Total PBMCs or HPMEC were incubated for determined time points on coverslips alone or with spikes (12 µg/mL) for 18 h. Afterwards, cells were fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde and stained with Oil Red O (O-0625, Sigma-Aldrich, Missouri, USA) for LDs and with hematoxylin for the nuclei. Number of cells positive for LDs were counted manually and the percentage was calculated based on the total number of cells per field (for each condition 10 different fields were evaluated). Images were taken at 1000-fold magnification using a 100× oil immersion objective (Leica, Germany).
2.5. RNA isolation and gene expression analysis by RT-PCR
Human PBMCs cultured for 6 h without or with addition on spikes (as above) were collected for gene expression analysis. Total RNA isolation, cDNA synthesis and target gene analysis were performed as previously described [
18]. The following primers were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific: CD36 (Hs00169627_m1), PLIN2 (Hs00605340_m1), DDIT3 (Hs00358796_g1), CXCL8 (Hs00174103_m1), IL1B (Hs01555410_m1), TNFA (Hs00174128_m1), CCL2 (Hs00234140_m1), IL6 (Hs00985639_m1), SREBF1 (Hs01088691_m1), LDLR (Hs01092524_m1), HMGCS1 (Hs00266810_m1). HPRT1 (Hs02800695_m1) was used as a housekeeping gene in the same run. The measured gene expression was calculated according to the method 2∆Ct (Ct value of target gene − Ct value of reference gene).
2.6. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis and graphical data presentation of ELISA and RT-PCR were performed by using GraphPad Prism (Version 9.1.2 (226), GraphPad Software). The one-way ANOVA was applied to compare between groups. Data were presented as mean and standard deviation if the normality test did not fail. If the normality test failed, the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis followed by Mann-Whitney rank-sum test was performed. A p-value below 0.05 was considered as significant.
3. Results
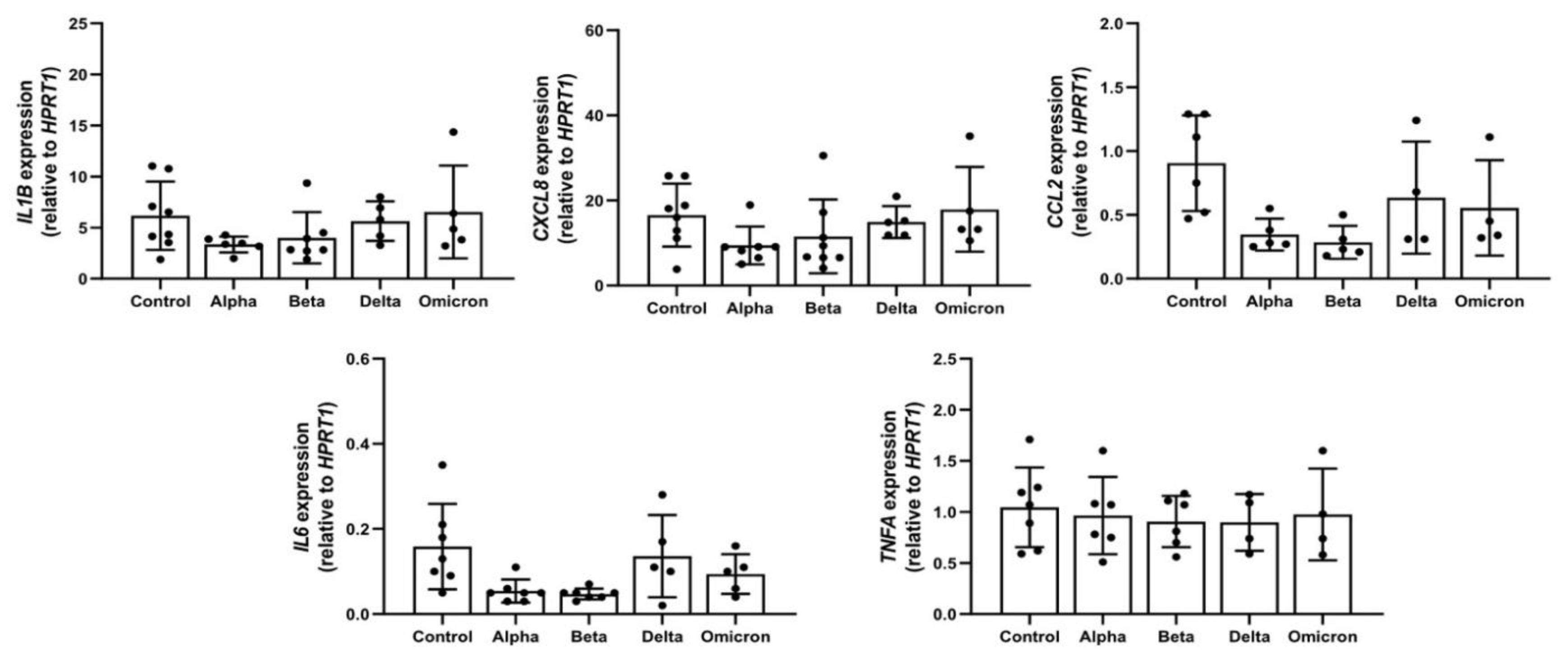
3.1. Spike proteins are endotoxin free and do not induce cytokine/chemokine release and expression in PBMCs
Previous studies reported that spike proteins contaminated with LPS are pro-inflammatory [
19] and that LPS can induce LD formation [
6]. According to LAL assay, in all spike variants endotoxin levels were below detection limits. In concordance, in supernatants of PBMCs treated with spikes, the levels of all analyzed pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2/MCP-1) were below detection limits of ELISA assays (data not shown). As illustrated in
Figure 1, these spike variants had no significant effects on the expression of analyzed cytokines/chemokines.
