1. Introduction
Chamomile is one of the most important and well-known medicinal plants all over the world which has many uses in the pharmaceutical, hygienic, cosmetic and food industries (1)(2). Botanically, chamomile is an annual plant, belonging to the Asteraceae family, native to Iran and it vegetates as a wild plant in Europe. In Iran, chamomile is expanded in the south, southwest, west and northwest of the country and its application has an ancient history in traditional medicine of Iran(3). The chamomile essential oil is widely utilized in pharmaceutical, cosmetics and food industries (4). Chamomile is a good source of bioactive compounds, and its phytochemical compositions of essential oils and plant parts have valuable pharmaceutical properties(5). The characteristic essential oil content of chamomile is even connected to a definitive level of differentiation within the development of flower heads(6). It is a popular treatment for numerous ailments, including sleep disorders, anxiety, digestion/intestinal conditions, skin infections/ inflammation (including eczema), wound healing, infantile colic, teething pains, and diaper rash(3). The essential oil content and compositions are various in the chamomile flower and they depend on plant genetics and environmental factors (7)(8).
The largest group of medically important compounds forming the essential oil are α-bisabolol, chamazulene and bisabolol oxide. Many medical properties of chamomile are associated to its essential oil. In the analyzed essential oils Over 120 constituents have been identified, which the most components present in essential oil include α-bisabolol, chamazulene, (Z)-spiroether, ß-farnesene, bisabolol oxides A and B and α-bisabolone oxide A (9)(10). Active CONSTITUENTS of German chamomile consist of flavonoids: luteolin, apigenin, quercetin; spiroethers: en-yn-dicycloether; terpenoids: α-bisabolol, α-bisabolol oxide A and B, chamazulene, sesquiterpenes; coumarins: umbelliferone; and other components (11).
The oil constituents in bred and wild chamomile populations contain α-bisabolol (24.0-41.5%), bisabolone oxide (2.0-7.0%), bisabolol oxide a (1.0-36.2%), bisabolol oxide B (3.6-20.42%) and chamazulene (5.0-24.0%). The content of sesquiterpenoid compounds was more than 70% of the total essential oil (12)(13). In one research 77 components were identified in the essential oil of chamomile consist of farnesene (71.1%), chamazulene (8.4%), bisabolol oxide A (11.2%) and Spathulenol (11.3%) that include 99% of (14).
Amino acids are involved in the synthesis of other organic compounds, such as protein, amines, alkaloids, vitamins, enzymes, terpenoids and plant hormones that control various plant processes(15). Amino acids are crucial to stimulating cell growth, act as buffers, provide a source of carbon and energy and protect the cells from ammonia toxicity, with amid formation(16).
In recent years, plasma-based agriculture has been widely noticed by researchers (17)(18). “Plasmas in agriculture and food processing” is new, emerging interdisciplinary field of plasma applications (17)(19)(20)(21)(22). Plasma is the last known form of matter which is formed by inserting energy such as electricity, intense radiation, radio frequencies or heat (23). Plasma is a complete or partly ionized gas composed of charged ions, electrons, and neutral and reactive species that drive its chemistry (24)(20). The plasmas can be created under atmospheric conditions and are widely used and in liquids on material surfaces for the killing or inactivation of microorganisms, bacteria, and spores. Many studies have demonstrated that Non-thermal plasmas can be used to generate PAW by treating water under specific conditions (25). Through the plasma activating process, nitrogen from air can be captured and reacted with water which leads to the formation of nitrogen resources capable to sustain plants. Also, reactive oxygen species decrease the stress of pathogens in the soil.
Škarpa et al., investigated the Effect of PAW foliar application on some growth parameters of maize (26). Mandici et al., reported that the PAW treatment raises the quality of Triticum aestivum L. cv. Glosa sprouts., and it also increases the antioxidant enzymes activity (27)..
It has been reported that wetting properties of the surfaces of some seeds including: wheat, lentils and beans can be modified using cold radiofrequency air plasma treatment. A significant reduction in apparent contact angle as well as improvement in germination rate and germination rate was achieved during air plasma treatment of seeds (28).
The objective of this study was to assess the influence of the spraying of PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatments on the physiological, biochemical and phytochemical parameters of German chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) cultivars under field conditions.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment Description
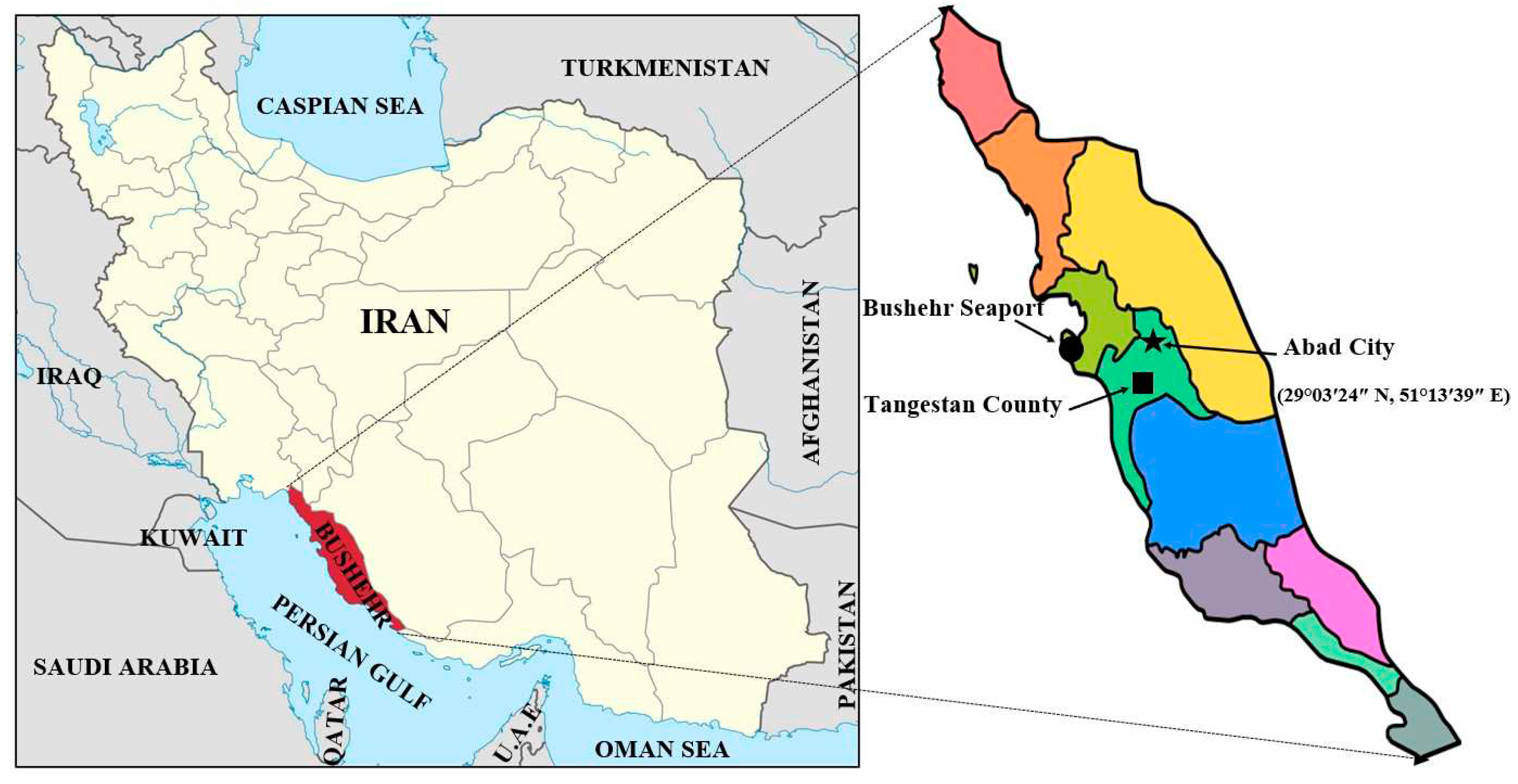
An experiment was performed at the research farm of Darya Zist Kavosh Co. Ltd., Abad City, Tangestan County, Bushehr province, Iran, during the 2020–2021 season. The geographical coordinates of the experiment site was 29°03′24″ N, 51°13′39″ E, with altitude of 271 m (
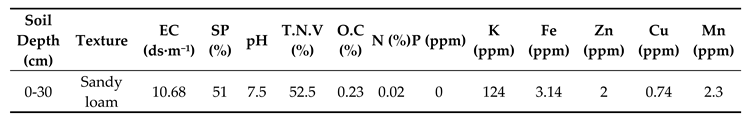
Figure 1). The soil chemical properties of the experimental location is presented in
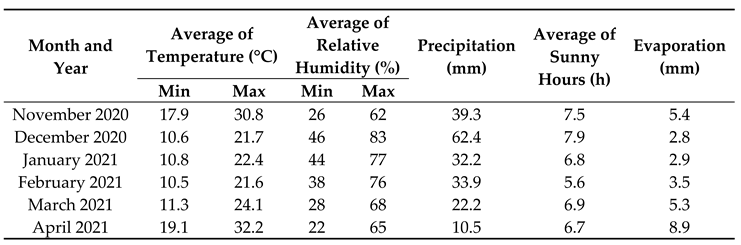
Table 1. The chamomile seeds were provided by the Department of Ecology, Faculty of Humanities and Natural Sciences, University of Prešov, Prešov, Slovakia. Each experimental plot size was 1 m × 1 m and in each plot, the plants were grown in three equidistant rows with adjacent rows being 30 cm apart. The seeds were sown superficially by hand and then were covered through a very thin layer of sandy soil. Meanwhile, we had not added organic matter or chemical fertilizers to the experimental field. The meteorological conditions during the experimental year (2020–2021) for growth and development of chamomile are presented in
Table 2.
2.2. Experimental design
A field experiment consisted of two factors: (i) chamomile cultivars (Bona, Bodegold, Lianka) and (ii) fertilizer levels (0 (control), 1, 2, 3 ml.L-1 foliar amino acid and 4 (PAW)) were designed and performed. The above-mentioned factors were combined and the experiments were set up as a factorial scheme with 15 treatments (5 fertilizer levels × 3 cultivars) replicated thrice in a randomized complete block design (RCBD). The experimental site had 45 plots (including 15 plots in each block).
2.3. Irrigation, weed and pest management
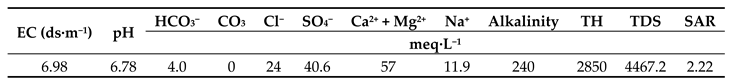
The irrigation was performed immediately after seeds sowing using an installed pipeline and dropping-tube system. The experimental field was irrigated every four days during cool months in the morning at 10:30 a.m until 11:30 a.m completely and uniformly. The chemical composition of irrigation water were presented in
Table 3. Weeding was performed two times during vegetative and reproductive phases by hand. Plant disease were not observed in the field so herbicide and pesticide were not used during this experiment.
2.4. Preparation of Plasma Activated Water (PAW)
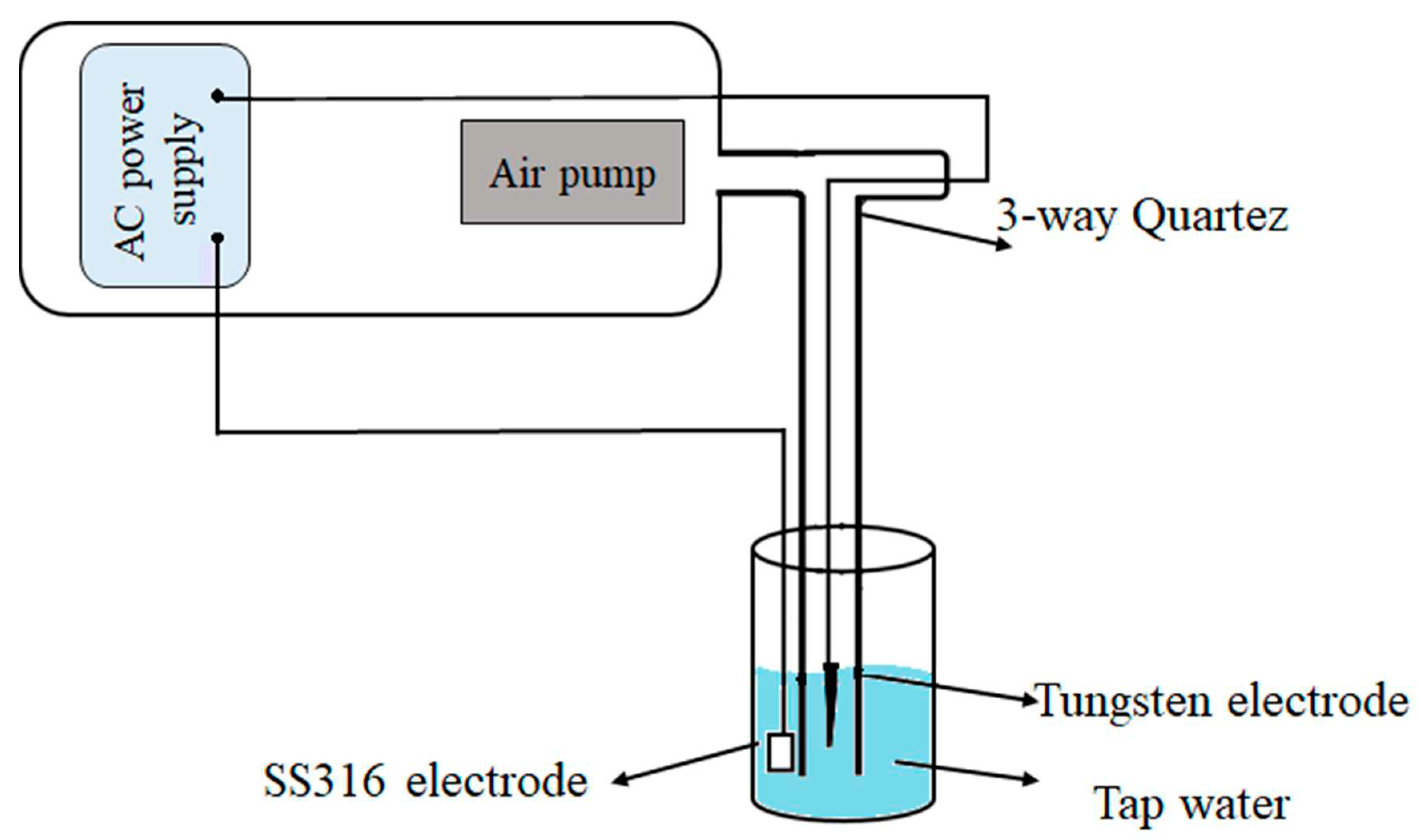
The fundamental method of generation of PAW involves operating a plasma generator inside or on the surface of the water to generate the ions and reactive species (29). The main components of the our setup include a high-voltage power supply, an air pump, and electrodes. Schematic diagram of the experimental setup have been presented in
Figure 2. The device was exactly designed to activate water by placing an electrode inside the water. The working gas for the plasma was normal air that was pumped by an air pump. Based on the preliminary study, the water volume, voltage, frequency, and airflow rate were set at 100 mL, 15 kV, 50 Hz, 30 mA, and 5 L/min, respectively. The time of plasma activation was 30 min. When plasma is applied to water-based liquids, it changes their characteristics (pH and electrical conductivity) and the resulting liquids are named as PAW. After activation, the PAW was transfered to the chamomile farm.
