Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Proposing an alternative approach based on the correlation coefficient of Hjorth parameters aimed to select general optimal channels among subjects while preserving the classification accuracy.
- Proposing a new methodology to extract important features from the general optimal channels.
- Validating and comparing the effectiveness of the proposed method with the state-of-the-art channel selection methods.
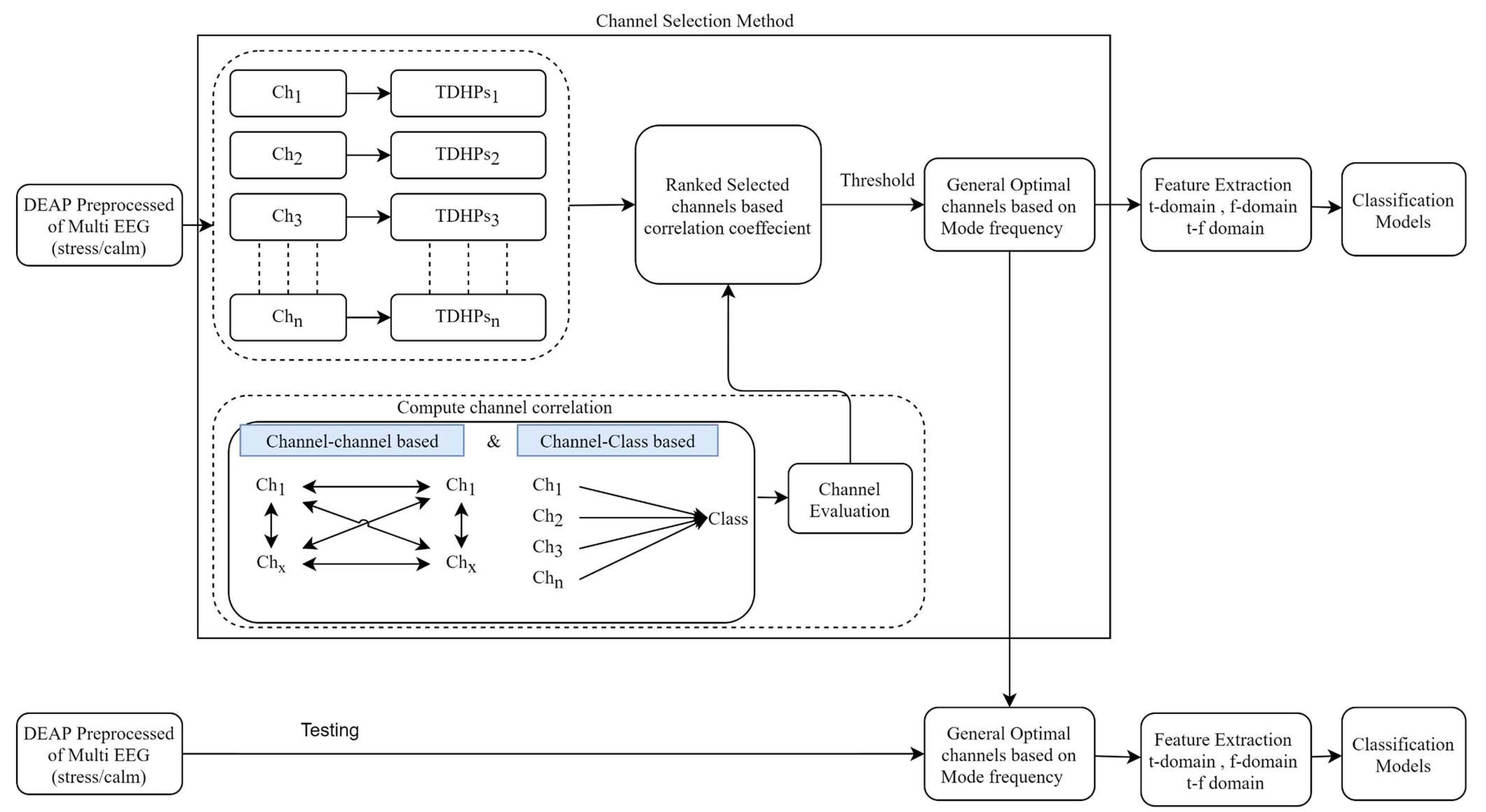
2. Methods and Material
2.1. EEG DATASET
2.2. EEG Data Annotation
3. Hjorth multi-Correlation coefficient
3.1. Correlation coefficient Measures

4. Feature Extraction
5. Classification
6. Result Analysis and Classification
6.1. Analysis of Channel Selection
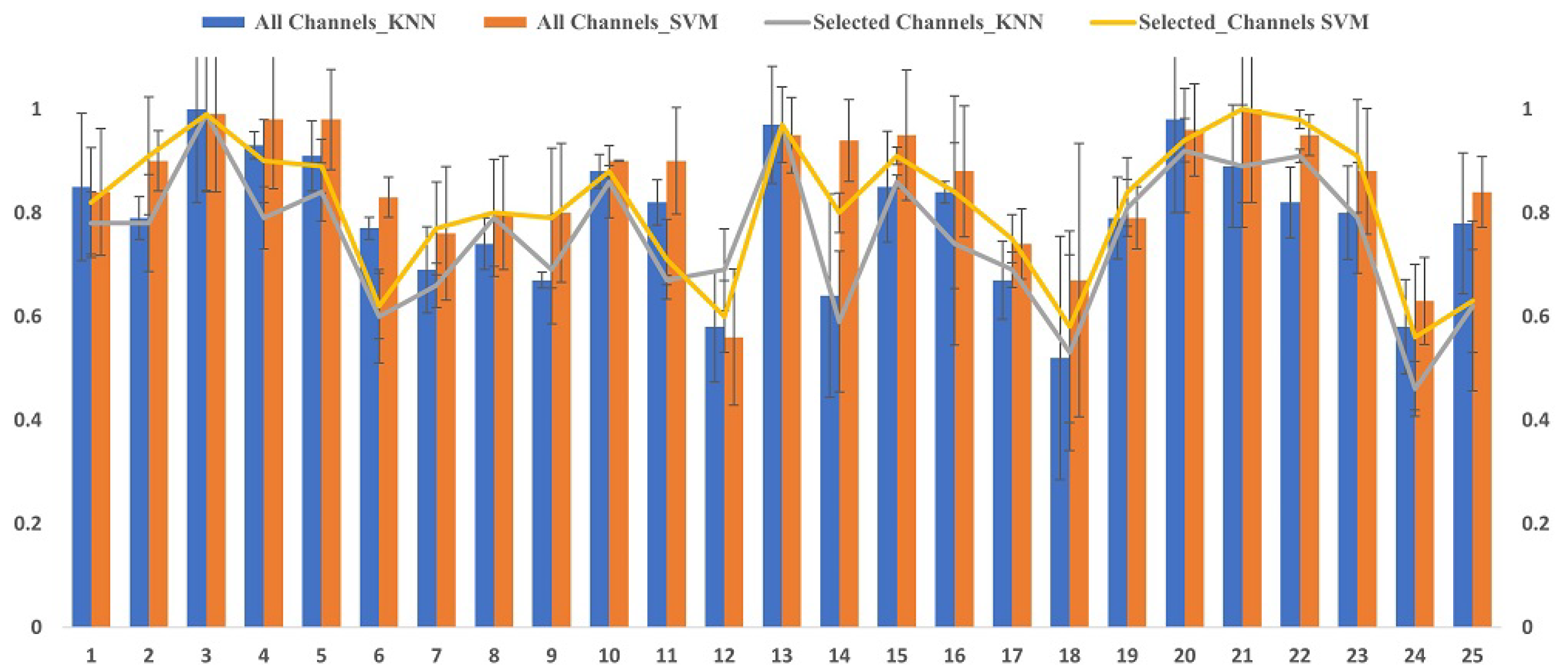
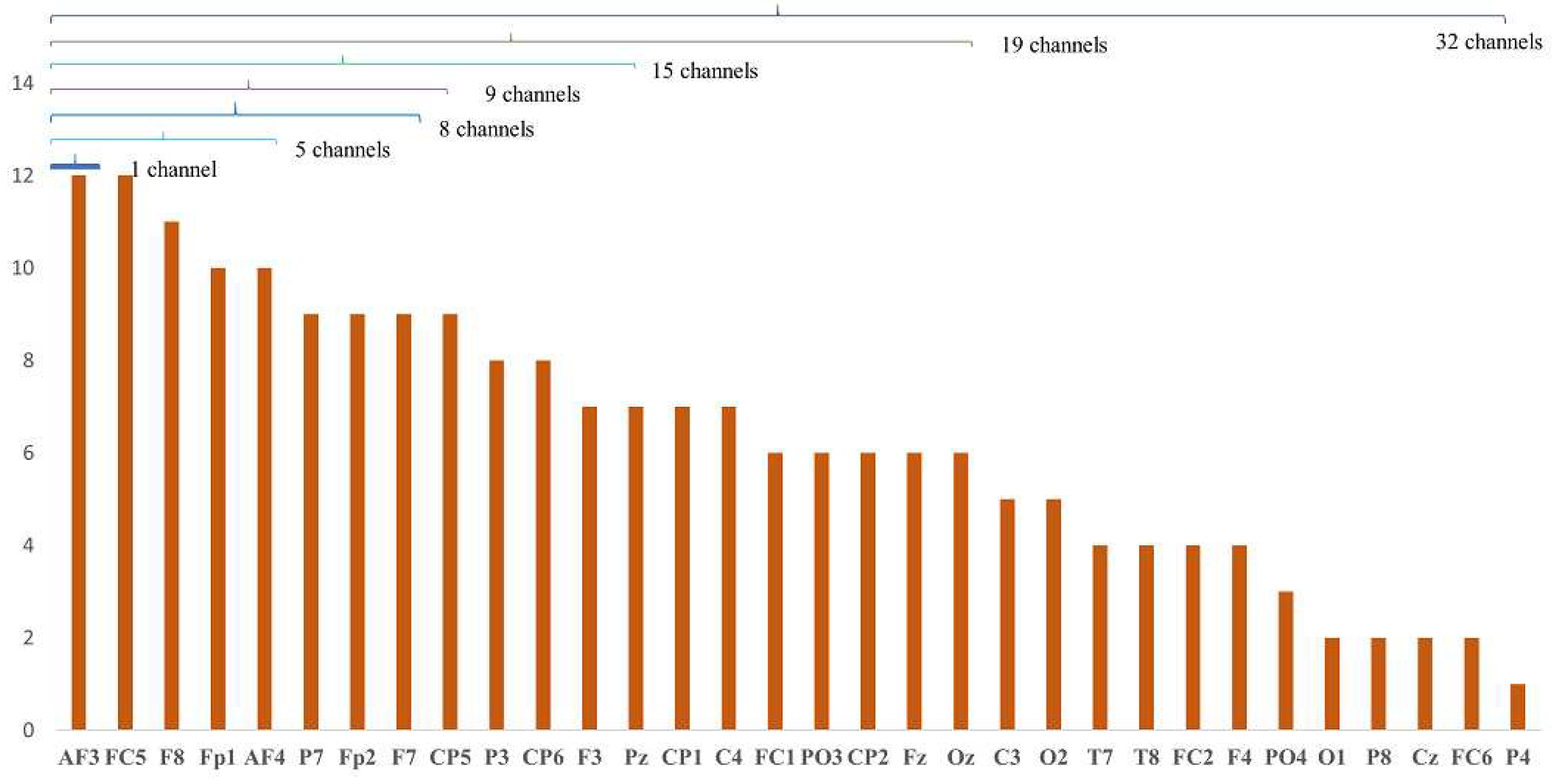
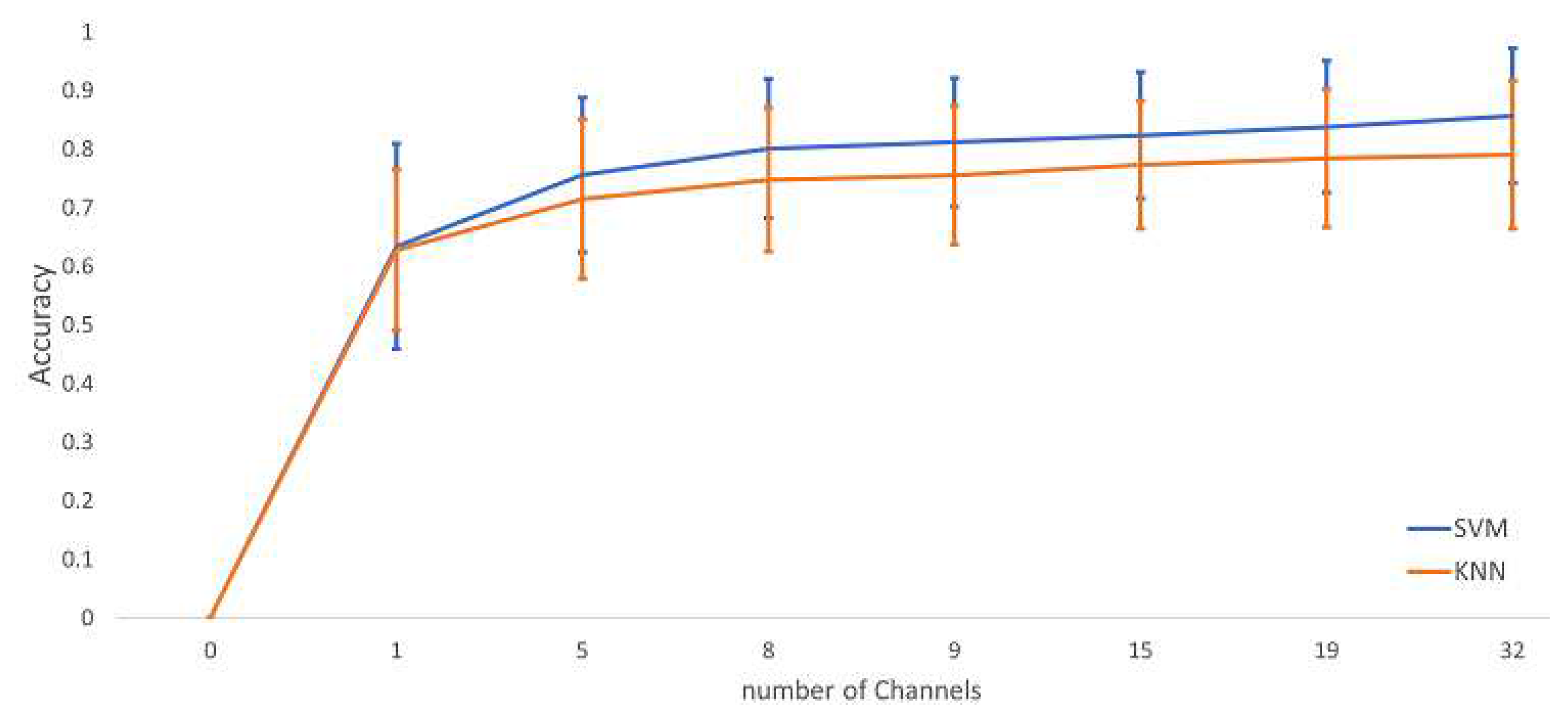
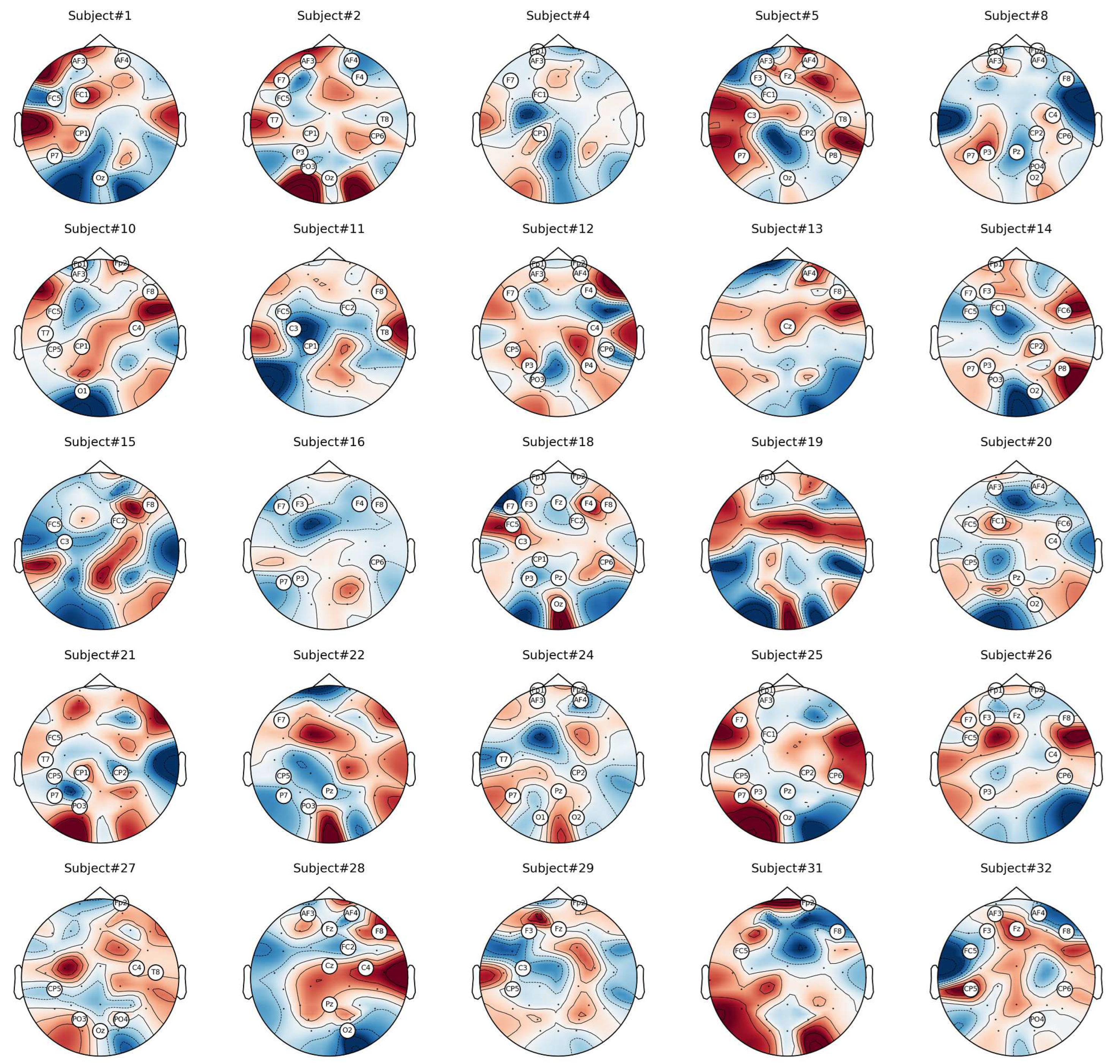
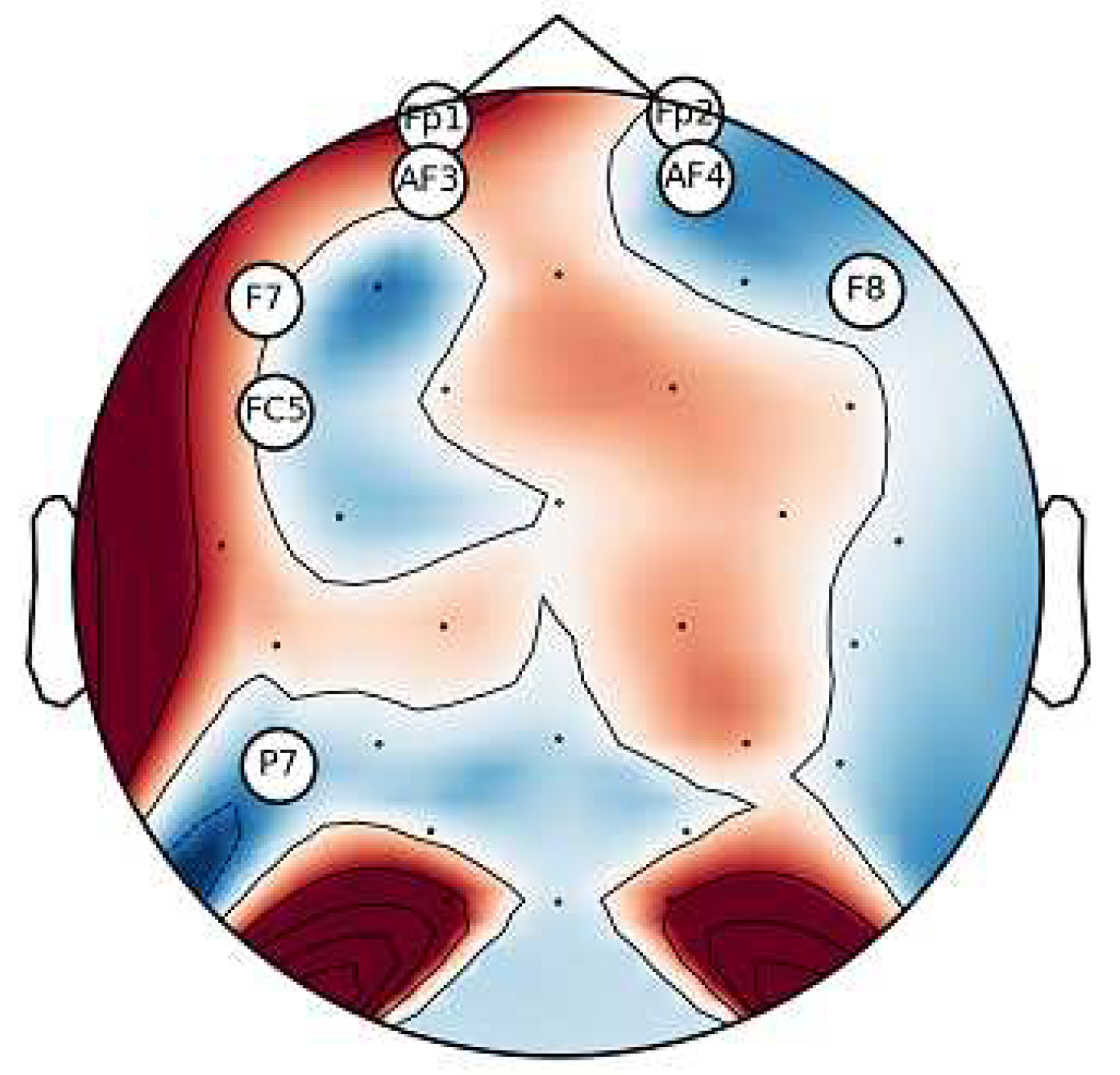
6.2. Classification Results
6.3. Performance Comparison of Mental Stress with Existing Methods In DEAP Dataset
7. Discussion
8. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Dedovic, K.; Renwick, R.; Mahani, N.K.; Engert, V.; Lupien, S.J.; Pruessner, J.C. The Montreal Imaging Stress Task: Using functional imaging to investigate the effects of perceiving and processing psychosocial stress in the human brain. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience 2005, 30, 319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Stress Assessment Based on Decision Fusion of EEG and fNIRS Signals. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19889–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Z.; Rehan, M. On identification of driving-induced stress using electroencephalogram signals: A framework based on wearable safety-critical scheme and machine learning. Information Fusion 2020, 53, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspiotis, V.; Miltiadous, A.; Kalafatakis, K.; Tzimourta, K.D.; Giannakeas, N.; Tsipouras, M.G.; Peschos, D.; Glavas, E.; Tzallas, A.T. Assessing Electroencephalography as a Stress Indicator: A VR High-Altitude Scenario Monitored through EEG and ECG. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peksa, J.; Mamchur, D. State-of-the-Art on Brain-Computer Interface Technology. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.S.; Raj Theeng Tamang, M.; Fu, C.H.Y.; Baker, A.; Alzahrani, A.I.; Alalwan, N. An Innovative Random-Forest-Based Model to Assess the Health Impacts of Regular Commuting Using Non-Invasive Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Hu, S.