Submitted:
20 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
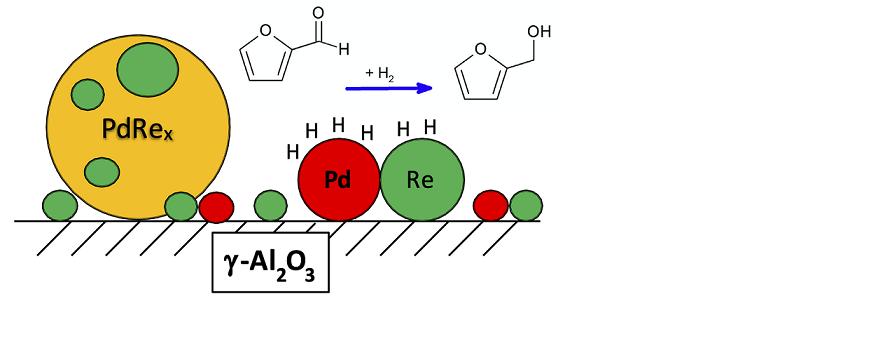
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
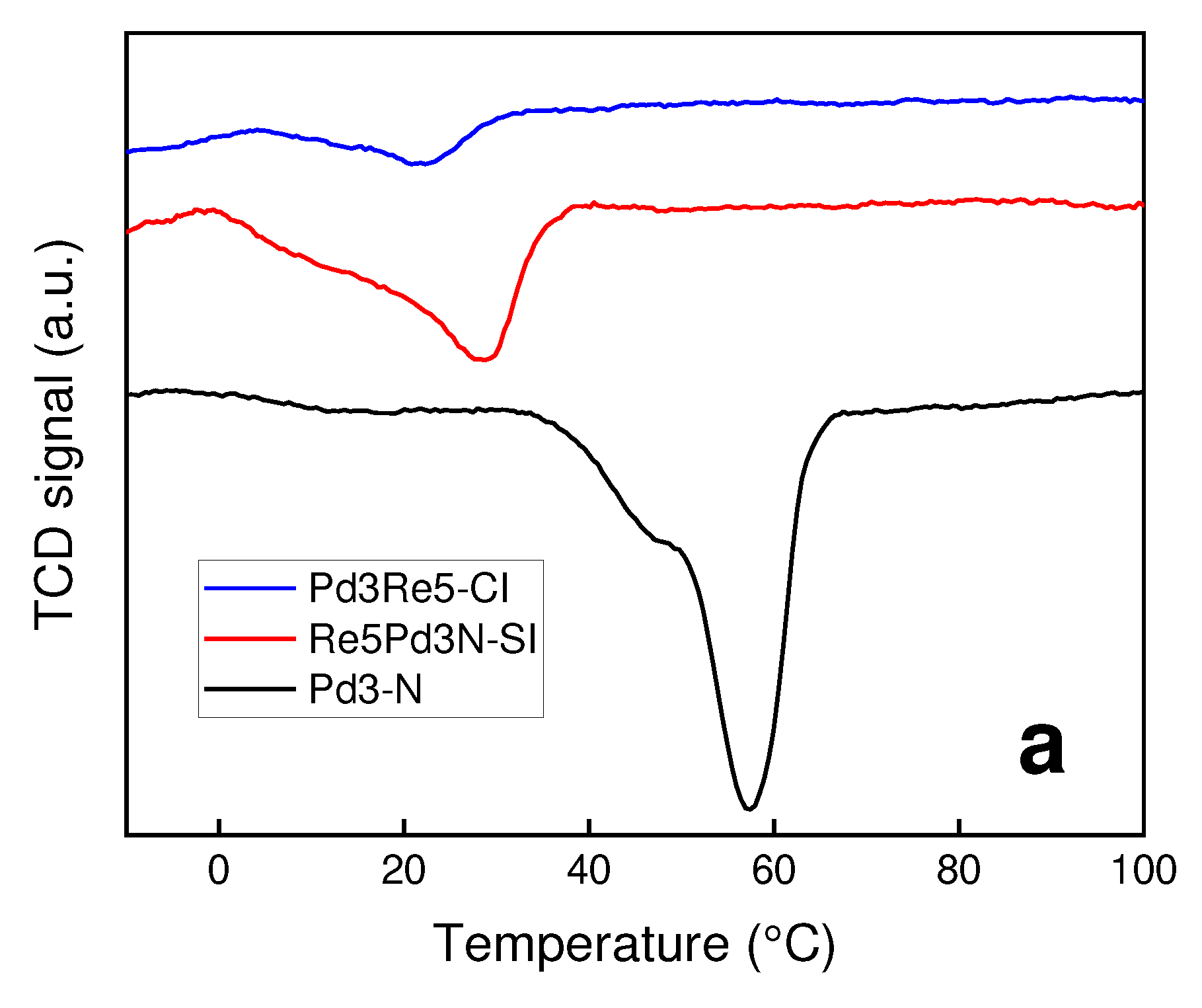
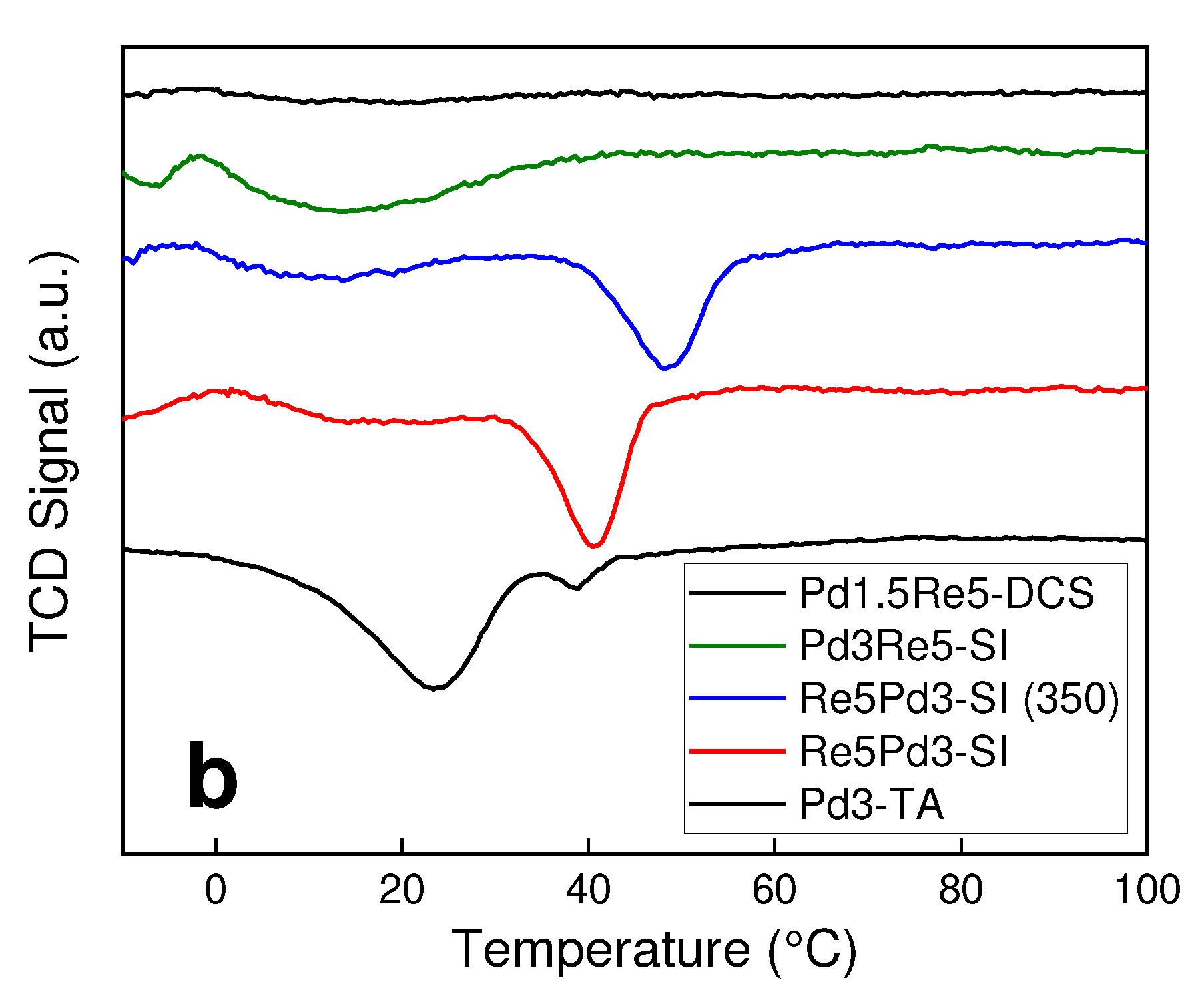
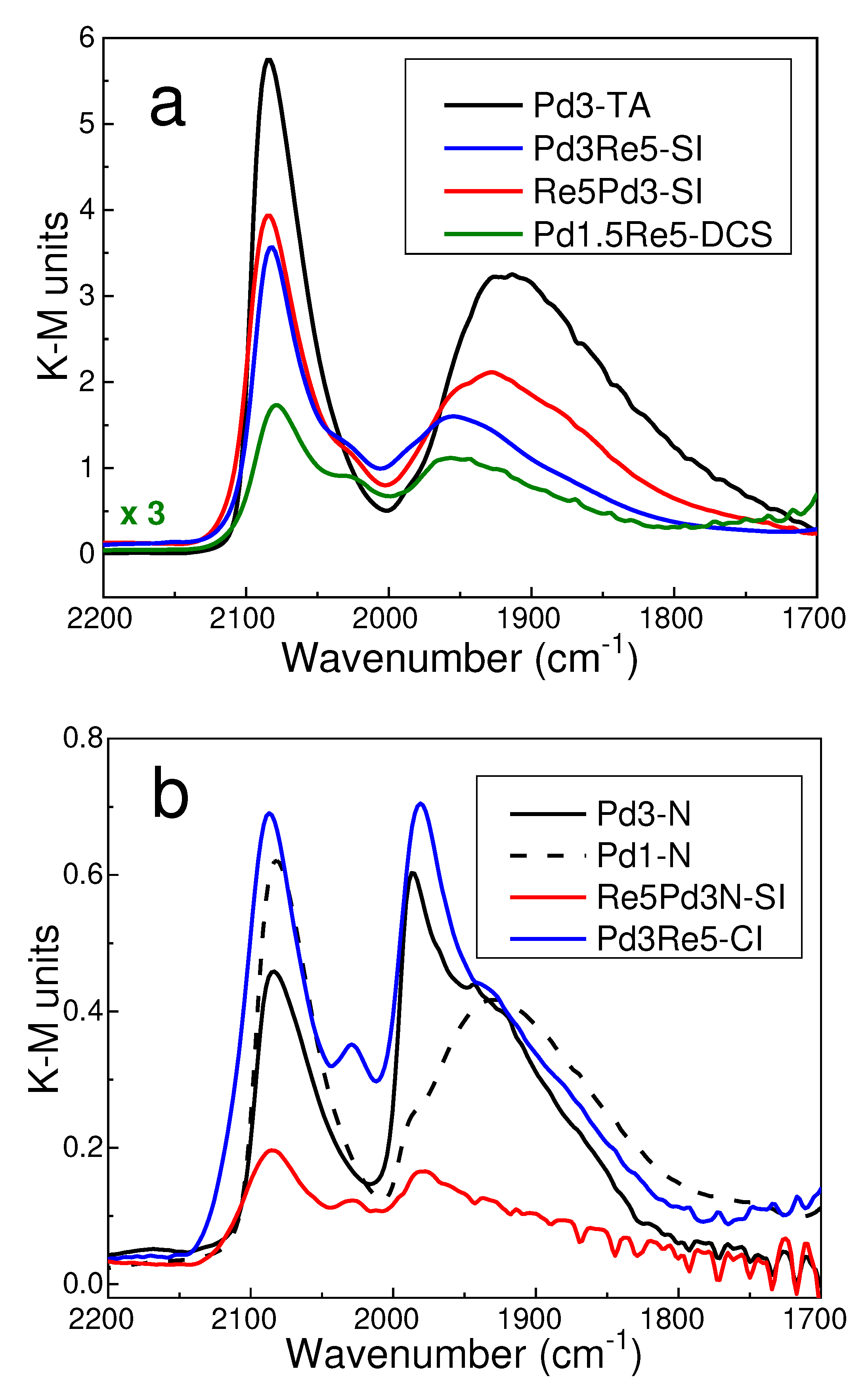
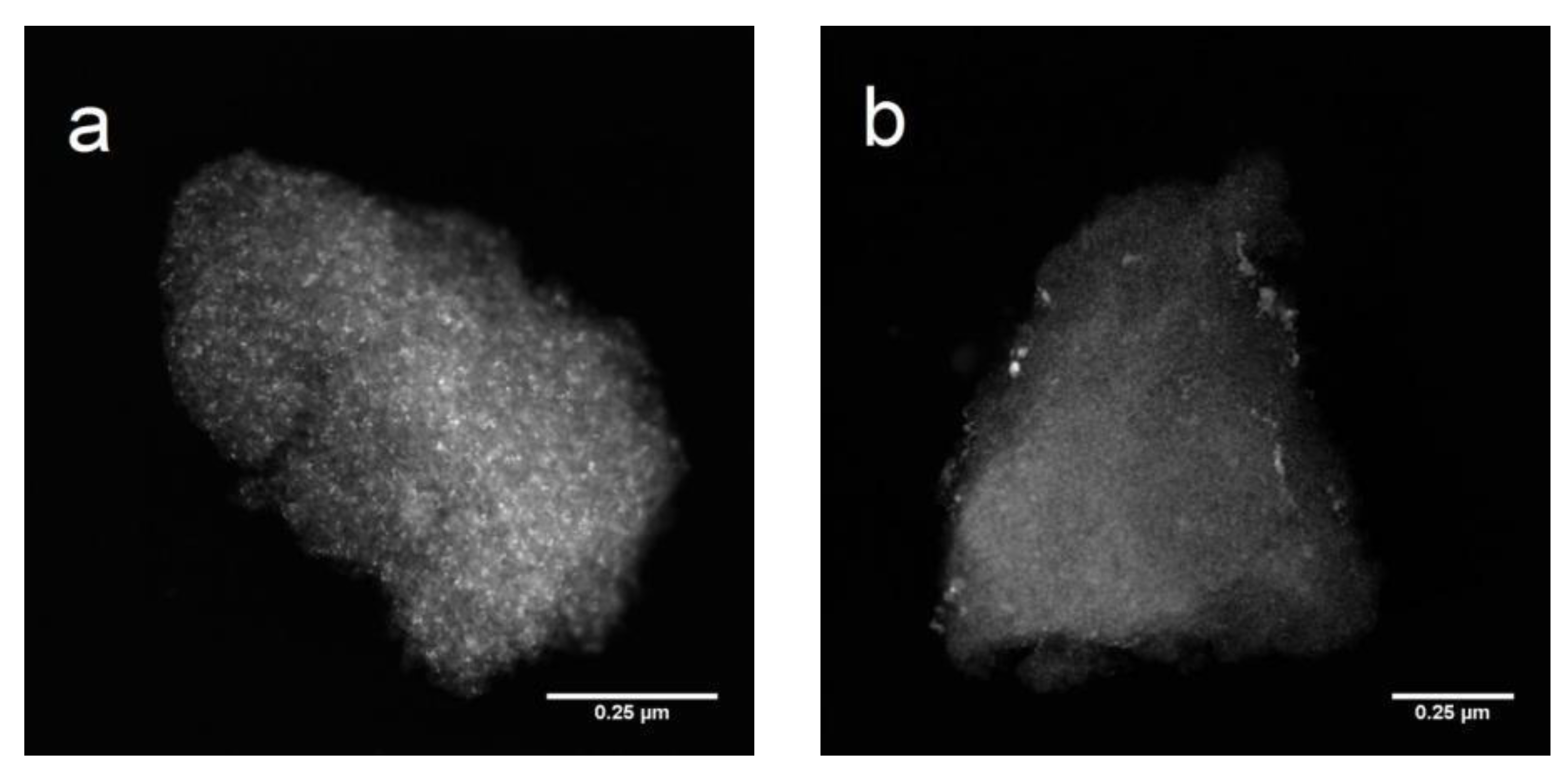
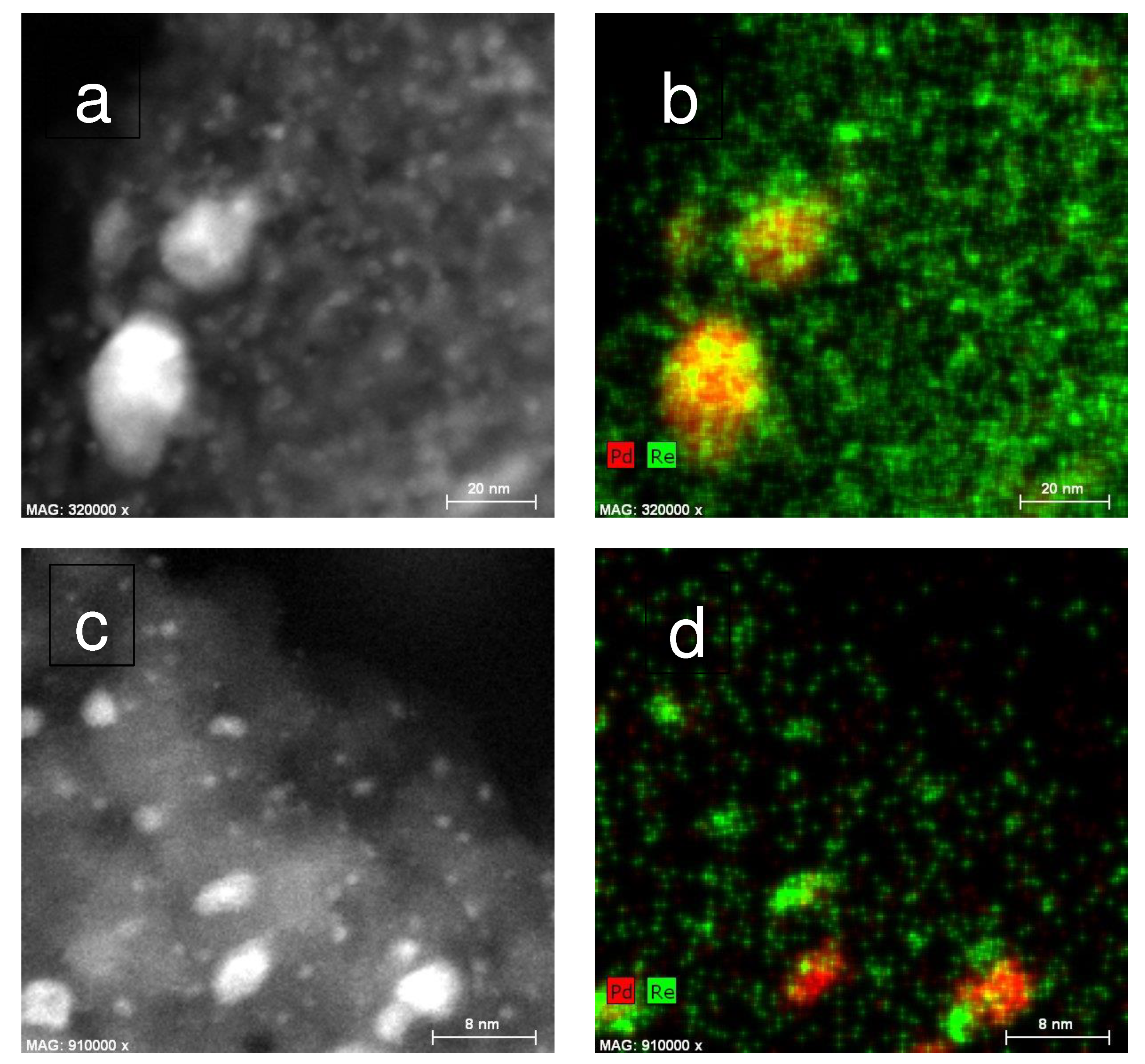
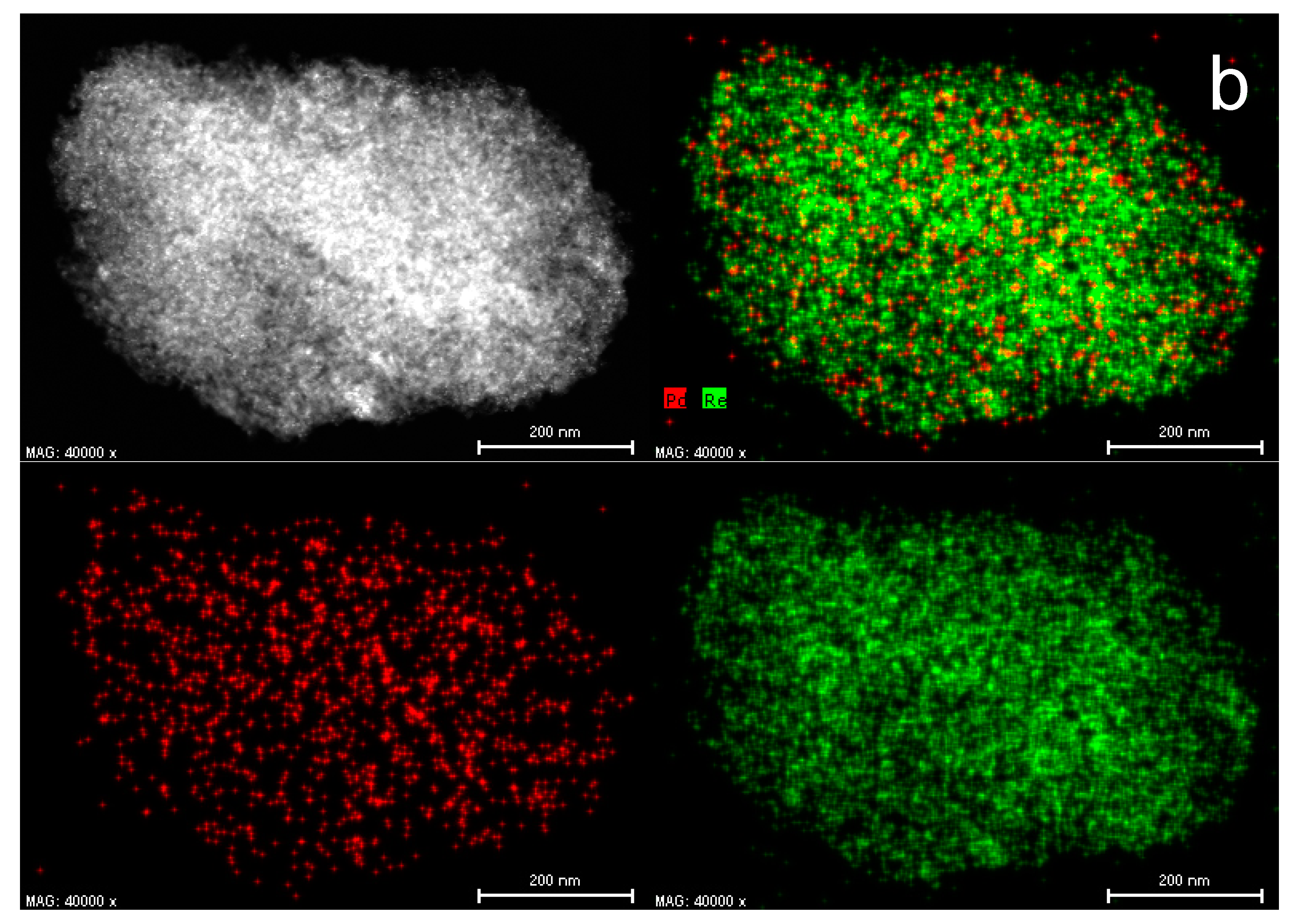
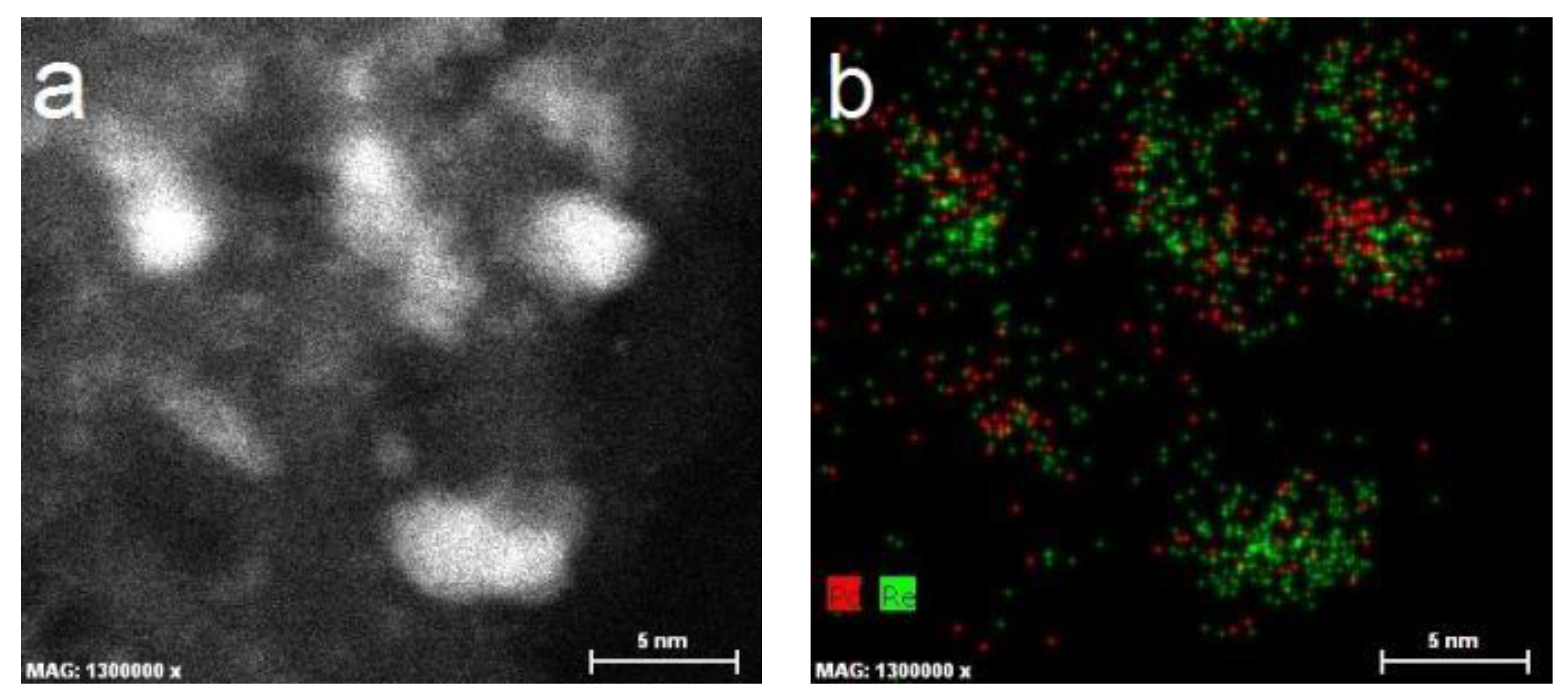
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
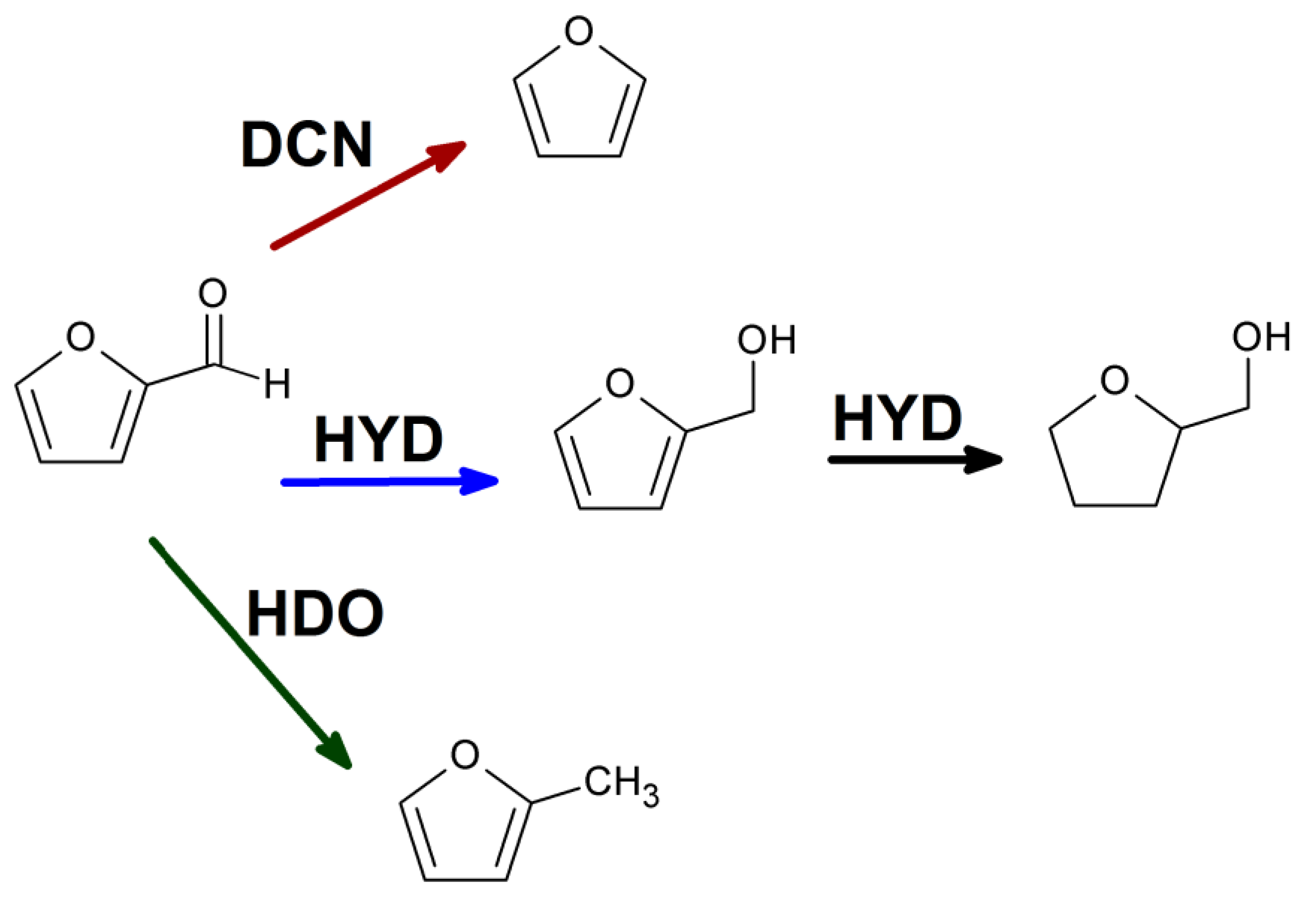
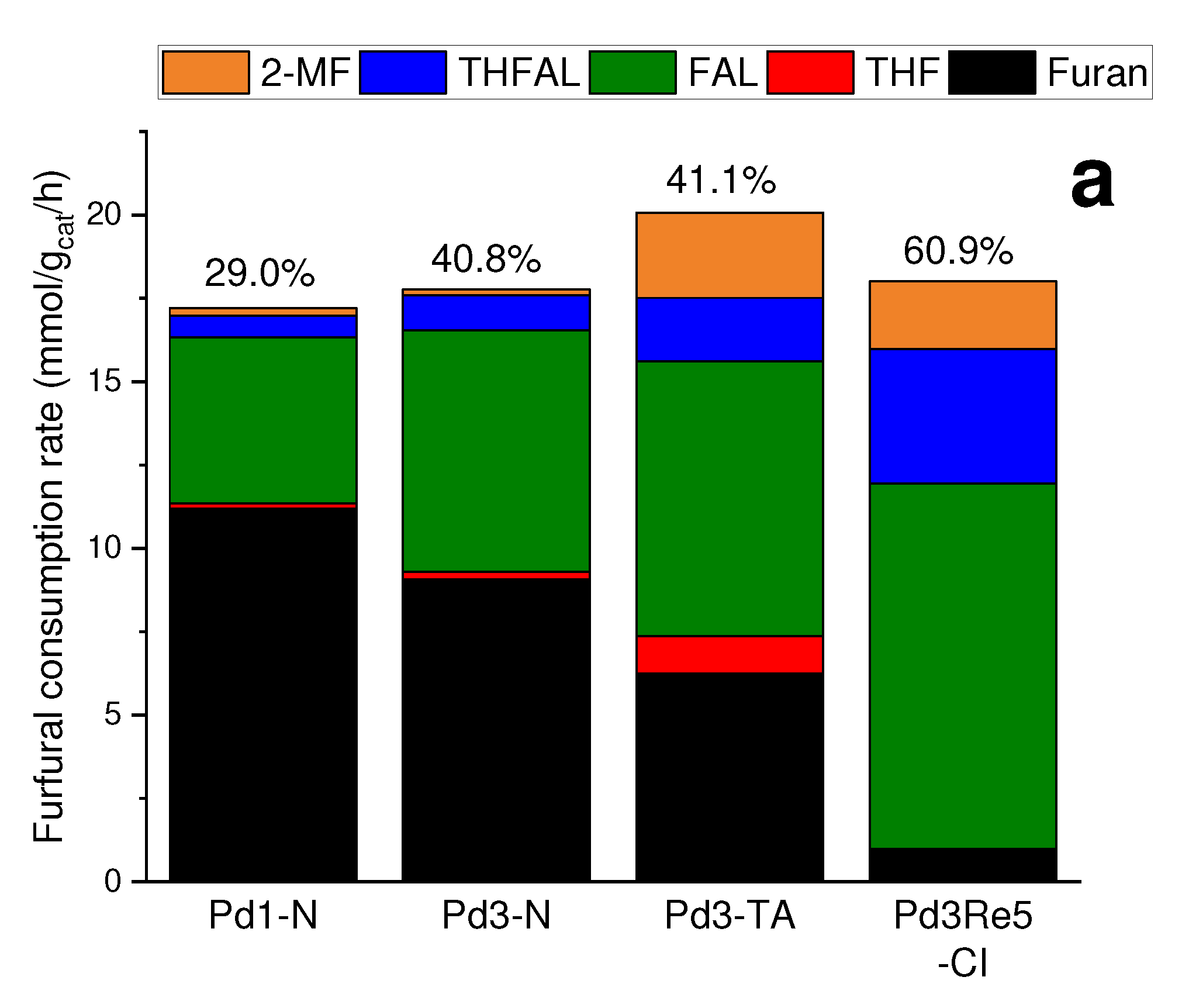
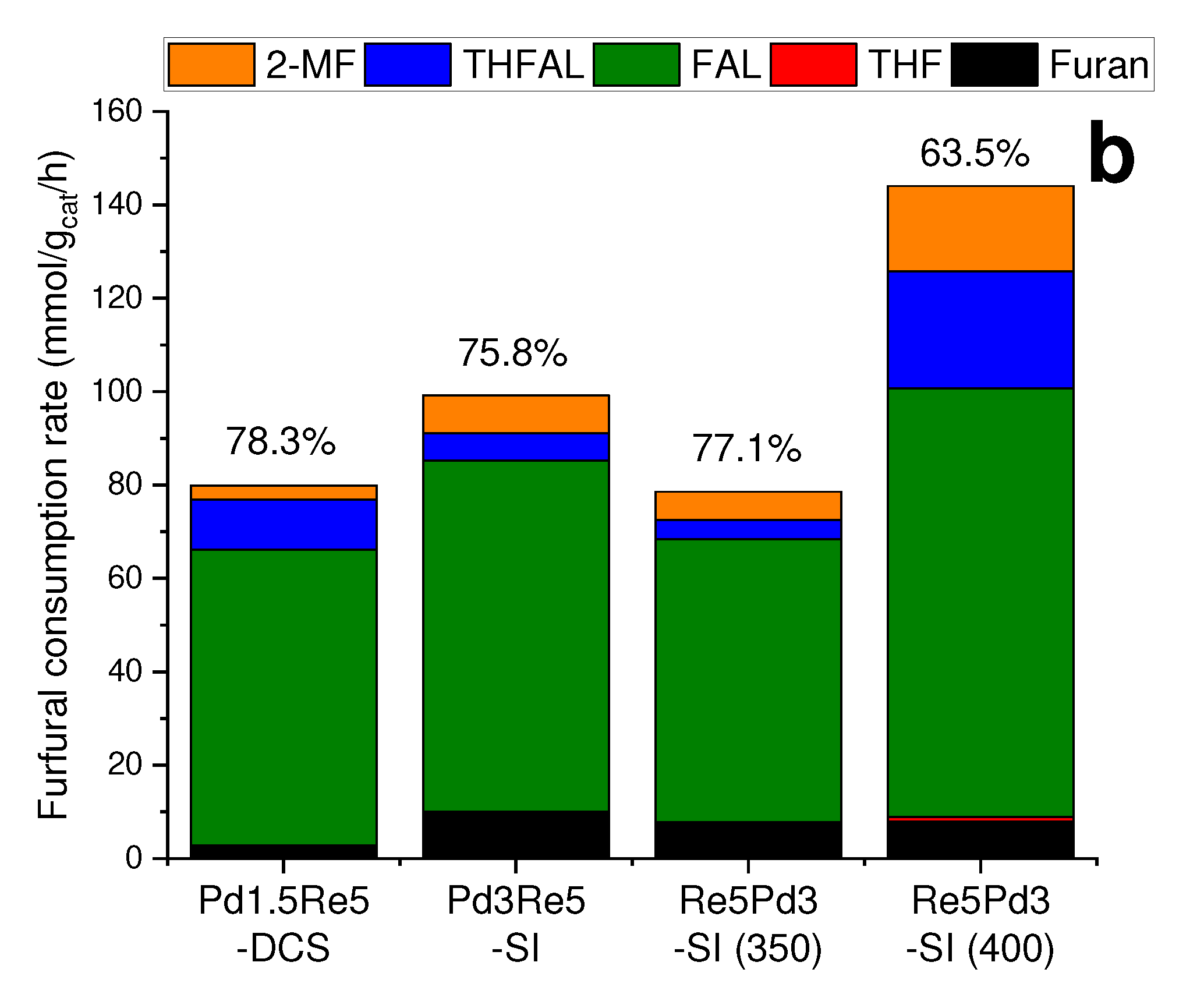
2.2. Furfural hydrogenation catalysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
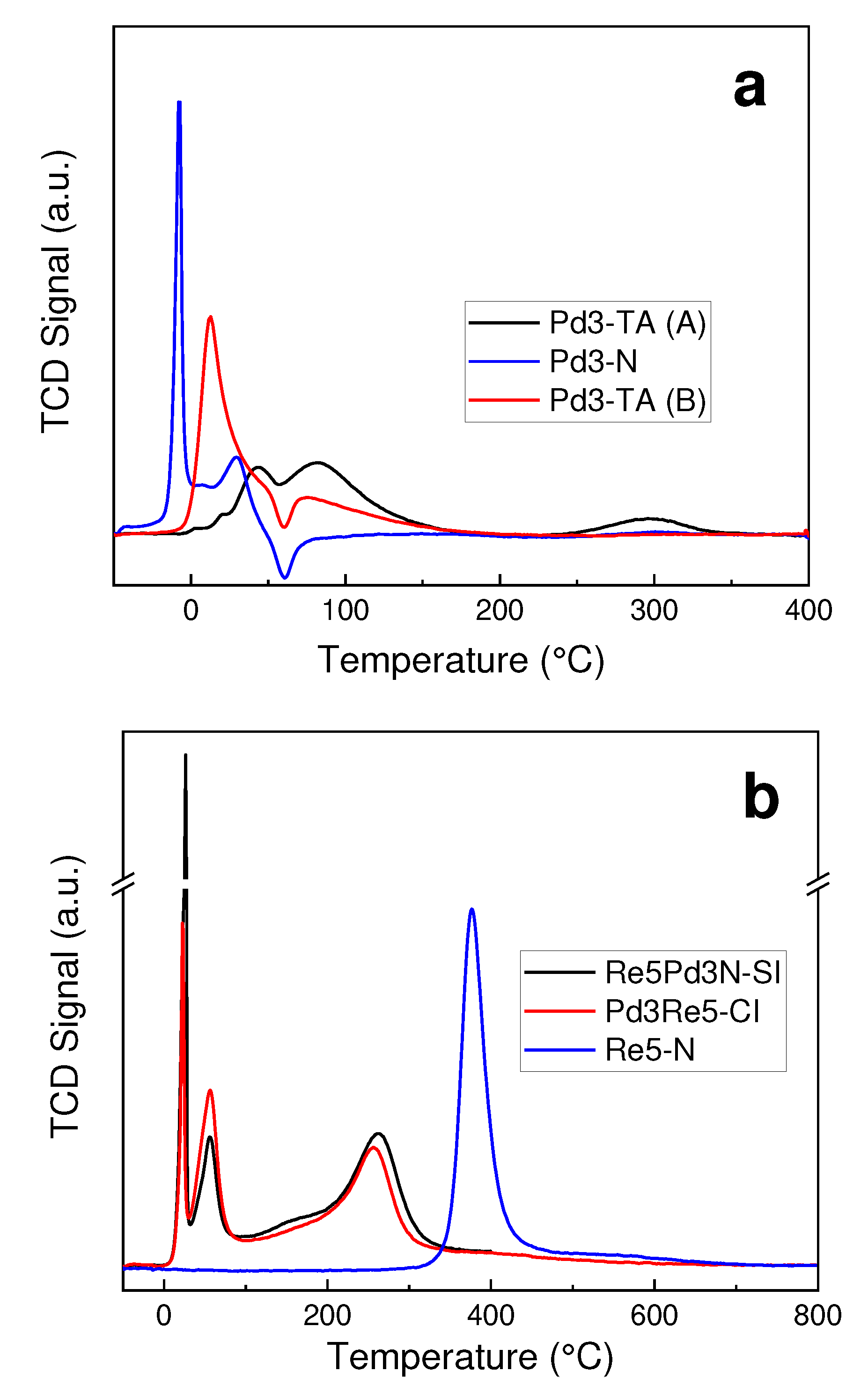
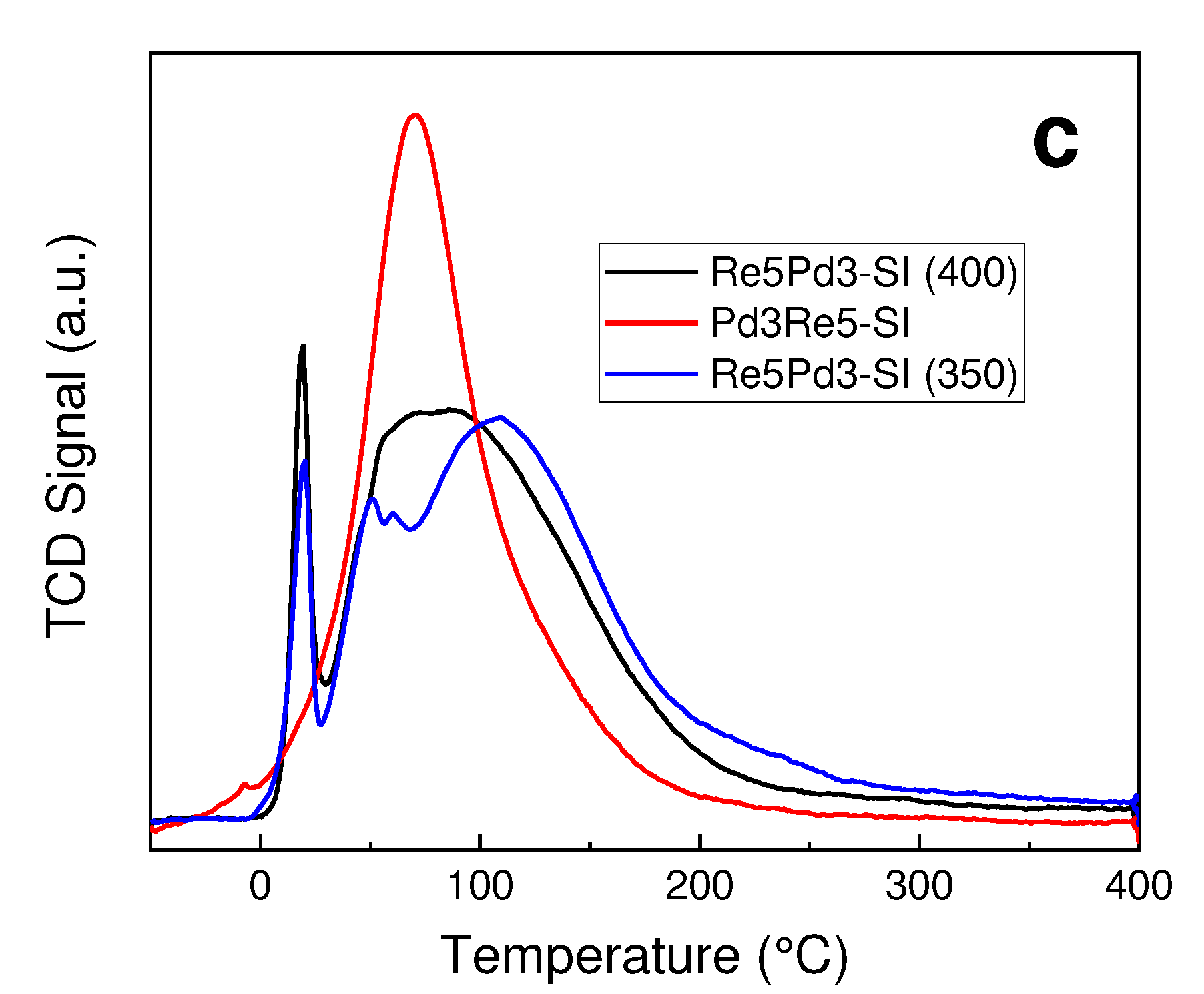
