Submitted:
11 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Quantitative Phytochemical Determinations
2.1.1. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds:
2.1.2. Determination of Concentration of Alkaloids
2.1.3. Determination of Total Tannins
2.1.4. Determination of Concentration of Flavonoids
2.1.5. Determination of Concentrations of Steroids
2.2. Acute Toxicity Studies (LD50) (Lorke’s Method)
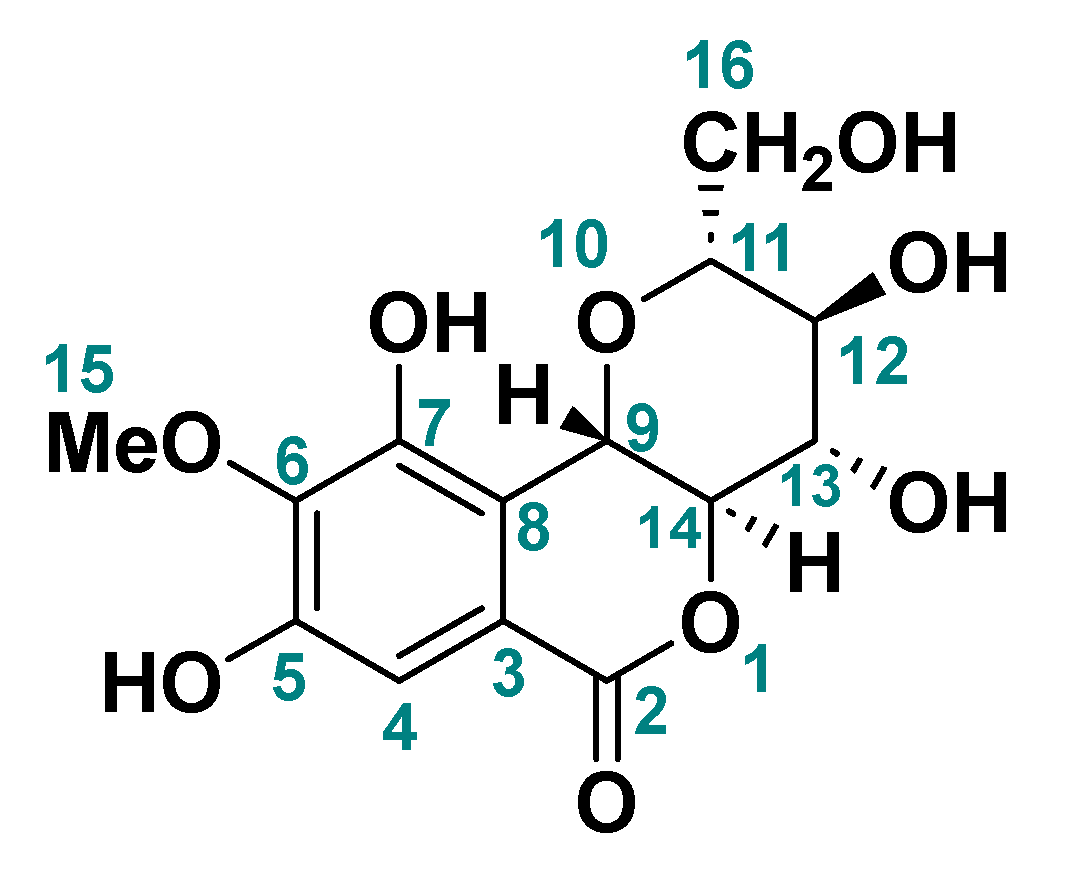
2.3. Identification of Bergenin
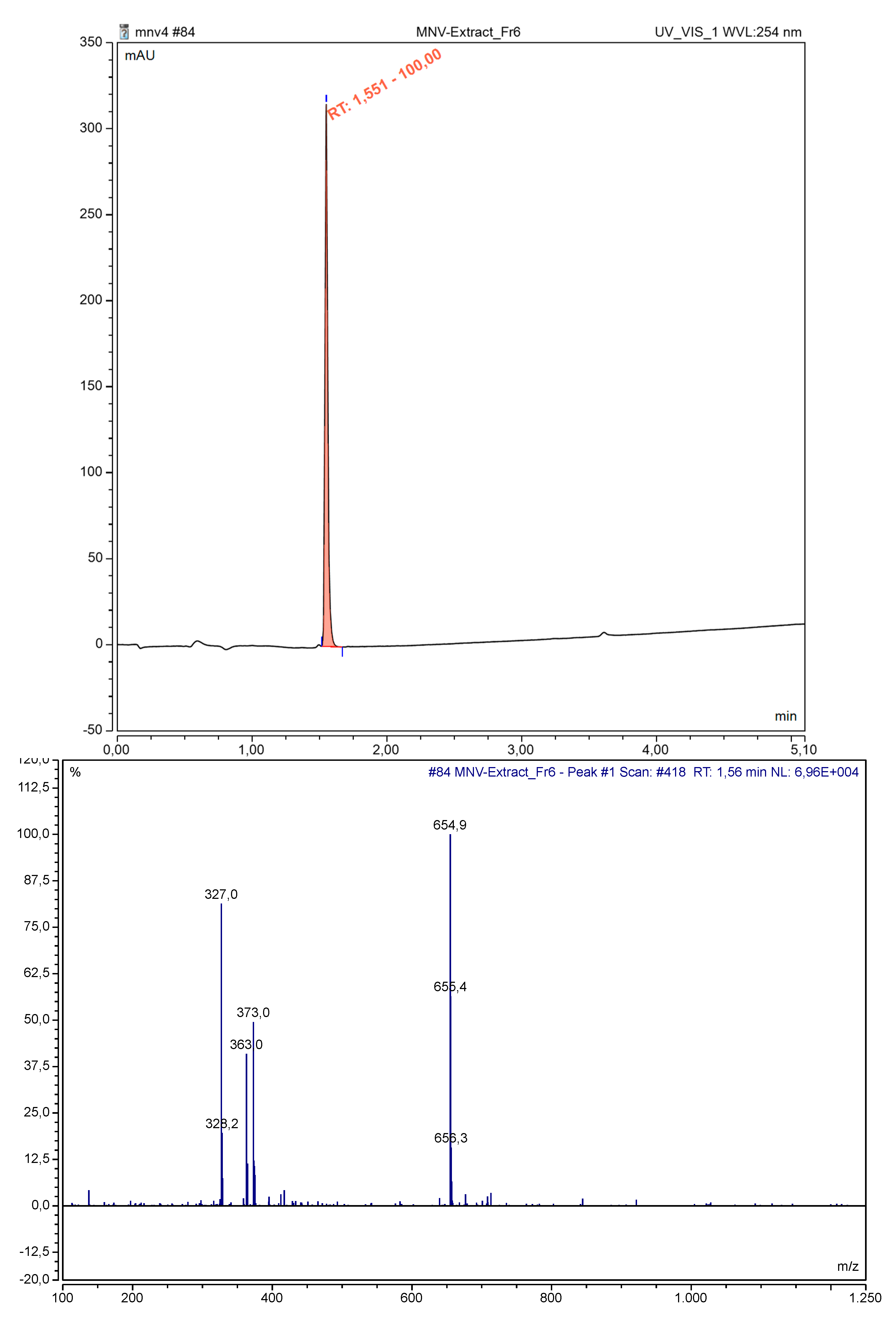
2.3.1. Bergenin Isolation by Preparative HPLC
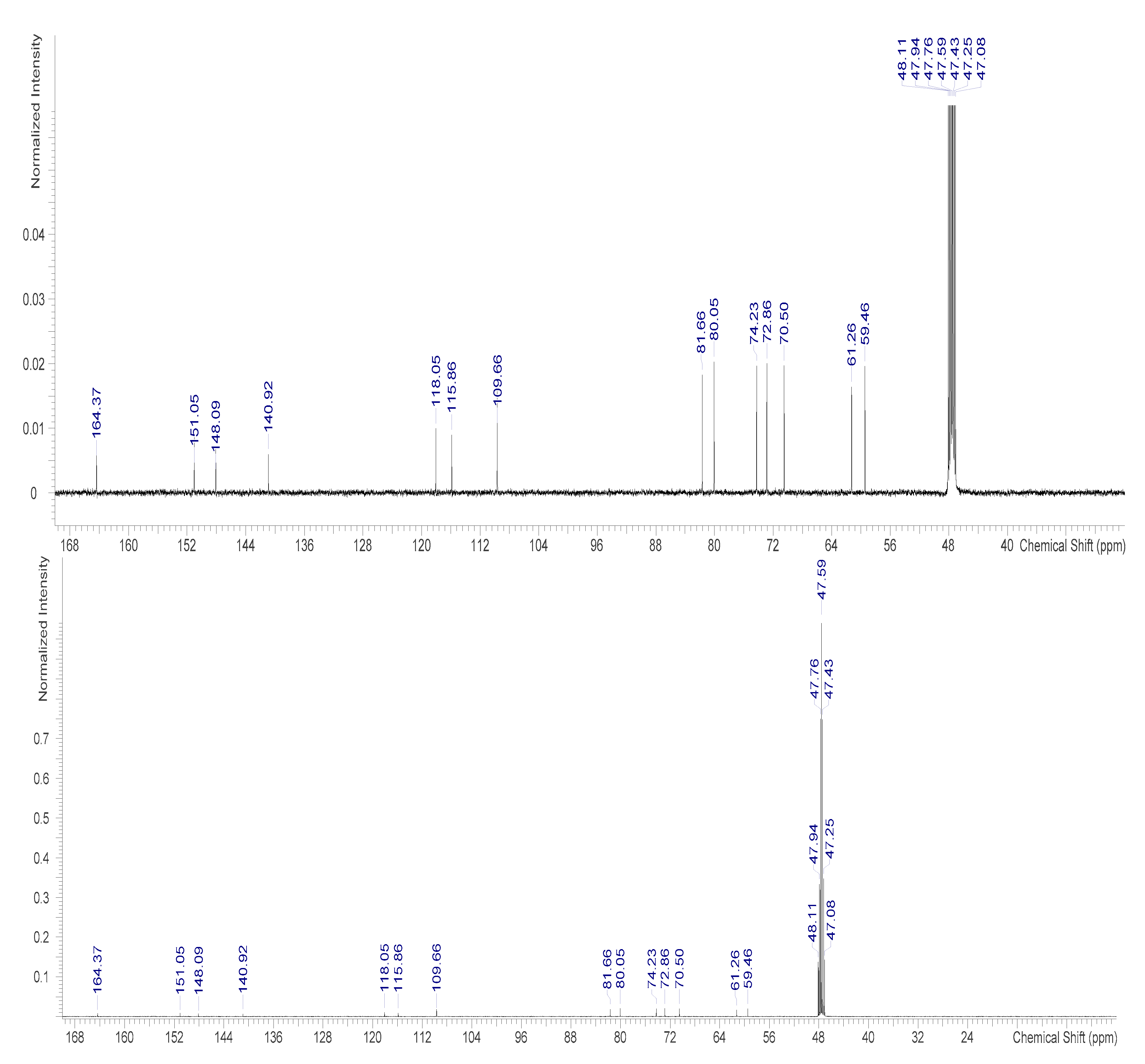
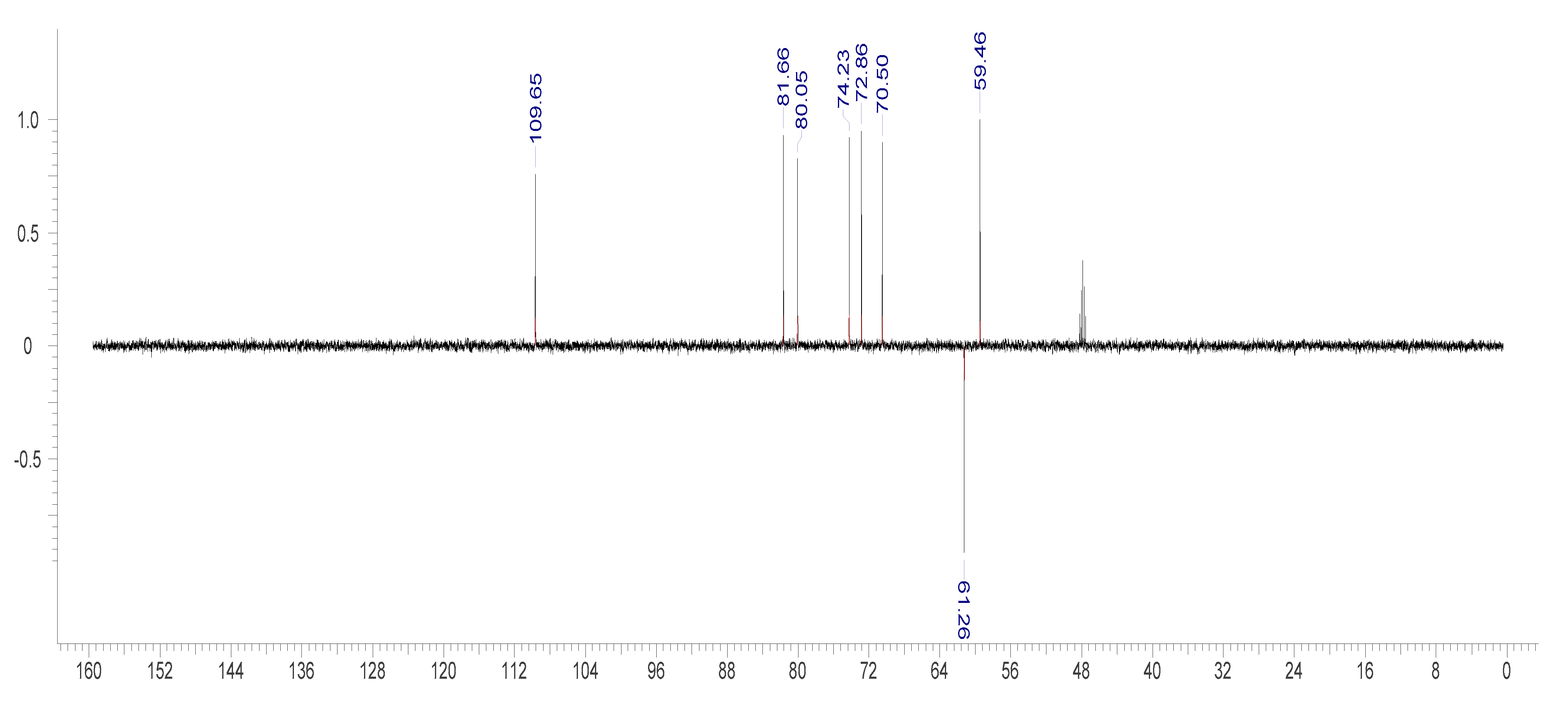
2.3.2. NMR Measurement
2.3.3. Analytical LC-MS Analysis
2.3.4. Infrared Spectroscopy:
2.4. In Vitro Antioxidant Assay
2.4.1. DPPH (1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) Radical Scavenging Assay
