Introduction
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) membranes have draw considerable attention in a variety of disciplines, including wastewater treatment, desalination, and fuel cells, due to their exceptional water permeability, thermal stability, and chemical resistance[
1,
2]. However, the naturally occurring brittleness of PVA membranes frequently hampers their practical use. To address this restriction, recent scientific research has focused on integrating glycerol as a plasticizer to improve the flexibility and mechanical capabilities of PVA membranes. PVA is a synthetic polymer made from vinyl acetate that has a strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding between its hydroxyl groups, which gives it its extremely crystalline structure[
3,
4,
5]. Although PVA membranes’ crystalline structure adds to their attractive qualities, it also makes them fragile and liable to cracking and failure when subjected to mechanical stress[
6]. As a result, researchers have investigated creative strategies to add flexibility without reducing the benefits of the membrane’s intrinsic properties[
7]. The efficiency of modular polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)-based membranes for aqueous filtration has been examined in a study by Vahid Vatanpour et al[
8]. The research showed that PVA had a favourable impact on the hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, and functionality of membranes. To create highly effective hydrophilic membranes with improved anti-fouling and rejection qualities as well as improved chemical and mechanical resistance, more research is necessary. The many alteration methods mentioned, like coating and grafting, provide straightforward, affordable, and chemical-free alternatives. The durability of these alterations over the long run, however, is still up for discussion. Although they frequently require the use of organic solvents and chemicals, chemical modification procedures including polymer blending and the addition of additives change the membrane’s structure and properties permanently. When compared to techniques like pervaporation and gas permeation membranes, water treatment filtration shows a higher tendency to foul. Although difficulties like agglomeration or aggregation may develop, the inclusion of nanoparticles into membranes has been suggested as a remedy. Therefore, to improve particle dispersion within membranes, future research should focus on strategies such surface functionalization of additives[
9].
The common plasticizer glycerol is a viable technique for improving the mechanical properties of PVA membranes. Due to its ability to act as a molecular lubricant and reduce the tensions between PVA chains, chain mobility is increased and crystallinity is decreased[
10]. The addition of glycerol seeks to improve the mechanical resilience, elongation at break, tensile strength, and flexibility of PVA membranes[
11]. The effects of water-soluble plasticizers such propylene glycol (PG), glycerol, and polyethylene glycol 600 (PEG) on the morphology and water resistance of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) films were studied by L. Y. Lim and Lucy S. C. Wan. The PVA films were made from aqueous solutions, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) were used to examine their morphology. After being submerged in distilled water at 37°C for three days, the films’ water resistance was evaluated by measuring the amount of water absorbed and the amount of film that dissolved. The DSC results showed that the three plasticizers had diverse effects on the growth of crystallites in the PVA films. The plasticizers may have introduced flaws into the crystal lattice since they not only decreased the amount of crystallinity in the films but also decreased the melting points of the crystals. The water-soluble plasticizers leached out when the plasticized PVA films were submerged in distilled water, reducing their ability to resist water. The characteristics of the PVA films were significantly influenced by the plasticizers’ compatibility with PVA. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding network of PVA is broken by the addition of glycerol, making the structure more amorphous[
12,
13,
14]. The membrane thus becomes more elastic, deformation-resistant, and fracture-resistant. Additionally, adding glycerol does not reduce the membrane’s permeability or selectivity to different solutes, making it a desirable tactic for membrane-based separation procedures. In addition, the effects of manufacturing methods, glycerol concentration, and PVA molecular weight on the characteristics of the resulting PVA-glycerol membranes have been investigated. Researchers have been able to modify the membrane features to match certain application requirements by methodically changing these factors. Studies on the long-term stability and ageing of PVA-glycerol membranes have also provided insight into the robustness and dependability of these modified membranes in real-world operational situations[
15].
This study’s goal is to research and assess how adding glycerol affects how flexible polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) membranes are. The objective is to comprehend how the mechanical characteristics and functionality of PVA membranes are affected by glycerol’s role as a plasticizer. The work intends to investigate the ideal glycerol concentration that can increase the flexibility of PVA membranes without sacrificing other crucial characteristics including water permeability, selectivity, and thermal stability. The goal is to offer important insights into the role of glycerol in reducing the brittleness of PVA membranes and laying a groundwork for the creation of more flexible and functional membranes for a variety of applications, including water treatment, filtration, and other membrane-based processes.
Materials
The Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) utilized in the research was procured from Aldrich Chemistry located in Darmstadt, Germany. The PVA had a molecular weight averaging between 85,000 and 124,000, and its hydrolysis degree was determined to be within the range of 87-89%. Glycerol, obtained from Biosynth Pharma (Pvt) Ltd. based in Karachi, Pakistan, was chosen as a component and exhibited an exceptional level of purity at 99.97%.
Method
A solution of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with a concentration of 15 wt% was prepared by dissolving PVA granules in de-ionized water. To achieve a homogeneous PVA solution, the mixture was heated on a hot plate at approximately 100 °C while being stirred at 500 rpm. It typically took around 3-4 hours to obtain a clear solution. Once clarity was achieved, glycerol solution was added to the solution in different weight percentages ranging from 0-5 wt% and thoroughly mixed using a mechanical tumbler. To remove any trapped air, the mixed solution was placed in a vacuum desiccator under a vacuum pressure of approximately 0.1 bar for approximately 30 minutes. After the solution was prepared, Membranes were formed on a Glass substrate using a blade coater. The Membrane preparation took place under ambient conditions, with a 1000 µm gap set on the applicator. The coating speed was maintained at a constant rate of 30 mm/s. Subsequently, the prepared films were carefully transferred to an oven (SS-00AB from MTI Corporation, Richmond, VA, USA) and subjected to a temperature of 60 °C for several hours to ensure complete drying. Once the Membranes were fully dried, they were peeled off from the Glass substrate and utilized as independent membrane for subsequent characterizations and tests.
Characterization
UV-Vis Transmittance
The UV-Vis spectra of the membrane samples were analyzed using a double beam UV-Vis spectrometer (Pharma Spec UV-1700, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The absorbance measurements were conducted within a wavelength range of 200 nm to 800 nm.
FTIR
The membrane samples were examined using an FT-IR instrument (Bruker ALPHA-P, Karlsruhe, Germany) that operated within a wavelength range of 500 cm−1 to 4000 cm−1. Spectra were acquired with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and by summing 64 scans.
