1. Introduction
As a major global chronic disease, non–alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has a disease spectrum that includes simple non−alcoholic fatty liver, non−alcoholic fatty hepatitis and related liver cirrhosis and liver cell carcinoma [
1]. NAFLD is associated with a bleak prognosis, including cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and even death [
1]. Recent trends in the treatment of NAFLD have focused on lifestyle modification [
2], bariatric surgery [
3], and medical therapy [4, 5]. Given the considerable risk associated with surgery, exploration of new therapeutic agents against NAFLD is essential but challenging. IMM−H014 (previously known as WS117) is a novel collateral phenyl−structured compound with a new mechanism of action involving a nuclear factor NF−E2- related factor agonist. IMM–H014 has anti-inflammatory activity and can increase insulin sensitivity, which may be useful in the treatment of NAFLD [
6].
In the treatment of chronic diseases, IMM–H014 requires long-term administration, and patients with NAFLD require continuous and effective medical care. IMM−H014 is easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with 96.3% oral bioavailability in rats, a short plasma drug concentration peak time (0.5 h), and a short plasma elimination half−life (rats 1.8 h, Beagle dog 3.5 h) [
7]. Drugs with a short half–life are given at shorter intervals and more frequently. To improve patient compliance, it is recommended that IMM−H014 should possess an extended– release (ER) profile after oral administration. ER solid dosage forms for oral administration may be effective to avoid frequent dosing and improve long-term therapeutic management with drug molecules that exhibit a narrow therapeutic range and/or are rapidly cleared from the blood [
8].
Inert polymers matrices have been widely used as skeleton materials to adjust the release rate in controlled release delivery formulate [
9,
10]. The mechanism of action of hydrophilic polymer matrix systems, which are widely used in controlled drug delivery, is based on the gel layer, formed by hydration of the polymer. The gel layer controls the drug release rate [
11,
12,
13]. The release of water-soluble drugs in vitro is in command of the diffusion of the gel layer outside, which depends on the gel viscosity. In contrast, the release of poorly water-soluble drugs is dependent on the dissolution of the polymer [
14,
15].
Cellulose derivatives have been widely used as hydrogel matrices for controlled drug delivery, among which, hydroxypropyl methycellulose (HPMC) is the most widely applied given that it is easy to use, widely available to purchase, and has low/no toxicity [
16]. Drug release is controlled by a gel layer formed on the matrix surface by hydration of HPMC, through which the loaded drug diffuses [
17].
In matrix tablets prepared with HPMC, a gel layer is produced on the surface of the tablets upon aquation. At a higher use level of HPMC, the greater degree of entanglement of the linear polymer chains results in “virtual crosslinking,” leading to the formation of a more robust gel layer [
18]. HPMC is a versatile polymer for the production of tablets and is widely accepted as a pharmaceutical excipient for oral administration [
19,
20]. HPMC can be used to control the release behavior of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs through swelling, diffusion, and erosion processes [
21].
In this study, we explored the feasibility of producing IMM−H014 extended–release tablets using a direct compression method based on HPMC as hydrophilic polymeric matrices. The effect of the polymer concentration on the in vitro and in vivo drug release rate was researched to establish the preferred formulation in terms of modified release. Besides, a point−to−point in vitro−in vivo correlation (IVIVC) was developed to relate the percentage of drug dissolved to the percentage of drug absorbed. The changes in drug absorption in the body can be evaluated by IVIVC based on the in vitro dissolution when the formulation is changed slightly [
22].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Solubility studies
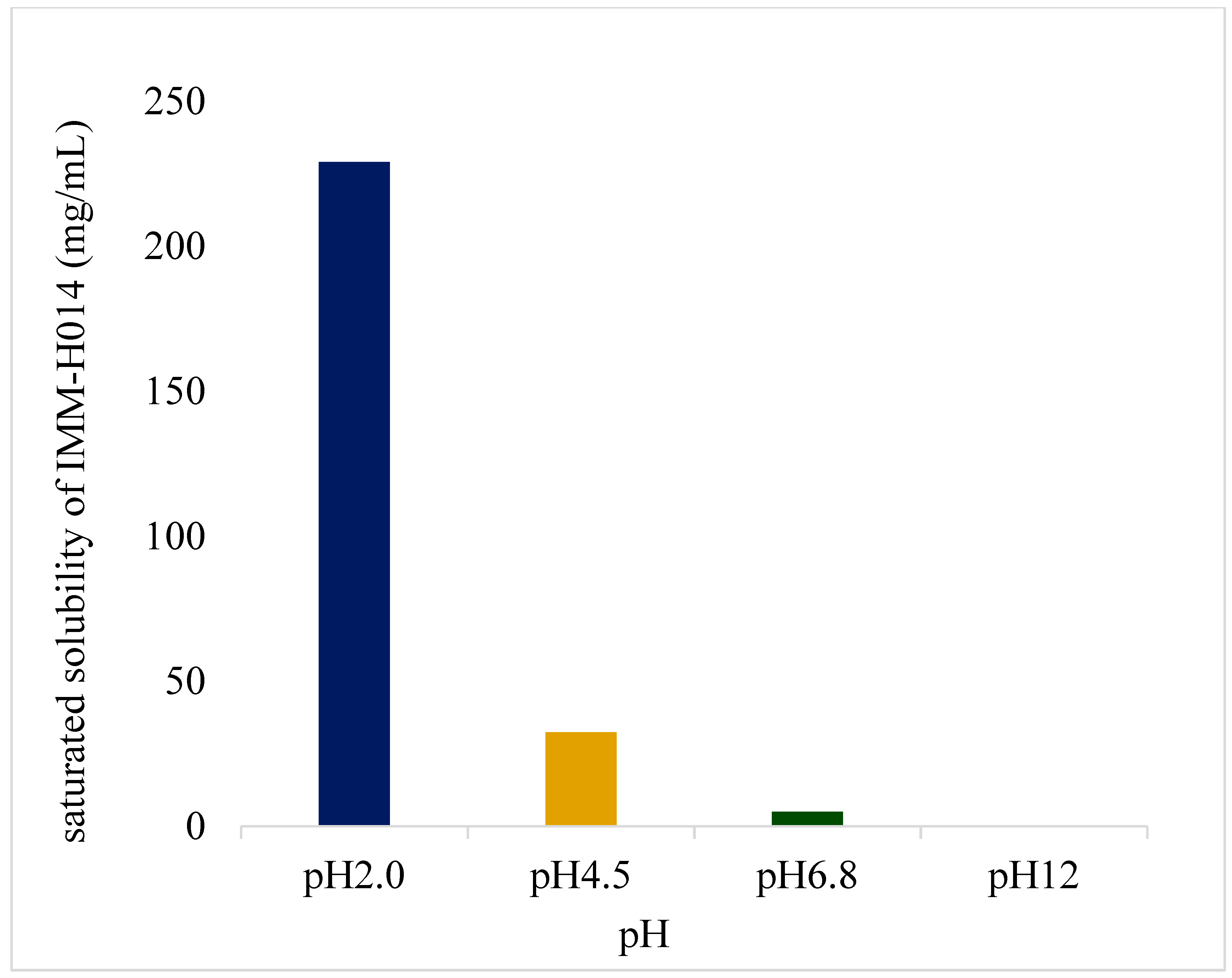
IMM–H014 possesses pH−dependent saturated solubility (as shown in
Figure 1 and in
supplementary materials Table S1), as well as high solubility under acidic conditions, with decreasing solubility observed with increasing pH of the medium. Furthermore, IMM−H014 exhibited pH−dependent solubility in different media.
