Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
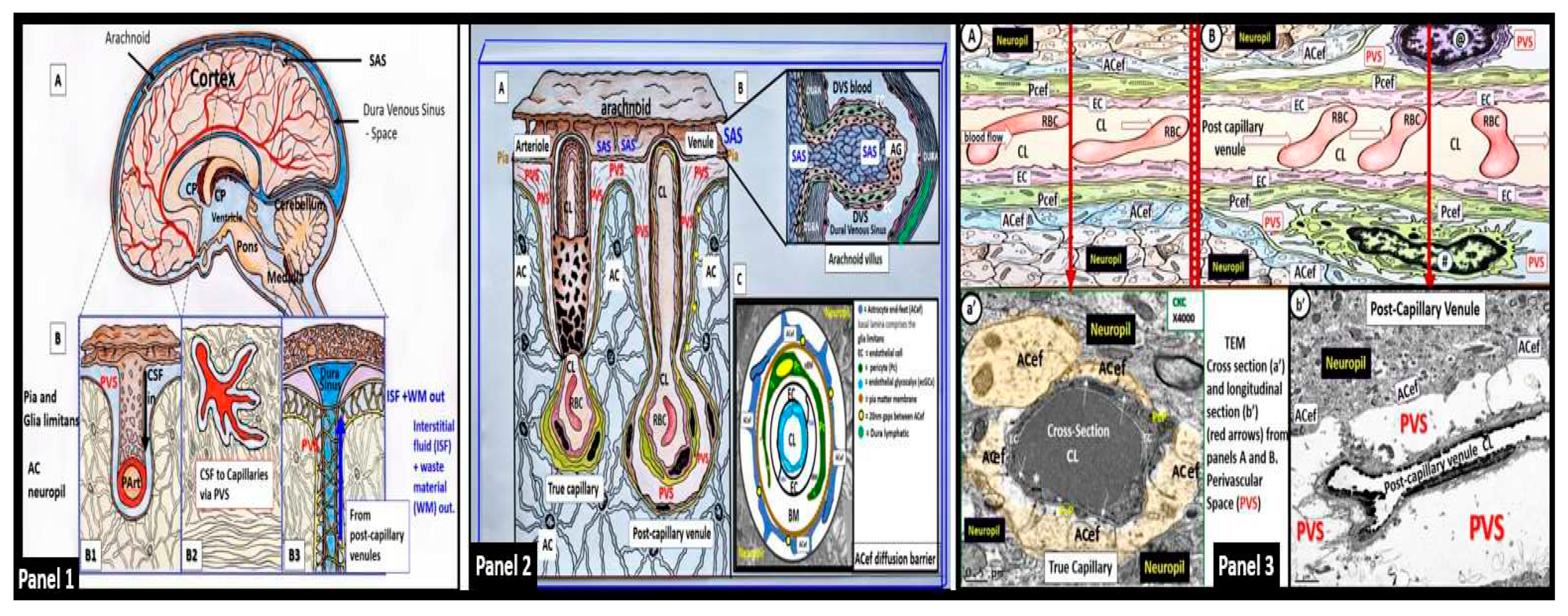
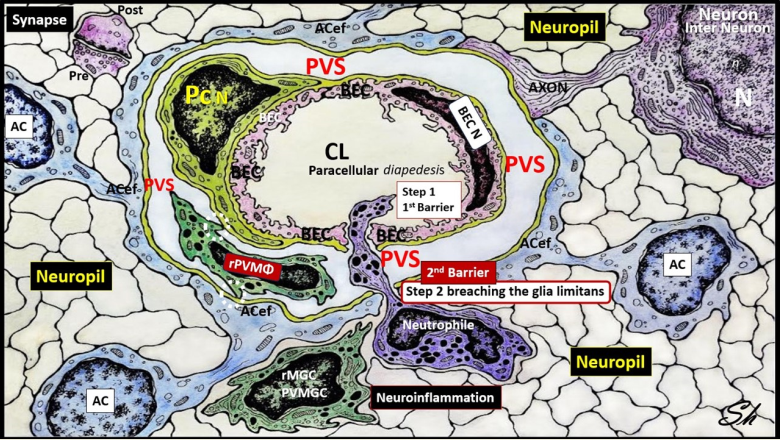
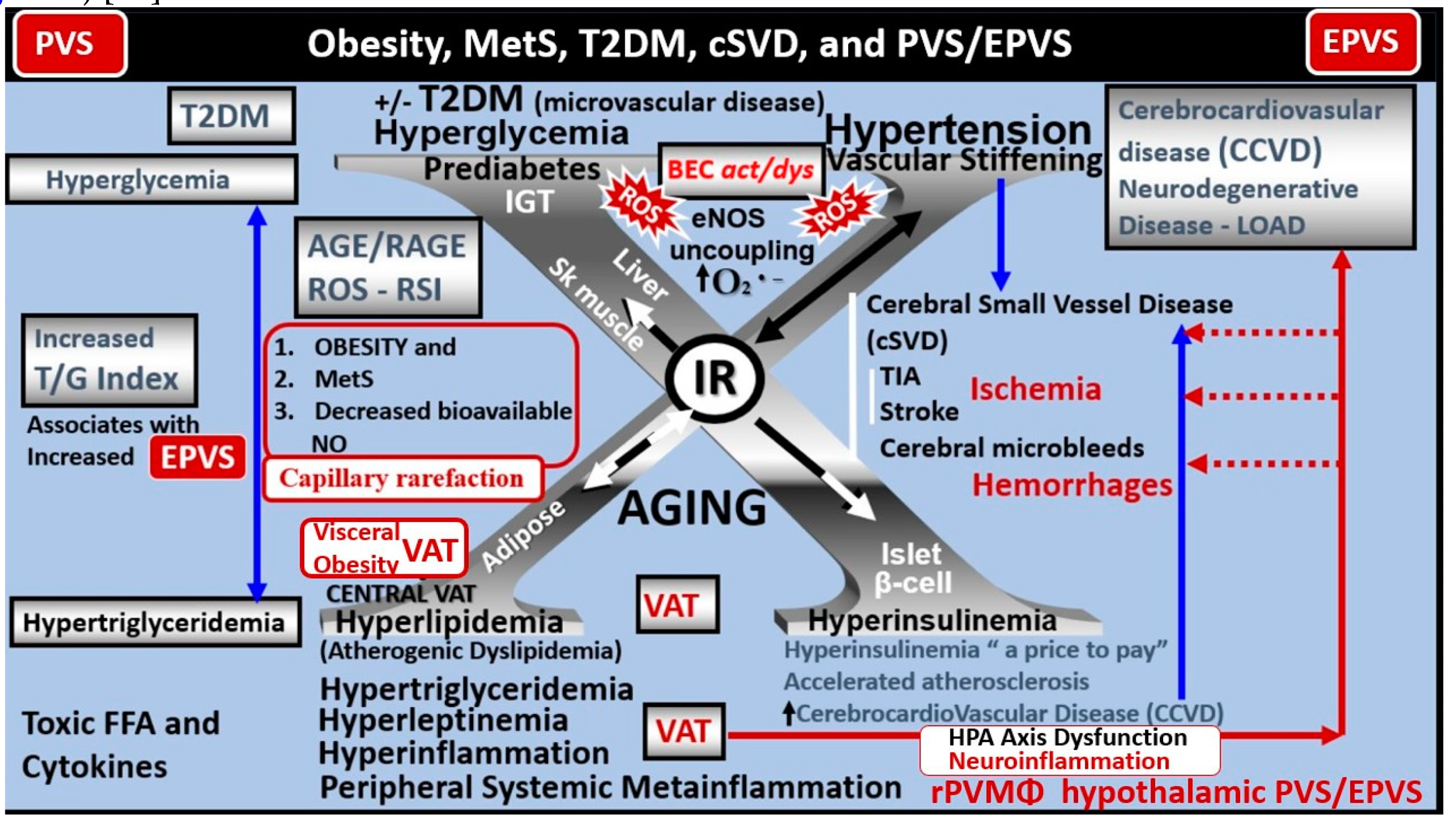
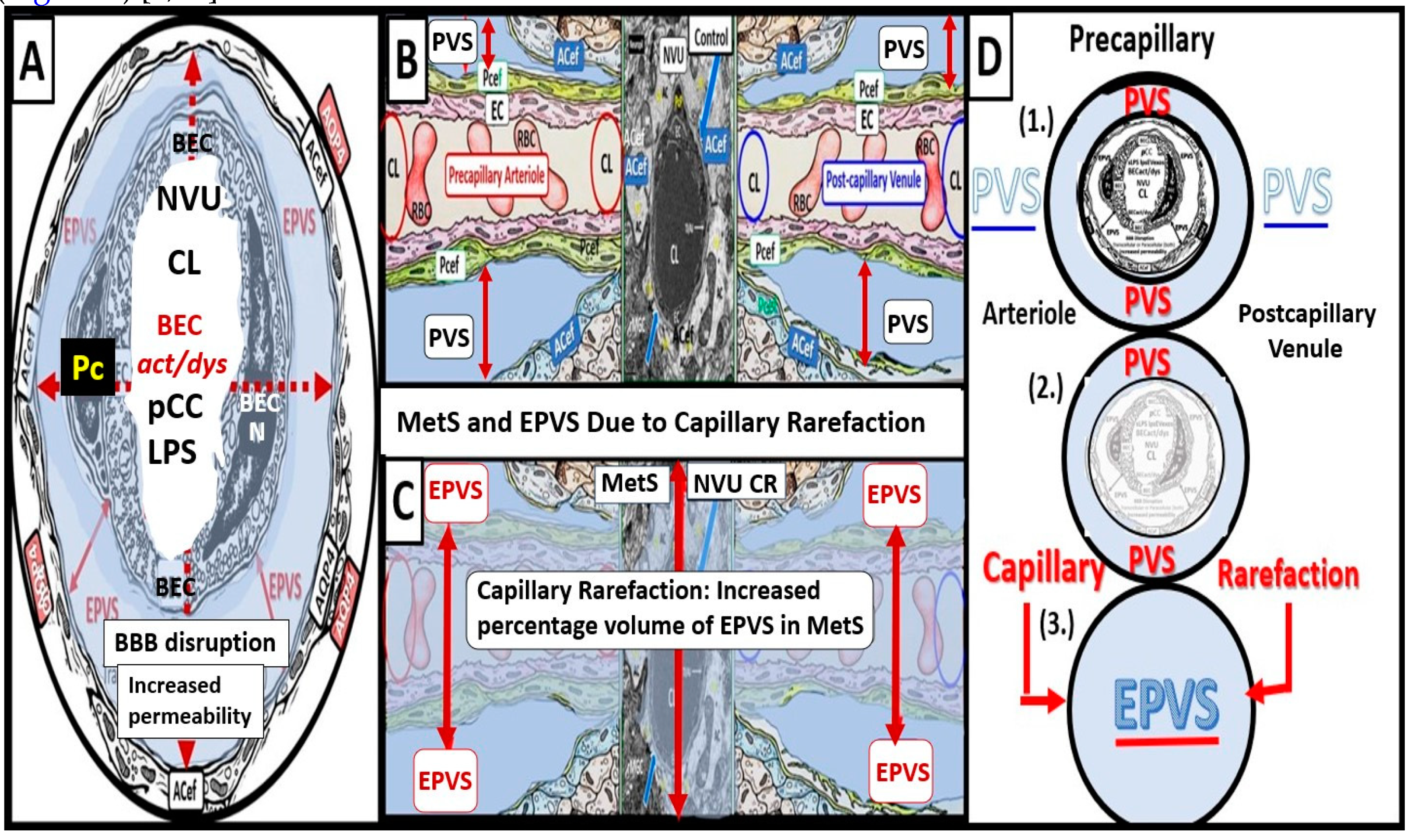
2. The PVS as an Anatomical Crossroads and Spaces that Provide Multicellular Crosstalk to Facilitate the Development of EPVS
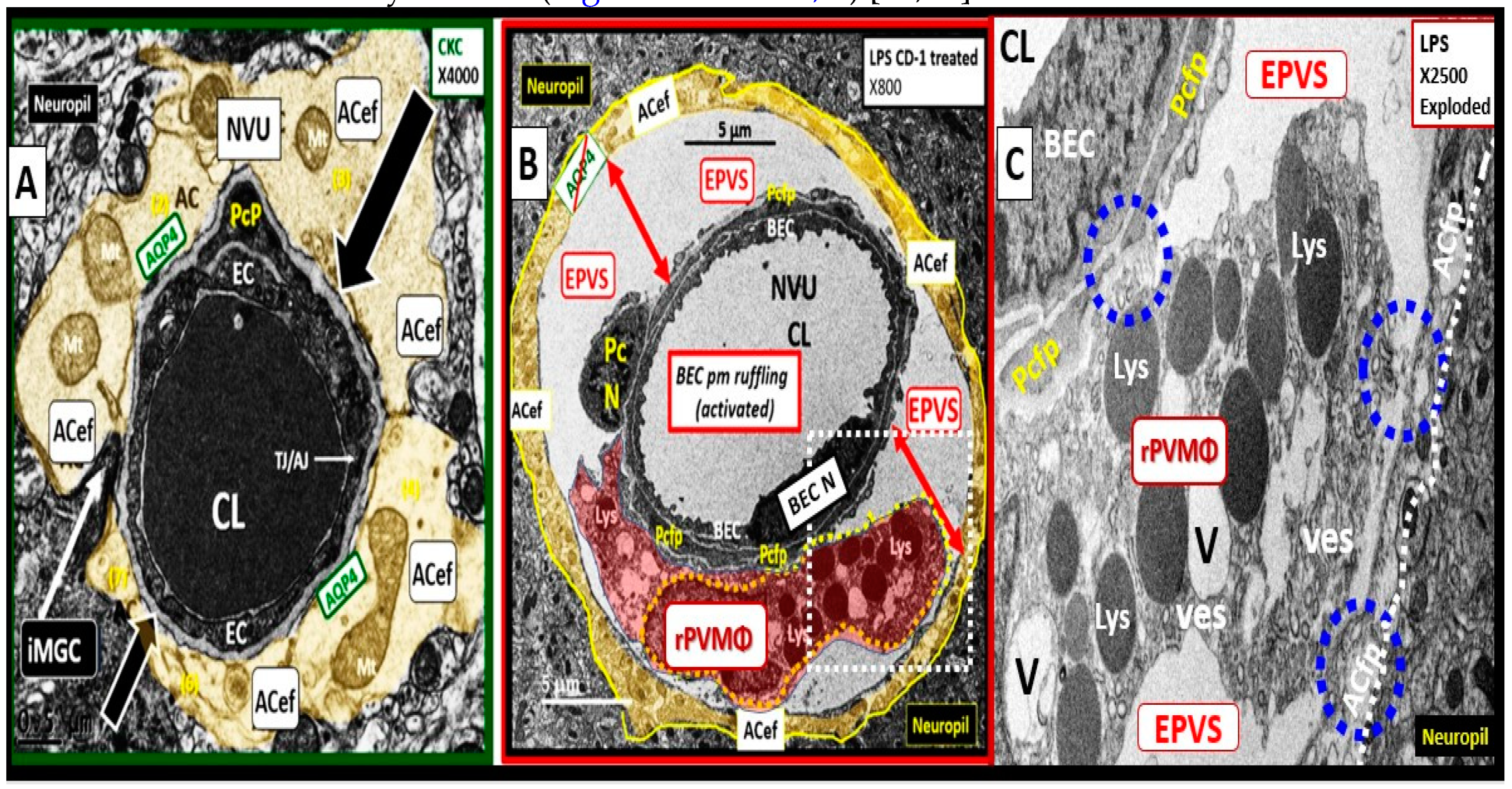
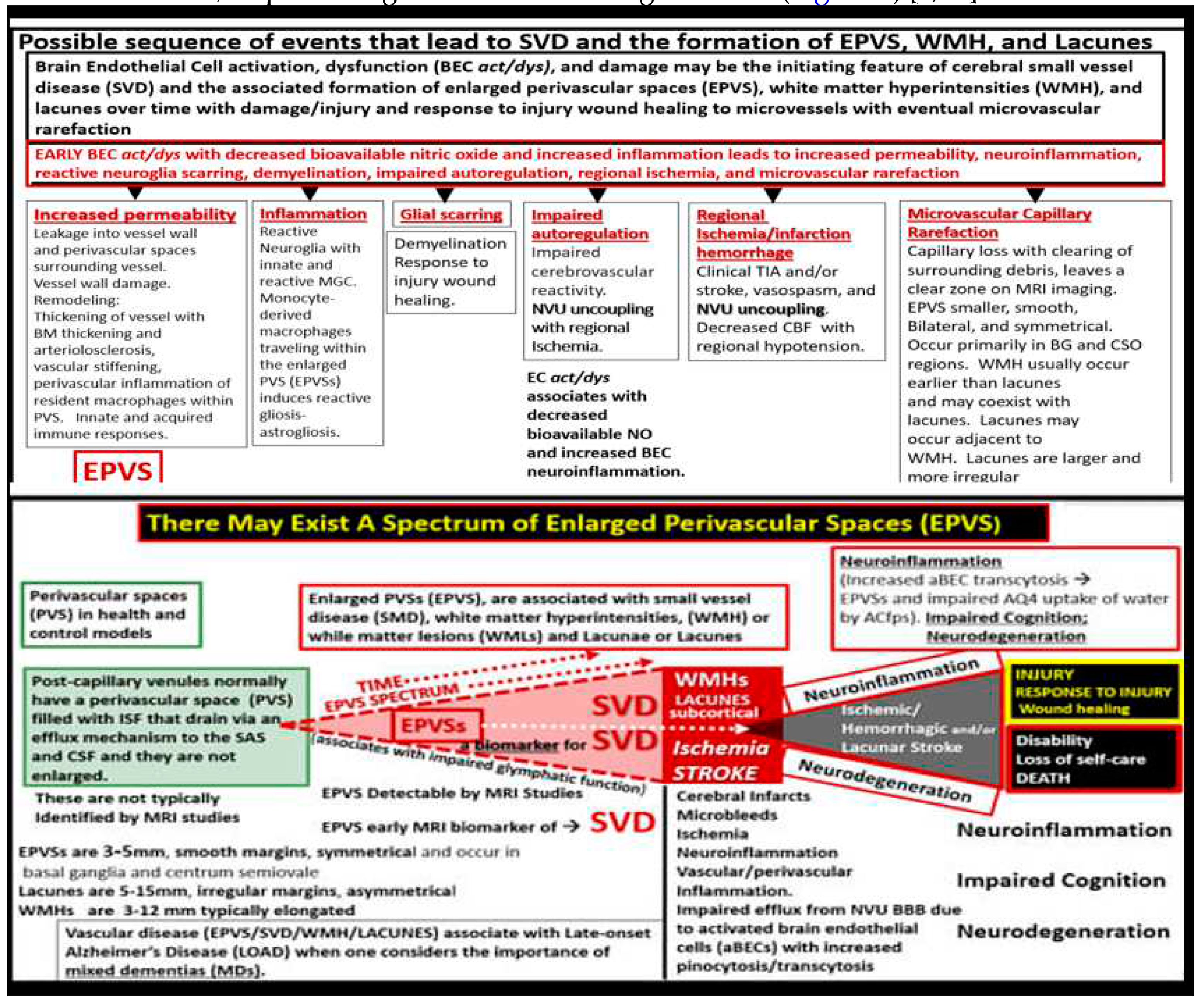
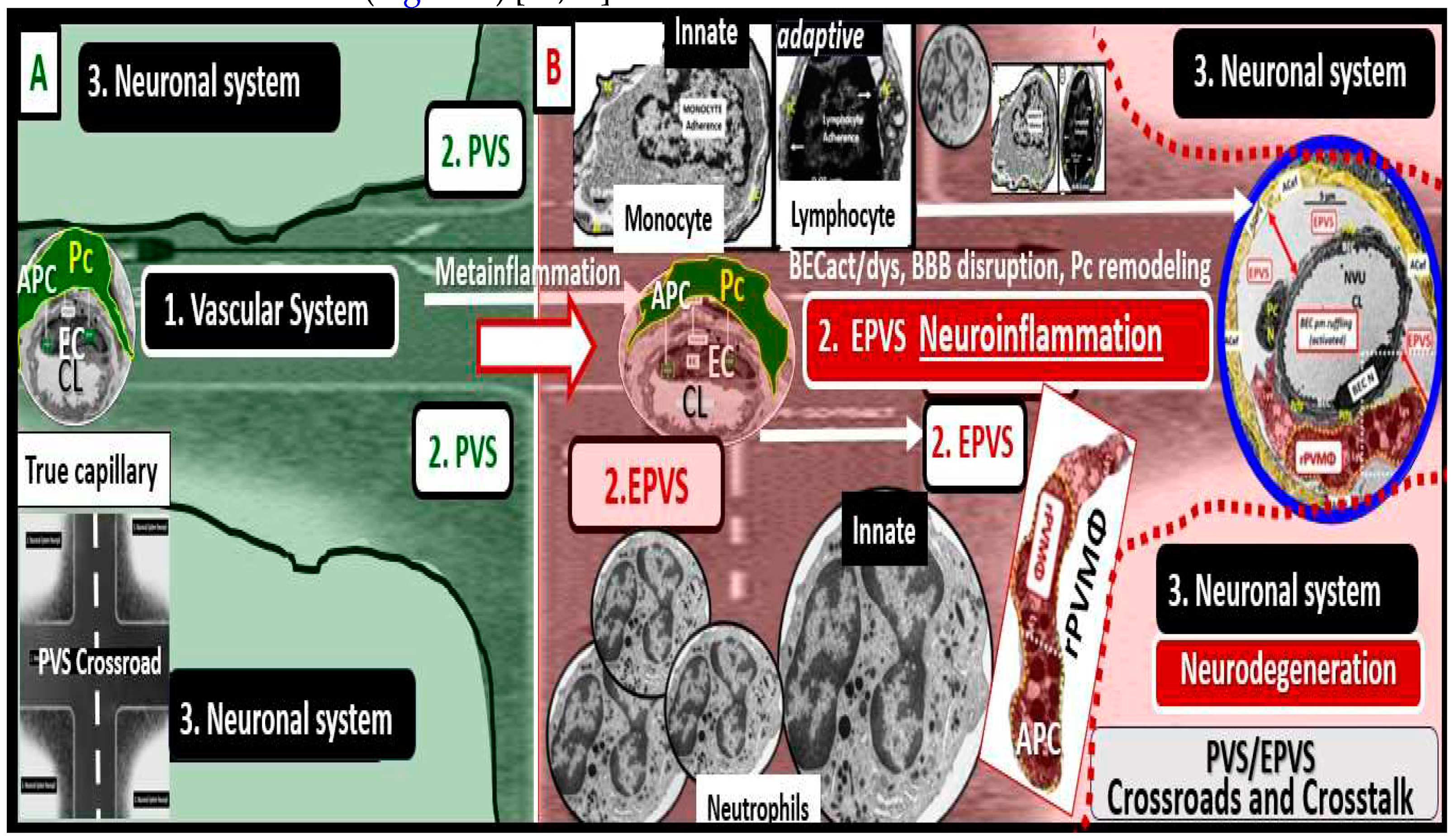
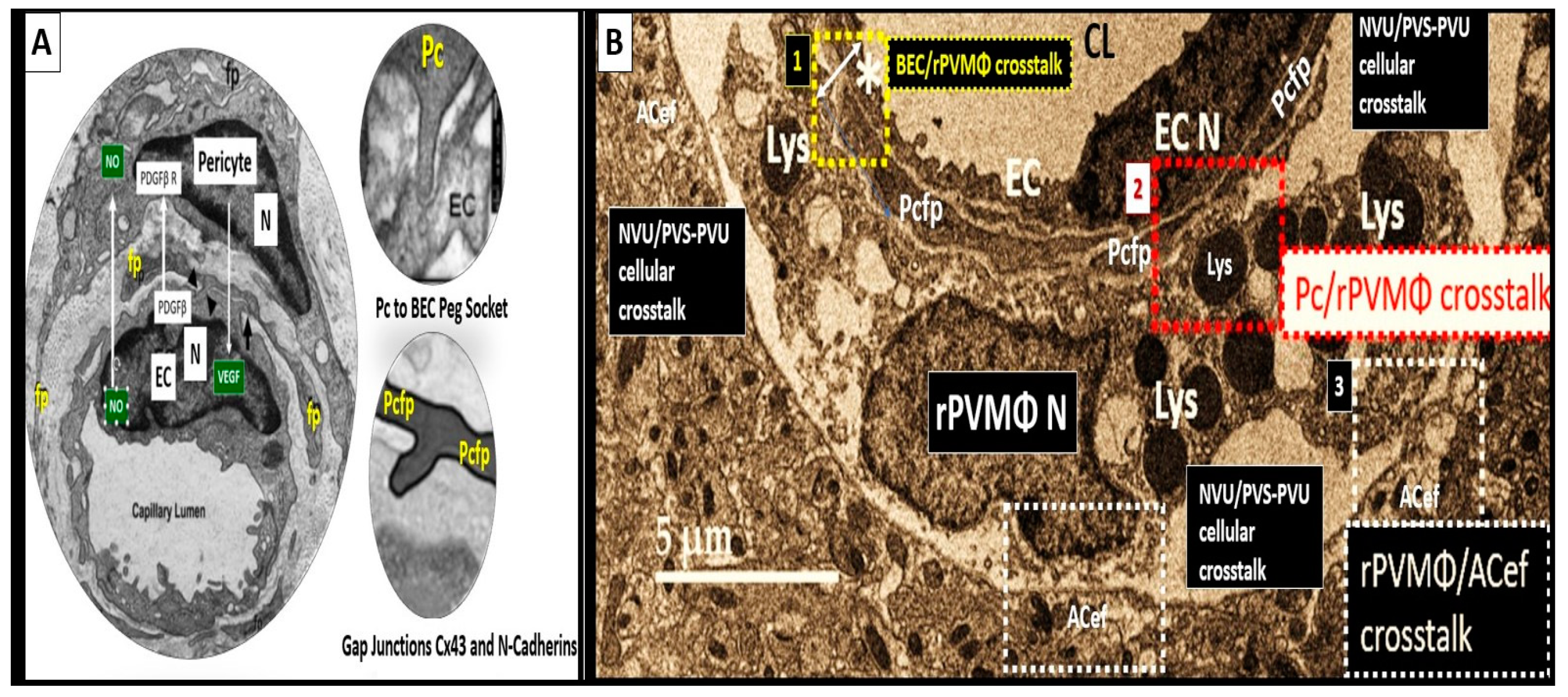
2.1. Reactive Juxtavascular Microglia Cells (rJVMGCs), Neuroinflammation, and Enlarged Perivascular Spaces (EPVS)
3. Conclusion
Abbreviations:
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, E.T.; Inman, B.E.; Weller, R.O. Interrelationships of the pia mater and the perivascular (Virchow-Robin) spaces in the human cerebrum. J. Anat. 1990, 170, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bown, C.W.; Carare, R.O.; Schrag, M.S.; Jefferson, A.L. Physiology and Clinical Relevance of Enlarged Perivascular Spaces. Neurology. 2022, 98, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Benveniste, H.; Black, S.E.; Charpak, S.; Dichgans, M.; Joutel, A.; Nedergaard, M.; Smith, K.J.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Wardlaw, J.M. Understanding the role of the perivascular space in cerebral small vessel disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, O’Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, et al. A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; He, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. Perivascular Spaces, Glymphatic System and MR. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 844938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, F.; Ballerini, L.; Wardlaw, J.M. Perivascular spaces and their associations with risk factors, clinical disorders and neuroimaging features: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Stroke. 