Tensile
The membrane’s tensile strength was evaluated following the guidelines of ASTM D882. A Z005 Zwick/Roell universal testing machine from Ulm, Germany, was utilized for the testing, maintaining a constant crosshead speed of 5 mm/min and a grip spacing of 50 mm. Rectangular samples measuring 30 mm in width and 150 mm in length were prepared specifically for the tensile testing. A 5 N load was applied during the test.
TGA
To investigate the thermal stability of the Membrane, a thermogravimetric analyzer (SDT Q-600 TA Instruments, Artisan Technology Group, Champaign, IL, USA) was utilized. Each test involved maintaining an initial sample weight of 5-8 mg. The heating process occurred gradually at a rate of 10 °C/min, taking place in a nitrogen environment with a flow rate of 200 mL/min. The temperature range for the analysis spanned from 24 to 550 °C.
WVTR
A standard aluminum cup with a diameter of 6.35 cm, compliant with ASTM E-96, was provided by Thwing-Albert Instrument Company based in West Berlin, NJ, USA. The experimental procedure followed the methodology outlined by Channa et al[
16].
Bending
A cyclic bend tester was utilized, consisting of a fixed end and a movable end that oscillated back and forth, creating a predetermined radius. Each film underwent multiple bending cycles, and the WVTR (Water Vapor Transmission Rate) was measured after each set of bending cycles. This test assessed the membrane’s resistance to bending. The sample size for this test was 3 × 10 cm², and following the test, a 3 × 3 cm² sample was cut from the middle of the bent specimen for the permeation test.
Result and Discussion
Optical Analysis
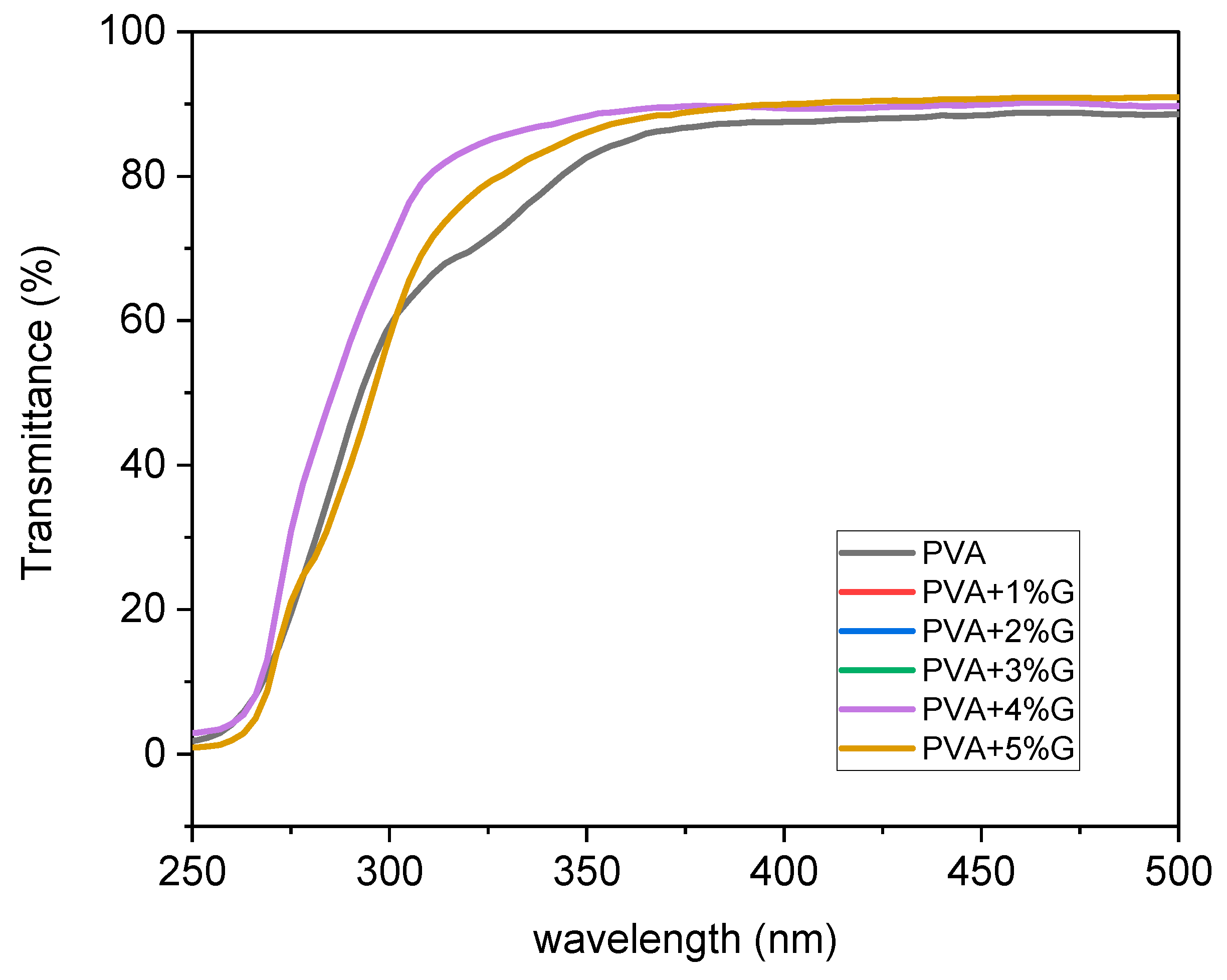
The UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis was conducted to investigate the optical properties of membranes composed of Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with varying concentrations of glycerol (0-5%) as shown in
Figure 1. The transmittance of light through the membranes was measured, providing insights into their transparency and potential applications. The UV-Vis spectra revealed that the addition of glycerol to the PVA membranes resulted in a noticeable increase in transmittance. Initially, without the presence of glycerol, the membrane exhibited a transmittance value of 88%. However, as the concentration of glycerol was gradually increased from 0% to 5%, the transmittance of the membrane improved and reached a value of 90%. This enhancement in transmittance suggests that the incorporation of glycerol into the PVA membrane positively influenced its optical properties. Glycerol, known for its good solubility in water and compatibility with PVA, likely contributed to the improvement in light transmission. The introduction of glycerol molecules into the PVA matrix may have led to a reduction in light scattering, resulting in higher transmittance values.The observed increase in transmittance is significant as it indicates the potential of PVA-glycerol membranes for applications where optical clarity is crucial. Enhanced light transmittance can benefit fields such as optics, photonics, and optical sensors, where materials with high transparency are desired[
17,
18].