2.2. Optimization of IMM−H014 ER tablet formulations
2.2.1. Screening of matrix materials
First, the type and viscosity of hydrogel matrix were investigated to achieve the desired ER of IMM-H014. The HPMC and hydroxy propyl cellulose (HPC) used for different tablets are displayed in
Table 6 as F1−F4.
As a sulfonate salt, IMM–H014 is unsuitable for wet granulation with ethanol because it could produce methanesulfonate which has genetic toxicity. However, hydrogel skeleton material is also unsuitable for wet granulation with water; instead, the suitable process is dry granule or direct powder pressing. Direct powder pressing is a simple and repeatable process, and can be used as the first choice. HPMC which can be used for direct pressing showed better liquidity than HPC, as confirmed by the values of angle of repose and weight variation (as shown in
Table 1). The repose angles of HPMC (90SH−4000SR and 90SH−10000SR) as the skeleton material are 26° and 27°, with Carr’s Index (CI) of 13.4 and 12.7, respectively. The repose angles of HPC (M-FP and H−FP) as the skeleton material are 35° and 37°, with a CI of 17.5 and 18.4. It is generally believed that when the repose angle is ≤30° or the CI is ≤15, the particle flowability is good, which can meet the pressing requirements. The results also showed that with the same tablet hardness (100N−130N), the weight variation of the tablet was greater when HPC was used as the excipient compared to HPMC.
The tablet made of HPMC (90SH−4000SR) showed ER in vitro, which could be completely released after 24 h, with a cumulative release of > 95%. The tablets produced with HPMC (90SH−10000SR) and HPC (M-FP and H−FP) as skeleton materials were incompletely released. (as shown in
Supplementary Materials Table S2 and
Figure S1). The research showed that the gel layer formed by the hydrogel matrix was the primary control behind the drug release. The hydration rate of the matrix was related to its viscosity. The gel layer of HPMC (90SH−4000SR) formed slowly with a weak strength, resulting in rapid release of IMM−H014. However, the gel layer formed by HPMC (90SH−10000SR), HPC ((M-FP), and HPC (H-PC) was formed rapidly with a high strength, preventing the release of IMM−H014. Therefore, HPMC (90SH−4000SR) was taken forward for use as the skeleton material of the IMM–H014 tablet.
2.2.2. HPMC concentration
Next, the concentration of HPMC was screened (as shown in the
Table 6; IR, F5–F10) to achieve the ideal release effect of IMM–H014 ER tablets. The amount of HPMC had a significant effect on the release profile, while the physical properties of F5–F10 demonstrated that the concentration of hydrophilic polymers did not influence the physical properties of the obtained granules and tablets, such as angle of repose, CI, hardness of tablets and weight variation of tablets (as shown in
Table 1).
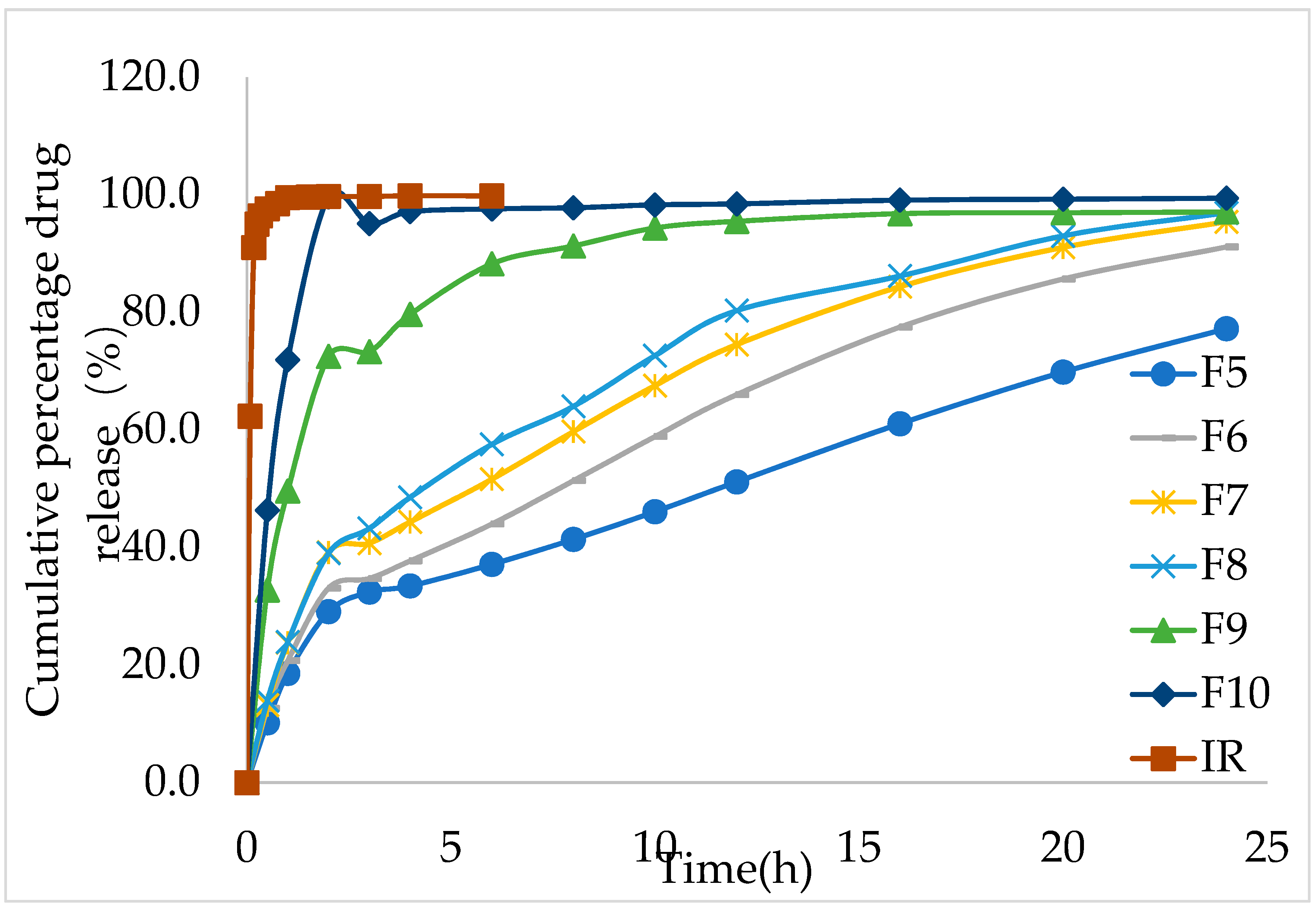
During the in vitro release study, the IMM–H014 tablets remained intact, although with a gel layer formed around them. The in vitro dissolution results showed that the in vitro release rate increased with the decrease in the ratio of HPMC in the formulation. The cumulative release amount of F5 and F10 was 19.1% and 71.9% in 1 h, respectively, while the cumulative immediate– release (IR) was 100% < 1 h (as shown in
Figure 2 and
supplementary materials Table S3).
