Submitted:
24 July 2023
Posted:
24 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preservation of Animals and Parasites
2.2. Molecular cloning of Ts-MAPRC2
2.3. rTs-MAPRC2 protein development
2.4. Developing an anti-rat polyclonal antibody against rTs-MAPRC2
2.5. Detection of the natural protein Ts-MAPRC2 by indirect immunofluorescence assay (IIFA)
2.6. In vitro phenotyping of rTs-MAPRC2-Ab effects on ML and NBL
2.7. In vivo assessment of the infectivity of ML treated with rTs-MAPRC2-Ab
2.8. Assessment of the infectivity of NBL treated with rTs-MAPRC2-Ab
2.9. Preparation of siRNA
| siRNA name | Sense (5′–3′) | Antisense (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| siRNA-180 | 5’-CUGGGAUUCUUGCGGUAAUTT-3 | 5’-AUUACCGCAAGAAUCCCAGTT-3 |
| siRNA-419 | 5’-GGUGGACCAUAUGGCUUAUTT-3’ | 5’-AUAAGCCAUAUGGUCCACCTT-3’ |
| siRNA-559 | 5’- GGCUAUGCAUGAGCUGAAATT-3’ | 5’-UUUCAGCUCAUGCAUAGCCTT-3’ |
| siRNA-Control | 5’-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3’ | 5’- ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3’ |
2.10. Transfection of siRNA to T. spiralis Worms
2.11. Protein expression of Ts-MAPRC2 as determined by Western blotting
2.12. Expression of Ts-MAPRC2 mRNA by RNA extraction and qPCR
2.13. In vitro phenotyping of siRNA effects on ML
2.14. Evaluation of siRNA-treated NBL for infectivity
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
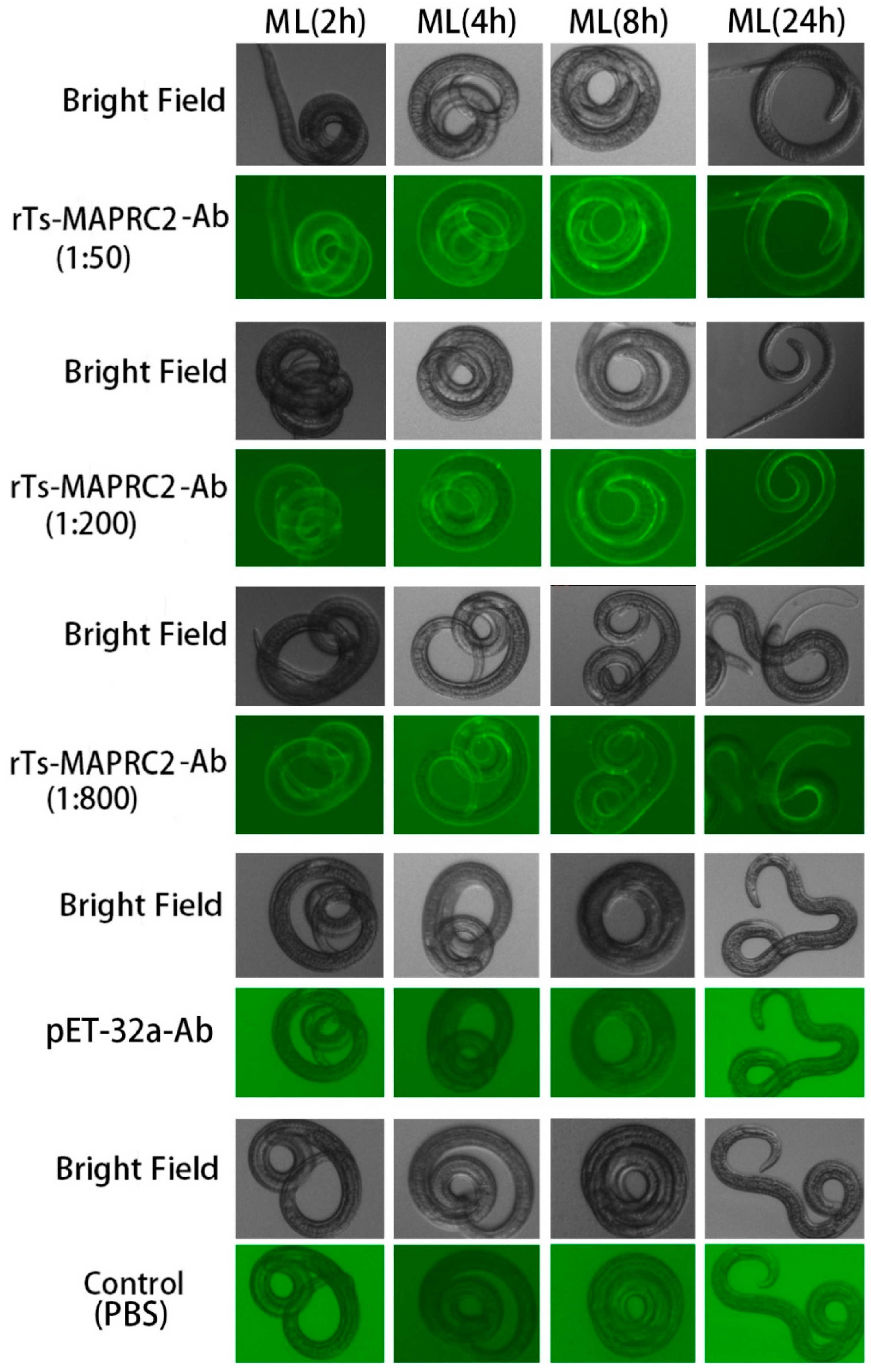
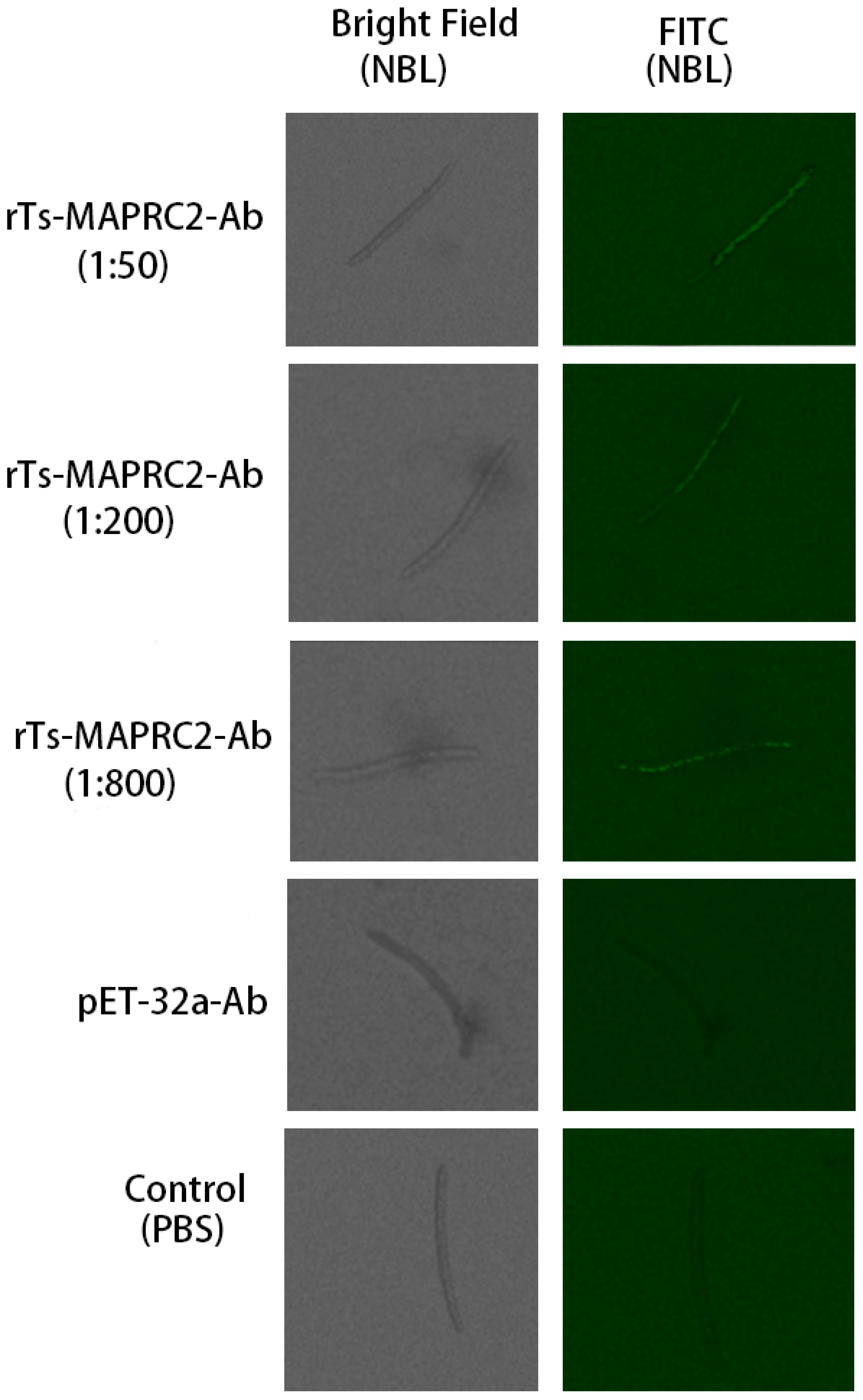
3.1. Indirect immunofluorescence assay (IIFA) in Muscle larvae (ML) and new borne larvae (NBL)
3.2. Effect of rTs-MAPRC2-Ab on ML and NBL in vitro
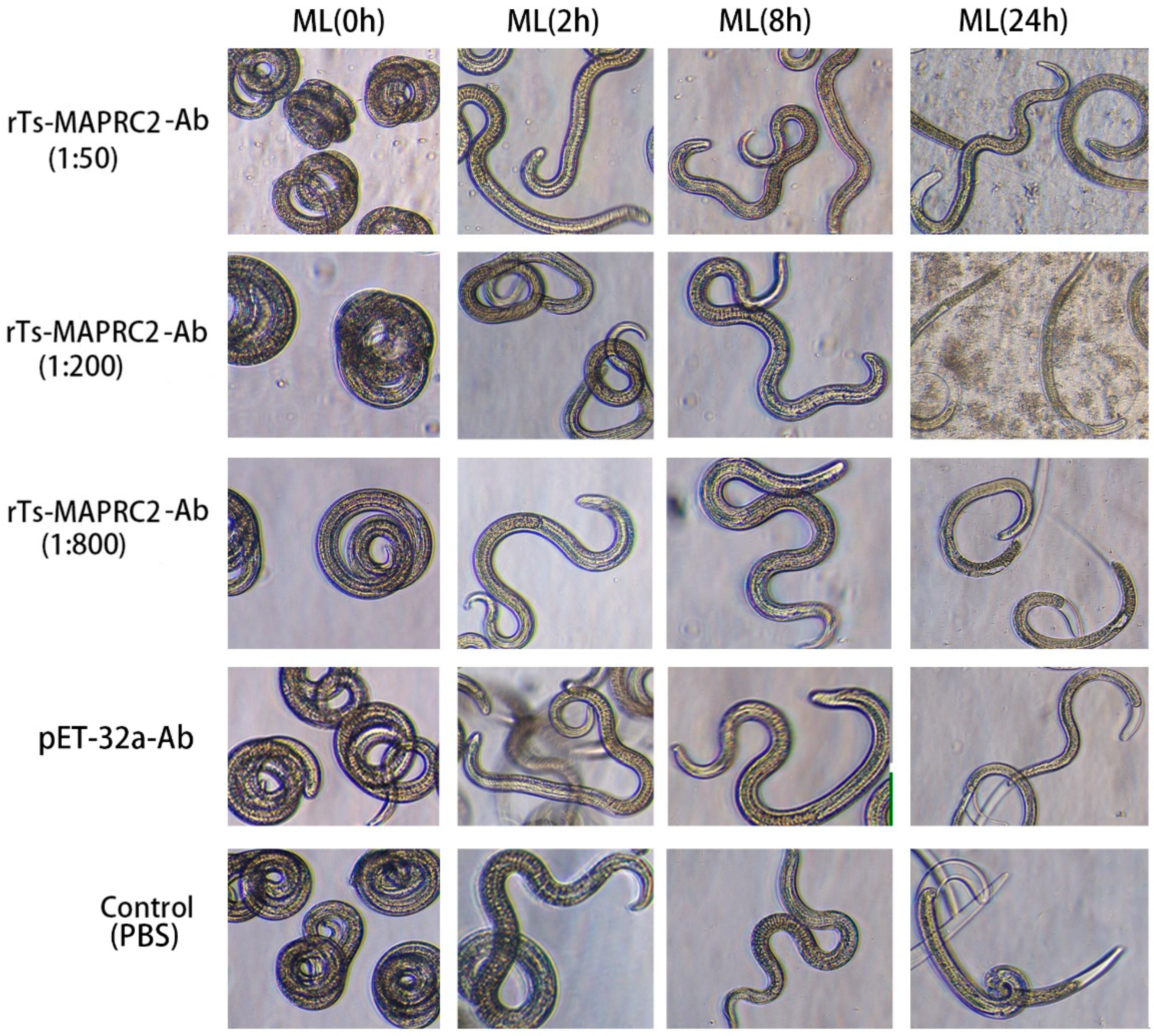
3.3. Assessing the infectivity of ML treated with rTs-MAPRC2-Ab in vivo
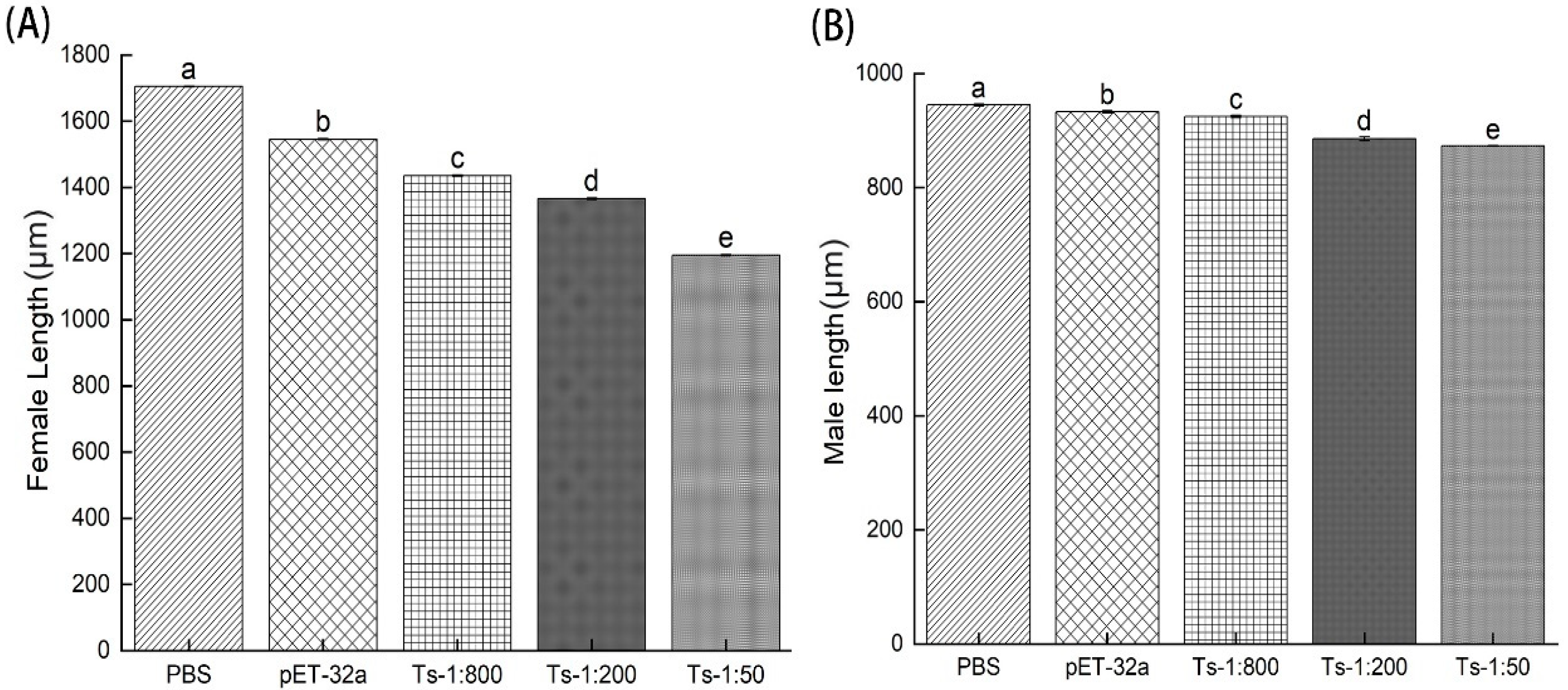
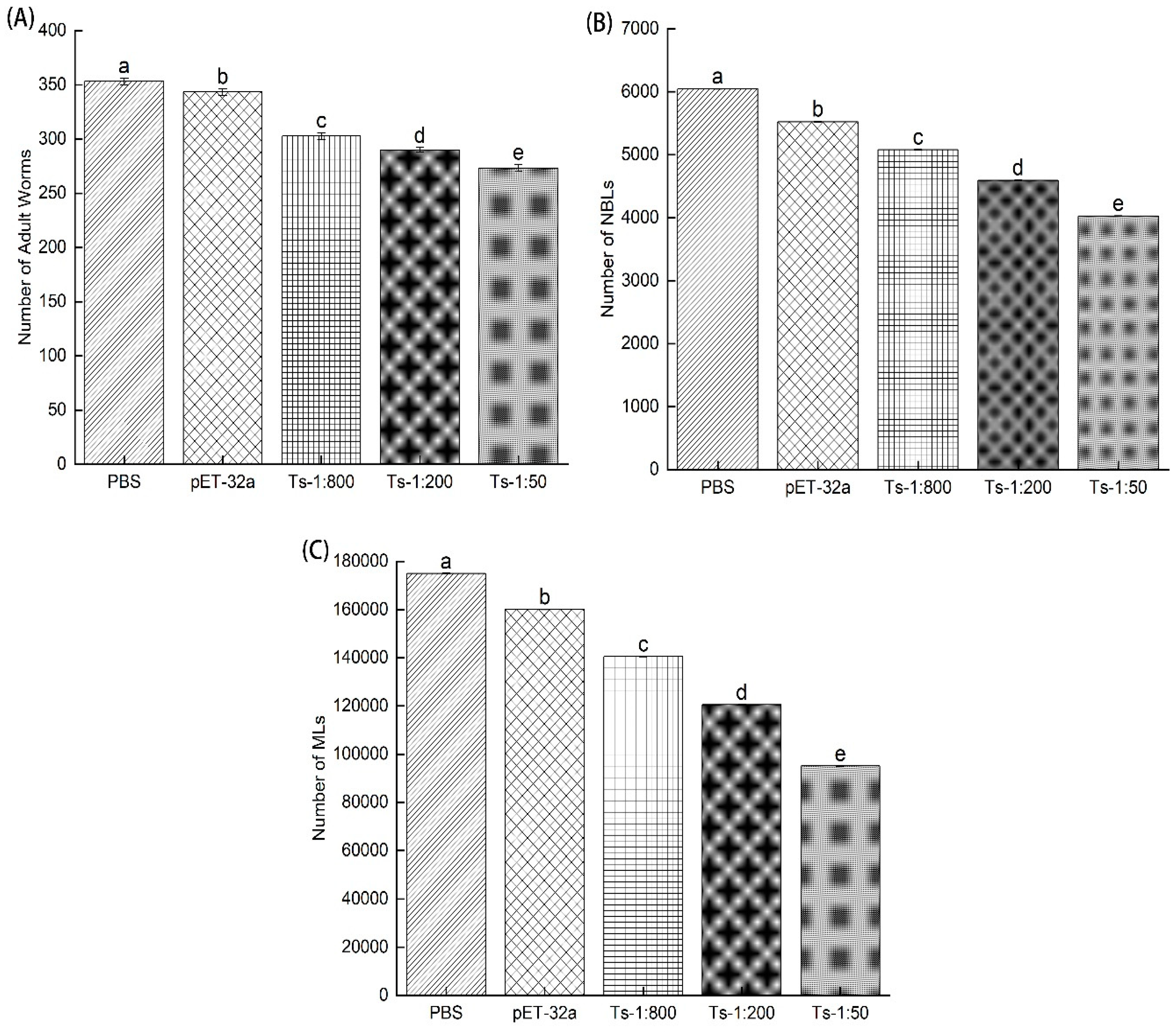
