1. Introduction
Biomass energy has always been an important energy source for human survival, ranking fourth in the world's total energy consumption after coal, oil and natural gas [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. At present, the world is facing the crisis of fossil energy exhaustion, biomass energy, as the only renewable carbon source at present, is an internationally recognized zero-carbon emission energy, with rich sources, clean low-carbon, renewable and other characteristics. China is rich in biomass resources, and the annual available biomass resources amount is about 600 ~ 700 million tons of standard coal, of which 247 million tons of standard coal can be used for energy conversion, and this data will further increase with the large-scale development of energy plants in the future [
6].Biomass Moulding Fuel, abbreviated as "BMF", is a biomass moulding fuel that uses agricultural and forestry residues such as wood chips, sawdust, bamboo chips, straw, rice bran, bagasse and fruit husks as raw materials through grinding, mixing, extrusion and drying processes. They can be made with a certain density and shape (such as pellet,briquette,block, rod, granular, etc.). and directly burn as a new type of clean fuel. Biomass molding fuel can increase the density of ordinary biomass from 40~150kg/m3 to 1000~1400kg/m3, not only saving transportation and storage costs, but also greatly improve its combustion status. The thermal efficiency of direct burning of crop straw is only 10%-30%, while the thermal efficiency of biomass molding fuel is up to 89%. In addition, the emission of NOx of biomass molding fuel is only 1/5 of that of coal, and the emission of SO2 is only 1/10 of that of coal, so biomass molding fuel is an efficient and clean fuel [
7,
8]. Biomass molding fuel has the advantages of carbon neutrality, low nitrogen and sulfur content, less flue gas pollution, etc. In addition to biomass gasification, direct combustion and mixed combustion power generation, it can also be widely used in heating boilers and other combustion equipment, which can significantly consume agricultural and forestry residues, reduce air pollution, achieve zero CO2 emissions, in line with the current concept of sustainable development of society. It is of great significance to the development of low-carbon economy and the establishment of a conservation-oriented society.
At present, it has become the consensus of the international community to achieve carbon peaking and carbon neutrality as soon as possible, and about 130 countries will achieve the goal of carbon neutrality by the middle of this century. China is a developing country with energy consumption on the coal side, energy efficiency on the low side, and oil and natural gas supply risk on the high side. The proposal of the goal of carbon neutralization is to further implement the concept of "lucid waters and green mountains are golden hills and silver mountains", and promote the transformation of low-carbon green economy through proper adjustment of economic structure. Among them, the study of biomass fuel not only contributes to the transition of our energy structure from fossil energy to non-fossil energy, and to a certain extent it can solve the environmental pollution problems caused by incorrect treatment of waste raw materials. Currently, the BMF production in Germany, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Canada and the United States can reach more than 20 million tons per year [
9]. However, the development of BMF in China still falls behind these countries.Although there are many researchers have studied BMF utilization way and technology in China [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16].