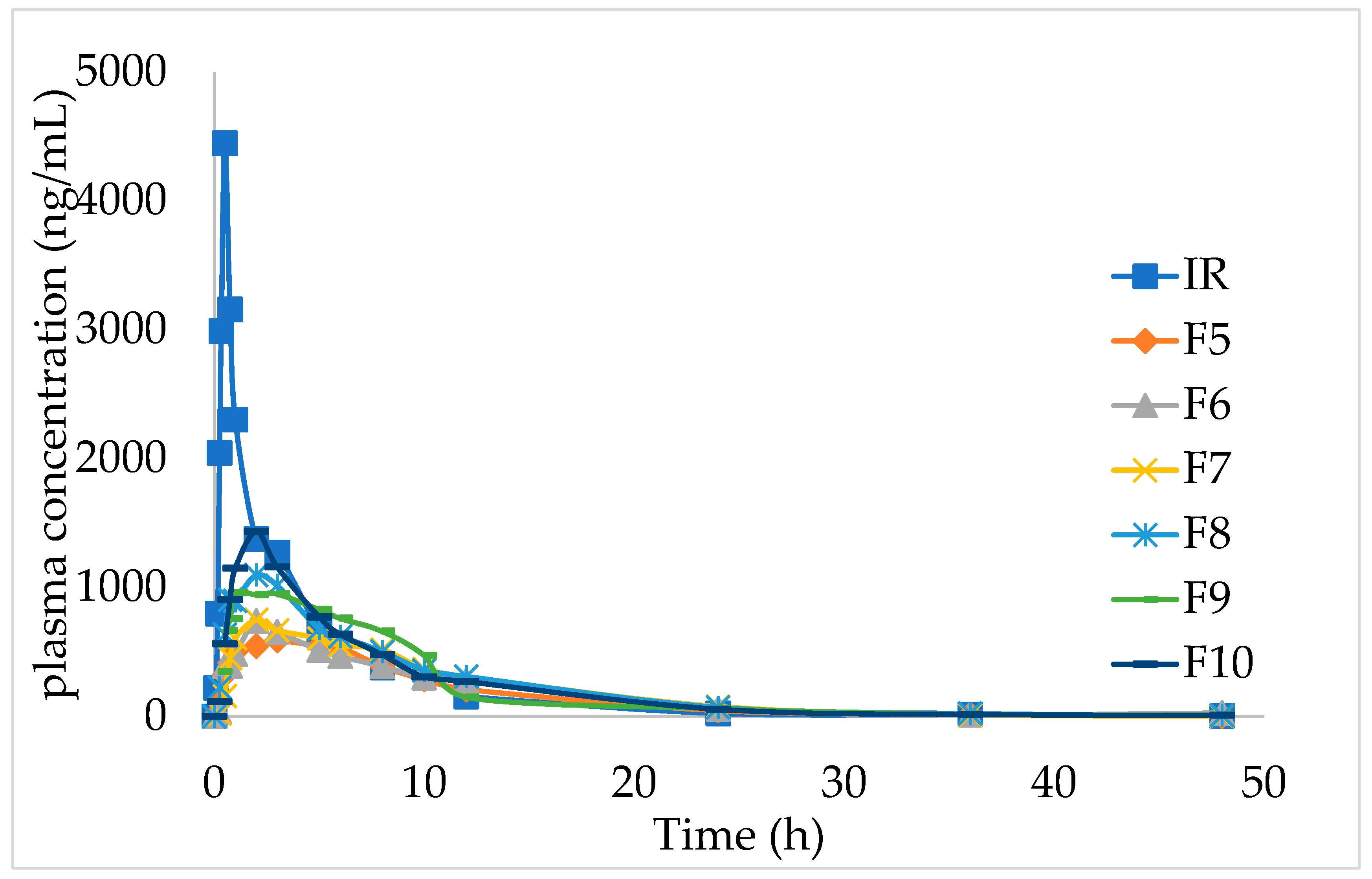
The effect of different HPMC dosages on the pharmacokinetics in beagle dogs showed that with the increase in the amount of matrix material, the release rate of IMM−H014 tablets in vitro, the absorption in vivo, and the absorption amount all decreased. When the amount of skeleton material was high, the bioavailability in beagles was low and could not be fully absorbed. When the dosage of skeleton material (HPMC) was 15% (F9), the area under curve (AUC) of the ER IMM–H014 tablet was equivalent to the IR preparation (as shown in
Table 6), the mean residence time (MRT) was significantly lengthened, the maximum plasma concentration (C
max) was significantly lowered, and the in vivo release was slower (as shown in
Figure 3 and
supplementary materials Table S4). It has been previously shown that diffusion is a key factor affecting the release of IMM-H014. With the increase in HPMC concentration, the thickness of the gel layer formed around the sustained-release tablets increases, as does the diffusion path. The mechanical properties of the polymer network were improved by creating a longer diffusion path, thus reducing the drug release from the tablets.