2019, 14, 174749301983032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulyatnikova, T.; Hayden, M.R. Why are Perivascular Spaces Important? Medicina (Kaunas). 2023, 59, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubal FN, Maclullich AMJ, Ferguson KJ, Dennis MS, Wardlaw JM. Enlarged Perivascular Spaces on MRI Are a Feature of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Stroke. 2010, 41, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney MD, Montagne A, Sagare AP, Nation DA, Schneider LS, Chui HC, et al. Vascular dysfunction-The disregarded partner of Alzheimer's Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2019, 15, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, C.M.J.; Klarenbeek, P.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Staals, J. Association between Perivascular Spaces and Progression of White Matter Hyperintensities in Lacunar Stroke Patients. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0137323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, P.; Trippier, S.; Lawrence, A.J.; Lambert, C.; Zeestraten, E.; Williams, O.A.; Patel, B.; Morris, R.G.; Barrick, T.R.; MacKinnon, A.D.; Markus, H.S. Lacunar Infarcts, but Not Perivascular Spaces, Are Predictors of Cognitive Decline in Cerebral Small-Vessel Disease. Stroke. 2018, 49, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arba F, Quinn TJ, Hankey GJ, Lees KR, Wardlaw JM, Ali M, et al. Enlarged perivascular spaces and cognitive impairment after stroke and transient ischemic attack. Int J Stroke. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Bokura, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, S. Distinguishing silent lacunar infarction from enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces: a magnetic resonance imaging and pathological study. J Neurol. 1998, 245, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, L.A.; Bauer, C.J.; Schwartz, L.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Morgello, S.; Deck, M.D. Large Virchow-Robin spaces: MR-clinical correlation. Am J Neuroradiol. 