Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
20 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background and Significance of the Research
2. Research Data
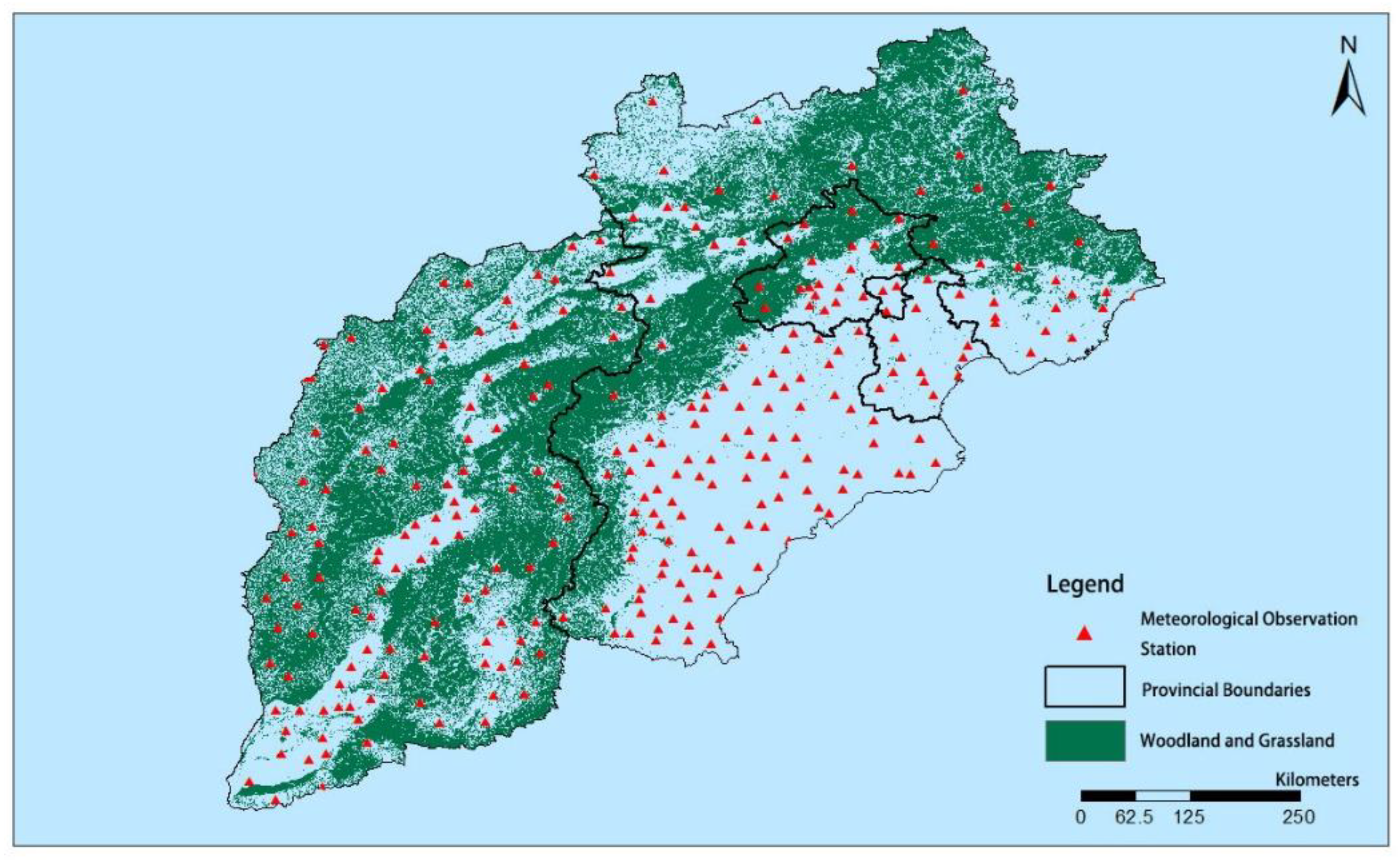
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
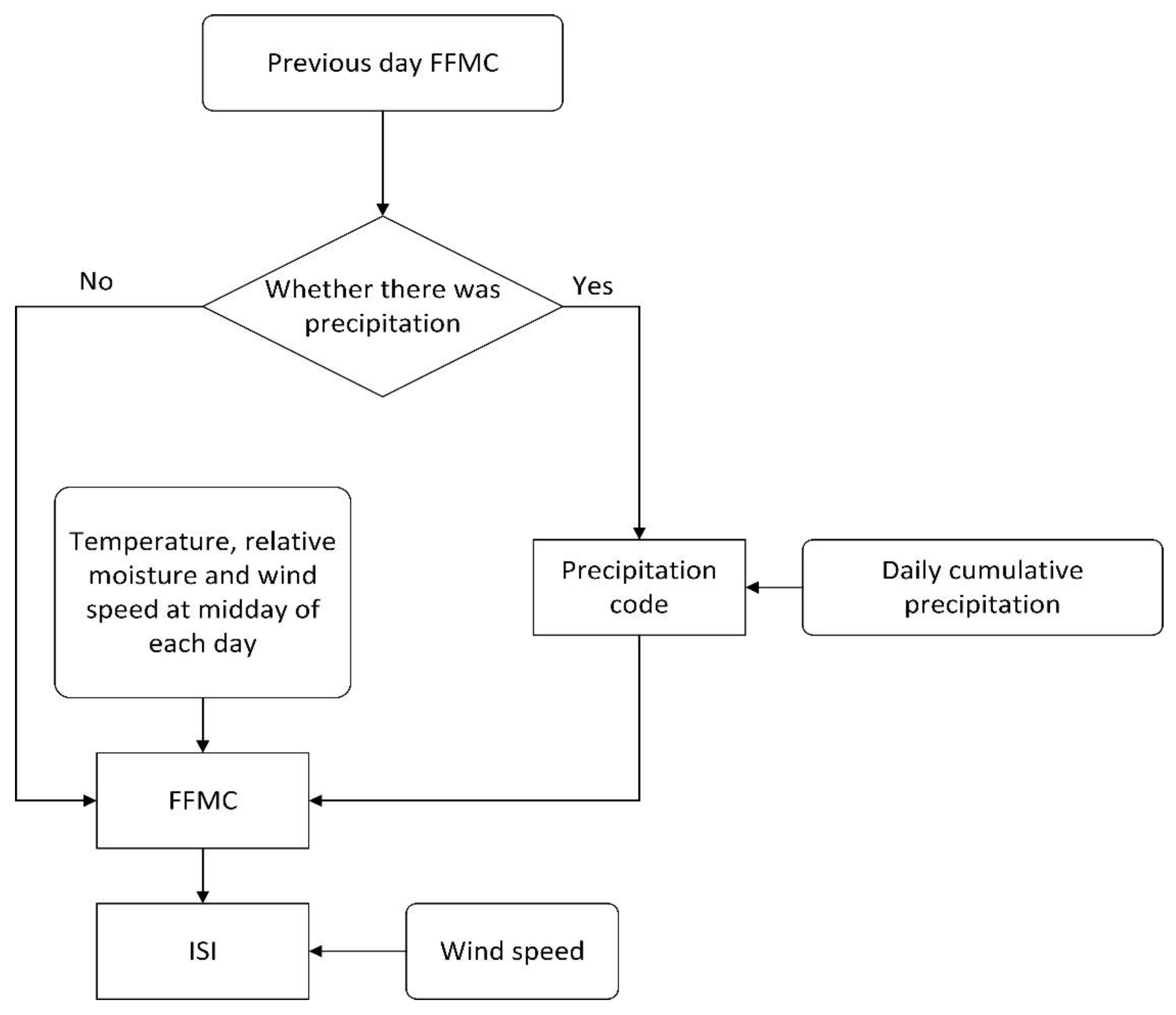
2.3. The Model Used
3. Results
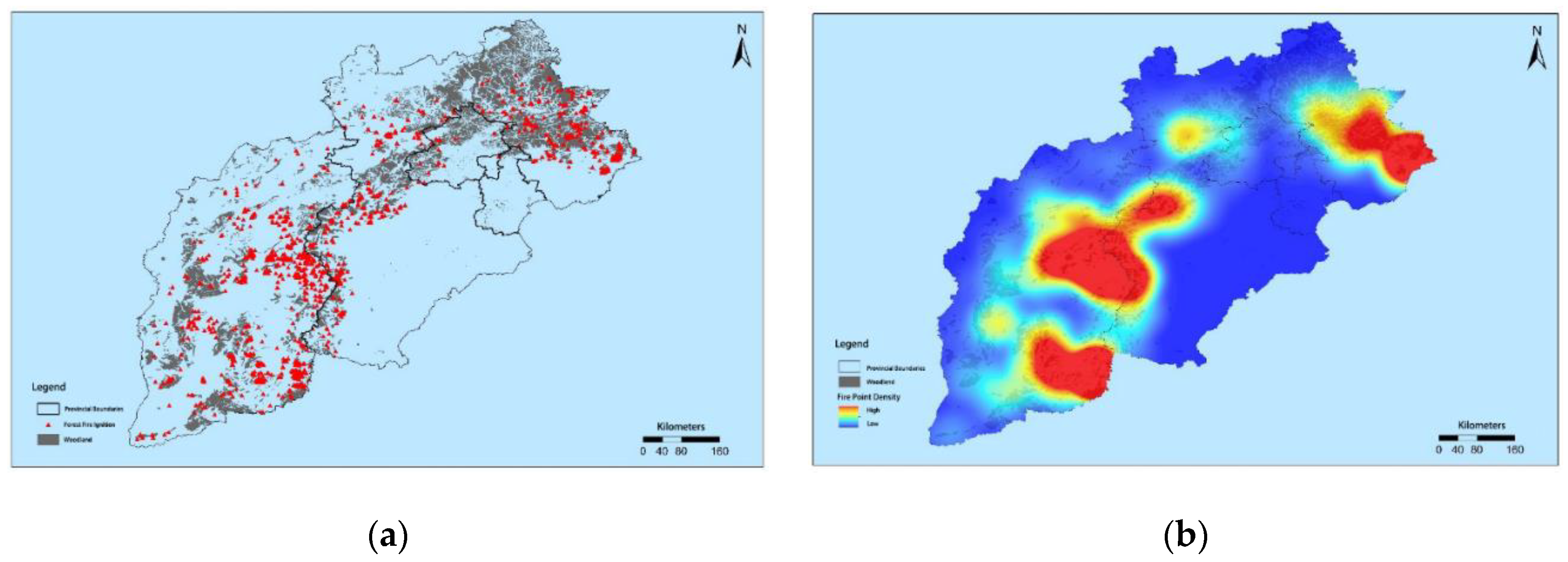
3.1. Forest Fire Distribution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi Region
3.2. Fire Risk Weather Index Analysis
3.2.1. Characteristics of the Fire Risk Weather Index
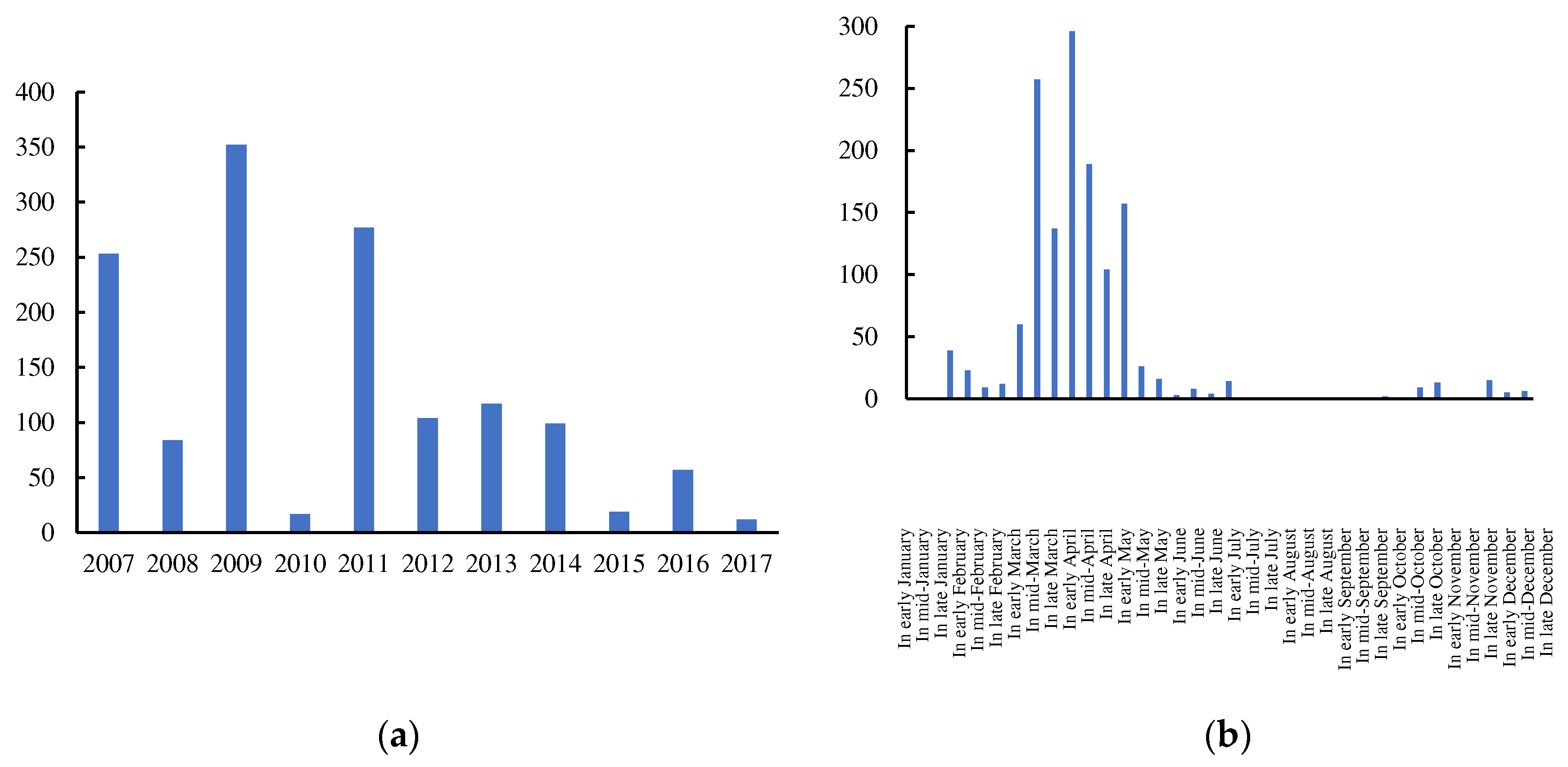
