Submitted:
21 July 2023
Posted:
24 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To study time subservient 2D bio-convectional cross nanofluid flow resulting from the cylindrical surface with the impression of living microbes, thermal conductivity, and melting phenomenon.
- The mathematical model of the nonlinear governing PDEs comprises momentum, temperature gradient, mass balances, and swimming microorganism.
- To engage numerical techniques for attaining the computational outcomes. Also, to render a convergence and stability analysis for optimizing flow fields.
- To unveil the graphical outlines of diversified emerging parameters on flow fields together with 3D visuals of skin friction, heat transfer, and mass flow coefficients.
2. Flow analysis and mathematical setup
- 1.
- Computational procedure.
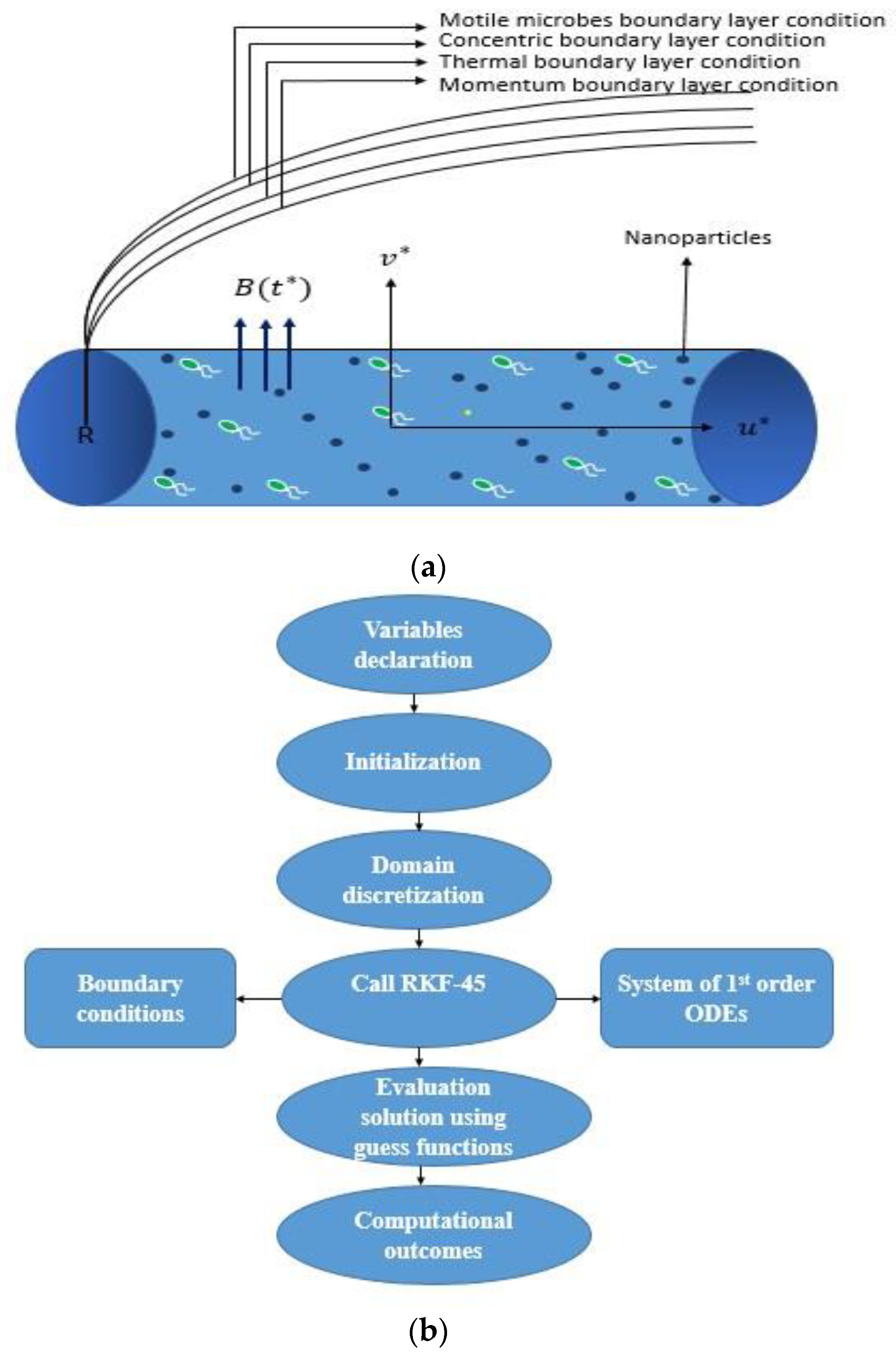