2.3. In vitro dissolution studies
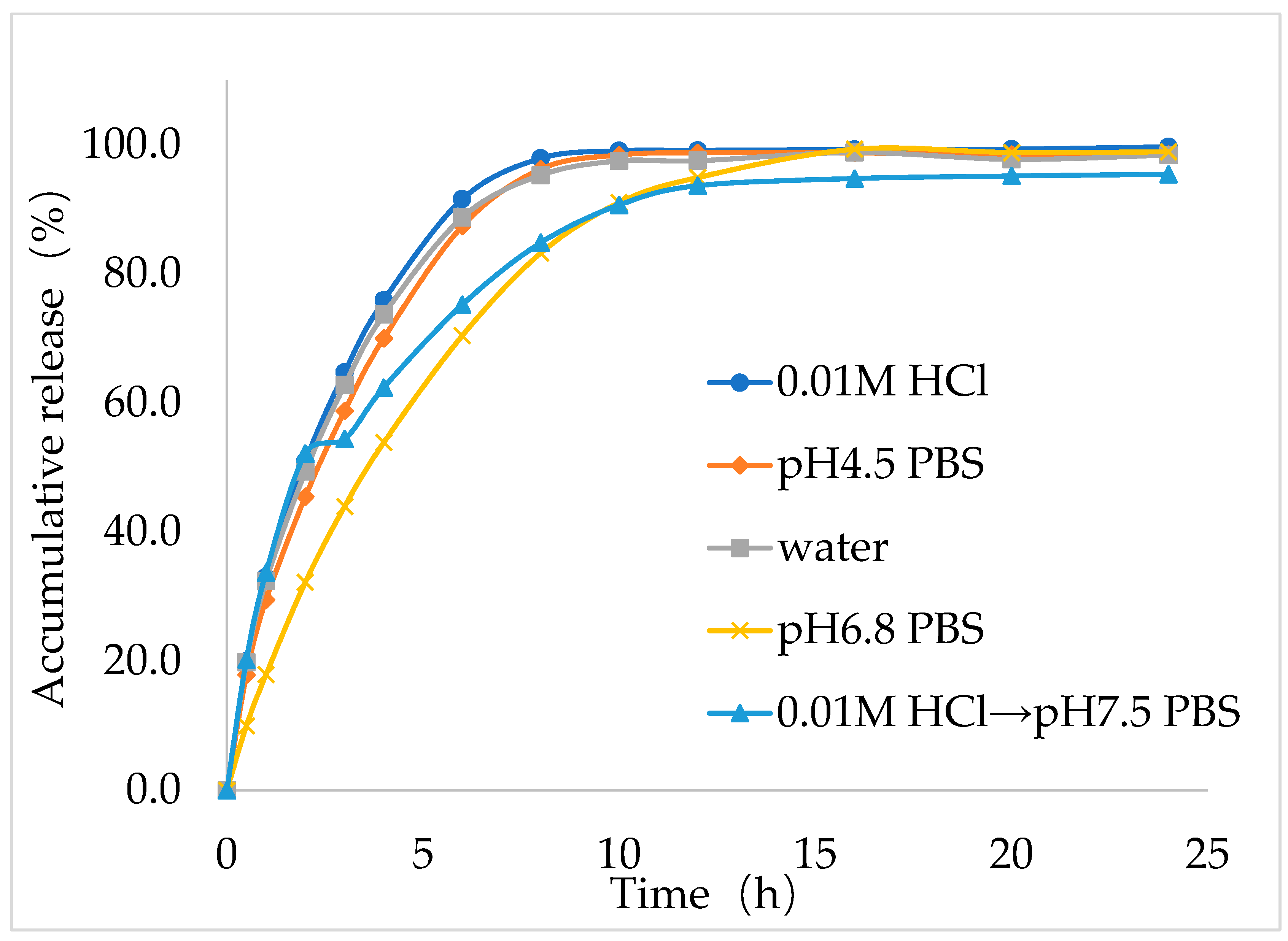
Next, to study the dissolution behavior of the best formulation (F9), in vitro dissolution study was performed for IMM–H014 ER tablets in the following five dissolution media: 0.01 N HCl, pH 4.5 acetate buffer extraction procedure (ABEP), pH 6.8 phosphate buffer saline (PBS), water, and pH 2.0→pH 7.5 PBS (as shown in
Figure 4), the total amount released within 24 h reached more than 90% in all five media. The optimal formulation (F9) showed good ER characteristics in the five dissolution medias. Notably, the in vitro release behavior of the optimal IMM–H014 ER tablets was affected by the pH of the dissolution media to some extent. The drug release within the initial stage (1 h) under conditions of pH 2.0 was higher than those in other medias. As the pH of the medium increased, the release rate decreased, which was consistent with the finding that IMM–H014 possessed pH-dependent saturated solubility.
2.4. Drug release mechanism studies
To elucidate the release kinetic characteristics of IMM–H014 ER tablets in pH 2.0→ pH 7.5 media, The zero–order, first–order, Higuchi, and Ritger–Peppas models were used to accommodate the drug release kinetics model (as shown in
Table 2). The fitting result was Q
t = 32.87 t
0.45, and the corresponding R
2 was 0.97521, which showed a good and reasonable correlation with the Ritger–Peppas model. Moreover, the n value was 0.45, which confirmed that IMM–H014 was released from the optimized formulation by diffusion, consistent with the high solubility of IMM–H014 in aqueous solution.
2.5. Reproducibility
For their further application in industry, the reproducibility of the production processes of the optimal IMM–H014 ER tablets was explored. Three batches each comprising 20,000 tablets were prepared. The results showed no pronounced difference in the visual appearance of three batches of products, and the IMM–H014 content was > 99% in all three batches. Moreover, the in vitro release profile (as shown in
Table 3;
supplementary materials Table S5 and Figure S2) showed that the calculated f
2 values among the different batches were all greater than 50 (
Table 3). The reproducibility and rationality were elucidated by the acceptable S.D. and similar drug release profiles.
2.6. Stability evaluation
The appearance, content, and in vitro release profile of the optimal IMM–H014 ER tablets were studied after being reposited for 6 months under accelerated circumstances (40°C, relative humidity (RH) 75% ± 5%) (As shown in
Table 4). The tablets showed no obvious change in terms of their appearance and content over the 6-month period. Additionally, the f
2 values of the IMM–H014 ER tablets in the five media were still higher than 50 after 6 months of storage, suggesting similar release behavior compared to that of the 0-month formulation.