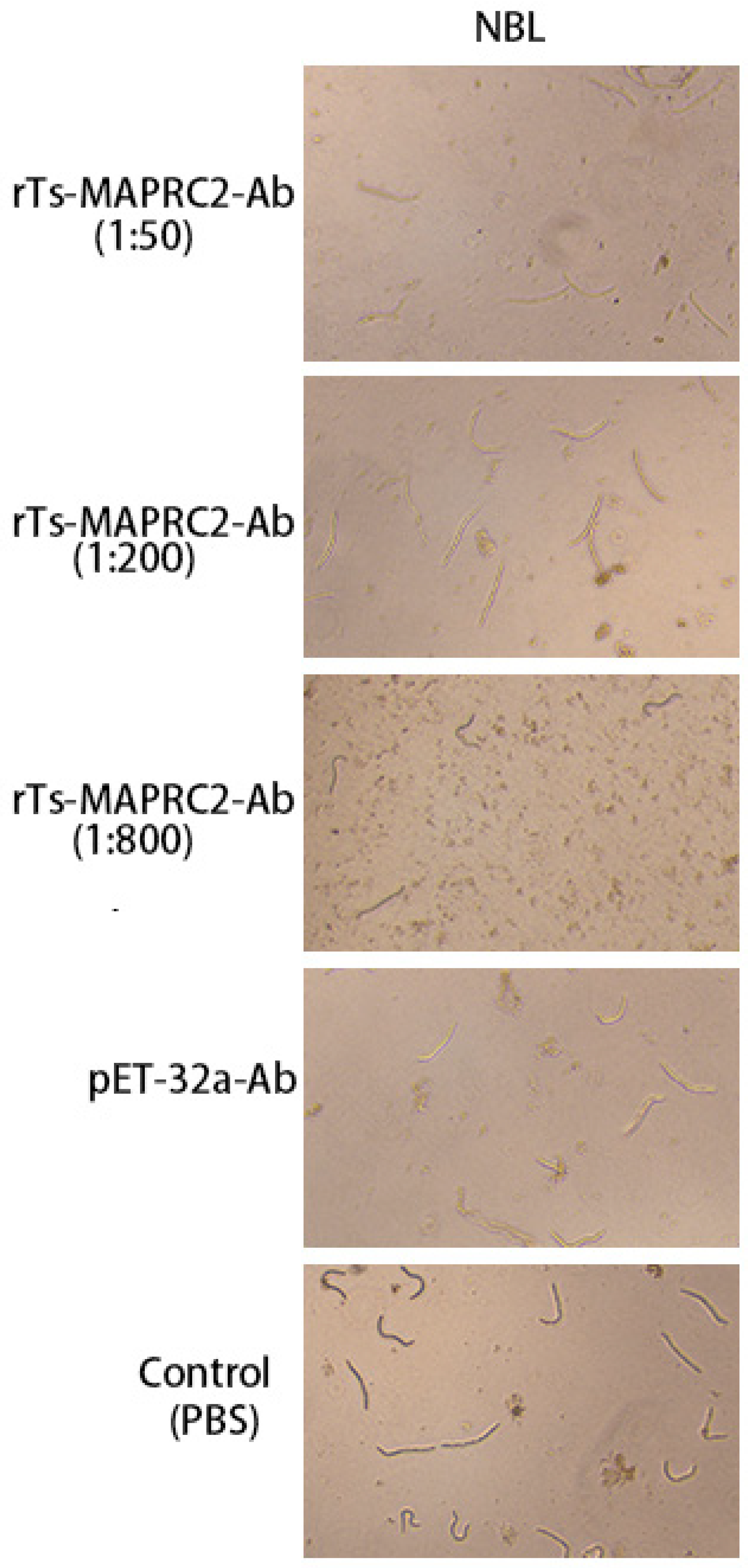
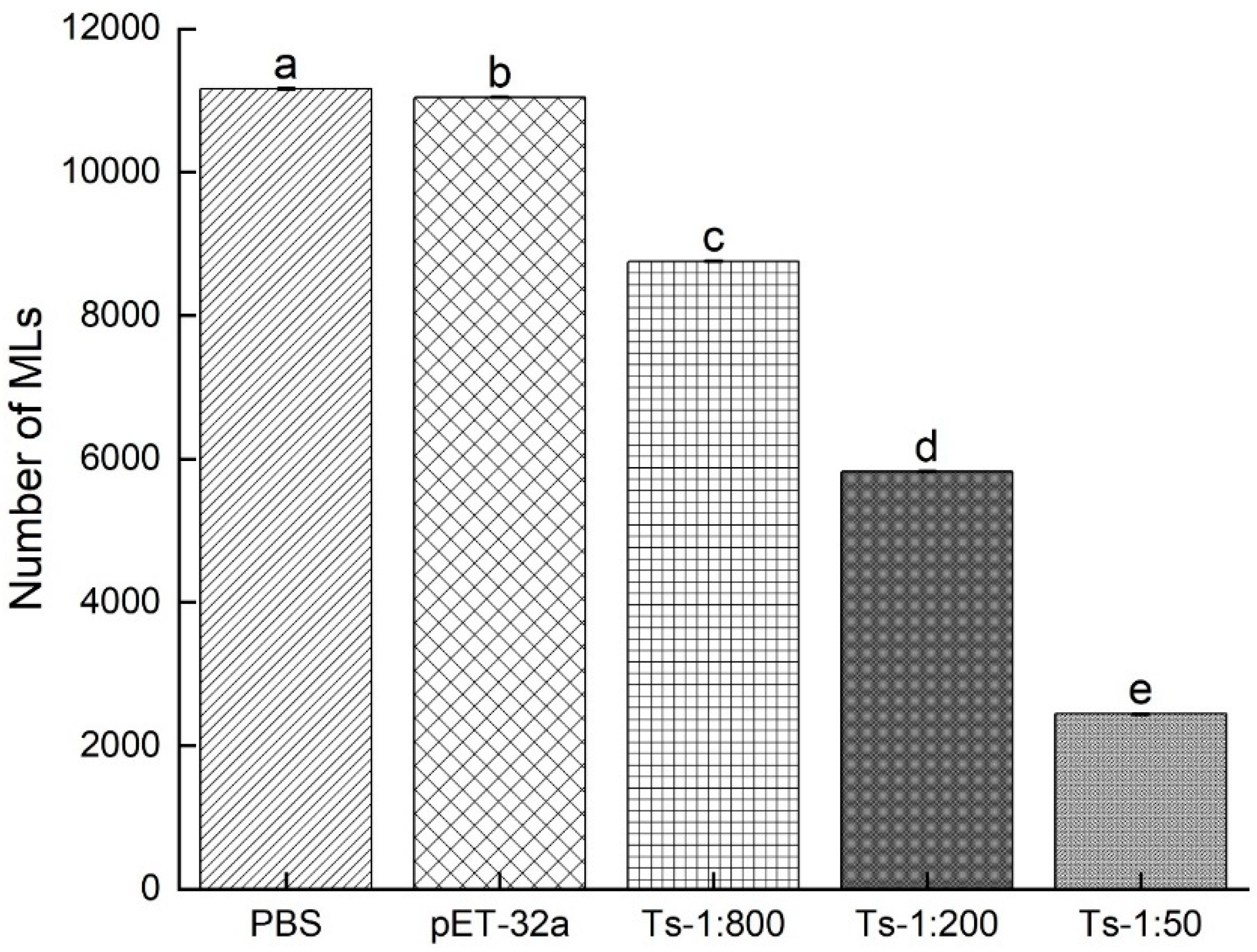
3.4. Infectivity of NBL treated with rTs-MAPRC2-Ab
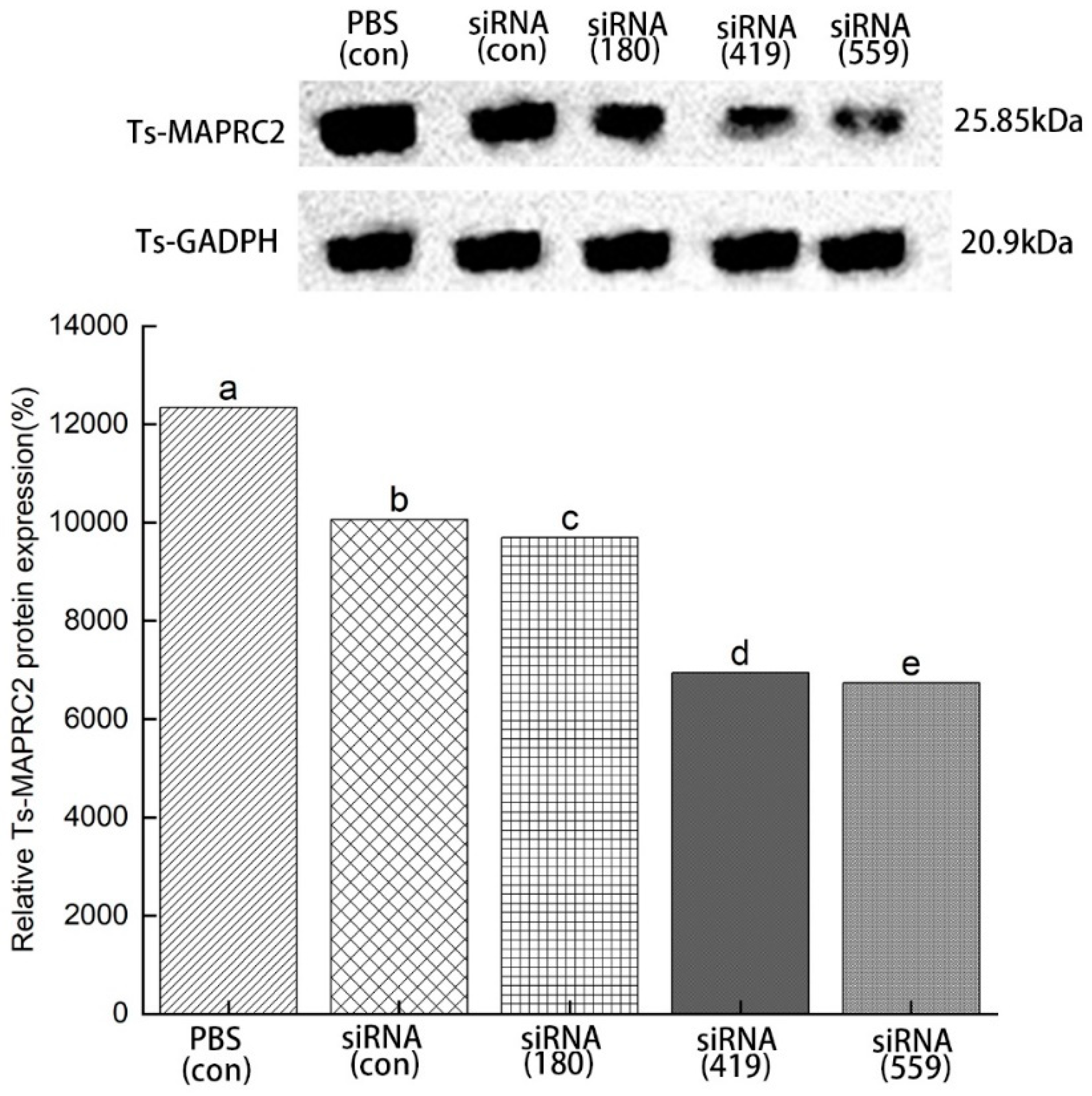
3.5. Specific siRNA-mediated suppression of Ts-MAPRC2 protein expression
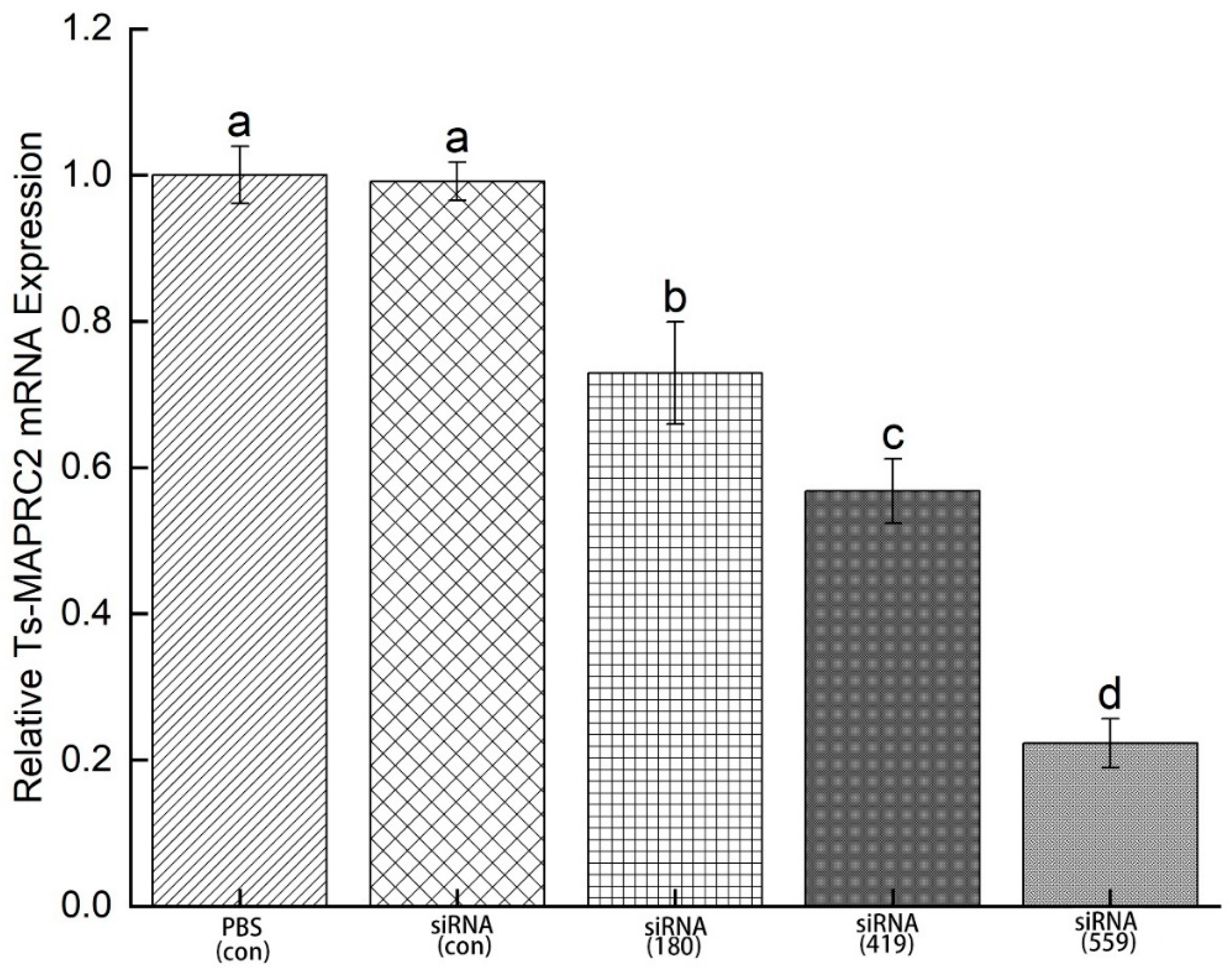
3.6. Specific siRNA-mediated suppression of Ts-MAPRC2 mRNA expression
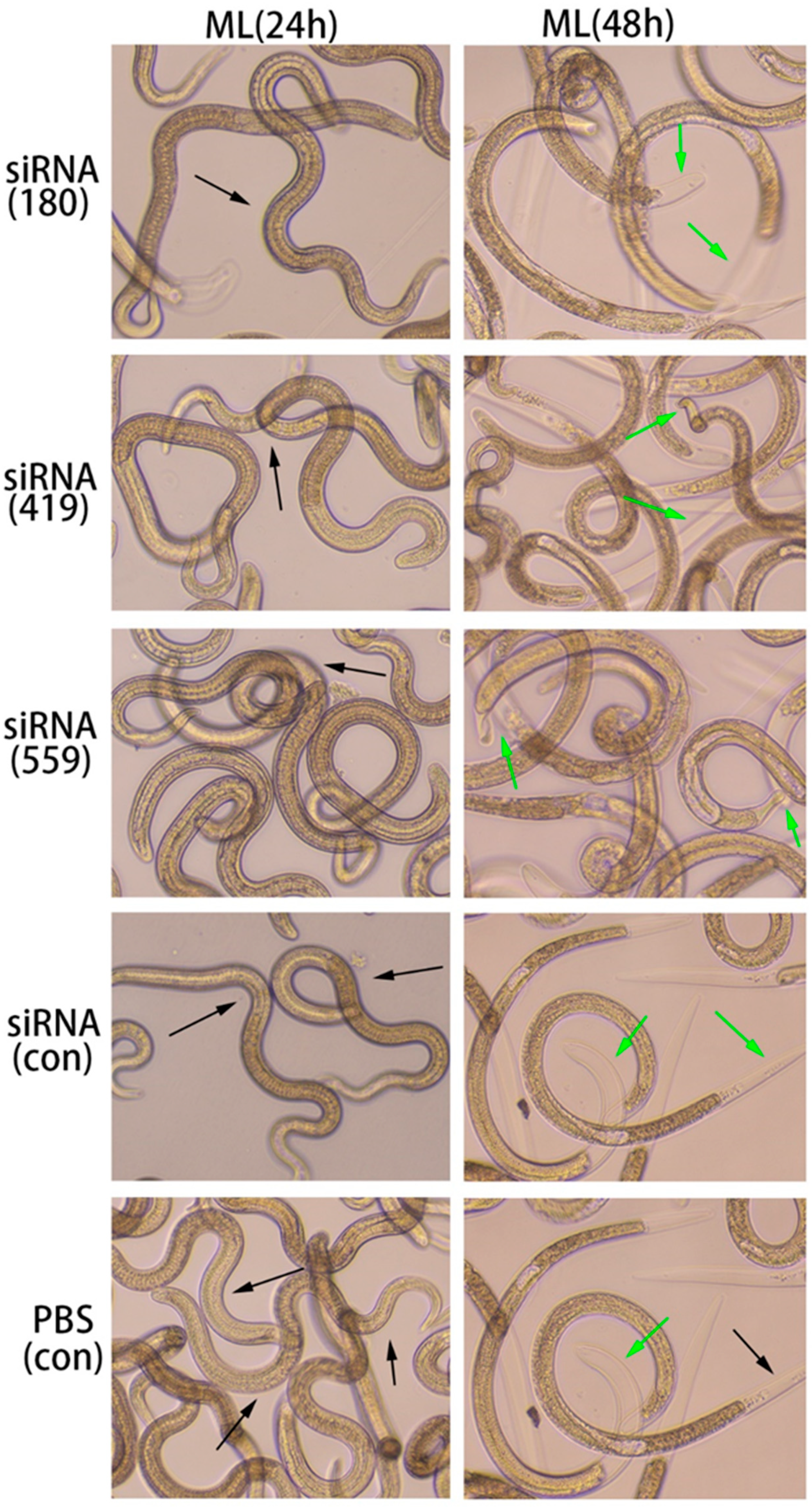
3.7. In vitro phenotyping of siRNA effects on ML
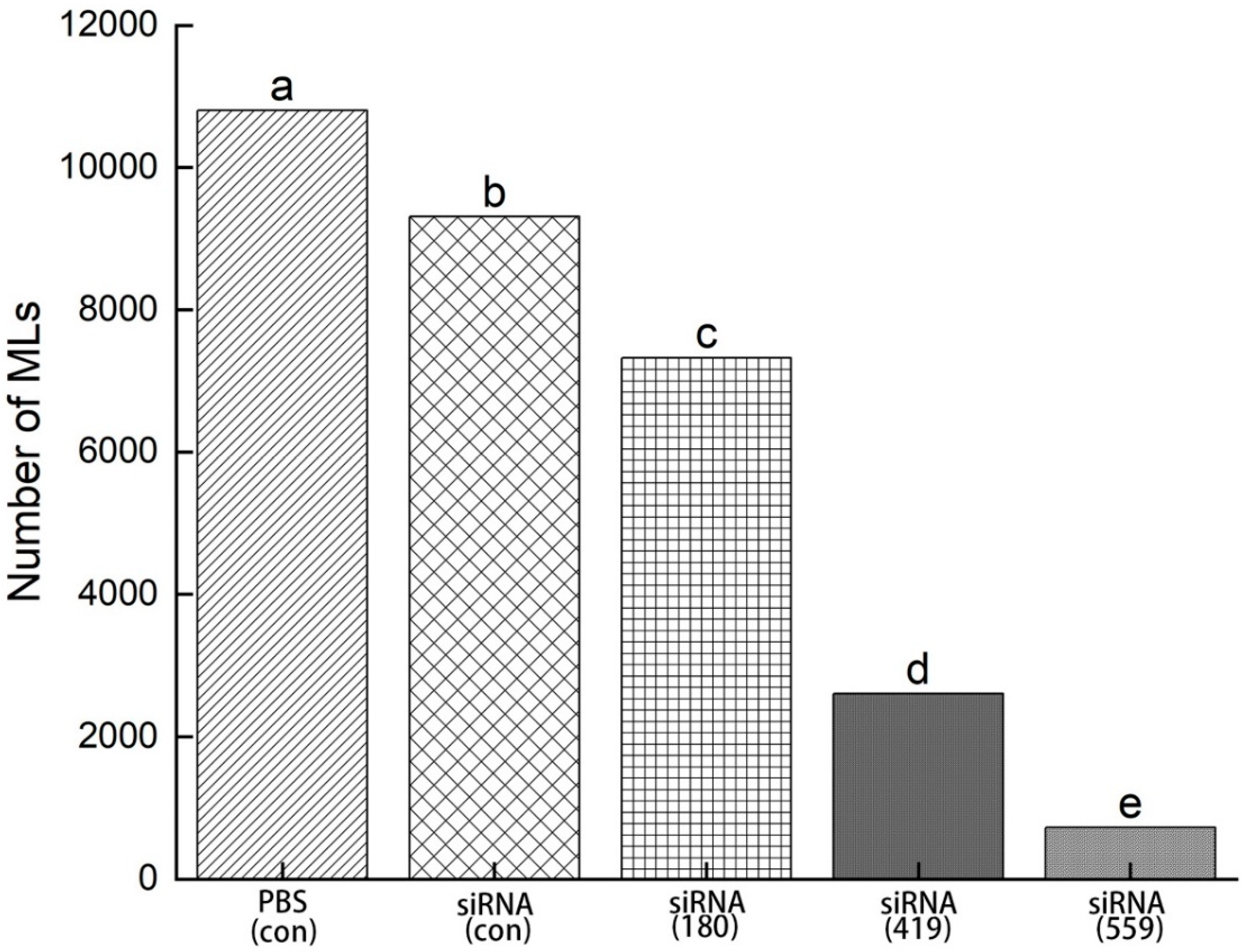
3.8. Evaluation of siRNA-treated NBL for infectivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, C.; Tong, M.; Zhang, P.; Cai, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, M. Molecular Characterization of Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase from Trichinella Spiralis and Its Potential in Inducing Immune Protection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. An Epidemiological Overview of Swine Trichinellosis in China. Vet. J. 2011, 190, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin Murrell, K.; Pozio, E. Worldwide Occurrence and Impact of Human Trichinellosis, 1986-2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2194–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.N. Food & Agriculture Organization; World Health Organization Multicriteria-Based Ranking for Risk Management of Foodborne Parasites [Preliminary Report]. 2012, 47.
- Cui, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, L.N.; Wang, Z.Q. Survey of Trichinella Infections in Domestic Pigs from Northern and Eastern Henan, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 194, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.A.; Han, L.H.; Yang, M.; Duan, J.Y.; Sun, G.G.; Qi, X.