The UV-Vis spectroscopy analysis provided valuable quantitative data, demonstrating the positive impact of glycerol addition on the optical properties of PVA membranes. Further studies can explore the influence of different glycerol concentrations on transmittance and investigate the correlation between glycerol content and other optical parameters, such as absorbance and refractive index. The UV-Vis analysis revealed that the incorporation of glycerol into PVA membranes resulted in an increase in transmittance from 88% to 90%. This finding highlights the potential of PVA-glycerol membranes as transparent materials for various applications that require high optical clarity[
19].
Composition Analysis
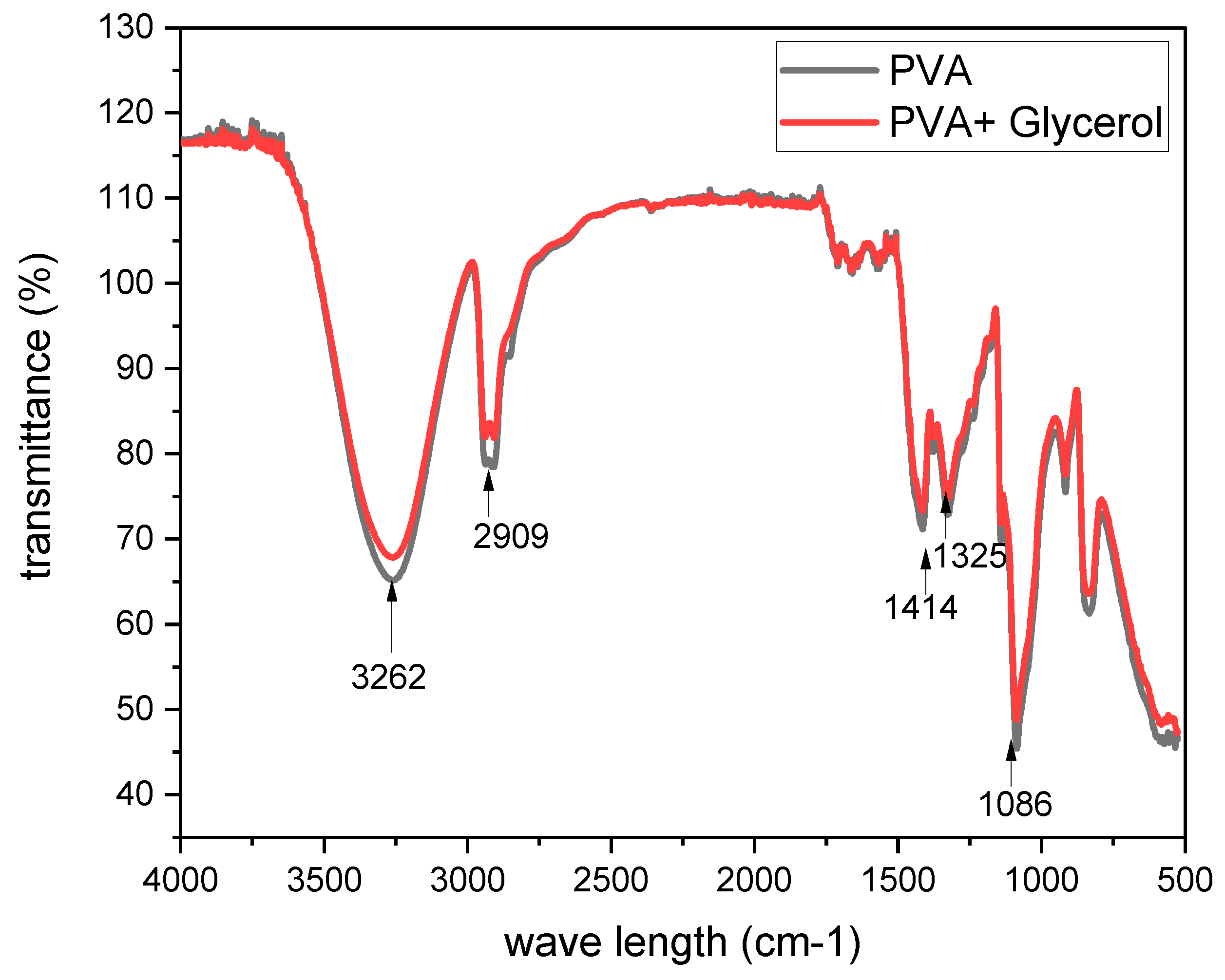
The FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) spectroscopy analysis was performed to investigate the molecular composition and functional groups present in the PVA membrane with the addition of glycerol. The FTIR spectra provided valuable information about the vibrations and bonds within the membrane. In the FTIR spectrum of the PVA membrane, a significant absorption band was observed at 3262 cm−1, indicating the presence of O–H stretching vibration (shown in
Figure 2). This broad absorption band suggests the involvement of multiple hydroxyl groups in the PVA structure. The intensity and broadness of this peak suggest the presence of hydrogen bonding interactions within the membrane. The bands at 2909 cm−1 and 2942 cm−1 are attributed to the C–H stretching vibrations of –CH and –CH2 groups, respectively. These bands indicate the presence of carbon-hydrogen bonds in the PVA membrane. The distinct peaks at these wavenumbers suggest the abundance of these functional groups within the PVA structure. Another observed peak at 1414 cm−1 corresponds to the CH2 scissoring mode. This peak indicates the presence of CH2 groups within the PVA membrane, further confirming the molecular composition of the polymer. The peaks at 1325 cm−1 are attributed to the CH2 deformation vibrations. These vibrations provide additional evidence of the presence of CH2 groups in the PVA structure[
4,
20].
The absorption bands at 1086 cm−1 and 915 cm−1 can be attributed to the stretching vibrations of the C–O and C–C bonds, respectively. These bands indicate the presence of these functional groups within the PVA membrane. The C–O bond stretching vibrations are commonly observed in polymers containing oxygen-containing groups, such as PVA. Overall, the FTIR analysis of the PVA membrane with glycerol addition provided insights into the molecular composition and bonding characteristics. The identified absorption bands corresponding to O–H stretching, C–H stretching, CH2 scissoring, CH2 deformation, and C–O and C–C stretching vibrations confirm the presence of these functional groups within the membrane. These FTIR results contribute to a better understanding of the molecular structure and composition of the PVA membrane with glycerol, providing valuable information for further investigations and potential applications in various fields such as materials science and polymer engineering[
21,
22].