3.2. TPR and TPHD
3.3. CO and H2 Chemisorption
3.4. CO DRIFTS
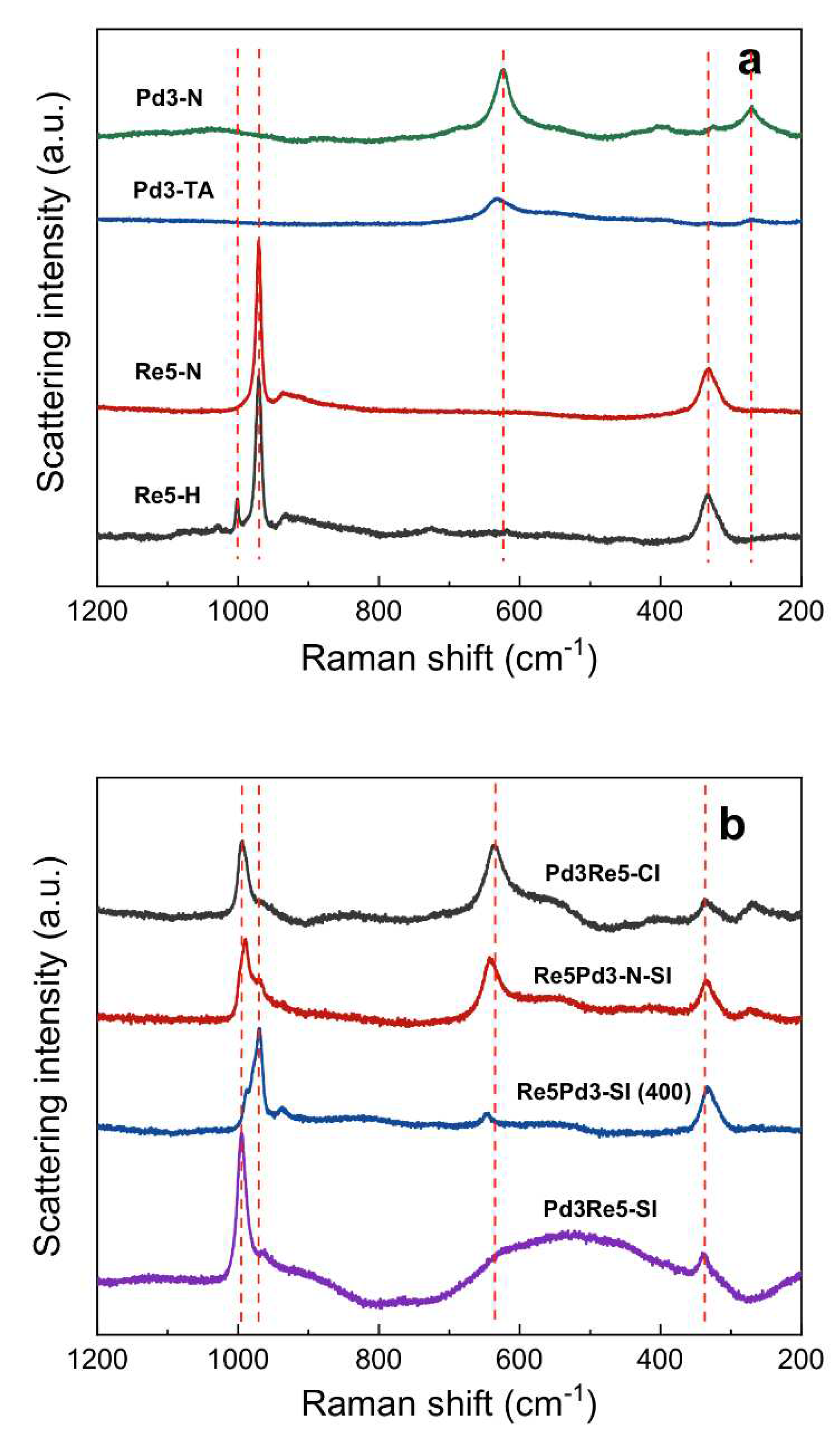
3.5. Raman Spectroscopy
3.6. HAADF-STEM-EDX
3.7. Furfural hydrogenation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- K.Y. Chen, S. Koso, T. Kubota, Y. Nakagawa, K. Tomishige, Chemoselective hydrogenolysis of tetrahydropyran-2-methanol to 1, 6-hexanediol over rhenium-modified carbon-supported rhodium catalysts. Chemcatchem, 2 (2010) 547-555. [CrossRef]
- S. Koso, Y. Nakagawa, K. Tomishige, Mechanism of the hydrogenolysis of ethers over silica-supported rhodium catalyst modified with rhenium oxide. J. Catal., 280 (2011) 221-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2011.03.018. [CrossRef]
