Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
19 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
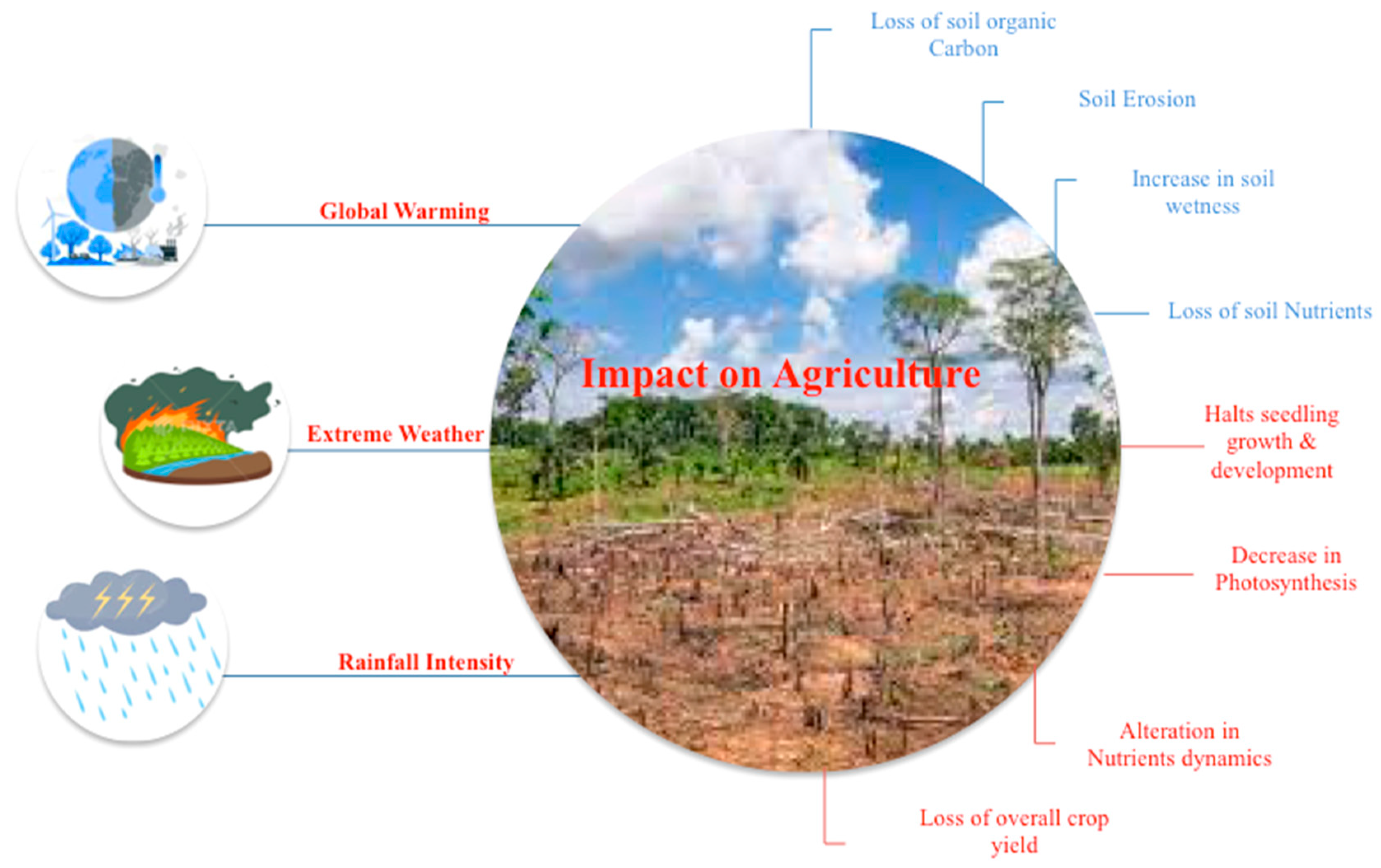
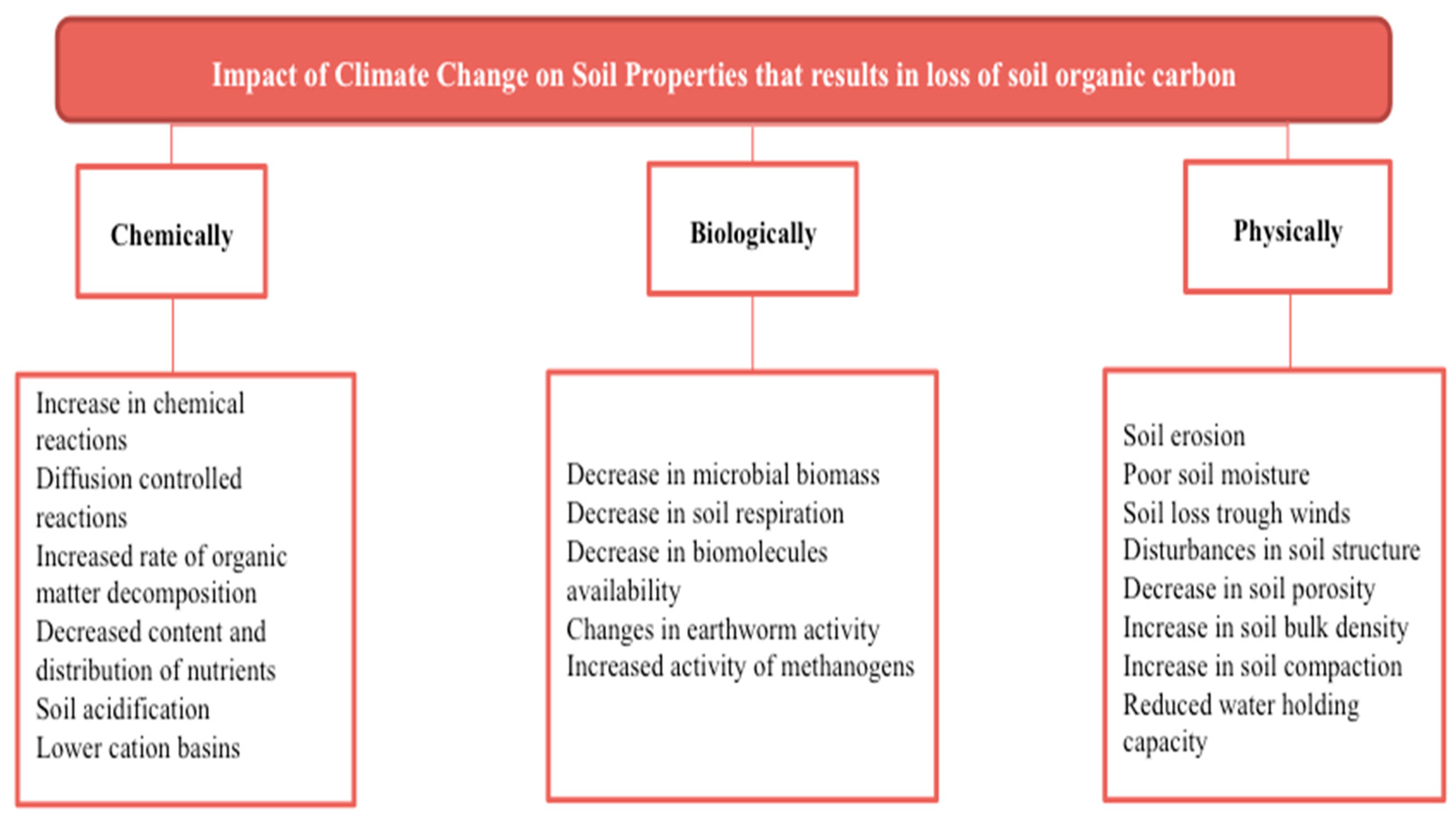
2. Impact of climate change on agriculture and soil properties
3. Crops physiochemical responses to various climate change parameters
4. Climate change mitigation strategies for improved agriculture
4.1. Biochar
4.2. Biostimulants
Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- J. O. Pope et al., “Investigation of future climate change over the British Isles using weather patterns,” Clim. Dyn., vol. 58, no. 9, pp. 2405–2419, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. K. Sovacool, S. B. K. Sovacool, S. Griffiths, J. Kim, and M. Bazilian, “Climate change and industrial F-gases: A critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 141, p. 110759, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Eftekhari, “Impacts of Climate Change on Agriculture and Horticulture,” in Climate Change: The Social and Scientific Construct, S. A. Bandh, Ed. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022, pp. 117–131.
- P. T. Aakko-Saksa et al., “Reduction in greenhouse gas and other emissions from ship engines: Current trends and future options,” Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., vol. 94, p. 101055, 2023. [CrossRef]
- C. Hergart, “Sustainable Transportation,” in Engines and Fuels for Future Transport, G. Kalghatgi, A. K. Agarwal, F. Leach, and K. Senecal, Eds. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2022, pp. 7–38.