2.4.2. Nitric Oxide (NO.) Radical Scavenging Activity:
2.4.3. Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) Assay:
2.4.4. FRAP (Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power) Assay:
2.5. In Vivo Antioxidant Activity:
2.5.1. Experimental Design
2.5.2. Catalase Assay
2.5.3. Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
2.5.4. Malondialdehyde (MDA)
2.5.5. Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Evaluation of Phytochemicals
3.2. Acute Toxicity
3.3. Identification of Bergenin
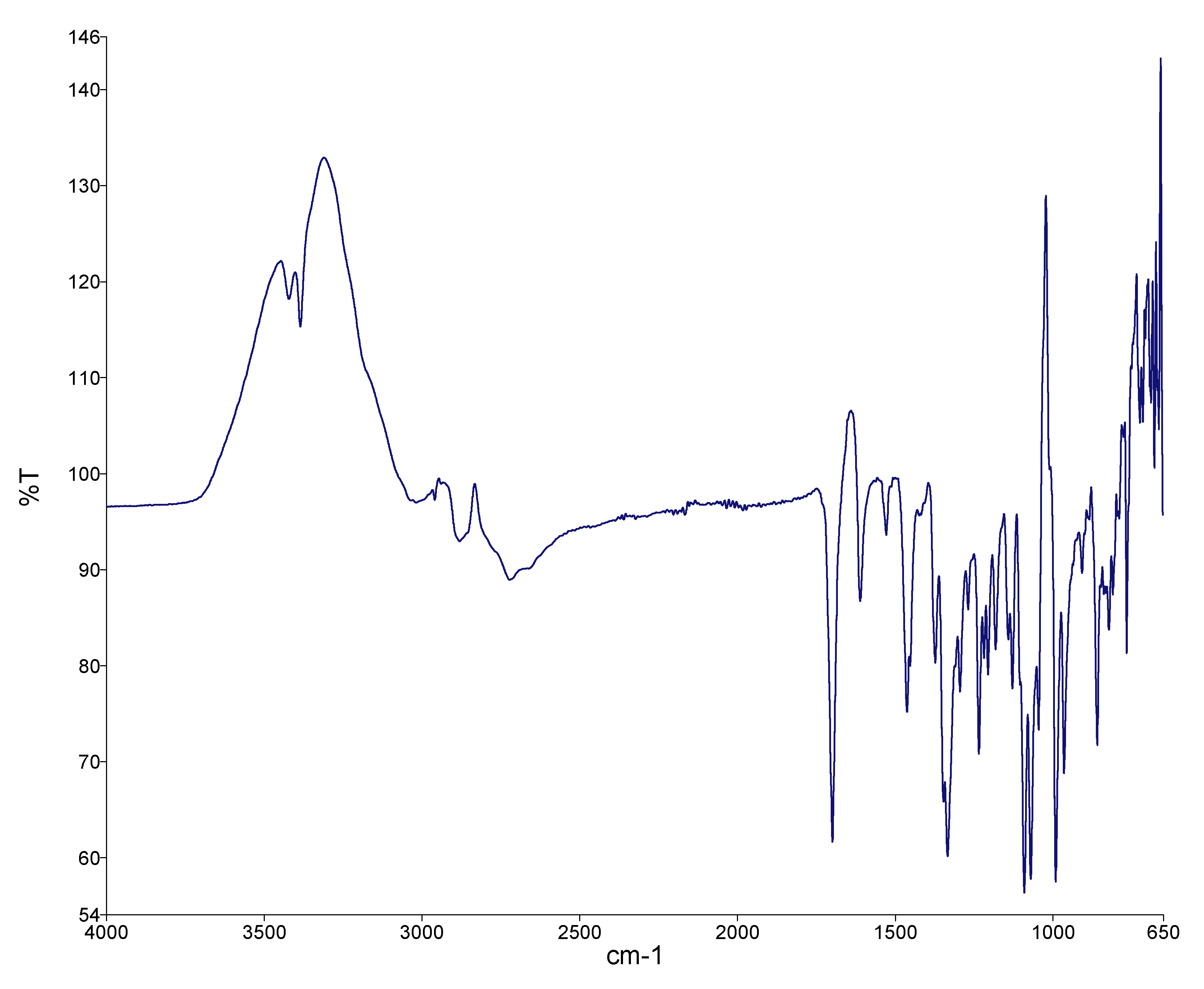
3.3.1. FTIR Spectroscopy of Bergenin
3.4. The In-Vivo Antioxidant Effect of Different Concentrations of Pentaclethra macrophylla Extracts, Determined by Using Malondialdehyde (MDA), Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), and Catalase (CAT), Is Shown in Table 3