Chinese hickory (Carya cathayensis Sarg.) is a well-known Chinese nut, widely distributed in the Zhejiang and Anhui provinces of China, whose kernel , leaves, and green husks have been widely investigated for nutraceutical components in recent decade[
17,
18,
19]. The hickory husks are a by-product, usually obtained after cracking and shelling process. The husks are produced in high quantity and considered as waste and could create environmental problems. Efforts have been made to extract valuable nutraceutical components, especially from food waste in recent years[
20]. Its kernel can be eaten, the shells can be made of activated carbon. But the husks are not edible, except for a few of the husks returned to the forest as fertilizer [
21,
22], most of the husks will be discarded by farmers at will, into rivers, streams, ditches, sewage terminal ponds and other places, causing serious pollution to the water and soil along the river basin. Some farmers burn the husks, and the husks ash produced contains alkali, which pollutes the lands to a certain extent. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to study the reuse of the hickory husks. In this paper, the optimum technology of hickory husks forming and its forming mechanism were analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental instruments and equipment
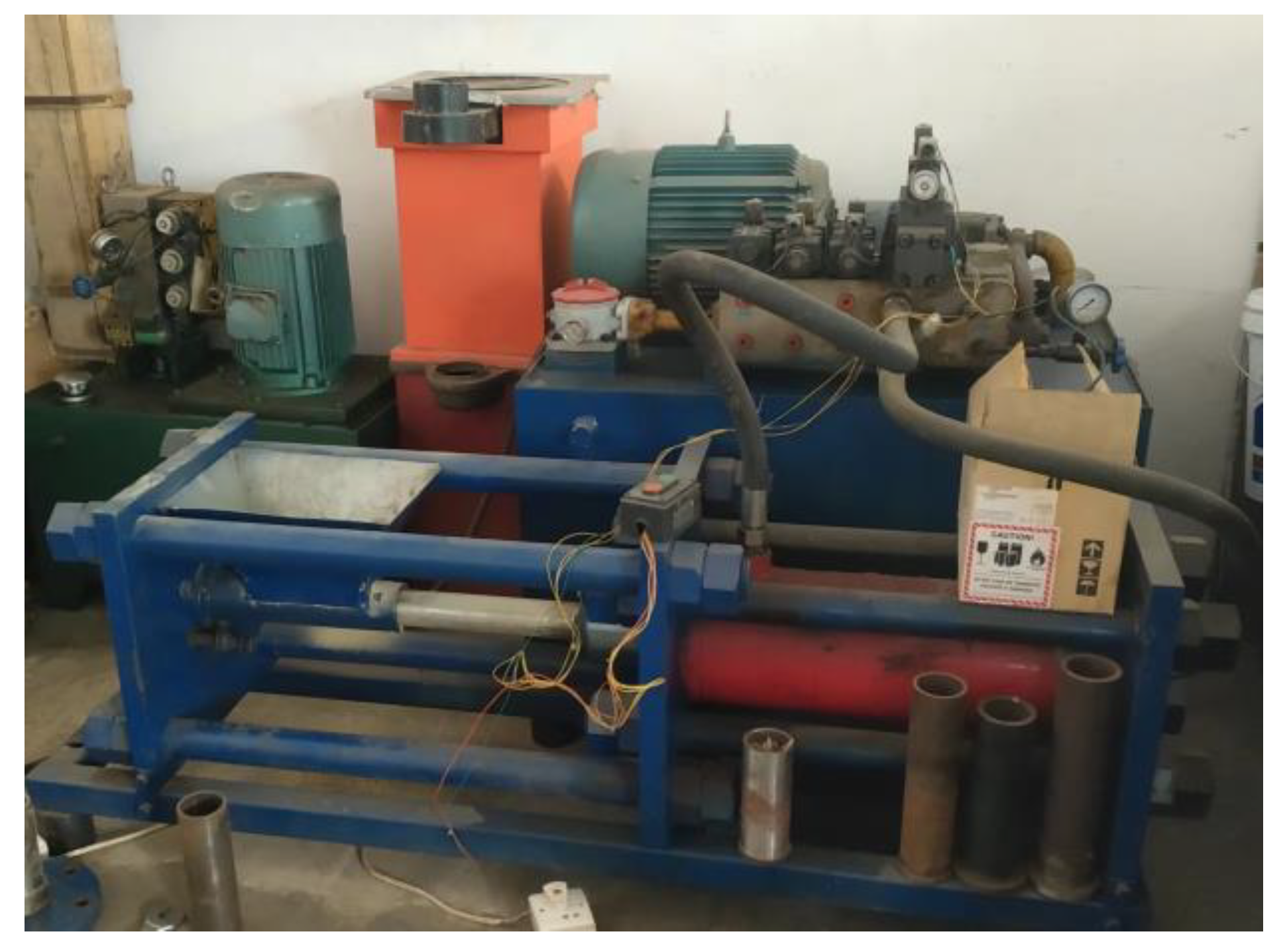
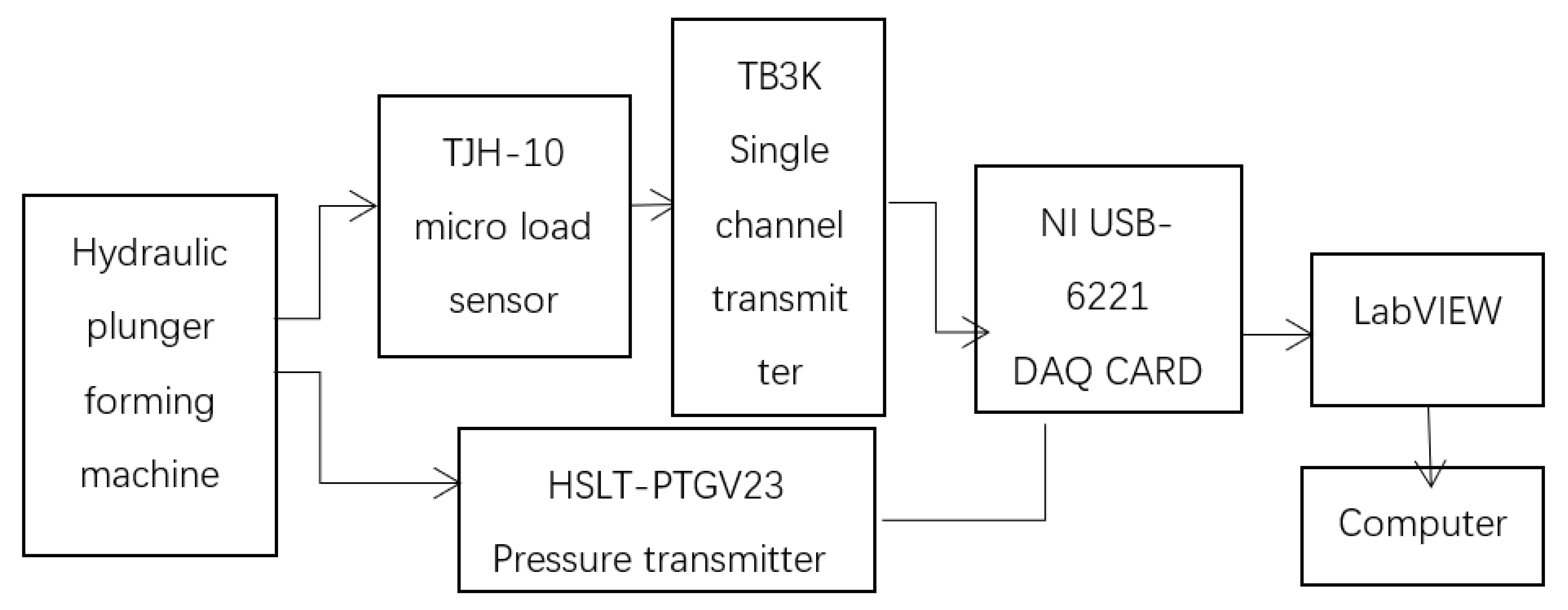
As is shown in
Figure 1, The test equipment mainly includes hydraulic plunger forming machine (made by Engineering College of Beijing Forestry University), NI USB-6221 data acquisition card, SC69-02 moisture rapid tester and Leica S8 APO stereo microscope, WV-CP470 digital color CCD camera, vernier caliper, SF-400S electronic scale (0.01g), portable scale (1g), sample bag, watering can, etc.The hydraulic part of the forming machine is made of BHD-32 hydraulic system produced by Shandong Hydraulic Machinery Manufacturing Corporation. The system pressure is 25MPa, the total power is 11kw, and the total flow is 45L·min-1. The material compression speed of the piston is 30.6mm/s, the diameter of the piston is 60mm, the theoretical maximum thrust is 508.9kN, and the maximum pressure is 180MPa. Self-made open forming sleeve was used in the experiment, the inner diameter was 60mm, the length was 180mm,210mm, 240mm, 270mm, 300mm,330mm, and the corresponding length-diameter ratio was3,3.5, 4, 4.5, 5,5.5 respectively.
In the experiment, HSLT-PTGV23 pressure transmitter was selected to measure the axial pressure of the material, and the pressure transmitter was directly installed on the hydraulic pipe of the oil inlet channel through a threaded connection.When the hydraulic forming machine is running, the pressure transmitter can measure the pressure of the hydraulic system.In the experiment, TJH-10 micro load sensor was used to measure the radial force on the material at different positions of the forming sleeve.The data collection flow chart is as follows.
2.2. Experimental materials
The raw material of the experiment was matured peeled hickory husk in autumn 2022 in Lin 'an District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province. Hickory husk refers to the green husk on the outer layer of green hickory fruit, rather than the hard shell on the outside of the nut, commonly known as "Guo Pu" in Chinese. After natural drying in the field, the husks were collected and crushed into 10 cm, with uneven shape and size. The husks were completely dried with a rapid moisture tester, and the total moisture was calculated to be about 6%.
