Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. AR bacteria and genes in Fermented Foods
2.1. ARGs and Associated Bacteria in Fermented Foods
2.1.1. Lactic Acid bacteria
2.1.2. Staphylococcus spp.
2.1.3. Enterococcus spp.
| Food type | Bacteria present | ARGs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheese | LAB, Staphylococcus (CNS) | Tetracycline, Chloramphenicol, erythromycin | [13,14] |
| Fermented meat/sausage | LAB, Staphylococcus (CNS) Salmonella Listeria monocytogenes |
Tetracycline, Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, Penicillins Amoxicillin, Gentamycin, Streptomycin, tetracycline Amoxicillin, benzyl penicillin, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin |
[11] [14] [14] |
| Fermented vegetables | LAB | Tetracycline, Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, Clindamycin | [11,13,14] |
| Yogurt |
Lactobacillus Streptococcus |
Mycostatin, nalidixic acid, neomycin, polymyxin B, trimethoprim, colimycin, sulfamethoxazole, and sulphonamides Colimycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, mycostatin, nalidixic acid, neomycin, polymyxin b, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, streptomycin, and sulfonamides |
[19] [19] |
| Vinegar | Acetic acid bacteria | Trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, erythromycin | [26] |
| Turkish cheese | Enterococcus | streptomycin, erythromycin, oxacillin, and vancomycin | [24] |