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; et al. Survey of Trichinella Infection from Domestic Pigs in the Historical Endemic Areas of Henan Province, Central China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4707–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, B.; Liu, M. Current Research of Trichinellosis in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, W.; Fu, B. Vaccines against Trichinella Spiralis: Progress, Challenges and Future Prospects. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Shi, H.; Tang, B.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Boireau, P.; Wang, F.; et al. Vaccination of Mice with an Antigenic Serine Protease-like Protein Elicits a Protective Immune Response against Trichinella Spiralis Infection. J. Parasitol. 2013, 99, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Huang, J.; Zhan, B.; Zhu, X. Vaccination with a Paramyosin-Based Multi-Epitope Vaccine Elicits Significant Protective Immunity against Trichinella Spiralis Infection in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Ren, H.N.; Sun, G.G.; Jiang, P.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. The Immune Protection Induced by a Serine Protease Inhibitor from the Foodborne Parasite Trichinella Spiralis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Pan, A.; Liao, W.; Zhou, X. A Novel Antigenic Cathepsin B Protease Induces Protective Immunity in Trichinella-Infected Mice. Vaccine 2018, 36, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.F.; Barbieri, R.L.; Gargiulo, A.R. Yen & Jaffe’s Reproductive Endocrinology: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management: Eighth Edition. Yen Jaffe’s Reprod. Endocrinol. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Clin. Manag. Eighth Ed. 2018, 1–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, M.P.; Giudizi, M.G.; Biagiotti, R.; Beloni, L.; Giannarini, L.; Sampognaro, S.; Parronchi, P.; Manetti, R.; Annunziato, F.; Livi, C. Progesterone Favors the Development of Human T Helper Cells Producing Th2-Type Cytokines and Promotes Both IL-4 Production and Membrane CD30 Expression in Established Th1 Cell Clones. J. Immunol. 1995, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaura, H.; Iwata, M. Direct and Indirect Inhibition of Th1 Development by Progesterone and Glucocorticoids. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzaldúa, S.R.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Cerbón, M.A. Histomorphological Changes in the Oviduct Epithelium of the Rabbit during Early Pregnancy. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2002, 31, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, G.G.; Gentile, T.; Costantino, S.N.; Sarchi, M.I.; Venturiello, S.M. In Vitro and in Vivo Effects of Progesterone on Trichinella Spiralis Newborn Larvae. Parasitology 2005, 131, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaka, L.; Chitanga, S.; Masola, B.; Mukaratirwa, S. Host Pregnancy Influences the Establishment of Trichinella Zimbabwensis in Balb C Mice. J. Parasit. Dis. 2017, 41, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Jia, L. The Unique Pharmacological Characteristics of Mifepristone (RU486): From Terminating Pregnancy to Preventing Cancer Metastasis. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 979–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-díaz, H.; Nava-castro, K.E.; Escobedo, G.; Domínguez-ramírez, L.; García-varela, M.; Río-araiza, V.H.; Palacios-arreola, M.I.; Morales-montor, J. A Novel Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component ( PGRMC ) in the Human and Swine Parasite Taenia Solium : Implications to the Host-Parasite Relationship. 2019. [CrossRef]
