1. Introduction
The Mediterranean Diet nutritional pattern is ranked as one of the healthiest worldwide, while scientific interest has turned around its role in maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases [
1]. One of the main components of the Mediterranean diet is assumed to be the high consumption of olive oil, which has been reported for its beneficial effect on secondary end points of cardiovascular disease (CVD). It has been reported that the frequent consumption of virgin olive oil may be the key to cardiovascular protection [
2]. In fact, large EPIC (European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition) cohorts indicate that olive oil consumption is inversely associated with mortality and incidence of CVD [
2,
3]. In addition, in the “Prevention with Mediterranean Diet” (PREDIMED) study, higher intake of polyphenols from Mediterranean diet sources, including olive oil, was associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic syndrome. [
4]. This beneficial role is related to its bioactive components, such as unsaturated fats, polyphenols, tocopherols etc., found in virgin and extra-virgin olive oil, but not in commercial, usual type [
2].
At this point, it is worth mentioning that, according to the European Council Regulation (1234/2007), olive oil is divided into four edible-commercial classes, categorized by organoleptic characteristics and quality: Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO), Virgin Olive Oil (VOO), olive oil consisting of Refined Olive Oil (ROO) and virgin olive oil and pomace olive oil [
5,
6]. Examining the content of these olive oil categories, although the fatty acid composition is similar, a gradation is observed in terms of total phenolic content [
7,
8]. Although ROO has the same glyceride composition as Virgin Olive Oil (VOO), its composition contains lower concentrations of α-tocopherol, squalene and hydroxytyrosol, degrading its antioxidant activity, compared to VOO and EVOO [
3,
13].
Recent research highlights the significance of studying the postprandial state, due to its relevance to atherosclerosis [
9]. A meal rich in saturated fat and carbohydrates induces a gradual increase in postprandial blood triglycerides and glucose levels. These conditions lead to the rapid induction of low-grade inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance, while at the same time an excessive production of free radicals by leukocytes is caused, increasing postprandial oxidative stress. These series of postprandial metabolic dysfunctions mentioned, is inextricably linked to high cardiometabolic risk [
10,
11]. Due to the important role of the aforementioned postprandial model to dietary intake and pathophysiology, scientific interest has turned around supplementation of high- fat meals with bioactive constituents [
10,
11].
In this context, the potential beneficial role of virgin olive oil on postprandial inflammation and metabolism, has been extensively studied. Carnevale et al. suggested that the supplementation of a lunch with EVOO may be associated with improved glycemic, lipidemic metabolism and oxidative stress status, in the postprandial state [
12]. Additionally, the previous results of a nutritional intervention demonstrated that the presence of olive paste polyphenols may lead to decreased, postprandial triacyclglycerols concentration [
13]. The protective role of virgin olive oil is mainly attributed to its potential antioxidant bioactivity, exerted by its functional components, such asoleic acid, tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein etc. [
14,
15].
However, given the variable composition of olive oil, it is observed that a large share of the olive oil market is occupied by ROO, due the low-cost technological interest from olive oil industries [
16]. Taking into account these data, in order to ensure the optimal intake of polyphenols through the usual diet, and under the sustainability prism, a novel strategy supports the enhancement of refined olive oil with bio-functional compounds, derived from the utilization of natural, food by-products [
13,
16]. Particularly, previous attempts to enrich the refined olive oil with polyphenols from olive leaves and pomace, but also from wastewater, resulted in a comparable phenolic content to virgin olive oil [
7,
8]. Latest strategies demonstrate the role of polyphenols intake to better management of dyslipidemia and other risk factors [
17]. Moreover, the findings of our previous clinical studies have shown that the supplementation of fatty and carbohydrate-rich meals, with orange peel polyphenols, may be an effective way to modulate postprandial endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress [
10,
18,
19].
Nevertheless, the polyphenolic content of the olive oil classes, may be reflected on graded cardiovascular modulation. A comparative clinical study from Khandouzi et al. demonstrated that the daily intake of ROO for six weeks led to higher levels of Low Density Lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-cholesterol), C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and selective inflammatory biomarkers, compared to the opposite effects of EVOO intake [
20]. Additionally, it has been mentioned that the consumption of ROO for three weeks led to relative higher oxidized LDL and hydroxy fatty acids levels, when compared with the corresponding effect of VOO, associated with the LDL-polyphenolic content [
21].