1989, 10, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trolli, F.; Cipollini, V.; Moci, M.; Morena, E.; Palotai, M.; Rinaldi, V.; Romano, C. Ristori G, Giubilei F, Salvetti M, Orzi F, Guttmann CRG, Cavallari M. Perivascular Unit: This Must Be the Place. The Anatomical Crossroad Between the Immune Vascular and Nervous System. Front Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Tzourio, C.; Soumaré, A.; Mazoyer, B.; Dufouil, C.; Chabriat, H. Severity of dilated Virchow-Robin spaces is associated with age, blood pressure, and MRI markers of small vessel disease: a population-based study. 2010, 41, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.R. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Increases The Risk of Late-Onset Alzheimer's Disease: Ultrastructural Remodeling of the Neurovascular Unit and Diabetic Gliopathy. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.; Rundek, T.; Ekind, M.S.V.; Sacco, R.L.; Wright, C.B. Perivascular Spaces Are Associated with Atherosclerosis: An Insight from the Northern Manhattan Study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, G.; Boulouis, M.P.; Frosch, J.C.; Baron, M.; Pasi, J.F.; Albucher, B.; et al. The Boston criteria version 2.0 for cerebral amyloid angiopathy: a multicentre, retrospective, MRI–neuropathology diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilor-Tejedor, N.; Ciampa, I.; Operto, G.; Falcón, C.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Crous-Bou, M.; et al. Perivascular spaces are associated with tau pathophysiology and synaptic dysfunction in early Alzheimer's continuum. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Gaubert, A.; Yew, B.; Jang, J.Y.; Dutt, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Enlarged perivascular spaces and plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio in older adults without dementia. Neurobiol Aging. 