Submitted:
06 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Centered Kernel Alignment Fundamentals
2.2. Gaussian Functional Connectivity from EEG Records
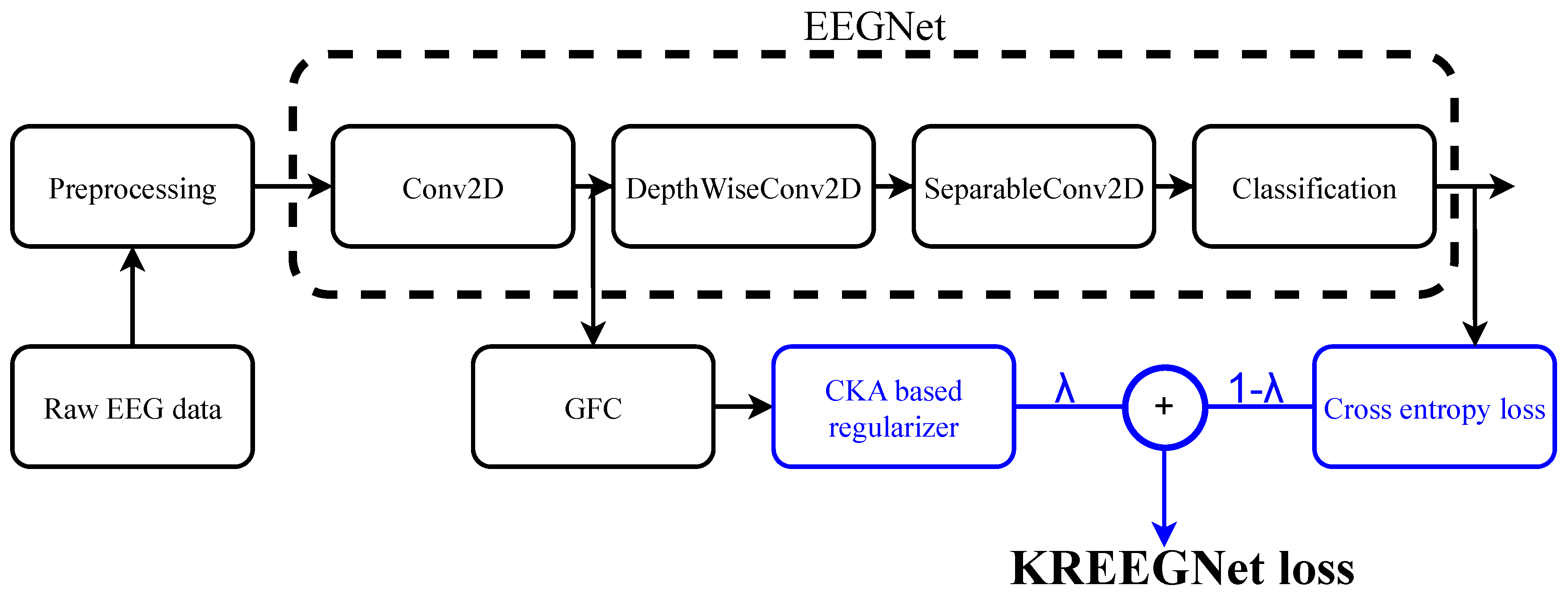
2.3. KREEGNet: Kernel-Based Regularized EEG Network
- –