- M. Chia, Y.J. Pagan-Torres, D. Hibbitts, Q.H. Tan, H.N. Pham, A.K. Datye, M. Neurock, R.J. Davis, J.A. Dumesic, Selective hydrogenolysis of polyols and cyclic ethers over bifunctional surface sites on rhodium–rhenium catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 133 (2011) 12675-12689. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2038358. [CrossRef]
- S. Koso, I. Furikado, A. Shimao, T. Miyazawa, K. Kunimori, K. Tomishige, Chem. Comm., (2009) 2035-2037.
- L. Ma, D.H. He, Z.P. Li, Promoting effect of rhenium on catalytic performance of Ru catalysts in hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediol. Catal. Comm., 9 (2008) 2489-2495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2008.07.009. [CrossRef]
- L. Ma, D.H. He, Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols over highly active Ru–Re bimetallic catalysts. Top. Catal., 52 (2009) 834-844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9231-3. [CrossRef]
- Y. Takeda, Y. Nakagawa, K. Tomishige, Catal. Sci. Tech., 2 (2012) 2221-2223.
- Shimao, S. Koso, N. Ueda, Y. Shinmi, I. Furikado, K. Tomishige, Promoting Effect of Re Addition to Rh/SiO2 on Glycerol Hydrogenolysis. Chem. Lett., 38 (2009) 540-541. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.2009.540. [CrossRef]
- S. Koso, H. Watanabe, K. Okumura, Y. Nakagawa, K. Tomishige, J. Phys. Chem. C, 116 (2012) 3079-3090.
- B.K. Ly, D.P. Minh, C. Pinel, M. Besson, B. Tapin, F. Epron, C. Especel, Effect of Addition Mode of Re in Bimetallic Pd–Re/TiO2 Catalysts Upon the Selective Aqueous-Phase Hydrogenation of Succinic Acid to 1,4-Butanediol. Top. Catal., 55 (2012) 466-473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-012-9813-3. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Mabry, W.W. Prichard, S.B. Ziemecki, in, E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, United States Patent 4550185, 1985.
- M. Kitson, P.S. Williams, in: U.S.P. Office (Ed.), The British Petroleum Company, United States Patent 5149680, 1992.
- A. Malinowski, W. Juszczyk, M. Bonarowska, J. Pielaszek, Z. Karpinski, Pd-Re/Al2O3: Characterization and catalytic activity in hydrodechlorination of CCl2F2. J. Catal., 177 (1998) 153-163. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1998.2062. [CrossRef]
- M. Bonarowska, A. Malinowski, Z. Karpinski, Hydrogenolysis of C–C and C–Cl bonds by Pd–Re/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A, 188 (1999) 145-154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(99)00241-0. [CrossRef]
- W. Juszczyk, Z. Karpinski, Hydrocarbon reactions on Pd–Re/Al2O3 catalysts. App. Catal. A, 206 (2001) 67-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00584-6. [CrossRef]
- G. Meitzner, G.H. Via, F.W. Lytle, J.H. Sinfelt, Structure of bimetallic clusters. Extended x-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) of Pt–Re and Pd–Re clusters. J. Chem. Phys., 87 (1987) 6354-6363. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.453465. [CrossRef]
- S.B. Ziemecki, J.B. Michel, G.A. Jones, Hydride formation as a measure of alloying in bimetallic systems containing palladium. React. Sol., 2 (1986) 187-202. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-7336(86)80082-1. [CrossRef]
- S.B. Ziemecki, G.A. Jones, J.B. Michel, Surface mobility of Re2O7 in the system Re7+Pd0γ-Al2O3. J. Catal., 99 (1986) 207-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(86)90213-7. [CrossRef]
- M.P. Latusek, B.P. Spigarelli, R.M. Heimerl, J.H. Holles, Correlation of H2 heat of adsorption and ethylene hydrogenation activity for supported Re@Pd overlayer catalysts. J. Catal., 263 (2009) 306-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2009.02.022. [CrossRef]
- M.D. Skoglund, J.H. Holles, Overlayer Bimetallic Catalysts or Particle Size Effects? A Comparison of Re@Pd Catalysts with Different Particle Sizes. Catal. Lett., 143 (2013) 966-974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-013-1052-0. [CrossRef]
- S.T. Thompson, H.H. Lamb, ACS Catal., 6 (2016) 7438-7447.
