Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
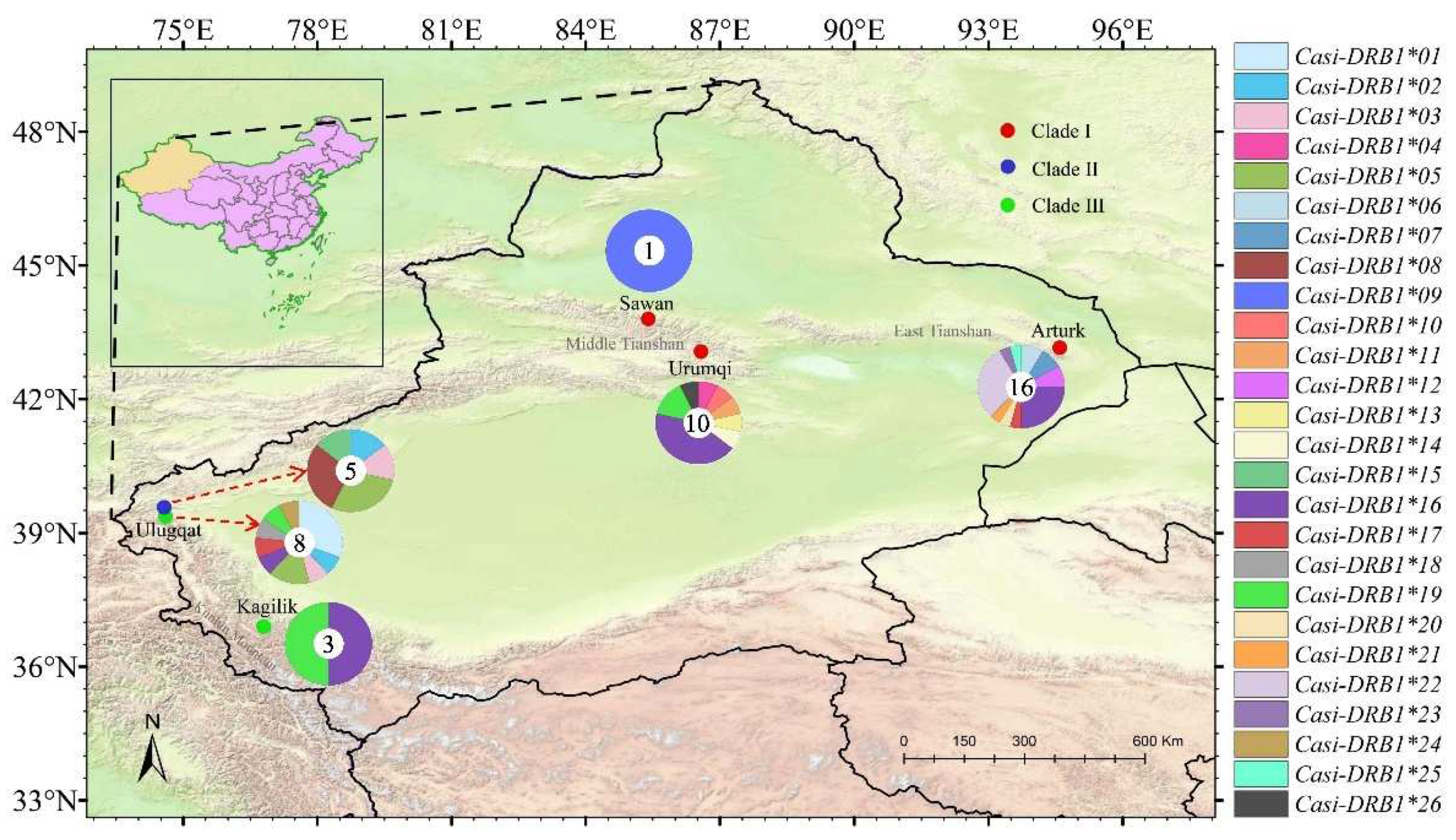
Samples
Experimental Procedures
MHC Genotyping
Data Analyses
Result
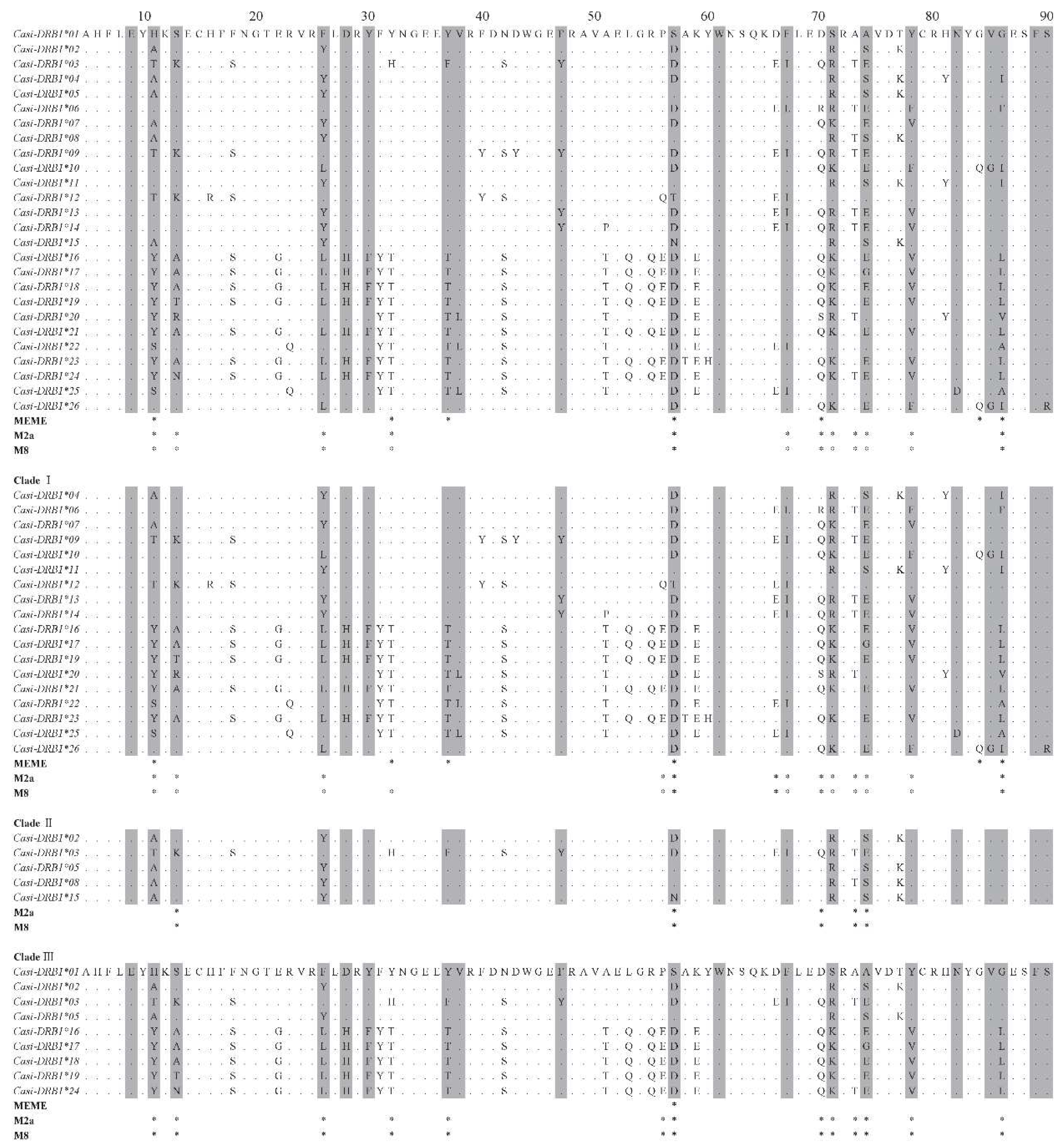
Diversity of DRB1 Alleles
Recombination and Selection on DRB1
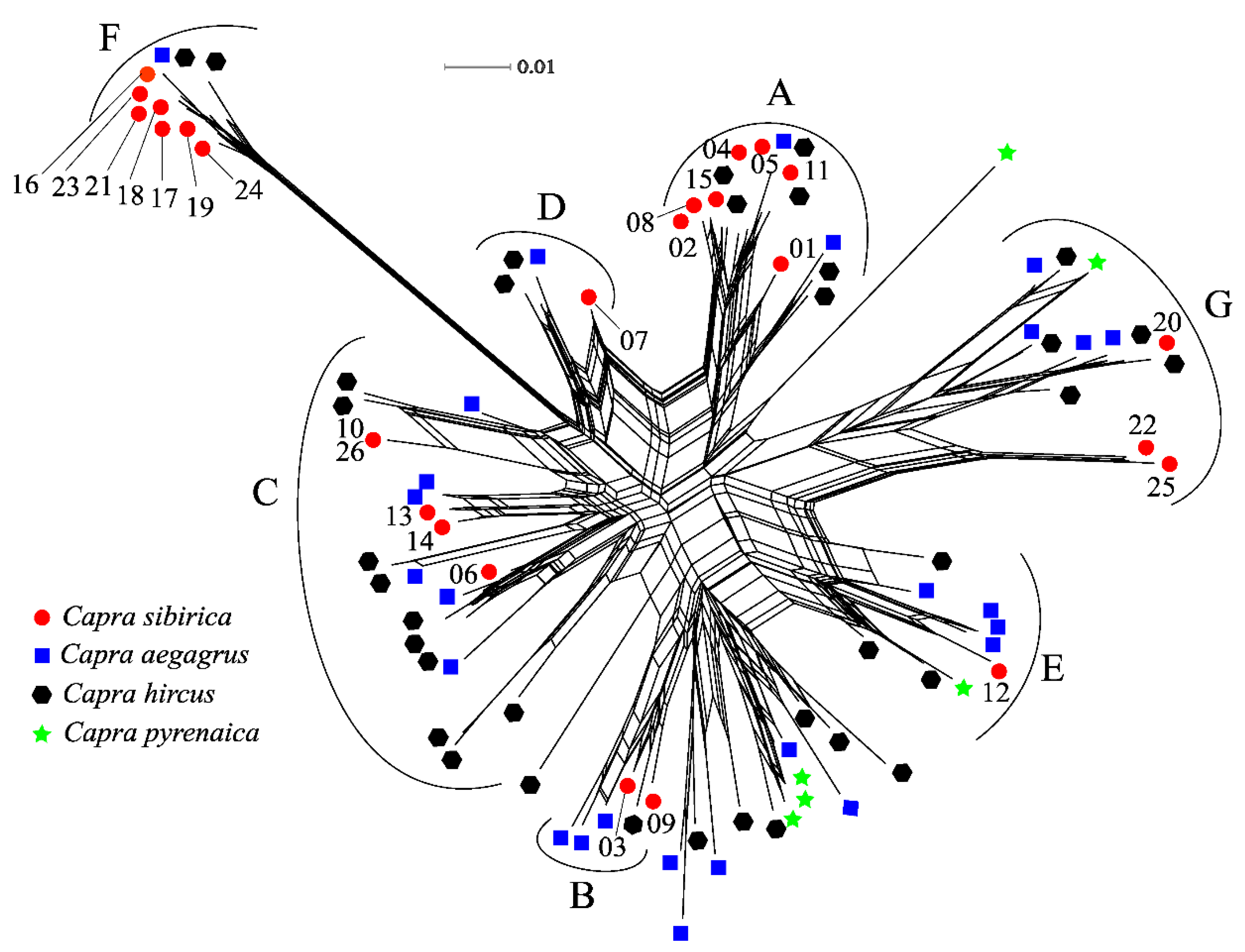
Phylogeny of DRB1 Alleles
Discussion
MHC DRB1 Diversity and Divergence
Evolution of the DRB1 Gene
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| No. | Clade | location | Individual identity | Casi-DRB1* | Number of verified alleles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | ||||||
| 1 | Ⅰ | Arturk | CSYW7 | + | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Arturk | CSYWa | + | + | + | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Arturk | CSYWb | + | + | + | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Arturk | CSYWc | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Arturk | CSYWd | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Arturk | CSYWe | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Arturk | CSYWi | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Arturk | CSYWj | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Arturk | CSYWk | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Arturk | CSYWB | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Arturk | CSYWD | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Arturk | CSYWE | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Arturk | CSYWF | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | Arturk | CSYWX1 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | Arturk | CSYWX2 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Arturk | CSYWX3 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | Sawan | SLG | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | Urumqi | CShx1 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | Urumqi | CShx2 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | Urumqi | CShx6 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | Urumqi | CShx10 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | Urumqi | CShx11 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | Urumqi | CShx13 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | Urumqi | CShx14 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | Urumqi | CShx16 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | Urumqi | CShx19 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | Urumqi | CShx20 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | Ⅱ | Ulugqat | CSnj1 | + | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | Ulugqat | CSnj3 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | Ulugqat | CSnjP1 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | Ulugqat | CSnjP2 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | Ulugqat | CSnjP3 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | Ⅲ | Ulugqat | CSnj5 | + | + | + | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | Ulugqat | CSnj6 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | Ulugqat | CSnj8 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | Ulugqat | CSnj9 | + | + | + | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | Ulugqat | CSnj10 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | Ulugqat | CSnj11 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | Ulugqat | CSnjJ1 | + | + | + | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | Ulugqat | CSnjJ2 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 41 | Kagilik | CSYC1 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 42 | Kagilik | CSYC2 | + | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 43 | Kagilik | CSYC3 | + | + | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 65 | ||||
References
- Ellegren, H. , Galtier, N. Determinants of genetic diversity. Nature Reviews Genetics 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J. Unfinished business: Evolution of the MHC and the adaptive immune system of jawed vertebrates. Annual Review of Immunology 2018, 36, 383–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, S. The importance of immune gene variability (MHC) in evolutionary ecology and conservation. Frontiers in Zoology 2005, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, L.A.; Bull, J.J. Fighting change with change: Adaptive variation in an uncertain world. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2022, 17, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Abduriyim, S.; Nishita, Y.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Raichev, E.; Vainola, R.; Kryukov, A.P.; Abramov, A.V.; Kaneko, Y.; Masuda, R. Evolution of MHC class I genes in Eurasian badgers, genus Meles (Carnivora, Mustelidae). Heredity 2019, 122, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduriyim, S.; Zou, D.H.; Zhao, H.B. Origin and evolution of the major histocompatibility complex class I region in eutherian mammals. Ecology and evolution 2019, 9, 7861–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungall, A.J.; Palmer, S.A.; Sims, S.K.; Edwards, C.A.; Ashurst, J.L.; Wilming, L.; Jones, M.C.; Horton, R.; Hunt, S.E.; Scott, C.E.; et al. The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6. Nature 2003, 425, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, M.; Abualrous, E.T.; Sticht, J.; Alvaro-Benito, M.; Stolzenberg, S.; Noe, F.; Freund, C. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Frontiers in Immunology 2017, 8, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, A.; Lahtela, E.L.; Anttila, V.; Petrek, M.; Grunewald, J.; van Moorsel, C.H.M.; Eklund, A.; Grutters, J.C.; Kolek, V.; Mrazek, F.; Kishore, A.; Padyukov, L.; Pietinalho, A.; Ronninger, M.; Seppanen, M.; Selroos, O.; Lokki, M.L. Snp variants in major histocompatibility complex are associate with sarcoidosis susceptibility—a joint analysis in four European populations. Frontiers in Immunology 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular biology of the cell. 5th Ed. New York: Garland Science. 2007.
- Brown, J.H.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Gorga, J.C.; Stern, L.J.; Urban, R.G.; Strominger, J.L.; Wiley, D.C. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature 1993, 364, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.W.; Dugdale, H.L.; Newman, C.; Macdonald, D.W.; Burke, T. MHC class II genes in the European badger (Meles meles): characterization, patterns of variation, and transcription analysis. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanth, K.U.; Nichols, J.D.; Kumar, N.S.; Link, W.A.; Hines, J.E. Tigers and their prey: Predicting carnivore densities from prey abundance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2004, 101, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawanshi, K.R.; Redpath, S.M.; Bhatnagar, Y.V.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Chaturvedi, V.; Smout, S.C.; Mishra, C. ; Impact of wild prey availability on livestock predation by snow leopards. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, G.; Li, H.; Tarif; Lv, H.; Ren, J.R.; Qiu, M.J.; Wang, H.B.; Anney; Aziguli; Abrimiti. Status of large mammals in the Taxkorgan Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Arid Zone Research 1987, 42, 53–71.