- 2.
- Graphical outcomes
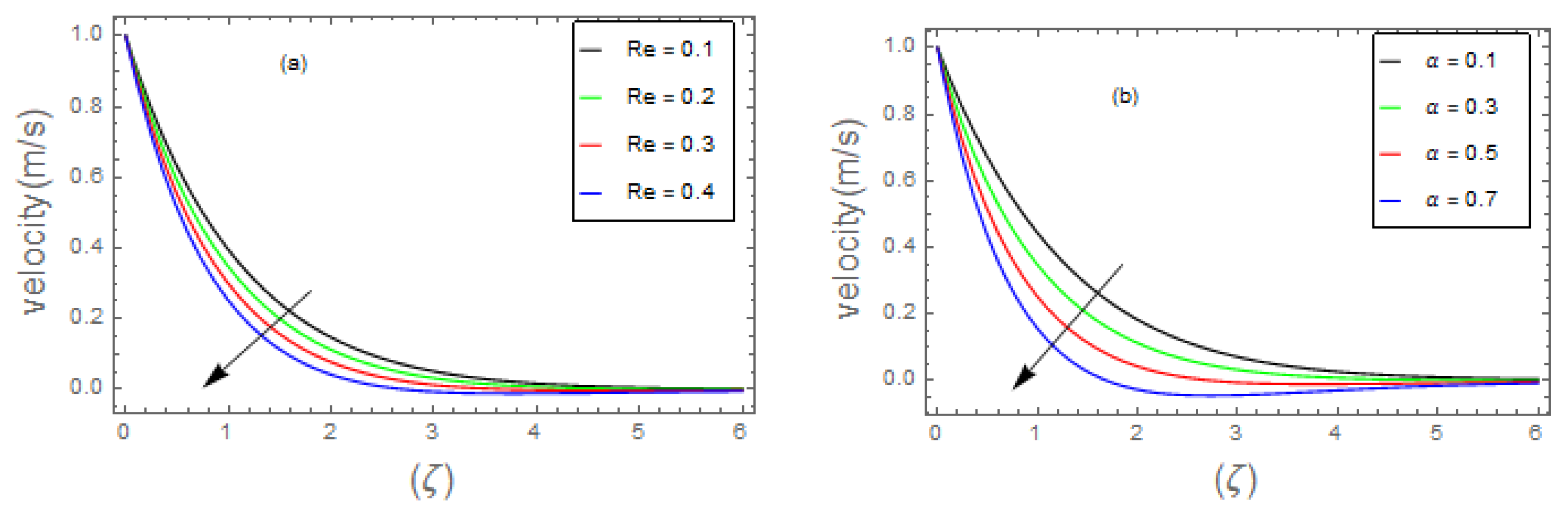
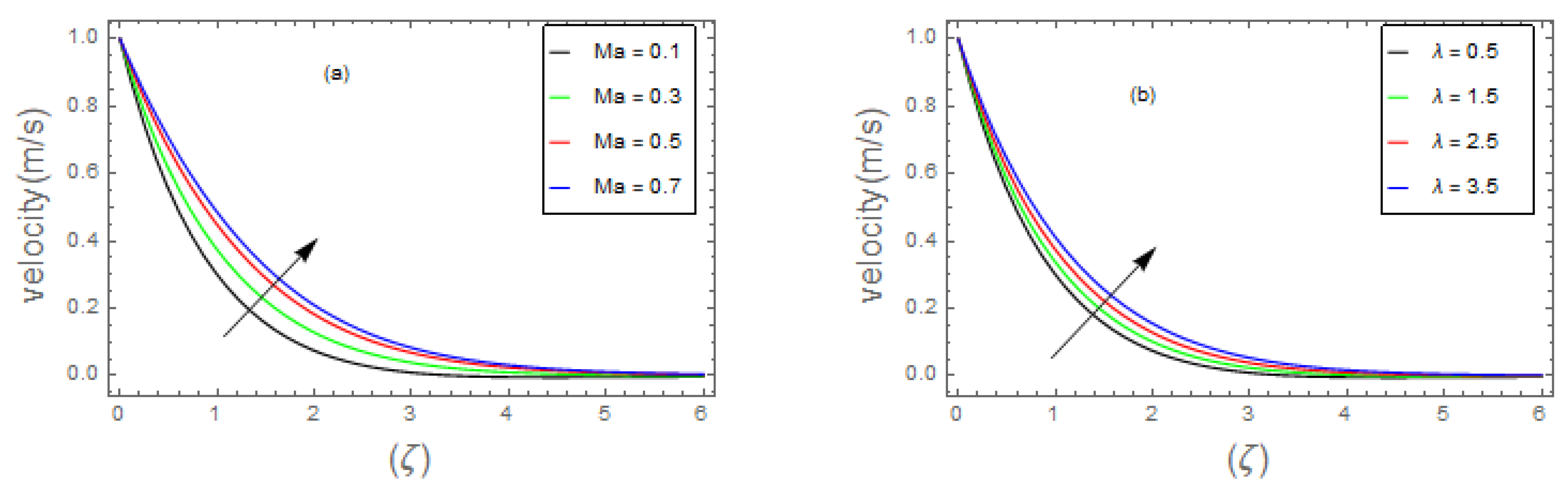
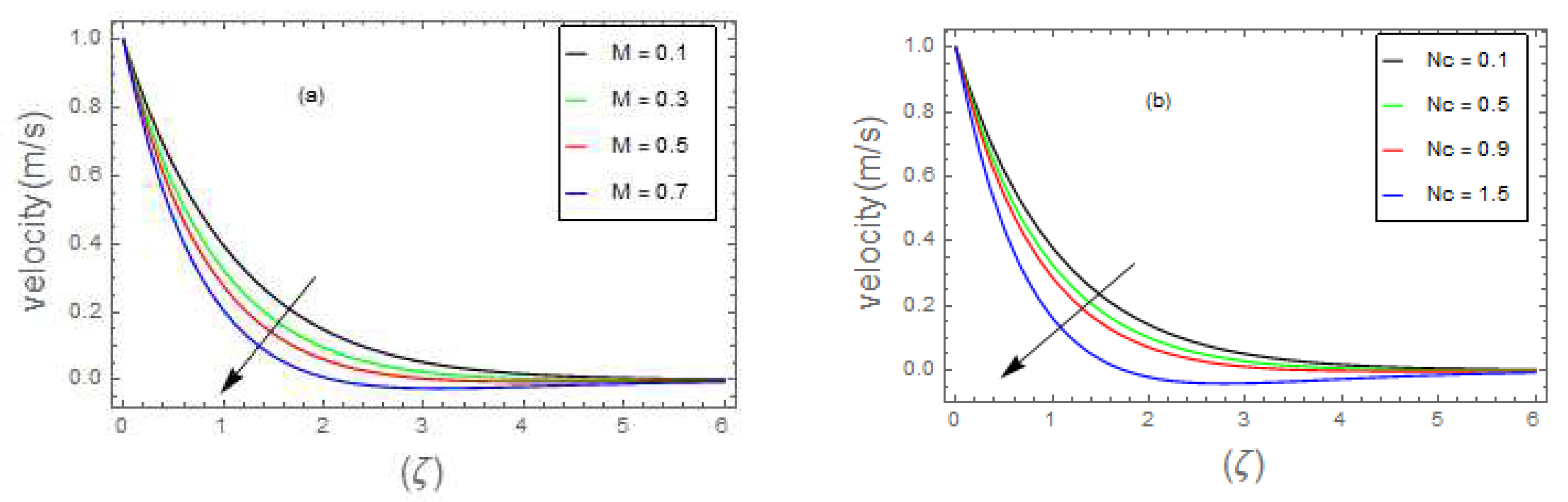
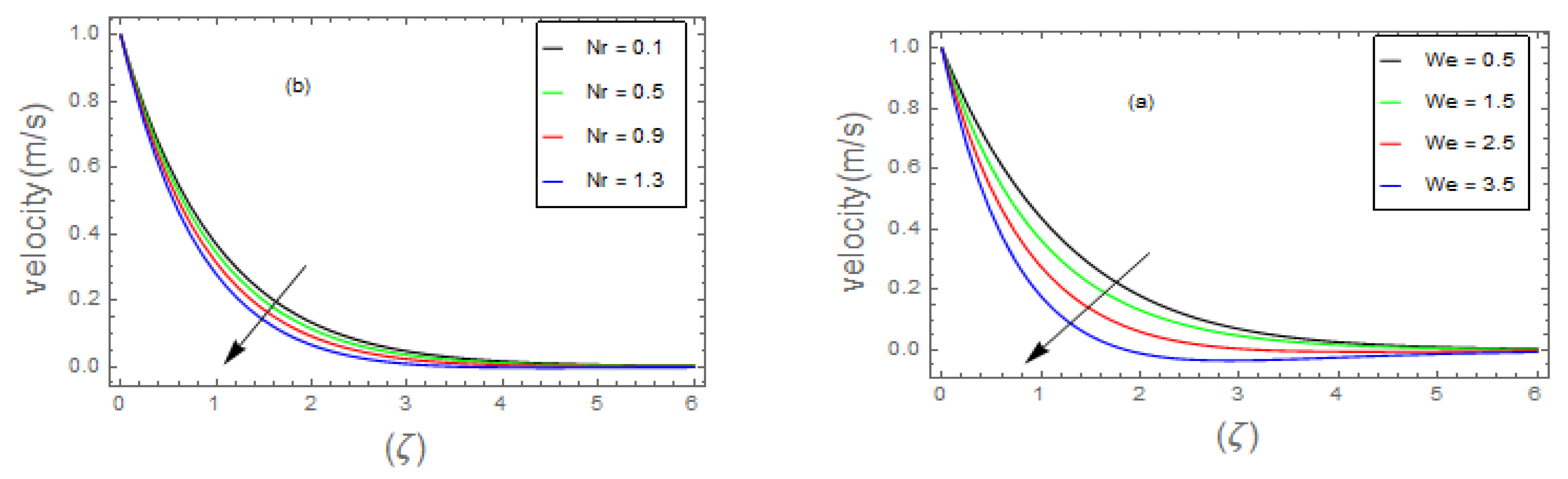
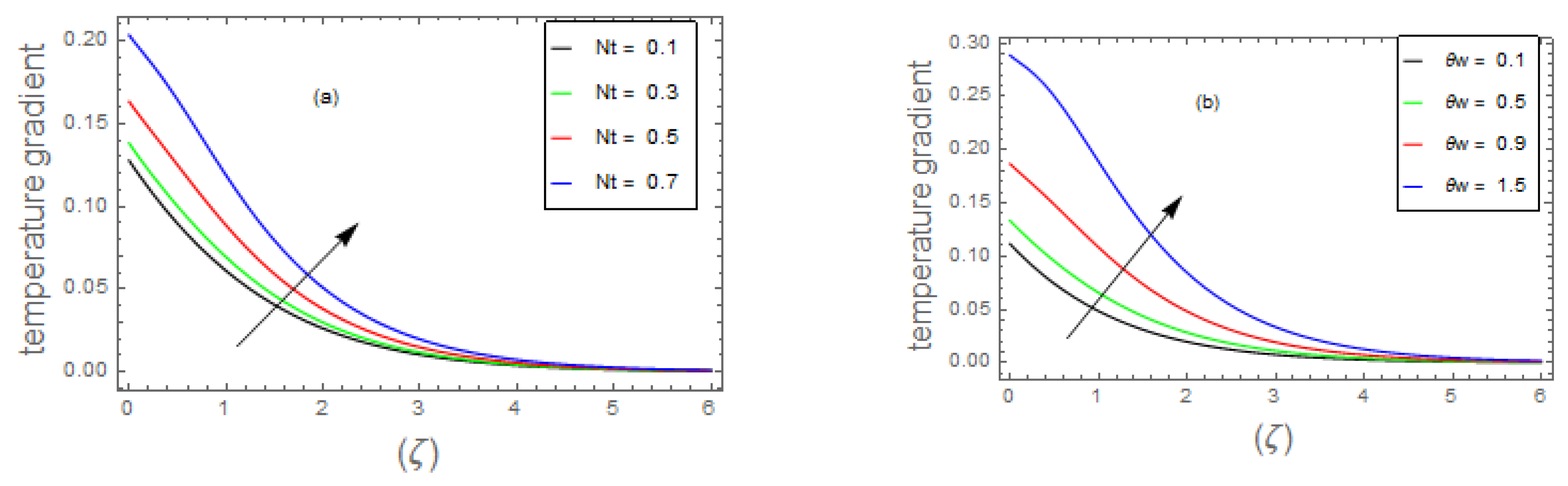
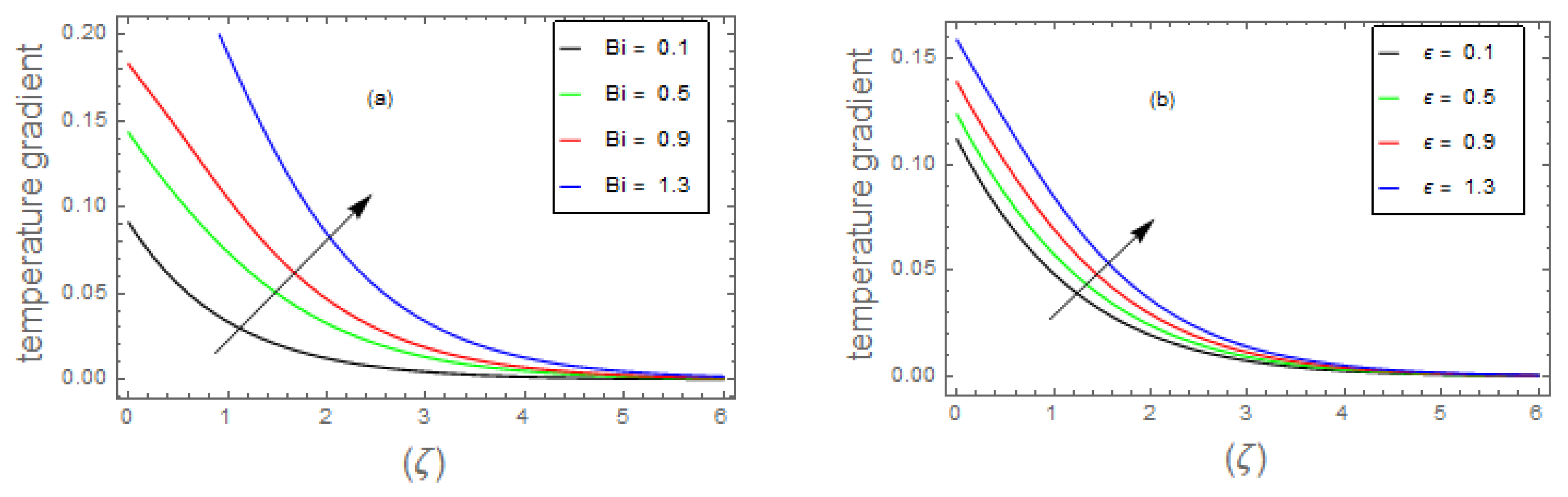
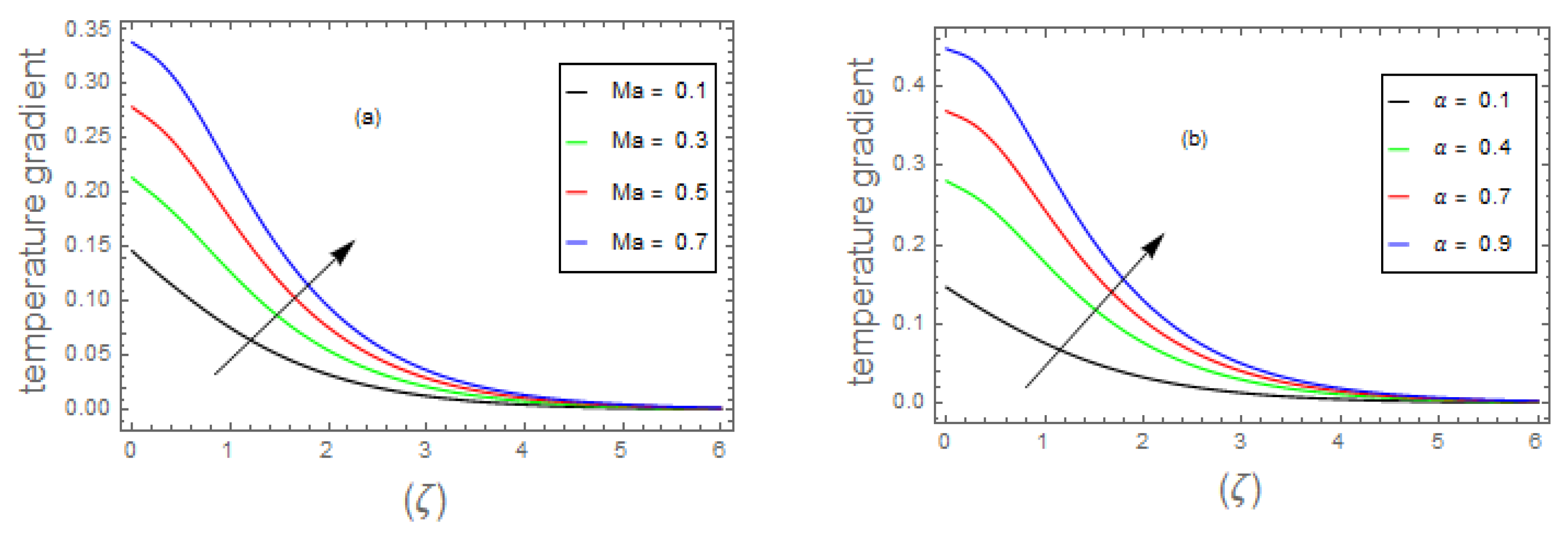
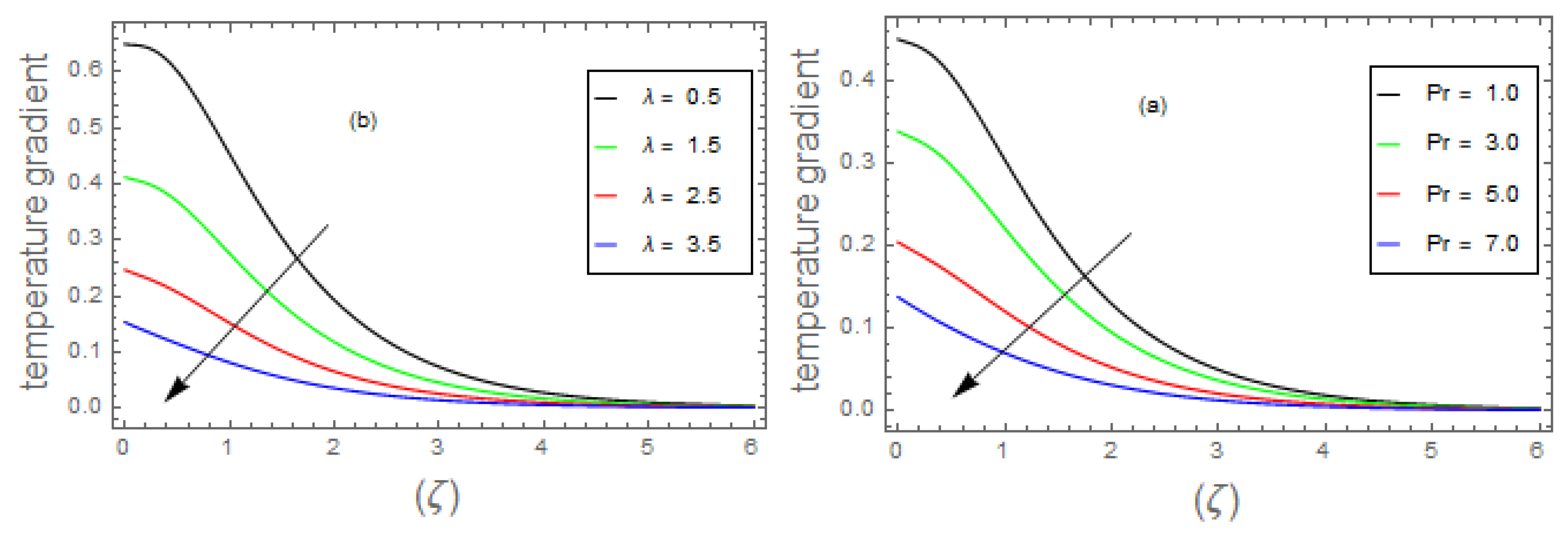
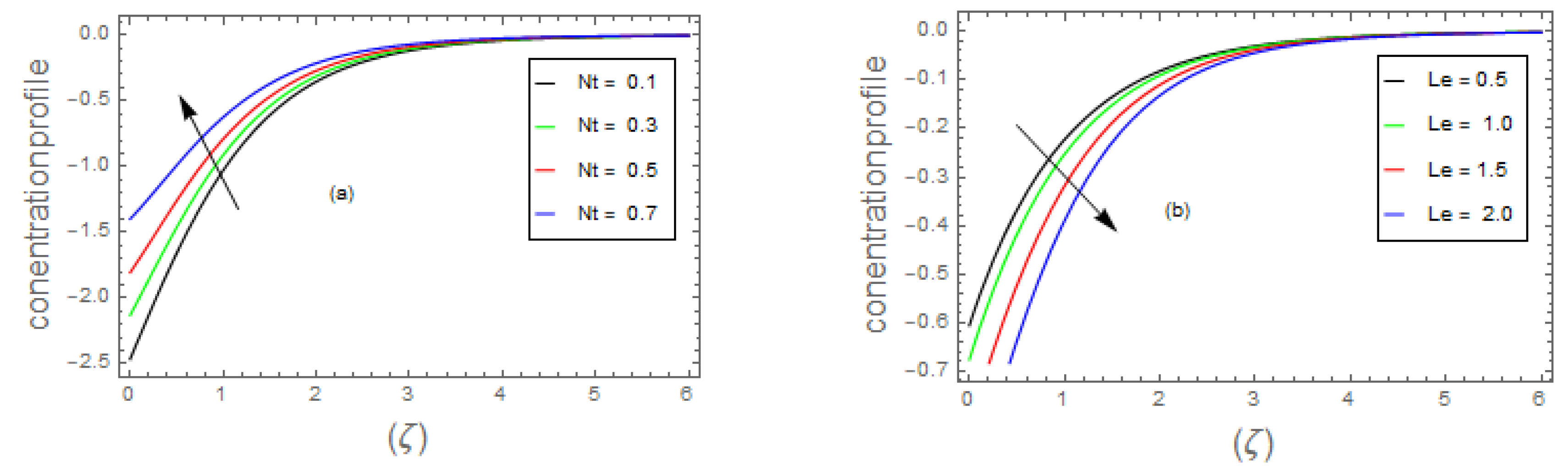