- B. Song et al., “Biochar-based agricultural soil management: An application-dependent strategy for contributing to carbon neutrality,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 164, p. 112529, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Hatfield et al., “Indicators of climate change in agricultural systems,” Clim. Change, vol. 163, no. 4, pp. 1719–1732, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Qiu, Z. J. Qiu, Z. Shen, and H. Xie, “Drought impacts on hydrology and water quality under climate change,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 858, p. 159854, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. de Alcantara, J. E. R. R. de Alcantara, J. E. R. Vieira Filho, and J. G. Gasques, “Farming Production in Brazil: Innovation and Land-Sparing Effect,” Int. J. Agric. Biosyst. Eng., vol. 15, no. 10, pp. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- S. I. Zandalinas, D. S. I. Zandalinas, D. Balfagón, A. Gómez-Cadenas, and R. Mittler, “Plant responses to climate change: metabolic changes under combined abiotic stresses,” J. Exp. Bot., vol. 73, no. 11, pp. 3339–3354, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, L. Epelde, and C. Garbisu, “Environmental parameters altered by climate change affect the activity of soil microorganisms involved in bioremediation,” FEMS Microbiol. Lett., vol. 364, no. 19, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Garbisu, I. C. Garbisu, I. Alkorta, P. Kidd, L. Epelde, and M. Mench, “Keep and promote biodiversity at polluted sites under phytomanagement,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., vol. 27, no. 36, pp. 44820–44834, 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Baldrian, R. P. Baldrian, R. López-Mondéjar, and P. Kohout, “Forest microbiome and global change,” Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Hung et al., “Climate change influence on the levels and trends of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and chemicals of emerging Arctic concern (CEACs) in the Arctic physical environment – a review,” Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts, vol. 24, no. 10, pp. 1577–1615, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Movilla-Pateiro, X. M. L. Movilla-Pateiro, X. M. Mahou-Lago, M. I. Doval, and J. Simal-Gandara, “Toward a sustainable metric and indicators for the goal of sustainability in agricultural and food production,” Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 1108–1129, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Xin, “Chemical fertilizer rate, use efficiency and reduction of cereal crops in China, 1998–2018,” J. Geogr. Sci., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 65–78, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Arora, G. S. Arora, G. Murmu, K. Mukherjee, S. Saha, and D. Maity, “A comprehensive overview of nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture,” J. Biotechnol., vol. 355, pp. 21–41, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Gonnella and M. Renna, “The Evolution of Soilless Systems towards Ecological Sustainability in the Perspective of a Circular Economy. Is It Really the Opposite of Organic Agriculture?,” Agronomy, vol. 11, no. 5, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. del C. Orozco-Mosqueda et al., “Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria as Bioinoculants: Attributes and Challenges for Sustainable Crop Improvement,” Agronomy, vol. 11, no. 6, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Du, H. Y. Du, H. Liu, H. Huang, and X. Li, “The carbon emission reduction effect of agricultural policy——Evidence from China,” J. Clean. Prod., p. 137005, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Jones et al., “Evidence supports the potential for climate-smart agriculture in Tanzania,” Glob. Food Sec., vol. 36, p. 100666, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Huang et al., “A global synthesis of biochar’s sustainability in climate-smart agriculture - Evidence from field and laboratory experiments,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 172, p. 113042, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Hussain et al., “A comprehensive review of climate change impacts, adaptation, and mitigation on environmental and natural calamities in Pakistan,” Environ. Monit. Assess., vol. 192, no. 1, p. 48, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Duchenne-Moutien and H. Neetoo, “Climate Change and Emerging Food Safety Issues: A Review,” J. Food Prot., vol. 84, no. 11, pp. 1884–1897, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Chaudhry and G. P. S. Sidhu, “Climate change regulated abiotic stress mechanisms in plants: a comprehensive review,” Plant Cell Rep., vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 1–31, 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. D. Rajput et al., “Coping with the Challenges of Abiotic Stress in Plants: New Dimensions in the Field Application of Nanoparticles,” Plants, vol. 10, no. 6, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yang et al., “Bibliometric Analysis on the Impact of Climate Change on Crop Pest and Disease,” Agronomy, vol. 13, no. 3, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Harvey et al., “Scientists’ warning on climate change and insects,” Ecol. Monogr., vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 1–37, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Au, H. Lee, T. Ye, U. Dave, and A. Rahman, “Bacteriophages: Combating Antimicrobial Resistance in Food-Borne Bacteria Prevalent in Agriculture,” Microorganisms, vol. 10, no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhao et al., “Global climate change and human health: Pathways and possible solutions,” Eco-Environment Heal., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 