- Wang, X.F. Diagnosis and treatment of viral keratoconjunctivitis in Capra sibirica. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine 2007, 307, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.S.; Wang, M.Y.; Yang, W.K.; David, B. Ecology and biology of Capra sibirica: Current situation of studies. Chinese Journal of Ecology 2015, 34, 3553–3559. [Google Scholar]
- Reading, R.; Michel, S.; Suryawanshi, K.; Bhatnagar, Y.V. Capra sibirica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020, e.T42398A22148720. https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42398A22148720.en. Accessed on 31 May 2023.
- Thermistor, H. Diagnosis of streptococcal disease in Capra sibirica. Chinese Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine 2008, 4, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.D.; Li, T.; Yakp. Laboratory diagnosis and prevention of death of wild Capra sibirica caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Xinjiang animal husbandry 2012, 7, 55–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bayendrigan; An, N. Diagnosis and control of anthrax infection in wild Capra sibirica. Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine 2015, 34, 124.
- Zhu, X.S. Studies on feeding habits and homoerotic clusters of Capra sibirica [D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016.
- Yang, Q.S.; Feng, Z.J. China Red Book of Endangered Animals: Mammals. Beijing: Beijing Science Press. 1998, 314-317.
- Reading, R.; Shank, C. Capra sibirica. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2009.
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y. Red List of Chinese Species. Beijing: Higher Education Press. 2004.
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration, National Park Administration, 2021, http://www.forestry.gov.cn.
- Radwan, J.; Kawako, A.; Wójcik, J.M.; Babik, W. Mhc-drb3 variation in a free-living population of the European bison, Bison bonasus. Molecular Ecology 2010, 16, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainguy, J.; Worley, K.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. Low MHC DRB class II diversity in the mountain goat: Past bottlenecks and possible role of pathogens and parasites. Conservation Genetics 2007, 8, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollmer, J.L., Vargas, F.H., Parker, P.G. Low MHC variation in the endangered Galápagos penguin (Spheniscus mendiculus). Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 593–602. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejsmond, M.J.; Radwan, J. MHC diversity in bottlenecked populations: a simulation model. Conservation Genetics 2011, 12, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.K.; Piertney, S.B. Selection Maintains MHC Diversity through a Natural Population Bottleneck. Mol. Biol. Evol 2012, 29, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.R.; Dong, P.P.; Hirata, D.; Abduriyim, S. Mitochondrial DNA analyses revealed distinct lineages in an alpine mammal, Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica) in Xinjiang, China. Ecology and evolution 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abduriyim, S.; Nabi, A.; Halik, M. Low genetic diversity in the goitered gazelle Gazella subgutturosa (Guldenstadt, 1780) (Artiodactyla: Bovidae) in North-western China as revealed by the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. Acta Zoologica Bulgarrica 2018, 70, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Abduriyim, S.; Zibibulla, G.; Eli, S.; Ismayil, Z.; Halik, M. Phylogeny and genetic structure of the goitered gazelle (Artiodactyla, Bovidae) in north-western China indicated by the hypervariable mitochondrial control region. Systematics and Biodiversity 2018, 16, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amills, M.; Francino, O.; Sanchez, A. Nested PCR allows the characterization of Taql and Pstl RFLPs in the second exon of the caprine MHC class II DRB gene. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 1995, 48, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.W.; Dugdale, H.L.; Newman, C.; Macdonald, D.W.; Burke, T. MHC class II genes in the European badger (Meles meles): characterization, patterns of variation, and transcription analysis. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduriyim, S.; Nishita, Y.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Raichev, E.; Väinölä, R.; Kryukov, A.P.; Abramov, A.V.; Kaneko, Y.; Masuda, R. Diversity and evolution of MHC class II DRB gene in the Eurasian badger genus Meles (Mammalia: Mustelidae). Biological Journal of The Linnean Society 2017, 122, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, L.J.; Altet, L.; Angles, J.M.; Barnes, A.; Carter, S.D.; Francino, O.; Thomson, W. Nomenclature for factors of the dog major histocompatibility system (DLA), 1998: first report of the ISAG DLA Nomenclature Committee. Animal Genetics 2000, 31, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Bontrop, R.E.; Dawkins, R.L.; Erlich, H.A.; Gyllensten, U.B.; Heise, E.R.; Watkins, D.I. Nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complexes of different species: a proposal. Immunogenetics 1990, 31, 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ballingall, K.T.; Todd, H. An official nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complex allele sequences from the domestic goat (Capra hircus). HLA 2019, 93, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Molecular Biology and Evolution 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.H.; Nielsen, R. Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 908–917. [Google Scholar]
- Reche, P.A.; Reinherz, E.L. Sequence variability analysis of human class I and class II MHC molecules: functional and structural correlates of amino acid polymorphisms. Journal of Molecular Biology 2003, 331, 623–641. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.H. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.; Yang, Z. Likelihood models for detecting positively selected amino acid sites and applications to the HIV-1 envelope gene. Genetics 1998, 148, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.H.; Bielawski, J.P. Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.H.; Wong, W.S.W.; Nielsen, R. Bayes empirical Bayes inference of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Pond, S.L.K. Datamonkey 2.0: a modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Pond, S.L.K. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.P.; Lemey, P.; Lott, M.; Moulton, V.; Posada, D.; Lefeuvre, P. RDP3: a flexible and fast computer program for analyzing recombination. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2462–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.P.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A.; Williamson, C. A modified bootscan algorithm for automated identification of recombinant sequences and recombination breakpoints. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrov. 2005, 21, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Posada, D.; Gravenor, M.B.; Woelk, C.H.; Frost, S.D.W. GARD: a genetic algorithm for recombination detection. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 3096–3098. [Google Scholar]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W.; Pond, S.L.K. Datamonkey 2010: a suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huson, D.H.; Bryant, D. Application of Phylogenetic Networks in Evolutionary Studies, Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 254–267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wang, J.; Huang, G.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, L.M.; Li, H.J.; Li, M.; Zheng, N. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Cloud Liquid Water Volume over Three Main Mountains in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Research 2018, 35, 846–854. [Google Scholar]
- Ujvari, B.; Belov, K. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) markers in conservation biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5168–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Mainguy, J.; Worley, K.; Côté, S.D.; Coltman, D.W. Low MHC DRB class II diversity in the mountain goat: Past bottlenecks and possible role of pathogens and parasites. Conservation Genetics 2007, 8, 885–891. [Google Scholar]
- Bollmer, J.L., Vargas, F.H., Parker, P.G. Low MHC variation in the endangered Galápagos penguin (Spheniscus mendiculus). Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 593–602.
