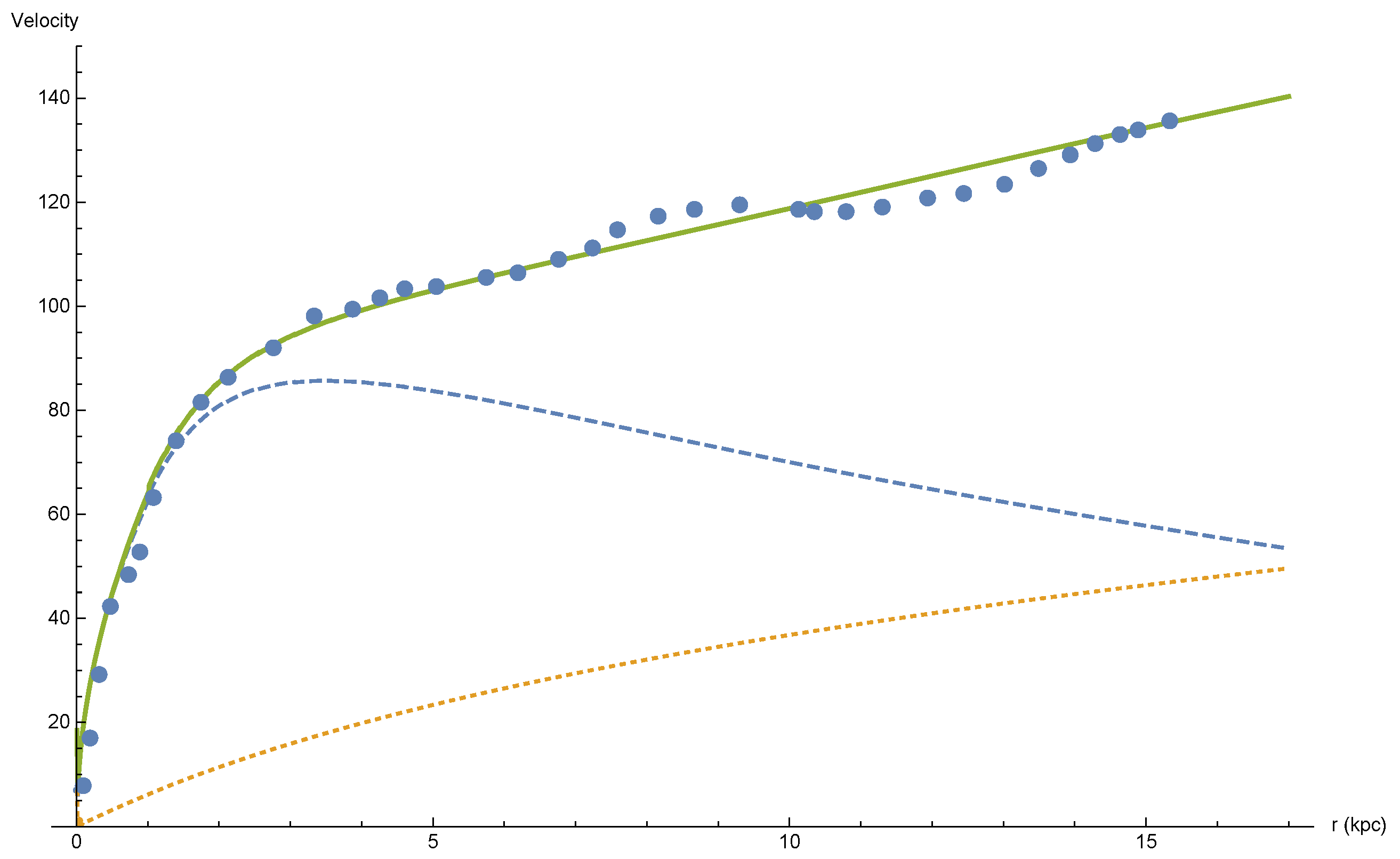1. Introduction
It is known that general relativity (GR) was corroborated by many types of observations. However, at this time, Einstein gravitational theory is at a crossroads. It has many observations to support it, and it has some very disturbing challenges. The triumphs that it has achieved in both astrophysical and cosmological scales have to be contrasted with the fact that GR needs to use two unconfirmed ingredients, dark matter and energy, to explain some of the observations. Dark matter has not only been speculated since the 1920s (when it was known as missing mass), but it has also become desperately needed as more and more of it had to be assumed on larger scales as new observations have become available. Here we will be concerned in the excess dark matter needed to explain observed gravitational lensing. Moreover, 40-year-underground and accelerator experimentation have failed to find any trace of it. The situation has become even more disquieting in the last years as the Large Hadron Collider did not find any super symmetric particles, the popular solution to the dark matter enigma.