In addition to the naturally dried husks, it is also necessary to adjust the water content of 10%, 14%, 18%, 22%, 26% of husks as test raw materials. Specific treatment process: Adjust the moisture content on the basis of the total moisture of natural dried husks, and determine the amount of water added by calculation; Put the test raw materials into a plastic bag, spray water with a watering can, stir continuously, seal, and stand at room temperature for 72 hours, so that water and materials are fully and evenly mixed; The water content of the husks after standing is measured. If it does not meet the test requirements, the water content should be adjusted again.
The formula for calculating water content is:
In the formula,M refers to material moisture content, %;
m refers to material quality before drying;
M0 refers to material quality after complete drying.
2.3. Experimental method
The test was carried out on a hydraulic plunger forming machine at an ambient temperature of 18~25 ℃. The plunger is driven by hydraulic cylinder to squeeze the hickory husks intermittently. With the accumulation and compression of the husks in the forming sleeve, the friction between the material and the inner wall of the sleeve gradually increases, and the material is compressed in the sleeve. The shape and size of the husks have been determined without secondary crushing, and the influence of its particle size is not needed to be considered. In this paper, the water content and the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve are taken as the test parameters. The self-made open forming sleeve was used in the test, the inner diameter was 60 mm, the length was 180,210,240,270,300,330 mm, and the corresponding length-diameter ratios were 3,3.5, 4,4.5, 5,5.5 respectively. A total of 36 constitutive tests were carried out by controlling the water content of the husks and the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeves respectively.
During the test, after each extrusion of the plunger, the material with roughly the same quality is added to the hopper to ensure that the degree of compressed material is uniform each time, and the pressure change in the oil inlet tube is recorded by the pressure transmitter measurement and data acquisition card, and the pressure exerted by the plunger is converted. The plunger movement stops at the end of the stroke and is discharged after 10 s for the next extrusion.
2.4. Experimental design
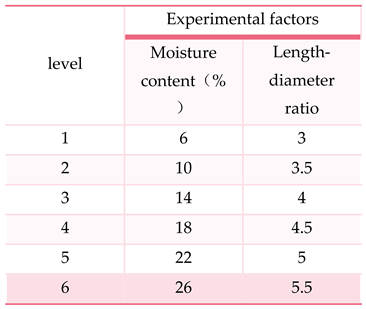
The physical properties of raw materials and the length of molding sleeves will affect the molding process. In order to verify the molding mechanical laws of hickory husks under different molding conditions, this paper takes the moisture content of raw materials and the length-diameter ratio of molding sleeves as experimental factors, and the levels of experimental factors are shown in
Table 1:
According to
Table 1, 36 groups of single factor experiments were carried out on hickory husks to measure the axial and radial pressures of raw materials forming under different experimental factors and levels, and the values were measured multiple times under the same factor level. The 3 groups of pressure values under stable forming conditions were taken and their average values were calculated, which was used as the actual measured pressure.
2.5. Data acquisition and processing
In the forming experiment, TJH-10 miniature load sensor is used to measure the radial force on the material at different positions of the forming sleeve. The surface of the pressure sensor can sense the change of pressure and convert the pressure value into voltage signal.However, due to the small force area, the voltage signal generated in the case of small change in pressure value is weak, so the voltage signal needs to be amplified by the TB3K single-channel transmitter after output.At the same time, HSLT-PTGV23 pressure transmitter is used to measure the pressure of the hydraulic system of the hydraulic forming machine, and the pressure value is also output by voltage signal.The USB-6221 data acquisition card A/D system of American NI Company is used to collect voltage signals output by two pressure sensors in real time, and the voltage analog signals are controlled, monitored and saved to the computer through LabVIEW2017 virtual instrument software. In order to reduce external interference, the terminal is configured as RSE, and the actual sampling rate is 100.The number of samples is 10.According to the corresponding relationship between voltage and pressure, the voltage value can be converted on the computer, and the corresponding pressure value can be obtained.The radial compressive stress of the material at a fixed point of the forming sleeve is:
Where, σF- radial compressive stress on the material, MPa;
F- The radial pressure on the boss measured by the sensor, N;
r- Convex radius, mm.
The pressure value of the hydraulic system of the forming machine is measured by the HSLT-PTGV23 pressure transmitter. It is also necessary to convert the pressure of the hydraulic system into the plunger pressure according to Formula 2, and the converted value is the axial pressure value of the material in the molding process.The inner diameter of the hydraulic cylinder of the hydraulic forming machine is 180mm, the front end of the piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder is consolidated with the plunger, and the diameter of the plunger is 60mm. The pressure exerted by the plunger during the movement can be obtained, that is, the axial compressive stress of the material.
Where,σP - Axial compressive stress of the material, MPa;
σS- Hydraulic system pressure, MPa.
2.6. Quality evaluation index of biomass molding fuel
2.6.1. The relaxation density
In this experiment, the relaxation density and surface quality of the biomass molding fuel were used as evaluation indexes to evaluate the influence of different forming conditions on the forming quality, which was used as the basis for determining the forming conditions of straw biomass raw materials. After molding, the compression density of the biomass molding block gradually decreases due to elastic deformation and stress relaxation, and the density of the molding block becomes stable after a certain period of time. At this time, the density of the molding block is called relaxation density . After each group of tests, three rod-shaped molding blocks are randomly selected, and their mass, length and diameter are measured after being placed in the natural state for 72 hours, and the average relaxation density is calculated to evaluate the molding quality.
In order to study the influence of each experimental variable on the molding quality of the molding fuel, the density and diameter of the molding fuel were used in this experiment. The pressure resistance and the surface quality of the forming block are used as an evaluation index of the forming quality. To obtain the density of the forming fuel,the quality of the forming fuel is measured using an electronic scale (model: SF-400) and the vernier caliper is used to measure the diameter and length of the forming fuel. To ensure the reliability of its results, multiple locations are selected during measurement and the measurement junction is combined.
Take the mean value and calculate the fuel density according to the formula .
Where: ρ is the density of molded fuel (unit: g/cm3);
m is the quality of the sample of molded fuel taken (unit: g);
D is the diameter of the molded fuel sample (unit: cm);
L is the length of the molded fuel sample taken (unit: cm).
2.6.2. The microstructure of biomass molding fuel
In this experiment, the evaluation of the surface quality of molded fuel is mainly based on the number of surface cracks. For convenience check the processing and analysis of the data, the surface quality of the molding block is quantified, and the processing method is as follows: 1- Poor molding effect; 2- More cracks on the surface of molded fuel; 3- Less cracks on the surface of the molded fuel; 4- Smooth surface of the molded fuel.