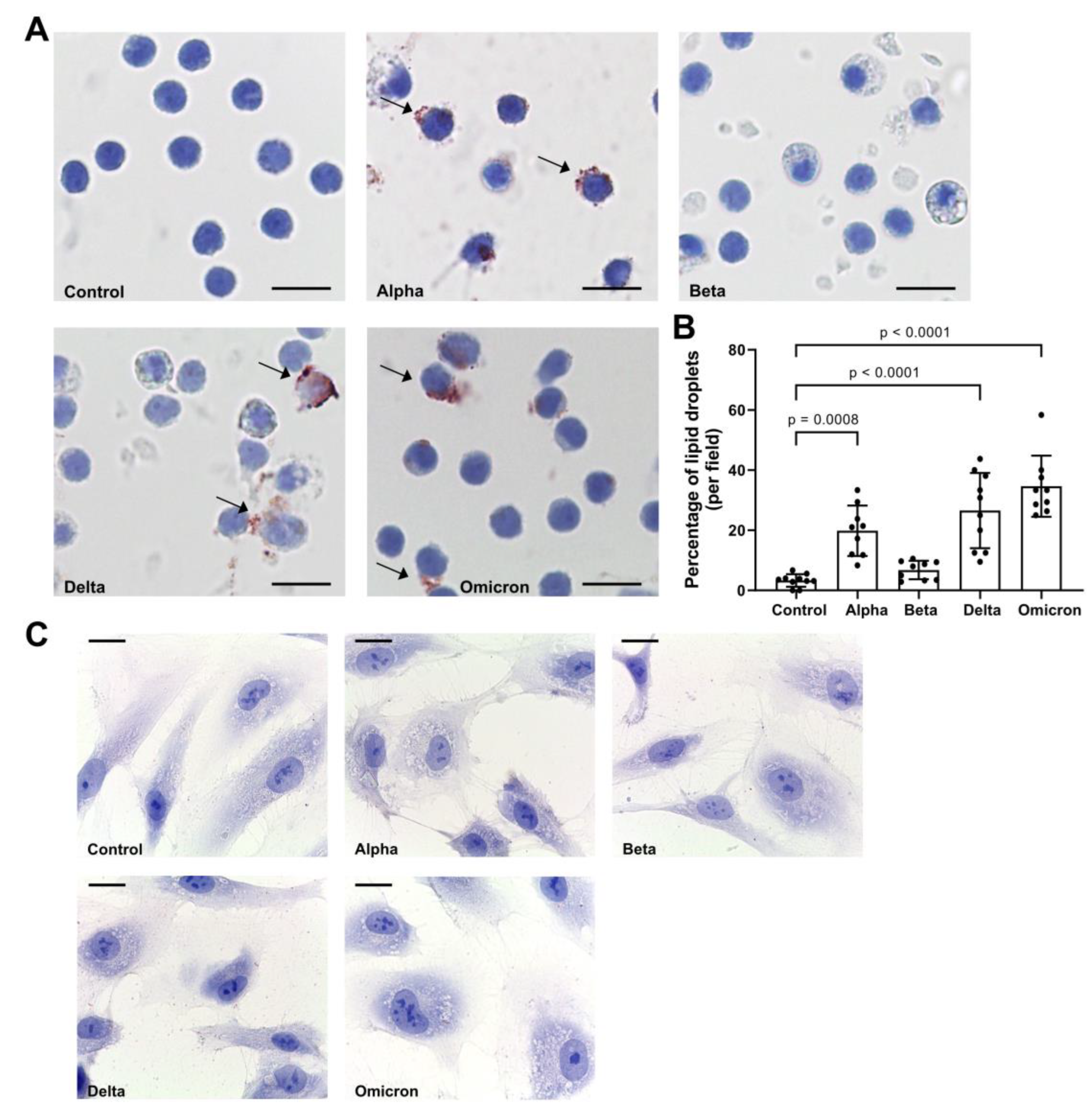
3.2. Spike proteins induce lipid droplet (LD) formation in PBMCs
As shown in
Figure 2A,B, spike variants added to total PBMCs for 18 h to different extend induced LD formation. Notably, spike “Beta” showed lowers effect on LDs as compared to other variants. By contrast, spikes did not induce LD formation in HPMEC (
Figure 2C) and we did not perform further analyses with these cells.