While the dark matter hypothesis may eventually prevail, the situation is disturbing enough to consider the option that the paradigm might need to be amended if not replaced altogether. The present essay suggests such a modification. Unlike other solutions such as Milgrom’s MOND—modified Newtonian dynamics [
1], Mannheim’s Conformal Gravity [
2,
3,
4], Moffat’s MOG [
5] or
theories and scalar-tensor gravity [
6], the present approach is, the minimalist one adhering strictly to the razor of Occam principle. It suggests to replace dark matter by effects within standard GR. This is line with the teachings of Einstein himself: "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler".
Fritz Zwicky noticed in 1933 that the velocities of Galaxies within the Comma Cluster are much higher than those predicted by the virial calculation that assumes Newtonian theory [
7]. He calculated that the amount of matter required to account for the velocities could be 400 times greater with respect to that of visible matter, which led to suggesting dark matter throughout the cluster. In 1959, Volders, pointed out that stars in the outer rims of the nearby galaxy M33 do not move according to Newtonian theory [
8]. The virial theorem coupled with Newtonian Gravity implies that
, thus the expected rotation curve should at some point decrease as
. During the seventies Rubin and Ford [
9,
10] showed that, for a large number of spiral galaxies, this behavior can be considered standard: velocities at the outskirts of galaxies do not diminish— but they attain a plateau (or start to increase in a characteristic way) at some unique velocity, which differs for every galaxy. In previous works it was shown that such velocity curves can be deduced directly from GR if retardation is not neglected. The derivation of the retardation effect is described in previous publications [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17], this is depicted in
Figure 1. Similar graphs describing rotation curves of other galaxies can be found in [
18]. The Tully-Fisher relations [
19] can be also deduced from retarded gravity [
20].
Previous work assumed a test particle moving slowly as is appropriate for the case of galactic rotation curves, this is not so when the test particle is moving in the speed of light as in the case of gravitational lensing. Here, a different approach is needed as described in [
22,
23]. Yet, it is concluded that the apparent "dark mass" must be the same as in the galactic rotation curves.
In a recent work the virial theorem which was used by Zwicky to calculate the mass of the Comma cluster taking into account the velocities of Galaxies within the cluster was analyzed in the frame work of retarded gravity [
24]. It was concluded that any excess mass above the baryonic mass in the cluster can be explained using retardation effects. Thus retardation can also explain "dark matter" effects on scales which are large by many orders of magnitude than the galactic scales.
The connections between MOND and retarded gravity exist on many levels. Indeed MOND preceded the retarded gravity explanation of "dark matter" effects and thus served as an inspiration for the need to look more deeply into gravitational theory rather than invoke superficially some new type of matter in nature (which is not different in essence from the "quintessence" of ancient times). Another connecting feature of the two ideas, is the significance of the second derivative. In MOND the acceleration of the test particle is the feature that makes the gravitational force not Newtonian that is if it is lower than a certain acceleration . In retarded gravity it is the second derivative of mass density which cause retarded gravity to be different in a measurable way from Newtonian gravity.
In this paper we shall discuss the criteria of validity of corrections to Newtonian gravity in both theories, showing the similarities and differences. We will also show how both theories can be put in a similar mathematical form. Finally we discuss the relations between MOND and retarded gravity to general relativity.
2. Linear GR
Only in cases of extreme compact objects (black holes and neutron stars) and the very early universe we consider the solution of the full non-linear Einstein Equations [
11]. In most cases of astronomical interest (including the galactic case) a linear approximation to those equations around the flat Lorentz metric
is used, such that:
One then defines the quantity:
for non diagonal terms. For diagonal terms:
It was shown ([
25] page 75, exercise 37, see also [
26,
27,
28]) that for a proper gauge the Einstein equations are:
Equation (
4) can be solved such that [
29,
30]:
In [
31,
32,
33,
34] we explain why the symmetry between space and time is broken, which justifies the use of different notations for space and time.