53–62, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Abbass, M. Z. K. Abbass, M. Z. Qasim, H. Song, M. Murshed, H. Mahmood, and I. Younis, “A review of the global climate change impacts, adaptation, and sustainable mitigation measures,” Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., vol. 29, no. 28, pp. 42539–42559, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. U. A. Rezvi et al., “Rice and food security: Climate change implications and the future prospects for nutritional security,” Food Energy Secur., vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Neupane et al., “Does Climate Change Affect the Yield of the Top Three Cereals and Food Security in the World?,” Earth, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 45–71, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Pathak, “Impact, adaptation, and mitigation of climate change in Indian agriculture,” Environ. Monit. Assess., vol. 195, no. 1, p. 52, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. Biswal, “Soil Nematodes as the Silent Sufferers of Climate-Induced Toxicity: Analysing the Outcomes of Their Interactions with Climatic Stress Factors on Land Cover and Agricultural Production,” Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., vol. 195, no. 4, pp. 2519–2586, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Li et al., “Transformation of soil organic matter subjected to environmental disturbance and preservation of organic matter bound to soil minerals: a review,” J. Soils Sediments, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 1485–1500, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. L. Yu, P. L. K. L. Yu, P. L. Show, H. C. Ong, T. C. Ling, W. H. Chen, and M. A. M. Salleh, “Biochar production from microalgae cultivation through pyrolysis as a sustainable carbon sequestration and biorefinery approach,” Clean Technol. Environ. Policy, 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu, Z. X. Liu, Z. Fu, W. Zhang, S. Xiao, H. Chen, and K. Wang, “Soluble carbon loss through multiple runoff components in the shallow subsurface of a karst hillslope: Impact of critical zone structure and land use,” CATENA, vol. 222, p. 106868, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sarika and, H. Manek, “Chapter 18 - Plant functional traits: mountainous soil function and ecosystem services,” in Understanding Soils of Mountainous Landscapes, R. Bhadouria, S. Singh, S. Tripathi, and P. Singh, Eds. Elsevier, 2023, pp. 347–373.
- G. Wessolek, K. G. Wessolek, K. Bohne, and S. Trinks, “Validation of Soil Thermal Conductivity Models,” Int. J. Thermophys., vol. 44, no. 2, p. 20, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Yu et al., “Biochar amendment improves crop production in problem soils: A review,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 232, pp. 8–21, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Luis Moreno et al., “Response of soil chemical properties, enzyme activities and microbial communities to biochar application and climate change in a Mediterranean agroecosystem,” Geoderma, vol. 407, p. 115536, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Nel, C. E. T. Nel, C. E. Clarke, and A. G. Hardie, “Evaluation of simple and multivariate linear regression models for exchangeable base cation conversion between seven measurement techniques on South African soils,” Geoderma Reg., vol. 30, p. e00571, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Corami, “Nanotechnologies and Phytoremediation: Pros and Cons,” in Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants, Volume 7, L. Newman, A. A. Ansari, S. S. Gill, M. Naeem, and R. Gill, Eds. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023, pp. 403–426.
- E. D. Whalen et al., “Clarifying the evidence for microbial- and plant-derived soil organic matter, and the path toward a more quantitative understanding,” Glob. Chang. Biol., vol. 28, no. 24, pp. 7167–7185, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. H. Hassan, H. H. W. H. Hassan, H. H. Hussein, and B. K. Nile, “The effect of climate change on groundwater recharge in unconfined aquifers in the western desert of Iraq,” Groundw. Sustain. Dev., vol. 16, p. 100700, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Nievola, C. P. C. C. Nievola, C. P. Carvalho, V. Carvalho, and E. Rodrigues, “Rapid responses of plants to temperature changes,” Temperature, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 371–405, 2017. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang et al., “Pesticides Xenobiotics in Soil Ecosystem and Their Remediation Approaches,” Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 6, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. V. K. Jagadish, “Heat stress during flowering in cereals – effects and adaptation strategies,” New Phytol., vol. 226, no. 6, pp. 1567–1572, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. I. Lizaso et al., “Impact of high temperatures in maize: Phenology and yield components,” F. Crop. Res., vol. 216, pp. 129–140, 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhu, C. F. T. Zhu, C. F. Fonseca De Lima, and I. De Smet, “The heat is on: how crop growth, development, and yield respond to high temperature,” J. Exp. Bot., vol. 72, no. 21, pp. 7359–7373, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. O. A. Abdelhakim et al., “Elevated CO2 Improves the Physiology but Not the Final Yield in Spring Wheat Genotypes Subjected to Heat and Drought Stress During Anthesis,” Front. Plant Sci., vol. 13, no. March, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Rai, “Heat Stress in Crops: Driver of Climate Change Impacting Global Food Supply,” in Contemporary Environmental Issues and Challenges in Era of Climate Change, P. Singh, R. P. Singh, and V. Srivastava, Eds. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020, pp. 99–117.