2023, 128, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, G.; Kim, H.J.; Fox, Z.; Jäger, H.R.; Wilson, D.; Charidimou, A.; Na, H.K.; Na, D.L.; Seo, S.W.; Werring, D.J. MRI-visible perivascular space location is associated with Alzheimer's disease independently of amyloid burden. Brain. 2017, 140, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passiak, B.S.; Liu, D.; Kresge, H.A.; Cambronero, F.E.; Pechman, K.R.; Osborn, K.E.; et al. Perivascular spaces contribute to cognition beyond other small vessel disease markers. 2019, 92, e1309–e1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudie, J.D.; Rauschecker, A.M.; Nabavizadeh, S.A.; Mohan, S. Neuroimaging of Dilated Perivascular Spaces: From Benign and Pathologic Causes to Mimics. J neuroimaging. 2018, 28, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradise, M.; Crawford, J.D.; Lam, B.C.P.; Wen, W.; Kochan, N.A.; Makkar, S.; Dawes, L.; Trollor, J.; Draper, B.; Brodaty, H.; Sachdev, P.S. Association of Dilated Perivascular Spaces With Cognitive Decline and Incident Dementia. Neurology. 2021, 96, e1501–e1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okar, S.V.; Hu, F.; Shinohara, R.T.; Beck, E.S.; Reich, D.S.; Ineichen, B.V. The etiology and evolution of magnetic resonance imaging-visible perivascular spaces: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Front in Neuroscience. 2023, 17, 1038011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.R. Brain Endothelial Cells Play a Central Role in the Development of Enlarged Perivascular Spaces in the Metabolic Syndrome. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023, 59, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.R. Overview and New Insights into the Metabolic Syndrome: Risk Factors and Emerging Variables in the Development of Type 2 Diabetes and Cerebrocardiovascular Disease. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023, 59, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javierre-Petit, C.; Schneider, J.A.; Kapasi, A.; Makkinejad, N.; Tamhane, A.A.; Leurgans, S.E.; Mehta, R.I.; Banes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Arfanakis, K. Neuropathologic and Cognitive Correlates of Enlarged Perivascular Spaces in a Community-Based Cohort of Older Adults. Stroke. 