; is a tiny number, hence, in the above calculation one can take
, to zeroth order in
. We now evaluate the affine connection in the linear approximation:
Notice that the affine connection has first order terms in
; hence, to the first order
appearing in the geodesic equation,
must be taken to zeroth order. In which:
For velocities much smaller than the speed of light in vacuum:
Hence, the current paper does not discuss the post-Newtonian approximation, in which matter travels at speeds close to the speed of light, but we do consider the retardation effects which are due to the finite propagation speed of the gravitational field. We emphasize that assuming
is not the same as stating
(with
R being the typical size of a galaxy) since:
now since in galaxies,
is huge (
seconds); it follows that,
can be dismissed but not
, for which
seconds. Inserting Equations (
6) and (
8) in the geodesic equation, we arrive at the approximate equation:
Taking a standard matter
, assuming
and, taking into account Equation (
8), we arrive at
, while the remaining tensor components are much smaller. Therefore,
is larger than other components of
. Notice that it is not possible to deduce from the magnitudes of quantities that a similar difference exists between the derivatives of those quantities. Gauge conditions in Equation (
4) lead to:
Thus, the zeroth derivative of
(which contains a
) is of similar order as the spatial derivative of
. Also the zeroth derivative of
(see equation (
10)) is of similar order as the spatial derivative of
. However, we can compare spatial derivatives of
and
and conclude that the former is larger. Taking into account equation (
3) and the above consideration, we write equation (
10) as:
Thus, the gravitational potential
can be estimated using Equation (
5):
and
is the force per unit mass. In the case that the mass density
does not depend on time, we may use the Newtonian instantaneous action at a distance. Notice, however, that it is improbable that
is static for a galaxy, as it accretes intergalactic medium gas. Also notice that the velocity of galactic and intergalactic matter components (stars, dust & gas) are implicit in the above formulation as the a time dependent density requires a velocity field according to the continuity Equation (52) of [
15].
Inserting equation (
13) into equation (
12) will lead to:
Thus a retarded potential does not only imply a retarded Newtonian force
, but in addition a pure "retardation" force
which decreases slowly than the Newtonian force with distance, explaining the peculiar form of the galactic rotation curves. We emphasize that this result is independent of any perturbation expansion in the delay time
as was done in [
15]. However, the perturbation expansion does shed some light on the nature of those force terms as will be explained in the next section.
3. Retardation Effects Beyond the Newtonian Approximation
The duration
may be tens of thousands of years, but may be short with respect to the duration in which the galactic density changes considerably. Thus, we write a Taylor series for the density:
By inserting Equations (
15) into Equation (
13), we will obtain:
The Newtonian potential is the first term, the second term has null contribution, and the third term is the lower order correction to the Newtonian theory:
The expansion given in Equation (
16), being a Taylor series expansion, is only valid for limited radii determined by the convergence of the infinite sum:
hence the current approximation can only be used in the near field regime, this is to be contrasted with the far field approximation used for gravitational radiation [
35,
36,
37]. The restriction is even more severe when one uses a second order expansion as was done in [
15].
If
terms can be neglected the total force per unit mass can be approximated as:
In the above
is a
non retarded Newtonian force. To see how this comes about from the existence of a Newtonian retarded force and retardation force as defined in equation (
14) we write those expressions up to order
using equation (
15), we thus have:
Adding those two terms we see that the first order terms in
cancel and we are left with the zeroth and second order terms which only partially cancel, as detailed in equation (
19). The cancellation of first order terms is indeed remarkable as was pointed out by Feynman [
38] with respect to the electromagnetic case.
first introduced by Newton is attractive, however, the retardation force
can be either attractive or repulsive. Newtonian force decreases as
, however, the retardation force doe not depend on distance as long as the Taylor approximation given in Equation (
15) holds. Below a certain distance, the Newtonian force dominates, but for larger distances the retardation force has the upper hand. Newtonian force can be neglected for distances significantly larger compared to the retardation distance:
is a duration associated with the second order derivative of the density . For , retardation can be neglected and only Newtonian forces need to be considered; this is the situation in the solar system.
