Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
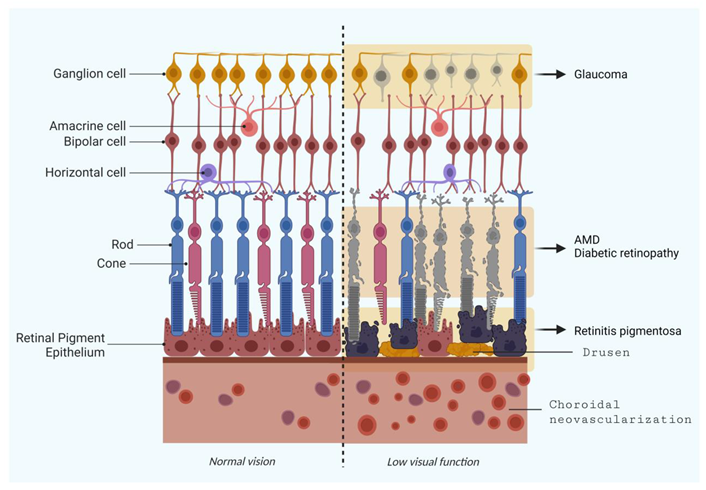
2. Selected Retinal Degeneration Diseases
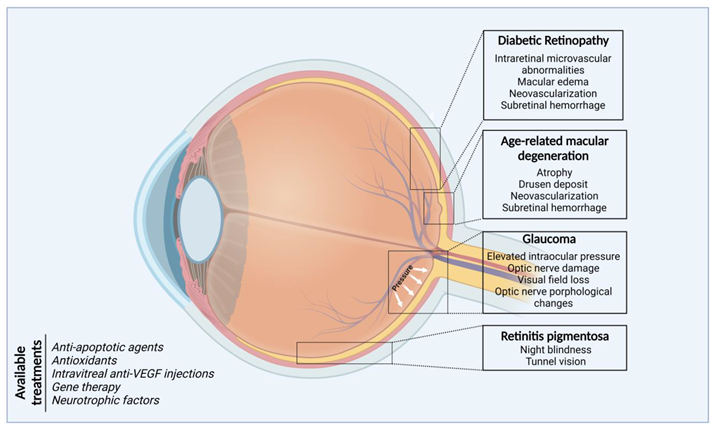
2.1. Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
2.2. Retinal Ganglion Cell Degeneration (Glaucoma)
2.2.1. Glaucoma hallmarks and genetic basis
2.2.2. Therapeutic approaches in glaucoma research
2.3. Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
Genetic background
2.4. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
Molecular and genetic factors of diabetic retinopathy
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartong, D.T.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Retinitis Pigmentosa. Lancet (London, England) 2006, 368, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Imanishi, Y. Drug Discovery Strategies for Inherited Retinal Degenerations. Biology (Basel). 2022, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masek, M.; Zang, J.; Mateos, J.M.; Garbelli, M.; Ziegler, U.; Neuhauss, S.C.F.; Bachmann-Gagescu, R. Studying the Morphology, Composition and Function of the Photoreceptor Primary Cilium in Zebrafish. In; 2023; pp. 97–128.