- K. Wagaw, “Review on Mechanisms of Drought Tolerance in Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) Basis and Breeding Methods,” Acad. Res. J. Agri. Sci. Res, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 87–99, 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Byers et al., “Global exposure and vulnerability to multi-sector development and climate change hotspots,” Environ. Res. Lett., vol. 13, no. 5, 2018. [CrossRef]
- et al. , “Vascular epiphytes contribute disproportionately to global centres of plant diversity,” Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr., vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 62–74, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Sadok and S. V. K. Jagadish, “The Hidden Costs of Nighttime Warming on Yields,” Trends Plant Sci., vol. 25, no. 7, pp. 644–651, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. S. Karthika, I. K. S. Karthika, I. Rashmi, and M. S. Parvathi, “Biological Functions, Uptake and Transport of Essential Nutrients in Relation to Plant Growth,” in Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance, M. Hasanuzzaman, M. Fujita, H. Oku, K. Nahar, and B. Hawrylak-Nowak, Eds. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2018, pp. 1–49.
- P. Bhantana et al., “Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and its major role in plant growth, zinc nutrition, phosphorous regulation and phytoremediation,” Symbiosis, vol. 84, no. 1, pp. 19–37, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Gondek, D. C. M. Gondek, D. C. Weindorf, C. Thiel, and G. Kleinheinz, “Soluble Salts in Compost and Their Effects on Soil and Plants: A Review,” Compost Sci. \& Util., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 59–75, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Heiskanen, H. J. Heiskanen, H. Ruhanen, and M. Hagner, “Effects of compost, biochar and ash mixed in till soil cover of mine tailings on plant growth and bioaccumulation of elements: A growing test in a greenhouse,” Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 2, p. e08838, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Shuai, H. Y. Shuai, H. Sui, G. Tao, Q. Huo, C. Li, and N. Shao, “Food Contaminants,” in Nutritional Toxicology, L. Zhang, Ed. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022, pp. 107–166.
- P. K. Rai, S. S. P. K. Rai, S. S. Lee, M. Zhang, Y. F. Tsang, and K.-H. Kim, “Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management,” Environ. Int., vol. 125, pp. 365–385, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Oyewo, A. A. Oyewo, A. Adeniyi, M. F. Bopape, and M. S. Onyango, “Chapter 4 - Heavy metal mobility in surface water and soil, climate change, and soil interactions,” in Climate Change and Soil Interactions, M. N. V. Prasad and M. Pietrzykowski, Eds. Elsevier, 2020, pp. 51–88.
- F. García-Sánchez et al., “Multiple stresses occurring with boron toxicity and deficiency in plants,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 397, p. 122713, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Latheef and K. Soundhirarajan, “Heavy Metal Contamination in Irrigation Water and Its,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol., vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 3704–3710, 2018.