2.7. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies
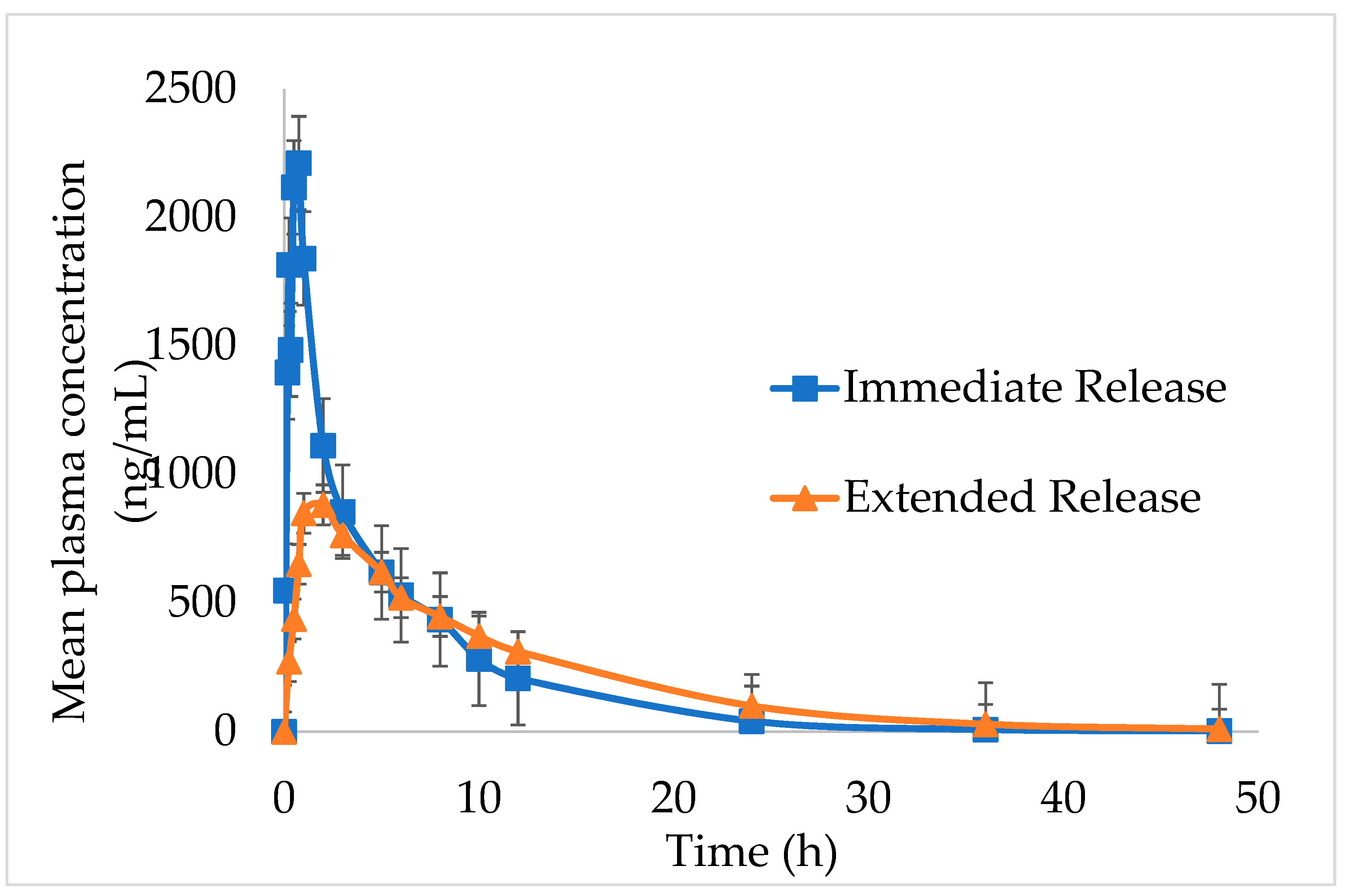
The in vivo pharmacokinetic outlines and calculated pharmacokinetic parameters after oral administration of IMM–H014 ER and IR to beagles are shown in
Figure 5 and
Table 5. The IMM–H014 content in plasma was analyzed at different points. As expected, compared to IR, the plasma concentration of IMM–H014 ER tablets was more stable. The T
max of IR and ER tablets was 0.7 h and 2.5 h, respectively, demonstrating a delayed T
max of IMM–H014. The C
max of the plasmatic IMM–H014 concentration for the IR and ER tablets were 3106.894 ng/mL and 1067.956 ng/mL, respectively, demonstrating an obviously decreased C
max of IMM–H014. The values of MRT for IR and ER were 6.1 h and 9.8 h, respectively, indicating slower elimination of IMM–H014 ER tablets. Meanwhile, there was significant difference in T
max, C
max, and MRT between IMM–H014 IR and ER tablets (P < 0.05). Additionally, the relative bioavailability F of IMM–H014 ER tablets compared to IR based on AUC
0→t was 97.9%, suggesting that they exhibited similar absorption in the circulation. Compared to IR, the ER tablets showed an obvious ER effect.
2.8. In vivo– in vitro correlation
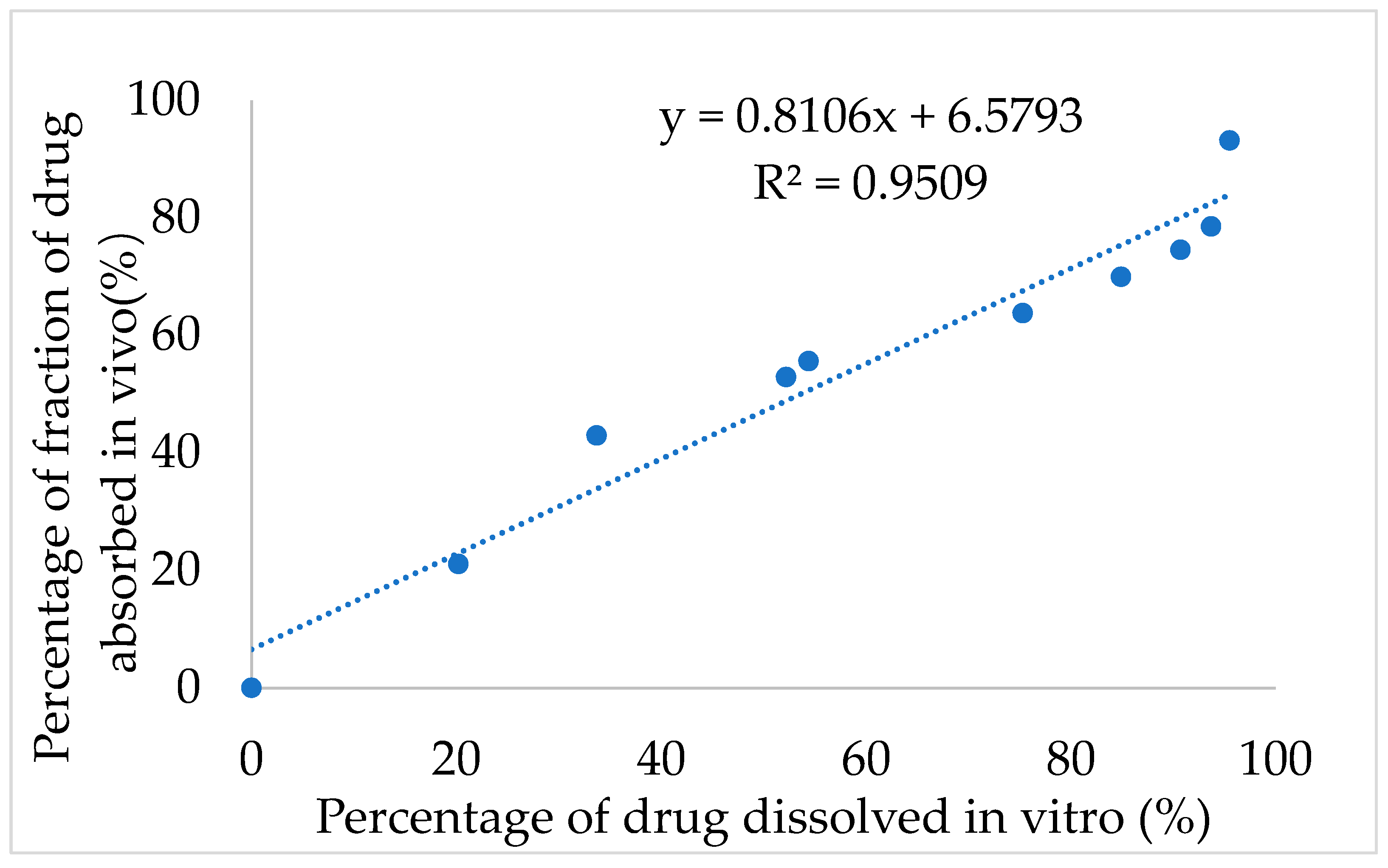
Next, the IVIVC for IMM–H014 was examined. After validation using the DAS2.0 (drug and statistics for Windows) program, the optimization single compartment model was determined for the drug dosage forms. The percentage of drug release in 0.01 N HCl→ pH 7.5 PBS medium of ER tablets and the drug absorption fraction in beagle dogs under a fasted condition were used to investigate the IVIVC. According to the Loo–Riegelman method, the accumulative absorption fraction of IMM–H014 was calculated. As shown in
Figure 6, the correlation coefficient (R
2) between the drug in vitro release and in vivo absorption percentage was 0.9509, demonstrating a good association between the drug release and fraction absorption. Therefore, the in vitro drug release could predicate the in vivo absorption behavior.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
IMM–H014 was produced in the author’s laboratory; hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) was purchased from Shin–Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. (Dalian, China); lactose was purchased from DFE pharma GmbH & Co. KG. (Shanghai, China); silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate were purchased from Anhui Sunhere Pharmaceutical Excipients Co., Ltd. (Huainan, China); and acetonitrile (HPLC grade) and methanol (HPLC grade) were purchased from Honeywell. The other reagents were analytical grade.
Animal: Beagles (female or male, weighing 6~8 kg, purchased from Beijing Marshall Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) were used for in vivo pharmacokinetic studies. During the experiment, the beagles were given a standard diet and allowed to drink freely. The study followed ethical guidelines and the protocol was approved by Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College ethically (animal ethical clearance protocol number: 00005367, 08/12/2020).
3.2. Solubility test
The saturation solubility of IMM–H014 in pH 2.0, pH 4.5, pH 6.8, and pH 12 media were investigated. An appropriate amount of API was added into different pH media at 37.0 ± 0.5°C, before shaking the flask for 24 h, filtering, and taking the continuous filtrate. The amount of the dissolved drug was quantified by HPLC as described in
Section 3.6.4
3.3. Production of the immediate–release (IR) capsule of IMM–H014