The results of nitrate, nitrite, and pH levels of PAW have been presented in table 4. Producing plasma inside the water volume along with air flow increased the amount of nitrate and nitrite and decreased pH as presented in table 4. Depending on the nature of the discharge gas, reactive oxygen species (ROS – ozone, O
3, H
2O
2, ·OH) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS
– ONOO
−, NO
3−, NO
2−, and the corresponding acids, nitrogen oxides NO
x) are produced in the solution (30). After the treatment pH of the solution was measured using a pH meter. Nitrite concentration in PAW was determined using standard USEPA diazotization method and absorbance was read by spectrophotometer at 507 nm (31). Nitrate concentrations were measured photometrically by using the Spectroquant® nitrate assay kit (Merck Chemicals) (32). The pH value of PAW dropped significantly from 7.58 to 3.16 during 30 minutes of treatment as shown in
Table 4, implying that the water has undergone acidification. The reactions taking place between the chemical species formed in the plasma and water result in acidification. In addition, it was known that acidic solutions are highly effective in bacterial inactivation (29). Several researchers have studied the impact of acidification to reduce bacterial colony formation (33)(29)(25). The results show that the concentration of nitrate increases with treatment time (Tabel 1). this is due to capturing nitrogen from air that acts as a fertilizer (17). It is found antimicrobial property of a solution containing nitric ion with a pH around 4-5 is high. Both ROS and RNS play important role in bacteria inactivation. The major evidence for the production of RNS is the present of nitrates and nitrites compounds in the PAW. So This solution would be a well fertilizer candidate which can acts similar to conventional nitrogen-based fertilizers. Reactions between gas-phase species and water molecules advance the generation of aqueous species like hydrogen peroxide nitrite and nitrate.
2.5. Application of Amino Acid Fertilizer and Plasma Activated Water Treatments
Amino acid concentrations including four levels (0 (control), 1, 2, 3 ml·L−1 and PAW treatment were prepared and used on three chamomile cultivars (Lianka (diploid), Bona (diploid) and Bodegold (tetraploid). The Fuego Base™ (Amino acid foliar fertilizer) was purchased from Grow More
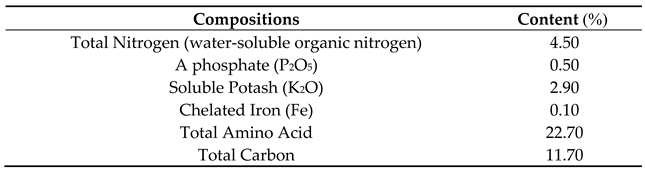
® Co. (Gardena, California, USA). The compositions of Fuego Base (Amino acid) foliar fertilizer according to the guaranteed analysis presented on the fertilizer bottle are presented in
Table 5. The Fuego Base™ is composed of all natural vegetable extracts plus amino acids and poly-peptides complex that supply organic nitrogen, natural chelating and complexing agents, natural occurring minor nutrients and growth stimulating co-enzymes. Foliar spray using Fuego Base™ (Amino acid fertilizer) and PAW was done during the growth and flowering stages of chamomile plants. The amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments were used three times in the vegetative and reproductive phases every 30 days. The first stage of amino acid and PAW foliar spray were at 30 days after planting. The spray was done at 15:30 p.m. until 17:30 p.m. for each treatment and plot. Spraying were done to the shoots evenly using a hand pump sprayer. The volume of amino acid and PAW sprayed was 4 L for each plot. Precise dates of foliar spraying using amino acid and PAW solutions are presented in
Table 6. Harvesting dried flowers was carried by hand and just the flowers were picked up and then they were dried at room temperature ( around 20-25 ᵒC) after harvest.
2.6. Physiological Characteristics
The evaluated physiological and biochemical characters included plant height (cm), fresh and dried flower weight (g.m-2), Chlorophyll a, b, carotenoids, CHN elements percentage, C:N ratio, total protein, and amino acids profile (mg.g-1). The plant height was measured at full bloom period as a mean height of 10 plants per plot using meter. After harvest samples were weighed (±0.001 g) using balance set and after drying at room temperature (20–25 °C) dried flower weight of each plot was calculated (3). The chamomile flowering was initiated in late February 2021 and it continued for two months. Harvesting was performed once time.
2.7. Leaf Chlorophyll a, b and Carotenoids contents
In order to estimate the chlorophyll a, b and carotenoids, leaf samples were collected and dried for 48 h at a temperature of 75 °C. Chlorophyll measurement was conducted according to the method presented by Lichtenthaler et al. (34).
2.8. Elemental analysis and carbon to nitrogen ratio
An elemental analysis was performed to determine/quantify carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen content/level by combustion analysis with a CHNOS Elemental Analyzer Model-ECS 4010 (Costech, Italy). Samples were prepared by loading 1–3 mg of dried leaf tissue into tin wrappers, and were then placed into the analyzer for combustion. Triplicates were prepared from each sample, and data generated by the analyzer were collected from the software package EA Data Manager (Costech, Italy). Data collected from EA Data Manager were then transferred to Excel to calculate carbon-to-nitrogen (C:N) ratios. Total protein contents (%w/w) were estimated using formula = %N × 4.78 (35).
2.9. Amino acids Content Measurement
The fresh leaves of chamomile (M. Chamomilla L.) were collected from the field (Abad city, Tangestan, Bushehr, Iran). The HPLC system used was an Agilent HPLC Infinity Isocratic LC 1220, (Agilent; Palo Alto, CA, USA). The assay of amino acids compositions were carried out according to (36).
2.10. Flower harvesting and oil extraction
The harvesting of flowers was performed by hand and then the flowers were dried at temperature of 25 °C. The essential oil of 30 g dried flower was extracted by hydrodistillation for 4 h, using a Clevenger system in 500 mL round-bottom flask with 300 mL distillated water according to method described by British Pharmacopeia [
10]. The essential oil was dried with anhydrous sodium sulphate, kept in dark glass bottles and then was stored in refrigerator (4 °C) until the next analysis (3)(1).
2.11. GC/MS analysis
The chamomile oil analysis was performed using gas chromatograph connected with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) model (QP2010 SE, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with fused silica capillary HP-5 column (50 m length × 0.20 mm i.d., 0.25µm film thickness). Sample volume 1.0 µl were utilized manually type of injection. The carrier gas was Helium at a flow rate of 1 ml/min and the oven temperature was held at 60 °C. Then the column was sequentially heated from to 60 °C to 150 °C at a rate of 10 °C.min-1, held for 5 min. Then, the column was heated 150 °C to 180 °C at a rate of 5 °C.min-1, for 3 min. Finally, it was heated at from 180 °C to 280 °C a rate of 7 °C.min-1, for 25 min. detector and injection and temperature were programmed at 250 °C and 280, respectively (37).
2.12. The chamomile oil constituent’s identification and quantification
The procedure of phytochemical components identification and quantification has been described in detail in Ghasemi et al (3).
2.13. Determination of total apigenin content
Total apigenin quantification was conducted using HPLC method according to the procedure described in United States Pharmacopoeia [
24]. This procedure has been presented in detail in Baghalian et al (39). The HPLC system used was an Agilent HPLC Infinity Isocratic LC 1220, (Agilent; Palo Alto, CA, USA).
2.14. Statistical Analysis
After physiological and biochemical evaluation, statistical analyses were performed by using DSAASTAT software version 1.022, Preugia, Italy. Data were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the mean results were compared by using Duncan's multiple range test.
3. Results
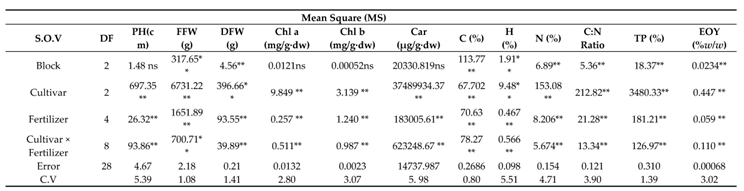
The analysis of variance for physiological and biochemical parameters showed that all the studied traits were significantly influenced by chamomile cultivars and fertilizer treatments (
Table 7). The interaction of cultivar × fertilizer was significant on them at the statistical level (p≤0.05) (
Table 7).
3.1. Plant Height
The analysis of variance indicated that the plant height traits was significantly impressed by cultivars and fertilizer treatments (
Table 7). The interaction between cultivars and fertilizer treatments was significant (
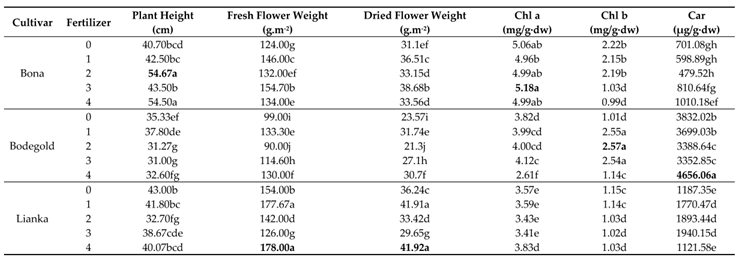
Table 7). The mean comparison for the interaction between cultivars and fertilizer treatments demonstrated that the Bona cultivar had the highest plant height with an average of 54.67 and 54.50 cm at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments respectively. On the other hand, the Bodegold cultivar had the lowest plant height with an average of 31.00 cm under 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8). The PAW and amino acid fertilizer increased the plant height in Bona cultivar, while these treatments had not significant effect on the Lianka and Bodegold cultivars.
3.2. Fresh Flower Weight
The analysis of variance demonstrated that the cultivar and fertilizer had a great impact on fresh flower weight at the statistical level (
p ≤ 0.01). The fresh flower weight was also significantly impressed by the interaction cultivar × fertilizer (
Table 7). Duncan analysis for the interaction between cultivar × fertilizer showed that the Lianka cultivar gained the highest fresh flower weight with an average of 178.00 and 177.67g·m
−2 under PAW and 1ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment respectively. In contrast, the lowest fresh flower weight was obtained for Bodegold cultivar with an average of 90.00 g·m
−2 at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer (
Table 8).
3.3. Dried Flower Weight
The analysis of variance demonstrated that the dried flower weight was significantly influenced by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction of cultivar and fertilizer (
p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). Duncan analysis for the interaction between the cultivar and fertilizer showed that the Lianka cultivar had the greatest dried flower yield with averages of 41.92 and 41.91 g·m
−2 under PAW and 1m.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatments, respectively. Also, the Bodegold cultivar had the lowest dried flower yield with an average of 21.30 g·m
−2 at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer (
Table 8). Also, the lowest dried flower yield was yield for Bodegold cultivar with an average of 21.30 g·m
−2 at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer (
Table 8).
3.4. Chlorophyll a Content
The analysis of variance demonstrated that the chlorophyll a content was significantly impacted by the cultivars, fertilizer and the interaction of cultivar and fertilizer (
p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). The mean comparison for the chlorophyll a content showed that the highest chlorophyll a content was 5.18 mg/g·dw at the concentration of 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. While, the lowest chlorophyll a content was related to Bodegold cultivar with an average of 2.61mg/g·dw under PAW treatment.
3.5. Chlorophyll b Content
The analysis of variance showed that the chlorophyll b content was significantly influenced by the cultivars, fertilizer and the interaction of cultivar and fertilizer (
p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). The highest chlorophyll b content belonged to Bodegold cultivar with average of 2.57 mg/g·dw under 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. In contrast, the lowest content of the chlorophyll b attained was an average of 0.99 mg/g·dw under PAW treatment.