- is a convolutional layer holding filters, a batch normalization, and a linear activation.
- –
- is a depthwise convolutional layer holding ELU activation ( gathers the number of spatial filters), followed by an average pooling and a dropout operation.
- –
- is a separable convolutional layer with ELU activation ( is the number of pointwise filters), setting a batch normalization, an average pooling, and a dropout.
- –
- is a fully connected classification layer fixing a flatten operation and a softmax activation.
3. Experimental Set-Up
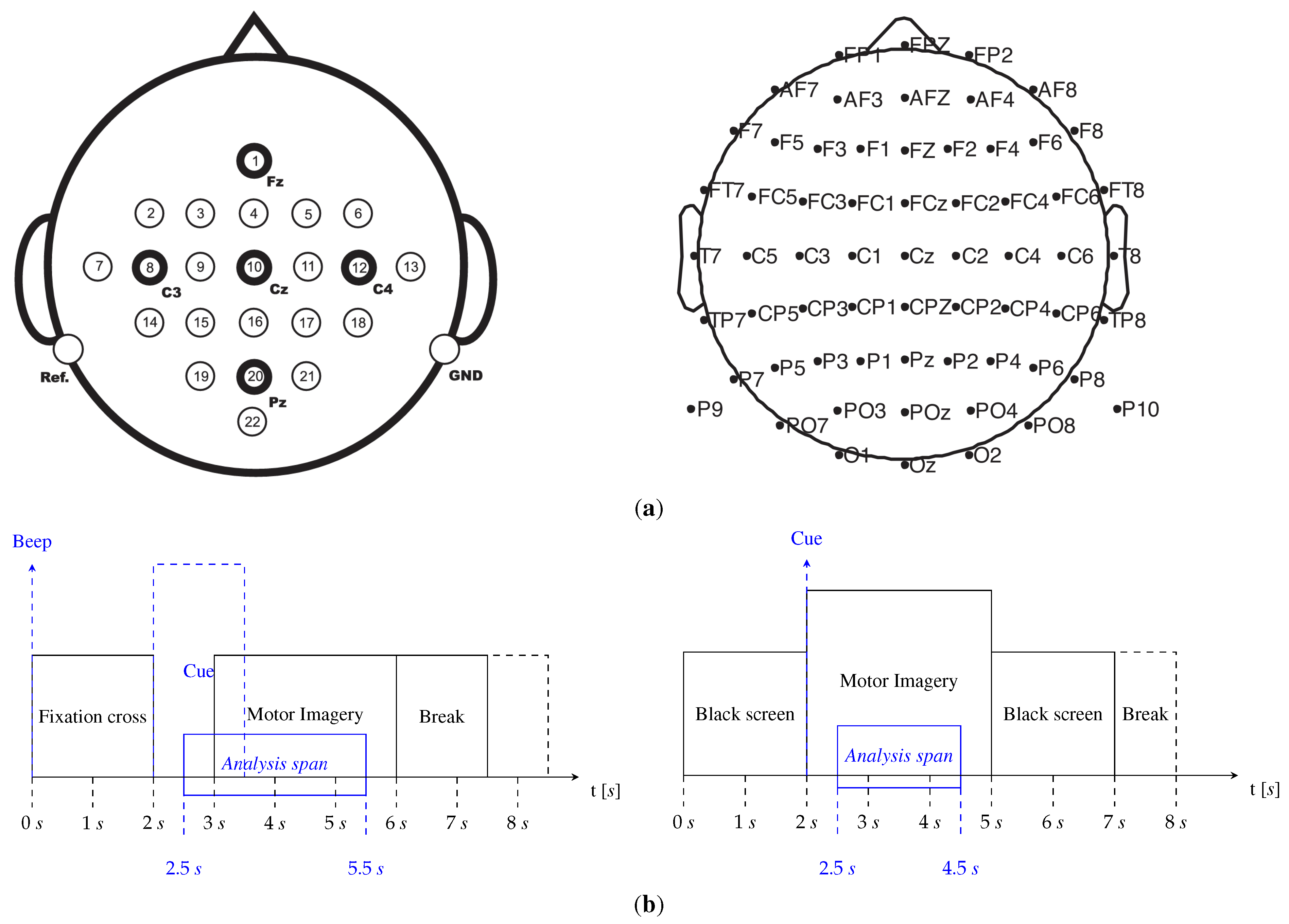
3.1. Datasets Description