- Wilson, A.M.; Di Polo, A. Gene Therapy for Retinal Ganglion Cell Neuroprotection in Glaucoma. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angueyra, J.M.; Kindt, K.S. Leveraging Zebrafish to Study Retinal Degenerations. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, L.L.; Hanovice, N.J.; George, S.M.; Gabriel, A.E.; Gross, J.M. The Immune Response Is a Critical Regulator of Zebrafish Retinal Pigment Epithelium Regeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global Prevalence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Disease Burden Projection for 2020 and 2040: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet. Glob. Heal. 2014, 2, e106-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M. Macular Degeneration Epidemiology: Nature-Nurture, Lifestyle Factors, Genetic Risk, and Gene-Environment Interactions – The Weisenfeld Award Lecture. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, M.; Keenan, T.D.L.; Guymer, R.H.; Chakravarthy, U.; Schmitz-Valckenberg, S.; Klaver, C.C.; Wong, W.T.; Chew, E.Y. Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Knudtson, M.D.; Meuer, S.M.; Swift, M.; Gangnon, R.E. Fifteen-Year Cumulative Incidence of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, F.L.; Wilkinson, C.P.; Bird, A.; Chakravarthy, U.; Chew, E.; Csaky, K.; Sadda, S.R. Clinical Classification of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Age-Related Eye Disease Study System for Classifying Age-Related Macular Degeneration from Stereoscopic Color Fundus Photographs: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study Report Number 6. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 132, 668–681. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleckenstein, M.; Mitchell, P.; Freund, K.B.; Sadda, S.; Holz, F.G.; Brittain, C.; Henry, E.C.; Ferrara, D. The Progression of Geographic Atrophy Secondary to Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaide, R.F.; Jaffe, G.J.; Sarraf, D.; Freund, K.B.; Sadda, S.R.; Staurenghi, G.; Waheed, N.K.; Chakravarthy, U.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Holz, F.G.; et al. Consensus Nomenclature for Reporting Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Data. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 616–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yu, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, X.; Xin, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L. Role of Flavonoids in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 159, 114259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, K.R.; Aloney, A.; Skondra, D.; Chhablani, J. Effects of Systemic Drugs on the Development and Progression of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2023, 68, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanchi, F.; Bourne, R.; Downes, S.M.; Gale, R.; Rennie, C.; Tapply, I.; Sivaprasad, S. An Update on Long-Acting Therapies in Chronic Sight-Threatening Eye Diseases of the Posterior Segment: AMD, DMO, RVO, Uveitis and Glaucoma. Eye 2022, 36, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyttinen, J.M.T.; Blasiak, J.; Kaarniranta, K. Non-Coding RNAs Regulating Mitochondrial Functions and the Oxidative Stress Response as Putative Targets against Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbioso, M.; Franzone, F.; Lambiase, A.; Bonfiglio, V.; Limoli, P.G.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Vingolo, E.M.; Greco, A.; Polimeni, A. Oxidative Stress Implication in Retinal Diseases—A Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, V.; Smith, R.L.; Sivaprasad, S. Retinal Biochemistry, Physiology, and Cell Biology. In Retinal Pharmacotherapy; Elsevier, 2010; pp. 15–22.
- Miller, J.W. Age-Related Macular Degeneration Revisited--Piecing the Puzzle: The LXIX Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 1–35.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, N.; Rui, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xiong, S.; Xia, X. New Insight of Metabolomics in Ocular Diseases in the Context of 3P Medicine. EPMA J. 2023, 14, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Siggs, O.M.; Knight, L.S.W.; Staffieri, S.E.; Ruddle, J.B.; Birsner, A.E.; Collantes, E.R.; Craig, J.E.; Wiggs, J.L.; D’Amato, R.J. Thrombospondin 1 Missense Alleles Induce Extracellular Matrix Protein Aggregation and TM Dysfunction in Congenital Glaucoma. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munemasa, Y.; Kitaoka, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Retinal Ganglion Cell Degeneration in Glaucoma and Future Prospects for Cell Body and Axonal Protection. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, Y.-C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.-Y. Global Prevalence of Glaucoma and Projections of Glaucoma Burden through 2040: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Fukuchi, T. What Is Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy? Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 64, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Xu, M.-X.; Zhou, H.; Cheng, S.; Li, F.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Aggravates Gliosis and Inflammation of Activated Retinal Müller Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.J.; Huh, J.; Jeong, E.; Park, C.K.; Park, H.Y.L. Angiotensin II Related Glial Cell Activation and Necroptosis of Retinal Ganglion Cells after Systemic Hypotension in Glaucoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassim, A.H.; Fan, Y.; Pappenhagen, N.; Nsiah, N.Y.; Inman, D.M. Oxidative Stress and Hypoxia Modify Mitochondrial Homeostasis During Glaucoma. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezel, G.; Yang, X.; Luo, C.; Peng, Y.; Sun, S.L.; Sun, D. Mechanisms of Immune System Activation in Glaucoma: Oxidative Stress-Stimulated Antigen Presentation by the Retina and Optic Nerve Head Glia. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, M.A.; Heuer, D.K.; Higginbotham, E.J.; Johnson, C.A.; Keltner, J.L.; Miller, J.P.; Parrish, R.K.; Wilson, M.R.; Gordon, M.O. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: A Randomized Trial Determines That Topical Ocular Hypotensive Medication Delays or Prevents the Onset of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. (Chicago, Ill. 1960) 2002, 120, 701–713, discussion 829-830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.U.; Ha, A.; Kim, D.W.; Jeoung, J.W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, Y.K. Risk Factors for Disease Progression in Low-Teens Normal-Tension Glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharahkhani, P.; Jorgenson, E.; Hysi, P.; Khawaja, A.P.; Pendergrass, S.; Han, X.; Ong, J.S.; Hewitt, A.W.; Segrè, A. V.; Rouhana, J.M.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies 127 Open-Angle Glaucoma Loci with Consistent Effect across Ancestries. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichter, P.R.; Musch, D.C.; Gillespie, B.W.; Guire, K.E.; Janz, N.K.; Wren, P.A.; Mills, R.P. CIGTS Study Group Interim Clinical Outcomes in the Collaborative Initial Glaucoma Treatment Study Comparing Initial Treatment Randomized to Medications or Surgery. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, B.R.; Liu, P.; Onay, T.; Du, J.; Tompson, S.W.; Misener, S.; Purohit, R.R.; Young, T.L.; Jin, J.; Quaggin, S.E. Cellular Crosstalk Regulates the Aqueous Humor Outflow Pathway and Provides New Targets for Glaucoma Therapies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoskuviene, A.; Siaudvytyte, L.; Januleviciene, I.; Vaitkus, A.; Simiene, E.; Bakstyte, V.; Ragauskas, A.; Antman, G.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. The Relationship between Intracranial Pressure and Visual Field Zones in Normal-Tension Glaucoma Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMonnies, C.W. Glaucoma History and Risk Factors. J. Optom. 2017, 10, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, P.A.; Girkin, C.A.; Zangwill, L.M.; Jain, S.; Racette, L.; Becerra, L.M.; Weinreb, R.N.; Medeiros, F.A.; Wilson, M.R.; De León-Ortega, J.; et al. The African Descent and Glaucoma Evaluation Study (ADAGES): Design and Baseline Data. Arch. Ophthalmol. (Chicago, Ill. 1960) 2009, 127, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Wang, M.; Frueh, L.; Rosner, B.; Wiggs, J.L.; Elze, T.; Pasquale, L.R. Cohort Study of Race/Ethnicity and Incident Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Characterized by Autonomously Determined Visual Field Loss Patterns. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Grover, A. Myocilin-Associated Glaucoma: A Historical Perspective and Recent Research Progress. Mol. Vis. 2021, 27, 480–493. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Park, C.K.; Chae, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, W.; Chi, H.Y.; Park, H.