- MT, A.; J, S.; Z, Y.; Z, W.; Y, Z.; M, L.; SA, L.; M, H.; H, A.; MW, H.; et al. Characterization of Membrane-Associated Progesterone Receptor Component-2 (MAPRC2) from Trichinella Spiralis and Its Interaction with Progesterone and Mifepristone. Vaccines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, M.T.; Khan, A.; Wen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, K.; Shaukat, A.; Chen, C.; Rehman, T.U.; Lu, M.; Xu, L.; et al. Molecular Docking and in Silico Simulation of Trichinella Spiralis Membrane-Associated Progesterone Receptor Component 2 (Ts-MAPRC2) and Its Interaction with Human PGRMC1. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, M.T.; Yan, R.; Khan, A.; Asrar, R.; Shakoor, A.; Asif, A.; Wen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Malik, M.A.; Tauseef-ur-Rehman; et al. Advances in the Development of Anti- Trichinella Spiralis Vaccine, Challenges, and Future Prospective. Parasit. Helminths Zoonoses - From Basic to Appl. Res. [Working Title] 2022. [CrossRef]
- Britton, C.; Laing, R.; Devaney, E. Small RNAs in Parasitic Nematodes – Forms and Functions. Parasitology 2020, 147, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.Q.; Zeng, J.; Sun, X.Y.; Yue, X.; Hu, C.X.; Jiang, P.; Liu, R.D.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Trichinella Spiralis: RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Serine Protease Results in Reduction of Intrusion, Development and Fecundity. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 37, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, C.; Winter, A.D.; Marks, N.D.; Gu, H.; McNeilly, T.N.; Gillan, V.; Devaney, E. Application of Small RNA Technology for Improved Control of Parasitic Helminths. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, T.X.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.Y.; Yan, S.W.