3.2. KREEGNet Training Details and Assessment
3.3. Method Comparison
4. Results and Discussion
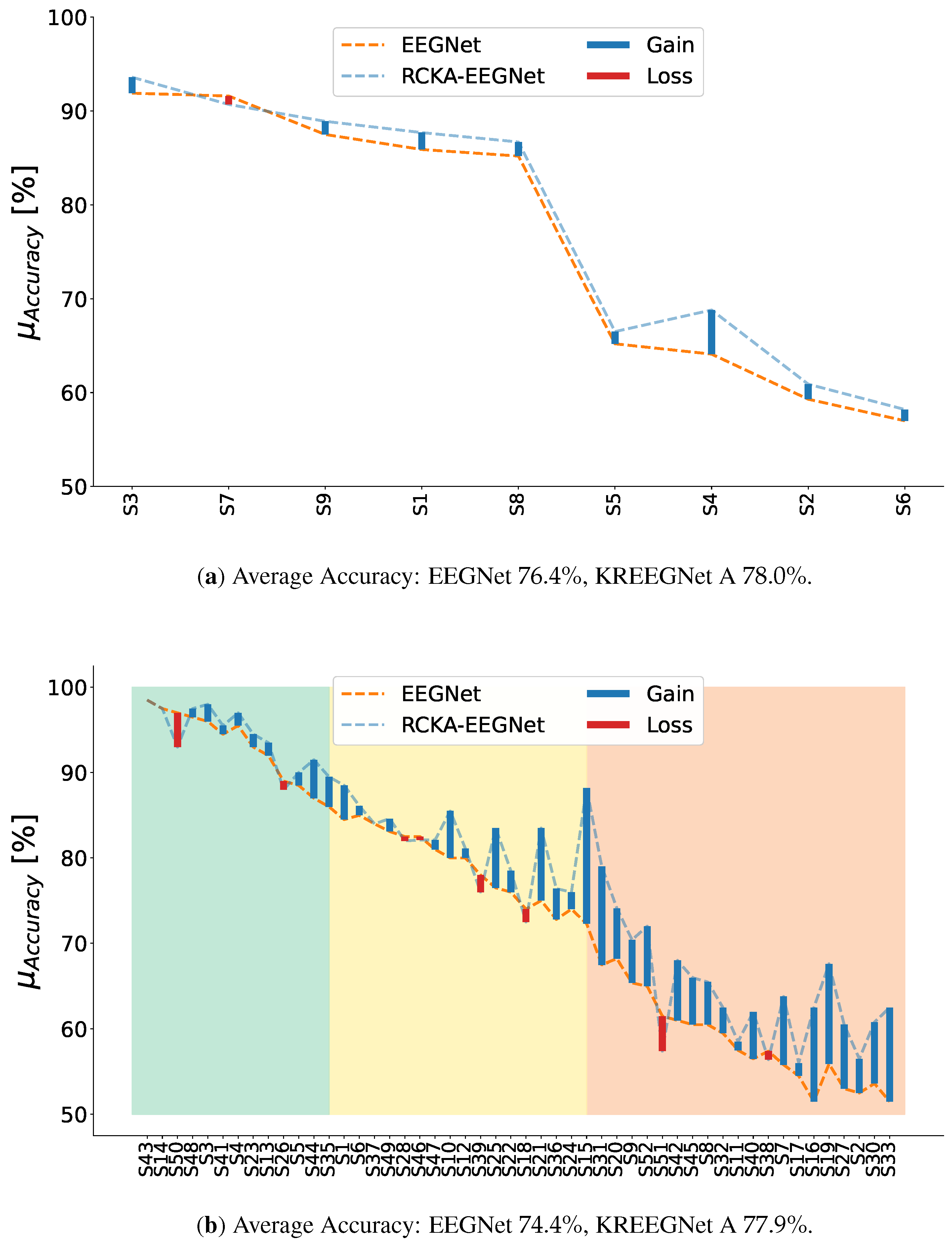
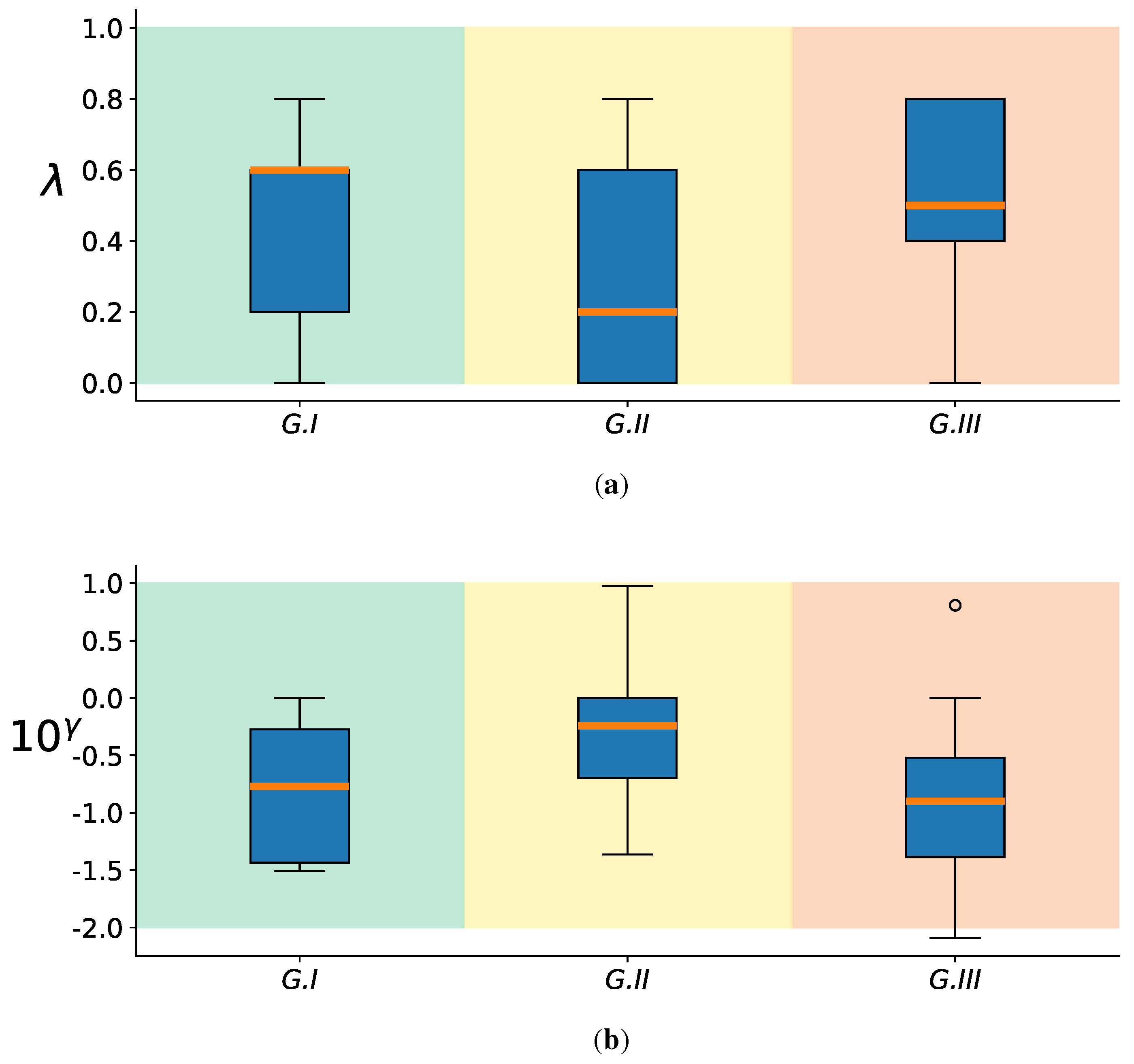
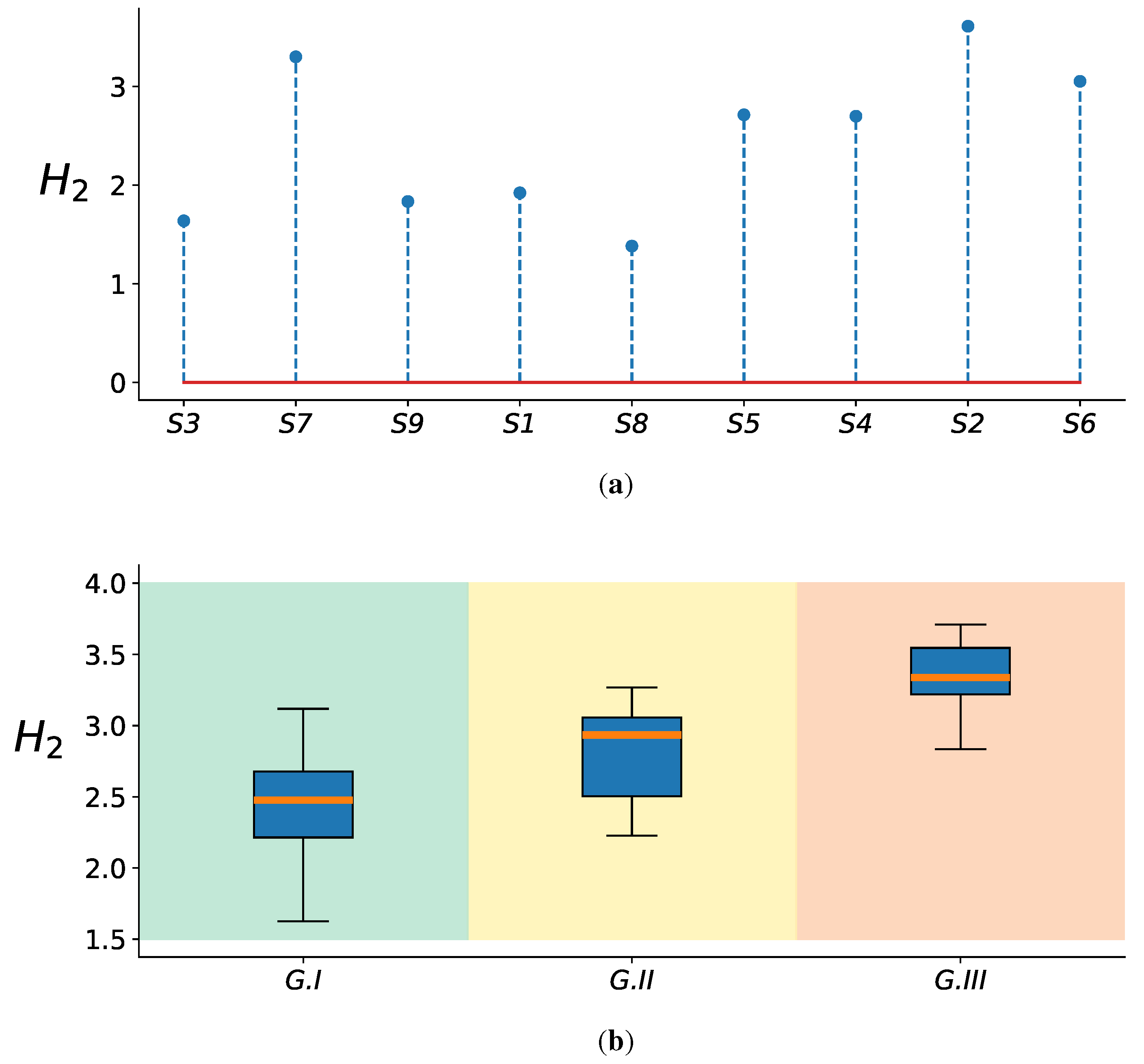
4.1. Baseline EEGNet vs. KREEGNet: Subject and Group-Level Results