The appropriate amount of IMM–H014 active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) was loaded into the gelatin capsule shell as the IMM–H014 immediate–release preparation.
3.4. Production of IMM–H014 ER tablets
IMM–H014 ER tablets were produced by pressing the powder directly. The required quantities of drug and ingredients were passed through an 80–mesh screen (stainless steel). IMM–H014, HPMC, and lactose were mixed completely using the equivalent addition method. Then, after adding silicon dioxide and magnesium, the sample was mixed for a further 10 min. Finally, the tablets were compressed using a flat–faced 8-mm punch. Each tablet contained 35 mg of IMM–H014, with the tablet weight and hardness maintained at 200 mg and between 100–130 N, respectively. The composition of the tablets is shown in
Table 6.
Table 6.
Composition (in mg) of IMM–H014 tablets.
Table 6.
Composition (in mg) of IMM–H014 tablets.
| Code |
IR |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
F6 |
F7 |
F8 |
F9 |
F10 |
| IMM–H014 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
25 |
| HPMC (90SH–4000SR) |
– |
60 |
– |
– |
– |
90 |
65 |
50 |
40 |
30 |
20 |
| HPMC (90SH–10000SR) |
– |
– |
60 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| HPC (M–FP) |
– |
– |
– |
60 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| HPC (H–FP) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
60 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| lactose |
– |
111 |
111 |
111 |
111 |
81 |
106 |
121 |
131 |
141 |
151 |
| Silicon dioxide |
– |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| Magnesium stearate |
– |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
| Total weight |
25 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
3.5. Evaluation of granules
3.5.1. Angle of repose
The granules’ angle of repose was measured using the funnel method. The granules were precisely weighed and located in the funnel, and the height of the funnel was adjusted so that the cusp of the funnel just touched the top of the granule cone. The granules ran freely through the funnel to the surface. The diameter of the particle cone was evaluated and the angle of repose was figured by Equation (1).
where h is the height of the granule cone and r is the radius of the granule cone.
3.5.2. Bulk Density
Approximately 5.0 g of particles, which were weighed without any aggregation, were placed in a 10.0-mL measuring cylinder to acquire the volume. The cylinder was dropped from a height of 2.5 cm on a flat surface every 2 s and knocked until there was no further change in volume. Loose bulk density (LBD) and tapped bulk density (TBD) data were calculated using Equations (2) and (3).
3.5.3. Compressibility index
The Carr’s Index [
23] was used to determine the compressibility index of granules and calculated using the following Equation (4).
3.6. Evaluation of tablets
3.6.1. Weight variation test
An electronic balance was used to weigh 20 tablets that were taken randomly from each formulation, with weight values were determined in milligrams (mg) (Mettler Toledo, USA).
3.6.2. Hardness test
Six tablets were taken randomly from each formulation and determined using a hardness tester, with hardness values reported in Newton (N) (Tianda Tianfa Instrument. Tianjin, China).
3.6.3. Friability test
Approximately 6.5 g tablets were taken from each formulation and accurately weighed and placed in the friability tester (Xixin Instrument, Tianjin, China) and set to 100 revolutions for 4 min. After the ultimate tablets were dedusted and reweighed, the percentage weight lost was counted as the friability using Equation (5).