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Characterization of a Novel Glutamine Synthetase From Trichinella Spiralis and Its Participation in Larval Acid Resistance, Molting, and Development. Front. cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapp, N.; Whyte, P.; Tang, J.; Jackson, E.; Brahmi, D. A Review of Evidence for Safe Abortion Care. Contraception 2013, 88, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YR, Y.; YF, Q. Progress in Treatment and Prevention of Trichinellosis. J. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cui, J.; Hu, D.D.; Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q. Identification of Early Diagnostic Antigens from Major Excretory-Secretory Proteins of Trichinella Spiralis Muscle Larvae Using Immunoproteomics. Parasites and Vectors 2014, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lacour, S.A.; Lainé-Prade, V.; Versillé, N.; Grasset-Chevillot, A.; Feng, S.; Liu, M.Y.; Boireau, P.; Vallée, I. Trichinella Spiralis Newborn Larvae: Characterization of a Stage Specific Serine Proteinase Expression, NBL1, Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Parasitology 2015, 142, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Aleem, M.T.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X. Recombinant Toxoplasma Gondii Ribosomal Protein P2 Modulates the Functions of Murine Macrophages In Vitro and Provides Immunity against Acute Toxoplasmosis In Vivo. Vaccines 2021, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Ren, H.N.; Song, Y.Y.; Sun, G.G.; Liu, R.D.; Jiang, P.; Long, S.R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Experimental Parasitology Characterization of a Putative Glutathione S-Transferase of the Parasitic Nematode Trichinella Spiralis. Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 187, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Naqvi, M.A.U.H.; Naqvi, S.Z.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X.; Yan, R. Trichinella Spiralis: Knockdown of Gamma Interferon Inducible Lysosomal Thiol Reductase (Gilt) Results in the Reduction of Worm Burden. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshimura, J.; Morishita, S.; Ui-Tei, K. SiDirect 2.0: Updated Software for Designing Functional siRNA with Reduced Seed-Dependent off-Target Effect. BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, N.; Yu, P.; Wu, L.; Liu, Z.; Guan, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Lu, Y. RNAi-Mediated Silencing of Trichinella Spiralis Serpin-Type Serine Protease Inhibitors Results in a Reduction in Larval Infectivity. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimulajiang, K.; Cao, M.; Liao, S.; Naqvi, M.A.-H.; Tian, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, M.; Lakho, S.A.; Li, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Development and Potential Application of Ras Domain Containing Protein from Haemonchus Contortus for Diagnosis of Goat Infection. Anim. 2020, Vol. 10, Page 138 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.D.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, L.; Long, S.R.; Ren, H.J.; Cui, J. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes of Trichinella Spiralis Larvae Activated by Bile and Cultured with Intestinal Epithelial Cells Using Real-Time PCR. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 4113–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Jin, Y.M.; Liu, P.P.; Wu, Q.J.; Liu, J.M.; Lin, J.J. RNAi Silencing of Calcium-Regulated Heat-Stable Protein of 24 kDa in Schistosoma Japonicum Affects Parasite Growth. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, M.A. Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1: An Integrative Review. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 105, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lösel, R.M.; Besong, D.; Peluso, J.J.; Wehling, M. Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component 1--Many Tasks for a Versatile Protein. Steroids 2008, 73, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenstein, E.; Meyer, C.; Eisen, C.; Scriba, P.C.; Wehling, M. Full-Length cDNA Sequence of a Progesterone Membrane-Binding Protein from Porcine Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 229, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, J.J. Multiplicity of Progesterone’s Actions and Receptors in the Mammalian Ovary. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 75, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.X.; Jiang, P.; Yue, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, X.Z.; Song, Y.Y.; Liu, R.D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Cui, J. Molecular Characterization of a Trichinella Spiralis Elastase-1 and Its Potential as a Diagnostic Antigen for Trichinellosis. Parasites and Vectors 2020, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardo, L.F.; McVay, C.S.; Appleton, J.A. Molting, Ecdysis, and Reproduction of Trichinella Spiralis Are Supported in Vitro by Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Han, Y.; Yue, X.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.Y.; Yan, S.W.; Lei, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Z.Q. Vaccination of Mice with a Recombinant Novel Cathepsin B Inhibits Trichinella Spiralis Development, Reduces the Fecundity and Worm Burden. Parasites and Vectors 2019, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