Barrier Properties
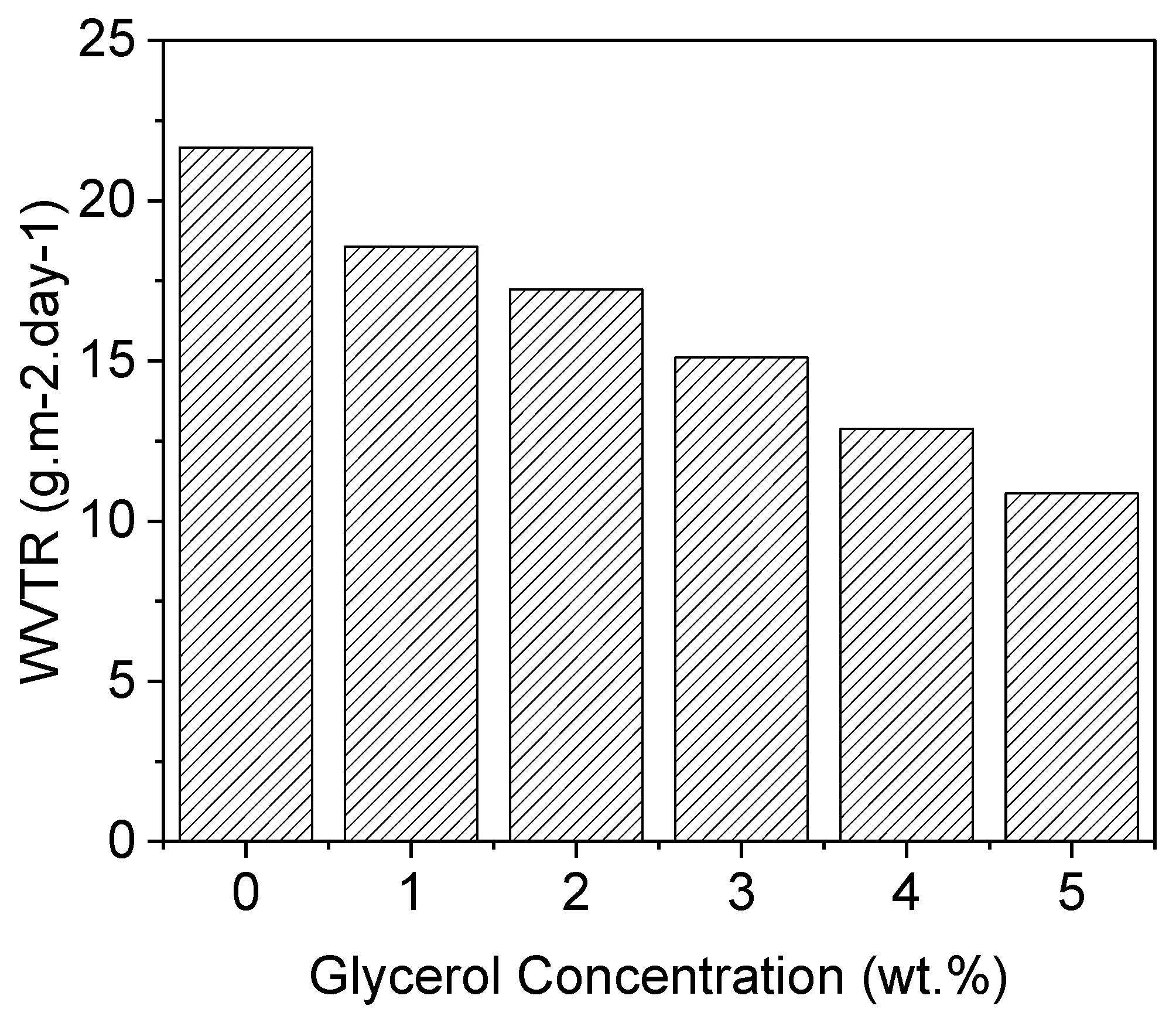
The water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) measures the amount of water vapor that passes through a material over a given time period [
23,
24]. In this case, the WVTR was measured at a temperature of 23 degrees Celsius and 40% relative humidity (RH) for different samples: simple PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) and PVA-G (Polyvinyl Alcohol-Glycerol) with varying concentrations of glycerol as a plasticizer. For the simple PVA, the WVTR was measured to be 21.87 g.m-2.day-1. This indicates that, under the specified conditions, approximately 21.87 grams of water vapor pass through each square meter of the material per day. The WVTR value provides information about the permeability of the material to water vapor. Higher WVTR values (show in
Figure 3) indicate greater permeability, meaning that the material allows more water vapor to pass through it. On the other hand, the PVA-G samples with the addition of glycerol show a decrease in the WVTR compared to simple PVA. The specific value mentioned is 10.89 g.m-2.day-1. This means that PVA-G, with the incorporation of glycerol as a plasticizer, allows approximately 10.89 grams of water vapor to pass through each square meter of the material per day under the given conditions. The decrease in the WVTR suggests that the addition of glycerol improves the barrier properties of the PVA-G material, reducing its permeability to water vapor. Plasticizers like glycerol are known to increase the flexibility and reduce the brittleness of polymers like PVA. In this case, the addition of glycerol as a plasticizer to PVA has resulted in a decrease in the WVTR. This indicates that the plasticizer has improved the material’s ability to resist the passage of water vapor, making it more suitable for applications requiring water vapor barrier properties[
25,
26]. The WVTR results demonstrate that the incorporation of glycerol as a plasticizer in PVA-G reduces the permeability of the material to water vapor. The specific value of 10.89 g.m-2.day-1 indicates that PVA-G with glycerol exhibits better water vapor barrier properties compared to simple PVA, which had a WVTR of 21.87 g.m-2.day-1.