- Wenink, P.W.; Groen, A.F.; Roelke-Parker, M.E.; Prins, H.H.T. African buffalo maintain high genetic diversity in the major histocompatibility complex in spite of historically known population bottlenecks. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaiger, F.W.; Weyers, E.; Epplen, C.; Brün, J.; Ruff, G.; Crawford, A.; Epplen, J.T. The paradox of MHC-DRB exon/intron evolution: α-helix and β-sheet encoding regions diverge while hypervariable intronic simple repeats coevolve with β-sheet codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 37, 260–272. [Google Scholar]
- Angelone, S.; Jowers, M.J.; Min, A.R.M.; Fandos, P.; Prieto, P.; Pasquetti, M.; Cano-Manuel, F.J.; Mentaberre, G.; Olvera, J.R.L.; Raez-Bravo, A.; Espinosa, J.; Perez, J.M.; Soriguer, R.C.; Rossi, L.; Granados, J.E. Hidden MHC genetic diversity in the Iberian ibex (Capra pyrenaica). BMC Genet. 2018, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Blank, D.; Wang, M.Y.; da Silva, A. A.; Yang, W.K.; Ruckstuhl, K.; Alves, J. Diet differences between males and females in sexually dimorphic ungulates: A case study on Siberian ibex. European journal of wildlife research 2020, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Blank, D.; Wang, M.Y.; Yang, W.K. Different environmental requirements of female and male Siberian ibex, Capra sibirica. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadi, A.; Ben Slimen, H.; Smith, S.; Knauer, F.; Makni, M.; Suchentrunk, F. Positive selection and climatic effects on MHC class II gene diversity in hares (Lepus capensis.) from a steep ecological gradient. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 11514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Lansink, G.M.J.; Holmala, K.; Aspi, J.; Masuda, R. Diversity of the MHC class II DRB gene in the wolverine (Carnivora: Mustelidae: Gulo gulo) in Finland. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepfli, K.P.; Deere, K.A.; Slater, G.J.; Begg, C.; Begg, K.; Grassman, L.; Lucherini, M.; Veron, G.; Wayne, R.K. Multigene phylogeny of the Mustelidae: Resolving relationships, tempo and biogeographic history of a mammalian adaptive radiation. BMC Biol. 2008, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishita, Y.; Abramov, A.V.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Lin, L.K.; Watanabe, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Masuda, R. Genetic variation of the MHC class II DRB genes in the Japanese weasel, Mustela itatsi, endemic to Japan, compared with the Siberian weasel, Mustela sibirica. Tissue Antigens 2015, 86, 431–442. [Google Scholar]
- Amaike, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Uraguchi, K.; Masuda, R. Genetic Diversity of MHC Class II DRB1 Exon 2 in the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes) on Hokkaido, Japan. Zoological Science 2018, 35, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.A.B.; Browning, T.L.; Eldridge, M.D.B. Reduced mhc class ii diversity in island compared to mainland populations of the black-footed rock-wallaby (petrogale lateralis lateralis). Conservation Genetics 2011, 12, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Smaragdov, M.G.; Kudinov, A.A.; Uimari, P. Assessing the genetic differentiation of Holstein cattle herds in the Leningrad region using Fst statistics. Agricultural and Food Science 2018, 27, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meirmans, P.G. Using the AMOVA framework to estimate a standardized genetic differentiation measure. Evolution 2006, 60, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaschl, H.; Wandeler, P.; Suchentrunk, F.; Obexer-Ruff, G.; Goodman, S.J. Selection and recombination drive the evolution of MHC class II DRB diversity in ungulates. Heredity 2006, 97, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusch, T.B.; Langefors, Å. Inter- and Intralocus Recombination Drive MHC Class IIB Gene Diversification in a Teleost, the Three-Spined Stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 61, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartocillo, A.M.F.; Nishita, Y.; Abramov, A.V.; Masuda, R. Molecular evolution of MHC class II DRB exon 2 in Japanese and Russian raccoon dogs, Nyctereutes procyonoides (Carnivora: Canidae). Biological Journal of The Linnean Society 2020, 129, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishita, Y.; Kosintsev, P.A.; Haukisalmi, V.; Väinölä, R.; Raichev, E.G.; Murakami, T.; Abramov, A.V.; Kaneko, Y.; Masuda, R. Diversity of MHC class II DRB alleles in the Eurasian population of the least weasel, Mustela nivalis (Mustelidae: Mammalia). Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 2017, 121, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Sato, A.; Nagl, S.; O’hUigín, C. Molecular trans-species polymorphism. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 29, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartocillo, A.M.F.; Nishita, Y.; Abramov, A.V.; Masuda, R. Evolution of MHC class I genes in Japanese and Russian raccoon dogs, Nyctereutes procyonoides (Carnivora: Canidae). Mamm. Res. 2021, 66, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, E.; Murphy, W.J.; O’Brien, S.J. Molecular Dating and Biogeography of the Early Placental Mammal Radiation. Journal of Heredity 2001, 92, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clade | Sample | Number | Diversity indices | Tajima's D | ||
| size | π | aa | Supertype | |||
| Ⅰ | 27 | 18/16/14 | 0.092 | 0.190 | 0.427 | 0.184 |
| Ⅱ | 5 | 5/5/4 | 0.035 | 0.078 | 0.228 | -0.793 |
| Ⅲ | 11 | 9/8/8 | 0.084 | 0.177 | 0.402 | 0.705 |
| Total | 43 | 26/23/20 | 0.089 | 0.179 | 0.406 | 0.277 |
| Clade | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ |
| Ⅰ | 0.364 | 0.030 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.267 | 0.560 | |
| Ⅲ | -0.013 | 0.343 |
| Substitution type | Number of codons | Clade I | Clade II | Clade III | |
| dN | ABS | 20 | 1.203 ± 0.209 | 0.244 ± 0.149 | 0.690 ± 0.186 |
| Non-ABS | 66 | 0.288 ± 0.140 | 0.051± 0.084 | 0.132 ± 0.096 | |
| Overall | 86 | 0.514 ± 0.127 | 0.101 ± 0.081 | 0.257 ± 0.100 | |
| dS | ABS | 20 | 0.658 ± 0.293 | 0.087± 0.288 | 0.392± 0.298 |
| Non-ABS | 66 | 0.159 ± 0.170 | 0.015± 0.122 | 0.068± 0.208 | |
| Overall | 86 | 0.293± 0.158 | 0.037 ± 0.144 | 0.167± 0.180 | |
| ω | ABS | 20 | 1.828 | 2.805 | 1.760 |
| Non-ABS | 66 | 1.811 | 3.400 | 1.941 | |
| Overall | 86 | 1.754 | 2.730 | 1.539 |
| Clade | Models | lnL | Parameter estimates | PSS | LRT | d.f. | P value |
| Ⅰ | M1a | -1010.99 | P0 = 0.860, P1 = 0.140, ω0 = 0.041, ω1 = 1.000 | M1a vs M2a | 2 | <0.01 | |
| M2a | -972.69 | P0 = 0.572, P1 = 0.401, P2 = 0.026, ω0 = 0.099, ω1 = 1.000, ω2 = 13.181 | 11, 13, 26, 56, 57, 66, 67, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | ||||
| M7 | -1014.03 | P = 0.025, q = 0.155 | M7 vs M8 | 2 | <0.01 | ||
| M8 | -972.72 | P0 = 0.974, P = 0.107, q = 0.116, P1 = 0.026, ω = 13.366 | 11, 13, 26, 32, 56, 57, 66, 67, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | ||||
| Ⅱ | M1a | -445.45 | P0 = 0.524, P1 = 0.476, ω0 = 0.000, ω1 = 1.000 | M1a vs M2a | 2 | 0.0103 | |
| M2a | -440.88 | P0 =0.858, P1 = 0.000, P2 = 0.142, ω0 = 0.000, ω1 = 1.000, ω2 = 11.496 | 13, 57, 70, 73, 74 | ||||
| M7 | -446.65 | P = 1.970, q = 0.005 | M7 vs M8 | 2 | <0.01 | ||
| M8 | -440.88 | P0 = 0.859, P = 0.005, q = 2.990, P1 = 0.142, ω = 11.496 | 13, 57, 70, 73, 74 | ||||
| Ⅲ | M1a | -640.12 | P0 = 0.737, P1 = 0.263, ω0 = 0.000, ω1= 1.000 | M1a vs M2a | 2 | <0.01 | |
| M2a | -622.57 | P0 = 0.963, P1 = 0.000, P2 = 0.037, ω0 = 0.546, ω1= 1.000, ω2 = 18.992 | 11, 13, 26, 32, 37, 56, 57, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | ||||
| M7 | -640.26 | P = 0.005, q = 0.012 | M7 vs M8 | 2 | <0.01 | ||
| M8 | -622.47 | P0 = 0.969, P = 0.008, q = 0.005, P1 = 0.031, ω = 20.626 | 11, 13, 26, 32, 37, 56, 57, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | ||||
| All | M1a | -1132.10 | P0 = 0.898, P1 = 0.102, ω0 = 0.039, ω1 = 1.000 | ||||
| M2a | -1081.75 | P0 = 0.978, P1 = 0.000, P2 = 0.022, ω0 = 0.468, ω1 = 1.000, ω2 = 14.736 | 11, 13, 26, 32, 57, 67, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | M1a vs M2a | 2 | <0.01 | |
| M7 | -1134.53 | P = 0.016, q = 0.103 | |||||
| M8 | -1079.73 | P0 = 0.979, P = 0.021, q = 0.026, P1 = 0.021, ω = 14.775 | 11, 13, 26, 32, 57, 67, 70, 71, 73, 74, 78, 86 | M7 vs M8 | 2 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