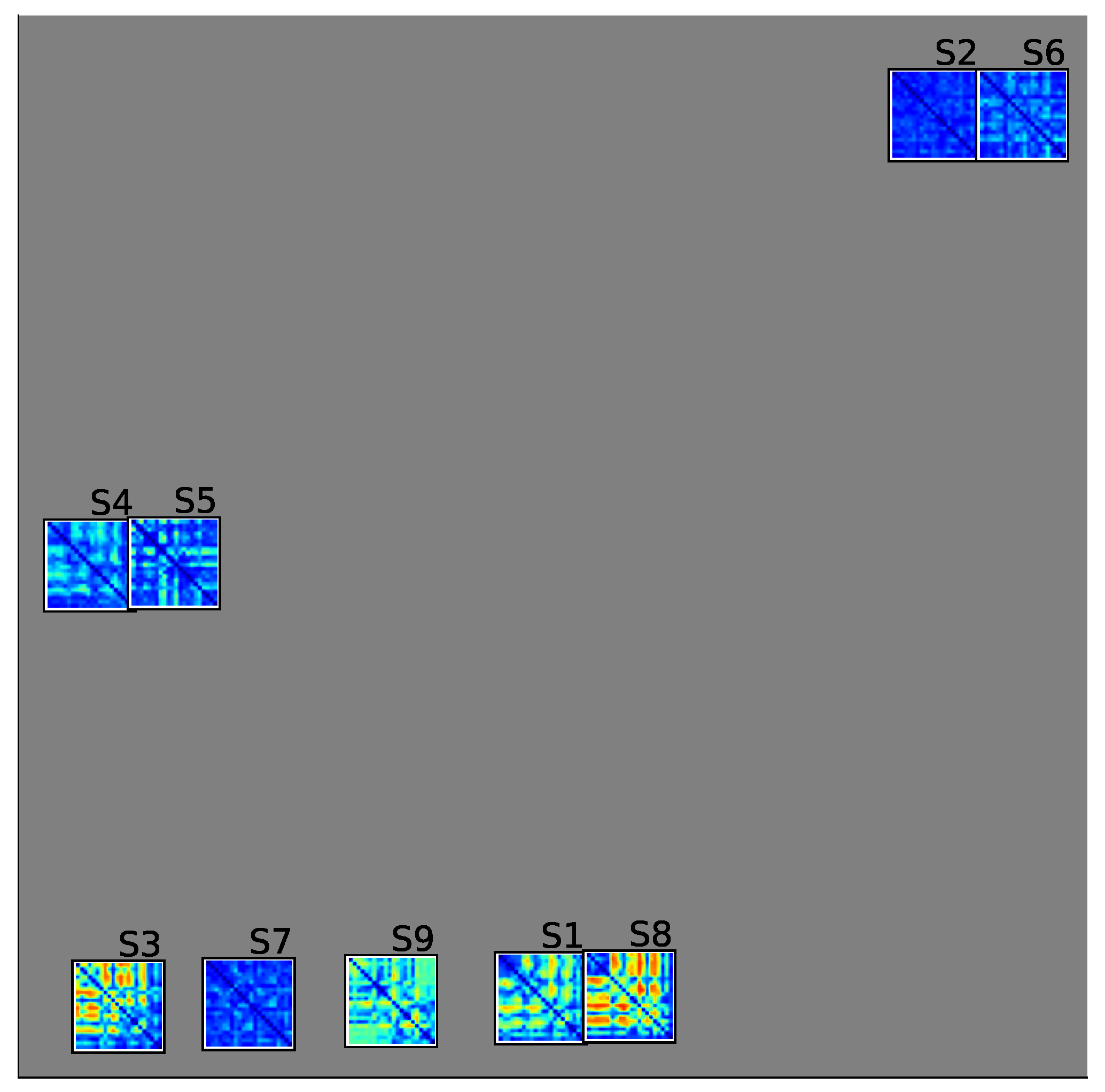
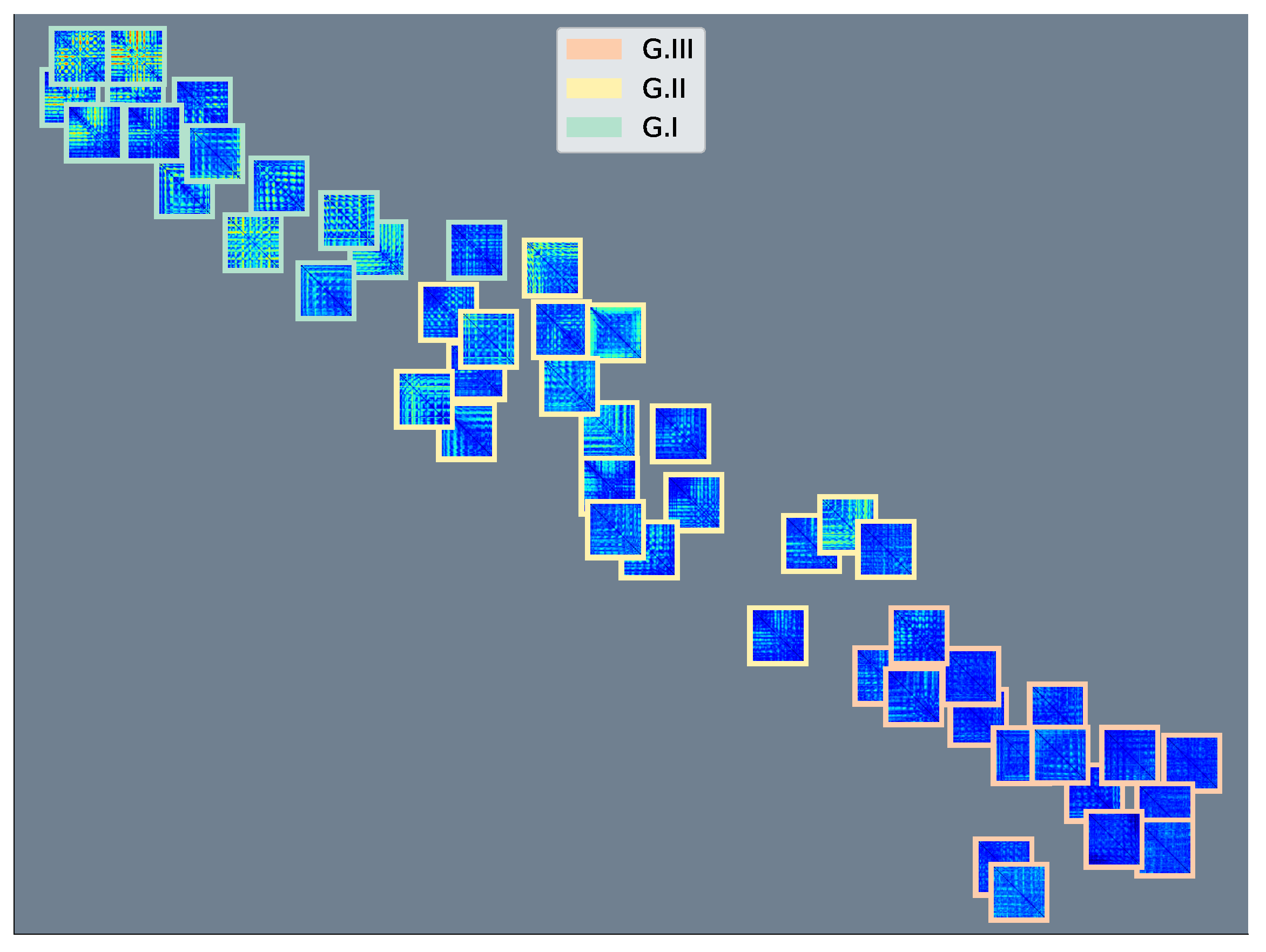
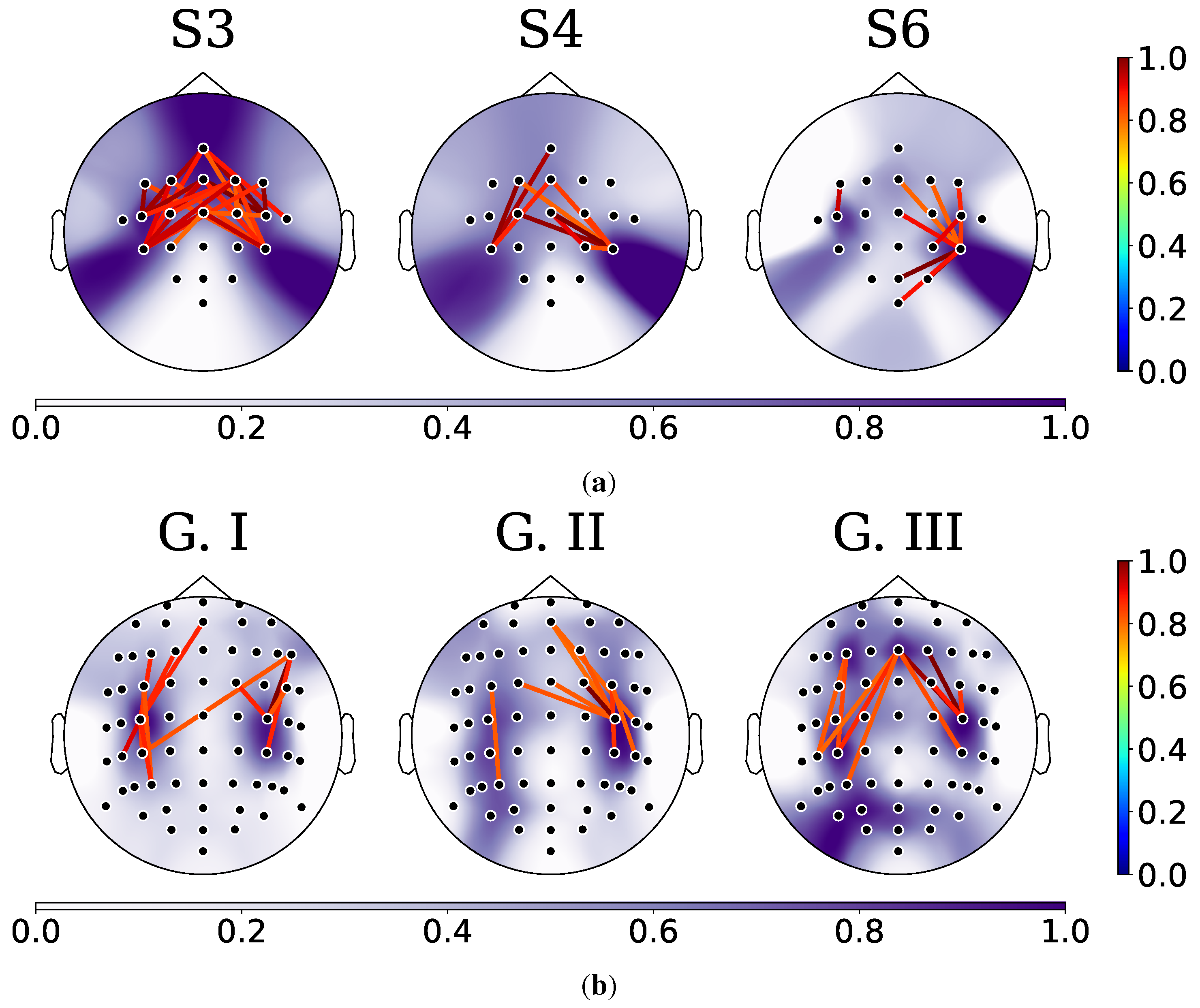
4.2. Relevance Analysis Results
- –
- We categorized each connection’s trials for an individual based on the label, forming the right and left sample sets.