| Groups | MDA (mg/ml) | GPx U/mg | SOD U/mg | Cat U/mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| One | 1.04±0.03 | 47.67±4.73 | 11.44±0.03 | 1.76±0.93 |
| Two | 1.16±0.07 | 59.03±11 | 11.39±0.04 | 0.71±0.39 |
| Three | 1.2±0.05 | 48.33±4.44 | 11.42±0.06 | 1.61±0.98 |
| Four | 1.34±0.00 | 47.61±0.00 | 11.37±0.00 | 1.8±0.00 |
| Five | 1.26±0.02 | 48.09±5.61 | 11.16±0.45 | 1.11±0.23 |
| Six | 1.25±0.12 | 47.02±4.28 | 11.08±0.71 | 1.42±0.50 |
In Vitro Antioxidant
4.0. Discussion
4.1. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Authors’ Declaration
References
- Elimastas, M., Gulcin, I., Beydemir, S., Kufrevioglu, O., & Aboul-Enein, H. A study on the in vitro antioxidant activity of Juniper (Juniperus communis L.) fruit extract. Analytical letters 2018, 39, 47–65. [CrossRef]
- Huyut, Z., Beydemir, Ş., & Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant and antiradical properties of selected flavonoids and phenolic compounds. Biochemistry research international 2017, 7616791. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztaskın, N., Taslimi, P., Maraş, A., Gülcin, İ., & Göksu, S. Novel antioxidant bromophenols with acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory actions. Bioorganic chemistry 2017, 74, 104–114. [CrossRef]
- Anraku, M., Gebicki, J. M., Iohara, D., Tomida, H., Uekama, K., Maruyama, T., ...& Otagiri, M. Antioxidant activities of chitosans and its derivatives in in vitro and in vivo studies. Carbohydrate Polymers 2018, 199, 141–149. [CrossRef]
- Capanoglu, E., Kamiloglu, S., Ozkan, G., & Apak, R. Evaluation of antioxidant activity/capacity measurement methods for food products. Measurement of antioxidant activity & capacity: Recent trends and applications 2018, 273–286.