| Fermented fish | Staphylococcus (CNS) | tetracyclines, penicillins, chloramphenicol, and macrolides | [20] |
2.1.4. AR genes in Other Bacteria
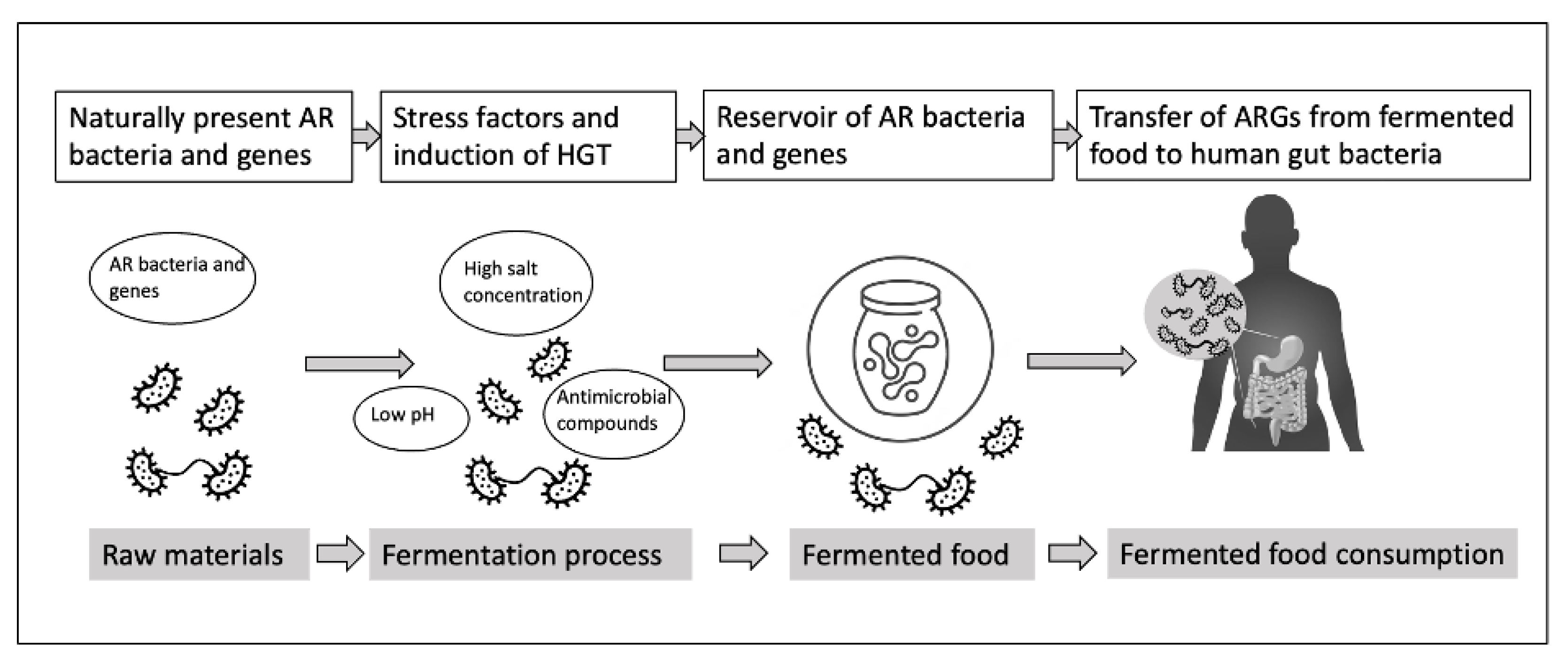
3. Role of Bacterial Adaptation and Gene Transfer in Fermented Foods
3.1. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Fermented Food
3.2. Stress Response Contributing to Gene Transfer
3.3. Transfer of ARGs from Fermented Food to Human Microbiota
4. Other Contributing Factors to AR in Fermented Food
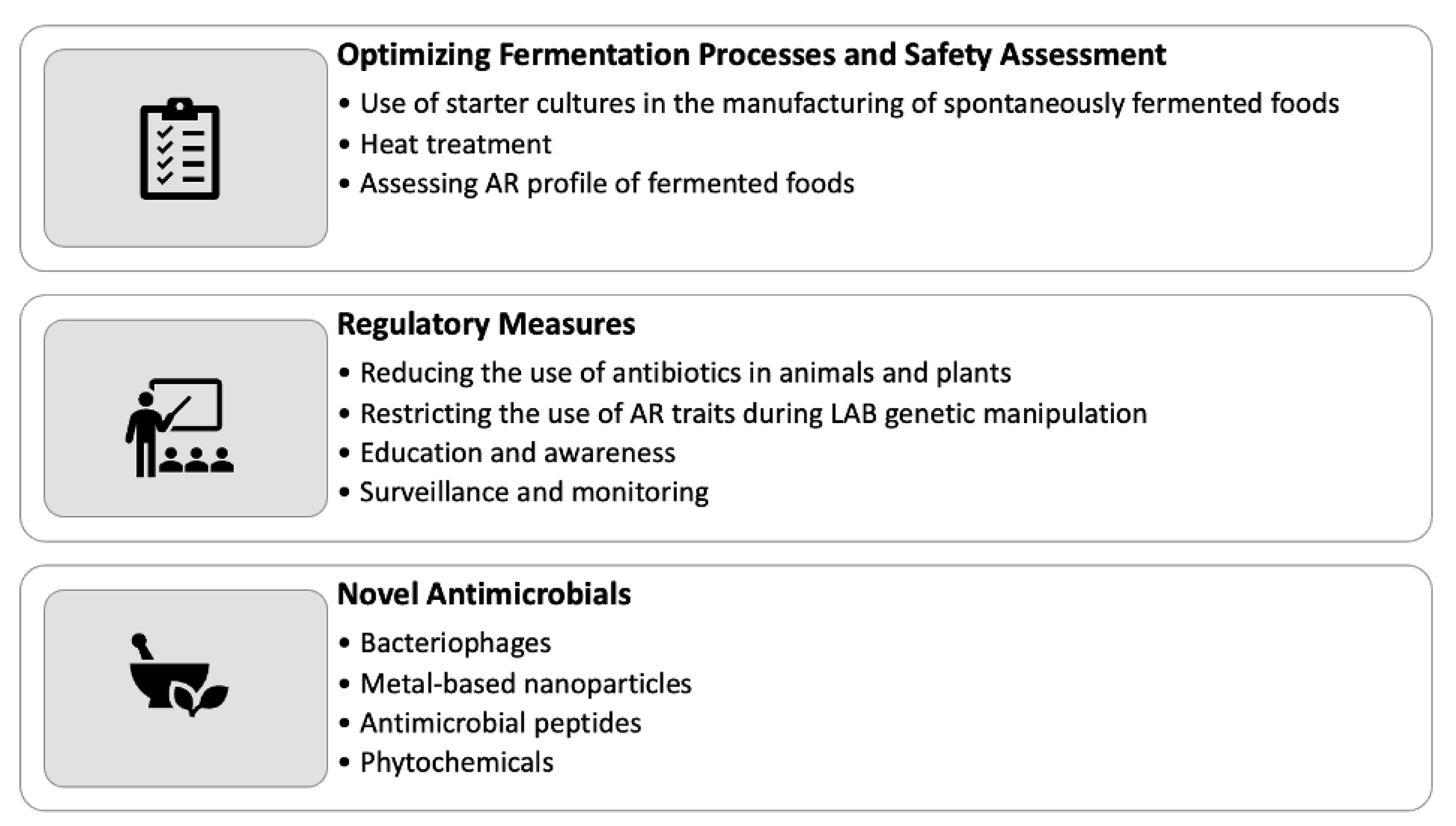
5. Mitigation strategies
5.1. Optimizing Fermentation Processes and Safety Assessment
5.2. Regulatory Measures for Combating AR in Fermented Foods
5.3. Novel Antimicrobials
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligné, B.; Gänzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Pihlanto, A.; et al. Health Benefits of Fermented Foods: Microbiota and Beyond. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2017, 44, 94–102. [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Cox, S.R.; Rossi, M.; Whelan, K. Fermented Foods: Definitions and Characteristics, Impact on the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Gastrointestinal Health and Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.G.; Csabai, I.; Maróti, G.; Jerzsele, Á.; Dubecz, A.; Patai, Á. V; Judge, M.F.; Nagy, S.Á.; Makrai, L.; Bányai, K.; et al. A Glimpse of Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Diversity in Kefir and Yoghurt. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.; Zhanel, G.G.; Sparling, R.; Holley, R.A. Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance from Enterococcus Faecium of Fermented Meat Origin to Clinical Isolates of E. Faecium and Enterococcus Faecalis. Int J Food Microbiol 2015, 199, 78–85. [CrossRef]
- Jasiak, K.; Amund, D. Are Spontaneously Fermented Plant-Based Foods Potential Sources of Transferable Antibiotic Resistance Genes? Food Front 2022, 3, 46–55. [CrossRef]
- Hummel, A.S.; Hertel, C.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Antibiotic Resistances of Starter and Probiotic Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 2007, 73, 730–739. [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.P.; Lee, T.A.; Bolanos, J.T.; Danziger, L.H. Pathogenic Relevance of Lactobacillus: A Retrospective Review of over 200 Cases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2005, 24, 31–40. [CrossRef]
- Land, M.H.; Rouster-Stevens, K.; Woods, C.R.; Cannon, M.L.; Cnota, J.; Shetty, A.K. Lactobacillus Sepsis Associated with Probiotic Therapy. Pediatrics 2005, 115, 178–181. [CrossRef]
- Anadón, A.; Rosa Martínez-Larrañaga, M.; Aranzazu Martínez, M. Probiotics for Animal Nutrition in the European Union. Regulation and Safety Assessment. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2006, 45, 91–95. [CrossRef]
- The WHO Regional Office for Europe.