In parallel to LD formation, the expression of genes related to lipid-metabolism, such as sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (
SREBF1), 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase 1 (
HMGCS1), low-density lipoprotein receptor (
LDLR) and DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (
DDIT3), also known as C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), decreased significantly in spike-treated PBMCs. Moreover, spikes to different degree lowered the expression of fatty acid translocase, also known as (
CD36), but did not affect perilipin 2 (
PLIN2) expression (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
In this study we show that endotoxin-free spike variants of SARS-CoV-2 added to human PBMCs within 18 h induce LD formation. Cytoplasmic accumulation of LDs in leukocytes and other cells can be a hallmark of inflammation [
20,
21,
22,
23]. Although the molecular mechanisms that govern LD biogenesis are incompletely understood, it is thought that inducible LD may occur due to inflammatory stimuli-induced lipid uptake, lipolysis inhibition, and/or new lipid synthesis. For example, resting PBMCs show no LDs but can rapidly form LDs when activated through bacterial and/or host-generated cytokines and chemokines [
23,
24]. We therefore investigated effects of spike proteins on cytokines/chemokine production in human total PBMCs. According to previous studies, effects of spike proteins on inflammatory markers are sterility and time-dependent, with highest effect observed at 8 h post-stimulation [
19,
25]. Therefore, we first confirmed that our spike proteins are endotoxin-free and chosen to analyze cytokine/chemokine production in human PBMCs after exposure to spikes for 6 h. Under this experimental condition none of the spikes increased cytokine/chemokine (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1 and TNF-α) release or expression. Likewise, spikes did not induce IL-1β or IL-6 after 18 h. Hence, our data imply that LDs formation in PBMCs is not solely depended on the amplified cytokine/chemokine production.
Intriguingly, in response to spikes, PBMCs formed LDs under complete lipid deprivation (serum-free medium) conditions. According to other studies, emerging formation of LDs might be necessary for the protection of cell integrity and function during the stress [
4,
26,
27]. Hence, hypothetically, under nutrients limited conditions, an interaction between spike protein and cells, might induce stress-related LD formation in majority of PBMCs.
Spike proteins induced LD formation but also lowered the expression of genes known to be involved in lipid metabolism, such as
HMGCS1,
LDLR1, and
SREBF1. The
HMGCS1 is the rate-limiting enzyme of the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway whereas
LDLR1 mediates cholesterol influx [
28,
29]. Hence, spike-induced reduction in
HMGCS1 and
LDLR1 expression in PBMCs support a notion that strong lipid deprivation may lead to LD formation. This latter might be also dependent on the reduction in expression of
SREBF1, a key transcriptional factor that regulates the expression of
HMGCS1 and
LDLR.
Spike proteins did not affect the expression of
PLIN2 gene that is the second Plin-family member encoding LD surface-coating protein [
30]. Most cells have high
PLIN2 mRNA but contain a modest amount of the protein because of its rapid proteasomal degradation that is not associated with LDs [
31]. This latter may explain why spikes showed no effect on
PLIN2 levels. Finally, as compared to controls, PBMCs treated with spikes showed slight reduction in expression of
CD36. The CD36 is involved in the regulation of fatty acid storage or usage [
32], and it is known as a fatty acid transporter protein, which belongs to the class B scavenger receptor family. Some studies show that the uptake of fatty acids is required for CD36-dependent LDs formation [
33]. Since our experiments were performed under serum-free conditions, LDs formation probably was independent on CD36 expression.
The reduction in expression of lipid metabolism-related genes and LD formation in PBMCs cultured with spikes under deprivation of lipids can simply be associated with cellular stress-induced blockage of lipid release. This property might be very important for immune cells exposed to rapidly changing conditions of stress like feeding/starvation or hypoxia/reoxygenation [
34,
35]. In line, decreased
DDIT3 expression in human PBMCs exposed to spikes, might be related to anti- damage and/or cell survival mechanisms [
36].