If we need to calculate a gravitational force far away from the main mass we may write equation (
19) as:
This leads to the definition of a "dark matter" mass within a radius
r as:
As the galaxy accretes intergalactic gas, the galactic mass M becomes larger thus ; however, the intergalactic gas is depleted, and thus the rate at which the mass is accreted decreases resulting in , hence we have an attractive retardation force.
One may claim that since for the galaxy
and the total mass is conserved it must be that
for the matter outside the galaxy and thus retardation forces
inside and outside the galaxy should cancel out. This derivation, however, is false because equation (
19) is only valid when
is small, it is certainly not small if the rest of the universe outside the galaxy is taken into account. We have shown [
16] by a detailed model that a retardation force exist regardless if one assumes the expansion of equation (
15) or not.
4. When is Retardation Important?
As mass is accumulated in the galaxy or galaxy cluster, it must be depleted in the surrounding medium. This is due to the fact that the total mass is conserved; still, it is of interest to see if this intuition is compatible with a model of gas dynamics. For simplicity, we assume that the gas is a barotropic ideal fluid and its dynamics are described by the Euler and continuity equations as follows:
where the pressure
is assumed to be a given function of the density,
is a partial temporal derivative,
has its standard meaning in vector analysis and
is the material temporal derivative. We have neglected viscosity terms due to the low gas density.
4.1. General Considerations
Let us now take a partial temporal derivative of equation (
24) leading to:
Using equation (
24) again we obtain the expression:
We divide the left and right hand sides of the equation by
as in equation (
14) and obtain:
Since
is rather small in galaxies and galaxy clusters it follows that
is also small unless the density or the velocity have significant spatial derivatives. A significant acceleration
resulting from a considerable force can also have a decisive effect. The depletion of available gas can indeed cause such gradients. Taking the volume integral of the left and right hand sides of equation (
28) and using Gauss theorem we arrive at the following equation:
The surface integral is taken over a surface encapsulating the galaxy or galaxy cluster. This leads according to equation (
23) to a "dark matter" effect of the form:
Thus we obtain the order of magnitude estimation:
In the above we define three gradient lengths:
We can also write:
in which the smallest gradient length will be the most significant one in terms of the "dark matter" phenomena. Thus:
In the depletion model we assume that
associated with density gradients is the shortest length scale. For galaxies we have
, hence the factor
should be around
to have a significant "dark matter" effect. A detailed model of the depletion process in galaxies leading to the desired second derivative of galactic mass is given in [
15] and will not be repeated here.
4.2. Retardation in Terms of Acceleration
MOND changes Newton’s gravity when the acceleration
a is about the size of a small typical acceleration
or smaller, it coincides with Newton’s theory when
. Retardation is important according to equation (
34) when:
Where
is a certain fraction of the Newtonian force, say
. Now if we define a radial acceleration
it follows that for retardation effects to become important we must have:
However, as decreases as this means that this inequality will be satisfied more easily for larger r. Thus "dark matter" effects can be interpreted in terms of acceleration as MOND postulates. However, acceleration does not need to be small or equal to in order to have "dark matter" effects, rather acceleration must be bigger than some critical acceleration which depends on radial distance. Thus, the inequality becomes more easy to satisfy at large radial distances, in which case the acceleration is indeed quite small. A small acceleration is of course the hallmark of MOND and signifies the parameter domain in which MOND corrections are required.
5. MOND and Retarded Gravity Compared
According to MOND [
1] the force of gravity is modified as follows:
In the above
, is the interpolation function that should be one for
. Let us assume a "standard interpolating function":
if
,
. A particle revolving in a unchanging radius will have a centrifugal acceleration of
and thus:
For the constant
v at a far away distance, this expression is similar to the retardation force given in equation (
22) and thus:
Milgrom found
to be most fitting to the data. The velocity at
from the center of the M33 galaxy is 135,640
. We thus obtain
and a retardation time of:
This amounts to a typical accumulation acceleration time scale of
20,129 years and a retardation distance of:
which seems reasonable according to our fitting estimates [
15]. Hence, MOND can help estimate retardation theory quantities. Of course equation (
40) does not make much sense as the left hand side is constant and the right hand side depends on the distance as
(provided
v is constant). Hence it can be used for a single distance at most.