- Wolfe, B.E. Are Fermented Foods an Overlooked Reservoir of Antimicrobial Resistance? Curr Opin Food Sci 2023, 51, 101018. [CrossRef]
- Leech, J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Macori, G.; Walsh, C.J.; Barton, W.; Finnegan, L.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Claesson, M.J.; et al. Fermented-Food Metagenomics Reveals Substrate-Associated Differences in Taxonomy and Health-Associated and Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. mSystems 2020, 5. [CrossRef]
- Flórez, A.B.; Delgado, S.; Mayo, B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Cheese Environment. Can J Microbiol 2005, 51, 51–58. [CrossRef]
- Fraqueza, M.J. Antibiotic Resistance of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Dry-Fermented Sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 2015, 212, 76–88. [CrossRef]
- SUKMARINI, L.; MUSTOPA, A.Z.; NORMAWATI, M.; MUZDALIFAH, I. Identification of Antibiotic-Resistance Genes from Lactic Acid Bacteria in Indonesian Fermented Foods. Hayati 2014, 21, 144–150. [CrossRef]
- Çataloluk, O.; Gogebakan, B. Presence of Drug Resistance in Intestinal Lactobacilli of Dairy and Human Origin in Turkey. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2004, 236, 7–12. [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, M.; Wind, A. Susceptibility of Lactobacillus Spp. to Antimicrobial Agents. Int J Food Microbiol 2003, 82, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Chinese Fermented Foods. Food Control 2011, 22, 1316–1321. [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Singh, R. Antibiotic Resistance in Food Lactic Acid Bacteria--a Review. Int J Food Microbiol 2005, 105, 281–295. [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, D.W. Food-Derived Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus as Starter Cultures for Fermented Foods. Food Sci Biotechnol 2020, 29, 1023–1035. [CrossRef]
- Verraes, C.; Van Boxstael, S.; Van Meervenne, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Butaye, P.; Catry, B.; de Schaetzen, M.A.; Van Huffel, X.; Imberechts, H.; Dierick, K.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Food Chain: A Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2013, 10, 2643–2669. [CrossRef]
- Fowoyo, P.T.; Ogunbanwo, S.T. Antimicrobial Resistance in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Nigerian Traditional Fermented Foods. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2017, 16. [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Jeong, D.W.; Lee, J.H. Genetic Diversity and Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcus Saprophyticus Isolates from Fermented Foods and Clinical Samples. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 2015, 58, 659–668. [CrossRef]
- Çitak, S.; Yucel, N.; Orhan, S. Antibiotic Resistance and Incidence of Enterococcus Species in Turkish White Cheese. Int J Dairy Technol 2004, 57, 27–31. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Valenzuela, A.; Lavilla Lerma, L.; Benomar, N.; Gálvez, A.; Pérez Pulido, R.; Abriouel, H. Phenotypic and Molecular Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Enterococcus Faecalis and Enterococcus Faecium Isolated from Different Traditional Fermented Foods. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2013, 10, 143–149. [CrossRef]
- Cepec, E.; Trček, J. Antimicrobial Resistance of Acetobacter and Komagataeibacter Species Originating from Vinegars. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19. [CrossRef]
- Giraffa, G.; Carminati, D. Molecular Techniques in Food Fermentation: Principles and Applications. Molecular Techniques in the Microbial Ecology of Fermented Foods 2008, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, J.G.; Rinker, D.C. The Genomics of Microbial Domestication in the Fermented Food Environment. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2015, 35, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Jiang, N.; Lin, H.; An, F.; Wu, C.; Yue, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, R. Recent Developments in Horizontal Gene Transfer with the Adaptive Innovation of Fermented Foods. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2023, 63, 569–584. [CrossRef]
- Steensels, J.; Gallone, B.; Voordeckers, K.; Verstrepen, K.J. Domestication of Industrial Microbes. Current Biology 2019, 29, R381–R393. [CrossRef]