- Çakmakçı, S., Topdaş, E. F., Kalın, P., Han, H., Şekerci, P., P. Köse, L., & Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant capacity and functionality of oleaster (E laeagnus angustifolia L.) flour and crust in a new kind of fruity ice cream. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 2015, 50, 472–481.
- IIhami, G. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: an updated overview. Archives of Toxicology 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuolo, M. M., Lima, V. S., & Junior, M. R. M. Phenolic compounds: Structure, classification, and antioxidant power. In Bioactive compounds; Woodhead Publishing, 2019; pp. 33–50.
- Bursal, E. Bursal, E., Aras, A., & Kılıç, Ö. Evaluation of antioxidant capacity of endemic plant Marrubium astracanicum subsp. macrodon: Identification of its phenolic contents by using HPLC-MS/MS. Natural product research 2019, 33, 1975–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureen, S., Riaz, A., Arshad, M., & Arshad, N. In vitro selection and in vivo confirmation of the antioxidant ability of Lactobacillus brevis MG 000874. Journal of applied microbiology 2019, 126, 1221–1232.
- Enujiugha, V. N., Akanbi, C. T., & Adeniran, H. A. (2008). Evaluation of starters for the fermentation of African oil bean (Pentaclethra macrophylla Benth) seeds. Nutrition & Food Science 2008, 38, 451–457. [CrossRef]
- Enujiugha, V. N., & Olagundoye, T. V. Comparative nutritional characteristics of raw fermented and roasted African oil bean (Pentaclethra macrophylla Benth) seeds. Rivista Italiana delle Sostanze Grasse, 2001, 78, 247–250.