Data from our study and other experimental models imply that spikes interfere with lipid metabolism pathways [
14,
15,
37], and this warrants further investigations.
5. Conclusions
Our results show that under lipid-free culture conditions spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 without triggering of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines induce LD deposition in human PBMCs. Whether this spike-induced LD formation is beneficial or detrimental remains to be investigated.
Author Contributions
S.J., F.M.W. and M.J.W. designed the study. P.P., G.R., S.A., Ch.M., and N.D. produced and characterized recombinant spike variants. K.S. and J.H. performed cell culture experiments. K.S. and S.W. analyzed the data and helped with manuscript preparation. M.J.W., F.M.W. and T.W. conducted writing-review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors attest they meet the ICMJE criteria for authorship.
Funding
Study is supported by the project: “COVAAT – TP1: Alpha-1-Antitrypsin zur COVID-19 Therapie ZW7-85152684” from Enterprise Europe Network Niedersachsen (EEN) of the NBank. The funding body helped to obtain reagents for experiments.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Murphy, D.J. The dynamic roles of intracellular lipid droplets: from archaea to mammals. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 541–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.L.S.; Barreto, E.A.; Fazolini, N.P.B.; Viola, J.P.B.; Bozza, P.T. Lipid droplets: platforms with multiple functions in cancer hallmarks. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, M.A. Proteins under new management: lipid droplets deliver. Trends Cell Biol 2007, 17, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dierendonck, X.; Vrieling, F.; Smeehuijzen, L.; Deng, L.; Boogaard, J.P.; Croes, C.A.; Temmerman, L.; Wetzels, S.; Biessen, E.; Kersten, S.; et al. Triglyceride breakdown from lipid droplets regulates the inflammatory response in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2114739119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, K.; Stojak, M.; Pacia, M.Z.; Zieba, A.; Baranska, M.; Chlopicki, S.; Kaczor, A. Lipid Droplets Formation Represents an Integral Component of Endothelial Inflammation Induced by LPS. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardacci, R.; Colavita, F.; Castilletti, C.; Lapa, D.; Matusali, G.; Meschi, S.; Del Nonno, F.; Colombo, D.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Zumla, A.; et al. Evidences for lipid involvement in SARS-CoV-2 cytopathogenesis. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, S.S.G.; Soares, V.C.; Ferreira, A.C.; Sacramento, C.Q.; Fintelman-Rodrigues, N.; Temerozo, J.R.; Teixeira, L.; Nunes da Silva, M.A.; Barreto, E.; Mattos, M.; et al. Lipid droplets fuel SARS-CoV-2 replication and production of inflammatory mediators. PLoS Pathog 2020, 16, e1009127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, M.Z.X.; Fu, J.; Chen, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, Q. Genetic variety of ORF3a shapes SARS-CoV-2 fitness through modulation of lipid droplet. J Med Virol 2023, 95, e28630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Oton, J.; Qu, K.; Cortese, M.; Zila, V.; McKeane, L.; Nakane, T.; Zivanov, J.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 2020, 588, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, B.J.; van der Zee, R.; de Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J Virol 2003, 77, 8801–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, J.M.; Chou, C.W.; Kuo, H.C.; Javanmardi, K.; Hsieh, C.L.; Goldsmith, J.; DiVenere, A.M.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Byrne, P.O.; et al. Expression and characterization of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins. Nat Protoc 2021, 16, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042 e1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halma, M.T.J.; Plothe, C.; Marik, P.; Lawrie, T.A. Strategies for the Management of Spike Protein-Related Pathology. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Cao, X.; Tian, Y.; Carver, W.; Kiaris, H.; Cui, T.; Tan, W. The Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Impairs Lipid Metabolism and Increases Susceptibility to Lipotoxicity: Implication for a Role of Nrf2. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excellgene. Developing a Variant-Proof SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: a CEPI-funded ExcellGene Partnership with Bharat Biotech and the University of Sydney. Available online: https://excellgene.com/2022/07/developing-a-variant-proof-sars-cov-2-vaccine/ (accessed on 29th May 2023).