3.2.2. Weather Index Characteristics of Fire Starting Days at Fire Points from 2010 to 2017
3.2.3. ISI Frequency Characteristics in Priority Areas
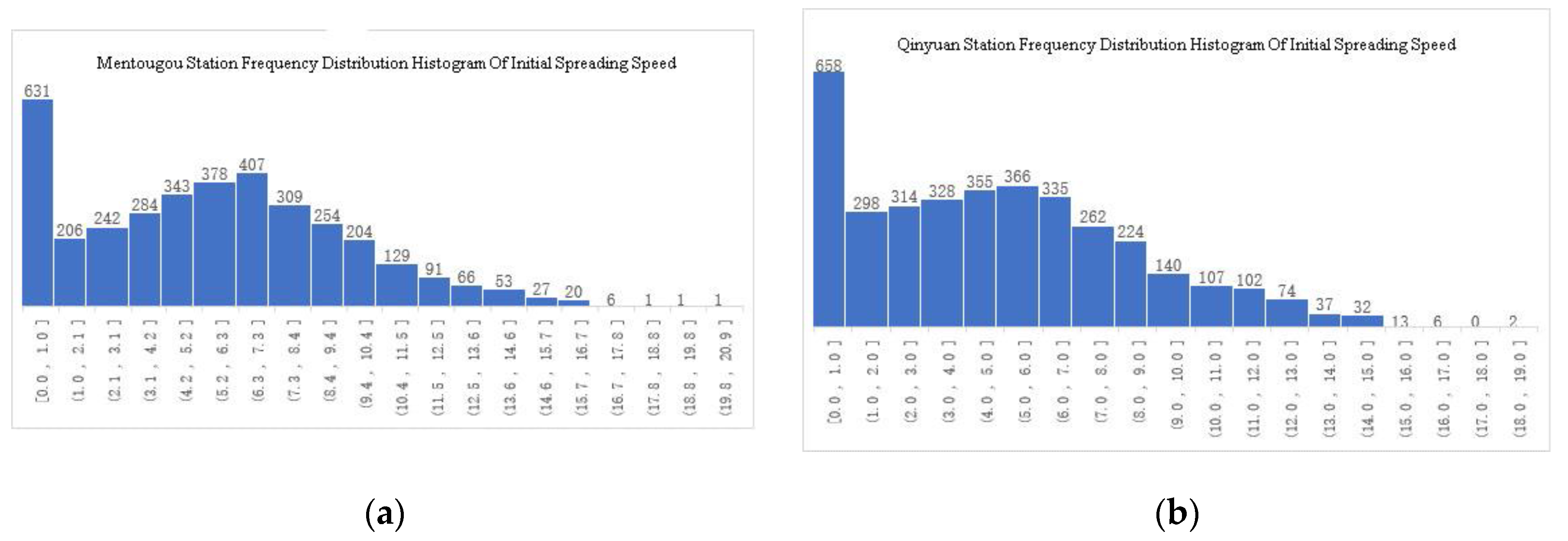
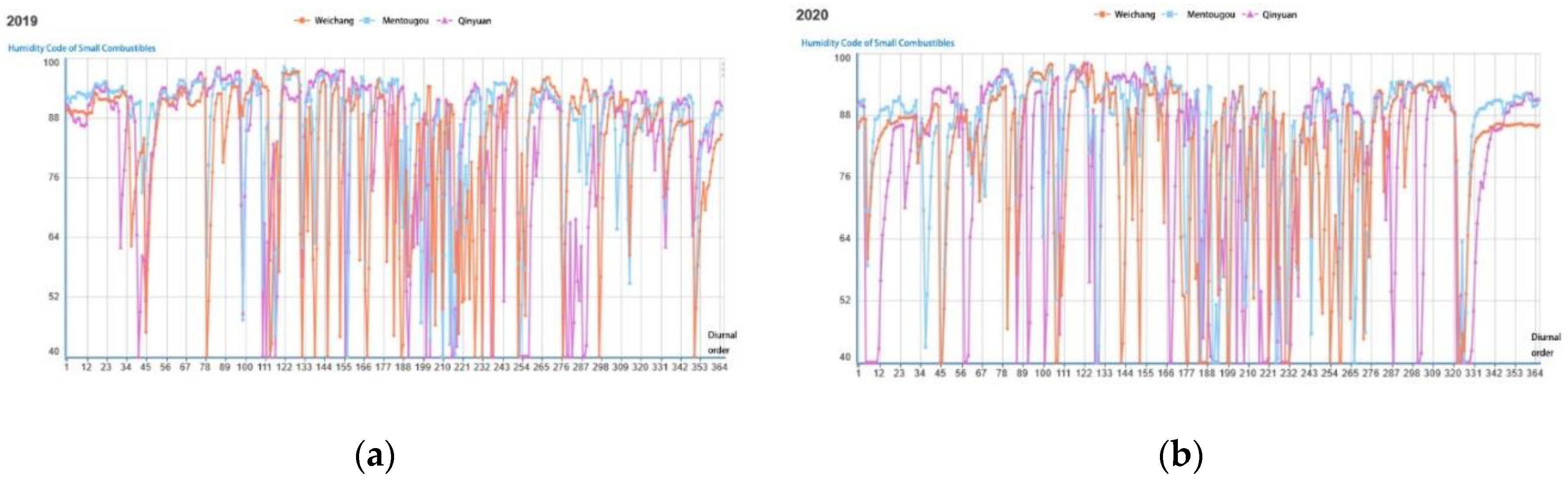
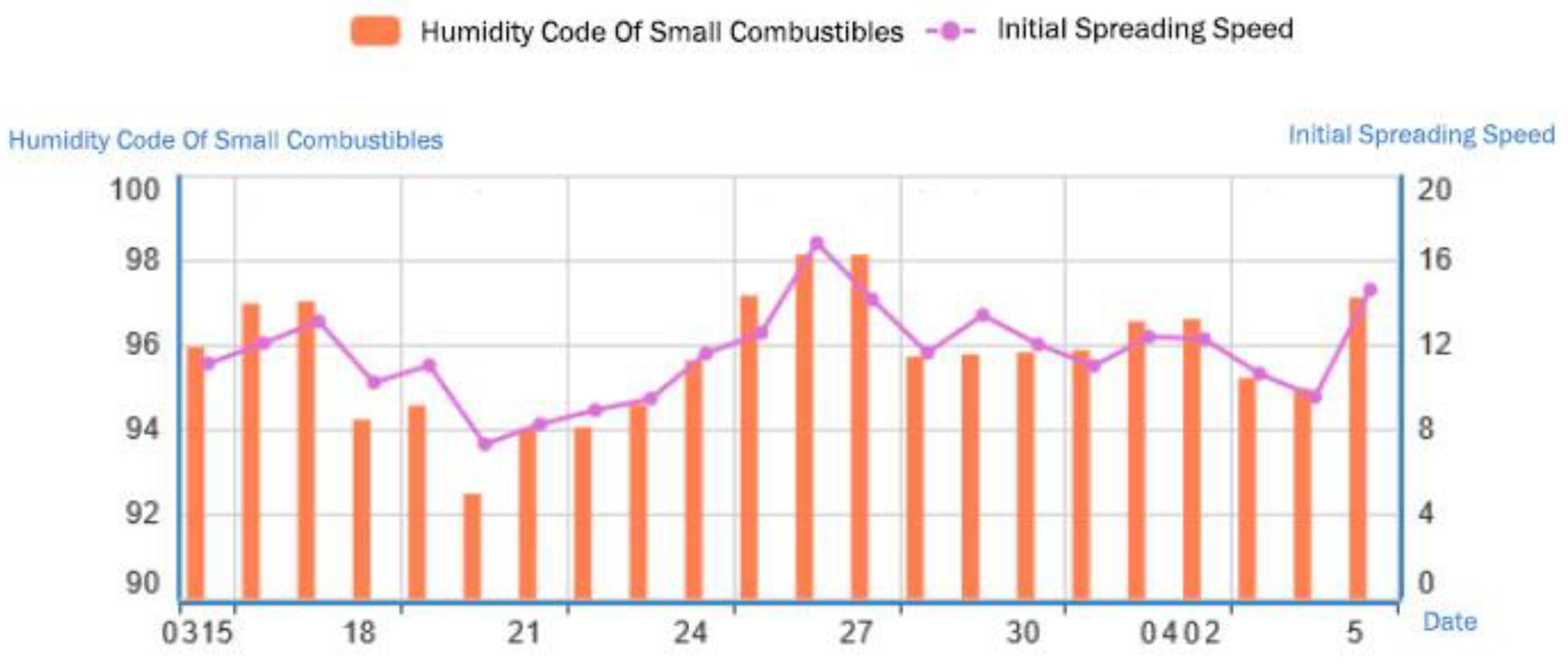
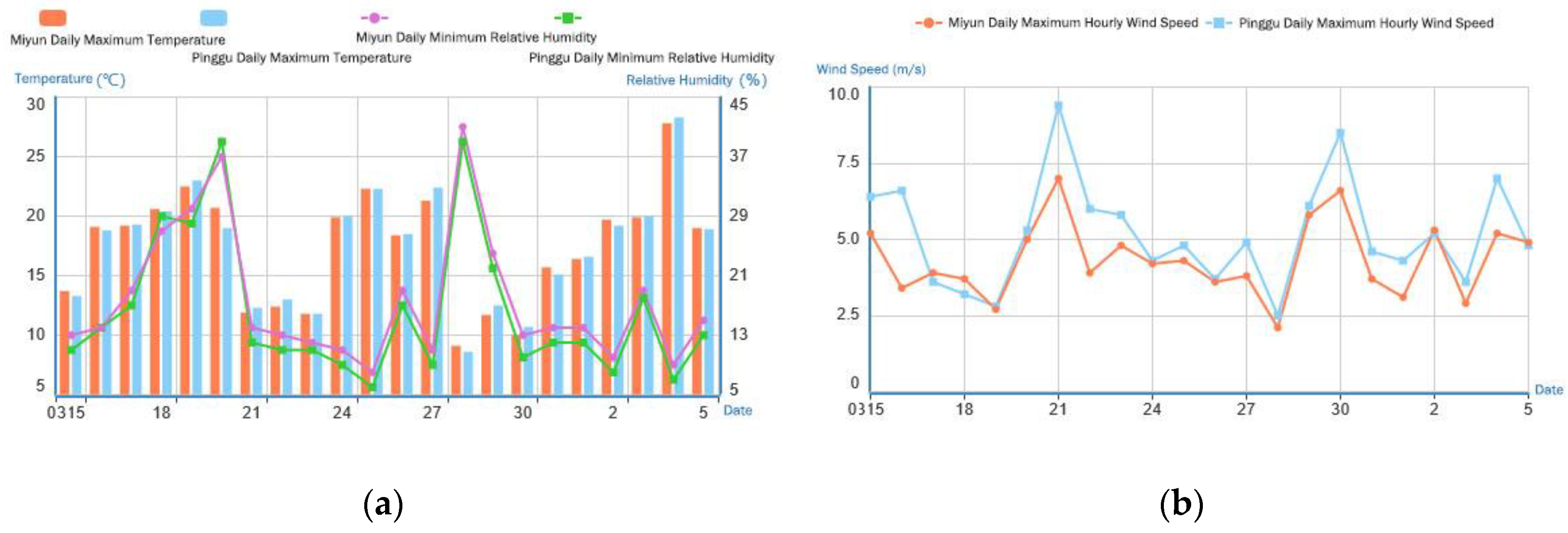
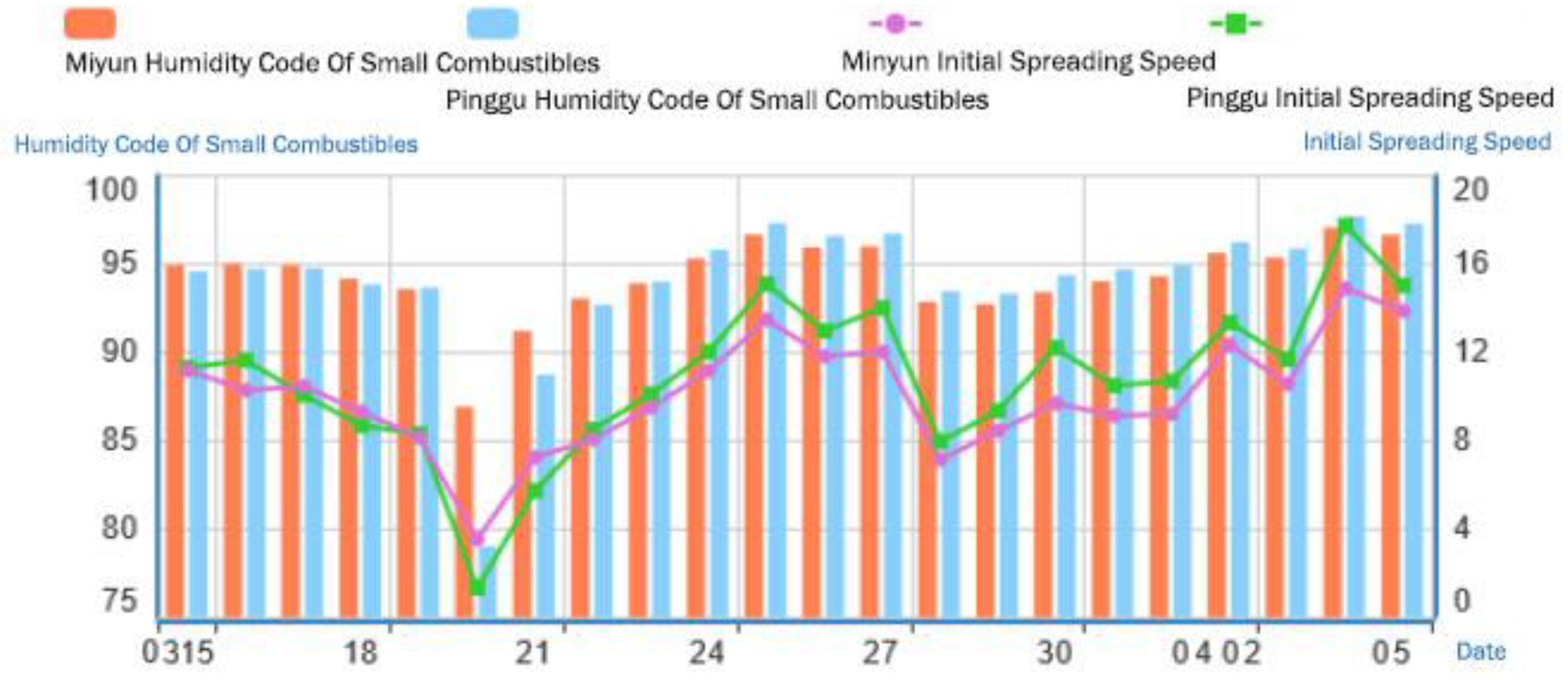
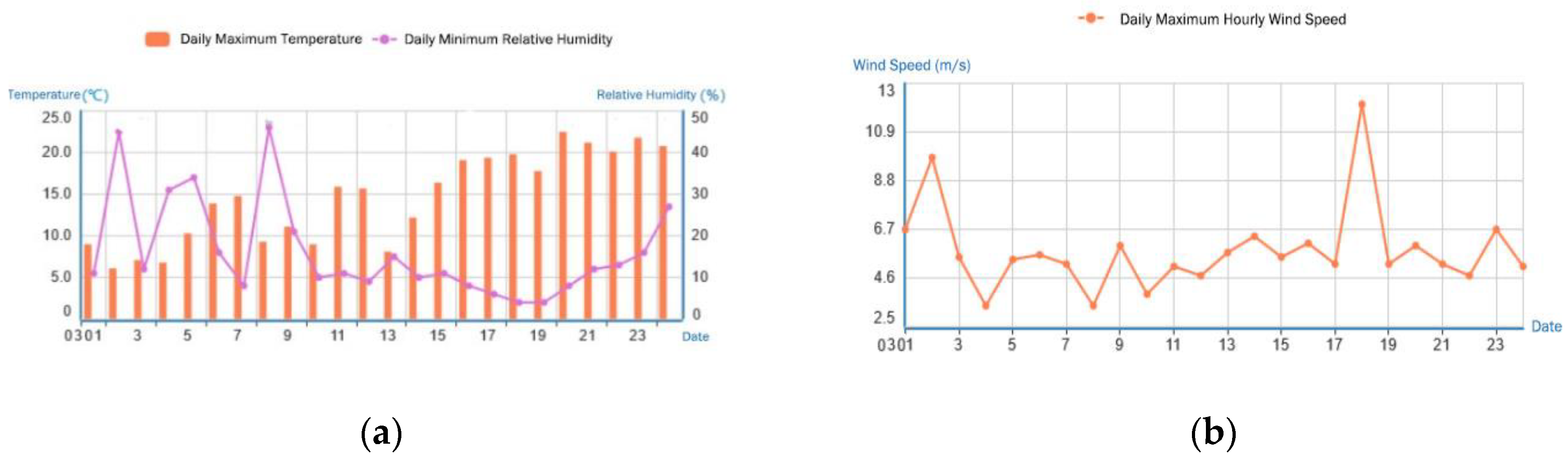
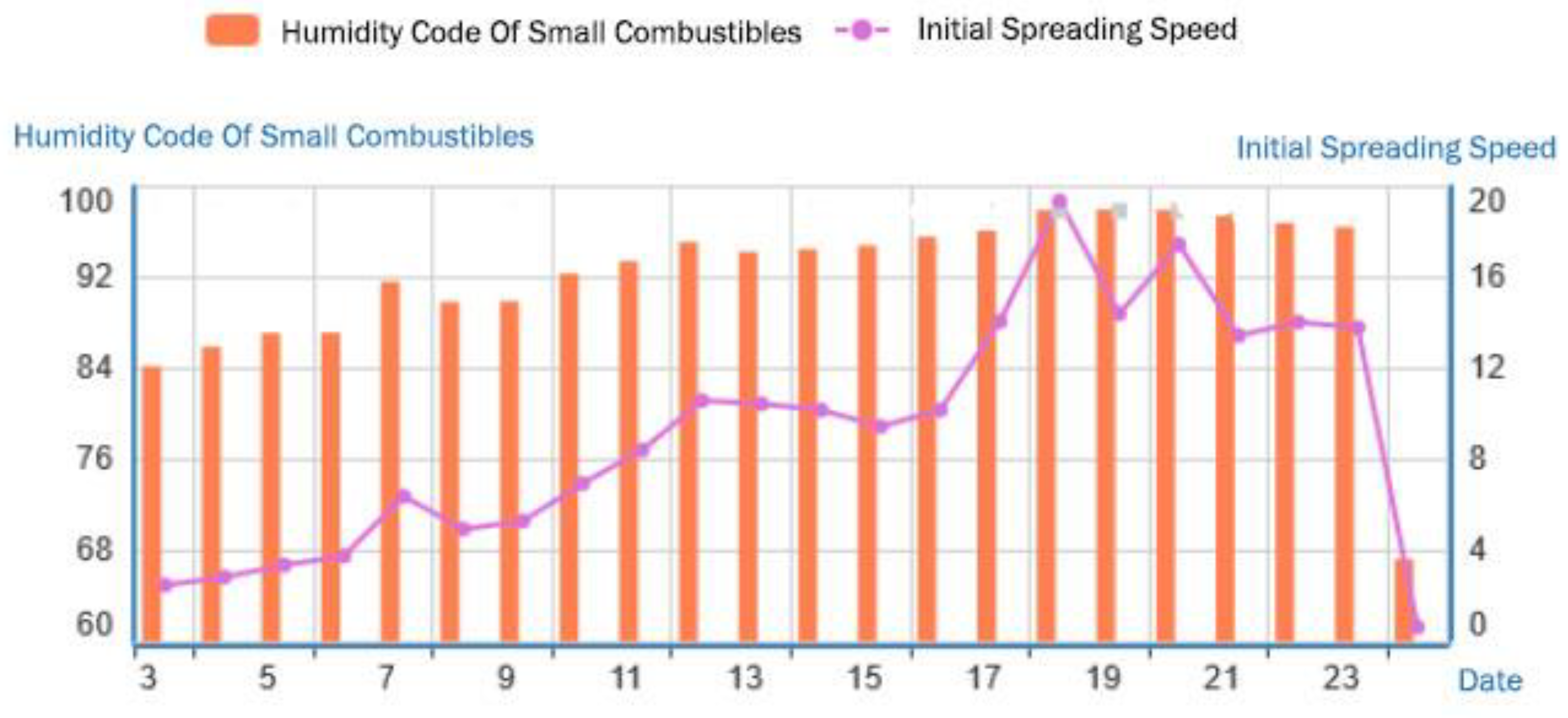
3.2.4. Typical Fire Weather Index Analysis
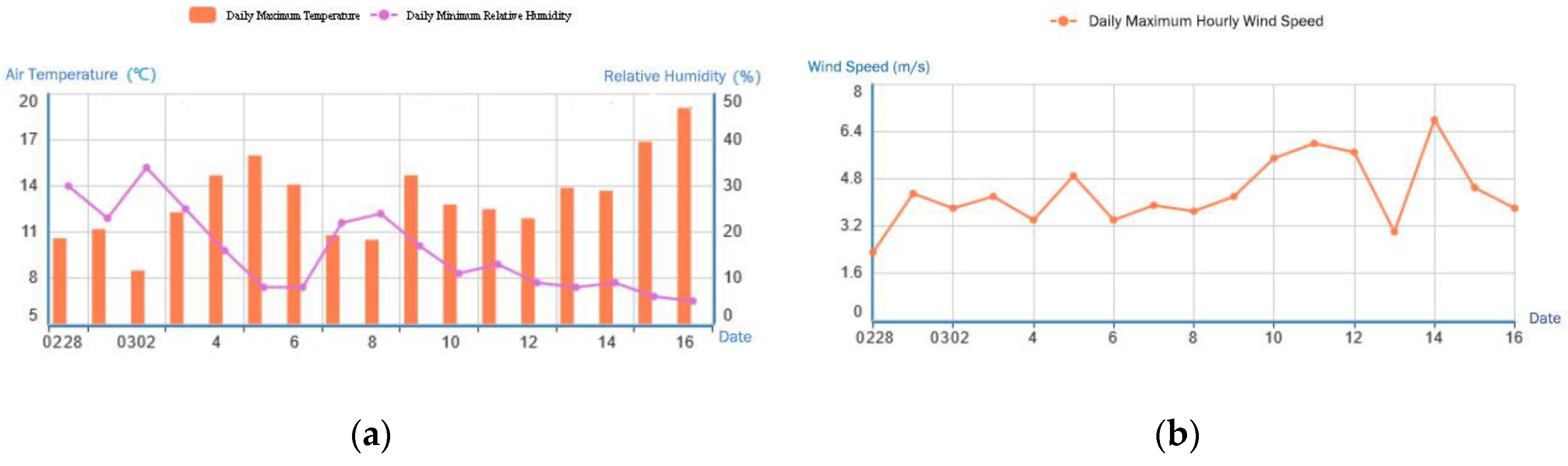
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Historically, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi region has a high frequency of fires, which means that it is a key area for fire prevention and should be strengthened with the construction of fire prevention projects in areas with a high density of fire points (Xinzhou, Yangquan, Changzhi, Chengde, Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Qinhuangdao and other cities located in the Taihang Mountains and Yanshan Mountains).
- (2)
- The winter and spring fire prevention periods in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei- Shanxi region are lengthy, while the period from March to May in spring is a priority fire prevention time, during which the fire prevention, emergency and meteorological departments should pay close attention to high risk weather such as drought, wind and high temperatures, to forecast early on weather processes that have a strong impact on fires, and to issue fire risk warning information promptly.
- (3)
- This research provides a preliminary analysis for the beginning and end of the fire prevention period. There are significant differences in the timing of the beginning and end of fire prevention periods in different areas of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi region in different years, which are closely related to the weather of the year. The present research recommends changing the time for the beginning and end of the fire prevention period from a fixed date to a dynamically managed date, according to the comprehensive evaluation of the actual weather conditions of the year and the medium- and long-term fire risk weather index forecasts. For example, if the precipitation is earlier and more frequent in May, the fire prevention period can be ended in advance; or if a drought occurs, with late and less frequent rainfall, and combustibles remain dry and flammable, the fire prevention period can be extended in June.