Despite the encouraging evidence presented by previous in vitro and clinical studies on refined olive oil enrichment, it is noteworthy the lack of scientific data observed, regarding the possible effect of a refined olive oil, enhanced with bioactive compounds, in the context of a high-fat and carbohydrates meal, on postprandial metabolic biomarkers.
So, the purpose of the present nutritional interventional study was to investigate whether the consumption of a conventional refined olive oil and a refined olive oil, enhanced with 10% w/v orange peel extract, have differential metabolic response on postprandial lipemia, glycemia and oxidative stress biomarkers, in cardiometabolic risk participants. The postprandial response of LDL-cholesterol concentration on the test meals, was set as the primary outcome of the present, pilot study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
After initial screening of 40 perspective volunteers, 21 participants at cardiometabolic risk, who met eligibility criteria, were enrolled in this nutritional intervention. Prerequisites for inclusion in the study, followed the criteria set by Mezhal et al. [
22] with some modifications. More specifically, these included participants to be between 30-65 years old and to satisfy at least three of the following parameters: to have been diagnosed with i) hypertension (Systolic pressure ≥ 140 mm Hg or diastolic pressure ≥ 90 mm Hg) and/or ii) High levels of Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)-cholesterol (≥130 mg/dL); and/or iii) Elevated plasma triglycerides (≥150 mg/dL); and/or iv) Central obesity (waist-to-hip ratio ≥0.85 for women and ≥ 0.90 for men); Lack of family history with myocardial infarction or sudden death in a 1st degree relative under 55 years old); and/or v) High fasting glucose (100-125 mg/dL). From this nutritional intervention-clinical study, were excluded individuals who were outside the above specified age limit (<30 or >65 years), were diagnosed with diabetes or were following an antidiabetic treatment. In addition, individuals with malignancies or liver disease were also excluded. Parallel participation in another clinical-interventional study, or history of inability to donate blood, were included in the exclusion criteria. Finally, taking antihypertensive medication and statins were not assumed as exclusion criteria.
2.2. Recruiting and screening
This interventional study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles defined by the Declaration of Helsinki, approved by the University of the Aegean Ethical Committee (Approval: 13902/15.06.2022). The study protocol was registered in the clinicaltrials.gov database, prior to participant recruitment and enrollment, with the identifier NCT05771571. The study was carried out between 12 May, 2022 and 19 May, 2022 in the Laboratory of Nutrition and Public Health of the University of the Aegean in Lemnos, Greece.
Participants were recruited via poster advertisements that was shared in social media. Between 2 and 3 weeks before prior to the clinical study, all prospective participants visited the Human Nutrition Unit, to test their eligibility. During initial screening, data on demographics, clinical history, general and nutritional habits were collected via personal interviews with the study researchers. In addition, anthropometric measurements (height, weight, body composition) using a body composition analyzer (Tanita SC 330, TANITA EUROPE B.V., Netherlands) and blood pressure determination using an automatic monitor (Omron HEM-7121, Omron Healthcare Co., Japan), were conducted.