6. Retarded Gravity as a New Type of MOND
Let us assume a new type of interpolation function which is admittedly nonstandard:
if
,
. A particle revolving in a unchanging radius will have a centrifugal acceleration of
and thus:
For the constant
v at a far away distance (deep MOND regime), this expression is similar to the retardation force given in equation (
22) and thus we obtain a spatial independent expression for the mass second derivative:
which leads to the Tully-Fisher relation:
alternatively we may express
in terms of
as follows:
In this sense retardation theory is just a MOND type theory with non-standard interpolation function:
7. Conclusions
Retardation theory is a legitimate approximation to GR, MOND with a standard interpolation function is not, hence it is in contradiction to GR, this is openly admitted. All the attempts to build a theory which satisfies diffeomorphism symmetry and give MOND as a limit (TEVES for example) have violated even a more basic rule of science the rule of parsimony (William of Occam, Newton & Einstein) which states: "That everything must be explained as simple as possible but not simpler than that" (Einstein’s version). This means that it is forbidden to postulate new fields, axioms & laws of nature, if the phenomena under consideration can be explained with the known laws of nature.
Under linear approximation we have solved Einstein field equations in term of retarded solutions. Those solutions were used to derive the trajectory of particles and light rays. This is followed by a discussion on the physical requirements needed in order to derive "dark matter" effects from retardation and a detailed model showing how those requirements are satisfied.
Lorentz symmetry invariance does not allow action at a distance potentials and forces, but retarded solutions are allowed. Retardation is significant for large distances and large second derivatives. It should be emphasized that the retardation approach does not require that velocities in,
v in the gravitating body are high; in fact, galactic & galactic cluster bodies (stars, gas) move slowly with respect to the speed of light—thus the quantity
. Typical velocities in galaxies are
(see
Figure 1), which makes
to be about
or smaller. However, every gravitational system, even if it consists of subluminal entities, has a retardation distance, above which retardation cannot be neglected. Natural systems, for example a star or a galaxy and even a galactic cluster, exchanges mass with its environment. The sun loses mass through solar wind and galaxies accrete matter which originate in the intergalactic medium. Thus all natural (gravitational) systems have a finite retardation distance. This leads to quantitative inquiry: what is the actual size of the retardation distance? The modification of the solar mass is quite small and thus the retardation distance of the solar system is extremely large, we can thus neglect retardation within the solar system. On the other hand, for the M33 galaxy, velocities indicate that retardation cannot be neglected. The retardation distance was calculated in [
15] to be roughly
kpc for M33; other galaxies of different types have shown similar results [
14,
18].
We underline, that if extra galactic mass is abundant (or totally consumed),
and the retardation force vanish. As was reported [
39] for NGC1052-DF2.
We emphasize that the terms in the GR equations responsible for gravitational radiation recently discovered are also the cause for the peculiar shape of the rotation curves of galaxies and gravitational lensing. The approximation used here is not a far field approximation but a near field one. Indeed, the expansion (
16), being second order, is only valid up to limited radii:
This is reasonable since the extension of the rotation curve in galaxies and the distance of lensing trajectories from galaxies is the same order of magnitude as the size of the galaxy. Further discussion of the relation between the approximation used and the exact expression can be found in [
16].
The case in which the dimensions of the source is much smaller than the distance to the observer will result in a different valid approximation, leading to the famous quadruple expression of gravitational radiation, as derived by Einstein [
35] and corroborated (indirectly) in 1993 by R. A. Hulse and J. H. Taylor. The observation of the Hulse–Taylor binary pulsar has given the first (indirect) proof of gravitational waves [
36]. On 11 February 2016, the LIGO and Virgo Collaboration announced that they made the first (direct) observation of gravitational waves. The observation was made somewhat earlier, on 14 September 2015, using the LIGO detectors. The gravitational waves were caused by the merging of a binary black hole system [
37]. Thus, in this paper we study only a near-field gravitational radiation as opposed to previous papers describing far- field results.