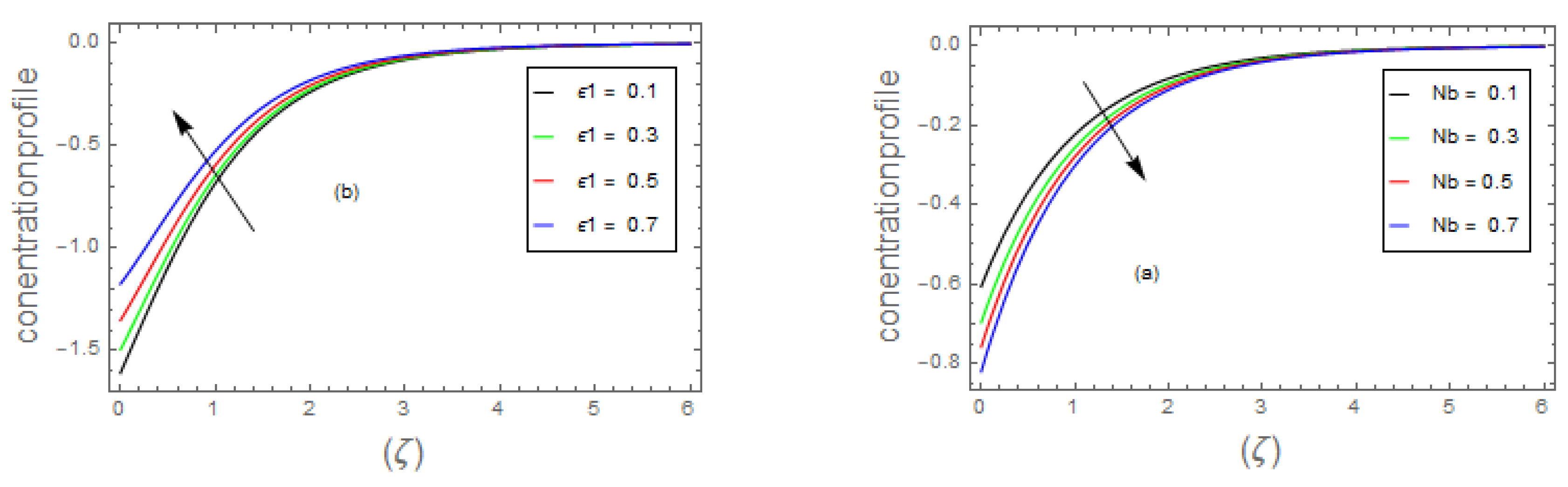
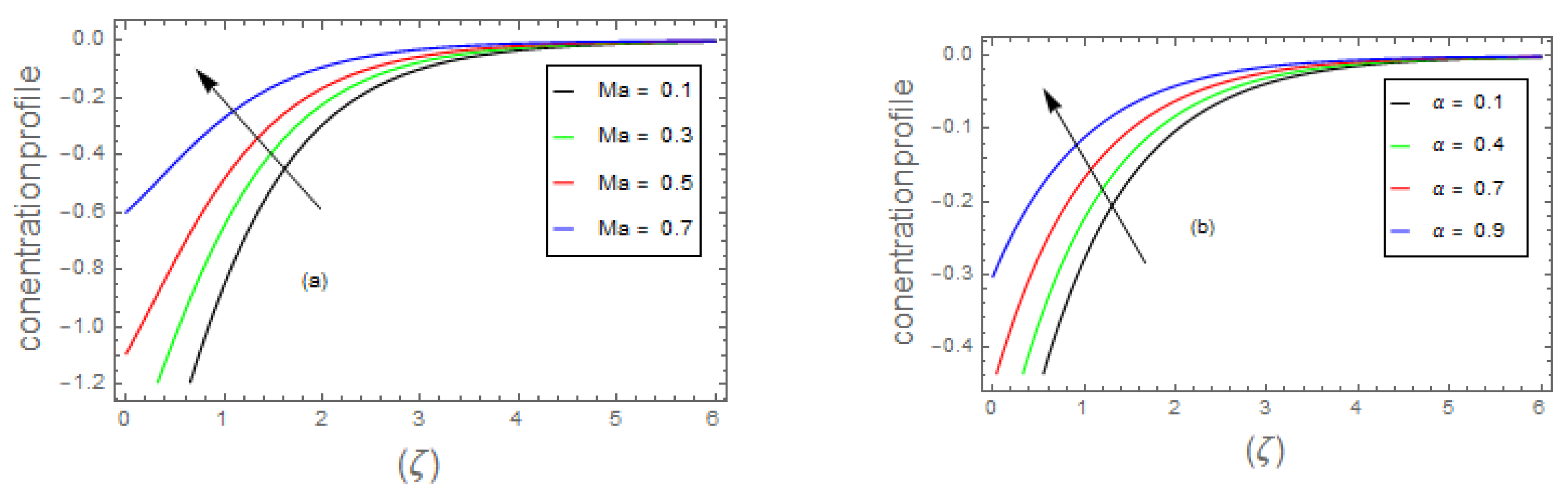
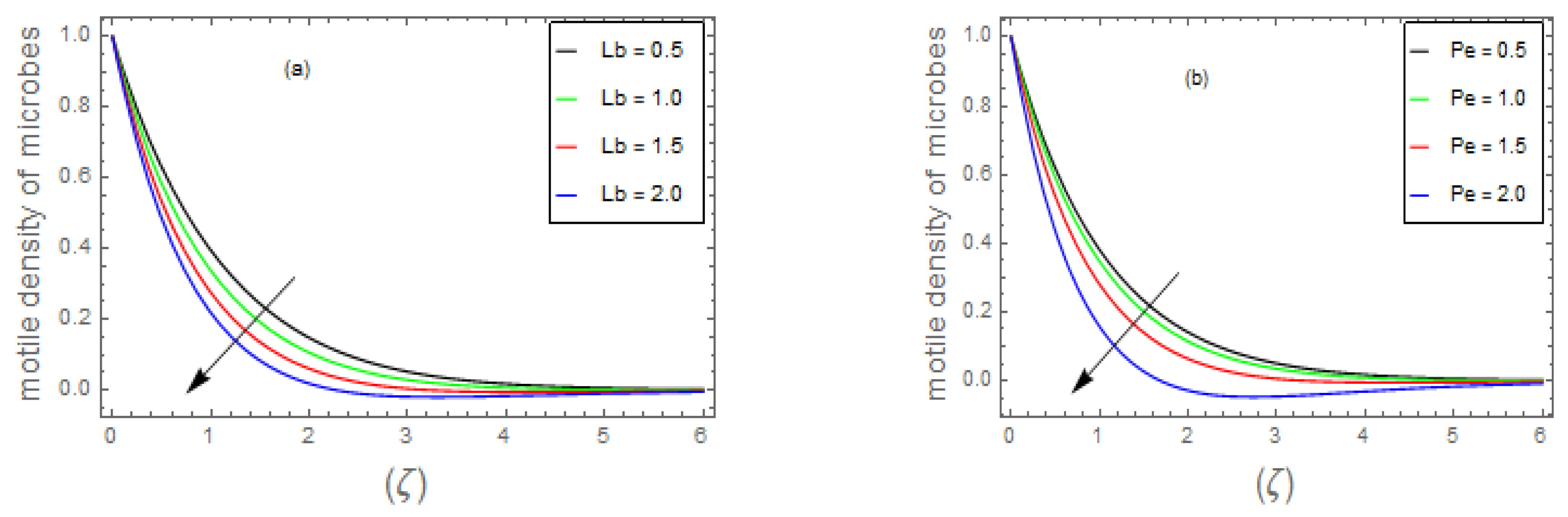
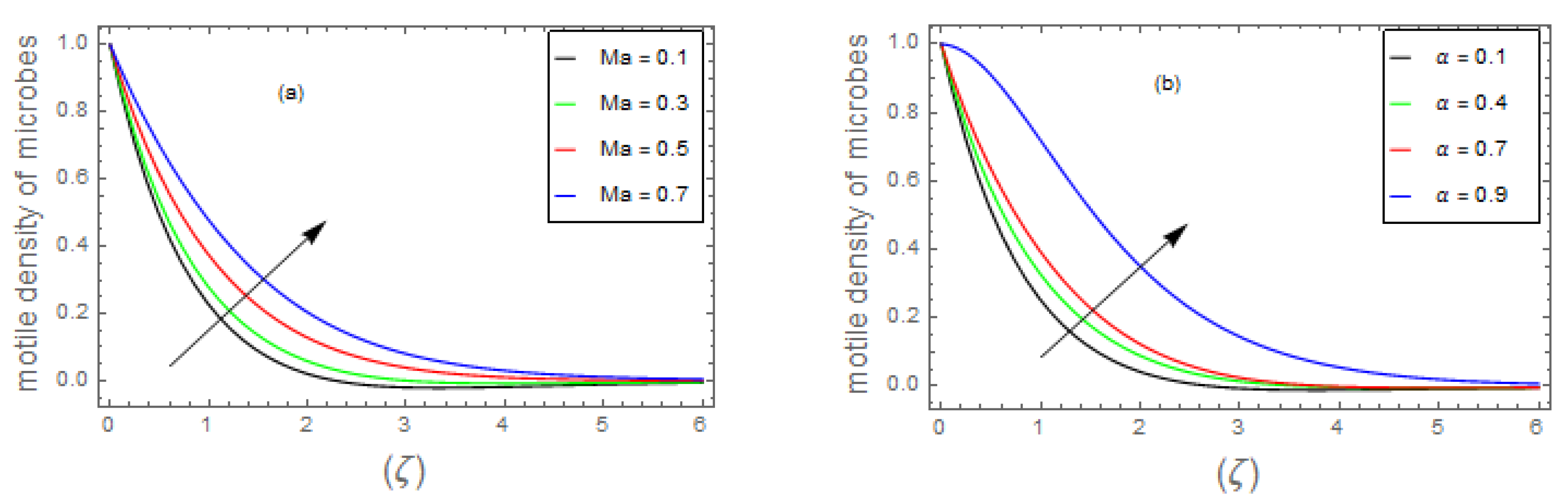
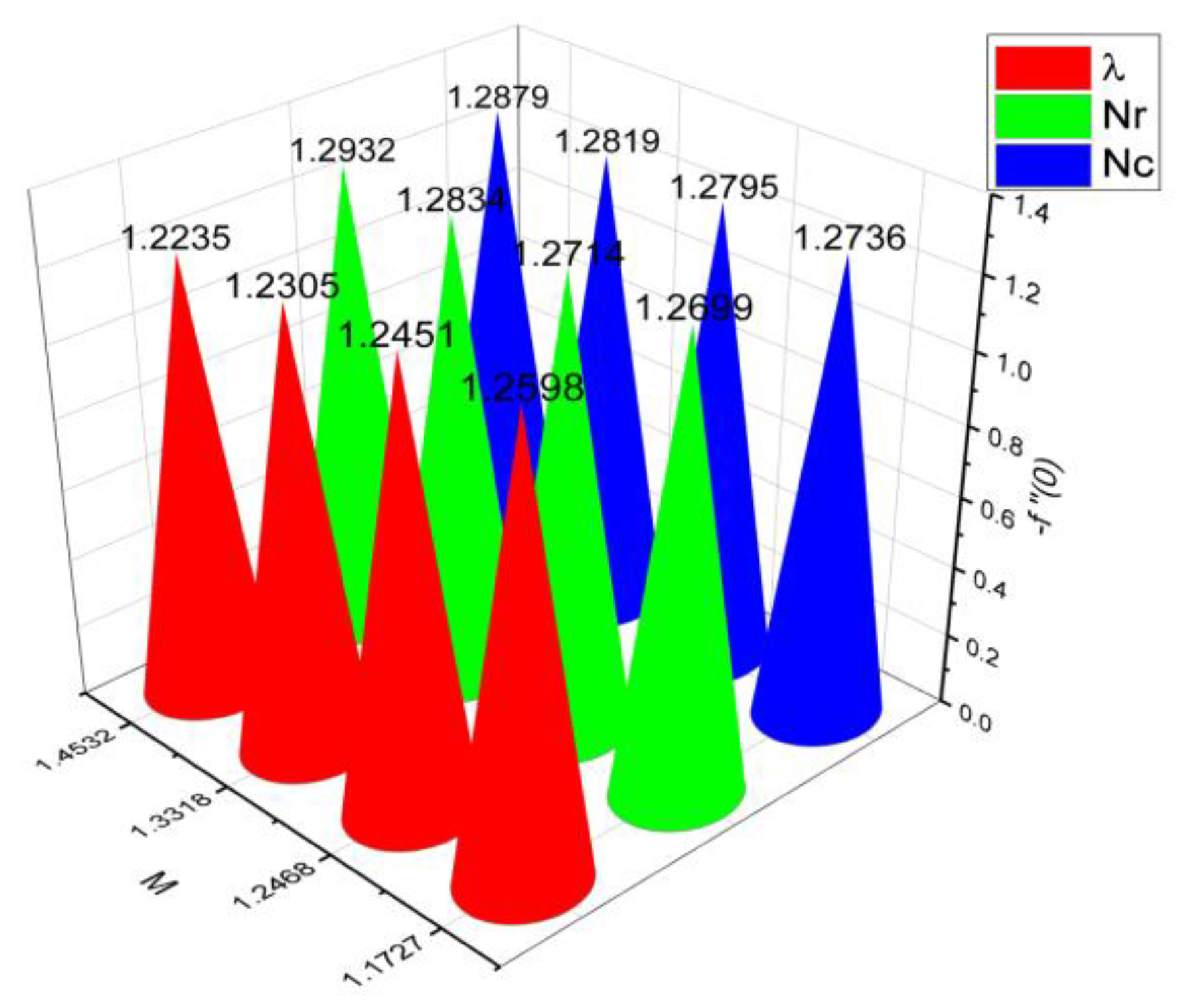
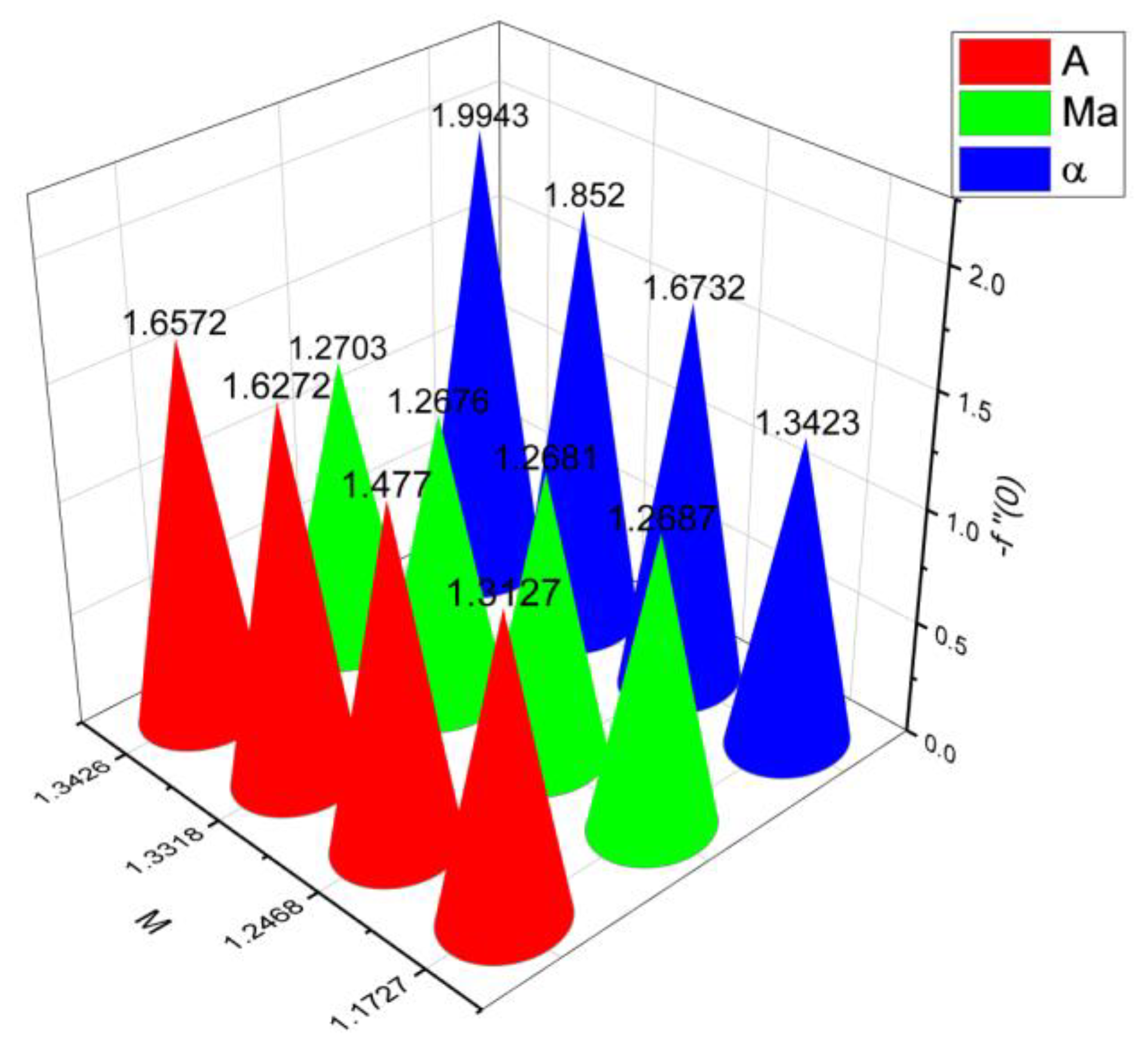
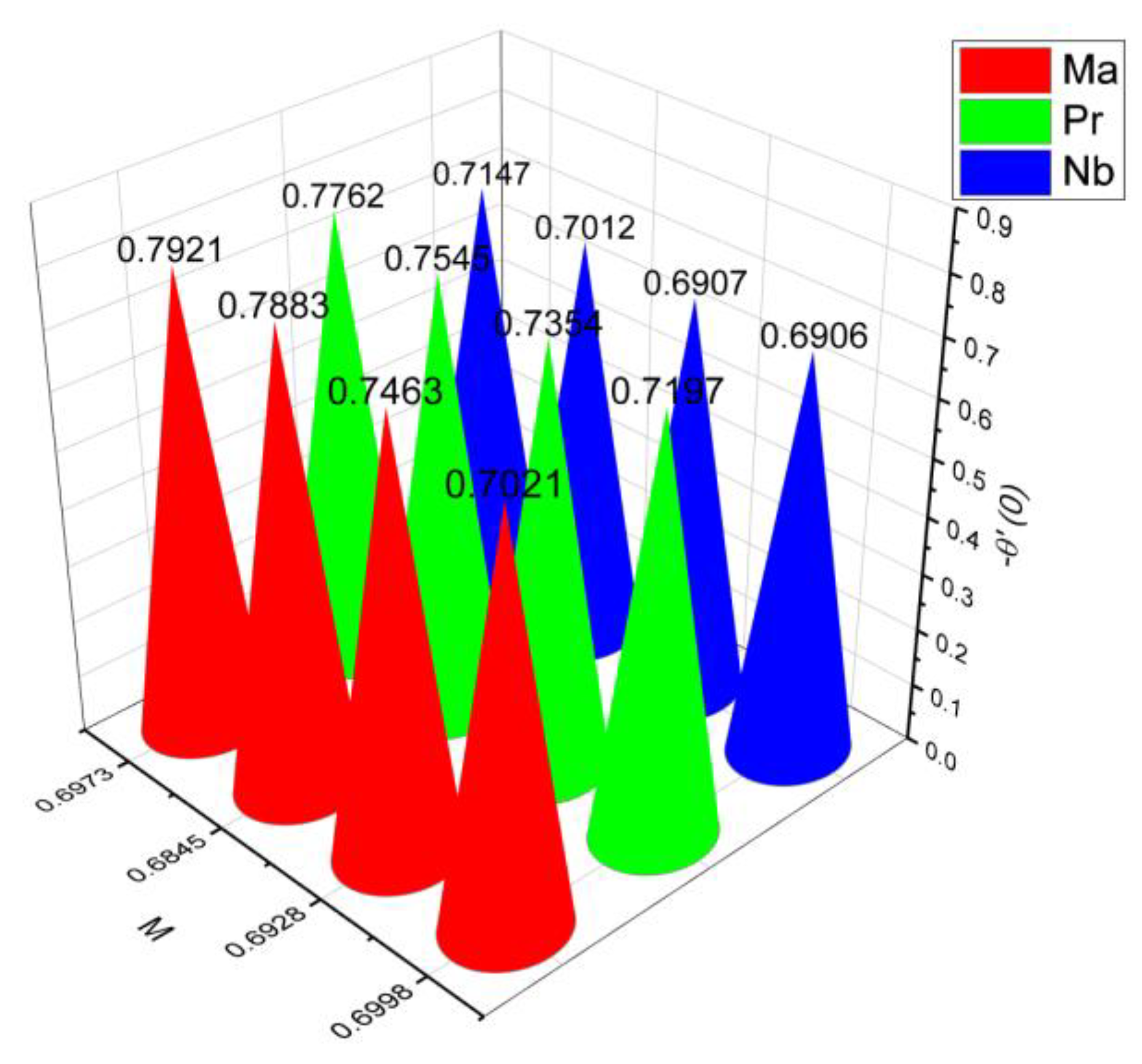
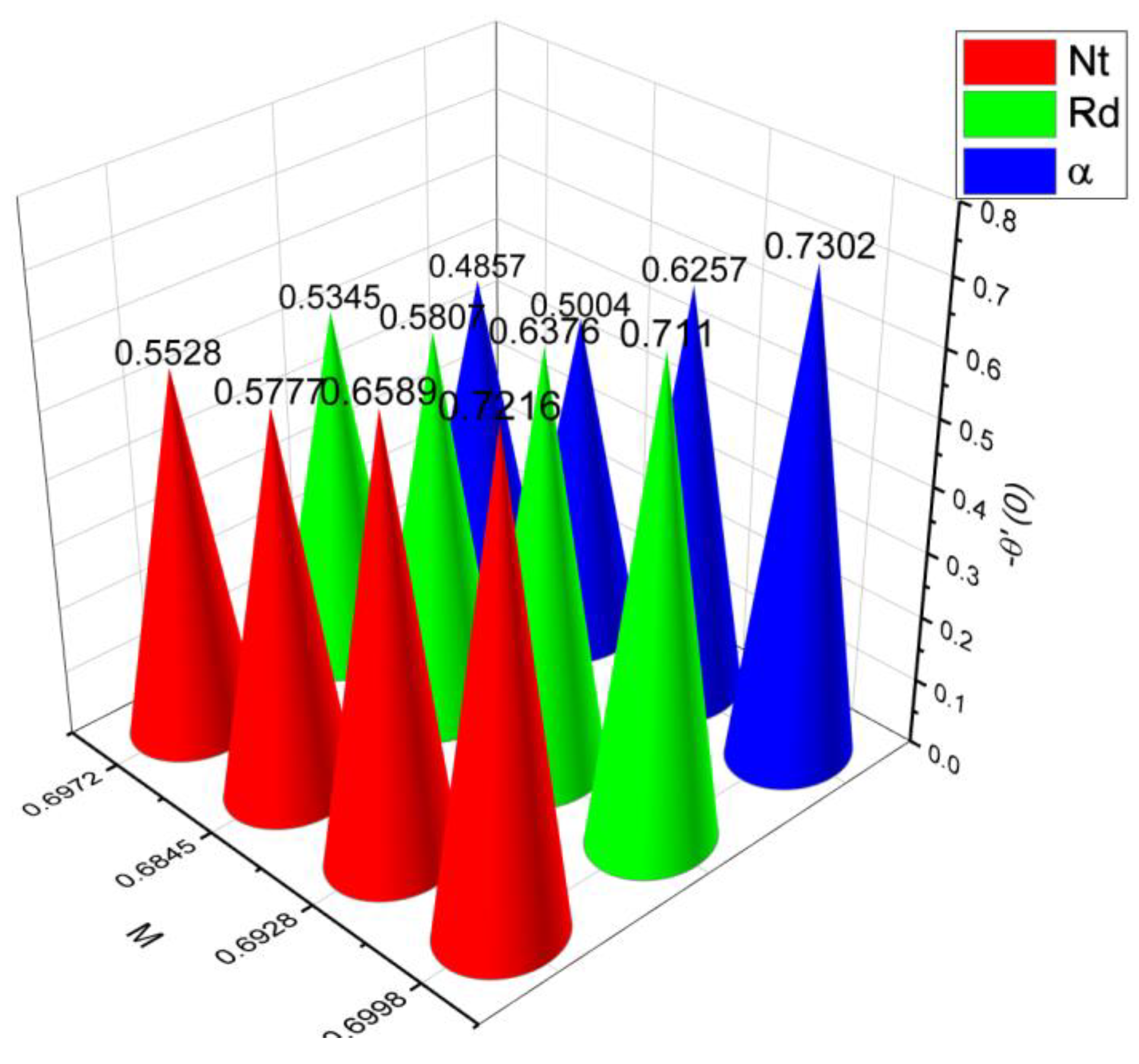
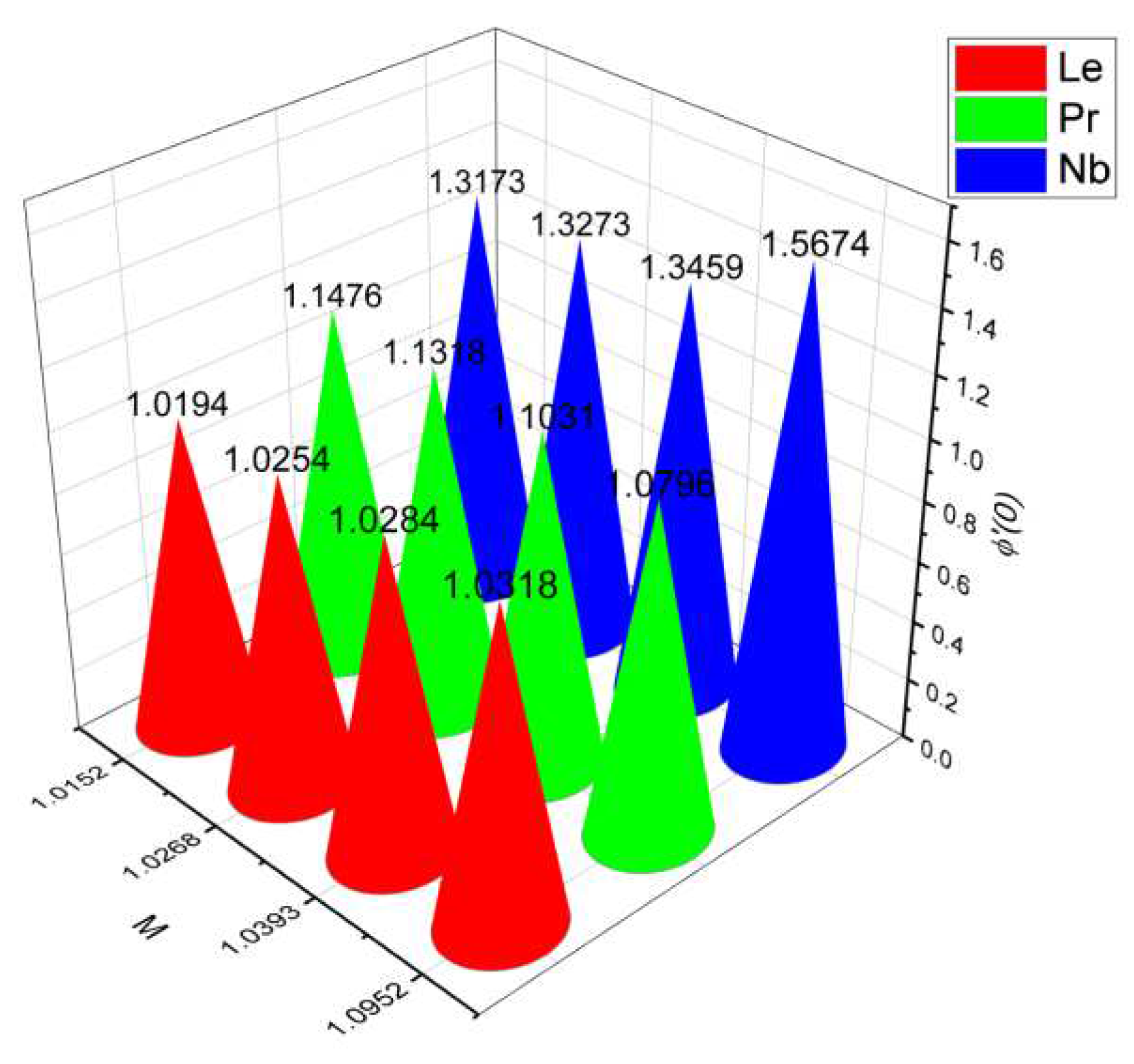
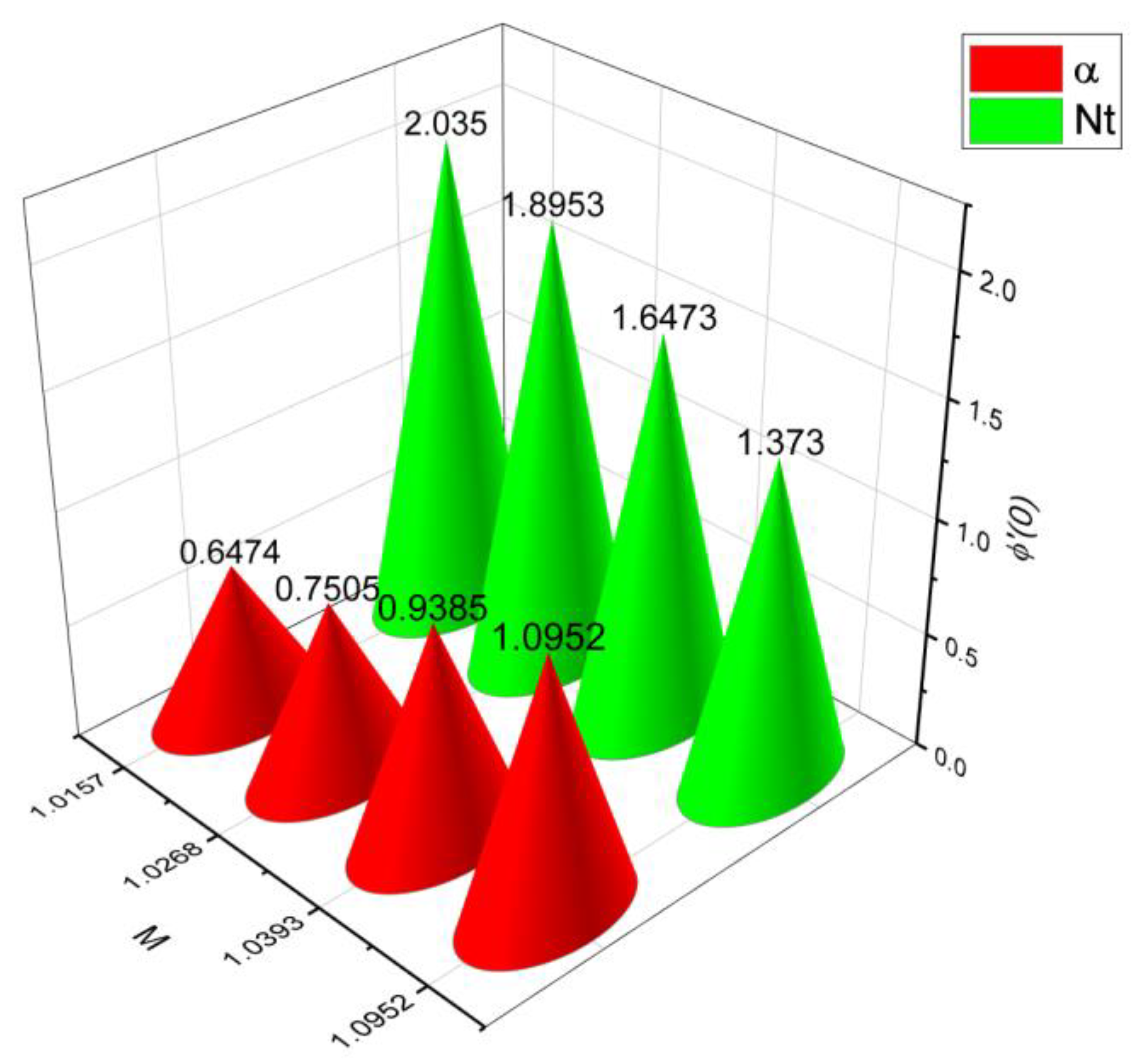
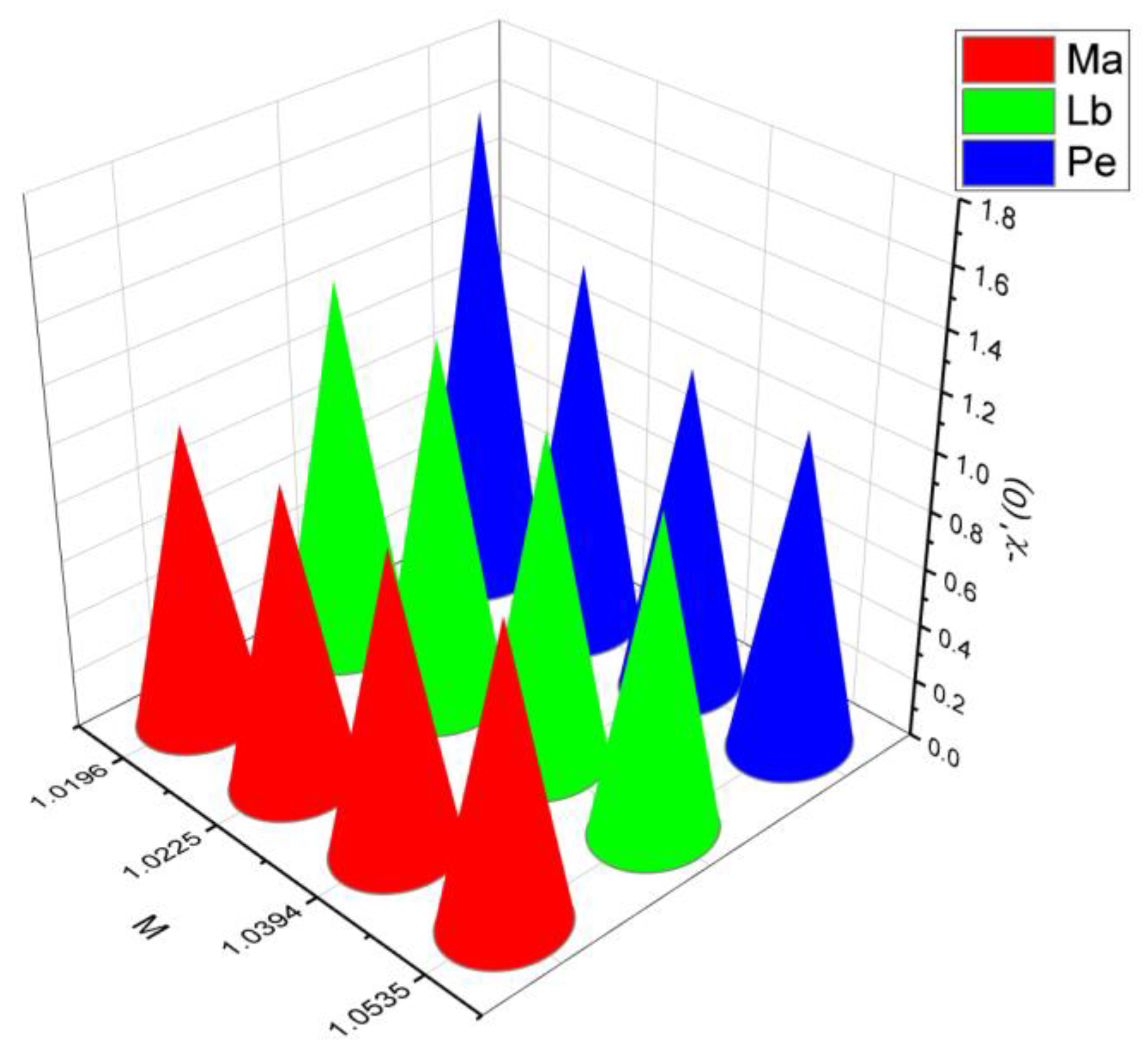
- 3.
- Closing points
- The velocity field of bio-nanofluid flow rises as the values of and parameter is increased, however, the velocity profile reduces with the expanding values of , and parameters.
- The fluid energy profile decremented with the mounting data of parameter and number but increases by , , and thermal number.
- Due to the increment in the magnitude of parameter, , and the concentric layer thickness increases. On the contrary, for growing data on the and dispersion effect the concentration profile decreases.
- It has been observed that the increasing trends of and numbers suppresses considerably the density profile of living microbes, whereas the and parameters boost the motile density of microorganism profile.
- The surface drag force coefficient decays via higher estimation of but it increments when and parameter are increased.
- It is observed that the mass flow rate increase when number as well as the parameter increased. On the contrary, it decreases when parameter and number increase.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S.U.S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, development and applications of non-Newtonian flows, in: D.A. Siginer, H.P. Wang(Eds.), ASME MD, vol. 231, 1995, pp. 99–110.