3.6.4. Content determination
Twenty tablets were taken at random from each lot and weighed, before placing in a mortar and porphyrizing with a pestle. A quantity equivalent to 5 mg of IMM–H014 (40 mg of powder) was pulled up with 100 mL hydrochloric acid solution (0.1 N) and supersonically extracted over 30 min. Then, the resulting 10 mL solution was filtered through a polytetrafluoroethylene filter membrane (PTFE, 0.45μm pore size, Jinteng, Tianjin, China). A C18 column was used as a stationary phase. The collected samples (20 μL) were analyzed using HPLC (Shimazu LC-20AT, Japan) with a UV detector wavelength of 230 nm. IMM–H014 was separated under a mobile phase consisting of ammonium formate PBS (pH 4.0): acetonitrile at a 60:40 (v/v) ratio using a C18 column (4.6 mm × 25 cm, 5.0μm). The flow velocity was 0.7 mL/min and the column temperature was of 35°C. The linearity for IMM–H014 ranged from 20.01 μg/mL to 60.02 μg/mL. The validation was conducted following the ICH guidelines.
3.6.5. In vitro release studies
A USP type II dissolution apparatus was used to test the in vitro release of IMM–H014 tablets. The dissolution profiles of five dissolution media were surveyed. The first dissolution medium was 700 mL of 0.01 N HCl (pH 2.0). At 2 h, 200 mL of 5.25 g/L (m/v) sodium phosphate solution was added to adjust the pH of the media to 7.5. The other dissolution mediums were 0.01 N HCl solution, pH 4.5 PBS, water, pH 6.8 PBS, with a volume of dissolution medium of 900 mL; the speed was 50 rpm, and the temperature was maintained at 37 ± 0.5°C throughout all experiments. The drug release was quantified by ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry at a wavelength of 230 nm. As a result, different dynamic equations were in accordance with the data of the first media, containing zero order, first order, Higuchi, and Ritger–Peppas.
The similarity factor (f
2) was calculated to compare the release profiles of the IMM–H014 ER tablets during the production and stability study periods, which were defined by Equation (6) [
24].
where n is the number of sampling times, and R
t and T
t are the dissolution value of the reference and test samples at each timing, respectively [
24].
3.6.6. Stability studies
The IMM–H014 tablets were packed in aluminum–aluminum blister packaging and placed under the acceleration conditions (40°C, RH75%) for 6 months. The similarity factor (f2) of the dissolution curve, appearance and content were used as the index of inspection.
3.7. Drug release mechanism
The following mathematical models with different equations were used to analyze the description of in vitro dissolution [
25].
Zero order model: Mt /M∞ =k0 t
First order model: ln (1– Mt/ M∞) = – k1t
Higuchi model: Mt /M∞ =kh t1/2
Ritger–Peppas model: Mt /M∞ =kk tn
where the drug release amount at time t is M
t, and the final drug release amount is M
∞. The zero- order release rate constant is k
0; the first order release rate constant is k
1; and the k
H is the zero- order release rate constant [
25].
In the Ritger–Peppas model, the diffusion mechanism is expressed by the value of n, with n ≤ 0.45 corresponding to a fickian diffusion mechanism, 0.45 < n < 0.89 corresponding to a diffusion and erosion skeleton common action mechanism, and n ≥ 0.89 corresponding to an erosion skeleton [
26]. For every model considered, the best fitting is indicated by the correlation coefficient (r), where an r closer to 1 indicates a better fitting effect.
3.8. In vivo pharmacokinetics study in beagles
3.8.1. Study design
The study was conducted to compare the pharmacokinetics of the IMM–H014 ER tablets to those of the IMM–H014 IR tablets, following the administration of single doses equivalent to 75 mg (three tablets per dose), with a two–treatment, two–period (time interval was 7 days), crossover design. Ten healthy beagle dogs of either sex were selected for the experiment and randomly divided into two groups (five dogs in each). Before the study, the dogs were fasted for approximately 12 h, with water provided freely. The sampling time points are different due to the different release rates of the ER and IR preparations. Venous blood samples (1–2 mL) were withdrawn into heparinized tubes at 0, 0.08, 0.17, 0.25, 0.33, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h after administration of the IR preparation, while the sampling times for the ER tablets were 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h after administration. The blood samples were promptly centrifuged at 4°C and 4000 rpm for 10 min to isolate plasma, which was stored at –20°C until analysis. A validated HPLC–MS analytical technique was developed to estimate the drug concentration in plasma samples, and the pharmacokinetic parameters (Cmax, Tmax, MRT and AUC) were estimated.
3.8.2. Statistical analysis
The plasma concentration of IMM–H014 was plotted versus time to exhibit the pharmacokinetic profiles. Statistical analysis was executed using DAS2.0 software (version 2.0, Mathematical Pharmacology Professional Committee, Shanghai, China). Key parameters of pharmacokinetics, such as C
max, T
max, MRT and AUC were analyzed. Statistical significance was defined at p < 0.05. The relative bioavailability (F) was calculated using the AUC
0–t of IR and ER tablets [
27].
3.9. IVIVC
The IVIVC was developed to relate the percentage of in vitro drug dissolution to the percentage in vivo drug absorption and was used for drug development. Based on a good correlation, the in vivo pharmacokinetic profile can be determined using the in vitro dissolution rate alone.
The fraction of the drug absorbed (Fa) was calculated by the Wagner–Nelson [
28] Equation (7).
where Fa is the fraction of the drug absorbed, C
t is the concentration of drug in the plasma at time point t, k is the elimination rate constant, AUC
0–t is the calculated area under the plasma concentration curve from zero to time t, and AUC
0–∞ is the calculated area under the plasma concentration curve from time zero to infinity [
28]. The percentage of drug absorption (Fa) at the specified timing was drawn against the percentage of drug dissolved in vitro at the same timepoint. The pertinence between the in vitro release and in vivo absorption was assessed by the linear regression coefficient (R).