Retardation theory’s approach described here is minimalistic (it satisfies the Occam’s razor rule), and is not related to observations that are beyond the near-field, thus it does not contradict GR observational consequences (nor Newtonian theory, as the retardation effect is negligible for "small" distances). The perfect fit to the rotation curve and gravitational lensing is achieved with a single parameter and we do not adjust the mass to light ratio in order to obtain a better fit as is done by some other authors. Retardation effects beyond gravity, in particular with respect to electromagnetic theory were studied in [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45].
We have shown that retardation theory can be thought of as a MOND type theory but with a non standard interpolation function. The low acceleration condition of MOND is compatible with the condition for the necessity of retardation corrections.
References
- Milgrom, M. A modification of the Newtonian dynamics as a possible alternative to the hidden mass hypothesis. Astrophys. J. 1983, 270, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, P.D.; Kazanas, D. Exact vacuum solution to conformal Weyl gravity and galactic rotation curves. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, P.D. Linear Potentials and Galactic Rotation Curves. Astrophys. J. 1993, 149, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, P.D. Are Galactic Rotation Curves Really Flat? Astrophys. J. 1997, 479, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, J. W. (2006). "Scalar-Tensor-Vector Gravity Theory". Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics. 2006 (3): 4. arXiv:gr-qc/0506021.
- Corda, C. (2009) "Interferometric detection of gravitational waves: the definitive test for General Relativity" Int. Jour. Mod. Phys. D 18, 2275. arXiv:0905.2502 [gr-qc].
- Zwicky, F. On a New Cluster of Nebulae in Pisces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1937, 23, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volders, L.M.J.S. Neutral Hydrogen in M33 and M101. Bull. Astr. Inst. Netherl. 1959, 14, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, V.C.; Ford, W.K., Jr. Rotation of the Andromeda Nebula from a Spectroscopic Survey of Emission Regions. Astrophys. J. 1970, 159, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, V.C.; Ford, W.K., Jr.; Thonnard, N. Rotational Properties of 21 Sc Galaxies with a Large Range of Luminosities and Radii from NGC 4605 (R = 4kpc) to UGC 2885 (R = 122kpc). Astrophys. J. 1980, 238, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, A. The effect of Retardation on Galactic Rotation Curves. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1239 (2019) 012006.
- Yahalom, A. Retardation Effects in Electromagnetism and Gravitation. In Proceedings of the Material Technologies and Modeling the Tenth International Conference, Ariel University, Ariel, Israel, 20–24 August 2018. (arXiv:1507.02897v2). [Google Scholar]
- Yahalom, A. Dark Matter: Reality or a Relativistic Illusion? In Proceedings of Eighteenth Israeli-Russian Bi-National Workshop 2019, The Optimization of Composition, Structure and Properties of Metals, Oxides, Composites, Nano and Amorphous Materials, Ein Bokek, Israel, 17–22 February 2019.
- Wagman, M. Retardation Theory in Galaxies. Ph.D. Thesis, Senate of Ariel University, Samria, Israel, 23 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Asher Yahalom "Lorentz Symmetry Group, Retardation, Intergalactic Mass Depletion and Mechanisms Leading to Galactic Rotation Curves. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1693. [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, A. Effects of Higher Order Retarded Gravity. Universe. 2021; 7(7):207. [CrossRef]
- A. Yahalom "The Cosmological Decrease of Galactic Density and the Induced Retarded Gravity Effect on Rotation Curves" Proceedings of IARD 2020. 2021 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1956 012002.
- Michal Wagman, Lawrence P. Horwitz, and Asher Yahalom "Applying Retardation Theory to Galaxies" 2023 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2482 012005. Proceedings of the 13th Biennial Conference on Classical and Quantum Relativistic Dynamics of Particles and Fields (IARD 2022), 05/06/2022 - 09/06/2022 Prague, Czechia. [CrossRef]
- R. B. Tully and J. R. Fisher, Astron. Astrophys. 54 (1977) 661.