3.6. Carotenoids Content
The analysis of variance showed that the carotenoids content was significantly impacted by the cultivars, fertilizer and the interaction of cultivar and fertilizer (
p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). The mean comparison for the interaction of cultivar and fertilizer showed that the Bodegold cultivar had the highest carotenoids content with an average of 4656.06 µg/g·dw under Paw treatment. In contrast, the lowest amount of carotenoids content belonged to the Bona cultivar with an average of 479.52 µg/g·dw at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.7. Carbon Percentage
The analysis of variance demonstrated that the carbon percentage was significantly impressed by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (p ≤ 0.01) (
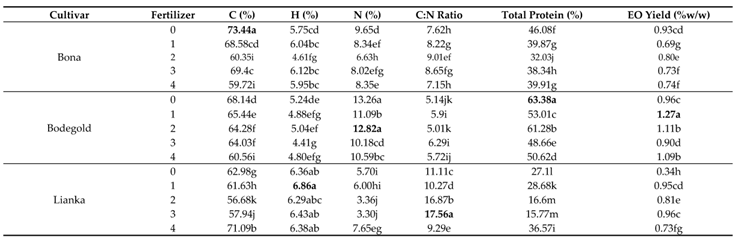
Table 7). The mean comparison of the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer illustrated that the Bona cultivar had the highest carbon percentage with average of 73.44% (w/w) under control treatment and the lowest carbon content with average of 56.88% (w/w) was belonged to the Lianka cultivar at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.8. Hydrogen Percentage
The analysis of variance indicated that the hydrogen percentage was significantly affected by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). Duncan analysis for the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer demonstrated that the Lianka cultivar had the greatest hydrogen percentage with average of 6.88% (w/w) at the concentration of 1ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. While, the lowest hydrogen percentage with average of 4.41% (w/w) was belonged to the Bodegold cultivar at the concentration of 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.9. Nitrogen Percentage
The analysis of variance illustrated that the nitrogen percentage was significantly impacted by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). The mean comparison of the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer showed that the Bodegold cultivar had the highest nitrogen percentage with average of 13.26 and 12.82% (w/w) under control and 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment, respectively. In contrast, the lowest nitrogen percentage with average of 3.30% (w/w) was belonged to the Lianka cultivar at the concentration of 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.10. C:N Ratio
The analysis of variance indicated that the C:N ratio was significantly affected by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). Duncan analysis for the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer displayed that the Lianka cultivar had the greatest C:N ratio with average of 17.56 at the concentration of 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. While, the lowest C:N ratio with average of 5.01 was belonged to the Bodegold cultivar at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.11. Total Protein Content
The analysis of variance revealed that the total protein content was significantly changed by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). The mean comparison of the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer indicated that the Bodegold cultivar had the highest total protein percentage with average of 63.38% (w/w) under control treatment. In contrast, the lowest total protein percentage with average of 15.77% (w/w) was belonged to the Lianka cultivar at the concentration of 3ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment (
Table 8).
3.12. Essential Oil Yield
The analysis of variance displayed that the essential oil yield was significantly impacted by the cultivar, fertilizer and interaction between cultivar and fertilizer (
p ≤ 0.01) (
Table 7). Duncan analysis for the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer showed that the Bodegold cultivar had the greatest essential oil yield with average of 1.27% (w/w) at the concentration of 1ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. While, the lowest essential oil yield with average of 0.34% (w/w) was belonged to the Lianka cultivar under control treatment (
Table 8).
3.13. Amino acids Profile analysis
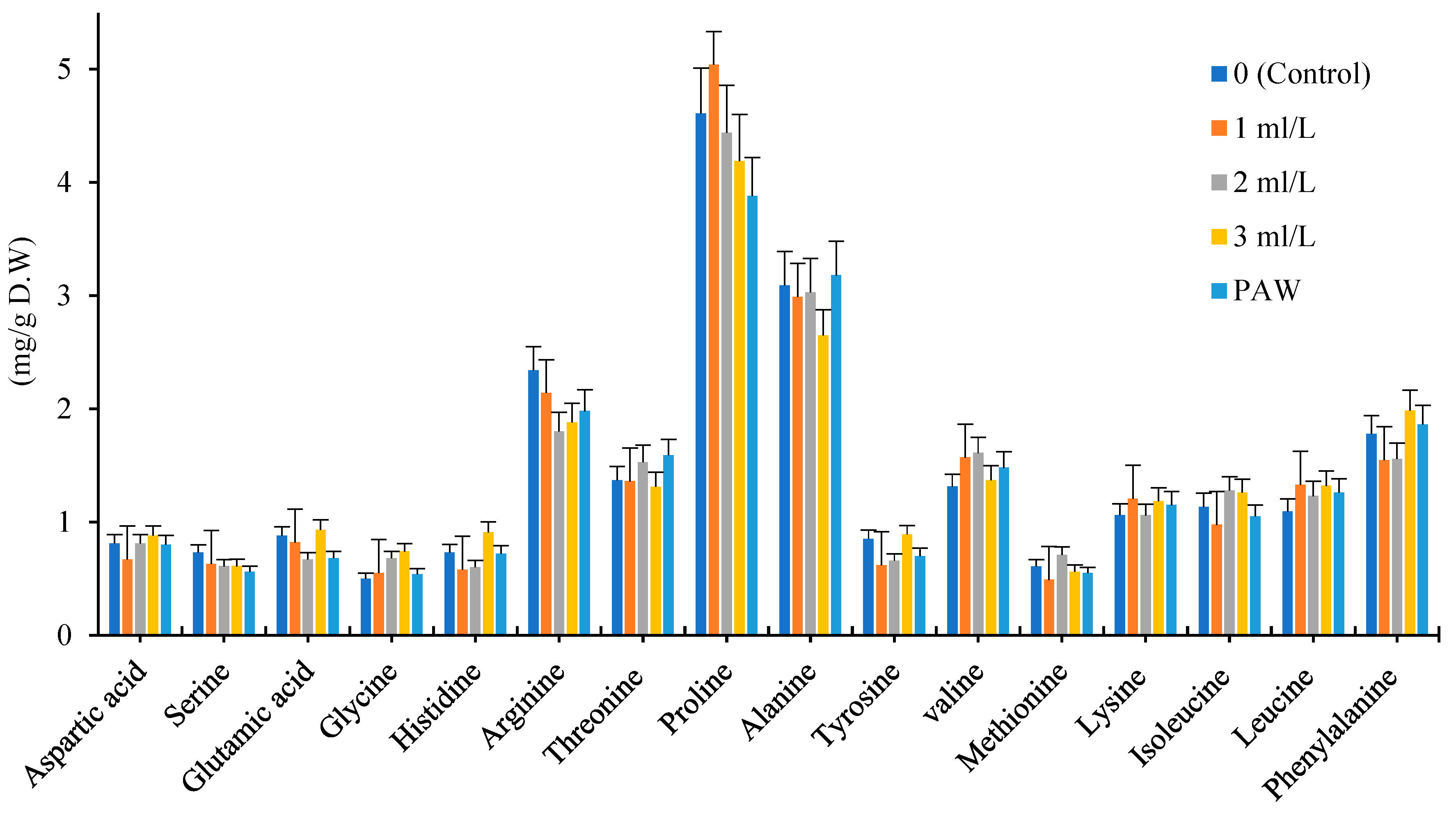
In this study, we measured 16 types of amino acids including Aspartic acid, Serine, Glutamic acid, Glycine, Histidine, Arginine, Threonine, Proline, Alanine, Tyrosine, Valine, Methionine, Lysine, Isoleucine, Leucine and Phenylalanine in dry powder of leaf chamomile cultivars. The significant changes were observed in chamomile amino acids profile under application of foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments which is shown in
Figure 3, 4, 5. The concentration of some amino acids composition increased after foliar application of amino acid and PAW treatment.
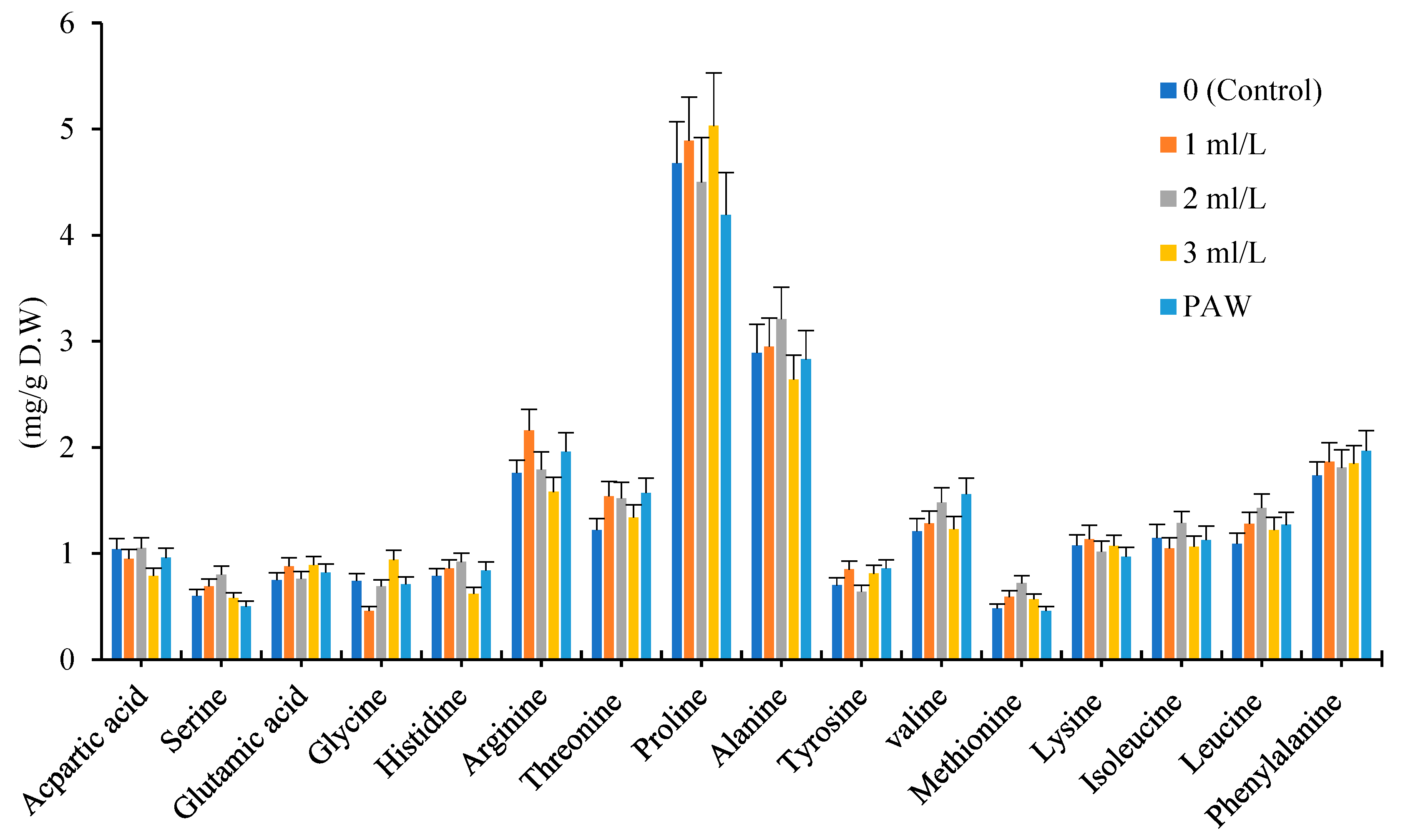
The Proline and Alanine amino acids were dominated among 16 amino acids in every three chamomile cultivars. Among 16 amino acids which assayed in Bona, Bodegold and Lianka cultivars, majority of them increased under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments in comparison with control. The proline, arginine, glycine, alanine and valine showed the most changes under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
The amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments increased the total amino acids content in Bona cultivar in comparison with control. In Bona cultivar, 7 types of amino acids increased under the influence of PAW treatment. The 13 types of amino acid increased at the concentration of 1ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. The 9 types of amino acids raised at the concentration of 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. In general, the concentration of 1 and 2ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatments showed the highest increase in the amount of amino acids in Bona cultivar (
Figure 3).
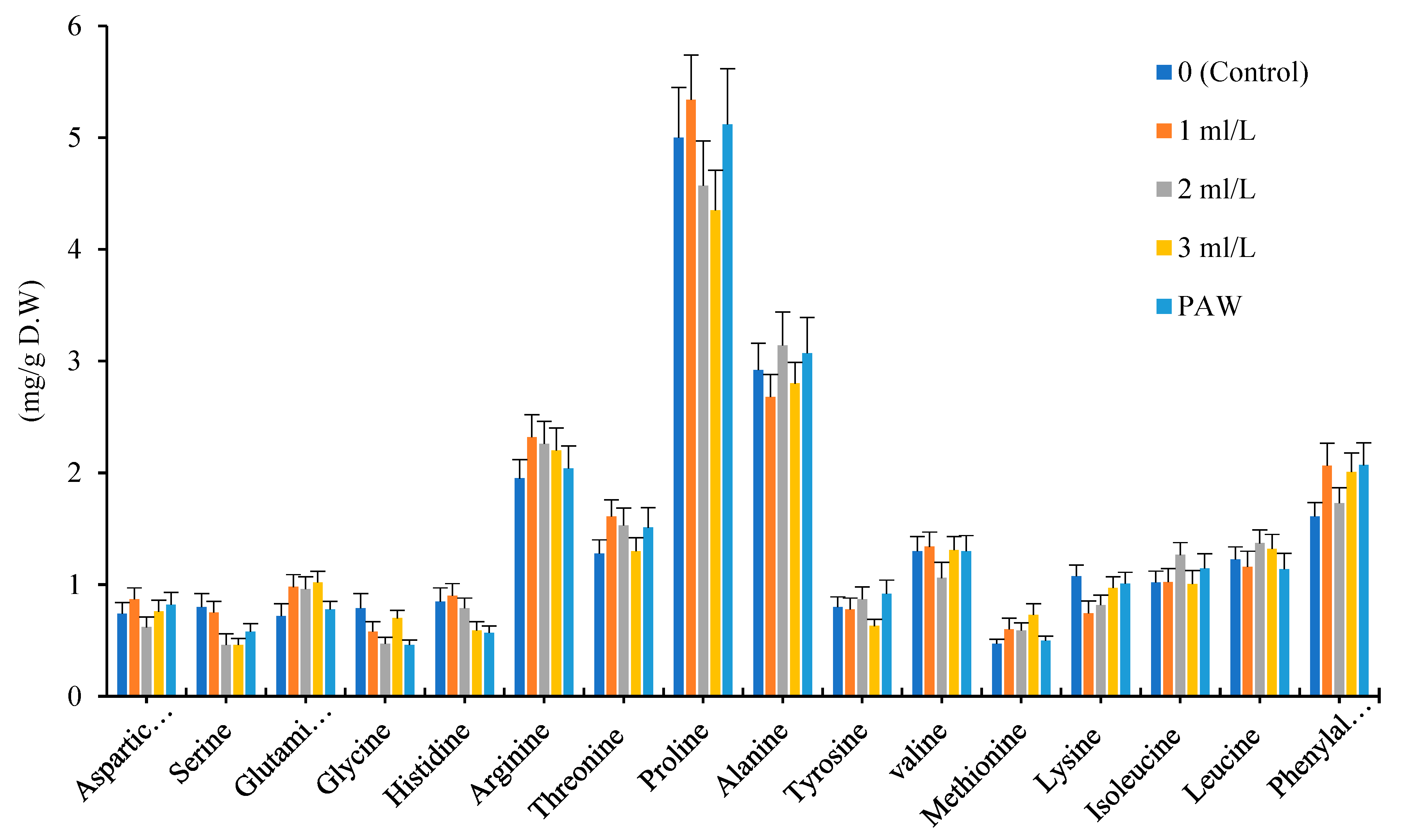
The amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments increased total amino acids content in Bodegold cultivar in comparison with control. The 11 types of amino acid were increased in Bodegold cultivar due to the effect of amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments. The concentration of 1ml.L
-1 and PAW treatments also demonstrated the greatest increase in total amount of amino acids (
Figure 4)
.
The amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments decreased the total amino acids content in Lianka cultivar in comparison with control. But the amounts of proline, alanine, valine, lysine, phenylalanine and tyrosine increased under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments. The 4 types of amino acids increased at the concentration of 1ml.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. The PAW treatment increased 6 types of amino acids in Lianka cultivar (
Figure 5).
3.14. Secondary Metabolite Profile Analysis
The hydro-distillation of the air-dried chamomile flowers gave dark blue oils in range of 0.34% to 1.27% (w/w) in this experiment. In total, thirty-six components were identified in three cultivars of chamomile treated with foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW. Identified volatile constituents in the essential oils of the chamomile flowers samples which were representing 92.91% of the oils, have been shown in
Table 9.
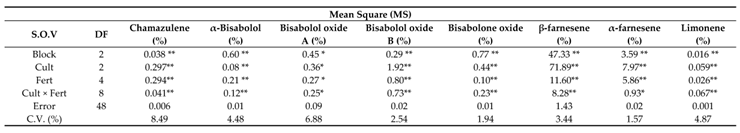
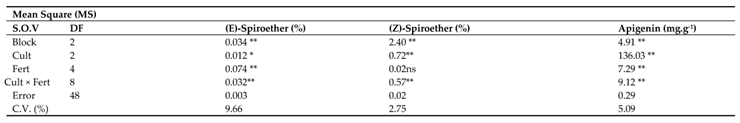
The analysis of variance for phytochemical compositions showed that all the presented compounds at section 3.14.1 to 3.14.10 were significantly influenced by chamomile cultivars and fertilizer treatments except (Z)-Spiroether compound that was not significant by fertilizer effect while the interaction of cultivar × fertilizer was significant on all compositions at the statistical level (p≤0.05) (
Table 10).
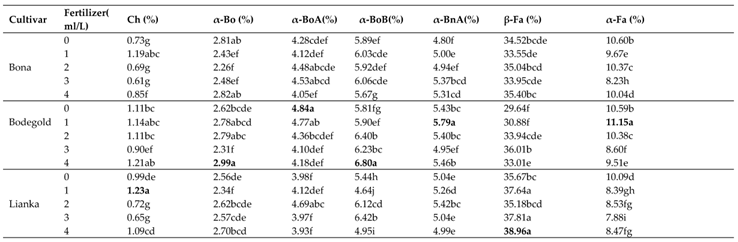
The highest percentage of major volatile constituents of the German chamomile oil were obtained as following: chamazulene (1.23%), α-bisabolol (2.99%), α-bisabolol oxide A (4.84%), α-bisabolol oxide B (6.80%), α-bisabolone oxide A (5.79%), (E)-β-farnesene (38.96%), (E)-α-farnesene (11.15%), (Z)-spiroether (5.88%), germacrene D (6.57%), α-pinene (4.50%) and (E)-β-ocimene (4.20%) (
Table 11).
According to GC-MS results, the amount of essential oil components such as chamazulene, α-bisabolone oxide A, (E)-α-farnesene, (E)-spiroether and limonene were increased using foliar amino acid fertilizer treatments while PAW treatment improved α-bisabolol, α-bisabolol oxide B and (E)-β-farnesene (
Table 11).
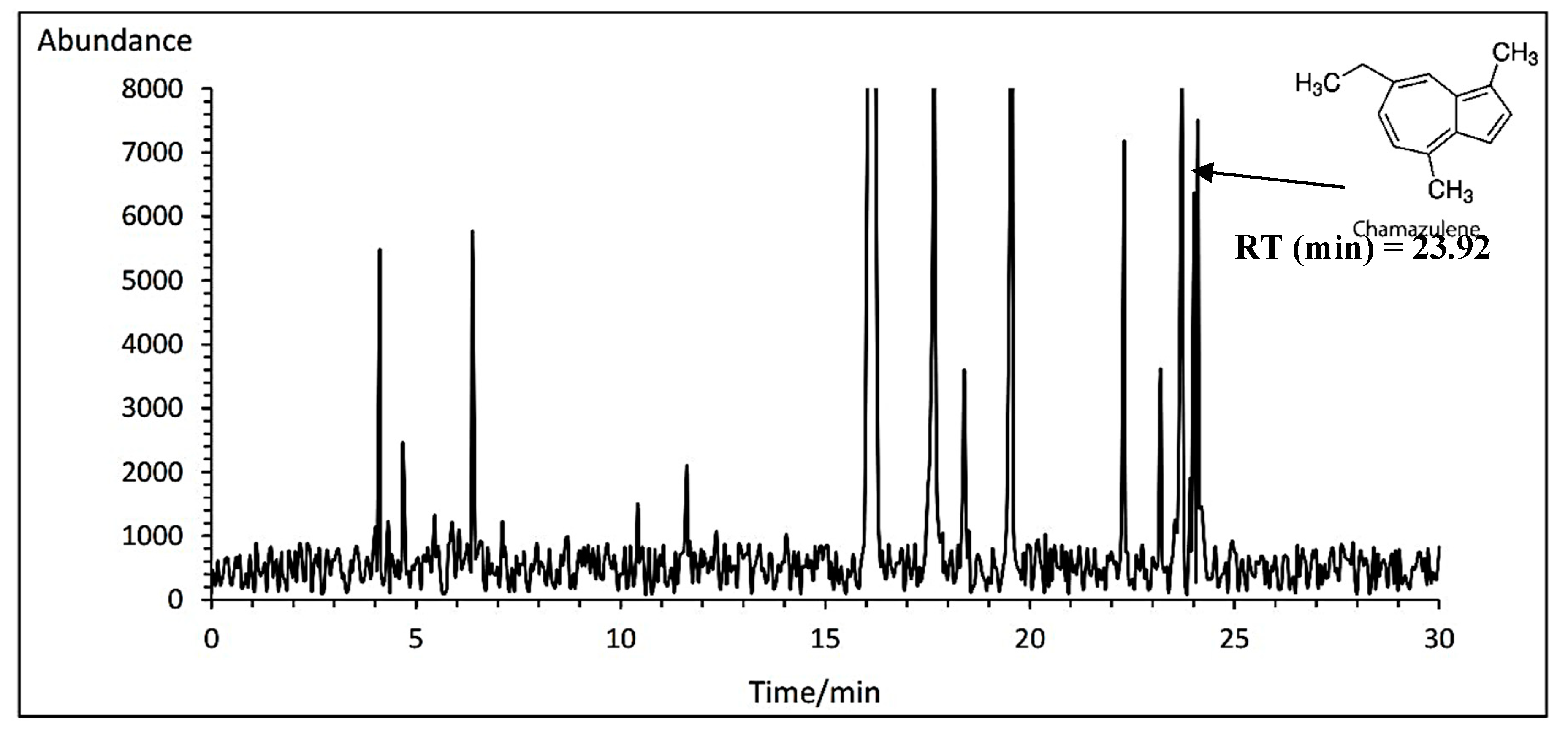
3.14.1. Chamazulene
Duncan analysis for the interaction between the cultivar and fertilizer showed that the highest chamazulene percent was obtained with an average of 1.23% at the concentration of 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment in Lianka cultivar. In contrast, the lowest percent was obtained with an average of 0.61% at the concentration of 3 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment in Bona cultivar (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of chamazulene of German chamomile oil is presented for Lianka cultivar treated with 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment (
Figure 6).
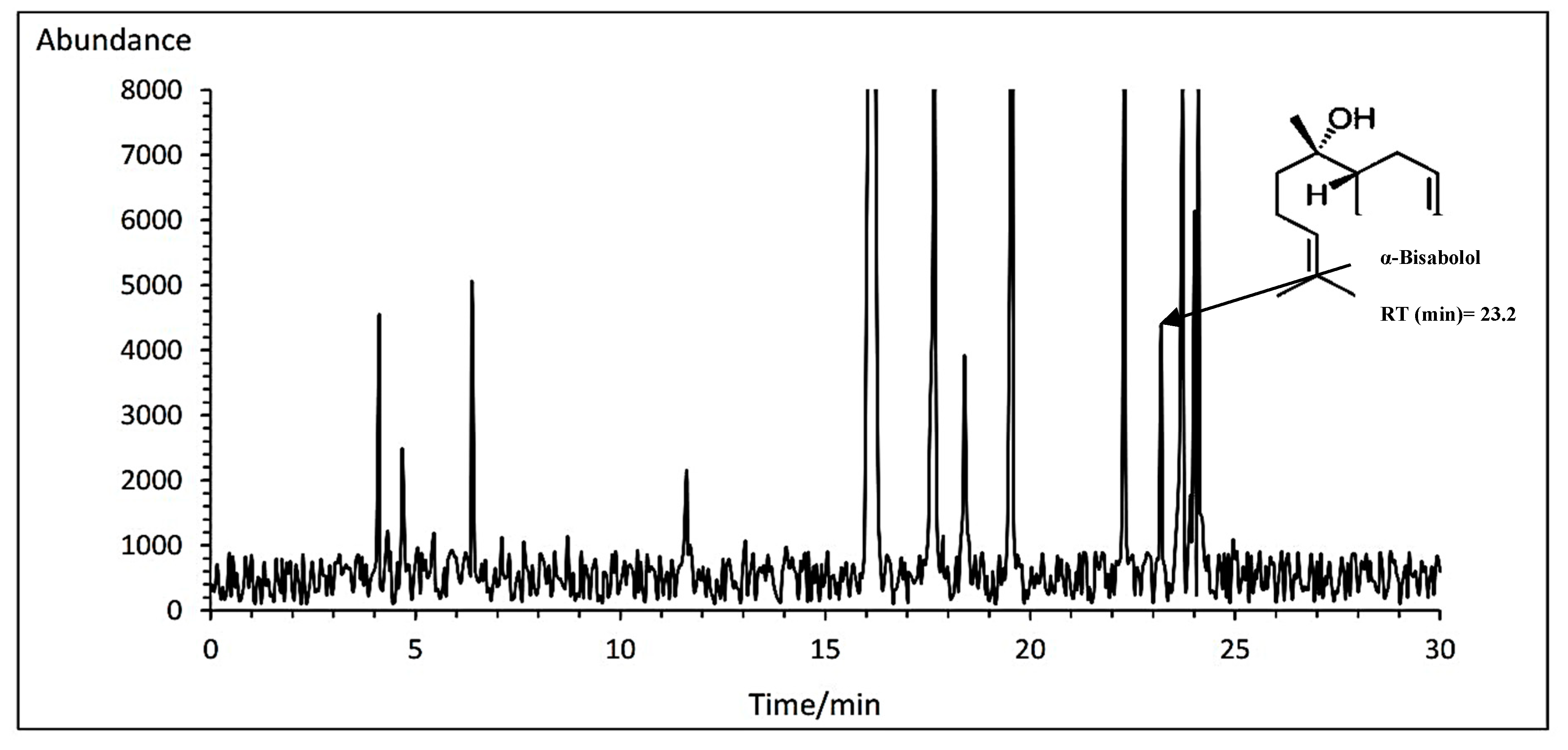
3.14.2. α-Bisabolol
The highest percent of α-bisabolol with an average of 2.99% belonged to Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment. In contrast, the Bona cultivar had the lowest amount of α-bisabolol with an average of 2.26% at the concentration of 2 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of α-bisabolol of German chamomile oil is presented for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment (
Figure 7).