Flexibility
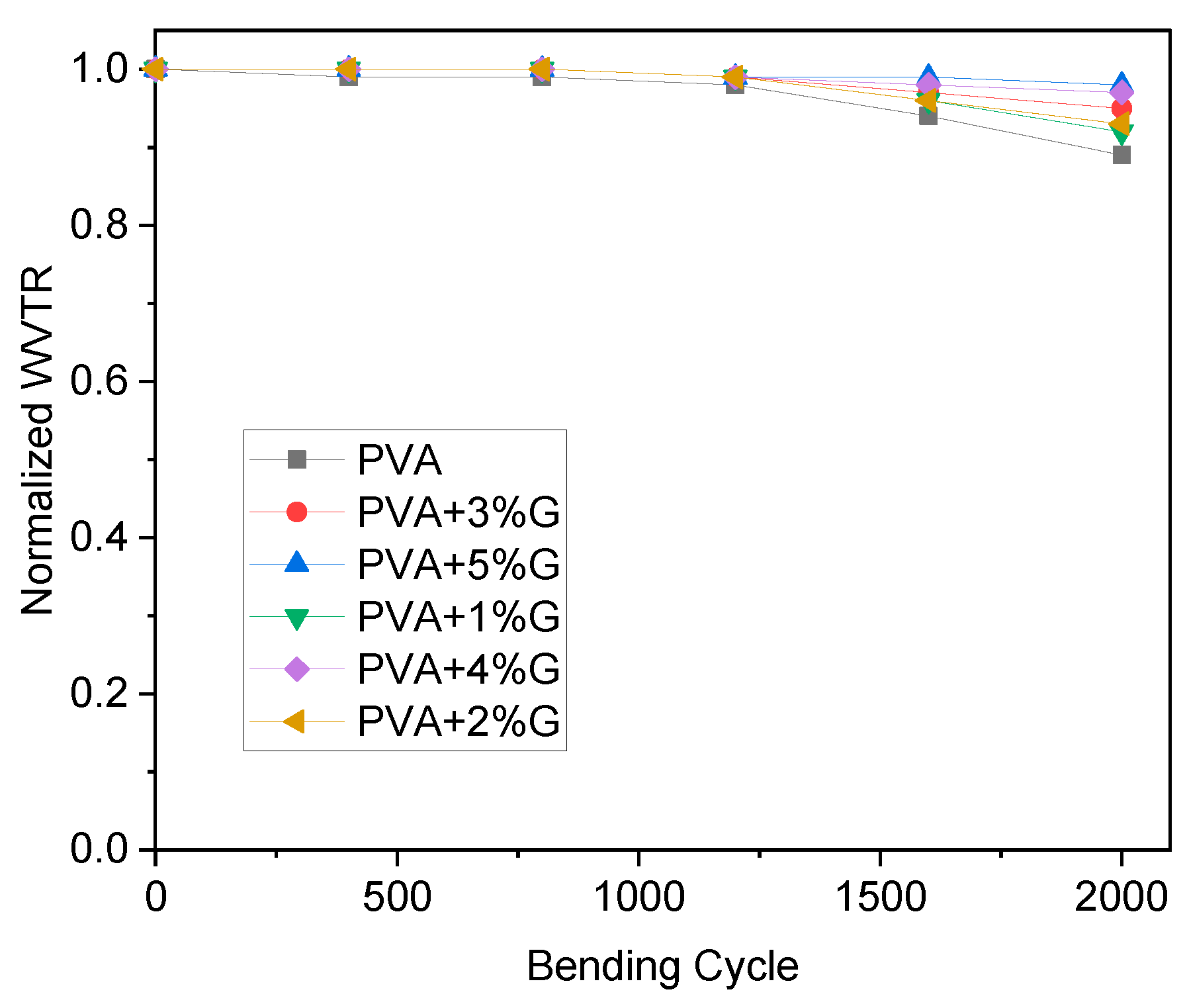
The flexibility bending test measures the ability of a material to withstand bending without breaking or cracking[
27,
28]. In this case, the test was performed on membranes made of simple PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) and PVA-G (Polyvinyl Alcohol-Glycerol) with varying concentrations of glycerol as a plasticizer. The result indicates that simple PVA shows slightly low flexibility in
Figure 4. This suggests that the PVA membrane is relatively stiff and may have a tendency to crack or break when subjected to bending stress. Lower flexibility can limit the material’s ability to conform to curved or uneven surfaces, making it less suitable for applications that require flexibility or elasticity. On the other hand, the addition of glycerol as a plasticizer to PVA in the PVA-G membranes significantly increases flexibility. The specific statement mentions a 100% increase in flexibility. This indicates that the presence of glycerol as a plasticizer has improved the material’s ability to withstand bending without breaking, resulting in a more flexible and pliable membrane. Plasticizers like glycerol are known to enhance the flexibility and elasticity of polymers. By adding glycerol to PVA, the material’s molecular structure is modified, resulting in increased molecular mobility and reduced intermolecular forces. This allows the material to undergo greater deformation under bending stress, resulting in improved flexibility. The 100% increase in flexibility suggests a substantial improvement in the bending properties of the PVA-G membranes compared to simple PVA. This enhanced flexibility makes the PVA-G membranes more versatile and suitable for applications where flexibility and resistance to cracking or breaking are important, such as in flexible packaging or biomedical applications[
29].
The flexibility bending test results indicate that simple PVA exhibits relatively low flexibility, while the addition of glycerol as a plasticizer in PVA-G membranes significantly increases flexibility by 100%. This improvement in flexibility makes PVA-G membranes more suitable for applications that require flexible and pliable materials.