- Roach, M.J.; Borneman, A.R. New Genome Assemblies Reveal Patterns of Domestication and Adaptation across Brettanomyces (Dekkera) Species. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Irlinger, F.; Mounier, J. Microbial Interactions in Cheese: Implications for Cheese Quality and Safety. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2009, 20, 142–148. [CrossRef]
- Leroy, S.; Christieans, S.; Talon, R. Tetracycline Gene Transfer in Staphylococcus Xylosus in Situ During Sausage Fermentation. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 392. [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Yang, C.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Metagenomic Features of Traditional Fermented Milk Products. LWT 2022, 155, 112945. [CrossRef]
- Vogel, R.F.; Becke-Schmid, M.; Entgens, P.; Gaier, W.; Hammes, W.P. Plasmid Transfer and Segregation in Lactobacillus Curvatus LTH1432 in Vitro and during Sausage Fermentations. Syst Appl Microbiol 1992, 15, 129–136. [CrossRef]
- Cocconcelli, P.S.; Cattivelli, D.; Gazzola, S. Gene Transfer of Vancomycin and Tetracycline Resistances among Enterococcus Faecalis during Cheese and Sausage Fermentations. Int J Food Microbiol 2003, 88, 315–323. [CrossRef]
- Haubert, L.; Cruxen, C.E. dos S.; Fiorentini, Â.M.; Silva, W.P. da Tetracycline Resistance Transfer from Foodborne Listeria Monocytogenes to Enterococcus Faecalis in Minas Frescal Cheese. Int Dairy J 2018, 87, 11–15. [CrossRef]
- Seifabadi, F.S.; Baserisalehi, M. Plasmid-Mediated Antibiotic-Resistant Pattern of Lactobacillus Spp. Isolated From Dairy Products. Avicenna Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2021, 8, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Bae, T.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, D.W. Transfer of a Lincomycin-Resistant Plasmid between Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci during Soybean Fermentation and Mouse Intestine Passage. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2019, 366, 113. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Qiao, S. Horizontal Transfer of VanA between Probiotic Enterococcus Faecium and Enterococcus Faecalis in Fermented Soybean Meal and in Digestive Tract of Growing Pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 2019, 10, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Novak, J.T.; Knocke, W.R.; Pruden, A. Elevation of Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Cold Temperatures: Implications for Winter Storage of Sludge and Biosolids. Lett Appl Microbiol 2014, 59, 587–593. [CrossRef]
- Schjørring, S.; Krogfelt, K.A. Assessment of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance Transfer in the Gut. Int J Microbiol 2011. [CrossRef]
- Tarrah, A.; Pakroo, S.; Corich, V.; Giacomini, A. Identification and Transferability of Tetracycline Resistance in Streptococcus Thermophilus during Milk Fermentation, Storage, and Gastrointestinal Transit. Fermentation 2021, Vol. 7, Page 65 2021, 7, 65. [CrossRef]
- Zarzecka, U.; Zadernowska, A.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Adamski, P. High-Pressure Processing Effect on Conjugal Antibiotic Resistance Genes Transfer in Vitro and in the Food Matrix among Strains from Starter Cultures. Int J Food Microbiol 2023, 388, 110104. [CrossRef]
- Mater, D.D.G.; Langella, P.; Corthier, G.; Flores, M.-J. Fax +41 61 306 12 34 E-Mail Karger@karger.Ch A Probiotic Lactobacillus Strain Can Acquire Vancomycin Resistance during Digestive Transit in Mice. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 2008, 14, 123–127. [CrossRef]
- Broaders, E.; Gahan, C.G.; Marchesi, J.R. Gut Microbes Mobile Genetic Elements of the Human Gastrointestinal Tract Potential for Spread of Antibiotic Resistance Genes. www.landesbioscience.com Gut Microbes 271 Gut Microbes 4, 271–280. [CrossRef]
- Coppola, R.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Reale, A.; Salzano, G.; Sorrentino, E. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Strains Isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese. Lait 2005, 85, 193–204. [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.J.C.; Tyrrell, K.L.; Citron, D.M. Lactobacillus Species: Taxonomic Complexity and Controversial Susceptibilities. Clin Infect Dis 2015, 60 Suppl 2, S98–S107. [CrossRef]