- Enujiugha, V. N., Thani, F. A., Sanni, T. M., & Abigor, R. D. Lipase activity in dormant seeds of the African oil bean (Pentaclethra macrophylla Benth). Food Chemistry, 2004, 88, 405–410. [CrossRef]
- Enujiugha, V. N. Quality dynamics in the processing of underutilized legumes and oil seeds. Crops: Growth, Quality and Biotechnology, WFL Publisher, Helsinki 2005, 732–746. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F. Y., Huang, S. T., Lin, M. L., & Lai, J. T. Polyphenol measurement and antioxidant activity of miracle fruit. International Journal of Chemical Engineering and Applications, 2015, 6, 211–214. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. C., Lin, K. S., Jhai, Y. F., Lee, B. H., Han, Y., Cui, Z., ... & Wu, S. C. Miracle fruit exhibits as a novel anti-hyperuricaemia agent. Molecules, 2016, 21, 140.
- Dioso, M. K. M., Satsatin, D. C. A., & Ching, J. A. (2016). www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com.
- Seong, J., Oyong, G. G., & Cabrera, E. C. Synsepalum dulcificum extracts exhibit cytotoxic activity on human colorectal cancer cells and upregulate c-fos and c-jun early apoptotic gene expression. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2018, 8, 173. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Y., Kang, Z. C., Yen, M. T., Huang, M. H., & Wang, B. S. Inhibitory effect of aqueous extracts from Miracle Fruit leaves on mutation and oxidative damage. Food Chemistry, 2015, 169, 411–416. [CrossRef]
- Benn, C. L., Dua, P., Gurrell, R., Loudon, P., Pike, A., Storer, R. I., & Vangjeli, C. Physiology of hyperuricemia and urate-lowering treatments. Frontiers in medicine, 2018, 5, 160. [CrossRef]
- Jeremiah, O. J., Ilesanmi, O. R., & Ige, M. M. Evaluation of the anticonvulsant potential of aqueous fraction of Pentaclethra macrophylla seed extract in mice. European Journal of Medicinal Plants, 2015, 9, 1–8.
- Huang, W., Chung, H. Y., Xuan, W., Wang, G., & Li, Y. The cholesterol-lowering activity of Pentaclethra macrophylla. Journal of food biochemistry, 2020, 44, e13185.
- Harbone, J. B. Phytochemical Methods: A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant Analysis. 1st Edn. Chapman and Hall, London 1973, Pp. 109-119.
- Lorke, D. Anew approach for acute toxicity testing. Archives of Toxicology 1983, 54, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I. Strain, J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a measure of Antioxidant Power. The FRAP Assay. Analytical Biochemistry 1996, 239, 70–76. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, H. E. Catalase. In: Methods of enzymatic analysis. 3rd Edn. (Bergmeyer, H. U. et al eds). Weinheim. Deerfield Beach FL. 1983, Pp 273-285.
- Xin, Z., Waterman, D. E. F., Henken, R. M. and Harmon, R. J. Effects of copper status on neutrophil function, superoxide dismutase and copper distribution in stress. Journal of Diary Science 1991, 74, 3078. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paglia, D. E. and Valentine, W. N. Colimetric determination of glutathione peroxidase. Journal of Laboratory Clinical Medicine 1967, 70, 158.
- Bashir, K.; Khan, M.F.A.; Alhodaib, A.; Ahmed, N.; Naz, I.; Mirza, B.; Tipu, M.K.; Fatima, H. Design and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Nanoformulation of Bergenin Isolated from Bergenia ciliata. Polymers 2022, 14, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedric, Y., Payne, V. K., Nadia, N. A. C., Kodjio, N., Kollins, E., Megwi, L., & Kuiate, J. R. In vitro antioxidant and anticoccidial studies of pentaclethra macrophylla extracts against eimeria magna, eimeria flavescens, eimeria intestinalis eimeria stiedae oocysts and sporozoites of rabbits. J. Adv. Parasitol 2018, 5, 38–48.