-Y.L.; Park, S.H. Molecular Analysis of Myocilin and Optineurin Genes in Korean Primary Glaucoma Patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N. Myocilin Gene Mutation Induced Autophagy Activation Causes Dysfunction of Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Front. cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 900777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.F.; Fan, B.J.; Lam, D.S.C.; Lee, W.S.; Tam, P.O.S.; Chua, J.K.H.; Tham, C.C.Y.; Lai, J.S.M.; Fan, D.S.P.; Pang, C.P. Different Optineurin Mutation Pattern in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3880–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.N.; Lu, S.; Chen, L.J.; Tam, P.O.S.; Zhang, B.N.; Leung, C.K.S.; Pang, C.P.; Tham, C.C.Y.; Chu, W.K. Coding Region Mutation Screening in Optineurin in Chinese Normal-Tension Glaucoma Patients. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 5820537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Vishal, M.; Banerjee, D.; Sen, A.; Ray, K. WDR36 Variants in East Indian Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 2618–2627. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Z.-L.; Yasumoto, F.; Sergeev, Y.; Minami, M.; Obazawa, M.; Kimura, I.; Takada, Y.; Iwata, T. Mutant WDR36 Directly Affects Axon Growth of Retinal Ganglion Cells Leading to Progressive Retinal Degeneration in Mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3806–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarie, J.M.; Link, B.A. The Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Gene WDR36 Functions in Ribosomal RNA Processing and Interacts with the P53 Stress-Response Pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 2474–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaif, H.S.; Khan, A.O.; Patel, N.; Alkuraya, H.; Hashem, M.; Abdulwahab, F.; Ibrahim, N.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; Alkuraya, F.S. Congenital Glaucoma and CYP1B1: An Old Story Revisited. Hum. Genet. 2019, 138, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, S.; Luthra-Guptasarma, M.; Prasher, D.; Dhingra, D.; Singh, N.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.P.; Kaur, H.; Snehi, S.; Thattaruthody, F.; et al. CYP1B1 and MYOC Variants in Neonatal-Onset versus Infantile-Onset Primary Congenital Glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.; Yousaf, S.; Sheikh, S.A.; Sajid, Z.; Shabbir, A.S.; Kausar, T.; Tariq, N.; Usman, M.; Shaikh, R.S.; Ali, M.; et al. Identities and Frequencies of Variants in CYP1B1 Causing Primary Congenital Glaucoma in Pakistan. Mol. Vis. 2019, 25, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pasquale, L.R.; Loomis, S.J.; Kang, J.H.; Yaspan, B.L.; Abdrabou, W.; Budenz, D.L.; Chen, T.C.; Delbono, E.; Friedman, D.S.; Gaasterland, D.; et al. CDKN2B-AS1 Genotype-Glaucoma Feature Correlations in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Patients from the United States. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 155, 342–353.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, N.; Kupani, M.; Mannan, R.; Pruthi, A.; Mehrotra, S. Genetic Association between CDKN2B/CDKN2B-AS1 Gene Polymorphisms with Primary Glaucoma in a North Indian Cohort: An Original Study and an Updated Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. Genomics 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Gonsalvez, G.B.; Mysona, B.A.; Smith, S.B.; Bollinger, K.E. Sigma 1 Receptor Contributes to Astrocyte-Mediated Retinal Ganglion Cell Protection. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gidday, J.M. Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α in Preconditioning-Induced Protection of Retinal Ganglion Cells in Glaucoma. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margeta, M.A.; Yin, Z.; Madore, C.; Pitts, K.M.; Letcher, S.M.; Tang, J.; Jiang, S.; Gauthier, C.D.; Silveira, S.R.; Schroeder, C.M.; et al. Apolipoprotein E4 Impairs the Response of Neurodegenerative Retinal Microglia and Prevents Neuronal Loss in Glaucoma. Immunity 2022, 55, 1627–1644.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munemasa, Y.; Ahn, J.H.; Kwong, J.M.K.; Caprioli, J.; Piri, N. Redox Proteins Thioredoxin 1 and Thioredoxin 2 Support Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival in Experimental Glaucoma. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.C.; Campanelli, J.; Sande, P.; Sánez, D.A.; Keller Sarmiento, M.I.; Rosenstein, R.E. Retinal Oxidative Stress Induced by High Intraocular Pressure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.M.; Park, H.Y.; Park, C.K. Retinal Ganglion Cell Death Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Chronic Glaucoma Model. Brain Res. 2010, 1308, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, X.; Sun, N.; Fan, Z. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Is Involved in Retinal Injury Induced by Repeated Transient Spikes of Intraocular Pressure. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 22, 746–756. [CrossRef]