- –
- Following this, we calculated the KS statistic for the connectivity between each pair of EEG channels along the training set trials. A KS value nearing 1 signifies a high level of distinguishability for the connectivity between two channels, whereas a value approaching 0 suggests a low level of separability.
- –
- Moreover, we utilized the maximum operator across the estimated feature maps to establish a KS statistic matrix. This matrix denotes the class-separability of each connectivity.
- –
- In order to illustrate the variations in each KS statistic matrix across subjects and groups, we depicted each matrix of KS statistic values on a two-dimensional scatter representation. Both dimensions were calculated employing the widely accepted t-SNE algorithm [66].
- –
- Lastly, to fully comprehend the key connectivities and channels involved in the MI classification, we used topoplots from the KS statistic matrix.
4.3. Method Comparison Results: Binary and Multi-Class MI Classification
5. Conclusions
References
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Venkatachalam, K.; Devipriya, A.; Maniraj, J.; Sivaram, M.; Ambikapathy, A.; Iraj, S.A. A Novel Method of motor imagery classification using eeg signal. Artificial intelligence in medicine 2020, 103, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, N. HS-CNN: a CNN with hybrid convolution scale for EEG motor imagery classification. Journal of neural engineering 2020, 17, 016025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, P.; McCreadie, K.; Pachori, R.B.; Wang, H.; Prasad, G. An automatic subject specific channel selection method for enhancing motor imagery classification in EEG-BCI using correlation. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 68, 102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Das, R.; Iversen, H.K.; Puthusserypady, S. Review on motor imagery based BCI systems for upper limb post-stroke neurorehabilitation: From designing to application. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2020, 123, 103843. [Google Scholar]
- Kanna, R.K.; Vasuki, R. Classification of Brain Signals Using Classifiers for Automated Wheelchair Application. International Journal of Modern Agriculture 2021, 10, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Hu, W.; Yin, H.; Zhang, K. Spatial-frequency feature learning and classification of motor imagery EEG based on deep convolution neural network. Computational and mathematical methods in medicine 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padfield, N.; Zabalza, J.; Zhao, H.; Masero, V.; Ren, J. EEG-based brain-computer interfaces using motor-imagery: Techniques and challenges. Sensors 2019, 19, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, A. A review on analysis of EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advances in Computer Engineering and Applications. IEEE; 2015; pp. 957–960. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.; Mazumder, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Tibarewala, D.N.; Hayashibe, M. Functional connectivity analysis of motor imagery EEG signal for brain-computer interfacing application. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). IEEE; 2015; pp. 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Nenadic, Z.; Im, C.H. Electroencephalography-based endogenous brain–computer interface for online communication with a completely locked-in patient. Journal of neuroengineering and rehabilitation 2019, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazos-Huertas, D.F.; Álvarez-Meza, A.M.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Spatial interpretability of time-frequency relevance optimized in motor imagery discrimination using Deep&Wide networks. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 68, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Baumert, M. Intra-and inter-subject variability in EEG-based sensorimotor brain computer interface: a review. Frontiers in computational neuroscience 2020, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Velasco, S.; Santamaria-Vazquez, E.; Martinez-Cagigal, V.; Marcos-Martinez, D.; Hornero, R. EEGSym: Overcoming Inter-Subject Variability in Motor Imagery Based BCIs With Deep Learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2022, 30, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghier, M.L.; Price, C.J. Interpreting and utilising intersubject variability in brain function. Trends in cognitive sciences 2018, 22, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannelli, C.; Vidaurre, C.; Müller, K.R.; Blankertz, B. A large scale screening study with a SMR-based BCI: Categorization of BCI users and differences in their SMR activity. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0207351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidaurre, C.; Blankertz, B. Towards a cure for BCI illiteracy. Brain topography 2010, 23, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo-Acosta, J.; Castaño, G.A.; Acosta-Medina, C.; Alvarez-Meza, A.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Deep Neural Regression Prediction of Motor Imagery Skills Using EEG Functional Connectivity Indicators. Sensors 2021, 21, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LK Jaya Shree, B. Automatic Detection of EEG as Biomarker using Deep Learning: A review. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology 2021, pp. 6502–6511.
- Shoka, A.; Dessouky, M.; El-Sherbeny, A.; El-Sayed, A. Literature review on EEG preprocessing, feature extraction, and classifications techniques. Menoufia J. Electron. Eng. Res 2019, 28, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salami, A.; Andreu-Perez, J.; Gillmeister, H. EEG-ITNet: An explainable inception temporal convolutional network for motor imagery classification. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 36672–36685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, B.; Francart, T.; Bertrand, A. A generic EEG artifact removal algorithm based on the multi-channel Wiener filter. Journal of neural engineering 2018, 15, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Han, S.; Kim, K.; Jun, S.C. Super-resolution for improving EEG spatial resolution using deep convolutional neural network—feasibility study. Sensors 2019, 19, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotte, S.; Dabbakuti, J.K. Methods for removal of artifacts from EEG signal: A review. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2020, Vol. 1706, p. 012093.