The test samples were placed on the stereo microscope stage, and the microscopic structure of the end face of the shaped block was photographed by the camera. The bonding state at the boundary of the husks was observed, and the forming state of the husks under different conditions was analyzed from the microscopic point of view.
3. Results
3.1. Different quality molding block quality
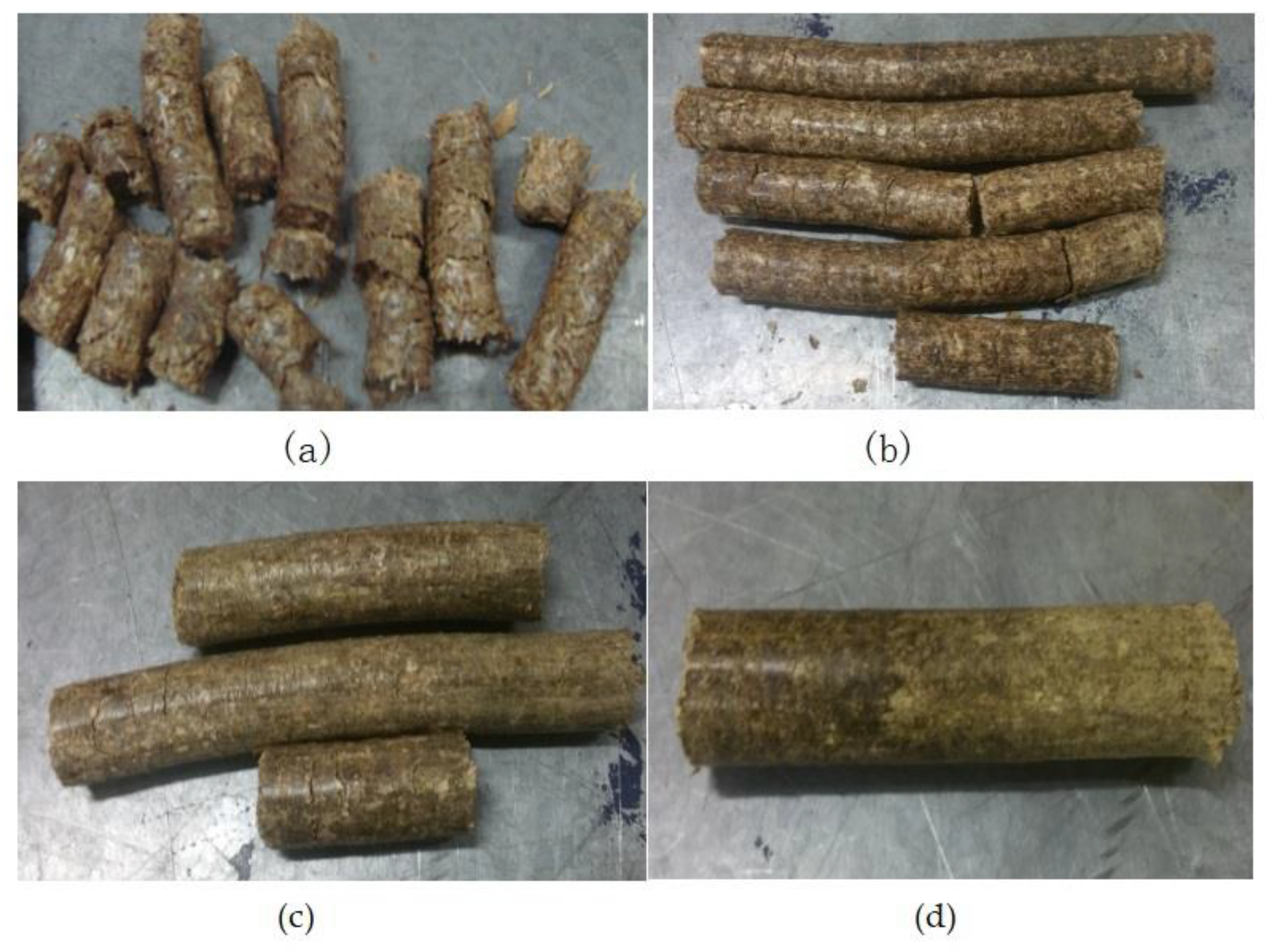
The forming block obtained by hydraulic plunger molding is formed by a number of forming pieces combined with each other, each movement cycle of the plunger will compress the material into a small forming block, because the plunger is intermittent compression of the material, and the hydraulic system efficiency is low compression interval time is long, there will be a border crack between the adjacent forming blocks, but better forming conditions will improve the state of the crack.When the moisture content is constant, the forming quality of the material can be improved by appropriately increasing the length-diameter ratio.FIG.5 shows the forming effect of hickory cattails under different forming conditions.As shown in
Figure 2 below, the surface quality of the molded fuel is divided into figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) respectively.
It indicates that the forming effect of the forming fuel is poor, the surface cracks of the forming fuel are more, the surface cracks of the forming fuel are less, and the forming fuel is formed.
The fuel surface is smooth. They were numerically converted to 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively, and the experimental results were recorded.
Figure 3.
Surface quality of pellets.
Figure 3.
Surface quality of pellets.
3.2. Test forming result
The experimental data of different experimental conditions are sorted out, and the water content, the length-diameter ratio of molding sleeve and the density of molding fuel are obtained.
The experimental data of degree and surface quality of molded fuel are shown in
Table 2 below.