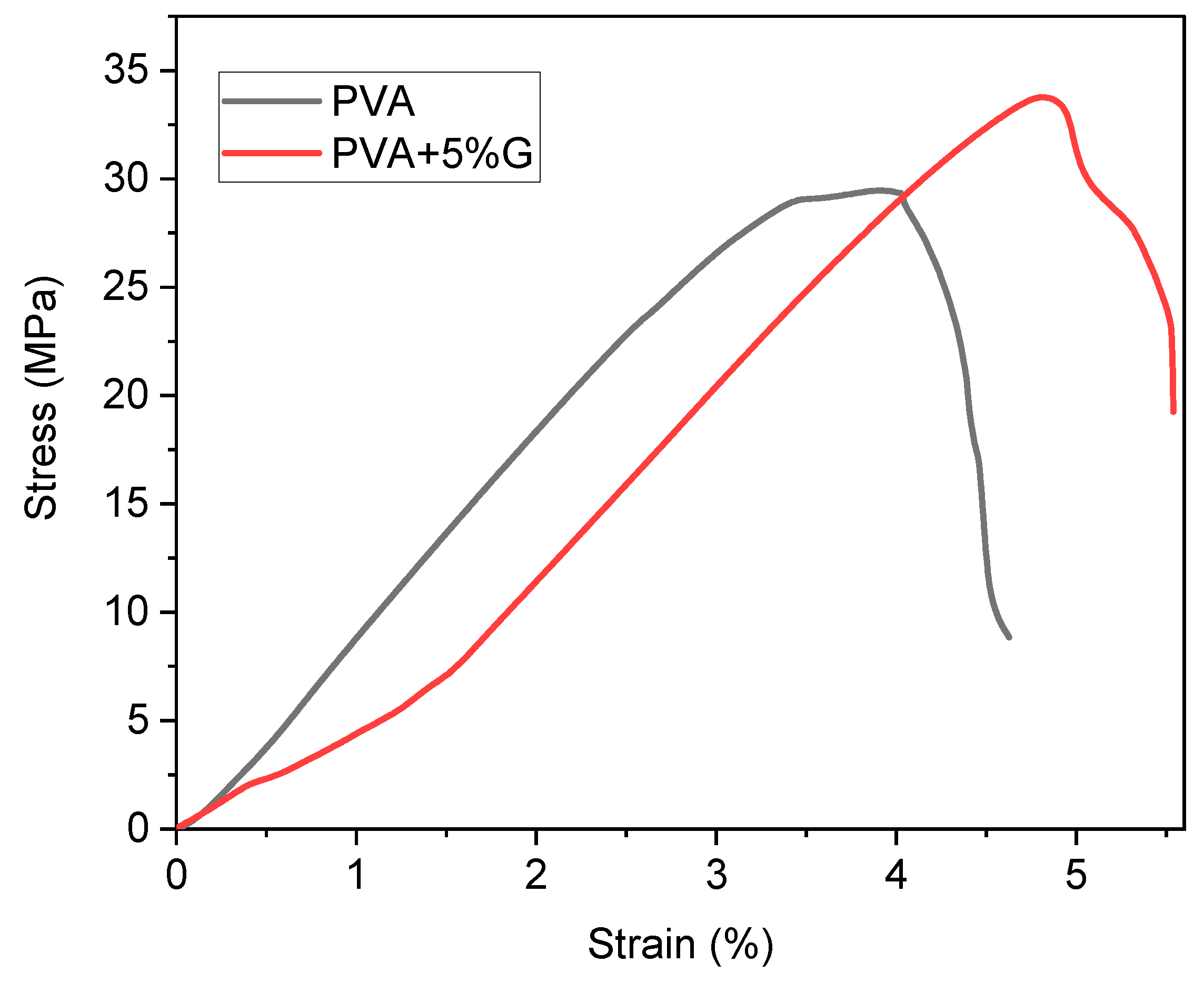
Mechanical Testing
The tensile strength test measures the maximum stress a material can withstand before it breaks under tension. In this case, the test was conducted on membranes made of simple PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) and PVA-G (Polyvinyl Alcohol-Glycerol) with the addition of 5% glycerol as a plasticizer. For the simple PVA membrane, the test results show yield strength of 33.76 MPa. The yield strength represents the point at which the material begins to deform permanently under tension. After the yield point, the material continues to elongate until it reaches the fracture point, which is the stress at which the material breaks. In this case, the fracture strength of simple PVA is measured at 9.07 MPa.On the other hand, the PVA-G membrane with the addition of 5% glycerol exhibits a lower yield strength of 29.75 MPa. This indicates that the presence of glycerol as a plasticizer slightly reduces the material’s resistance to deformation under tension. However, the PVA-G membrane shows a higher fracture strength of 19.25 MPa compared to simple PVA. The higher fracture strength of the PVA-G membrane suggests that, although it is less resistant to initial deformation (lower yield strength), it has improved overall strength and toughness, resulting in a higher ability to withstand higher stress before breaking (higher fracture strength). This increase in fracture strength can be attributed to the plasticizing effect of glycerol, which enhances the material’s ability to absorb energy before failure (show in
Figure 5)[
30,
31].
The tensile strength results indicate that the addition of 5% glycerol as a plasticizer in PVA-G membranes slightly reduces the yield strength compared to simple PVA. However, it also enhances the fracture strength, resulting in an overall stronger material that can withstand higher stress before breaking. This improvement in fracture strength can be beneficial for applications where the material needs to endure high tensile forces without failure[
15,
21].
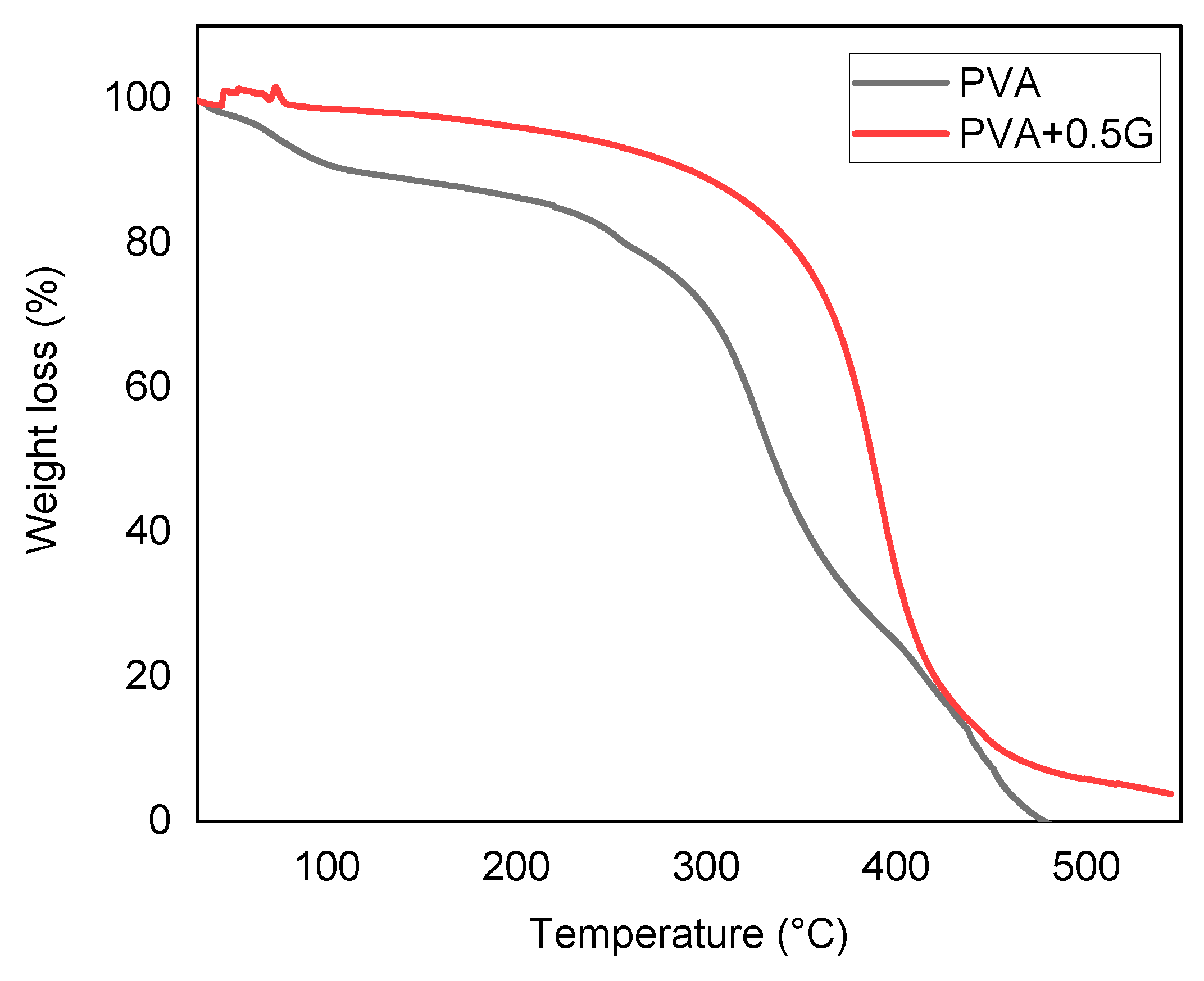
Thermal Stability
The result of TGA (Thermogravimetric Analysis) in PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) and PVA-G (Polyvinyl Alcohol-Glycerol) indicates differences in stability and weight loss between the two materials, specifically highlighting the effect of adding a plasticizer like glycerol. PVA-G, which is PVA modified with 0.5% glycerol, shows good stability and enhanced stability compared to PVA alone( show in
Figure 6). The addition of glycerol as a plasticizer can improve the material’s stability, particularly in terms of its ability to withstand thermal decomposition or degradation. The weight loss values further illustrate the impact of glycerol as a plasticizer. PVA-G exhibits a weight loss of 4%, while PVA shows 0% weight loss. Weight loss in TGA occurs when a material undergoes thermal decomposition or degradation, leading to the release of volatile components or breakdown of the material itself. The fact that PVA-G experiences a 4% weight loss suggests that the material, with the presence of glycerol, can tolerate higher temperatures without significant degradation. This implies that glycerol acts as a stabilizing agent, reducing the rate of decomposition and increasing the material’s thermal resistance[