- Rozpędek-Kamińska, W.; Wojtczak, R.; Szaflik, J.P.; Szaflik, J.; Majsterek, I. The Genetic and Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mediated Molecular Mechanisms of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garhöfer, G.; Schmetterer, L. Nitric Oxide: A Drug Target for Glaucoma Revisited. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Song, M.; Li, L.; Niu, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, B.; Sun, X.; Yang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Chen, X. Endogenous Dual Stimuli-Activated NO Generation in the Conventional Outflow Pathway for Precision Glaucoma Therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 277, 121074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhani, H.; Domb, A.J.; Sharifzadeh, G.; Nahum, V. Gene Therapy for Regenerative Medicine. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, L.-P.; Liang, J.-J.; Chen, J.-H.; Harvey, A.R.; Ng, T.K.; Zhang, M.; Pang, C.P.; Cui, Q.; Fan, Y.-M. AAV-Mediated Transfer of RhoA ShRNA and CNTF Promotes Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration. Neuroscience 2017, 343, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Rong, R.; Ji, D.; Xia, X. From Bench to Bed: The Current Genome Editing Therapies for Glaucoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, C.; Shah, R.; Ghiam, S.; Kramerov, A.A.; Ljubimov, A. V Gene Therapy in the Anterior Eye Segment. Curr. Gene Ther. 2022, 22, 104–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Starr, C.; Mohns, E.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, E.P.; Yoon, Y.; Kellner, C.P.; Tanaka, K.; Wang, H.; et al. Preservation of Vision after CaMKII-Mediated Protection of Retinal Ganglion Cells. Cell 2021, 184, 4299–4314.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipnis, J.; Schwartz, M. Dual Action of Glatiramer Acetate (Cop-1) in the Treatment of CNS Autoimmune and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, R.J. Medical Therapy for Glaucoma: A Review. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 2022, 50, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, C.; Yan, N. Neuroinflammation in Retinitis Pigmentosa: Therapies Targeting the Innate Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Kulbay, M.; Toameh, D.; Xu, A.Q.; Kalevar, A.; Tran, S.D. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Novel Therapeutic Targets and Drug Development. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Peng, J.; Ying, D.; Peng, Q.H. A Brief Review on the Pathological Role of Decreased Blood Flow Affected in Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 3249064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neal, T.B.; Luther, E.E. Retinitis Pigmentosa. StatPearls 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Parain, K.; Lourdel, S.; Donval, A.; Chesneau, A.; Borday, C.; Bronchain, O.; Locker, M.; Perron, M. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Models of Retinitis Pigmentosa Reveal Differential Proliferative Response of Müller Cells between Xenopus Laevis and Xenopus Tropicalis. Cells 2022, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsevich, C.; Gopalakrishnan, P.; Obolensky, A.; Banin, E.; Sharon, D.; Beryozkin, A. Retinal Structure and Function in a Knock-in Mouse Model for the FAM161A-p.Arg523∗ Human Nonsense Pathogenic Variant. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2023, 3, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beryozkin, A.; Matsevich, C.; Obolensky, A.; Kostic, C.; Arsenijevic, Y.; Wolfrum, U.; Banin, E.; Sharon, D. A New Mouse Model for Retinal Degeneration Due to Fam161a Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Venkatraman, P.; Chong, L.; Cho, J.; Bonilla, S.; Jin, Z.-B.; Pang, C.P.; Ko, K.M.; et al. A Naturally-Derived Compound Schisandrin B Enhanced Light Sensation in the Pde6c Zebrafish Model of Retinal Degeneration. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0149663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Du, J.; Chen, N.; Jia, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, L. In Vivo CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing Mitigates Photoreceptor Degeneration in a Mouse Model of X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumerson, J.D.; Alsufyani, A.; Yu, W.; Lei, J.; Sun, X.; Dong, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, T. Restoration of RPGR Expression in Vivo Using CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing. Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Song, J.; Prieskorn, D.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Dolan, D.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jayasundera, K.T.; Yang, J.; et al. USH2A Gene Mutations in Rabbits Lead to Progressive Retinal Degeneration and Hearing Loss. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaw, K.; Carvalho, L.S.; Aung-Htut, M.T.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Chen, F.K.; McLenachan, S. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Usher Syndrome Type IIA. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. (Philadelphia, Pa.) 11, 369–379. [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.; Wenck, N.; Janik, K.; Linnert, J.; Stingl, K.; Kohl, S.; Nagel-Wolfrum, K.; Wolfrum, U. The Usher Syndrome 1C Protein Harmonin Regulates Canonical Wnt Signaling. Front. cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1130058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bulgakov, O. V.; Darrow, K.N.; Pawlyk, B.; Adamian, M.; Liberman, M.C.; Li, T. Usherin Is Required for Maintenance of Retinal Photoreceptors and Normal Development of Cochlear Hair Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 4413–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.A.; Gyürüs, P.; Fleischer, L.L.; Bingham, E.L.; McHenry, C.L.; Apfelstedt-Sylla, E.; Zrenner, E.; Lorenz, B.; Richards, J.E.; Jacobson, S.G.; et al. Genetics and Phenotypes of RPE65 Mutations in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander, A.I.; Roepman, R.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Cremers, F.P.M. Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Genes, Proteins and Disease Mechanisms. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducloyer, J.-B.; Le Meur, G.; Cronin, T.; Adjali, O.; Weber, M. La Thérapie Génique Des Rétinites Pigmentaires Héréditaires. médecine/sciences 2020, 36, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Yao, K. Retinitis Pigmentosa: Progress in Molecular Pathology and Biotherapeutical Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamdi, A.H. Al Clinical Predictors of Diabetic Retinopathy Progression; A Systematic Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Tang, J. Intestinal Flora-Derived Kynurenic Acid Protects Against Intestinal Damage Caused by Candida Albicans Infection via Activation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safi, S.Z.; Qvist, R.; Kumar, S.; Batumalaie, K.; Ismail, I.S. Bin Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Retinopathy, General Preventive Strategies, and Novel Therapeutic Targets. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, F.S.; Allkabes, M.; Salsini, G.; Bonifazzi, C.; Perri, P. The Importance of Glial Cells in the Homeostasis of the Retinal Microenvironment and Their Pivotal Role in the Course of Diabetic Retinopathy. Life Sci. 2016, 162, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Ed. 2021.
- International Diabetes Federation and The Fred Hollows Foundation Diabetes Eye Health: A Guide for Health Care Professionals. 2015.
- Mustafi, D.; Saraf, S.S.; Shang, Q.; Olmos de Koo, L.C. New Developments in Angiography for the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 167, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kim, D. Retinal Capillary Basement Membrane Thickening: Role in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 82, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaq, R.S.; Aldalati, A.M.Z.; Alexander, J.S.; Harris, N.R. Diabetic Retinopathy: Breaking the Barrier. Pathophysiology 2017, 24, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, N.; Mitchell, P.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy. Lancet 2010, 376, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, J.W.Y.; Rogers, S.L.; Kawasaki, R.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Kowalski, J.W.; Bek, T.; Chen, S.-J.; Dekker, J.M.; Fletcher, A.; Grauslund, J.; et al. Global Prevalence and Major Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropasqua, R.; Toto, L.; Cipollone, F.; Santovito, D.; Carpineto, P.; Mastropasqua, L. Role of MicroRNAs in the Modulation of Diabetic Retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 43, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.K.; Aiello, L.P.; Abràmoff, M.D.; Antonetti, D.A.; Dutta, S.; Pragnell, M.; Levine, S.R.; Gardner, T.W. Updating the Staging System for Diabetic Retinal Disease. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Council of Ophthalmology. ICO Guidelines for Diabetic Eye Care; 2017.