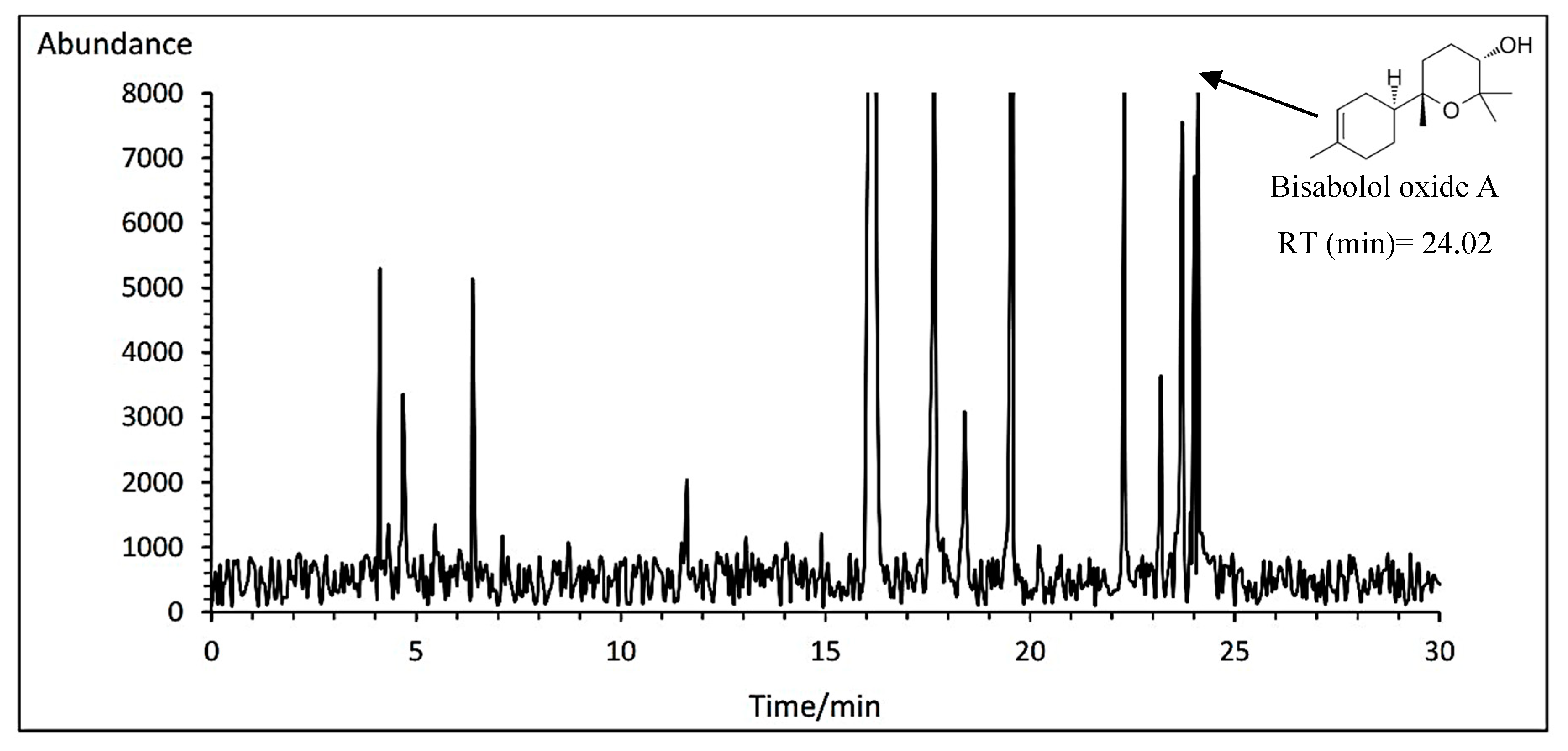
3.14.3. Bisabolol oxide A
The means comparison of the interaction between cultivar and fertilizer indicated that the Bodegold cultivar had the highest bisabolol oxide A amount with average of 4.84% under control treatment. While, the Lianka cultivar had the lowest amount with an average of 3.93% under PAW treatment (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide A of German chamomile oil is presented for Bodegold cultivar under control treatment (
Figure 8).
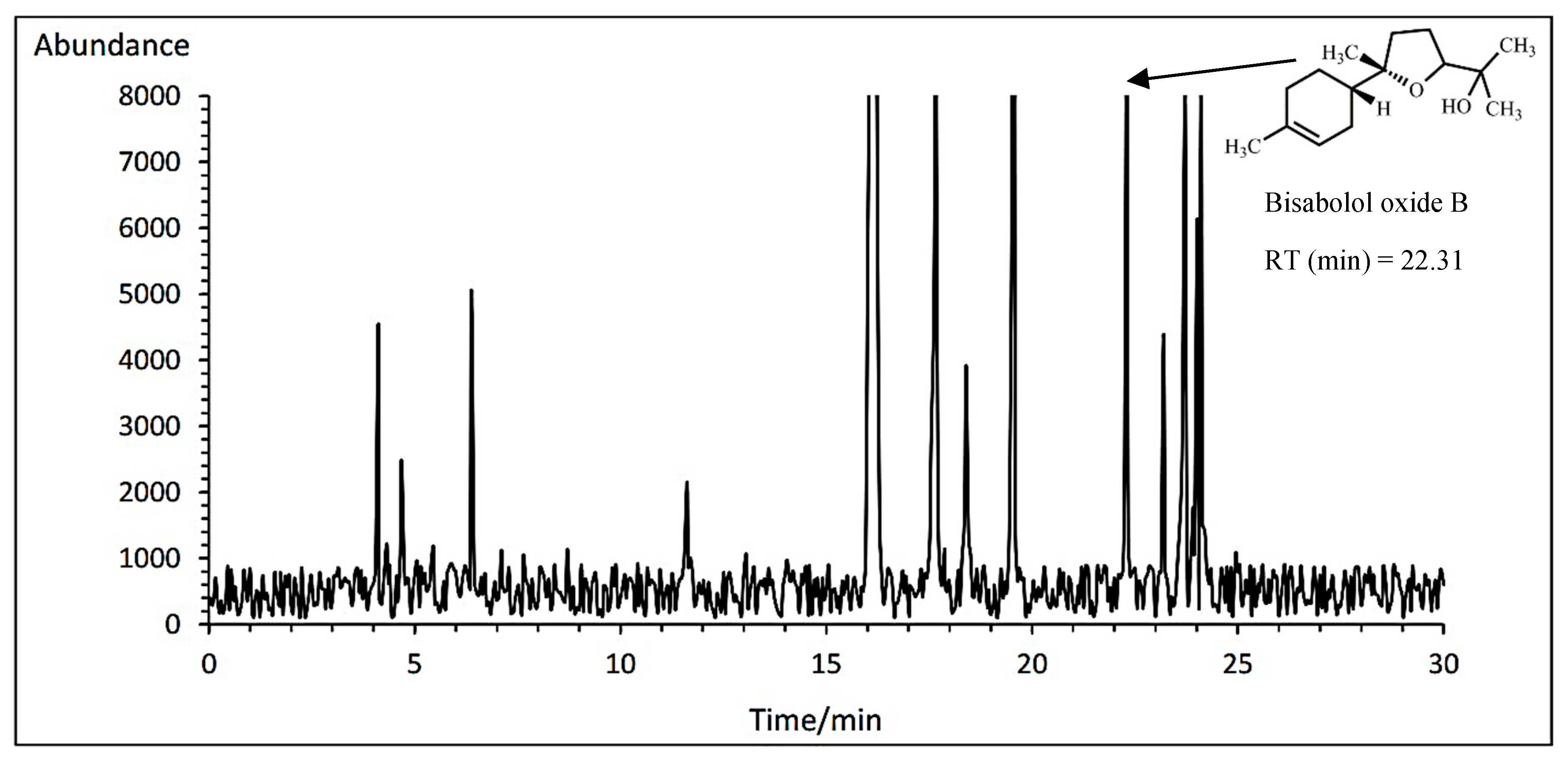
3.14.4. Bisabolol oxide B
The Bodegold cultivar had the highest bisabolol oxide B amount with average of 6.80% under PAW treatment. While, the Lianka cultivar had the lowest bisabolol oxide B amount with an average of 6.64% at the concentration of 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide B of German chamomile oil is presented for Lianka cultivar treated with 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment (
Figure 9).
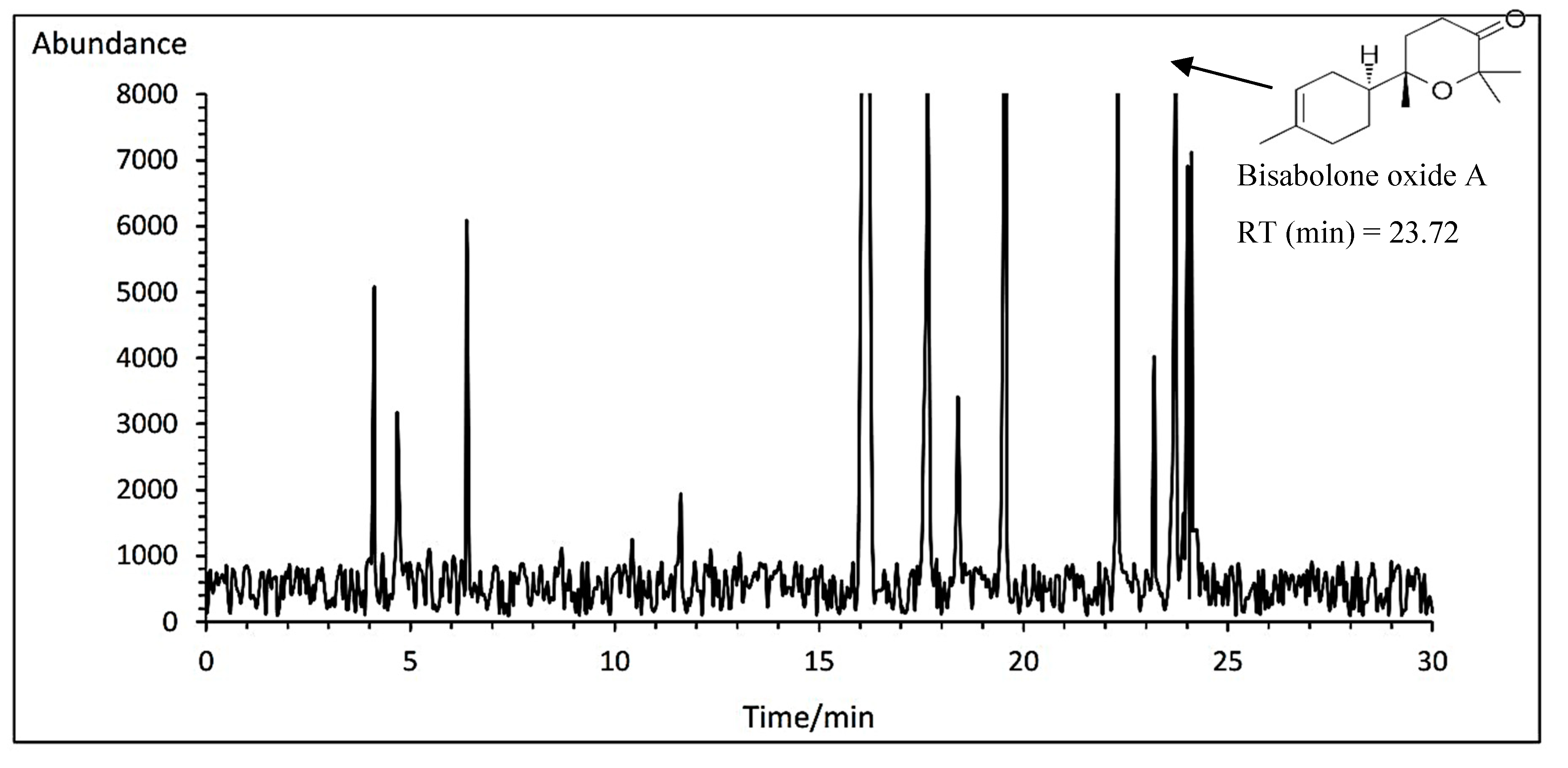
3.14.5. Bisabolone oxide A
The highest average of bisabolone oxide A was obtained with an average of 5.79% at the concentration of 1 mg.L
-1 amino acid fertilizer in Bodegold cultivar. Whereas the lowest amount of bisabolone oxide A was attained with an average of 4.80% under control treatment in Bona cultivar (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolone oxide A of German chamomile oil is presented for Bodegold cultivar treated with 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid treatment (
Figure 10).