All participants who met inclusion criteria were given a detailed explanation of the protocol and signed an informed consent.
2.3. Experimental design
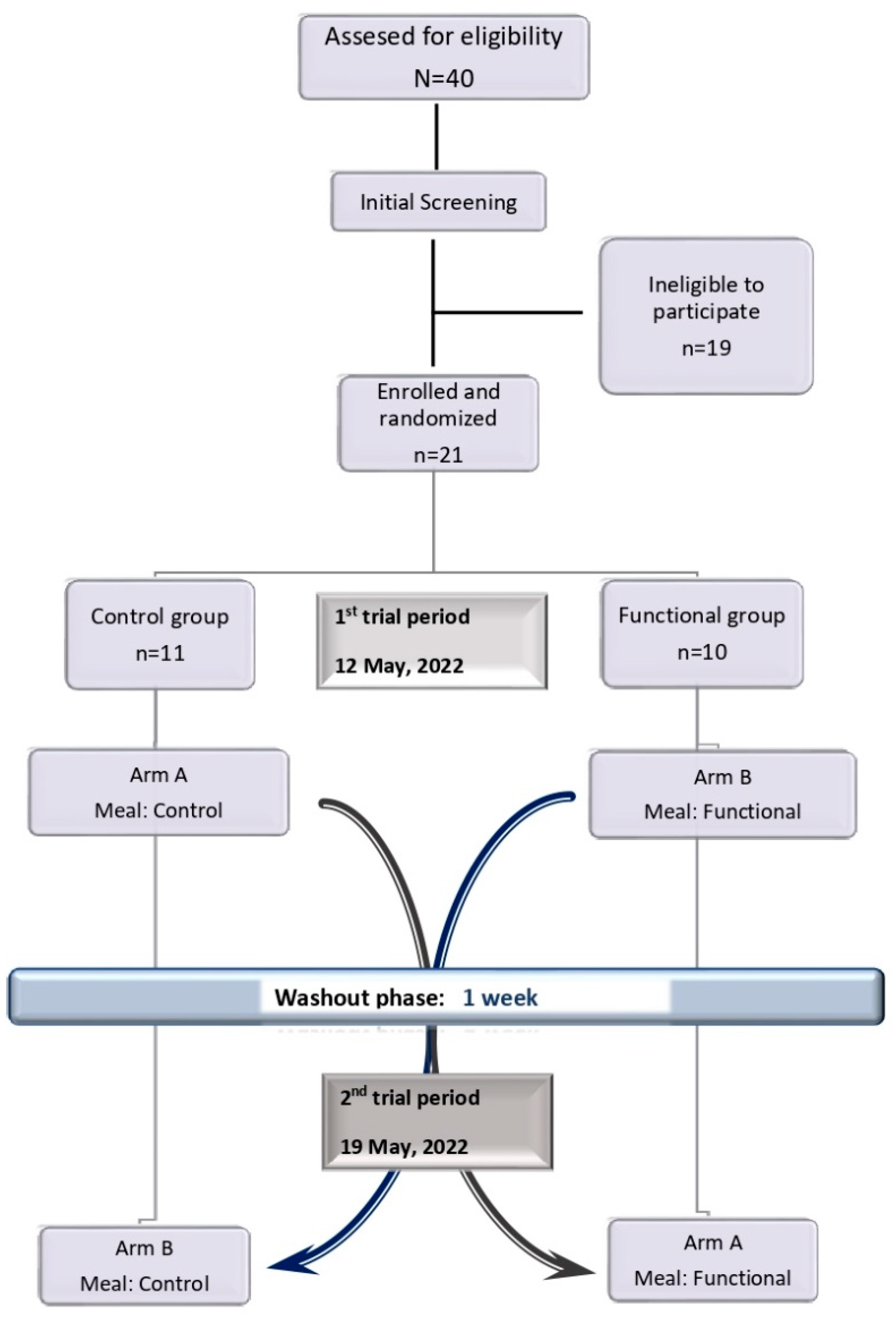
The study was a randomized, single-blinded, cross over, controlled nutritional intervention-clinical trial. The study included 2 trial periods, separated by a 1 washout week, throughout which participants followed their usual diet. Each enrolled participant took part in 2 tests from 9:00 am to 12:15 pm. Eligible participants were assigned to one of the different study arms of refined olive oil and novel refined olive oil consumption, enriched with orange peel extract, performing a computer-generated block randomization procedure (Microsoft Office 16 Excel, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond WA, USA). Each arm included a first meal assignment, followed by a washout phase of 1 week, and then by a second meal assignment. Study flow diagram of the nutritional intervention is presented in Σφάλμα! Το αρχείο προέλευσης της αναφοράς δεν βρέθηκε..
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram of the present study.
Figure 1.
Study flow diagram of the present study.
Enrolled participants were instructed, one week before the beginning of the study as well as throughout the trial period, to abstain from medication, nutritional supplementation and alcohol intake, as well as to maintain their usual physical activity level and diet patterns. Participants taking antihypertensive agents (n = 2), lipid-lowering drugs (n = 4), were instructed to continue the regimen. Furthermore, in order to increase the accuracy of determining the test meals effect, 12 hours prior to each trial period participants were asked to fasten; 24 hours prior to each trial period they were also asked not to consume polyphenol-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, wine, olive oil. Compliance with the instructions given for background diet was evaluated before each trial period, using a short, self-administrated questionnaire, including a 24-h dietary recall.
In the morning of the day of the trial, participants arrived at the study site (Human Nutrition Unit). Venous blood sampling was operated prior to the intervention-meal consumption (baseline) and at 30 min, 1.5 h & 3 h after the meal consumption. Participants stayed at the study site the entire time for 3 h and 15 min. Aiming to follow a cross-over design, participants were randomly enrolled in the Control or Functional group. Control group participants received the control meal in the first trial period, while in the second trial period they consumed the functional meal. Participants who enrolled in the Functional group, consumed the meals in the reverse order. The study meals were served in participant ID-labelled dishes, due to single-blinding process and to avoid possible bias on the part of the participants, knowing in advance the test meal.