- Gueimonde, M.; Sánchez, B.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Margolles, A. Antibiotic Resistance in Probiotic Bacteria. Front Microbiol 2013, 4, 51661. [CrossRef]
- Simpson, W.J.; Hammond, J.R.M.; Miller, R.B. Avoparcin and Vancomycin: Useful Antibiotics for the Isolation of Brewery Lactic Acid Bacteria. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 1988, 64, 299–309. [CrossRef]
- Campedelli, I.; Mathur, H.; Salvetti, E.; Clarke, S.; Rea, M.C.; Torriani, S.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; O’Toole, P.W. Genus-Wide Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance in Lactobacillus Spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 2018, 85. [CrossRef]
- Abriouel, H.; Casado Muñoz, M. del C.; Lavilla Lerma, L.; Pérez Montoro, B.; Bockelmann, W.; Pichner, R.; Kabisch, J.; Cho, G.S.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Gálvez, A.; et al. New Insights in Antibiotic Resistance of Lactobacillus Species from Fermented Foods. Food Res Int 2015, 78, 465–481. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Amaretti, A.; Raimondi, S. Folate Production by Probiotic Bacteria. Nutrients 2011, 3, 118. [CrossRef]
- Charteris, W.P.; Kelly, P.M.; Morelli, L.; Collins, J.K. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Potentially Probiotic Lactobacillus Species. J Food Prot 1998, 61, 1636–1643. [CrossRef]
- Casado Muñoz, M. del C.; Benomar, N.; Lerma, L.L.; Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H. Antibiotic Resistance of Lactobacillus Pentosus and Leuconostoc Pseudomesenteroides Isolated from Naturally-Fermented Aloreña Table Olives throughout Fermentation Process. Int J Food Microbiol 2014, 172, 110–118. [CrossRef]
- Knudtson, L.M.; Hartman, P.A. Antibiotic Resistance Among Enterococcal Isolates from Environmental and Clinical Sources. J Food Prot 1993, 56, 489–492. [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, H.W.; Konings, W.N. The ABC Family of Multidrug Transporters in Microorganisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998, 1365, 31–36. [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, T.; Smiley, M.B. Antibiotic Resistances of Yogurt Starter Cultures Streptococcus Thermophilus and Lactobacillus Bulgaricus. Appl Environ Microbiol 1980, 40, 862–865. [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, V.; Fragasso, M.; Romaniello, R.; Berbegal, C.; Russo, P.; Spano, G. Spontaneous Food Fermentations and Potential Risks for Human Health. Fermentation 2017, Vol. 3, Page 49 2017, 3, 49. [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, M.; Pérez-Nevado, F.; Regodón, J.A.; Zamora, E.; Álvarez, M.L.; Rebollo, J.E.; Ramírez, M. A Low-Cost Procedure for Production of Fresh Autochthonous Wine Yeast. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2011, 38, 459–469. [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Cotter, P.D.; Endo, A.; Han, N.S.; Kort, R.; Liu, S.Q.; Mayo, B.; Westerik, N.; Hutkins, R. Fermented Foods in a Global Age: East Meets West. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2020, 19, 184–217. [CrossRef]
- Devirgiliis, C.; Zinno, P.; Stirpe, M.; Barile, S.; Perozzi, G. Functional Screening of Antibiotic Resistance Genes from a Representative Metagenomic Library of Food Fermenting Microbiota. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Teuber, M.; Meile, L.; Schwarz, F. Acquired Antibiotic Resistance in Lactic Acid Bacteria from Food. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology 1999, 76, 115–137. [CrossRef]
- Mantravadi, P.K.; Kalesh, K.A.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Hudson, A.O.; Parthasarathy, A. The Quest for Novel Antimicrobial Compounds: Emerging Trends in Research, Development, and Technologies. Antibiotics (Basel) 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, E.C. Listeria Monocytogenes : Food Sources, Prevalence & Management Strategies.
- Neil, K.; Allard, N.; Roy, P.; Grenier, F.; Menendez, A.; Burrus, V.; Rodrigue, S. High-efficiency Delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 by Engineered Probiotics Enables Precise Microbiome Editing. Mol Syst Biol 2021, 17, 10335. [CrossRef]
- Romero-Luna, H.E.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Peredo-Lovillo, A. Bioactive Peptides Produced by Engineered Probiotics and Other Food-Grade Bacteria: A Review. Food Chem X 2022, 13, 100196. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