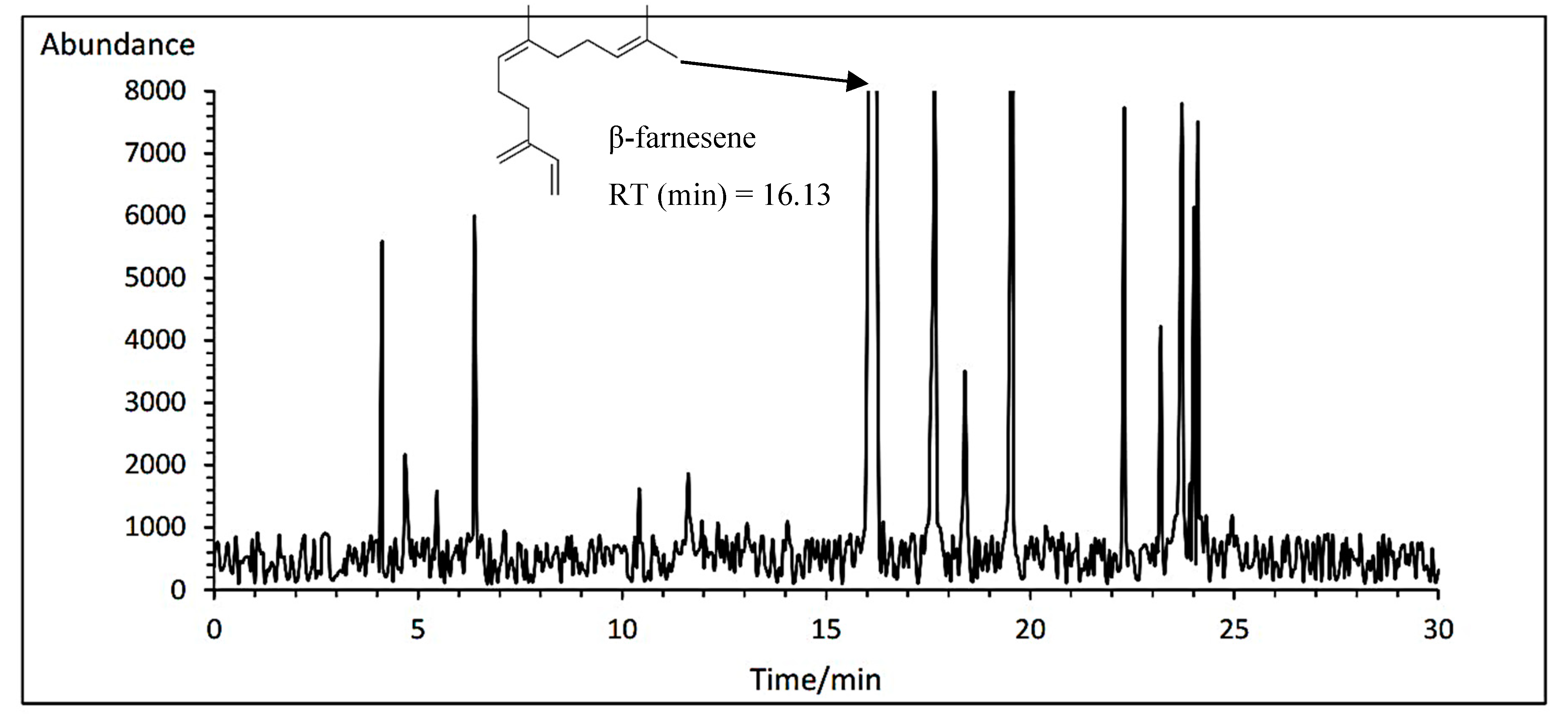
3.14.6. β-farnesene
The means comparison of the interaction between the cultivar and fertilizer showed that the Lianka cultivar had the highest β-farnesene amount with average of 38.96% under PAW treatment. While, the Bodegold cultivar had the lowest β-farnesene amount with an average of 29.64% under control treatment (
Table 11). A typical GC-MS chromatogram of β-farnesene of German chamomile oil is presented for Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment (
Figure 11).
3.14.7. α-farnesene
The highest percent of α-farnesene with an average of 11.15% belonged to Bodegold cultivar at the concentration of 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer. In contrast, the Lianka cultivar had the lowest amount of α-farnesene with an average of 7.88% at the concentration of 3 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer (
Table 11).
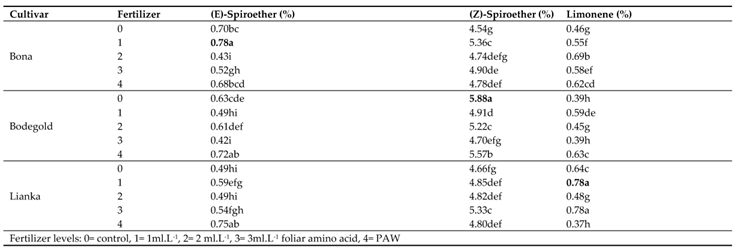
3.14.8. (E)-Spiroether
The highest average of (E)-Spiroether was obtained with an average of 0.78% at the concentration of 1 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer in Bona cultivar. Whereas the lowest amount of (E)-Spiroether was attained with an average of 0.42% at the concentration of 3 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer in Bodegold cultivar (
Table 11).
3.14.9. (Z)-Spiroether
The means comparison of the interaction between the cultivar and fertilizer indicated that the highest (Z)-spiroether percent was obtained with an average of 5.88% under control treatment for Bodegold cultivar. In contrast, the lowest percent was obtained with an average of 4.54% under control treatment for Bona cultivar (
Table 11).
3.14.10. Limonene
Duncan analysis for the interaction of cultivar and fertilizer indicated that the Lianka cultivar had the highest amount of limonene percent with an average of 0.78% at the concentration of 3 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer, whereas the Lianka cultivars had the lowest amount with an average of 0.37% under PAW treatment (
Table 11).
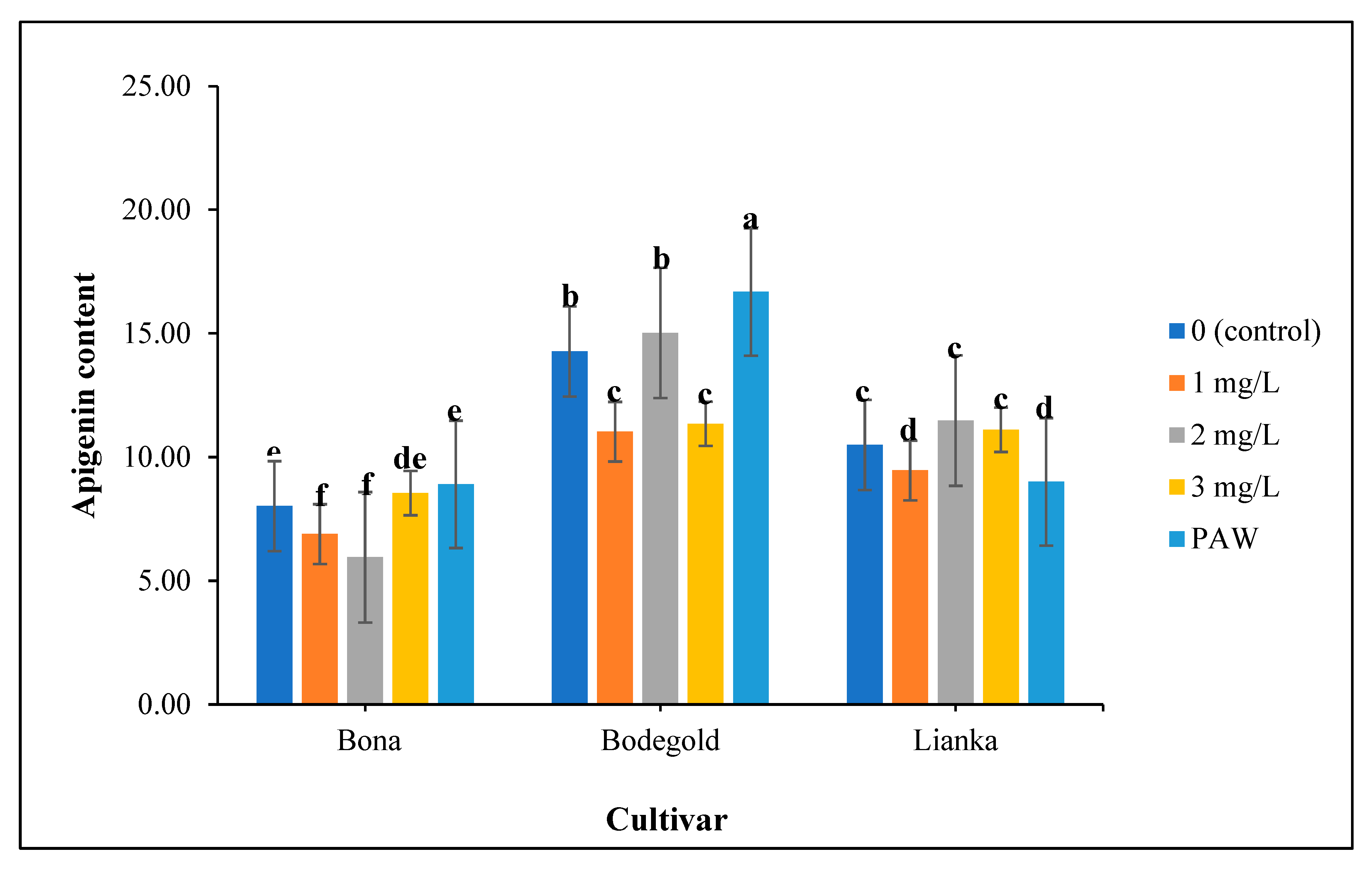
3.15. Apigenin content evaluation
The analysis of variance showed that the apigenin content was significantly influenced by chamomile cultivars, fertilizer treatments and the interaction of cultivar × fertilizer was significant on its at 99% level of probability (
Table 10). The highest average of apigenin was obtained with an average of 16.68mg.g
-1 under PAW treatment in Bodegold cultivar. Whereas the lowest amount of apigenin was attained with an average of 5.95mg.g
-1 at the concentration of 2 ml·L
−1 amino acid fertilizer in Bona cultivar (
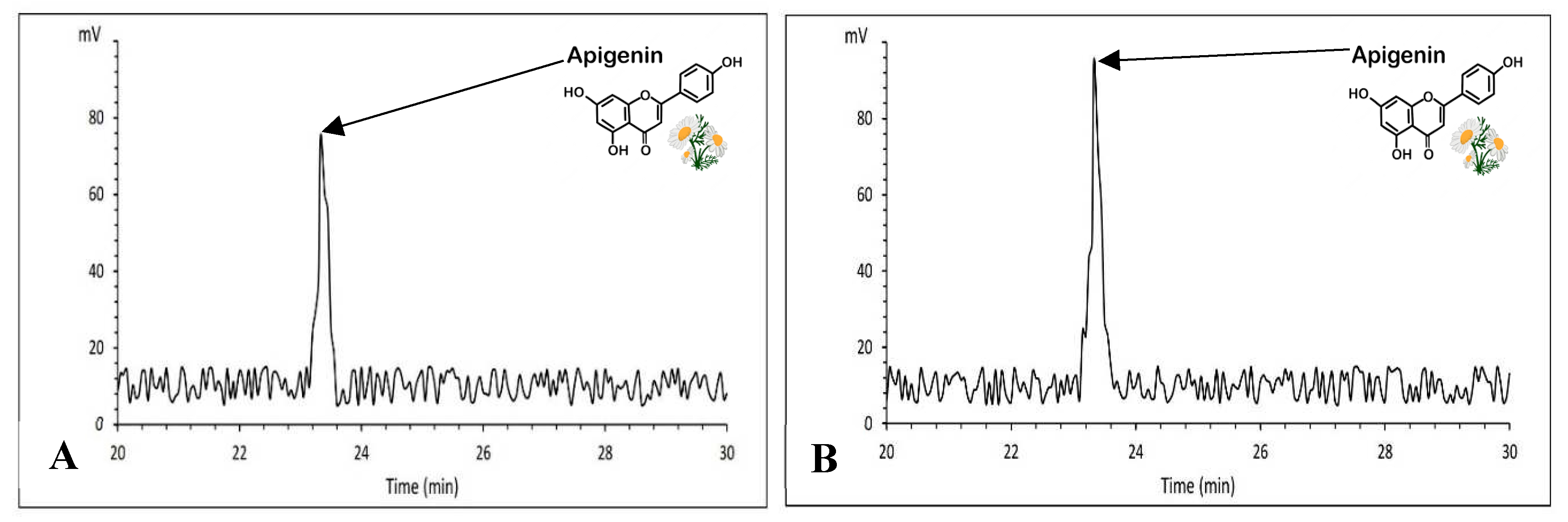
Figure 12). A typical HPLC chromatogram of apigenin of German chamomile oil are presented for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment (
Figure 13).
4. Discussion
This study demonstrated that the foliar spraying of plasma activated water and amino acid fertilizer had significant impact on physiological traits and essential oil yield in chamomile cultivars under field conditions. These results are in agreement with Omer et al. (15) and Kučerová et al. (40). Alexander (2005) reported that the plant height had a higher value in Bona as a diploid cultivar in comparison with the Goral and Lutea as tetraploid cultivars (35). Omer et al. reported that the plant height, fresh and dried flower weight of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) were increased under the foliar application of amino acid fertilizer in Egypt (15).
In the present research, the Lianka cultivar (diploid) produced the highest dried and fresh flower weight under PAW and 1ml.L-1 amino acid fertilizer treatments. It has been reported that the chamomile diploid cultivars had the greatest dried and fresh flower weight and yield (41)(42). In all three chamomile cultivars, PAW has increased the dried flower weight. Amino acid treatment has also increased the dried flower weight in most concentrations. Therefore, it is concluded that the plasma-activated water and amino acid fertilizer treatments can be increased the dried flower weight in appropriate concentration.
The content of Chlorophyll a did not change significantly under the influence of amino acid and PAW treatments. The amount of Chlorophyll b also increased only in Bodegold cultivar under the application of amino acid treatments. Also, the amount of carotenoid has raised significantly under the effect of PAW in Bona and Bodegold cultivars. The amino acid fertilizer treatments also increased carotenoid content only in Lianka cultivar in all used concentrations. Regarding to the results of the other investigations, the response of chamomile cultivars is different to amino acid fertilizer concentrations. The results of Kučerová et al. (40) showed that PAW improves the content of chlorophyll a, b and carotenoid in the wheat leaves. Photosynthetic pigments including chlorophylls and carotenoids are involved in physiological processes such as protection against oxidative stress, photosynthesis and metabolic reactions (43).
In this experiment, both PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatment enhanced the chlorophyll b and carotenoid content in chamomile cultivars. H2O2 and NO3− are key species in boost and expand of photosynthetic pigments. H2O2 raises the opening of stomata, thus promoting CO2 uptake, photosynthetic rate, and aggregation of photosynthetic pigments (19). The effect of NO3− is ascribed to up-regulation of the genes encoding δ-amino levulinic acid dehydratase, an effective enzyme in the biosynthesis of chlorophyll (27). Stoleru et al. demonstrated that the utilization of PAW had not remarkably effect on the content of chlorophyll in the lettuce leaves. Sajib et al. reported that the PAW treatment had significant affect on the enhancement of leaf chlorophyll level in black gram plants (21).
The carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur (CHNOS) are major precursors for protein, carbohydrates and lipids in plant and algal cells, are measured using combustion analysis (44). The carbon content was increased in Lianka cultivar under the PAW treatment. The amino acid fertilizer sprayed has elevated the hydrogen percentage in Bona and Lianka cultivars. While, the content of nitrogen has increased in Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment.
The C:N ration has increased in Bona and Lianka cultivars under amino acid fertilizer treatments. While, the C:N ratio increased under PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatments in Bodegold cultivar. The strong interactions between C assimilation and N assimilation have been reported in metabolic processes and energy levels (45) (46). It is noticable that both C and N contents were increased in Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment. This is probably due to linkage between carbon metabolism and nitrogen metabolism because they share organic carbon and energy provided by respiration, CO2 fixation or photosynthetic electron transport (46).
Proteins are essential elements of plant enzymes and fundamental players in plant growth [
29]. In our work, determination of total protein content via % nitrogen has almost decreased in all three chamomile cultivars under the influence of amino acid fertilizer treatments. While the amount of total protein has increased in Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment. The increase in content of protein is due to presence of NO3
− and NO2
− ions in PAW; both species are crucial sources of nitrogen which is necessitated for protein synthesis (31). Kucerová et al. also reported an enhancement in the content of soluble protein in the roots and shoots of wheat plants under PAW produced from tap water (40). Sajib et al. observed an increase in the total soluble protein content in the roots and above-ground parts of black gram plants germinated from the seeds under PAW treatment (47). Furthermore, nitrates are essential in plants nutrition given their pivotal role in the amino-acids, proteins and chlorophyll synthesis (48).
Amino acids are incorporated in the synthesis of some organic compounds, including plant hormones, vitamins, alkaloids,amines, enzymes, terpenoids and protein. These compounds control various plant processes (15). Nitrogen is used directly to synthesis amino acids, hrough a primary process involving the synthesis of glutamine and glutamate via the 2-oxoglutarate-glutamate synthase pathway (49)(50), and the increment of free amino acids could thus be attributed to the NO2− and NO3− that produced in PAW.
Proline and alanine are able to ameliorate various abiotic stress tolerance in different plants via osmotic adjustment, chlorophyll metabolism and free radical-scavenging (51)(52). According to this, the enhance of proline and alanine contents of chamomile under PAW and amino acid fertilizer in the present investigation was supposed to be related with the oxidative stress and osmotic stress caused by, NO2− , NO3− and low pH of PAW (49).
The reaction of chamomile cultivars were different to amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments under field conditions. The different response of chamomile cultivars can be attributed to genotype and planting environmental conditions (53). So that, the chamazulene and α-bisabolol contents were increased in Bona, Bodegold and Lianka cultivars under foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments at the specific concentration.
The chamomile essential oil yield has significantly increased under PAW treatment in Bodegold and Lianka cultivars. Also, amino acid treatments have caused a significant enhance in the essential oil content in Bodegold and Lianka chamomile cultivars, so that it has increased about 3 times in Lianka cultivar. Secondary metabolites biosynthesis is not solely controlled genetically but is also severly influenced by environmental factors (9). On the basis of the previous studies, the essential oil content was varied between 0.24% to 2.0% in chamomile dried flowers (8).Variation in essential oil content and composition in Iran is attributed to the impact of genetic, environmental factors and agricultural practices (12). The chamomile essential oil yield is depend on genotype, climate, and agro-technical practices (12). Furthermore, it may be due to different responses of chamomile genotypes to specific concentrations and/or certain ranges of exogenous amino acid. Nitrogen affected the essential oil production via acetyl-CoA formation and carbon metabolism through the mevalonate pathway (54). Generally, PAW and amino acid fertilizer can influence the quantity and quality of chamomile essential oil. Probably, the ROS species (H2O2, NO2-, NO3- and dissolved O3-) generated by PAW causes to be active mechanisms of production of the antioxidant enzyemes.
In fact, plant secondary metabolites and essential oils have increased resulting from stress metabolisms. Velicka et al. (54) have investigated the changes in essential oil content and flavonoid content of different mint species after foliar application of amino acids in field conditions. They reported that the foliar spray with aromatic amino acids can enhance the essential oil conetnt, and total flavonoids, and also can change the mint essential oil odor profile. The effect of amino acids on the essential oil content was only found in M. piperita ‘Granada’ plants (54).
The color of the extracted essential oil was blue to dark blue in our study which was in accordance with the previous works (55)(56). The bule color of the essential oil is ascribed to presence of chamazulene (3). In total, thirty-six costituents were recognised in three cultivar of chamomile treated with foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments where the most important ones include chamazulene, α-bisabolol, bisabolol oxides A and B, farnesene and α-bisabolonoxide A. Factors that influence the components, quantity and quality of extracted essential oil include isolation method, environmental conditions, nutrient condition, and some stresses (57). Flowering and the type of essential oil profile are also genetically controlled, but their amount depends on external factors.
The medicinal plant production is mostly depended on ecological conditions. So, monitoring and management of environmental parameters are very important (53). Some researchers showed that responce of the bis-aboloids to these situations was very intense while environmental conditions had no or only little effect on the yield of essential oil accumulation as well as on chamazulene content. However, they did not report any qualitative changes in the composition of essential oil due to experimental conditions (58)(53).
The bisabolol amount is depended to environmental conditions of growth but amount of chamazulene is more affected genetically in the chamomile essential oil (59)(60)(53). Besides the main effect of genetic factors, the environment has an important influence on the quantity and quality of essential oil.The increasing of chamazulene may attributed to interaction between genotype and environment and/or the impact of amino acid fertilizer on the expression of chamazulene controller genes, functional proteins and metabolic pathways. In addition, the amino acids signaling pathway is involved in biosynthesis of terpenoids including sesquiterpenoids (such as chamazulene), triterpenoids and diterpenoids (61). It has been reported thet the amount of chamazulene varies in different chamomile varieties in different years and climate conditions (62).
The content of α-bisabolol raises until full blooming stage which is due to the decrease in the amount of dicycloether and is not related to metabolism of the other substances (63). It seems that the temperature conditions have great impact on α-bisabolol content in chamomile flowers so that the highest amount of it occures during sunlight and sunset (60).
The environmental situation which is altered by chamomile plant ontogeny, and many other parameters are also known to have impact on chamomile essential oil yield and its composition (64). Results indicated the relative impact of amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments on essential oil, chamazulene and α-bisabolol contents. In general, the amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments were modified amount and composition of the essential oil of chamomile under field conditions. Changes in apigenin, as a flavonoid, are considered as a phytochemical adaptation to the abiotic and biotic environment (65). Previous research shows that the synthesis of apigenin is affected by various factors such as UV radiation, drought, ozone, plant pathogens and insecticides (66)(39). According to HPLC analysis, the apigenin content was improved under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study indicated that the foliar application of amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments caused a significant effect on the physiological traits including plant height, fresh flower and dried flower weight, chlorophyll a , b, carotenoids and biochemical parameters including total protein content and essential oil yield and phytochemical compounds of German chamomile under field conditions. But it had no significant effect on the carbon and hydrogen. However, the amino acid contents increased in response to apply foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW. It can be due to various responds of German chamomile varieties to special dosages or specific ranges of foliar amino acids fertilizer and PAW treatments. Nevertheless, the response of German chamomile cultivars was different to foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments under field conditions. Regarding these results, PAW accompanies foliar amino acid fertilizer can be proposed as a good candidate to produce an admissible yield in medicinal plants especially German chamomile. Findings of this research may support the positive effect of foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW on the improvement of quality and quantity of German chamomile essential oil yield and phytochemical compositions under field conditions. According to the obtained results, the application of PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatments caused great changes in amino acid values. Now, depending on the desired research goals, to increase the amount of each measured amino acids in German chamomile cultivars, PAW with special features and amino acid fertilizer with specific and optimal concentration can be selected and then applied. Morever, it sounds that more studies and experiments are needed to clarify biochemical functions of amino acid fertilizer concentrations and PAW in German chamomile cultivars. By comparing the results obtained from amino acid fertilizer and PAW, it can be concluded that PAW represents a promising method as a green technology in the crop production process.
Author Contributions
M.O., M.G. and I.S. conceived and designed the experiment; M.G., M.M. and M.O. carried out the experiments; M.G., M.O. and M.M. analyzed the data; M.G. and I.S. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; M.G., M.O. and I.S. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the director and technicians of the Darya Zist Kavosh Company, Abad City, Tangestan County, Bushehr Province, Iran, for the providing research field and experimental facilities in the present research. Plus, we declare our special thanks to the Persian Gulf Research and Study Institute, Persian Gulf University, Bushehr, Iran, for their valuable support and cooperation. Our special thanks also goes to Department of Ecology, Faculty of Humanities and Natural Sciences, University of Prešov, Prešov, 08001, Slovakia for providing seeds and valuable scientific advice during this investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ghasemi M, Modarresi M, Babaeian Jelodar N, Bagheri N, Jamali A. The Evaluation of Exogenous Application of Salicylic Acid on Physiological Characteristics, Proline and Essential Oil Content of Chamomile (Matricaria chamomila L.) under Normal and Heat Stress Conditions. Agriculture. 2016 Jul;6(3):31. [CrossRef]
- Salamon I, Ibraliu A, Kryvtsova M. Essential Oil Content and Composition of the Chamomile Inflorescences ( Matricaria recutita L.) Belonging to Central Albania. 2023.
- Ghasemi M, Jelodar NB, Modarresi M, Bagheri N, Jamali A. Increase of chamazulene and α-bisabolol contents of the essential oil of german chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla l.) using salicylic acid treatments under normal and heat stress conditions. Foods. 2016;5(3):1–14. [CrossRef]
- Shams-ardakani M, Ghannadi A, Rahimzadeh A, Asteraceae L, Garden B, Matricaria L. Volatile Constituents of Matricaria chamomilla L. from Isfahan, Iran traditionally have been used for the treatment macological effects of chamomile are mainly connected with its essential oil for its antispasmodic, antimicrobial and disinfective and a. Analysis. 2006;2(1):57–60.
- Gixhari B, Ibraliu A, Zhuri N. Variability of chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) populations as a valuable medicinal plant in Albania evaluated by morphological traits Documentation of Plant Genetic Resources and quality of characterization and evaluation data recorded in genebank datab. Albanian j agric sci [Internet]. 2019;(June). Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333995481.
- Šalamon, I. Effect of the internal and external factors on yield and qualitative quantitative characteristics of chamomile essential oil. Acta Hortic. 2007;749:45–64.
- Rafieiolhossaini, M.; Sodaeizadeh, H.; Adams, A.; De Kimpe, N.; Van Damme, P. Effects of planting date and seedling age on agro-morphological characteristics, essential oil content and composition of German chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) grown in Belgium. Ind Crop Prod. 2010;31:145–52.
- Salamon, I. Effect of the internal and external factors on yield and qualitative characteristics of chamomile essential oil. In: In Proceeding of the I International Symposium on Chamomile Research, Development and Production. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalian K, Abdoshah S, Khalighi-Sigaroodi F, Paknejad F. Physiological and phytochemical response to drought stress of German chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.). Plant Physiol Biochem PPB. 2011 Feb;49(2):201–7. [CrossRef]
- Baghalian K, Haghiry A, Naghavi MR, Mohammadi A. Effect of saline irrigation water on agronomical and phytochemical characters of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.). Sci Hortic. 2008;116:437–41. [CrossRef]
- Sharafzadeh S, Alizadeh O. German and roman chamomile. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2011;1(10):1–5.
- Salamon, I. Chamomile Biodiversity of the Essential oil Qualitative-Quantitative Characteristics. Springer Press. 2009;83–90. [CrossRef]
- Sashidhara, K.V. , Verma, S. R, Ram P. Essential oil composition of Matricaria recotita L. from the lower region of the Himalayas. Flavor Fragr J. 2006;21:274–6.
- Salamon I, Ibraliu A, Kryvtsova M. Essential Oil Content and Composition of the Chamomile Inflorescences (Matricaria recutita L.) Belonging to Central Albania. Horticulturae [Internet]. 2023;9(1). Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2311-7524/9/1/47.
- Omer EA, Ahl HAHS-A, Gendy AG El, Hussein MS. Effect of Amino Acids Application on Production, Volatile Oil and Chemical. J Appl Sci Res. 2013;9(4):3006–21.
- Nahed G, Abdel Aziz A, Mazher AM, Farahat MM. Response of Vegetative Growth and Chemical Constituents of Thuja orientalis L. Plant to Foliar Application of Different Amino Acids at Nubaria. J Am Sci. 2010;6(3):295–301.
- Puač N, Gherardi M, Shiratani M. Plasma agriculture: A rapidly emerging field. Plasma Process Polym. 2018;15(2):1–5. [CrossRef]
- Takashima K, Nor AS bin A, Ando S, Takahashi H, Kaneko T. Evaluation of plant stress due to plasma-generated reactive oxygen and nitrogen species using electrolyte leakage. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2021;60(1). [CrossRef]
- Stoleru V, Burlica R, Mihalache G, Dirlau D, Padureanu S, Teliban G-C, et al. Plant growth promotion effect of plasma activated water on Lactuca sativa L. cultivated in two different volumes of substrate. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2020;10(1):20920. [CrossRef]
- Varilla C, Marcone M, Annor GA. Potential of Cold Plasma Technology in Ensuring the Safety of Foods and Agricultural Produce : A Review. 2020;1–17. [CrossRef]
- Sajib SA, Billah M, Mahmud S, Miah M, Hossain F, Omar FB, et al. Plasma activated water: the next generation eco-friendly stimulant for enhancing plant seed germination, vigor and increased enzyme activity, a study on black gram (Vigna mungo L.). Plasma Chem Plasma Process [Internet]. 2020;40(1):119–43. [CrossRef]
- Feng X, Ma X, Liu H, Xie J, He C, Fan R. Argon plasma effects on maize: pesticide degradation and quality changes. J Sci Food Agric [Internet]. 2019 Sep 14;99(12):5491–8. [CrossRef]
- Sayed WAA, Hassan RS, Sileem TM, Rumpold BA. Impact of plasma irradiation on Tribolium castaneum. J Pest Sci (2004) [Internet]. 2021;(0123456789). [CrossRef]
- Li, H. measurements of electron energy distribution function and neutral gas temperature in an inductively coupled plasma. University of Saskatchewan; 2006.