- J.D. Kammert, A. Chemburkar, N. Miyake, M. Neurock, R.J. Davis, Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism for the Catalytic Reduction of Propionic Acid over Supported ReOx Promoted by Pd. ACS Catal., 11 (2021) 1435-1455. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c04328. [CrossRef]
- K. Otto, C.P. Hubbard, W.H. Weber, G.W. Graham, Raman spectroscopy of palladium oxide on γ-alumina applicable to automotive catalysts: Nondestructive, quantitative analysis; oxidation kinetics; fluorescence quenching. App. Catal. B, 1 (1992) 317-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0926-3373(92)80056-6. [CrossRef]
- A. Baylet, P. Marecot, D. Duprez, P. Castellazzi, G. Groppi, P. Forzatti, In situ Raman and in situXRD analysis of PdO reduction and Pd° oxidation supported on γ-Al2O3catalyst under different atmospheres . Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 13 (2011) 4607-4613. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CP01331E. [CrossRef]
- F.D. Hardcastle, I.E. Wachs, J.A. Horsley, G.H. Via, The structure of surface rhenium oxide on alumina from laser raman spectroscopy and x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy. J. Mol. Catal., 46 (1988) 15-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-5102(88)85081-8. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Vuurman, I.E. Wachs, In situ Raman spectroscopy of alumina-supported metal oxide catalysts. J. Phys. Chem., 96 (1992) 5008-5016. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100191a051. [CrossRef]
- D.S. Kim, I.E. Wachs, Surface rhenium oxide-support interaction for supported Re2O7 catalysts. J. Catal., 141 (1993) 419-429. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1993.1151. [CrossRef]
- J.R. McBride, K.C. Hass, W.H. Weber, Resonance-Raman and lattice-dynamics studies of single-crystal PdO. Phys. Rev. B, 44 (1991) 5016-5028. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.44.5016. [CrossRef]
- S.C. Su, J.N. Carstens, A.T. Bell, A Study of the Dynamics of Pd Oxidation and PdO Reduction by H2and CH4. J. Catal., 176 (1998) 125-135. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1998.2028. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Mamede, G. Leclercq, E. Payen, P. Granger, J. Grimblot, In situ Raman characterisation of surface modifications during NO transformation over automotive Pd-based exhaust catalysts. J. Mol. Struc., 651 (2003) 353-364. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(03)00111-X. [CrossRef]
- T. Arai, T. Shima, T. Nakano, J. Tominaga, Thermally-induced optical property changes of sputtered PdOx films. Thin Sol. Films, 515 (2007) 4774-4777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2006.11.040. [CrossRef]
- L. Jiao, J.R. Regalbuto, The synthesis of highly dispersed noble and base metals on silica via strong electrostatic adsorption: I. Amorphous silica. J. Catal., 260 (2008) 329-341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2008.09.022. [CrossRef]
- J. Okal, L. Kepinski, L. Krajczyk, W. Tylus, Oxidation and redispersion of a low-loaded Re/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. J. Catal., 219 (2003) 362-371. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9517(03)00165-9. [CrossRef]
- C. Sumner, W. Burchett, Developments in the Pd Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Oxygenated Organic Compounds. Top. Catal., 55 (2012) 480-485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-012-9820-4. [CrossRef]
- J.A. McCaulley, In-situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy studies of hydride and carbide formation in supported palladium catalysts. J. Phys. Chem., 97 (1993) 10372-10379. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100142a018. [CrossRef]
- B. Predel, O.E. Madelung, in: Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry, SpringerMaterials.
- J.H. Sinfelt, Bimetallic Catalysts: Discoveries, Concepts, and Applications, John Wiley and Sons, 1983.
- S.T. Thompson, H.H. Lamb, Catalysts for selective hydrogenation of furfural derived from the double complex salt [Pd(NH3)4](ReO4)2 on γ-Al2O3. J. Catal., 350 (2017) 111-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2017.03.019. [CrossRef]
- G.W. Chadzynski, H. Kubicka, Chemisorption of hydrogen and oxygen on γ-alumina-supported rhenium: Part 1. Chemisorption of hydrogen. Thermochim.Acta, 158 (1990) 353-367. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6031(90)80083-B. [CrossRef]
- J.B. Giorgi, T. Schroeder, M. Baumer, H.J. Freund, Study of CO adsorption on crystalline-silica-supported palladium particles. Surf. Sci., 498 (2002) L71-L77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(01)01756-3. [CrossRef]
- G. Agostini, R. Pellegrini, G. Leofanti, L. Bertinetti, S. Bertarione, E. Groppo, A. Zecchina, C. Lamberti, Determination of the Particle Size, Available Surface Area, and Nature of Exposed Sites for Silica−Alumina-Supported Pd Nanoparticles: A Multitechnical Approach. J. Phys. Chem. C, 113 (2009) 10485-10492. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9023712. [CrossRef]
- T. Lear, R. Marshall, J.A. Lopez-Sanchez, S.D. Jackson, T.M. Klapotke, M. Baumer, G. Rupprechter, H.J. Freund, D. Lennon, J. Chem. Phys., 123 (2005) 13.
- W. Daniell, T. Weingand, H. Knozinger, Redox properties of Re2O7/Al2O3 as investigated by FTIR spectroscopy of adsorbed CO. J. Mol. Catal., 204 (2003) 519-526. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-1169(03)00334-0. [CrossRef]
- S.R. Bare, S.D. Kelly, F.D. Vila, E. Boldingh, E. Karapetrova, J. Kas, G.E. Mickelson, F.S. Modica, N. Yang, J.J. Rehr, Experimental (XAS, STEM, TPR, and XPS) and Theoretical (DFT) Characterization of Supported Rhenium Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C, 115 (2011) 5740-5755. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1105218. [CrossRef]
| Catalyst | Metal precursor(s) | Pd loading (wt%) | Re loading (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd1-N | Pd(NO3)2 | 0.91 | --- |
| Pd3-N | Pd(NO3)2 | 2.66 | --- |
| Pd3-TA | Pd(NH3)4(NO3)2 | 2.34 | --- |
| Pd3Re5-CI | Pd(NO3)2 and HReO4 | 2.43 | 4.41 |
| Pd3Re5-SI | Pd(NH3)4(NO3)2 and HReO4 | 2.80 | 4.63 |
| Re5Pd3N-SI | HReO4 and Pd(NO3)2 | 2.15 | 5.73 |
| Re5Pd3-SI (350) | NH4ReO4 and Pd(NH3)4(NO3)2 | 2.56 | 4.23 |
| Re5Pd3-SI | NH4ReO4 and Pd(NH3)4(NO3)2 | 2.27 | 4.24 |
| Re5Pd1.5-DCS | Pd(NH3)4(ReO4)2 | 1.42 | 4.65 |
| Re5-H | HReO4 | --- | 5.29 |
| Re5-N | NH4ReO4 | --- | 4.54 |
| Catalyst | H/metal ratio(TPR)1 | Re oxidation state (TPR)2 | H/Pd(TPHD)4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd3-N | 2.1 | -- | 0.32 |
| Pd3-TA | 2.4 | -- | 0.13 |
| Pd3Re5-CI | 4.4 | 0.4 | 0.063 |
| Pd3Re5-SI | 3.6 | 0.73 | 0.058 |
| Re5Pd3N-SI | 5.0 | 0.7 | 0.18 |
| Re5Pd3-SI (350) | 4.3 | 0.3 | 0.11 |
| Re5Pd3-SI | 4.5 | 0.2 | 0.12 |
| Re5-N | 4.9 | 2.1 | -- |
| Catalyst | CO chemisorption | H2 chemisorption | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35°C | 35°C | 100°C | ||||||
| CO uptake a | CO/metal | H2 uptakea | H/metal | H/CO | H2 uptake | H/metal | H/CO | |
| Pd1-N | 28.5 | 0.333 | 12.7 | 0.297 | 0.89 | 8.8 | 0.204 | 0.62 |
| Pd3-N | 32.4 | 0.130 | 16.7 | 0.133 | 1.03 | 12.4 | 0.100 | 0.76 |
| Pd3-TA | 103 | 0.469 | n/a | -- | -- | n/a | -- | -- |
| Pd3Re5-CI | 59.0 | 0.127 | 26.7 | 0.115 | 0.90 | 27.3 | 0.117 | 0.92 |
| Pd3Re5-SI | 80.5 | 0.157 | 17.9 | 0.070 | 0.44 | 21.6 | 0.084 | 0.54 |
| Re5Pd3N-SI | 50.5 | 0.099 | n/a | -- | -- | n/a | -- | -- |
| Re5Pd3-SI (350) | 96.2 | 0.206 | 20.9 | 0.089 | 0.43 | 26.7 | 0.114 | 0.56 |
| Re5Pd3-SI | 92.6 | 0.210 | 20.3 | 0.092 | 0.44 | 21.1 | 0.096 | 0.46 |
| Pd1.5Re5-DCS | 44.6 | 0.116 | 7.6 | 0.040 | 0.34 | 11.0 | 0.057 | 0.49 |
| Re5-N | 33.8 | 0.139 | 2.3 | 0.019 | 0.14 | 14.5 | 0.119 | 0.86 |
| Catalyst | TOF (min-1)a | |
|---|---|---|
| CO | H | |
| Pd1-N | 10.1 | 11.3b |
| Pd3-N | 9.1 | 8.9b |
| Pd3-TA | 3.2 | n/a |
| Pd3Re5-CI | 5.1 | 5.5 |
| Pd3Re5-SI | 20.5 | 38.3 |
| Re5Pd3-SI (350) | 13.6 | 24.5 |
| Re5Pd3-SI | 26.0 | 57.0 |
| Pd1.5Re5-DCS | 29.9 | 60.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