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.D. An Attention-Based Wavelet Convolution Neural Network for Epilepsy EEG Classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2022, 30, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashempour, S.; Boostani, R.; Mohammadi, M.; Sanei, S. Continuous Scoring of Depression From EEG Signals via a Hybrid of Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2022, 30, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lucas, M.V.; Fonzo, G.A.; Rolle, C.E.; Cooper, C.; Chin-Fatt, C.; Krepel, N.; Cornelssen, C.A.; et al. . An electroencephalographic signature predicts antidepressant response in major depression. Nature Biotechnology 2020, 38, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yin, Y.; Xu, P. A Customized ECA-CRNN Model for Emotion Recognition Based on EEG Signals. Electronics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Kiguchi, M. Towards multilevel mental stress assessment using SVM with ECOC: an EEG approach. Medical & biological engineering & computing 2018, 56, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hag, A.; Handayani, D.; Pillai, T.; Mantoro, T.; Kit, M.H.; Al-Shargie, F. A wearable single EEG channel analysis for mental stress state detection. 2021 IEEE 7th International Conference on Computing, Engineering and Design (ICCED), 2021, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Hag, A.; Handayani, D.; Altalhi, M.; Pillai, T.; Mantoro, T.; Kit, M.H.; Al-Shargie, F. Enhancing EEG-Based Mental Stress State Recognition Using an Improved Hybrid Feature Selection Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, E.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D. An Asynchronous Hybrid Spelling Approach Based on EEG–EOG Signals for Chinese Character Input. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2019, 27, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Chung, W. Optimal Channel Selection Using Correlation Coefficient for CSP Based EEG Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 111514–111521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, A.M.; Patrinos, P.; Bertrand, A. Optimal Versus Approximate Channel Selection Methods for EEG Decoding With Application to Topology-Constrained Neuro-Sensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2021, 29, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, P.; McCreadie, K.; Pachori, R.B.; Wang, H.; Prasad, G. An automatic subject specific channel selection method for enhancing motor imagery classification in EEG-BCI using correlation. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 68, 102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wu, M.; Gao, J.; Lu, D.; Ding, Z.; Hu, B. An Optimal Channel Selection for EEG-Based Depression Detection via Kernel-Target Alignment. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2021, 25, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Meng, M.; She, Q.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Z. Optimal channel-based sparse time-frequency blocks common spatial pattern feature extraction method for motor imagery classification. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 2021, 18, 4247–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Wu, W.; Yu, Z.L.; Gu, Z.; Wen, Z.; Yu, T.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal-Filtering-Based Channel Selection for Single-Trial EEG Classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 2021, 51, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Jin, J.; Lam, H.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cichocki, A. Improved SFFS method for channel selection in motor imagery based BCI. Neurocomputing 2016, 207, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.Z.M.; Hu, S.Y.S.Y.; Song, H. Channel Selection Method for EEG Emotion Recognition Using Normalized Mutual Information. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143303–143311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavkar, S.; Iyer, B.; Deosarkar, S. Optimal EEG channels selection for alcoholism screening using EMD domain statistical features and harmony search algorithm. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 2021, 41, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Miao, Y.; Daly, I.; Zuo, C.; Hu, D.; Cichocki, A. Correlation-based channel selection and regularized feature optimization for MI-based BCI. Neural Networks 2019, 118, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Ai, Q.; Ma, L. Research on Channel Selection and Multi-Feature Fusion of EEG Signals for Mental Fatigue Detection. Entropy 2021, 23, 457. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, H.N. A Novel EEG Feature Extraction Method Using Hjorth Parameter. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering 2014, 2, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, B. EEG analysis based on time domain properties. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 1970, 29, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, J.P.R. Heartbeat classification with low computational cost using Hjorth parameters. IET Signal Processing 2018, 12, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sarkar, A.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.R.; Hossain, M.B.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. Recognition of human emotions using EEG signals: A review. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 136, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, M.S.; Safi, S.M.M. Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease from EEG signals using Hjorth parameters. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 65, 102338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, Z.L. Cross-correlation based discriminant criterion for channel selection in motor imagery BCI systems. Journal of Neural Engineering 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xiao, R.; Daly, I.; Miao, Y.; Wang, X.; Cichocki, A. Internal Feature Selection Method of CSP Based on L1-Norm and Dempster-Shafer Theory. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020; 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Mühl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A database for emotion analysis; Using physiological signals. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.D. OBSERVATIONS: SAM: The Self-Assessment Manikin - An Efficient Cross-Cultural Measurement of Emotional Response. Journal of Advertising Research 1995, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.J.; Kim, J.M. A hybrid feature pool-based emotional stress state detection algorithm using EEG signals. Brain sciences 2019, 9, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Shon, D.; Im, K.; Park, J.H.; Lim, D.S.; Jang, B.; Kim, J.M. Emotional Stress State Detection Using Genetic Algorithm-Based Feature Selection on EEG Signals. International journal of environmental research and public health 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kyrgyzov, O.; Wiart, J.; Bloch, I. Subject-specific channel selection for classification of motor imagery electroencephalographic data. ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing - Proceedings, 2013; 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, R.; Vachtsevanos, G.; Echauz, J.; Litt, B. A Comparison of waveform fractal dimension algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications 2001, 48, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyakitanont, P.; Lek-uthai, A.; Chomtho, K.; Songsiri, J. A review of feature extraction and performance evaluation in epileptic seizure detection using EEG. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2020, 57, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Han, J.; Chen, Y.; Sha, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, B.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; others. A pervasive approach to EEG-based depression detection. Complexity 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, A.R.; Mumtaz, W.; Naufal, M.; Mohamed, B.I.N.; Kamel, N.; Malik, A.S. Machine Learning Framework for the Detection of Mental Stress at Multiple Levels. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 13545–13556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Dass, S.C.; Kiguchi, M. Mental stress assessment based on feature level fusion of fNIRS and EEG signals. 2016 6th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS), 2016, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Zheng, S.; Shi, Y. Spectral entropy can predict changes of working memory performance reduced by short-time training in the delayed-match-to-sample task. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 2017, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candra, H.; Yuwono, M.; Chai, R.; Handojoseno, A.; Elamvazuthi, I.; Nguyen, H.T.; Su, S. Investigation of window size in classification of EEG-emotion signal with wavelet entropy and support vector machine. Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, 2015; 2015-Novem, 7250–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebelli, H.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S.H. EEG-based workers’ stress recognition at construction sites. Automation in Construction 2018, 93, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Demuru, M.; Crobe, A.; Marrosu, F.; Stam, C.J.; Hillebrand, A. The effect of epoch length on estimated EEG functional connectivity and brain network organisation. Journal of Neural Engineering 2016, 13, 036015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Alex, M.; Mir, H.; Al-Nashash, H. Emotion Recognition Based on Fusion of Local Cortical Activations and Dynamic Functional Networks Connectivity: An EEG Study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 143550–143562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, M.; Tariq, U.; Al-Shargie, F.; Mir, H.S.; Al