- Chen T, Liang J, Su T. Plasma-activated water : antibacterial activity and artifacts ? Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018;25(27):26699–706.
- Škarpa, P. , Klofáč D., Krčma F., Šimečková J., Kozáková Z. Effect of Plasma Activated Water Foliar Application on Selected Growth Parameters of Maize (Zea mays L.). Water 2020. 2020;12(12):3512. [CrossRef]
- Mandici A, Cretu DE, Burlica R, Astanei D, Beniuga O, Rosu C, et al. Preliminary Study on the Impact of Non-Thermal Plasma Activated Water on the Quality of Triticum aestivum L. cv. Glosa Sprouts. Horticulturae. 2022;8(12).
- Bormashenko E, Grynyov R, Bormashenko Y, Drori E. Modifies Wettability and Germination. 2012;3–10.
- Soni A, Choi J, Brightwell G. Plasma-activated water (PAW) as a disinfection technology for bacterial inactivation with a focus on fruit and vegetables. Foods. 2021;10(1):1–13. [CrossRef]
- Thirumdas R, Kothakota A, Annapure U, Siliveru K. Plasma activated water (PAW): Chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci Technol [Internet]. 2018;77(May):21–31. [CrossRef]
- Punith N, Harsha R, Lakshminarayana R, Hemanth M, S. Anand M, Dasappa S. Plasma Activated Water Generation and its Application in Agriculture. Adv Mater Lett. 2019;10(10):700–4. [CrossRef]
- Tsoukou E, Bourke P, Boehm D. Temperature stability and effectiveness of plasma-activated liquids over an 18 months period. Water (Switzerland). 2020;12(11):1–18. [CrossRef]
- Lin CM, Chu YC, Hsiao CP, Wu JS, Hsieh CW, Hou CY. The optimization of plasma-activated water treatments to inactivate Salmonella enteritidis (ATCC 13076) on shell eggs. Foods. 2019;8(10). [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, HK. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzym. 1987;148:350–82. [CrossRef]
- Gill S, Willette S, B D, Jarvis J, Schaub T, VanLeeuwen D. Suboptimal Temperature Acclimation Affects Kennedy Pathway Gene Expression, Lipidome and Metabolite Profile of Nannochloropsis salina during PUFA Enriched TAG Synthesis. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(11):1–21.
- Ma X, Zhao D, Li X, Meng L. Chromatographic method for determination of the free amino acid content of chamomile flowers. Pharmacogn Mag. 2015;11(41):176–9. [CrossRef]
- Šalamon, I. The Slovak gene pool of German chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) and comparison in its parameters. Hortic Sci. 2004;31(2):70–5.
- Adams, P. R. Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy. IL: Allured, Carol Stream; 2007.
- Baghalian K, Haghiry A, Naghavi MR, Mohammadi A. Effect of saline irrigation water on agronomical and phytochemical characters of chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.). Sci Hortic (Amsterdam). 2008;116(4):437–41. [CrossRef]
- Kučerová K, Henselová M, Slováková Ľ, Hensel K. Effects of plasma activated water on wheat: Germination, growth parameters, photosynthetic pigments, soluble protein content, and antioxidant enzymes activity. Plasma Process Polym. 2019;16(3):1–14. [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, L. Yield and Essential Oil Components in Common Chamomile (Chamomilla recutita (L.) Rauschert ) Cultivars Grown in Southern Italy. J Herbs Spices Med Plants. 2002;37–41. [CrossRef]
- Circella, G.; De Mastro, G.; Nano, G.M.; D’Andrea, L. Comparison of Chamomile Biotypes (chamomilla recutal. Rauschert). In: In Proceeding of the WOCMAP I-Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Conference. 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Gálvez A, Viera I, Roca M. Carotenoids and Chlorophylls as Antioxidants. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2020 Jun;9(6). [CrossRef]
- Gill SS, Willette S, Dungan B, Jarvis JM, Schaub T, Van Leeuwen DM, et al. Suboptimal temperature acclimation affects kennedy pathway gene expression, lipidome and metabolite profile of nannochloropsis salina during PUFA enriched TAG synthesis. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(11):1–21.
- Fait A, Nesi AN, Angelovici R, Lehmann M, Pham PA, Song L, et al. Targeted enhancement of glutamate-to-γ-aminobutyrate conversion in Arabidopsis seeds affects carbon-nitrogen balance and storage reserves in a development-dependent manner. Plant Physiol. 2011 Nov;157(3):1026–42. [CrossRef]
- Hu W, Coomer TD, Loka DA, Oosterhuis DM, Zhou Z. Potassium deficiency affects the carbon-nitrogen balance in cotton leaves. Plant Physiol Biochem [Internet]. 2017;115:408–17. [CrossRef]
- Sajib SA, Billah M, Mahmud S, Miah M, Hossain F, Omar FB, et al. Plasma activated water: the next generation eco-friendly stimulant for enhancing plant seed germination, vigor and increased enzyme activity, a study on black gram (Vigna mungo L.). Plasma Chem Plasma Process [Internet]. 2020;40(1):119–43. [CrossRef]
- Lo Porto C, Ziuzina D, Los A, Boehm D, Palumbo F, Favia P, et al. Plasma activated water and airborne ultrasound treatments for enhanced germination and growth of soybean. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol [Internet]. 2018;49(May):13–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Cheng JH, Sun DW. Enhancement of Wheat Seed Germination, Seedling Growth and Nutritional Properties of Wheat Plantlet Juice by Plasma Activated Water. J Plant Growth Regul [Internet]. 2022;(0123456789). [CrossRef]
- Rossi S, Chapman C, Yuan B, Huang B. Improved heat tolerance in creeping bentgrass by γ-aminobutyric acid, proline, and inorganic nitrogen associated with differential regulation of amino acid metabolism. Plant Growth Regul [Internet]. 2021;93(2):231–42. [CrossRef]
- Rossi S, Chapman C, Huang B. Suppression of heat-induced leaf senescence by γ-aminobutyric acid, proline, and ammonium nitrate through regulation of chlorophyll degradation in creeping bentgrass. Environ Exp Bot [Internet]. 2020;177:104116. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098847220301428. [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Gawad HG, Mukherjee S, Farag R, Abd Elbar OH, Hikal M, Abou El-Yazied A, et al. Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced signaling events and field performance associated with mitigation of drought stress in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Feb;16(2):1853384.
- Rafieiolhossaini M, Sodaeizadeh H, Adams A, De Kimpe N, Van Damme P. Effects of planting date and seedling age on agro-morphological characteristics, essential oil content and composition of German chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L.) grown in Belgium. Ind Crops Prod. 2010;31(1):145–52.
- Velička A, Tarasevičienė Ž, Hallmann E, Kieltyka-Dadasiewicz A. Impact of Foliar Application of Amino Acids on Essential Oil Content, Odor Profile, and Flavonoid Content of Different Mint Varieties in Field Conditions. Plants. 2022;11(21):2938. [CrossRef]
- Bita CE, Gerats T. Plant tolerance to high temperature in a changing environment : scientific fundamentals and production of heat stress-tolerant crops. Front Plant Sci. 2013;4:1–18. [CrossRef]
- Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR. Heat tolerance in plants: An overview. Environ Exp Bot. 2007;61:199–223. [CrossRef]
- Rowshan V, Khoi MK, Javidnia K. Effects of Salicylic Acid on Quality and Quantity of Essential oil Components in Salvia macrosiphon. 2010;4(11):77–82.
- Salamon, I. Effect of the internal and external factors on Yield and qualitative characteristics of Chamomile Essential oil. In: ISHS Acta Horticulture 749: I International Symposium on Chamomile Research, Development and Prodution. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Honcariv R, Repcak M. Chemotypes of Matricaria Chamomilla L. Herba Pol. 1979;25:261–7.
- Mann C, Staba E. The Chemistry, Pharmacology, Commercial Formulation of Chamomile. Herbs Spices Med Plants. 1975;1:235–79.
- F S, Hadian J HM, A M, M G, R G. Effects of Exogenous Salicylic Acid Application on Growth, Metabolic Activities and Essential Oil Composition of Satureja khuzistanica Jamzad. J Med Plants. 2013;12(47):70–82.
- Galambosi B, Repcok M. Varition The Yield and essential oil of four chamomile varieties grown in Finland in 1985-1988. J Agric. 1991.
- Letchamo, W. A Comparative Study of Chamomile yield Essential oil Flavonoides Content under two sowing season and nitrogen levels. Herbs Spices Med plants. 1992;2:342–52.
- Kwiatkowski, CA. Yield and quality of chamomile (Chamomilla recutita (L.) Rausch.) raw material depending on selected foliar sprays and plant spacing. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus. 2015;14(1):143–56.
- Dixon, R. , Paiva N. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7. 1995;1085–97.
- Nikolova MT, Ivancheva SV. Quantitative flavonoid variations of Artemisia vulgaris L. and Veronica chamaedrys L. in relation to altitude and polluted environment. Acta Biol Szeged. 2005;49:29–32.
Figure 1.
The geographical map of experiment location in Abad city, Tangestan county, Bushehr province, Iran.
Figure 1.
The geographical map of experiment location in Abad city, Tangestan county, Bushehr province, Iran.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of PAW device.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of PAW device.
Figure 3.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Bona cultivar.
Figure 3.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Bona cultivar.
Figure 4.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Bodegold cultivar.
Figure 4.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Bodegold cultivar.
Figure 5.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Lianka cultivar.
Figure 5.
Effect of different treatments of amino acid fertilizer and plasma activated water on amino acid profile for Lianka cultivar.
Figure 6.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of chamazulene of German chamomile oil for Lianka cultivar treated with 1 ml·L−1 amino acid treatment.
Figure 6.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of chamazulene of German chamomile oil for Lianka cultivar treated with 1 ml·L−1 amino acid treatment.
Figure 7.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of α-bisabolol of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 7.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of α-bisabolol of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 8.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide A of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under control treatment.
Figure 8.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide A of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under control treatment.
Figure 9.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide B of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 9.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolol oxide B of German chamomile oil for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 10.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolone oxide A of German chamomile oil is presented for Bodegold cultivar treated with 1 ml·L−1 amino acid treatment.
Figure 10.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of bisabolone oxide A of German chamomile oil is presented for Bodegold cultivar treated with 1 ml·L−1 amino acid treatment.
Figure 11.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of β-farnesene of German chamomile oil for Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 11.
A typical GC-MS chromatogram of β-farnesene of German chamomile oil for Lianka cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 12.
The interaction of cultivar × fertilizer on apigenin content of German chamomile different cultivars and fertilizer treatments.
Figure 12.
The interaction of cultivar × fertilizer on apigenin content of German chamomile different cultivars and fertilizer treatments.
Figure 13.
A) A typical HPLC chromatogram of apigenin for Bona cultivar at the concentration of 2 ml.L-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. B) A typical HPLC chromatogram of apigenin for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Figure 13.
A) A typical HPLC chromatogram of apigenin for Bona cultivar at the concentration of 2 ml.L-1 amino acid fertilizer treatment. B) A typical HPLC chromatogram of apigenin for Bodegold cultivar under PAW treatment.
Table 1.
Chemical features for the soil of research field.
Table 1.
Chemical features for the soil of research field.
Table 2.
Meteorological data during the experimental year (2020–2021) for growth and development of chamomile in Abad city, Tangestan County, Bushehr province, Iran.
Table 2.
Meteorological data during the experimental year (2020–2021) for growth and development of chamomile in Abad city, Tangestan County, Bushehr province, Iran.
Table 3.
Chemical characteristics of the irrigation water used in this study.
Table 3.
Chemical characteristics of the irrigation water used in this study.
Table 4.
Chemical properties of PAW used in this experiment.
Table 4.
Chemical properties of PAW used in this experiment.
Table 5.
Compositions of Fuego Base (Amino acid) foliar fertilizer according to the guaranteed analysis presented on the fertilizer bottle, Manufactured by Grow More®, Gardena, California, USA.
Table 5.
Compositions of Fuego Base (Amino acid) foliar fertilizer according to the guaranteed analysis presented on the fertilizer bottle, Manufactured by Grow More®, Gardena, California, USA.
Table 6.
Spraying dates of chamomile plants using amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments under field conditions.
Table 6.
Spraying dates of chamomile plants using amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments under field conditions.
Table 7.
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) for physiological and biochemical traits of German chamomile under amino fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 7.
The analysis of variance (ANOVA) for physiological and biochemical traits of German chamomile under amino fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 8.
Mean comparison of the interaction of cultivar × fertilizer on physiological and biochemical parameters of German chamomile under amino fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 8.
Mean comparison of the interaction of cultivar × fertilizer on physiological and biochemical parameters of German chamomile under amino fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 9.
Identified phytochemical compounds in the chamomile essential oil treated with foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 9.
Identified phytochemical compounds in the chamomile essential oil treated with foliar amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 10.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for identified phytochemical compounds of German chamomile cultivars under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 10.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for identified phytochemical compounds of German chamomile cultivars under amino acid fertilizer and PAW treatments.
Table 11.
Duncan analysis for major phytochemical compositions of German chamomile cultivars under PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatments.
Table 11.
Duncan analysis for major phytochemical compositions of German chamomile cultivars under PAW and amino acid fertilizer treatments.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).