2020, 51, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucsek, Z.; Toth, P.; Tarantini, S.; Sosnowska, D.; Gautam, T.; Warrington, J.P.; Giles, C.B.; Wren, J.D.; Koller, A.; Ballabh, P.; et al. Aging exacerbates obesity-induced cerebromicrovascular rarefaction neurovascular uncoupling cognitive decline in mice, J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavonsalo S, Lackman MH, KaramanS. Capillary Rarefaction in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases—Organ Specificity and Possible Mechanisms. Cells. 2020, 9, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantler, P.D.; Shrader, C.D.; Tabone, L.E.; d’Audiffret, A.C.; Huseynova, K.; Brooks, S.D.; Branyan, K.W.; Grogg, K.A.; Frisbee, J.C. Cerebral Cortical Microvascular Rarefaction in Metabolic Syndrome is Dependent on Insulin Resistance and Loss of Nitric Oxide Bioavailability. Microcirculation 2015, 22, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.R. Brain Injury: Response to Injury Wound Healing Mechanisms and Enlarged Perivascular Spaces in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Preprints.org. 2023, 2023061202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dinther, M.; Voorter, P.H.M.; Jansen, J.F.A.; Jones, E.A.V.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Staals, J.; Backes, W.H. Assessment of microvascular rarefaction in human brain disorders using physiological magnetic resonance imaging. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022, 42, 718–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Ayyadurai, S.; Zlokovic, B.V. Pericytes of the neurovascular unit: Key functions and signaling pathways. Nat Neurosci. 