Nashash, H. Discrimination of genuine and acted emotional expressions using EEG signal and machine learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191080–191089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hag, A.; Handayani, D.; Pillai, T.; Mantoro, T.; Kit, M.H.; Al-Shargie, F. EEG Mental Stress Assessment Using Hybrid Multi-Domain Feature Sets of Functional Connectivity Network and Time-Frequency Features. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Assessment of mental stress effects on prefrontal cortical activities using canonical correlation analysis: an fNIRS-EEG study. Biomedical Optics Express 2017, 8, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katmah, R.; Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Babiloni, F.; Al-Mughairbi, F.; Al-Nashash, H. A Review on Mental Stress Assessment Methods Using EEG Signals. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Badruddin, N.; Kiguchi, M. Simultaneous measurement of EEG-fNIRS in classifying and localizing brain activation to mental stress. IEEE 2015 International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, ICSIPA 2015 - Proceedings, 2016, pp. 282–286. [CrossRef]
- Al-shargie, F.; Tang, T.B.; Kiguchi, M. Mental stress grading based on fNIRS signals. 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2016, pp. 5140–5143. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; Li, R.; He, Z.; Xiao, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F.; Pan, J. Enhancing BCI-based emotion recognition using an improved particle swarm optimization for feature selection. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W. Emotion recognition based on framework of BADEBA-SVM. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2019, 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, A.G.; Oliva, D.; Houssein, E.H.; Juan, A.A.; Yu, X. Binary whale optimization algorithm for dimensionality reduction. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Luo, Y.; Qiu, S.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Bi, Y. EEG-Based Emotion Classification Using a Deep Neural Network and Sparse Autoencoder. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience 2020, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.M.; Hassanin, O.; Tariq, U.; Al-Nashash, H. EEG-Based Semantic Vigilance Level Classification Using Directed Connectivity Patterns and Graph Theory Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115941–115956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shargie, F.; Tariq, U.; Hassanin, O.; Mir, H.; Babiloni, F.; Al-Nashash, H. Brain Connectivity Analysis Under Semantic Vigilance and Enhanced Mental States. Brain Sciences 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Domain | Features | Equations | Description | #no. features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line Length [38] [39] | Called curve length, is the total vertical length of the signal | 1 | ||
| Time | Kurtosis [40] | Shows the sharpness of EEG signals’ peak | 1 | |
| Peak to peak amplitude | Time of EEG signal peaks between the various windows | 1 | ||
| Skewness [40] | A asymmetry of an EEG signal | 1 | ||
| Hjorth Parameters [36,40] | A variance of the time function. | 1 | ||
| A mean frequency or the proportion of standard deviation of the power spectrum. | 1 | |||
| Indicates how the shape of a signal is similar to a pure sine wave. | 1 | |||
| Frequency | Relative Power [41] of: theta (4-8Hz) alpha(8-12Hz) sigma(12-15Hz) low beta(15-20Hz) high beta (20-30Hz) |
Average absolute power of the given band interval. | 5 | |
| Time-Freqeucny | Energy of Wavelet decomposition coefficients (db4, 6 level) [11,42]. |
Measure the square sum of wavelet coefficients of each db level | 6 | |
| Spectral Entropy (PSD,Welch) [43] |
|
Measure the distribution of signal power over frequency. | 1 | |
| katz Fractal Dimension [38] | Compute the maximum distance between the first point and any other point of the Signal’ time window. | 1 |
| No. | Classifier | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SVM | C=1.0, Kernal = Radial Basis Function (RBF), |
| 2 | KNN | K=10, distance function= euclidean distance |
| All Channels+KNN | All Channels+ SVM | Proposed Channels+KNN | Proposed Channels+SVM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participant Id | precision | recall | accuracy | precision | recall | accuracy | precision | recall | accuracy | precision | recall | accuracy |
| 1 | 0.92 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.65 | 0.82 |
| 2 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 5 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| 8 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 10 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 |
| 11 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.71 | 0.77 |
| 12 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.64 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.80 |