4. Discussion
4.1. The influence of experimental parameters on molding pressure
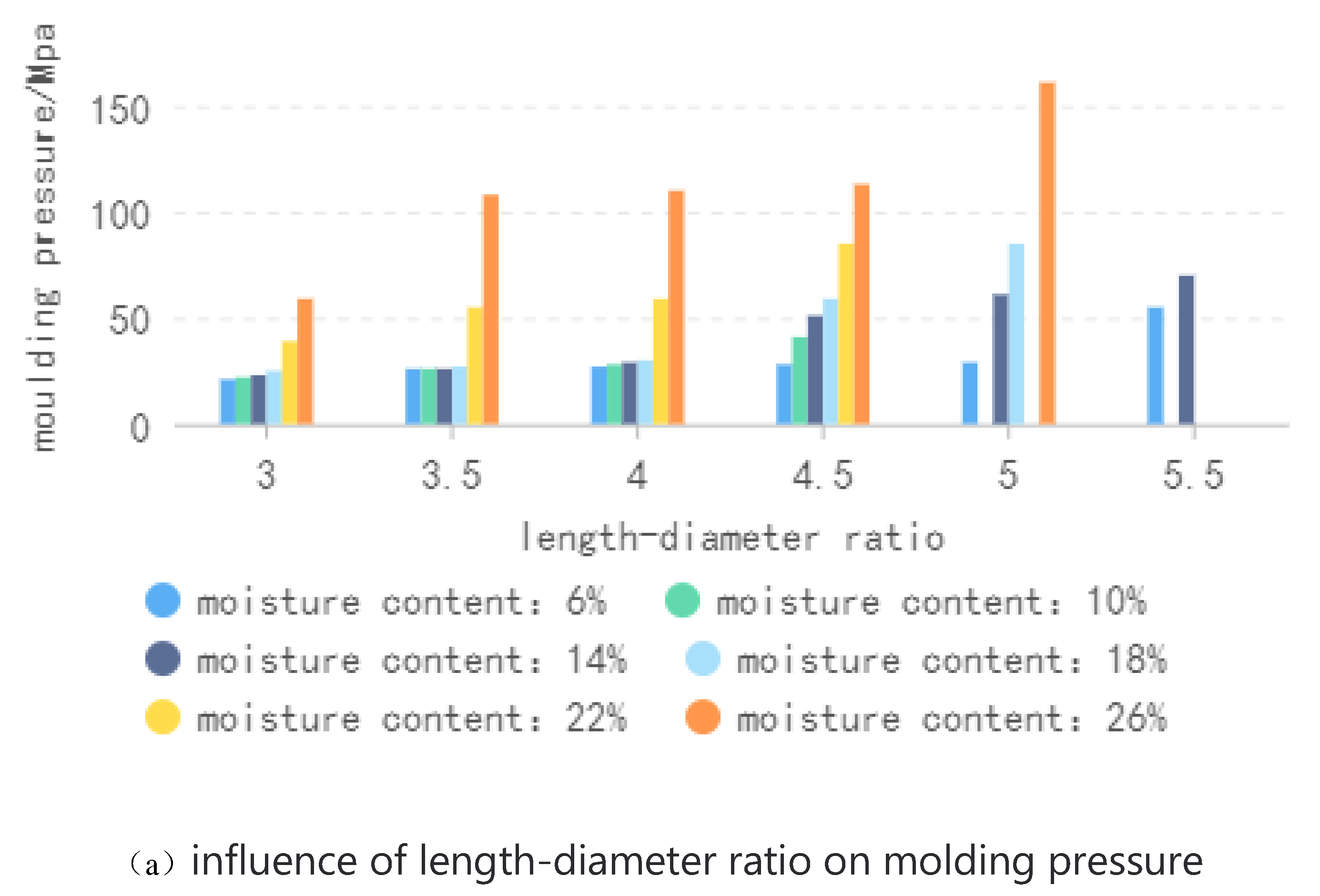
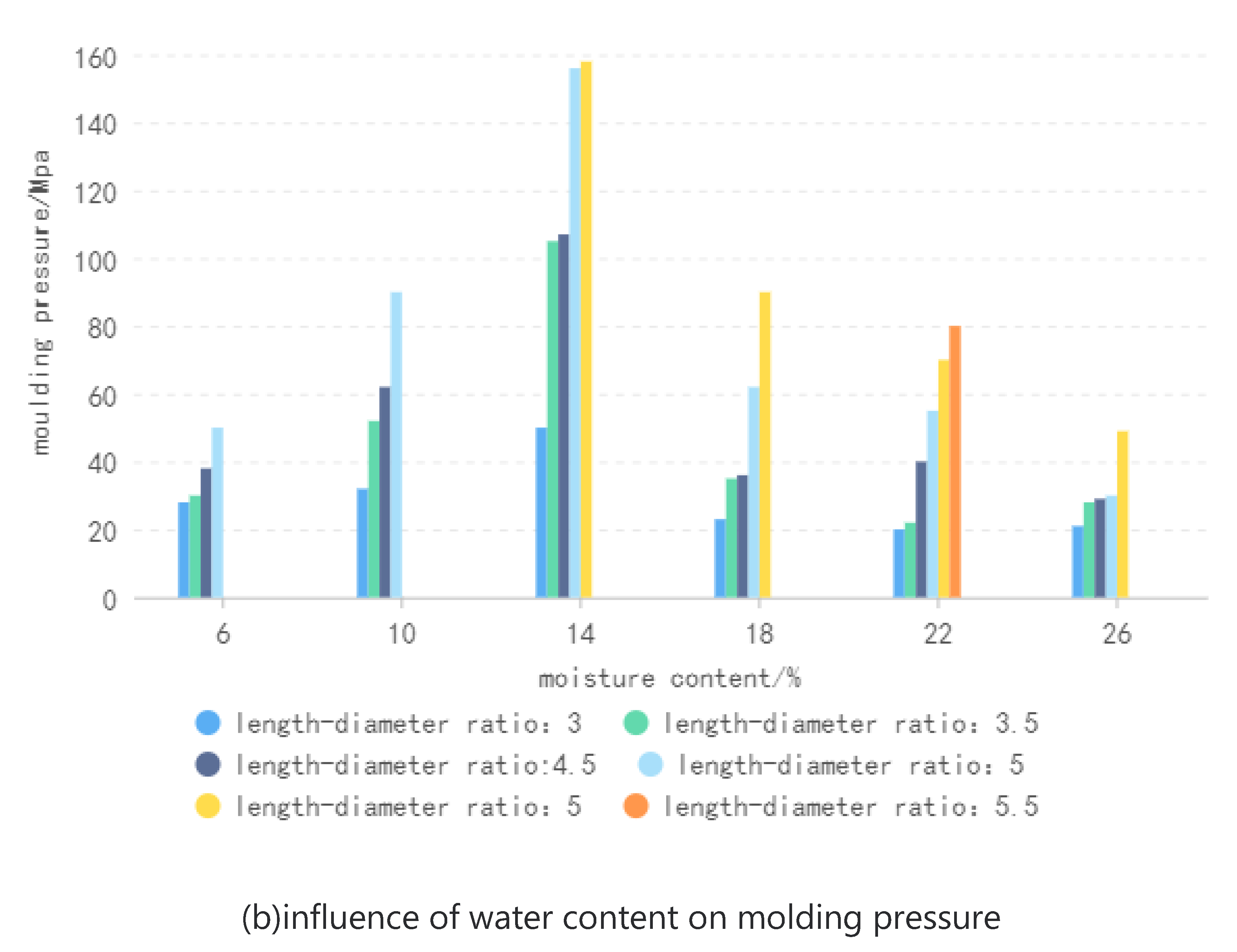
In the molding process, the materials will go through the compression stage, compaction stage and molding stage, and the pressure of the materials at each stage is different. Through the measurement of axial pressure by the pressure transmitter, the pressure change curve of the plunger compression materials can be obtained.When the plunger moves to the end of the stroke, the thrust is greater than the maximum pressure of the hydraulic system, resulting in the overflow of the relief valve, making the maximum pressure value of the curve tend to 160 MPa.Figure. 4 (a) shows the law of influence of length-diameter ratio of molding sleeve on molding pressure under different moisture content. It can be seen that with the increase of length-diameter ratio, the pressure required for molding raw materials shows an upward trend. As the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve increases, the material in the sleeve increases, the friction between the material and the inner wall of the sleeve increases, and the molding pressure required to overcome the friction increases. The molding pressure is too large, and the molding energy consumption increases correspondingly, which is not conducive to actual production.