- Nabi, R. Parwez, T. Aftab, M. M. A. Khan, and M. Naeem, “Triacontanol Protects Mentha arvensis L. from Nickel-Instigated Repercussions by Escalating Antioxidant Machinery, Photosynthetic Efficiency and Maintaining Leaf Ultrastructure and Root Morphology,” J. Plant Growth Regul., vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 1594–1612, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N.-H. Ghori et al., “Heavy metal stress and responses in plants,” Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 1807–1828, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang et al., “Lead-contaminated soil induced oxidative stress, defense response and its indicative biomarkers in roots of Vicia faba seedlings,” Ecotoxicology, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 1130–1139, 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Sachdev, S. A. S. Sachdev, S. A. Ansari, M. I. Ansari, M. Fujita, and M. Hasanuzzaman, “Abiotic Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species: Generation, Signaling, and Defense Mechanisms,” Antioxidants, vol. 10, no. 2, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, M. Xu, and Y. Gan, “Chromium-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation by Altering the Enzymatic Antioxidant System and Associated Cytotoxic, Genotoxic, Ultrastructural, and Photosynthetic Changes in Plants,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 21, no. 3, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, Z. Sokołowska, and P. Boguta, “Biochar physicochemical properties: pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects,” Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 191–215, 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. Vijay et al., “Review of Large-Scale Biochar Field-Trials for Soil Amendment and the Observed Influences on Crop Yield Variations,” Front. Energy Res., vol. 9, no. August, pp. 1–21, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Joseph et al., “How biochar works, and when it doesn’t: A review of mechanisms controlling soil and plant responses to biochar,” GCB Bioenergy, vol. 13, no. 11, pp. 1731–1764, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Singh, B. K. H. Singh, B. K. Northup, C. W. Rice, and P. V. V. Prasad, “Biochar applications influence soil physical and chemical properties, microbial diversity, and crop productivity: a meta-analysis,” Biochar, vol. 4, no. 1, p. 8, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Samoraj et al., “Biochar in environmental friendly fertilizers - Prospects of development products and technologies,” Chemosphere, vol. 296, p. 133975, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Yang, W. Xie, R. Yao, and X. Wang, “Effect of Biochar Application on Soil Fertility, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Balance in Coastal Salt-Affected Soil under Barley–Maize Rotation,” Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Oni, O. A. Oni, O. Oziegbe, and O. O. Olawole, “Significance of biochar application to the environment and economy,” Ann. Agric. Sci., vol. 64, no. 2, pp. 222–236, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Ayaz, D. M. Ayaz, D. Feizienė, V. Tilvikienė, V. Feiza, E. Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, and S. Ullah, “Biochar with Inorganic Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduces Direct Greenhouse Gas Emission Flux from Soil,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 5, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Grafmüller, H.-P. J. Grafmüller, H.-P. Schmidt, D. Kray, and N. Hagemann, “Root-Zone Amendments of Biochar-Based Fertilizers: Yield Increases of White Cabbage in Temperate Climate,” Horticulturae, vol. 8, no. 4, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tisserant and, F. Cherubini, “Potentials, Limitations, Co-Benefits, and Trade-Offs of Biochar Applications to Soils for Climate Change Mitigation,” Land, vol. 8, no. 12, 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. A. Kurniawan et al., “Challenges and opportunities for biochar to promote circular economy and carbon neutrality,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 332, p. 117429, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Woolf, J. Lehmann, S. Ogle, A. W. Kishimoto-Mo, B. McConkey, and J. Baldock, “Greenhouse Gas Inventory Model for Biochar Additions to Soil,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 55, no. 21, pp. 14795–14805, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, E. S. Azzi, A. Enell, and C. Sundberg, “Biochar produced from wood waste for soil remediation in Sweden: Carbon sequestration and other environmental impacts,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 776, p. 145953, 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Yang et al., “Impact of biochar on greenhouse gas emissions and soil carbon sequestration in corn grown under drip irrigation with mulching,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 729, p. 138752, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Armah et al., “Biochar: Production, Application and the Future,” in Biochar, M. Bartoli, M. Giorcelli, and A. Tagliaferro, Eds. Rijeka: IntechOpen, 2022.
- I. Osman et al., Biochar for agronomy, animal farming, anaerobic digestion, composting, water treatment, soil remediation, construction, energy storage, and carbon sequestration: a review, vol. 20, no. 4. Springer International Publishing, 2022.
- Gross, T. Bromm, and B. Glaser, “Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration after Biochar Application: A Global Meta-Analysis,” Agronomy, vol. 11, no. 12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Rawat, J. J. Rawat, J. Saxena, and P. Sanwal, “Biochar: A Sustainable Approach for Improving Plant Growth and Soil Properties,” in Biochar, V. Abrol and P. Sharma, Eds. Rijeka: IntechOpen, 2019.