- A. Yahalom "Tully - Fisher Relations and Retardation Theory for Galaxies" International Journal of Modern Physics D, (2021), Volume No. 30, Issue No. 14, Article No. 2142008 (8 pages). ©World Scientific Publishing Company. [CrossRef]
- Corbelli, E. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2003; 342, 199–207. [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, A. Lensing Effects in Retarded Gravity. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Yahalom "Lensing Effects in Galactic Retarded Gravity: Why "Dark Matter" is the Same for Both Gravitational Lensing and Rotation Curves" IJMPD Vol. 31, No. 14, 2242018 (10 pages), received 23 May 2022, Accepted 31 August 2022, published online 30 September 2022. [CrossRef]
- Asher Yahalom "The Virial Theorem for Retarded Gravity" accepted for publication in the International Journal of Modern Physics D. (Honourable mention Gravity Research Foundation 2023). [CrossRef]
- Narlikar, J.V. Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Eddington, A.S. The Mathematical Theory of Relativity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.S.; Wheeler, J.A. Gravitation; W.H. Freeman & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, T. (2010) "Gravitation - Foundations and Frontiers" Cambridge University Press.
- Sean M. Carroll, "Lecture Notes on General Relativity", https://arxiv.org/abs/gr-qc/9712019. 9712.
- Yahalom, A. The Geometrical Meaning of Time. Found. Phys. 2008, 38, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, A. The Gravitational Origin of the Distinction between Space and Time. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2009, 18, 2155–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher Yahalom "Gravity and the Complexity of Coordinates in Fisher Information" International Journal of Modern Physics D, Vol. 19, No. 14 (2010) 2233–2237, ©World Scientific Publishing Company. [CrossRef]
- Asher Yahalom "Gravity, Stability and Cosmological Models". International Journal of Modern Physics D. Published: 10 October 2017 issue (No. 12).
- Einstein, A. Näherungsweise Integration der Feldgleichungen der Gravitation. Sitzungsberichte der Königlich Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften Berlin; Part 1; 1916; pp. 688–696. The Prusssian Academy of Sciences, Berlin, Germany.
- Nobel Prize, A. Press Release The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences; 1993.The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Stockholm, Sweden.
- Castelvecchi, D.; Witze, W. Einstein’s gravitational waves found at last. Nature News 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. P. Feynman, R. B. Leighton & M. L. Sands, Feynman Lectures on Physics, Basic Books; revised 50th anniversary edition (2011).
- van Dokkum, P.; Danieli, S.; Cohen, Y.; Merritt, A.; Romanowsky, A.J.; Abraham, R.; Brodie, J.; Conroy, C.; Lokhorst, D.; Mowla, L.; et al. A galaxy lacking dark matter. Nature 2018, 555, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuval, M.; Yahalom, A. Newton’s Third Law in the Framework of Special Relativity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2014, 129, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuval, M.; Yahalom, A. Momentum Conservation in a Relativistic Engine. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2016, 131, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, A. Retardation in Special Relativity and the Design of a Relativistic Motor. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailendra Rajput, Asher Yahalom & Hong Qin "Lorentz Symmetry Group, Retardation and Energy Transformations in a Relativistic Engine" Symmetry 2021, 13, 420. [CrossRef]
- Rajput, Shailendra, and Asher Yahalom. 2021. "Newton’s Third Law in the Framework of Special Relativity for Charged Bodies" Symmetry 13, no. 7: 1250. [CrossRef]
- Yahalom, Asher. 2022. "Newton’s Third Law in the Framework of Special Relativity for Charged Bodies Part 2: Preliminary Analysis of a Nano Relativistic Motor" Symmetry 14, no. 1: 94. [CrossRef]
- Herbert Goldstein, Charles P. Poole, Jr., John L. Safko, Classical Mechanics, 3rd Edition ©2002, Pearson.
- Lasserre, T., et al., and EROS Collaboration, 2000, Astron. Astrophys. 355, L39.
- Tisserand, P., et al. (EROS-2 Collaboration). Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 387.
- Rega, M.W.; Vogel, S.N. Astrophysical Journal 1994, 434, 536. [CrossRef]
- Fodera-Serio, G.; Indorato, L.; Nastasi, P. Hodierna’s Observations of Nebulae and his Cosmology. J. Hist. Astron. 1985, 16, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bergh, S. The Galaxies of the Local Group; Cambridge Astrophysics Series 35; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; p. 72. ISBN 978-0-521-65181-3. [Google Scholar]
- Binney, J.; Tremaine, S. Galactic Dynamics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Corbelli, E.; Salucci, P. The extended rotation curve and the dark matter halo of M33. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).