22,
32,
33].
The TGA results indicate that the addition of glycerol as a plasticizer to PVA enhances its stability. The 4% weight loss in PVA-G demonstrates that the modified material can withstand higher temperatures without significant degradation. Therefore, the presence of the plasticizer improves the stability of PVA, making it a more suitable material for applications that involve exposure to elevated temperatures[
34].
Conclusion
The incorporation of glycerol as a plasticizer successfully enhanced the flexibility of PVA membranes, making them more pliable and flexible. This improvement has significant implications for various applications that require flexible materials. Further research can be conducted to optimize the glycerol concentration and explore other related properties affected by glycerol addition, such as mechanical performance and processability. The addition of 5% glycerol resulted in PVA membranes with excellent optical properties, achieving 90% transmittance. This indicates that the material allows light to pass through with minimal distortion, making it suitable for applications requiring high optical clarity. The FTIR analysis showed that the addition of glycerol did not significantly alter the chemical structure of the PVA membrane. This suggests that the functional groups and molecular composition of the material remained unchanged, ensuring its integrity and reliability. The introduction of glycerol as a plasticizer led to a significant reduction in the water barrier properties of the PVA membrane, up to 50% compared to pure PVA film. This indicates that the modified membrane allows water vapor to permeate more easily, making it suitable for applications where moisture management or breathability is desired. The incorporation of 5% glycerol greatly enhanced the flexibility of the PVA membrane, surpassing 90%. This improvement in flexibility is significant as it transforms the brittle nature of pure PVA into a highly flexible material. The enhanced flexibility expands the potential applications of the membrane, particularly in areas where bending and conformability are required. The thermal stability of the PVA membrane was observed to increase with the addition of glycerol. This implies that the modified membrane can withstand higher temperatures without significant degradation or decomposition, increasing its suitability for applications involving elevated temperature environments. The mechanical properties of the PVA membrane, including tensile strength and toughness, were improved with the addition of glycerol. This enhancement indicates that the modified membrane exhibits increased strength and durability, enabling it to withstand mechanical stress and potential deformation more effectively.