- (4)
- The climatic characteristics of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi region are highly consistent. In spring, the high temperature, windy and low moisture weather processes are often synchronized and consistent as well, meaning that the areas where high fire risk level weather occurs tend to be relatively large and there is a great risk of concurrent as well as multiple regional fires, putting considerable pressure on fire prevention. Consequently, the allocation of fire prevention resources, especially the deployment of firefighting forces and resources for fire suppression, should take this risk characteristic into account.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Region | Year | Number of forest fires (times) | General fire | Large fire | Major fire | Especially significant fire | Total fire area (hectare) | ||
| Beijing | 2011 | 3 | 3 | 2 | |||||
| Tianjin | 5 | 5 | 24 | ||||||
| Hebei | 108 | 94 | 13 | 1 | 2169 | ||||
| Shanxi | 40 | 18 | 18 | 4 | 6372 | ||||
| Beijing | 2012 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| Tianjin | 11 | 11 | 46 | ||||||
| Hebei | 83 | 73 | 10 | 2112 | |||||
| Shanxi | 20 | 10 | 10 | 480 | |||||
| Beijing | 2013 | 1 | 1 | 6 | |||||
| Tianjin | 4 | 1 | 3 | 31 | |||||
| Hebei | 52 | 43 | 9 | 422 | |||||
| Shanxi | 32 | 15 | 17 | 2145 | |||||
| Beijing | 2014 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Tianjin | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||||||
| Hebei | 93 | 78 | 15 | 1168 | |||||
| Shanxi | 10 | 10 | 760 | ||||||
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei-Shanxi region | 2011-2014 | 466 | 355 | 106 | 5 | 15743 |
References
- Zhou, G.; Lu, Q. Forest grassland fire hazard and disaster situation. In Meteorology & Forest and grassland fires, China Meteorological Press: Beijing, 2009, pp, 4-6.
- Restaino, J.C.; Peterson, D.L. Wildfire and fuel treatment effects on forest carbon dynamics in the western United States. For.Ecol.Manage. 2013, 303, 46-60. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Q.; Wei, S.J.; Sun, L.; Wang, M.Y. Interaction among climate change, fire disturbance and ecosystem carbon cycle. Arid.L.Geography. 2013, 36, 57-75. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, V.H.F.; VieiraI, C.G.; Salomão, R.P.; Steege, H. Amazonian tree species threatened by deforestation and climate change. Nat.Clim.Change. 2019, 9, 547-553. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.Q.; Roberts, D.A. Drought in the Congo Basin. Nature,2014, 509, 36-37. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang. G. Climate Change and Forest Fire Danger: A Case Study of the Greater Khingan Mountainous Area, Heilongjiang Province, China. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Press: Harbin, 2011, pp, 3-5.
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, G.; Ding, H.; Yu, M. Research Progress of Forest Fires Spread Trend Forecasting in Heilongjiang Province. Atmosphere. 2022, 13, 2110. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shu, L. Characteristics of forest fire response and trend under the scenarios of climate change in China(In Chinese with English preface), Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015, pp, 18-20.
- Di, G.F.; Pappenberger, F.; Wetterhall, F.; Krzeminski, B.; Camia, A.; Libertá, G.; Miguel, J.S. The potential predictability of fire danger provided by numerical weather prediction. J Appl Meteorol Climatol, 2016, 55:2469-2491. [CrossRef]
- Yao, T. A study on liability for environmental pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Procedia Computer Science. 2022, 214, 859–866. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tian, B.; Gu, S.; Hu, Y. Spatial-temporal Evolution of Ecological Vulnerability in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on PSRM Model[J/OL]. Environ. Sci.(Beijing, China). [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Canada. Forest Fire Danger Rating Tool--The Canadian Forest Fire Danger Rating System. [EB/OL] https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/forests/fire-insects-disturbances/fire/14470, 2018.7.25.
- Tian Xiaorui, D·J·McRae, Zhang Youhui. Assessment of Forest Fire Danger Rating Systems. World Forestry Research, 2006 (2): 39-46.
- Masinda, M.M.; Li, F.; Qi, L.; Sun, L.; Hu, T. Forest fire risk estimation in a typical temperate forest in Northeastern China using the Canadian forest fire weather index: case study in autumn 2019 and 2020. Nat Hazards, 2022, 111, 1085–1101. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang Baohua, Sun Zhijun, Zhou Lixia, et al. Forest Fire Danger Forecast Based on Comprehensive Fire Danger Index [J], Fire Management Study, 2011, 30 (12): 1181-1185.
- Dimitrakopoulos, A.P.; Bemmerzouk, A.M.; Mitsopoulos, I.D. Evaluation of the Canadian fre weather index system in an eastern Mediterranean environment. Meteorol Appl, 2011, 18:83–93. [CrossRef]
- Vitolo C, Di Giuseppe F, Krzeminski B, San-Miguel-ayanz J. Data descriptor: a 1980–2018 global fre danger re-analysis dataset for the Canadian fire weather indices. Sci Data,2019, 6:1–10. [CrossRef]
- National Rural Fire Authority. Fire Weather Index System Tables for New Zealand [R]. Wellington: National Rural Fire Authority, 1993.
- Yin L, Kong, X.G., Ma, H.B., Wang R. Missing value filling method of meteorological data based on adaptive genetic algorithm. CN201810512093.4[P]. CN201810512093.4[2023-07-04].
- Xin Xiaoying, Jiang Hong, Zhou Guomo, et al. Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index (FWI) System: A Review [J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2011, 28 (2): 314-318.
- TAYLOR S W,ALEXANDER M E. Science,technology,and human factors in fire danger rating: The Canadian experience [J]. International Journal of Wildland Fire,2006,15 ( 1) : 121-135. [CrossRef]
- Equations and FORTRAN program for the Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index System. 1985. Van Wagner, C.E.; Pickett, T.L. Canadian Forestry Service, Petawawa National Forestry Institute, Chalk River, Ontario. Forestry Technical Report 33.
- Shen Jiaojiao, et al. Characteristics of Forest Fires and the Relationship between Forest Fires and Key Climate Factors in Shaanxi Province [J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2016 (02): 99-105.
- Zhang Heng, Ma Yunjia. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Forest Fires in Northern China from 2003 to 2016 [J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2019, 34 (1): 163-169.
- SAN-MIGUEL-AYANZ J, BARBOSA P, LIBERTA G, et al. The European Forest Fire Information System: a European Strategy Towards Forest Fire Management [R]. Washington D C: U S Dep Interior, Bur Land Manage CD-ROM, 2003.
- He Zeneng, Tang Xiaoping, Tan Bingquan. Study on Meteorological Conditions and Forecast of Forest Fire Danger Grading – A Case Study in Shapingba District of Chongqing [J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2013 (02): 46-50.