- Zeng, Q.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, F.; Xiong, D.; He, B.; Hua, Q.; Lin, M.; Deng, L.; Sang, X.; Xie, W.; et al. p62-Nrf2 Regulatory Loop Mediates the Anti-Pulmonary Fibrosis Effect of Bergenin. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, H.; Wehnert, H.U. Distribution of arbutin and bergenine in bergenia plants (author’s transl). Arch. Pharm. 1973, 306, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Amin, H.; Ullah, A.; Saba, S.; Rafique, J.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, N.; Badshah, S.L. Antioxidant and Antiplasmodial Activities of Bergenin and 11-O-Galloylbergenin Isolated from Mallotus philippensis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1051925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Liu, R.; Lv, C.; Miao, Y.; Yue, M.; Tao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Xia, Y.; Dai, Y. Bergenin impedes the generation of extracellular matrix in glomerular mesangial cells and ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress via the mTOR/β-TrcP/Nrf2 pathway. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farombi, E.O., I.A. Adedara, A.P. Ebokaiwe, R. Teberen and T. Ehwerhemuepha. Nigerian Bonny light crude oil disrupts antioxidant systems in testes and sperm of rats. Arch. Environ. Contam Toxicol. 2010, 59, 166–174. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawel, N., K. Dorota, B. Pawel, K. Jerzy and K. Slawomir. Herbal formulations as feed additives in the course of rabbit subclinical coccidiosis. Ann. Parasitol. 2014, 60, 65–69.
- Oyinloye, A.M. and Enujiugha, V.N. Antioxidant Properties of African Oil Bean (Pentaclethra macrophylla Benth) Seed Phenolics as Influenced by Extraction Solvents and Heat Treatments. Applied Tropical Agriculture, 2019, 24, 42–48.

| Phytochemicals | Mean Quantity ± SD (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|
| Alkaloids | 961.94±3.76 |
| Flavonoids | 230.56±0.21 |
| Tannins | 16.74±0.81 |
| Total phenolics | 4407.53±3.72 |
| Steroids | 3.38±0.05 |
| Terpenoids | 135.87±17.28 |
| Reducing sugar | 99.78±5.23 |
| Glycosides | 2.11±0.03 |
| First stage of investigation | |||
| Group | Number of mice | Dose (mg/kg) | Mortality |
| I | 3 | 10 | 0/3 |
| II | 3 | 100 | 0/3 |
| III | 3 | 1000 | 0/3 |
| Second stage of investigation | |||
| Group | Number of mice | Dose (mg/kg) | Mortality |
| I | 1 | 1,600 | 0/3 |
| II | 1 | 2,900 | 0/3 |
| III | 1 | 5000 | 0/3 |
| Concentration (µg/ml) | ASC Acid | DPPH | % Inhibitory NO | %TAC | % FRAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15.63 | 84.54±1.9 | 93.40±0.62 | 46.67±7.39 | 77.17±2.37 | 125.17±2.84 |
| 31.25 | 85.05±1.14 | 93.77±0.12 | 44.80±12.31 | 50.27±6.35 | 122.6±8.94 |
| 62.5 | 84.63±1.78 | 94.10±0.10 | 48.27±12.66 | 51.5±3.29 | 120.2±9.88 |
| 125 | 82.1±0.51 | 93.90±0.26 | 49.47±11.03 | 90.03±6.29 | 128.2±8.15 |
| 250 | 77.21±5.37 | 93.93±0.15 | 41.73±14.61 | 134.1±9.18 | 123.2±1.3 |
| 500 | 60.4±8.06 | 92.17±0.06 | 44.57±7.56 | 168.3±27.31 | 128.4±6.55 |
| Total | 78.99±9.63 | 93.54±0.71 | 45.92±9.81 | 95.23±45.55 | 124.63±6.65 |
| F(p value) | 16.15(0.000) | 18.034(0.000) | 0.186(0.962) | 43.265(0.000) | 0.643(0.672) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