All participants were requested to finish their meal within 15 minutes, under the supervision of the research team, as part of this controlled trial. After the meal consumption, participants remained seated in a waiting room, and they instructed not to consume any food or to smoke; they were allowed to drink water. Compliance with the instructions given was checked and recorded by the research team.
2.4. Test Meals
The test meals were prepared in the specially dedicated kitchen, at the facilities of the University of the Aegean, following a standardized protocol. Each component of the meal was weighted with accuracy, using a digital laboratory scale (OHAUS Scout SKX, USA). All food components were purchased from the local market of Lemnos. During the day of the trial, each participant consumed a meal consisted of mashed potatoes prepared as follows: potatoes were boiled in unsalted water, smashed with a fork, and served in portions of 250 g (45.53 g net carbohydrates). The mashed potatoes were then mixed thoroughly with 50 mL of refined olive oil (control meal) or with 50 mL of the novel refined olive oil, enhanced with 10% w/v orange peel extract (functional meal).
The novel, refined olive oil was prepared by an ultrasonic extraction (30 min, 30 °C), adding 10 g of orange peel to 100 mL refined olive oil, according to Soares et al. [
23]. Preliminary in vitro studies evaluated the total antioxidant capacity and the total phenolic content of the refined olive oil and the novel refined olive oil, enhanced with 10% w/v orange peel, performing the Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) assay and Folin–Ciocalteu method, respectively [
19]. The total antioxidant capacity is expressed as millimoles Fe2+ per liter (mmol Fe2+/L), and the total phenolic content of the samples are expressed as milligrams of gallic acid (GAE) per liter (mg GAE/L) of sample.
In total, each meal weighed 295.5 g. The meals that were prepared were isoenergetic (618.53 kcal), high in fat and carbohydrates and their nutritional composition was calculated using the Diet Analysis v7.0.1 software (Cengage Learning, Ltd, United Kingdom). The nutritional composition of the meals is summarized in
Table 1.
2.5. Blood sampling and analysis
Venous blood samples were collected from all participants, in fasting condition, before the meal intake (baseline), as well as 30 minutes, 1.5 h and 3 h after the meal consumption (
Figure 2). Blood samples were collected into plasma lithium-heparin, vacutainer tubes and plasma EDTA, vacutainer tubes (Weihei Hongyu Medical Devices C0., LTD). Plasma was separated by centrifugation at 4500 g for 15 min at 4° C. Plasma aliquots were immediately frozen in cryoboxes and stored at -40
0C for later processing.
Determination of plasma Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) was carried out by Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP assay), according to the study of Argyri et al. [
24,
25]. The plasma total, High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)- and LDL- cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose and uric acid concentrations were assessed using a biochemical, automated analyzer (COBAS c111, Roche, Switzerland).
2.6. Statistical analysis
2.6.1. Sample size
The sample size was computed, using G*power 3.1 (University of Düsseldorf, Germany). Sample size calculation showed that a total of 20 participants would be able to detect a significant difference of 25±3.5 mg/dL in LDL-Cholesterol between the control and the functional group, with a power of 80% holding for a repeated measure at a level of 5%. We increased sample size to n = 21 with respect to a drop-out rate of 5%.
2.6.2. Data analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS V21.0 for Windows (IBM Corporation, New York, NY, United States) and Prism 9 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). All data were taking into consideration. The significance level was defined at 0.05. Prior to statistical analysis, all biochemical variables were tested for the normal distribution by Kolmogorov–Smirnov normality test. Significant differences on initial population characteristics were evaluated, performing one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The 10-age cardiovascular risk was calculated for each volunteer, according to SCORE2 (European Society of Cardiology). All biomarkers were analysed, carrying out repeated-measures ANOVA, for the 2 factors (group, time) and their interactions. Post-hoc tests were carried out via Bonferroni test. When there was evidence for significant interaction terms, data within each group were analysed separately, performing paired samples t-tests for each change tested. All values are mentioned as Mean (Standard Deviation-SD).
4. Discussion
This controlled nutritional interventional study was designed to investigate whether the acute consumption of a functional refined olive oil, enhanced with bioactive compounds from orange peel extract, could have beneficial effect on the postprandial metabolic biomarkers of individuals at cardiometabolic risk. We hypothesized that the ingestion of the novel refined olive oil, enhanced with orange peel polyphenols, in parallel with a meal, rich in fat and carbohydrates, may lead to milder postprandial lipidemic, glycemic and oxidative stress responses, rather than the refined olive oil, in cardiometabolic risk participants based on the existing evidence, on the efficacy of polyphenols in the modulation of postprandial lipidemic, glycemic and oxidative dysmetabolism [
17,
21,
26].