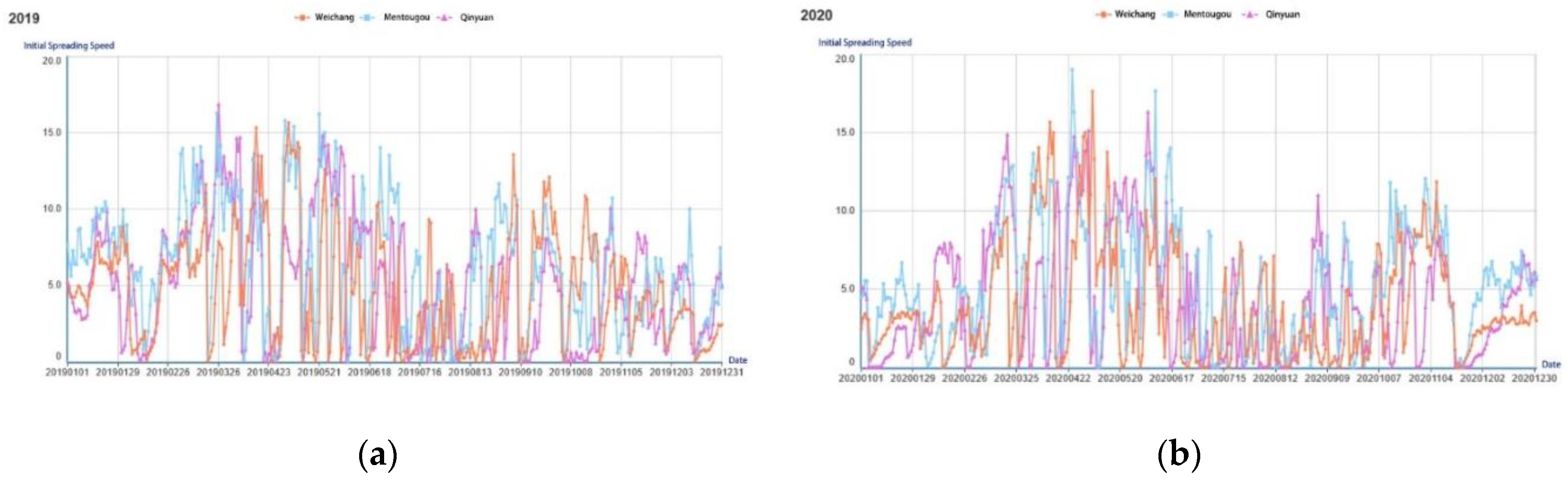
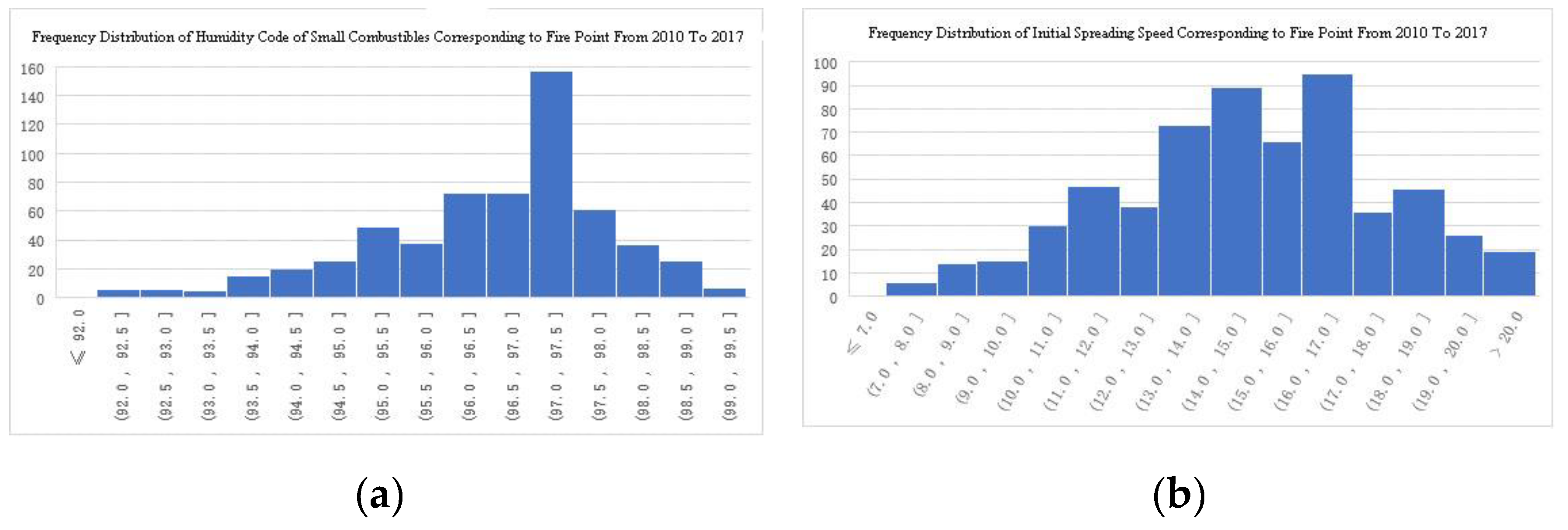
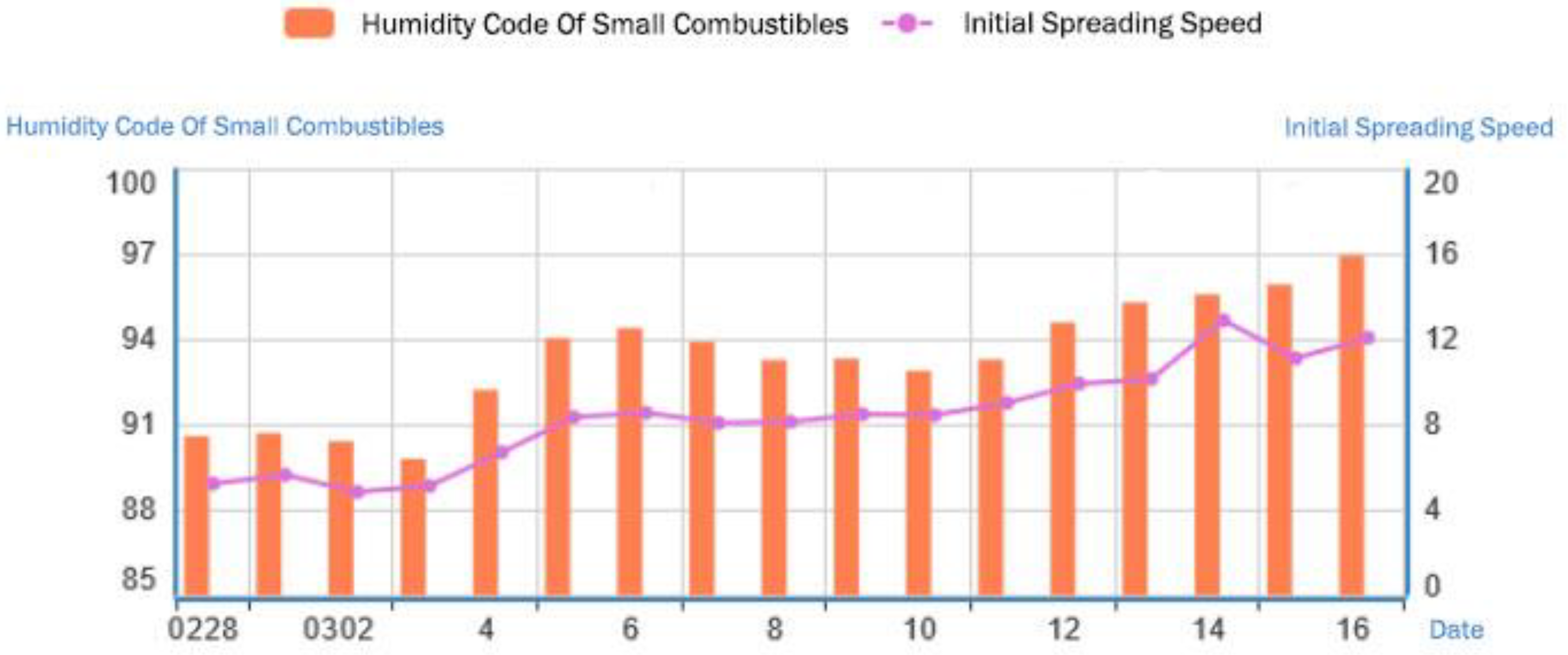
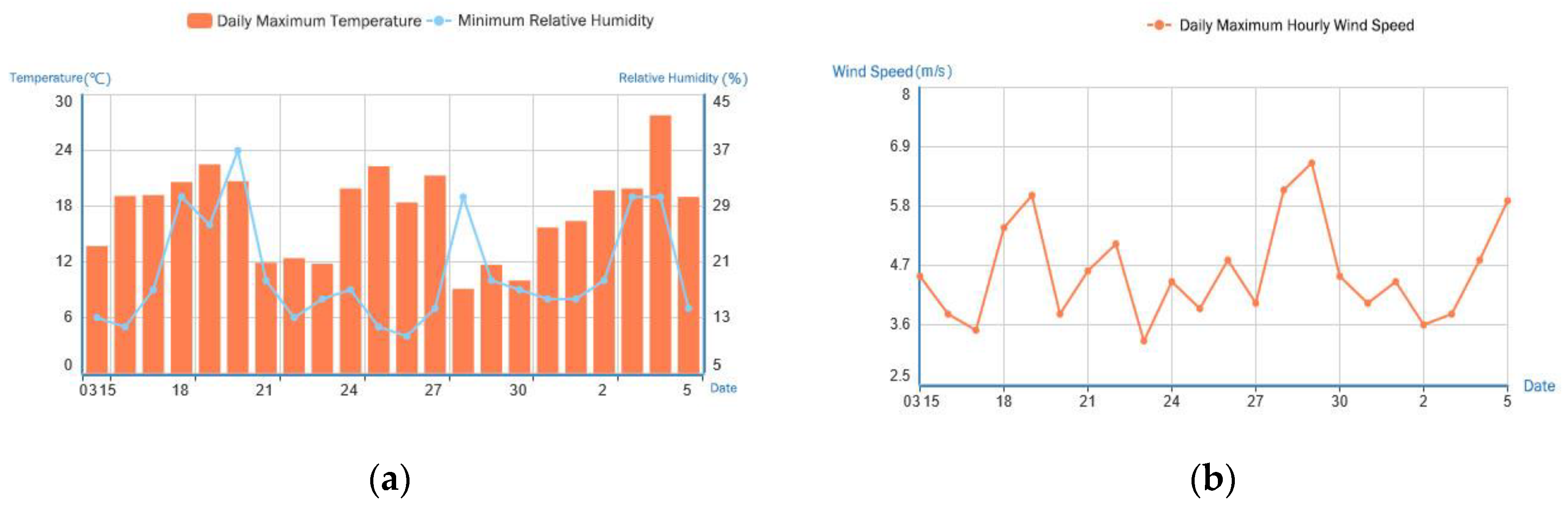
| No. | Province | Station No. | Station name |
| 1 | Hebei | 54311 | Weichang |
| 2 | Hebei | 54318 | Longhua |
| 3 | Hebei | 54420 | Luanping |
| 4 | Hebei | 54308 | Fengning |
| 5 | Hebei | 54430 | Chengde County |
| 6 | Hebei | 54436 | Qinglong |
| 7 | Hebei | 54434 | Qianxi |
| 8 | Hebei | 54425 | Xinglong |
| 9 | Hebei | 54404 | Chicheng |
| 10 | Hebei | 54304 | Chongli |
| 11 | Tianjin | 54428 | Jixian County |
| 12 | Beijing | 54416 | Miyun |
| 13 | Beijing | 54424 | Pinggu |
| 14 | Beijing | 54505 | Mentougou |
| 15 | Beijing | 54597 | Xiayunling |
| 16 | Hebei | 53599 | Laiyuan |
| 17 | Hebei | 53690 | Fuping |
| 18 | Hebei | 53693 | Jingxing |
| 19 | Hebei | 53890 | Wu’an |
| 20 | Hebei | 53886 | Shexian County |
| 21 | Shanxi | 53681 | Doucun Town, Wutai County |
| 22 | Shanxi | 53760 | Fangshan |
| 23 | Shanxi | 53767 | Zhongyang |
| 24 | Shanxi | 53860 | Jiaokou |
| 25 | Shanxi | 53864 | Puxian County |
| 26 | Shanxi | 53875 | Qinyuan |
| 27 | Shanxi | 53788 | Heshun |
| 28 | Shanxi | 53878 | Licheng |
| 29 | Shanxi | 53884 | Xiangyuan |
| 30 | Shanxi | 53663 | Wuzhai |
| 31 | Shanxi | 53888 | Pingshun |
| 32 | Shanxi | 53981 | Lingchuan |
| 33 | Shanxi | 53973 | Gaoping |
| 34 | Shanxi | 53968 | Yuanqu |
| 35 | Shanxi | 53965 | Jiangxian County |
| 36 | Shanxi | 53970 | Qinshui |
| 37 | Shanxi | 53786 | Zuoquan |
| No. | Province | Station No. | Station name | Threshold for very high risk | Threshold for high risk | Threshold for medium risk | Threshold for low risk |
| 1 | Hebei | 54311 | Weichang | 12.0 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 4.5 |
| 2 | Hebei | 54318 | Longhua | 12.0 | 9.1 | 6.8 | 5.0 |
| 3 | Hebei | 54420 | Luanping | 12.4 | 9.0 | 7.0 | 5.3 |
| 4 | Hebei | 54308 | Fengning | 14.2 | 10.3 | 7.7 | 5.7 |
| 5 | Hebei | 54430 | Chengde County | 11.7 | 9.0 | 6.9 | 5.3 |
| 6 | Hebei | 54436 | Qinglong | 11.7 | 9.0 | 6.8 | 5.3 |