- S.-H. Jien, C.-C. S.-H. Jien, C.-C. Wang, C.-H. Lee, and T.-Y. Lee, “Stabilization of Organic Matter by Biochar Application in Compost-amended Soils with Contrasting pH Values and Textures,” Sustainability, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 13317–13333, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao et al., “Biochar Acts as an Emerging Soil Amendment and Its Potential Ecological Risks: A Review,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- et al. , “Biochar impacts on runoff and soil erosion by water: A systematic global scale meta-analysis,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 871, p. 161860, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Xia et al., “Climate mitigation potential of sustainable biochar production in China,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 175, p. 113145, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zheng et al., “Non-additive effects of bamboo-derived biochar and dicyandiamide on soil greenhouse gas emissions, enzyme activity and bacterial community,” Ind. Crops Prod., vol. 194, p. 116385, 2023. [CrossRef]
- et al. , “Role of biostimulants in mitigating the effects of climate change on crop performance,” Front. Plant Sci., vol. 13, no. October, pp. 1–19, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Bulgari, G. R. Bulgari, G. Franzoni, and A. Ferrante, “Biostimulants Application in Horticultural Crops under Abiotic Stress Conditions,” Agronomy, vol. 9, no. 6, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Horoszkiewicz et al., “The Assessment of an Effect of Natural Origin Products on the Initial Growth and Development of Maize under Drought Stress and the Occurrence of Selected Pathogens,” Agriculture, vol. 13, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, G. Cocetta, B. Prinsi, A. Ferrante, and L. Espen, “Biostimulants on Crops: Their Impact under Abiotic Stress Conditions,” Horticulturae, vol. 8, no. 3, 2022. [CrossRef]
- U. Dave, E. U. Dave, E. Somanader, P. Baharlouei, L. Pham, and M. A. Rahman, “Applications of Chitin in Medical, Environmental, and Agricultural Industries,” J. Mar. Sci. Eng., vol. 9, no. 11, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. E. M. El Boukhari, M. M. E. M. El Boukhari, M. Barakate, Y. Bouhia, and K. Lyamlouli, “Trends in Seaweed Extract Based Biostimulants: Manufacturing Process and Beneficial Effect on Soil-Plant Systems.,” Plants (Basel, Switzerland), vol. 9, no. 3, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Tudi et al., “Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment.,” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, vol. 18, no. 3, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Rajabi Hamedani, Y. S. Rajabi Hamedani, Y. Rouphael, G. Colla, A. Colantoni, and M. Cardarelli, “Biostimulants as a Tool for Improving Environmental Sustainability of Greenhouse Vegetable Crops,” Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 12, 2020. [CrossRef]
- et al. , “Effects of Seaweed Extracts on the Growth, Physiological Activity, Cane Yield and Sucrose Content of Sugarcane in China,” Front. Plant Sci., vol. 12, no. May, pp. 1–13, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Baltazar, S. M. Baltazar, S. Correia, K. J. Guinan, N. Sujeeth, R. Bragança, and B. Gonçalves, “Recent Advances in the Molecular Effects of Biostimulants in Plants: An Overview.,” Biomolecules, vol. 11, no. 8, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Younes et al., “Effects of microbial biostimulants (Trichoderma album and Bacillus megaterium) on growth, quality attributes, and yield of onion under field conditions,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 3, p. e14203, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. A. T. Zakaria, S. Z. M. A. T. Zakaria, S. Z. Sakimin, M. R. Ismail, K. Ahmad, S. Kasim, and A. Baghdadi, “Biostimulant Activity of Silicate Compounds and Antagonistic Bacteria on Physiological Growth Enhancement and Resistance of Banana to Fusarium Wilt Disease,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 5, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. L. Sleighter, T. R. L. Sleighter, T. Hanson, D. Holden, and K. M. Richards, “Abiotic Stress Mitigation: A Case Study from 21 Trials Using a Natural Organic Matter Based Biostimulant across Multiple Geographies,” Agronomy, vol. 13, no. 3, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bantis and, A. Koukounaras, “Ascophyllum nodosum and Silicon-Based Biostimulants Differentially Affect the Physiology and Growth of Watermelon Transplants under Abiotic Stress Factors: The Case of Salinity,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 3, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Arias, S. Bonardd, S. Morales-Sierra, M. Â. Almeida Pinheiro de Carvalho, and D. Díaz Díaz, “Chitosan-Enclosed Menadione Sodium Bisulfite as an Environmentally Friendly Alternative to Enhance Biostimulant