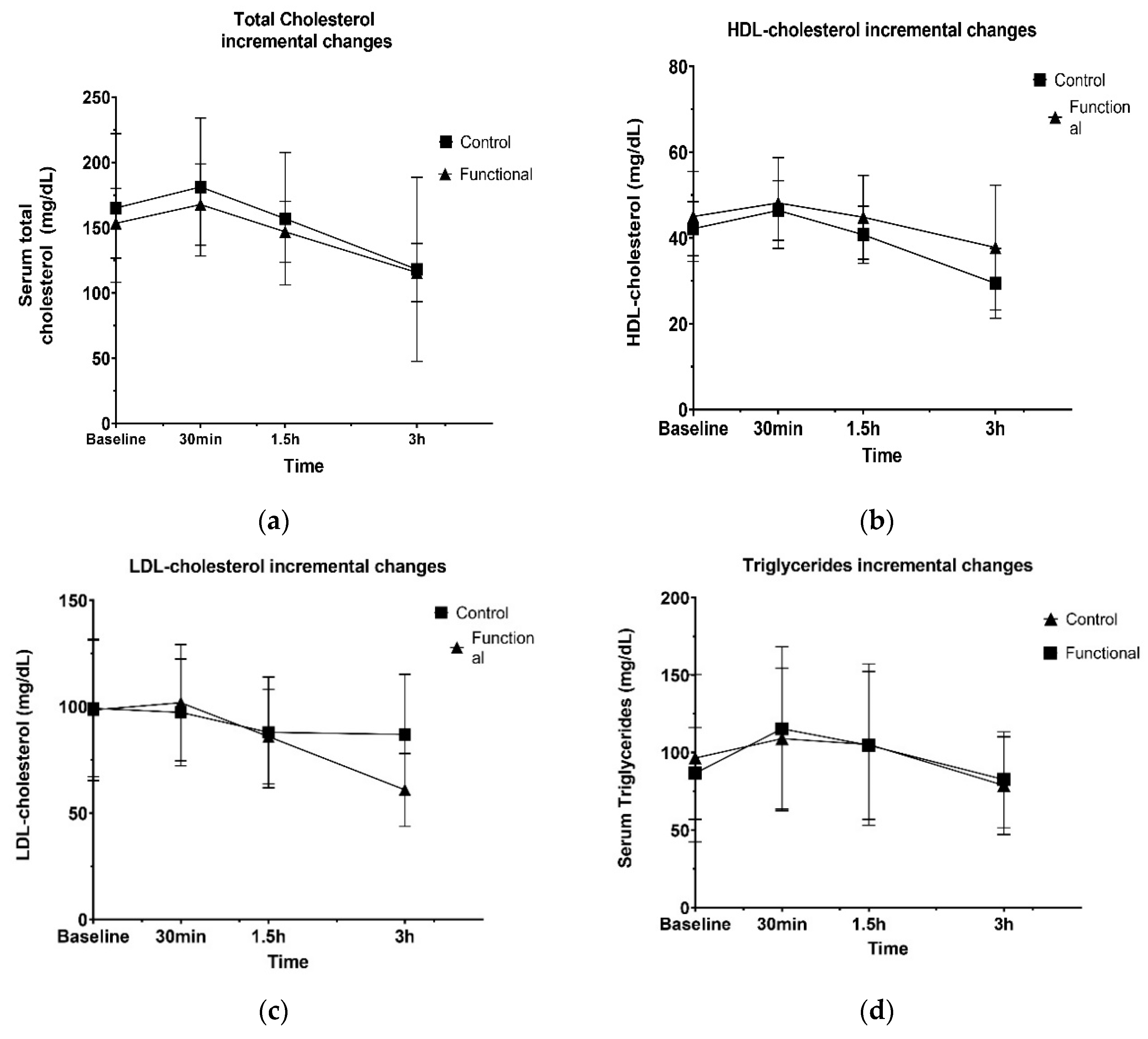
The primary finding of the study indicated that the acute intake of the novel refined olive oil, enhanced with 10% w/v orange peel extract, may lead to modulation of LDL-cholesterol postprandial metabolism, on comparison with the standard refined olive oil, in the context of a high-fat and high-carbohydrate meal. This effect was highlighted by a gradual decrease in LDL-cholesterol levels, during the 3-hour metabolism.