4. Conclusions
In this study, IMM–H014 was developed as an ER preparation to solve the problems of short oral administration half– life, short administration interval and high frequency administration of IMM–H014. IMM–H014 ER tablets composed of hydrophilic polymers were produced by a direct powder pressing method. The optimal formulation of IMM–H014 ER tablets was followed to accelerate stability research and remained stable over a 6-month period. For the in vitro dissolution studies, the optimal formulation showed an obvious ER compared to the IR preparation. The results from the in vivo pharmacokinetics study in beagle dogs also clearly indicated that the AUC of IMM–H014 ER tablets was equivalent to that of the IR preparation, the relative bioavailability was 97.9%, the Cmax was lowered to around 1/3, and the Tmax and MRT were meaningfully lengthened, with a visible ER impression. Moreover, the IVIVC correlation coefficient (R2) was 0.9509, suggesting that the prepared tablets followed a good correlation between in vitro release and pharmacokinetic effect. Therefore, the absorption in vivo can be predicted by the release in vitro.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Saturated solubility of IMM-H014 in different media; Table S2: Cumulative percentage drug release of IMM-H014 tablet with different matrix materials; Table S3 Cumulative percentage drug release of IMM-H014 tablet with HPMC concentration (IR, F5 to F10); Table S4. Pharmacokinetic parameters of ER with different HPMC concentration and IR; Table S5. Cumulative percentage drug release of IMM-H014 ER tablets in five different dissolution media; Figure S1. In vitro release profiles of tablet with different matrix materials (F1 to F4) in 0.01N HCl →pH; Figure S2. The in vitro release behaviors: IMM-H014 ER tablets in five different dissolution media; 0.01 N HCl→pH7.5 phosphate buffer saline (A), 0.01 N HCl (B), pH 4.5 acetate buffer extraction procedure (C), water (D), pH 6.8 phosphate buffer saline (E); three batches of IMM-H014 ER tablets (n = 12).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W., Q.-Y.Y., C.Z. and H.-H.S.; Formulation and process, C.Z., B.L. and J.Z.; Methodology, H.-H.S., Z.-S.H., and J.F.; Data curation, K.Z., Z.-S.H. and C.Z.; Resources, W.-X.Z.; Writing—original draft preparation, C.Z. and H.-H.S.; Writing—review and editing, Q.-Y.Y. and S.W.; Funding acquisition, C.Z., W.-X.Z. and S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS no. 2021-I2M-1-028), and Beijing Natural Science Foundation(7234404).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College ethically (animal ethical clearance protocol number: 00005367)
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Costante, F.; Airola, C.; Santopaolo, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; Pompili, M.; Ponziani, F.R. Immunotherapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Lights and shadows. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1622–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.-Y.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, M.; Koh, H.B.; Park, K.H.; Joo, Y.S.; Kim, H.W.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, J.T.; Kim, S.U. Exercise reduces the risk of chronic kidney disease in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 48, 101362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Lassailly; R. Caiazzo; L. C. N. Wandgi; et al. Bariatric surgery provides long–term resolution of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and regression of fifibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2020, 159, 1290–1301. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Li, Q.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, Y.; Fang, M.; Yu, Z.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Gao, Y.; et al. Therapeutic potential of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of NAFLD: A promising drug Potentilla discolor Bunge. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3529–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- C. Zhang; M. N. Shi; W. Kim; et al. Discovery of therapeutic agents targeting PKLR for NAFLD using drug repositioning. EBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104214. [CrossRef]
- Song Wu; Hua Sun; Wenxuan Zhang; et al. A class of dicyclic alcohols derivatives and their preparartion and application: China Patent CN107488162A [P]. 2016–10–19.
- Song Wu; Chi Zhang; et al. The invention relates to a drug sustained release tablet for the treatment of liver disease, preparation process and application thereof: China Patent CN114652692A [P]. 2022–04–28.
- Venkatesh DN; Meyyanathan SN; Shanmugam R; Zielinska A; Campos JR; Ferreira JD; Souto EB. Development, in vitro release and in vivo bioavailability of sustained release nateglinide tablets. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2020, 55, 101355. [CrossRef]
- Krukiewicz, K.; Stokfisz, A.; Zak, J.K. Two approaches to the model drug immobilization into conjugated polymer matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 54, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasini, N.; Haque, S.; Kaminskas, L.M. Polymer-drug conjugates as inhalable drug delivery systems: A review. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 31, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaodong Yan. Design and development of sustained–release and controlled–release preparations; The medicine science and technology press of China: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 68–90. [Google Scholar]
- Borgquist, P.; Körner, A.; Piculell, L.; Larsson, A.; Axelsson, A. A model for the drug release from a polymer matrix tablet—effects of swelling and dissolution. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hardy, RJ.; Gu, X. Effect of drug solubility on polymer hydration and drug dissolution from polyethylene oxide (PEO) matrix tablets. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2008, 9, 437–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, C.D. Hydrophilic matrix sustained release systems based on polysaccharide carriers. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1991, 8, 395–421. [Google Scholar]
- Alderman, D.A. A review of cellulose ethers in hydrophilic matrices for oral controlled release dosage forms. Int. J. Pharm. Tech.Prod. 1984, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Mishra, V.; Gharat, S.; Momin, M.; Omri, A. Cellulosic Polymers for Enhancing Drug Bioavailability in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasamy Venkatesh, D.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; Shanmugam, R.; Kamatham, S.S.; Campos, J.R.; Dias–Ferreira, J.; Sanchez–Lopez, E.; Cardoso, J.C.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B. Physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic characterization of isradipinetablets for controlled release. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, D.N.; Meyyanathan, S.N.; Kovacevic, A.; Zielińska, A.; Fonseca, J.; Eder, P.; Dobrowolska, A.; Souto, E.B. Effect of Hydrophilic Polymers on the Release Rate and Pharmacokinetics of Acyclovir Tablets Obtained by Wet Granulation: In Vitro and In Vivo Assays. Molecules 2022, 27, 6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman EN; Lerner F.; Joseph HM.; Alon M. Properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose–polyvinyl alcohol water systems, dispersants in vinyl chloride suspension polymerization. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 1993, 48, 435–442. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.C. Sol-Gel Behavior of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) in Ionic Media Including Drug Release. Materials 2011, 4, 1861–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco MV; Ford JL; Rowe P; Rajabi–Siahboomi AR. Influence of drug:hydroxypropylmethylcellulose ratio, drug and polymer particle size and compression force on the release of diclofenac sodium from HPMC tablets. J Control Release. 1999, 57, 75–85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-E. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation of Tianeptine Sodium Sustained-Release Dual-Layer Tablets. Molecules 2022, 27, 2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.B.; Tawakkul, M.A.; Khan, M.A. Comparative Evaluation of Flow for Pharmaceutical Powders and Granules. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xza, B., Yl, C., Zh, B., Yc, B., Zzb, D., & Xiao, Y. B. Development and pharmacokinetics evaluation of quetiapine fumarate sustained–release tablets based on hydrophilic matrix. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2019, 54, 101322–101322.
- Herrlich S; Spieth S; Messner S. Osmotic micropumpsfor drug delivery. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2012, 64, 1617–1627. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh T–O.; Kim JY; Ha JM. Preparation of highly porous gastroretentive metformin tablets using a sublimation method. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013, 83, 460–467. [CrossRef]
- Agoram, B.; Woltosz, W.S.; Bolger, M.B. Predicting the impact of physiological and biochemical processes on oral drug bioavailability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 50, S41–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Z–Q; He X; Gao X; et al. Study on dissolution and absorption of four dosage forms of isosorbide mononitrate: level A in vitro–in vivo correlation. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011, 79, 364–371. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).