2016, 19, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dore-Duffy P, Andre Katychev A, Xueqian Wang X, Van Buren E. CNS microvascular pericytes exhibit multipotential stem cell activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng L, Guo Y, Zhai X, Zhang YChen W, Zhu Z, Xuan W, Li P. CNS Perivascular macrophages in the CNS: From health to neurovascular diseases. Neurosci Ther. 2022, 28, 1908–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenhoven, J.; Jansson, D.; Smyth, L.C.; Dragunow, M. Brain Pericytes As Mediators of Neuroinflammation. Trends Pharmocol Sci. 2017, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, D.; Rustenhoven, J.; Feng, S.; Hurley, D.; Oldfield, R.L.; Bergin, P.S.; Mee, E.W.; Faull, R.L.M.; Dragunow, M. A role for human brain pericytes in neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2014, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Guo, R.; Zhang, F. Brain perivascular macrophages: Recent advances and implications in health and diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019, 25, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapenna, A.; De Palma, M.; Lewis, C.E. Perivascular macrophages in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018, 18, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, M.; Ookawara, S.; Kurihara, K. Uptake of exogenous substances and marked infoldings of the fluorescent granular pericyte in cerebral fine vessels. Am J Anat. 1980, 157, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Sugiyama, Y.; Lane, D.; Garcia-Bonilla, L.; Chang, H.; Santisteban, M.M.; et al. Perivascular macrophages mediate the neurovascular and cognitive dysfunction associated with hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2016, 126, 4674–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, T.; Bechmann, I.; Engelhardt, B. Perivascular Spaces and the Two Steps to Neuroinflammation. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurology. 