Figure 4 (b) shows the law of influence of water content on molding pressure under different molding sleeve length-diameter ratio. It can be seen that with the increase of water content, the molding pressure presents a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the moisture content is low (less than 14%), the molding pressure increases with the increase of the moisture content. At this time, the moisture acts as an essential free radical in the biomass, which plays a bonding role, and the combination between the particles of raw materials becomes closer, which increases the friction between the materials and increases the peak pressure. When the moisture content is high (greater than 14%), the molding pressure decreases with the increase of the moisture content. At this time, too much water forms a water film around the raw material, preventing the proximity of the raw material particles and the combination of particles. At the same time, the friction between the material and the inner wall of the molding sleeve will be reduced, making the molding pressure smaller.
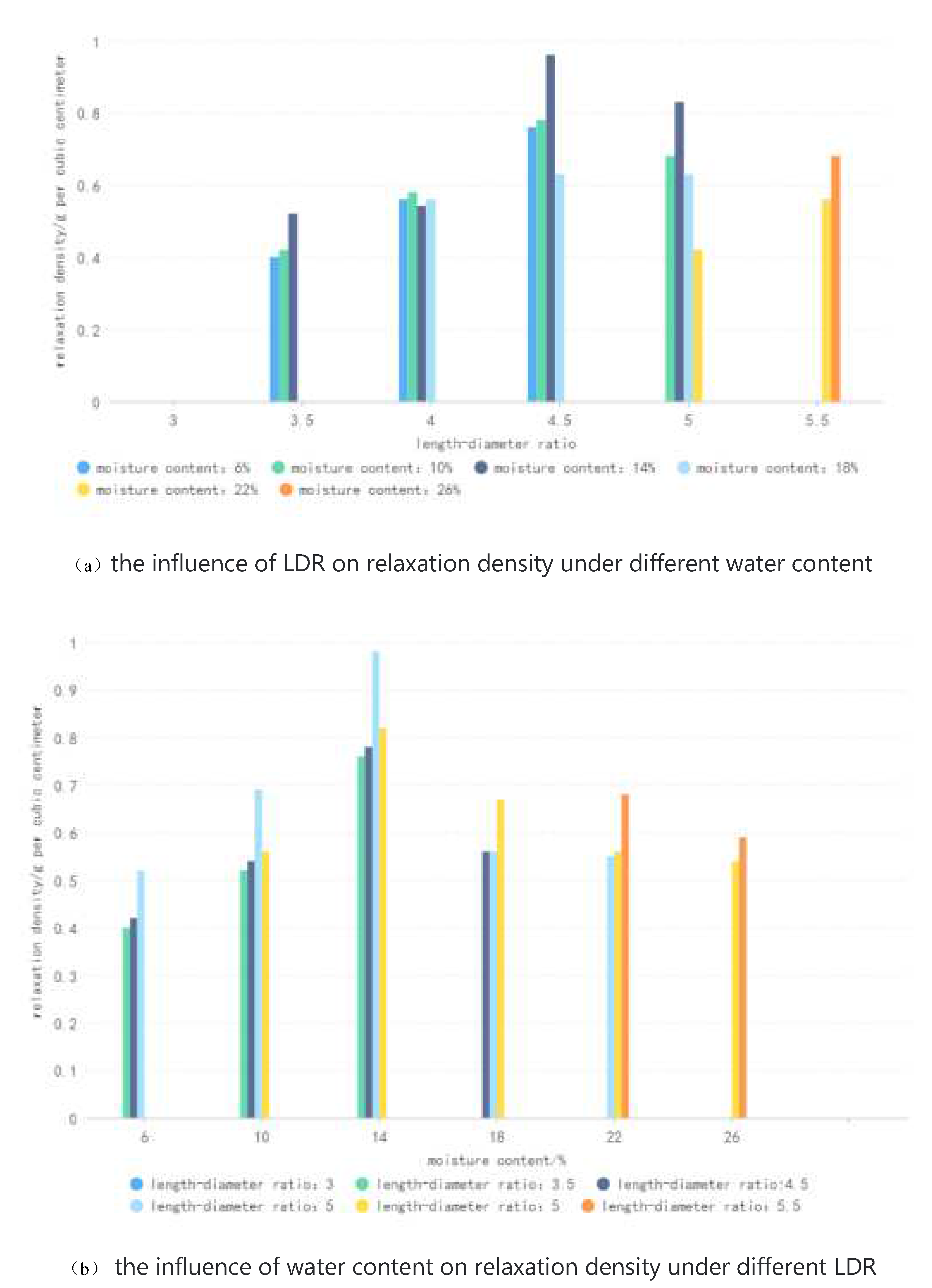
4.2. Effect of test parameters on relaxation density
Relaxation density is an important index to measure the physical quality characteristics of formed blocks. Figure. 5 (a) shows the influence rule of LDR on relaxation density under different water content. It can be seen that with the increase of LDR of molding sleeve, relaxation density shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the length diameter of the forming sleeve is small, the friction between the material and the inner wall of the sleeve and the material is small, the binding ability of adjacent materials is small, and the forming block is loose; When the length-diameter ratio of the forming sleeve increases, the forming pressure increases, the bonding ability between materials increases, and the density increases. However, when the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve is too large, in the extrusion process, a large amount of air is added to the materials, and the water between the materials is vaporized into water vapor due to friction heat. During compression, the air and water vapor accumulate in the molding sleeve and cannot be discharged in time, forming air pockets in the molding fuel. At the moment when the molding block is out of the mold, the high pressure gas is suddenly released, resulting in the cracking of the molding block and even the phenomenon of "shooting", which greatly reduces the density of the molding block and has safety risks.