It is well known that the olive oil can modulate postprandial cholesterol metabolism, due to the presence of bioactive components, such as unsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols, which are key contributors on the protection against the LDL-cholesterol oxidation, a pathway implicated in atherosclerosis process [
27]. In fact, there is evidence that the polyphenolic content of human LDL increases in a dose-dependent manner with the total phenolic content of virgin olive oil consumed [
2]. The main mechanism, described by De la Torre-Carbot et al. for this effect, is the polyphenols’ binding, mainly tyrosol and its metabolites, by human LDL. However, the same clinical study shown that after the intake of a refined olive oil, polyphenols were not detected in the blood, due to low concentration of polyphenols in the refined olive oil [
28]. This conclusion may explain the non-significantly changed concentrations of LDL-cholesterol, after the administration of the standard refined olive oil, rather than the novel refined olive oil, in participants at cardiometabolic risk.
The results of a nutritional intervention by Khandouzi et al., indicated that the daily intake of 25 mL ROO for six weeks, resulted to increased LDL-cholesterol levels, while the ingestion of the same amount of EVOO decreased this biomarker’s concentration, in participants with at least one of the major cardiovascular risk factor [
20]. Another clinical study, conducted by Hernáez et al. demonstrated that the 3-week supplementation of the diet with 25 mL/day of low-polyphenol- content ROO, significantly increased the number of total and small LDL particles, while the ingestion of high-polyphenol-content VOO for the same time period, resulted to decreased concentrations [
29].
It is worth mentioning that hesperidin, one of the main bio-flavonoid found in orange peel, has been reported to present hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects, possibly by the enhancement of the gene encoding the LDL receptor, expression [
30]. Giving the fact that refined olive oil contains minor polyphenolic concentration [
20], the LDL-cholesterol modulatory effect, could be attributed to the presence of almost four times higher concentration of polyphenols in the novel, refined olive oil, enhanced with orange peel extract. Besides, recent findings from an in vitro study by Kandyliari et al., evaluating the antioxidant capacity and the total polyphenolic content of selective fruit by-products, indicated that orange peel may provide 7.16 milligrams of Gallic Acid per gram of dry mass [
31].
However, the present nutritional intervention did not differentially affect the kinetics of postprandial lipids and cholesterol metabolism, in the three-hour postprandial phase. Total and HDL-cholesterol, as well as plasma triglycerides seemed to peak at 30 min after the meal intake, following by similar, incremental weakening until the endpoint. These findings are in contrast to the results of previous studies [
11]. In particular, there are indications that hesperidin in orange peel may exhibit bioactivity on endothelial function and other pro-inflammatory responses, but this is transient and limited to the postprandial state [
32]. Hesperidin and naringenin, presented in orange peel, may contribute to the reduction of cholesterol esterification, reducing lipoprotein capacity and allowing a lower degree of cholesterol transport into circulation [
33]; Nevertheless, our findings did not show such an acute effect. They may also inhibit the activity and expression of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) [
33]. It is worth mentioning that some researchers report that the data on the effect of citrus bioactives on cholesterol levels, are limited, while their ineffectiveness has been reported in moderately hypercholesterolemic individuals [
33].