2008, 67, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. Perivascular Spaces, Glymphatic System and MR. Front Neurol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergarrd, M. Garbage truck of the brain. Science 2013, 340, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Nedergaard, M. The Glymphatic System: A Novel Component of Fundamental Neurobiology. J Neurosci. 2021, 41, 7698–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennels, M.L.; Gregory, T.F.; Blaumanis, O.R.; Fujimoto, K.; Grady, P.A. Evidence for a ‘paravascular’ fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 1985, 326, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia-Freitas, K.; Bastos-Leite, A.J. Perivascular spaces and brain waste clearance systems: relevance for neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular pathology. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes; NF; Velloso, L. A. Perivascular macrophages in high-fat diet-induced hypothalamic inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2022, 19, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, L.; Viotti, A.; Martino, G. Microglia in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration: From Understanding to Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 15, 742065. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms Underlying Inflammation in Neurodegeneration. Cell. 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Joh, T.H. Microglia, major player in the brain inflammation: their roles in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2006, 38, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, W.J.; Mrak, R.E.; Griffin, W.S.T. Microglia and neuroinflammation: a pathological perspective. J Neuroinflammation. 2004, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charisis, S.; Rashid, T.; Liu, H.; Ware, J.B.; Jensen, P.N.; Austin, T.R.; et al. Assessment of Risk Factors and Clinical Importance of Enlarged Perivascular Spaces by Whole-Brain Investigation in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023, 6, e239196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Zhai, X.; Yunlu Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Trends