Figure 5 (b) shows the law of influence of water content on relaxation density under different length-diameter ratio of molding sleeve. It can be seen that under the same length-diameter ratio, with the increase of water content, the relaxation density presents a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The moisture content is too low, the small amount of water in the material is not enough to play the role of binder, and the contact area between the particles is small, and the material is not easy to combine; The moisture content is too high, the moisture content of the corresponding molding block is high, the molding block is easy to expand after the mold, and will become loose due to water evaporation under the natural environment.
4.3. Effect of test parameters on relaxation density
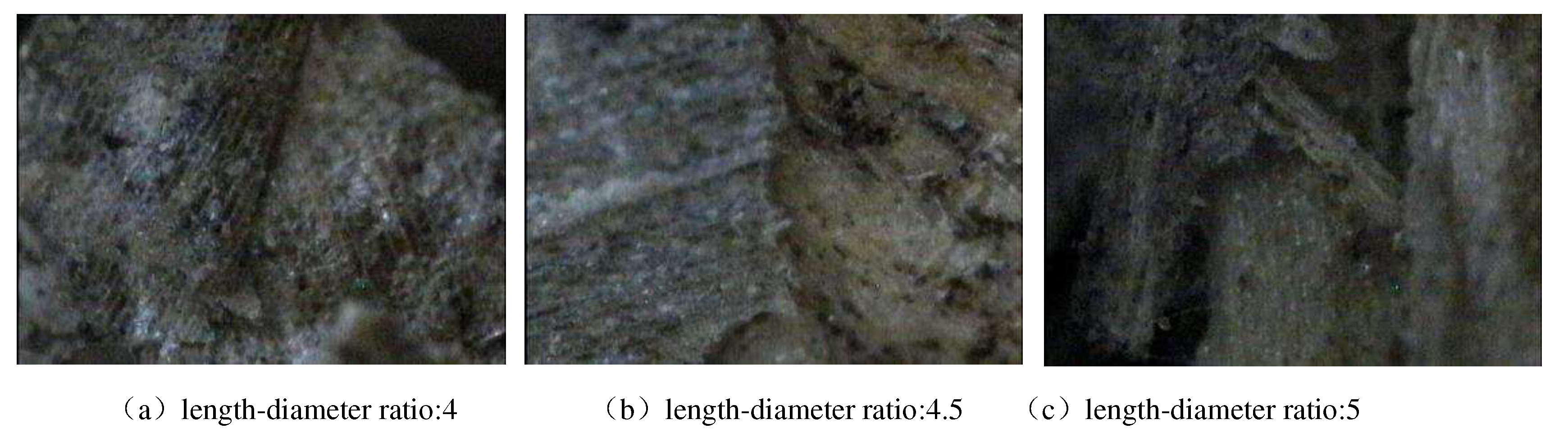
Figure. 6 shows the microstructure of the end face of the forming block under different aspect ratio of the forming sleeve when the water content is 16%. It can be seen that the hickory ceftail still maintains its original flake shape under the stereomicroscope because it has not been crushed twice. When the length to diameter ratio of the forming sleeve is 4, the boundary of the material is relatively clear, the flake fruit is stacked with each other, the bonding phenomenon is not obvious, and there are small gaps, indicating that the forming pressure is small, the extrusion effect is not enough, and the material is not completely compacted. When the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve is 4.5, the materials are compacted and chimeric, the combination is the closest, and the stacking phenomenon is not obvious. When the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve is 5, the boundary between the materials is clear and the gap is large, which is because the molding pressure is too large, the molding block expands after the mold, and the residual internal stress causes the material to rebound. It can be seen that the ratio of length to diameter of forming sleeve affects the bonding strength between materials on the micro level, thus affecting the macro forming effect.
Figure 6.
Microstructure of briquettes at different length-diameter ratio.
Figure 6.
Microstructure of briquettes at different length-diameter ratio.
4.4. Microstructure of molded block under different moisture content
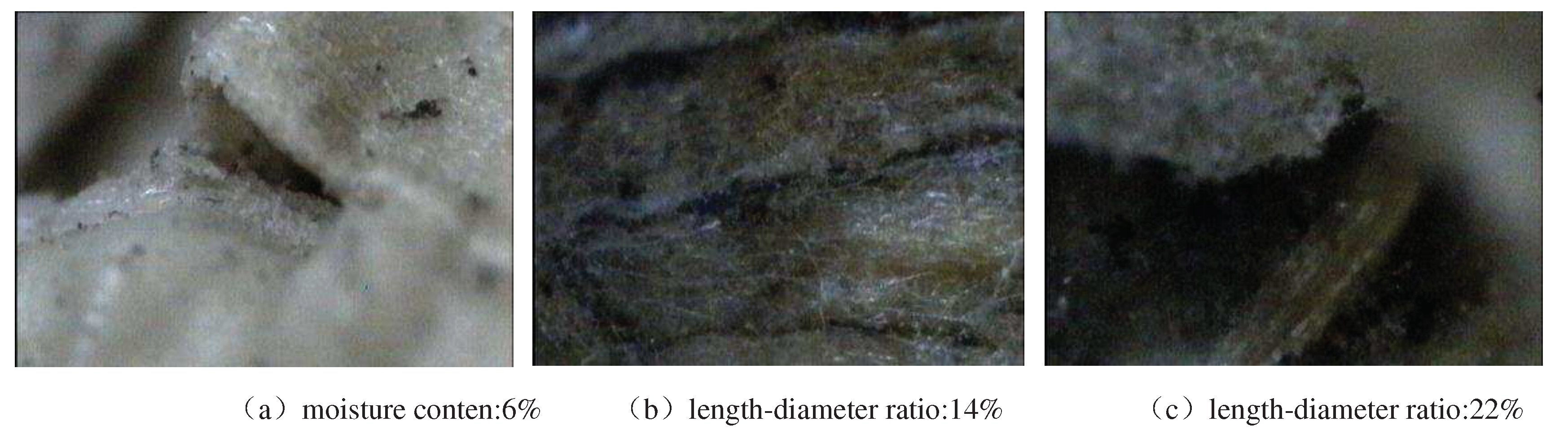
Figure 7 shows the microstructure of the end face of the forming block under different water content when the length-diameter ratio of the forming sleeve is 4.5. When the moisture content of hickory husks is 6%, there is warping phenomenon, there is a large gap between the materials, and the stacking phenomenon is obvious. Because a small amount of water vapor in the raw material is not conducive to the rapid conduction and uniform distribution of heat, it is not easy to reduce the softening point of lignin, and the bonding effect is not large at low temperature, and the particles are not sufficiently extended and cannot be closely combined. When the moisture content is 14%, the materials are extruded from each other, the lamination phenomenon is not obvious, and the bonding effect is the best. At this time, due to the increase of water, the material becomes soft, flat, and good ductility, and a small amount of water adsorbed on the surface can reduce the roughness, increase the contact area between the materials or reduce the spacing, thereby increasing the gravity. When the moisture content is 22%, the distance between the materials is large, and the combination does not occur. Too much water will increase the distance between the material particles, reduce the attraction between the particles, and lead to an increase in water vapor, occupying more space.