| 7 | Hebei | 54434 | Qianxi | 11.7 | 9.1 | 7.0 | 5.3 |
| 8 | Hebei | 54425 | Xinglong | 10.5 | 7.9 | 6.1 | 4.6 |
| 9 | Hebei | 54404 | Chicheng | 13.3 | 10.1 | 7.6 | 5.6 |
| 10 | Hebei | 54304 | Chongli | 11.1 | 8.3 | 6.3 | 4.3 |
| 11 | Tianjin | 54428 | Jixian County | 11.4 | 8.9 | 7.1 | 5.4 |
| 12 | Beijing | 54416 | Miyun | 11.1 | 8.7 | 7.1 | 5.4 |
| 13 | Beijing | 54424 | Pinggu | 11.1 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 5.4 |
| 14 | Beijing | 54505 | Mentougou | 13.0 | 10.1 | 8.2 | 6.4 |
| 15 | Beijing | 54597 | Xiayunling | 11.9 | 9.3 | 7.6 | 6.0 |
| 16 | Hebei | 53599 | Laiyuan | 13.0 | 10.0 | 7.9 | 6.1 |
| 17 | Hebei | 53690 | Fuping | 13.6 | 10.8 | 8.7 | 6.8 |
| 18 | Hebei | 53693 | Jingxing | 12.8 | 10.3 | 8.2 | 6.1 |
| 19 | Hebei | 53890 | Wu’an | 13.5 | 10.5 | 8.2 | 6.0 |
| 20 | Hebei | 53886 | Shexian County | 12.7 | 10.1 | 8.1 | 6.4 |
| 21 | Shanxi | 53681 | Doucun Town, Wutai County | 12.2 | 9.6 | 7.3 | 5.6 |
| 22 | Shanxi | 53760 | Fangshan | 11.8 | 8.9 | 6.6 | 4.8 |
| 23 | Shanxi | 53767 | Zhongyang | 12.0 | 9.1 | 6.4 | 4.6 |
| 24 | Shanxi | 53860 | Jiaokou | 10.7 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 4.2 |
| 25 | Shanxi | 53864 | Puxian County | 12.5 | 9.8 | 7.2 | 5.5 |
| 26 | Shanxi | 53875 | Qinyuan | 12.2 | 9.4 | 7.4 | 5.6 |
| 27 | Shanxi | 53788 | Heshun | 11.6 | 9.1 | 7.5 | 5.7 |
| 28 | Shanxi | 53878 | Licheng | 12.7 | 9.8 | 7.7 | 6.1 |
| 29 | Shanxi | 53884 | Xiangyuan | 13.0 | 9.6 | 7.3 | 5.5 |
| 30 | Shanxi | 53663 | Wuzhai | 12.4 | 9.4 | 6.9 | 4.9 |
| 31 | Shanxi | 53888 | Pingshun | 11.3 | 8.4 | 6.7 | 5.1 |
| 32 | Shanxi | 53981 | Lingchuan | 10.7 | 7.8 | 6.0 | 4.3 |
| 33 | Shanxi | 53973 | Gaoping | 12.4 | 9.4 | 7.3 | 5.6 |
| 34 | Shanxi | 53968 | Yuanqu | 11.6 | 8.7 | 6.8 | 5.1 |
| 35 | Shanxi | 53965 | Jiangxian County | 10.4 | 7.7 | 5.7 | 4.3 |
| 36 | Shanxi | 53970 | Qinshui | 12.2 | 9.2 | 7.2 | 5.4 |
| 37 | Shanxi | 53786 | Zuoquan | 12.6 | 10.0 | 7.6 | 5.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