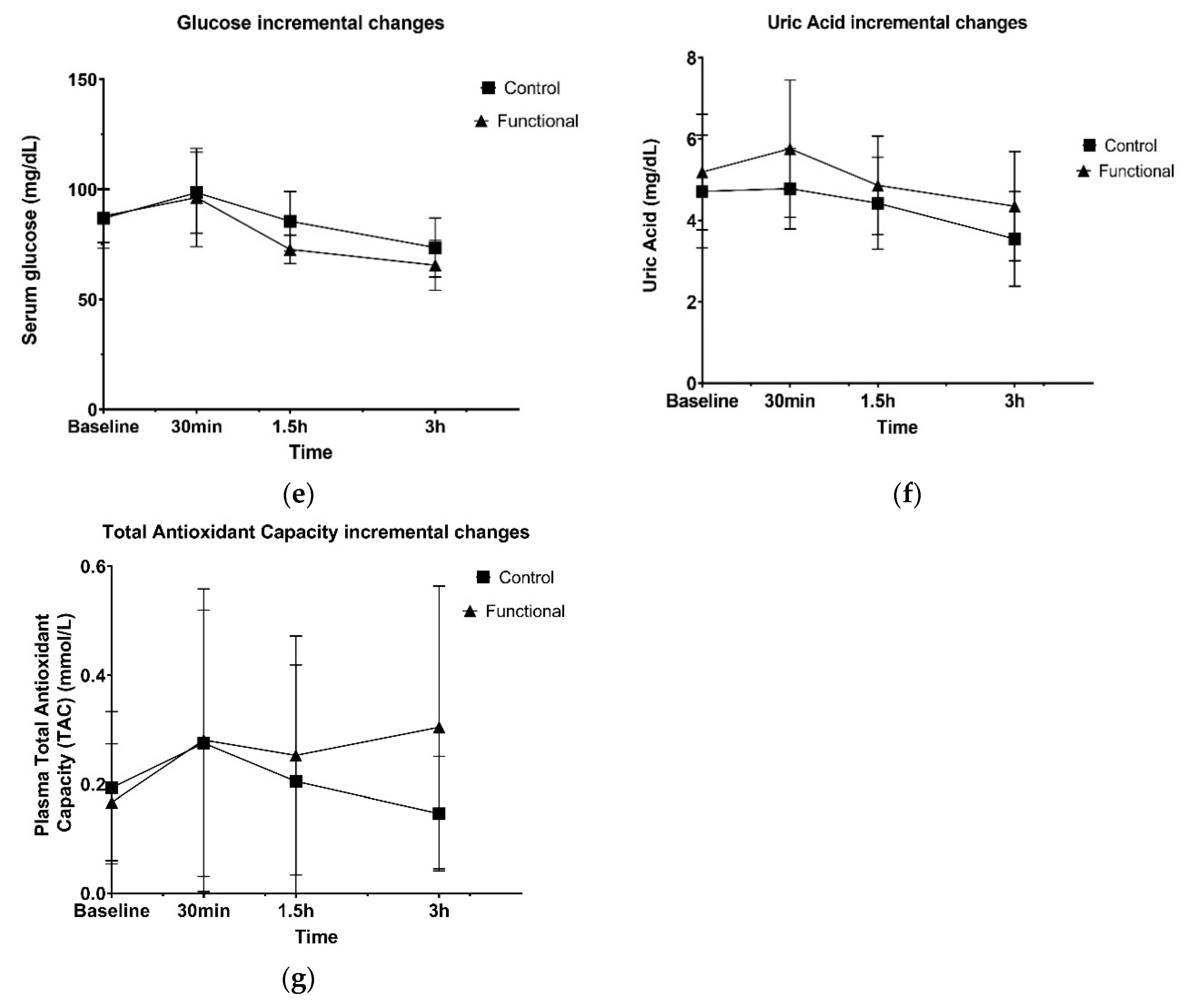
Orange peel flavonoids has been extensively mentioned for their antidiabetic activity, mainly due to their ability to increasing insulin levels in the blood, affecting the improvement of pancreatic beta cells [
34]. Also, in the postprandial phase, hesperidin has been suggested to be useful in preventing hyperglycemia, acting as an inhibitor of the intestinal glucose transporter [
35]. Nevertheless, these data did not confirm in the present study, as similar glycemic metabolism were observed, on both refined olive oils tested, in the specified measurements time frame. Possibly, the polyphenols concentration, provided by the orange peel extract, and by extension in the novel refined olive oil, was insufficient to exert postprandial bioactivity [
19], which could lead to better glycemic response.
Regarding plasma antioxidant status responses, total plasma antioxidant capacity showed an increase 30 min after receiving both meals, following by a similar concentration reduction until 1.5 h after meal consumption. A differential antioxidant metabolism was observed at the last time period until 3 h, highlighted by a 20% rise on antioxidant levels in the functional group, while in control group an 28.8% lowering levels were noticed. However, these differences were not captured in the overall antioxidant effect between the interventions over time, under the present analysis procedure. Despite the fact that previous findings indicate that polyphenolic metabolites may play a key role on the acute induction of antioxidant capacity, mainly 1.5 h after the ingestion [
10,
19], the present results are not completely clear and could describe only a trend of improved, postprandial antioxidant status. The presence of cardiometabolic risk factors in the clinical profile of the participants, may play a significant role in the differentiation of antioxidant responses, between healthy and non-healthy individuals [
36]. Further investigation is needed to clarify the possible beneficial effect. The significant supplementation of a challenge meal with natural antioxidants, has been reported to beneficially affect the acute, postprandial metabolic kinetics, and thus the analysis of our findings remains complicated, regarding the cardiometabolic effects [
11].