- G. Narsimulu, D. Gopal, Rama Udaikumar, Numerical approach for enhanced mass transfer of Bio-convection on Magneto-hydrodynamic Carreau fluid flow through a nonlinear stretching surface, Materials Today: Proceedings, 49, Part 5, 2022, 2267-2275. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Imran, Tahir Kamran, Shan Ali Khan, Taseer Muhammad, Hassan Waqas, Physical attributes of bio-convection in nanofluid flow through a paraboloid of revolution on horizontal surface with motile microorganisms, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 133, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Hassan Waqas, Shan Ali Khan, Sami Ullah Khan, M. Ijaz Khan, Seifedine Kadry, Yu-Ming Chu, Falkner-Skan time-dependent bioconvrction flow of cross nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation, activation energy and melting process, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 120, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Asmat Ullah Yahya, Nadeem Salamat, Danial Habib, Bagh Ali, Sajjad Hussain, Sohaib Abdal, Implication of Bio-convection and Cattaneo-Christov heat flux on Williamson Sutterby nanofluid transportation caused by a stretching surface with convective boundary, Chinese Journal of Physics, 73, 2021, 706-718. [CrossRef]
- J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluid, J.Heat Transfer 128 (3) (2006) 240–250. [CrossRef]
- K. Venkatadri, S. Abdul Gaffar, P. Rajarajeswari, V.R. Prasad, B.O. Anwar, K.B.M. Hidayathulla, Melting heat transfer analysis of electrically conducting nanofluid flow over an exponentially shrinking/stretching porous sheet with radiative heat flux under a magnetic field, Heat Transfer (2020). [CrossRef]
- H. Mondal, S. Bharti, Spectral Quasi-linearization for MHD nanofluid stagnation boundary layer flow due to a stretching/shrinking surface, Journal of Applied and Computational Mechanics 6 (4) (2020) 1058–1068. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ying, B. He, L. Su, Y. Kuang, D. He, C. Lin, Convective heat transfer of molten salt-based nanofluid in a receiver tube with non-uniform heat flux, Appl. Therm. Eng. 181 (2020), 115922. [CrossRef]
- N.A. Zainal, R. Nazar, K. Naganthran, I. Pop, Stability analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet with quadratic velocity, Alexandria Engineering Journal (2020). [CrossRef]
- M.R. Eid, M.A. Nafe, Thermal Conductivity Variation and Heat Generation Effects on Magneto-Hybrid Nanofluid Flow in a Porous Medium with Slip Condition. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 2020, pp. 1–25. [CrossRef]
- H. Eshgarf, R. Kalbasi, A. Maleki, M.S. Shadloo, A review on the properties, preparation, models and stability of hybrid nanofluids to optimize energy consumption, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) 1–25. [CrossRef]
- N. Khan, M.S. Hashmi, S.U. Khan, F. Chaudhry, I. Tlili, M.S. Shadloo, Effects of homogeneous and heterogeneous chemical features on Oldroyd-B fluid flow between stretching disks with velocity and temperature boundary assumptions, Math. Probl Eng. (2020). [CrossRef]
- I. Tlili, M. Rabeti, M.S. Shadloo, Z. Abdelmalek, Forced convection heat transfer of nanofluids from a horizontal plate with convective boundary condition and a line heat source embedded in porous media, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) 1–14. [CrossRef]
- F.S. Al-Mubaddel, U. Farooq, K. Al-Khaled, S. Hussain, S.U. Khan, M.O. Aijaz, H. Waqas, Double stratified analysis for bioconvection radiative flow of Sisko nanofluid with generalized heat/mass fluxes, Phys. Scripta 96 (5) (2021), 055004. [CrossRef]
- H. Waqas, U. Farooq, R. Naseem, S. Hussain, M. Alghamdi, Impact of MHD radiative flow of hybrid nanofluid over a rotating disk, Case Studies in Thermal Engineering 26 (2021), 101015. [CrossRef]
- H. Eshgarf, R. Kalbasi, A. Maleki, M.S. Shadloo, A review on the properties, preparation, models and stability of hybrid nanofluids to optimize energy consumption, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) 1–25. [CrossRef]
- M. Imran, U. Farooq, T. Muhammad, S.U. Khan, H. Waqas, Bioconvection transport of Carreau nanofluid with magnetic dipole and nonlinear thermal radiation, Case Stud. Ther. Eng. (2021) 101129. [CrossRef]
- I. Tlili, M. Rabeti, M.S. Shadloo, Z. Abdelmalek, Forced convection heat transfer of nanofluids from a horizontal plate with convective boundary condition and a line heat source embedded in porous media, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) 1–14. [CrossRef]
- M.H.A. Kamal, A. Ali, S. Shafie, N.A. Rawi, M.R. Ilias, G-Jitter effect on heat and mass transfer of 3-D stagnation point nanofluid flow with heat generation, Ain Shams Engineering Journal (2020). [CrossRef]
- N.S. Anuar, N. Bachok, N.M. Arifin, H. Rosali, Numerical solution of stagnation point flow and heat transfer over a non-linear stretching/shrinking sheet in hybrid nanofluid: stability analysis, Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences 76 (2) (2020) 85–98. [CrossRef]
- R. Rizwana, A. Hussain, S. Nadeem, Slip Effects on Unsteady Oblique Stagnation Point Flow of Nanofluid in a View of Inclined Magnetic Field, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S.S. Giri, K. Das, P.K. Kundu, Influence of nanoparticle diameter and interfacial layer on magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid flow with melting heat transfer inside rotating channel, Math. Methods Appl. Sci. (2020). [CrossRef]
- R.P. Sharma, N. Acharya, K. Das, On the Impact of Variable Thickness and Melting Transfer of Heat on Magnetohydrodynamics Nanofluid Flow Past a Slandering Stretching Sheet, 2020.
- J.R. Platt, Bioconvection patterns’ in cultures of free swimming organisms, Science 133 (1961) 1766–1767. [CrossRef]
- A.V. Kuznetsov, Nanofluid bioconvection in water-based suspensions containing nanoparticles and oxytactic microorganisms: oscillatory instability, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6 (2011) 100. [CrossRef]
- A.V. Kuznetsov, Non-oscillatory and oscillatory nanofluid bio-thermal convection in a horizontal layer of finite depth, Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid 30 (2010) 156–165. [CrossRef]
- F. Haq, M. Saleem, M. Ur Rahman, Investigation of natural bio-convective flow of Cross nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms subject to activation energy and magnetic field, Phys. Scripta 95 (10) (2020), 105219. [CrossRef]
- S. Ahmad, M. Ashraf, K. Ali, Nanofluid flow comprising gyrotactic microorganisms through a porous medium, J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 13 (5) (2020). [CrossRef]
- E. Elanchezhian, R. Nirmalkumar, M. Balamurugan, K. Mohana, K.M. Prabu, A. Viloria, Heat and mass transmission of an Oldroyd-B nanofluid flow through a stratified medium with swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 141 (2020) 2613–2623. [CrossRef]
- M.M. Bhatti, M. Marin, A. Zeeshan, R. Ellahi, S.I. Abdelsalam, Swimming of motile gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles in blood flow through anisotropically tapered arteries, Frontiers in Physics 8 (2020) 95. [CrossRef]
- S.U. Khan, I. Tlili, Significance of activation energy and effective Prandtl number in accelerated flow of Jeffrey nanoparticles with gyrotactic microorganisms, J. Energy Resour. Technol. 142 (11) (2020). [CrossRef]
- A. Shafiq, G. Rasool, C.M. Khalique, S. Aslam, Second grade bioconvective nanofluid flow with buoyancy effect and chemical reaction, Symmetry 12 (4) (2020) 621. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Kotnurkar, D.C. Katagi, Bioconvective Peristaltic Flow of a Third-Grade Nanofluid Embodying Gyrotactic Microorganisms in the Presence of Cu-Blood Nanoparticles with Permeable Walls. Multidiscipline Modeling in Materials and Structures, 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Muhammad, S.Z. Alamri, H. Waqas, D. Habib, R. Ellahi, Bioconvection flow of magnetized Carreau nanofluid under the influence of slip over a wedge with motile microorganisms, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. (2020) 1–13. [CrossRef]
- U. Farooq, H. Waqas, M.I. Khan, S.U. Khan, Y.M. Chu, S. Kadry, Thermally radioactive bioconvection flow of Carreau nanofluid with modified Cattaneo-Christov expressions and exponential space-based heat source, Alexandria Engineering Journal 60 (3) (2021) 3073–3086. [CrossRef]
- K. Hosseinzadeh, S. Roghani, A.R. Mogharrebi, A. Asadi, M. Waqas, D.D. Ganji, Investigation of cross-fluid flow containing motile gyrotactic microorganisms and nanoparticles over a three-dimensional cylinder, Alexandria Engineering Journal (2020). [CrossRef]
- Algehyne, E. A., Ahammad, N. A., Elnair, M. E., Zidan, M., Alhusayni, Y. Y., El-Bashir, B. O., ... & Alzahrani, F. (2023). Enhancing Heat Transfer in Blood Hybrid Nanofluid Flow with A g–T i O 2 Nanoparticles and Electrical Field in a Tilted Cylindrical W-Shape Stenosis Artery: A Finite Difference Approach. Symmetry, 15(6), 1242. [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, K., Eswaramoorthi, S., Chinnasamy, P., Jain, R., Sivasakthivel, R., Ali, R., & Devi, N. N. (2023). Heat and Mass Transport in Casson Nanofluid Flow over a 3-D Riga Plate with Cattaneo-Christov Double Flux: A Computational Modeling through Analytical Method. Symmetry, 15(3), 725. [CrossRef]
- Awwad, F. A., Ismail, E. A., & Gul, T. (2023). Heat and Mass Transfer Gravity Driven Fluid Flow over a Symmetrically-Vertical Plane through Neural Networks. Symmetry, 15(6), 1288. [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, R., Alessa, N., Eswaramoorthi, S., & Loganathan, K. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Darcy–Forchheimer Radiative Flow of a Water-Based Al2O3-Ag/TiO2 Hybrid Nanofluid over a Riga Plate with Heat Sink/Source. Symmetry, 15(1), 199. [CrossRef]
- T.A. Yusuf, F. Mabood, B.C. Prasannakumara, I.E. Sarris, Magneto-bioconvection flow of williamson nanofluid over an inclined plate with gyrotactic microorganisms and entropy generation, Fluid 6 (3) (2021) 109. [CrossRef]
- B.J. Gireesha, B.M. Shankaralingappa, B.C. Prasannakumar, B. Nagaraja, MHD flow and melting heat transfer of dusty Casson fluid over a stretching sheet with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model, Int. J. Ambient Energy (2020) 1–9. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Alazwari, M.R. Safaei, Combination effect of baffle arrangement and hybrid nanofluid on thermal performance of a shell and tube heat exchanger using 3-D homogeneous mixture model, Mathematics 9 (8) (2021) 881. [CrossRef]
- W.A. Khan, M. Ali, M. Shahzad, F. Sultan, M. Irfan, Z. Asghar, A note on activation energy and magnetic dipole aspects for Cross nanofluid subjected to cylindrical surface, Appl. Nanosci. 10 (8) (2020) 3235–3244. [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, HU, Zeeshan, Islam, S, Ali, B, Shah, Q, Ali, R. Implementation of shooting technique for Buongiorno nanofluid model driven by a continuous permeable surface. Heat Transfer. 2023; 52: 3119-3134. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