- Pino, P.; Kint, J.; Kiseljak, D.; Agnolon, V.; Corradin, G.; Kajava, A.V.; Rovero, P.; Dijkman, R.; den Hartog, G.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. Trimeric SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Produced from CHO Cells in Bioreactors Are High-Quality Antigens. Processes 2020, 8, 1539. [Google Scholar]
- Tumpara, S.; Grunding, A.R.; Sivaraman, K.; Wrenger, S.; Olejnicka, B.; Welte, T.; Wurm, M.J.; Pino, P.; Kiseljak, D.; Wurm, F.M.; et al. Boosted Pro-Inflammatory Activity in Human PBMCs by Lipopolysaccharide and SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Is Regulated by alpha-1 Antitrypsin. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Xie, T.; Fang, H.; Gao, C.; Stantchev, T.; Clouse, K.A.; Yuan, K.; Ju, T.; Frucht, D.M. Variable Induction of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines by Commercial SARS CoV-2 Spike Protein Reagents: Potential Impacts of LPS on In Vitro Modeling and Pathogenic Mechanisms In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, K.; Majzner, K.; Selmi, A.; Baranska, M.; Ozaki, Y.; Kaczor, A. Unsaturated lipid bodies as a hallmark of inflammation studied by Raman 2D and 3D microscopy. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daquinag, A.C.; Gao, Z.; Fussell, C.; Immaraj, L.; Pasqualini, R.; Arap, W.; Akimzhanov, A.M.; Febbraio, M.; Kolonin, M.G. Fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue is mediated by CD36 posttranslational modifications and intracellular trafficking. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacia, M.Z.; Sternak, M.; Mateuszuk, L.; Stojak, M.; Kaczor, A.; Chlopicki, S. Heterogeneity of chemical composition of lipid droplets in endothelial inflammation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2020, 1867, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Dutra, F.S.; Teixeira, L.; de Souza Costa, M.F.; Bozza, P.T. Fat, fight, and beyond: The multiple roles of lipid droplets in infections and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 2019, 106, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.C.; D'Avila, H.; Wan, H.C.; Bozza, P.T.; Dvorak, A.M.; Weller, P.F. Lipid bodies in inflammatory cells: structure, function, and current imaging techniques. J Histochem Cytochem 2011, 59, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shafiei, M.S.; Longoria, C.; Schoggins, J.W.; Savani, R.C.; Zaki, H. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, M.A.; Gould, A.P. Lipid droplet functions beyond energy storage. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 2017, 1862, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoorian, A.; Du, X.; Yang, H. Lipid droplet biogenesis and functions in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedó, L.; Metso, J.; Santos, D.; García-León, A.; Plana, N.; Sabate-Soler, S.; Rotllan, N.; Rivas-Urbina, A.; Méndez-Lara, K.A.; Tondo, M.; et al. LDL Receptor Regulates the Reverse Transport of Macrophage-Derived Unesterified Cholesterol via Concerted Action of the HDL-LDL Axis: Insight From Mouse Models. Circ Res 2020, 127, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, K.L.; Ruan, X.Z.; Liu, B.C. Dysregulation of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Pathway Is Involved in Lipid Disorder-Mediated Organ Injury. Int J Biol Sci 2016, 12, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasaemle, D.L.; Barber, T.; Wolins, N.E.; Serrero, G.; Blanchette-Mackie, E.J.; Londos, C. Adipose differentiation-related protein is an ubiquitously expressed lipid storage droplet-associated protein. J Lipid Res 1997, 38, 2249–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Sztalryd, C.; Lu, X.; Tansey, J.T.; Gan, J.; Dorward, H.; Kimmel, A.R.; Londos, C. Post-translational regulation of adipose differentiation-related protein by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 42841–42847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Wei, L.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Chen, Y.; et al. CD36 plays a negative role in the regulation of lipophagy in hepatocytes through an AMPK-dependent pathway. J Lipid Res 2019, 60, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.W.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Li, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; et al. CD36 facilitates fatty acid uptake by dynamic palmitoylation-regulated endocytosis. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fader Kaiser, C.M.; Romano, P.S.; Vanrell, M.C.; Pocognoni, C.A.; Jacob, J.; Caruso, B.; Delgui, L.R. Biogenesis and Breakdown of Lipid Droplets in Pathological Conditions. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 826248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarc, E.; Petan, T. Lipid Droplets and the Management of Cellular Stress. Yale J Biol Med 2019, 92, 435–452. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Scheuner, D.; Ron, D.; Pennathur, S.; Kaufman, R.J. Chop deletion reduces oxidative stress, improves beta cell function, and promotes cell survival in multiple mouse models of diabetes. J Clin Invest 2008, 118, 3378–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, Y.; Waldie, S.; Thépaut, M.; Micciulla, S.; Moulin, M.; Fieschi, F.; Pichler, H.; Trevor Forsyth, V.; Haertlein, M.; Cárdenas, M. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein removes lipids from model membranes and interferes with the capacity of high density lipoprotein to exchange lipids. J Colloid Interface Sci 2021, 602, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).