| 13 | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.78 | 0.58 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.79 |
| 14 | 0.79 | 0.73 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.67 | 0.90 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.65 | 0.88 |
| 15 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.71 |
| 16 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| 18 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.97 |
| 19 | 0.65 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.80 |
| 20 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
| 21 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.84 |
| 22 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.75 |
| 24 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.53 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.58 |
| 25 | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| 26 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| 27 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 28 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| 29 | 0.86 | 0.71 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| 31 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| 32 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.63 |
| Average | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.81 |
| Method | No. Channels | Channel Subsets | Classifier | Accuracy | Execution Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRMR | 11 | ’C4’, ’FC2’, ’CP6’, ’Cz’, ’T8’, ’F4’, ’F8’, ’P4’, ’Fz’, ’FC6’, ’Pz’ | SVM | 0.80±0.12 | 1.42 s |
| KNN | 0.74±0.12 | ||||
| STFT+MI | 15 | ’AF3’,’F7’,’FC5’,’P3’,’P7’,’Pz’,’O2’,’P4’,’FC6’,’Fp2’,’FC1’,’CP2’,’C4’,’F4’,’Fz’ | SVM | 0.82±0.11 | 4.46s |
| KNN | 0.74±0.12 | ||||
| GA | 13 | ’O2’, ’O1’, ’PO3’, ’AF3’, ’P4’, ’P8’, ’F8’, ’P7’, ’C4’, ’CP5’, ’Pz’, ’FC5’, ’Fp2’ | SVM | 0.82±0.12 | 1h 3min 34s |
| KNN | 0.76±0.13 | ||||
| Proposed | 8 | ’AF3’, ’FC5’, ’F8’, ’Fp1’, ’AF4’, ’P7’, ’Fp2’, ’F7’ | SVM | 0.81±0.11 | 0.34s |
| KNN | 0.75±0.12 |
| Author | Method | Number of EEG Channels | Dataset | Accuracy / Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shon [36] | Genetic Algorithm-Based Feature Selection | 32 | DEAP | 71.76% (Stress/Calm) |
| Hasan [35] | Boruta-based k-NN feature selection | 32 | DEAP | 73.38% (Stress/Calm) |
| Proposed | Full Channels SET+SVM | 32 | DEAP | 85.68% (Stress/Calm) |
| CCHP+SVM | 8 | DEAP | 81.56% (Stress/Calm) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