Τhis pilot clinical trial presented some limitations. In this dietary intervention, the total, LDL- and HDL-cholesterol, as well as the triglyceride levels were assessed, but the postprandial responses of oxidized LDL-cholesterol (ox-LDL) and the concentration of Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL), which have been reported as key biomarkers when investigating postprandial lipid metabolism with an impact on acute inflammatory pathways, were not determined [
28]. Other biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial function (e.g., C-Reactive Protein, Interleukins etc.), as well as the insulin determination, could be added to our measurements [
37]. In addition, despite the fact that hypertension was included in the entry criteria parameters, as it remains an important cardiometabolic risk factor, no blood pressure incremental measurements were performed in the present study [
2]. Further research is needed, investigating the acute metabolism of these biomarkers, to study the acute impact of the functional olive oil, enhanced with orange peel extract, on the biomarkers of endothelial activation and inflammation. It is noteworthy that the design of this clinical trial did not include the detection of the phenolic content, but also of individual polyphenols via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) in the blood, which limits the explanation of our findings, regarding the effect of polyphenols, provided by the test olive oils, on the plasma antioxidant status [
37]. Finally, our interventional study is limited by the time frame design. An expansion of this nutritional intervention in longer-term level, could draw safer conclusions about the possible beneficial effect of consuming refined olive oil, enhanced with orange peel extract, on the metabolic biomarkers regarding the modulation of cardiometabolic risk factors.
5. Conclusions
In this randomized, controlled, acute nutritional intervention in individuals at cardiometabolic risk, the consumption of the functional olive oil, enhanced with 10% orange peel extract, supplementing a fat and carbohydrated meal, induced significantly different responses on LDL-cholesterol, when compared with the standard refined olive oil. We concluded that, compared to the refined olive oil, the novel olive oil consumption modulates LDL-cholesterol levels, leading to lower concentration, 3h after ingestion. By contrast, no postprandial differences between the two groups were observed, regarding the total, HDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid and plasma total antioxidant capacity, as similar responses of both meals were found. The unique aspect of this acute clinical study is that was focused on population at cardiometabolic risk and used fat and carbohydrated meals to investigate the acute effect of the test, refined olive oils on cardiometabolic parameters. The mechanisms underlying lipidemic, glycemic and antioxidant responses, in the postprandial state are likely multifactorial. Additional research, especially larger clinical and epidemiological studies, is needed to ensure these primary findings, investigating the accurate mechanisms for the metabolic modulatory effects and the possible bioactivity of the functional olive oil, enhanced with orange peel extract, on cardiovascular and metabolic factors. The findings of these studies could form the basis for the possible establishment of health claims, regarding the improvement of the intake of polyphenols from refined, marketed olive oil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Olga Papagianni, Aikaterini Kandyliari and Antonios Koutelidakis; Data curation, Aikaterini Kandyliari and Panagiota Potsaki; Formal analysis, Olga Papagianni, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, Aikaterini Kandyliari and Kalliopi Almpounioti; Funding acquisition, Dimitrios Skalkos and Antonios Koutelidakis; Investigation, Olga Papagianni, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, Panorea Bousdouni and Camille Ouzaid; Methodology, Olga Papagianni, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, Aikaterini Kandyliari, Panagiota Potsaki, Panorea Bousdouni, Kalliopi Almpounioti, Camille Ouzaid, Anna-Kyriaki Mavrou, Vasiliki Panteli, Thomas Loukas, Athanasios Magkoutis, Haralabos Karantonis and Antonios Koutelidakis; Project administration, Dimitrios Skalkos and Antonios Koutelidakis; Resources, Olga Papagianni, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, Panagiota Potsaki, Camille Ouzaid, Anna-Kyriaki Mavrou, Vasiliki Panteli, Thomas Loukas and Athanasios Magkoutis; Software, Olga Papagianni, Chrysoula Kaloteraki, Panagiota Potsaki, Panorea Bousdouni, Kalliopi Almpounioti, Camille Ouzaid, Anna-Kyriaki Mavrou and Vasiliki Panteli; Supervision, Antonios Koutelidakis; Validation, Olga Papagianni, Aikaterini Kandyliari, Athanasios Magkoutis, Dimitrios Skalkos, Haralabos Karantonis and Antonios Koutelidakis; Visualization, Thomas Loukas, Haralabos Karantonis and Antonios Koutelidakis; Writing – review & editing, Olga Papagianni, Aikaterini Kandyliari and Antonios Koutelidakis.