5. Conclusions
The test shows that hickory husks can be compressed into a better quality molding block at room temperature. It can be considered to reduce the secondary crushing process or reduce the degree of crushing before the compression molding of biomass raw materials, so as to reduce the production energy consumption and cost, which has practical guiding significance for the determination of the production conditions of biomass fuel and the design of biomass molding equipment.When the water content is 14% and the length-diameter ratio of the molding sleeve is 4.5, the maximum relaxation density of forming block is 0.76g /cm3, the molding effect is the best, and the relaxation density of the molding block is 0.98g /cm3. By observing the microscopic structure of the end face of the forming block with a stereomicroscope, it is found that when the moisture content is 15% and the length-diameter ratio of the forming sleeve is 4.5, the bonding state between the materials is the best, which is consistent with the macroscopic forming effect.The hydraulic piston forming machine used in the test is suitable for compression molding of hickory husks.
Author Contributions
X.X.:Corresponding author, Conceptualization, Writing,Data Processing, Editing;G.Y.:Corresponding author, Review, Methodology; W.Z.: Funding acquisition; J.W.: Investigation, Review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Commonweal Project of Science and Technology Agency of Zhejiang Province of China, Grant No. LGN21C160006.
Institutional Review Board Statement
No ethical approval is required for this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Julia Garland (The Univeristy of Auckland,New Zealand)for English language editing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflflict of interest.
References
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G.; Vassilev, V.S. Advantages and disadvantages of composition and properties of biomass in comparison with coal: an overview. Fuel 2015, 158, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.S. Interfuel substitution and biomass use in the U.S. industrial sector: a differential approach. Energy 2016, 102, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Nakomcic-Smaragdakis, B.; Cepic, Z.; Dragutinovic, N. Analysis of solid biomass energy potential in Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 57, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Xiao, H.; Cai, W.; et al. Multi-scale sustainability assessments for biomassbased and coal-based fuels in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, M.; Asghar, A.; Ramzan, N.; et al. Biomass densifification: effect of cow dung on the physicochemical properties of wheat straw and rice husk based biomass pellets. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B. Assessment of Raw Material Supply Capability and Energy Potential of Biomass Resources in China. , 2018, (Ph.D. thesis). China Agricultural University, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
- He, Z.; Lou, C.; Fu, J.; et al. Experimental investigation on temporal release of potassium from biomass pellet combustion by flflame emission spectroscopy. Fuel 2019, 253, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suopajärvi, H.; Pongrácz, E.; Fabritius, T. The potential of using biomass-based reducing agents in the blast furnace: a review of thermochemical conversion technologies and assessments related to sustainability. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2013, 25, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, C.W.; Sun, Y.M.; Lv, X.F.; Chen, Y. Research status and future development strategy of biomass energy. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 434–442, (Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Tai, L.Y.; et al. Biomass molded fuel in China: Current status, policies and suggestions, Science of the Total Environment 2020, 724. [CrossRef]
- Lu, B. Research on Biomass Briquetting Device and Optimum Technologic Parameters of Densifification. (Master thesis). Harbin Institute of Technology 2016, Haerbin, China (in Chinese).
- Xiang, Y. Design and Experiment of Biochar Extrusion Molding Machine. (Master thesis). Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China (in Chinese), 2017.
- Zhao, R.X. Study on Optimization of Biomass Fuel Pressure Formation Process Parameter. (Master thesis). North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China (in Chinese), 2017.
- Guan, Y.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; et al. Air pollutant emissions from straw open burning: a case study in Tianjin. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, C.W.; Sun, Y.M.; Lv, X.F.; Chen, Y. Research status and future development strategy of biomass energy. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 34, 434–442, (Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Man, Y.; Xiao, H.; Cai, W.; et al. Multi-scale sustainability assessments for biomass based and coal-based fuels in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Zhou, F.; Xiong, L.N.; Mao, S.Q.; Hu, Y.Z.; Lu, B.Y. Comparison of phenolic compounds, tocopherols, phytosterols and antioxidant potential in Zhejiang pecan [Carya cathayensis] at different stir-frying steps. LWT-Food Science and Technology 2015, 62, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Ding, Z.S. Flavonoids from Carya cathayensis Sarg. leaves inhibit carotidartery lesion formation induced by low blood flow. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 94, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, R.Y.; Shen, X.Y.; Cai, C.G.; Mao, J.W. Study on optimization of juglone extraction conditions from hickory hull. Food Research and Development 2016, 37, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Belwal, T.; Ezzat, S.M.; Rastrelli, L.; Bhatt, I.D.; Daglia, M.; Baldi, A.; Atanasov, A.G. A critical analysis of extraction techniques used for botanicals: Trends, priorities, industrial uses and optimization strategies. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2018, 100, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; et al. Application of lignin in preparation of slow-release fertilizer: Current status and future perspectives. Industrial Crops and Products 2022, 176, 114267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; et al. Synergistic effect of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia on lignin. Industrial Crops and Products 2020, 146, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S.; Rosen, M.A. Biomass briquettes as an alternative fuel: a comprehensive review. Energy Technol 2019, 7, 1801011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y. Review of briquette binders and briquetting mechanism. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2018, 82, 477e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrodoy, S.V.; Kuznetsov, G.V.; Gutareva, N.Y.; ZhAKostoreva Kostoreva, A.A.; Nigay, N.A. Characteristics and conditions for ignition of bio-coal mixtures based on coal and forest combustible material. J Energy Inst 2020, 93, 1978e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).