- Singh, A.; Hussain, A.A.; Lal, S.; Guesgen, H.W. A comprehensive review on critical issues and possible solutions of motor imagery based electroencephalography brain-computer interface. Sensors 2021, 21, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiadis, C.; Kostaridou, V.D.; Klados, M.A. Which BSS method separates better the EEG Signals? A comparison of five different algorithms. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 72, 103292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Sulaiman, N.; PP Abdul Majeed, A.; Musa, R.M.; Bari, B.S.; Khatun, S.; et al. Current status, challenges, and possible solutions of EEG-based brain-computer interface: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in neurorobotics 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, L.F.S.; Stefano Filho, C.A.; de Oliveira, V.A.; da Silva Costa, T.B.; Rodrigues, P.G.; Soriano, D.C.; Boccato, L.; Castellano, G.; Attux, R. A correntropy-based classifier for motor imagery brain-computer interfaces. Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express 2019, 5, 065026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridha, M.; Das, S.C.; Kabir, M.M.; Lima, A.A.; Islam, M.; Watanobe, Y.; et al. Brain-Computer Interface: Advancement and Challenges. Sensors 2021, 21, 5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, L.; Song, A.; Wu, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Xu, G.; Li, H.; Zeng, H. Wavelet transform time-frequency image and convolutional network-based motor imagery EEG classification. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 6084–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobón-Henao, M.; Álvarez-Meza, A.; Castellanos-Domínguez, G. Subject-dependent artifact removal for enhancing motor imagery classifier performance under poor skills. Sensors 2022, 22, 5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, E.M.; Cassani, R.; Falk, T.H.; Fraga, F.J. Improved motor imagery brain-computer interface performance via adaptive modulation filtering and two-stage classification. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2020, 57, 101812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabioun, M. Motor imagery classification by active source dynamics. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2020, 61, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, S.; Bajaj, V. Motor imagery tasks-based EEG signals classification using tunable-Q wavelet transform. Neural Computing and Applications 2019, 31, 6925–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.T.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Fan, Z.; Rehman, A.U.; Li, G.; Xiao, G. Motor imagery EEG signals classification based on mode amplitude and frequency components using empirical wavelet transform. IEEE access 2019, 7, 127678–127692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, D.; Cui, L. A new motor imagery EEG classification method FB-TRCSP+ RF based on CSP and random forest. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 44944–44950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.Y. Improving classification accuracy of motor imagery EEG using genetic feature selection. Clinical EEG and neuroscience 2014, 45, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashashati, A.; Fatourechi, M.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. A survey of signal processing algorithms in brain–computer interfaces based on electrical brain signals. Journal of Neural engineering 2007, 4, R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Erp, J.; Lotte, F.; Tangermann, M. Brain-computer interfaces: beyond medical applications. Computer 2012, 45, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaheri, H.; Muhammad, G.; Alsulaiman, M.; Amin, S.U.; Altuwaijri, G.A.; Abdul, W.; Bencherif, M.A.; Faisal, M. Deep learning techniques for classification of electroencephalogram (EEG) motor imagery (MI) signals: A review. Neural Computing and Applications 2021, pp. 1–42. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Mu, C.; Li, T. Graph Convolution Neural Network based End-to-end Channel Selection and Classification for Motor Imagery Brain-computer Interfaces. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bian, D.; Xu, D.; Zou, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, N. A Spatio-Temporal Interactive Attention Network for Motor Imagery EEG Decoding. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC). IEEE; 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Jia, X.; Yang, L.; Xie, L. Transformer-based spatial-temporal feature learning for EEG decoding. arXiv 2021. arXiv:2106.11170 2021.
- He, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Shi, J. A channel attention based MLP-Mixer network for motor imagery decoding with EEG. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE; 2022; pp. 1291–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Wang, D.; Yue, K.; Zheng, N.; Shen, Z.J.M. EEG-based motor imagery classification with deep multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE; 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, L.; Valverde-Rebaza, J.; de Andrade Lopes, A. Link prediction in graph construction for supervised and semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE; 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Y. Ct-cad: Context-aware transformers for end-to-end chest abnormality detection on x-rays. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE; 2021; pp. 1385–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Song, Y.; Ma, K.; Xie, L. Motor imagery EEG decoding method based on a discriminative feature learning strategy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2021, 29, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phunruangsakao, C.; Achanccaray, D.; Hayashibe, M. Deep adversarial domain adaptation with few-shot learning for motor-imagery brain-computer interface. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 57255–57265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganin, Y.; Ustinova, E.; Ajakan, H.; Germain, P.; Larochelle, H.; Laviolette, F.; Marchand, M.; Lempitsky, V. Domain-adversarial training of neural networks. The journal of machine learning research 2016, 17, 2096–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halme, H.L.; Parkkonen, L. Across-subject offline decoding of motor imagery from MEG and EEG. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 10087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquand, A.F.; Brammer, M.; Williams, S.C.; Doyle, O.M. Bayesian multi-task learning for decoding multi-subject neuroimaging data. NeuroImage 2014, 92, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chowdhury, A.; McCreadie, K.; Prasad, G. Deep learning based inter-subject continuous decoding of motor imagery for practical brain-computer interfaces. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2020, 14, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chang, J.R.; Chen, L.F.; Chen, Y.S. Deep neural network with attention mechanism for classification of motor imagery EEG. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). IEEE; 2019; pp. 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The journal of machine learning research 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. pmlr; 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; He, X.; Han, J.; Huang, T.S. Graph regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for data representation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2010, 33, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Mohri, M.; Rostamizadeh, A. Algorithms for learning kernels based on centered alignment. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2012, 13, 795–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Meza, A.M.; Orozco-Gutierrez, A.; Castellanos-Dominguez, G. Kernel-based relevance analysis with enhanced interpretability for detection of brain activity patterns. Frontiers in neuroscience 2017, 11, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géron, A. Hands-on machine learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow; " O’Reilly Media, Inc.", 2022.