Properties against Drought,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 71, no. 7, pp. 3192–3200, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Castronuovo, A. Comegna, C. Belviso, A. Satriani, and S. Lovelli, “Zeolite and Ascophyllum nodosum-Based Biostimulant Effects on Spinach Gas Exchange and Growth,” Agriculture, vol. 13, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Benito, D. P. Benito, D. Ligorio, J. Bellón, L. Yenush, and J. M. Mulet, “Use of Yucca (Yucca schidigera) Extracts as Biostimulants to Promote Germination and Early Vigor and as Natural Fungicides,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Domingo, M. Marsoni, M. Álvarez-Viñas, M. D. Torres, H. Domínguez, and C. Vannini, “The Role of Protein-Rich Extracts from Chondrus crispus as Biostimulant and in Enhancing Tolerance to Drought Stress in Tomato Plants,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Top, B. S. Top, B. Vandoorne, E. Pauwels, M. Perneel, M. C. Van Labeke, and K. Steppe, “Plant Sensors Untangle the Water-Use and Growth Effects of Selected Seaweed-Derived Biostimulants on Drought-Stressed Tomato Plants (Solanum lycopersicum),” J. Plant Growth Regul., 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. M. Butkevičienė, V. L. M. Butkevičienė, V. Steponavičienė, R. Pupalienė, L. Skinulienė, and V. Bogužas, “Effect of Different Tillage Systems and Soil Biostimulants on Agrochemical Properties and Intensity of Soil CO2 Emission in Wheat Crop,” Agronomy, vol. 13, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Sangiorgio, A. D. Sangiorgio, A. Cellini, F. Spinelli, and I. Donati, “Promoting Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Stress Resistance, Growth, and Yield Using Native Bacterial Biostimulants,” Agronomy, vol. 13, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Rezaei-Chiyaneh et al., “Biostimulants alleviate water deficit stress and enhance essential oil productivity: a case study with savory,” Sci. Rep., vol. 13, no. 1, p. 720, 2023. [CrossRef]

| Sr. No | Biostimulant | Crop | Effect of treatment on crop | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trichoderma album and Bacillus megaterium | Onion | Overall better yield, enhanced levels of potassium by 105.7%, Proline by 34%, calcium by 37% and total free amino acids by 144% after treatment with T. albumPretreatment with T. album and B. megaterium both, enhanced total carbohydrates, antioxidants, activity of superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, ascorbic acid, and flavonoids | [105] |
| 2 | Silicate Compound and antagonistic bacteria Bacillus sp. | Banana | Treatment resulted in enhanced physiological growth performance of bananas, significantly resisted against Fusarium wil disease in bananas that results by pathogenic causative agent Fusarium cubense, the incidence of Fusarium wilt decreased by 56.25% | [106] |
| 3 | Natural organic matter based Biostimulant | TomatoesAvocados | Plants resisted drought stress and resulted in enhanced growth of plant roots (36%), and shoots (27%)Plants developed drought and salt resistance resulting in 45% increase in yield | [107] |
| 4 | Ascophyllum nodosum | Watermelon | In response to salt stress, the treatment of plants with Biostimulant provoked a positive phenotypic response | [108] |
| 5 | Menadione sodium bisulfite encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles | Tomatoes | Treatment of plants with Biostimulant increased the tolerance against drought stress and delay the need for retreatment by 1 week | [109] |
| 6 | Ascophyllum nodosum and zeolite | Spinach | Combined use of Biostimulant resulted in significant improvement in water storage capacity of plants | [110] |
| 7 | Yucca schidigera extracts | Broccoli | Treatment of plants with Biostimulant resulted in strong effect of plants against drought and salt stress, also promoted germination and early vigor | [111] |
| 8 | Chondrus crispus extracts | Tomatoes | Treatment resulted in drought tolerance in plants along with enhanced shoot height and biomass | [112] |
| 9 | Ascophyllum nodosum | Tomatoes | Plants developed drought resistance by 40% in comparison to control | [113] |
| 10 | Mixture of Ruinex, Penergetic, Azofix | Wheat | Humus content increased, Nitrogen and carbon content of soil increased, results over three years show that biostmilants resulted in promotion of mobile humic substance and mobile humic acid release better. | [114] |
| 11 | Pseudomonas fluorescens, Stenotrophomonas rhizopus, Agrobacterium rubi | Strawberry | Treatment resulted in seven-fold increase in plant growth and fruit production, also plants developed resistance against angular leaf spot disease caused by Xanthomonas fragariae | [115] |
| 12 | Amino acids | Savory | Treatment resulted in enhanced dry matter yield, essential oil content, carvacrol, gamma-terpinene, alpha-terpinene, p-cymene | [116] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