- Graham, P.S.; Kaidonis, G.; Abhary, S.; Gillies, M.C.; Daniell, M.; Essex, R.W.; Chang, J.H.; Lake, S.R.; Pal, B.; Jenkins, A.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies for Diabetic Macular Edema and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutty, G.A. Effects of Diabetes on the Eye. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, ORSF81-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Yang, C. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy: Molecular Mechanisms, Pathogenetic Role and Therapeutic Implications. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Nagai, R.; Ishibashi, T.; Inomata, H.; Ikeda, K.; Horiuchi, S. The Relationship between Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End Products and Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Human Diabetic Retinas. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, A.; Yee, P.; Vessey, K.A.; Phipps, J.A.; Jobling, A.I.; Fletcher, E.L. Early Inner Retinal Astrocyte Dysfunction during Diabetes and Development of Hypoxia, Retinal Stress, and Neuronal Functional Loss. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, T.M.; Hamilton, R.; Yong, P.-H.; McVicar, C.M.; Berner, A.; Pringle, R.; Uchida, K.; Nagai, R.; Brockbank, S.; Stitt, A.W. Müller Glial Dysfunction during Diabetic Retinopathy in Rats Is Linked to Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Advanced Lipoxidation End-Products. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shosha, E.; Xu, Z.; Narayanan, S.; Lemtalsi, T.; Fouda, A.; Rojas, M.; Xing, J.; Fulton, D.; Caldwell, R.; Caldwell, R. Mechanisms of Diabetes-Induced Endothelial Cell Senescence: Role of Arginase 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Garcia, S.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Dejda, A.; Ryan, R.D.; Fournier, F.; Chaney, S.Y.; Pilon, F.; Dogan, T.; Cagnone, G.; Patel, P.; et al. Pathological Angiogenesis in Retinopathy Engages Cellular Senescence and Is Amenable to Therapeutic Elimination via BCL-XL Inhibition. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 818–832.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, F.; Tang, S.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; et al. Common Variants in or near ZNRF1, COLEC12, SCYL1BP1 and API5 Are Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen–Bouterse, S.A.; Mohammad, G.; Kanwar, M.; Kowluru, R.A. Role of Mitochondrial DNA Damage in the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy, and the Metabolic Memory Phenomenon Associated with Its Progression. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, I.; Kotwani, A. Implication of Oxidative Stress in Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2016, 61, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ghosh, S.; Vaidya, T.; Bammidi, S.; Huang, C.; Shang, P.; Nair, A.P.; Chowdhury, O.; Stepicheva, N.A.; Strizhakova, A.; et al. Activated CGAS/STING Signaling Elicits Endothelial Cell Senescence in Early Diabetic Retinopathy. JCI Insight 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Kowluru, A.; Mishra, M.; Kumar, B. Oxidative Stress and Epigenetic Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 48, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, R.D.G.; Pyke, D.A. Diabetic Retinopathy in Identical Twins. Diabetes 1982, 31, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Azam, A.; Maqsood, S.I.; Muslim, I.; Bashir, S.; Fazal, N.; Riaz, M.; Ali, S.H.B.; Niazi, M.K.; Ishaq, M.; et al. Role of ACE and PAI-1 Polymorphisms in the Development and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0144557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Agarwal, A.; Soliman, M.K.; Sepah, Y.J.; Do, D. V. Diabetic Retinopathy: Variations in Patient Therapeutic Outcomes and Pharmacogenomics. Pharmgenomics. Pers. Med. 2014, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ng, M.C.Y.; Lee, S.-C.; So, W.-Y.; Tong, P.C.Y.; Cockram, C.S.; Critchley, J.A.J.H.; Chan, J.C.N. Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Associations of Two Aldose Reductase Gene Polymorphisms With Nephropathy and Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthalakshmi, B.; Anand, R.; Kim, R.; Mahalakshmi, R.; Karthikprakash, S.; Namperumalsamy, P.; Sundaresan, P. Association of VEGF and ENOS Gene Polymorphisms in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai, A.K.; Glasgow, B.J.; Pardridge, W.M. GLUT1 Glucose Transporter Expression in the Diabetic and Nondiabetic Human Eye. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, G.A.; Tang, J.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Kern, T.S. Diabetes Downregulates GLUT1 Expression in the Retina and Its Microvessels but Not in the Cerebral Cortex or Its Microvessels. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.; Mishra, M.; Ralph, S.; Read, I.; Davies, R.; Brenchley, P. Association of the VEGF Gene With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy But Not Proteinuria in Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaramanickavel, G.; Ramprasad, V.L.; Sripriya, S.; Upadyay, N.K.; Paul, P.G.; Sharma, T. Association of Gly82Ser Polymorphism in the RAGE Gene with Diabetic Retinopathy in Type II Diabetic Asian Indian Patients. J. Diabetes Complications 2002, 16, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Biarnés Costa, M.; Gerhardinger, C. IL-1β Is Upregulated in the Diabetic Retina and Retinal Vessels: Cell-Specific Effect of High Glucose and IL-1β Autostimulation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e36949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Li, H.; Wei, H.; Bi, F.; Liu, S.; Tang, K.; Guo, H.; Liu, W. Resveratrol Exhibits an Effect on Attenuating Retina Inflammatory Condition and Damage of Diabetic Retinopathy via PON1. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 181, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beránek, M.; Kan̆ková, K.; Benes̆, P.; Izakovic̆ová-Hollá, L.; Znojil, V.; Hájek, D.; Vlková, E.; Vácha, J. Polymorphism R25P in the Gene Encoding Transforming Growth Factor-Beta ( TGF-β 1 ) Is a Newly Identified Risk Factor for Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 109, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.G.; Tschiedel, B.; Schneider, J.; Souto, K.; Roisenberg, I. Diabetic Retinopathy in Euro-Brazilian Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Relationship with Polymorphisms in the Aldose Reductase, the Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and the Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Genes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2003, 61, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, M.A.; Tikhomirov, A.; Ramalingam, S.; Below, J.E.; Cox, N.J.; Nicolae, D.L. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis for Severe Diabetic Retinopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.-P.; Hallman, D.M.; Gonzalez, V.H.; Klein, B.E.K.; Klein, R.; Hayes, M.G.; Cox, N.J.; Bell, G.I.; Hanis, C.L. Identification of Diabetic Retinopathy Genes through a Genome-Wide Association Study among Mexican-Americans from Starr County, Texas. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 2010, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awata, T.; Yamashita, H.; Kurihara, S.; Morita-Ohkubo, T.; Miyashita, Y.; Katayama, S.; Mori, K.; Yoneya, S.; Kohda, M.; Okazaki, Y.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study for Diabetic Retinopathy in a Japanese Population: Potential Association with a Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA. PLoS One 2014, 9, e111715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, W.H.-H.; Kuo, J.Z.; Lee, I.-T.; Hung, Y.-J.; Lee, W.-J.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-S.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study in a Chinese Population with Diabetic Retinopathy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3165–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, H.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, F.-J. Genome-Wide Association Study of Diabetic Retinopathy in a Taiwanese Population. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.-L.; Wang, P.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-F.; Wang, J.-H.; Wong, V.H.Y.; Bui, B. V.; Liu, G.-S. Gene Therapy Intervention in Neovascular Eye Disease: A Recent Update. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 2120–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Hu, J.; Lin, S.; Hong, Y. Research Progress on Exosomes/MicroRNAs in the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