in perivascular macrophages research from 1997 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis. 2023, 29, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca ACC, Matias D, Garcia C, Amaral R, Luiz Geraldo H, Freitas C, Souza Lima FR. The impact of microglial activation on blood-brain barrier in brain diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow SA,Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Butt, A.M. Neuroglia: Function and Pathology. 1st ed.; Academic Press. 125 London Wall, London EC2Y 5AS, United Kingdom 525 B Street. Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
- Augusto-Oliveira, M.; Arrifano, G.P.; Delage, C.I.; Tremblay, M.E.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E.; Verkhratsky, A. Plasticity of microglia. Biol. Rev. 2022, 97, 217–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.R. Hypothesis: Neuroglia Activation Due to Increased Peripheral and CNS Proinflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines with Neuroinflammation May Result in Long COVID. Neuroglia. 2021, 2, 7–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, R.N.; Low, R.J.; Akrami, A. A review of cytokine-based pathophysiology of Long COVID symptoms. Front Med (Lausanne) 2023, 10, 1011936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng Q, Li K, Luo X, Wang S, Xu X, Jiaerken Y, Liu X, Hong L, Hong H, Li Z, Fu Y, Zhang T, Chen Y, Liu Z, Huang P, Zhang M; for behalf of Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). The association of enlarged perivascular space with microglia-related inflammation and Alzheimer's pathology in cognitively normal elderly. Neurobiol Dis. 2022, 170, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineichen, B.V.; Okar, S.V.; Proulx, S.T.; Engelhardt, B.; Lassmann, H.; Reich, D.S. Perivascular spaces and their role in neuroinflammation. Neuron. 2022, 110, 3566–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