- García-Murillo, D.G.; Álvarez-Meza, A.M.; Castellanos-Dominguez, C.G. KCS-FCnet: Kernel Cross-Spectral Functional Connectivity Network for EEG-Based Motor Imagery Classification. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: a compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. Journal of neural engineering 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lipton, Z.C.; Li, M.; Smola, A.J. Dive into deep learning. arXiv 2021. arXiv:2106.11342.
- Schirrmeister, R.T.; Springenberg, J.T.; Fiederer, L.D.J.; Glasstetter, M.; Eggensperger, K.; Tangermann, M.; Hutter, F.; Burgard, W.; Ball, T. Deep learning with convolutional neural networks for EEG decoding and visualization. Human brain mapping 2017, 38, 5391–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, Y.K.; AlFassam, N.I.; Muhammad, G.; Amin, S.U.; Alsulaiman, M.; Abdul, W.; Altaheri, H.; Bencherif, M.A.; Algabri, M. Electroencephalography-based motor imagery classification using temporal convolutional network fusion. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2021, 69, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, V.W.; Zhou, Y. Kolmogorov–smirnov test: Overview. Wiley statsref: Statistics reference online 2014.
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. Journal of machine learning research 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo, L.G.S.; Rao, M.; Principe, J.C. Measures of entropy from data using infinitely divisible kernels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2014, 61, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jia, S.; Lun, X.; Hao, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R.; Lv, J. GCNs-net: a graph convolutional neural network approach for decoding time-resolved eeg motor imagery signals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Pava Panche, I.; Gómez-Orozco, V.; Álvarez-Meza, A.; Cárdenas-Peña, D.; Orozco-Gutiérrez, Á. Estimating Directed Phase-Amplitude Interactions from EEG Data through Kernel-Based Phase Transfer Entropy. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Heng, P.A. Global Adaptive Transformer for Cross-Subject Enhanced EEG Classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
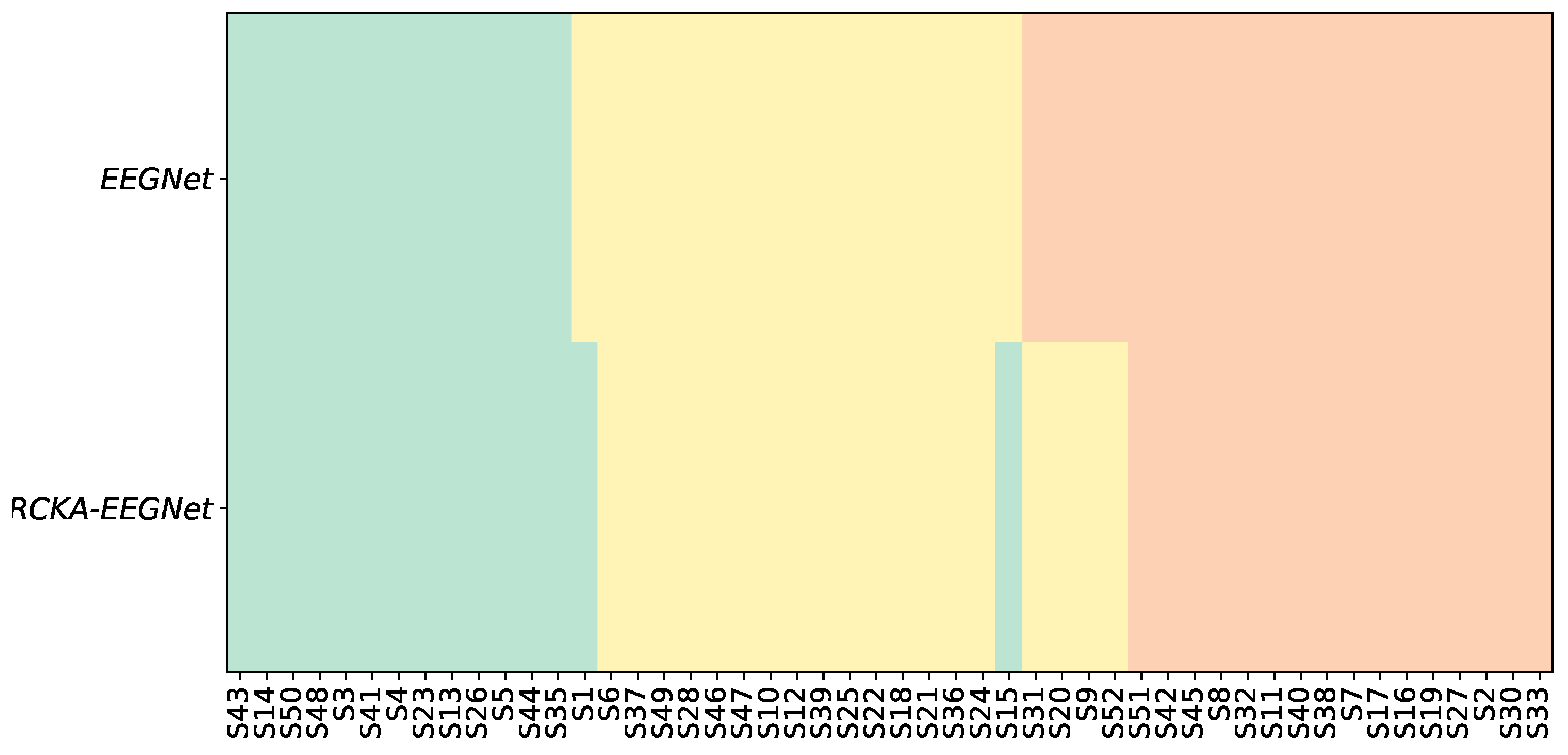
| Approach | Accuracy | Kappa | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deepconvnet [63] | |||
| Shallowconvnet [63] | |||
| EEGNet [61] | |||
| TCFussionnet [64] | |||
| KREEGNet (ours) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