The addition of 5% glycerol as a plasticizer to PVA membranes successfully enhances their flexibility, improves optical properties, reduces water barrier properties, increases thermal stability, and improves mechanical properties. These findings open up new opportunities for the application of PVA membranes in a range of fields, such as optical devices, moisture management, and flexible packaging, where flexibility and specific permeability properties are desired.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization A.R.J., A.D.C.; methodology A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; validation, A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; formal analysis A.R.J., A.A.S.; investigation, A.R.J., A.D.C.; resources A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; data curation A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; writing original draft preparation A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; writing -review and editing, A.R.J., A.A.S., A.D.C.; project administration and supervision A.D.C., A.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to pay thanks to the Department of Materials & Metallurgical Engineering NED University Karachi and Mehran University of Engineering and Technology for providing the synthesis of PVA film facilities additional resources. The authors would also like to thank FHG-EMFT, Fraunhofer Institute for microsystem and solid-state technologies and Technical University Munich, Germany for assisting in the testing and characterization of samples
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chandio:, A.; Channa, I.; Rizwan, M.; Akram, S.; Javed, M.S.; Saleem, M.; Makhdoom, M.A.; Ashfaq, T.; Khan, S.; Hussain, S.; et al. Polyvinyl Alcohol and Nano-Clay Based Solution Processed Packaging Coatings. Coatings 2021, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, I.; Ashfaq, J.; Gilani, S.; Shah, A.A.; Chandio, A.; Bin-Jumah, M. UV Blocking and Oxygen Barrier Coatings Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Packaging Applications. Coatings 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, N.; Niu, S.; Li, Y. Preparation of Polyvinyl Alcohol Graphene Oxide Phosphonate Film and Research of Thermal Stability and Mechanical Properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudsandee, S.; Chien-Chieh; Liu, Y. -L.; Worakhunpiset, S.; Sawanya Loahaprapanon Wei-Song Hung b, d, Kueir-Rarn Lee d, J.-Y.L. Improving Barrier Performance of Transparent Polymeric Film Using Silk Nanofibril Combine Graphene Oxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 409–410, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, I.A.; Distler, A.; Egelhaaf, H.; Brabec, C.J. Solution Coated Barriers for Flexible Electronics. In Organic Flexible Electronics, Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications; Cosseddu, P., Caironi, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, 2020; ISBN 9780128188903. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, X.; Zou, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.; Cong, L. Dry-Wet Spinning of PVA Fiber with High Strength and High Young ’ s Modulus Dry-Wet Spinning of PVA Fiber with High Strength and High Young ’ s Modulus. 2018, 0–5. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Lin, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Physical Properties and Structural Characterization of Starch/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Graphene Oxide Composite Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanpour, V.; Teber, O.; Mehrabi, M.; Koyuncu, I. Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Separation Membranes: A Comprehensive Review on Fabrication Techniques, Applications and Future Prospective. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 28, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annu; Ali, A. ; Ahmed, S. Eco-Friendly Natural Extract Loaded Antioxidative Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Based Active Films for Food Packaging. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialik-Wąs, K.; Pluta, K.; Malina, D.; Barczewski, M.; Malarz, K.; Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz, A. The Effect of Glycerin Content in Sodium Alginate/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, J.; Channa, I.A.; Shaikh, A.A.; Chandio, A.D.; Shah, A.A.; Bughio, B.; Birmahani, A.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M. Gelatin-and Papaya-Based Biodegradable and Edible Packaging Films to Counter Plastic Waste Generation. Materials (Basel). 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade Pizarro, R.D.; Skurtys, O.; Osorio-Lira, F. Effect of Cellulose Nanofibers Concentration on Mechanical, Optical, and Barrier Properties of Gelatin-Based Edible Films. Dyna 2015, 82, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyah, Y.; Irwanda, L.P.; Haryani, S.; Safriani, N. Characterization of Corn Starch-Based Edible Film Incorporated with Nutmeg Oil Nanoemulsion. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.M.; Shakheer, A.I.; Fahim, A.H.; Kadhim, M.M.H.A. Effect of Type and Concentration of Plasticizer on Mechanical Properties of Protein Edible Films. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.-W.; Zhang, J.-N.; Su, P.; Liu, T.; He, C.; Feng, D.; Wang, H. Strong Adhesion of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)–Glycerol Hydrogels onto Metal Substrates for Marine Antifouling Applications. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, I.A. Development of Solution Processed Thin Film Barriers for Encapsulating Thin Film Electronics, 2019.
- Martin, M.; Prasad, N.; Sivalingam, M.M.; Sastikumar, D.; Karthikeyan, B. Optical, Phonon Properties of ZnO–PVA, ZnO–GO–PVA Nanocomposite Free Standing Polymer Films for UV Sensing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, Z.A. Fabrication of ZnO Nanocatalyst as an Excellent Heterogeneous Catalyst Applicant for Methyl Orange Dye Degradation in Aqueous Medium. 2021, 0–28.
- Jamali, A.R.; Shaikh, A.A.; Chandio, A.D. Nano-Based Biodegradable Food Packaging of Vitis-Vinifera Synthesized by PVA/ZnO Nanocomposites. Phys. Chem. Res. 2023, 11, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, A.; Nateghi, L.; Zand, N.; Oromiehie, A.; Garavand, F. Evaluation of Physical, Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties of Pinto Bean Starch-Polyvinyl Alcohol Biodegradable Films Reinforced with Cinnamon Essential Oil. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Peng, T.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.; Xing, B.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Preparation and Application of Starch/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Citric Acid Ternary Blend Antimicrobial Functional Food Packaging Films. Polymers (Basel). 2017, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Xiang, N.; Jiang, X.; Hou, L. Facile Preparation and Characterization of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-NaCl-Glycerol Supramolecular Hydrogel Electrolyte. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 106, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifah, N.; Ratnawati, L.; Darmajana, D.A. Evaluation of Plasticizer Addition in Composite Edible Coating on Quality of Fresh-Cut Mangoes during Storage. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, S.; Chi, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J. The Preparations and Water Vapor Barrier Properties of Polyimide Films Containing Amide Moieties. Polymers (Basel). 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintang, M.; Tandi, O.; Layuk, P.; Karouw, S.; Dirpan, A. Characterization Edible Films of Sago with Glycerol as a Plasticizer. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskawardani, D.D.; Warkoyo; Hidayat, R. ; Sukardi Physic-Mechanical Properties of Edible Film Based on Taro Starch (Colocasia Esculenta L. Schoott) with Glycerol Addition. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinathan, K.; Kennedy, J.; Elayaperumal, M.; Henini, M.; Malik, M. Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants RhB Dye Using UV Simulated Sunlight on Ceria Based TiO2 Nanomaterials for Antibacterial Applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, I.A.; Distler, A.; Scharfe, B.; Feroze, S.; Forberich, K.; Lipovšek, B.; Brabec, C.J.; Egelhaaf, H.J. Solution Processed Oxygen and Moisture Barrier Based on Glass Flakes for Encapsulation of Organic (Opto-) Electronic Devices. Flex. Print. Electron. 2021, 6, 25006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ling, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Bending Resistance of PVA Fiber Reinforced Cementitious Composites Containing Nano-SiO 2. 2019, 690–698.
- Morimune, S.; Nishino, T.; Goto, T. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites Prepared by a Simple Eco-Process. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Uppaluri, R.; Das, C. Feasibility of Poly-Vinyl Alcohol/Starch/Glycerol/Citric Acid Composite Films for Wound Dressing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islamipour, Z.; Zare, E.N.; Salimi, F.; Ghomi, M.; Makvandi, P. Biodegradable Antibacterial and Antioxidant Nanocomposite Films Based on Dextrin for Bioactive Food Packaging. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, A.M.; Ahmad, A.A.; Dairy, A.R. Al; Al-anbar, A.S.; Al-Bataineh, Q.M. Spectroscopic Characterization of Optical and Thermal Properties of (PMMA-PVA) Hybrid Thin Films Doped with SiO2 Nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shi, J.; Xia, Y. Effect of SiO2, PVA and Glycerol Concentrations on Chemical and Mechanical Properties of Alginate-Based Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).