Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
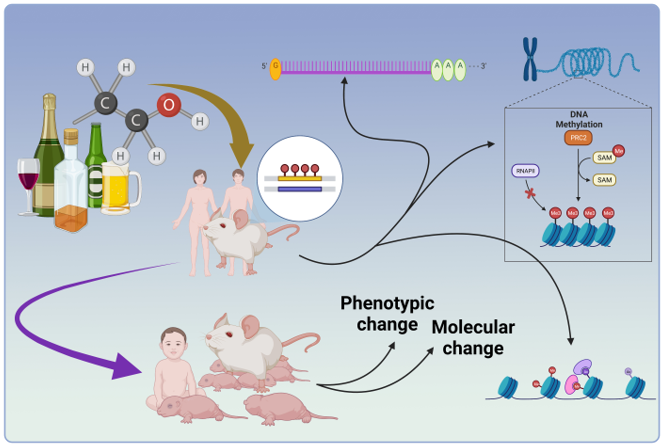
1. Introduction
2. Alcohol Abuse and Changes in the epigenome
2.1. Human Studies
2.2. Animal Studies
3. Transgenerational and Intergenerational Effects of Alcohol
3.1. Maternal Care and Pups Development in Preconception Model of Ethanol Exposure
3.2. phenotype Changes Followed by Preconception Parental Ethanol Exposure
3.2.1. Anxiety-like Behavior
3.2.2. Learning and Memory
3.2.3. Depression
3.2.4. Reward
3.2.5. Other Phenotypic Changes
3.3. Parental Ethanol Exposure and Endocrine Changes in the Offspring
3.4. Parental Ethanol Exposure before Gestation and Changes in Gene Expression
3.4.1. Epigeneome Changes
3.4.2. Changes in Gene Expression
4. Conclusion
Abbreviation
References
- Ilhan, M.N.; Yapar, D. Alcohol consumption and alcohol policy. Turk. J. Med Sci. 2020, 50, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkiewitz, K.; Litten, R.Z.; Leggio, L. Advances in the science and treatment of alcohol use disorder. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axley, P.D.; Richardson, C.T.; Singal, A.K. Epidemiology of Alcohol Consumption and Societal Burden of Alcoholism and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Schuckit, M. Alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerecke, M. Alcohol’s Impact on the Cardiovascular System. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffetta, P.; Hashibe, M. Alcohol and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2006, 7, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fan, X.; Miyata, T.; Kim, A.; Ross, C.K.C.-D.; Ray, S.; Huang, E.; Taiwo, M.; Arya, R.; Wu, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Understanding of Pathogenesis of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2023, 18, 411–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Yang, Q.; Joshi, R.B.; Liu, Y.; Akbar, M.; Song, B.-J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X. Role of Alcohol Drinking in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, C., C. G. Canning and S. M. Goldman. "Environment, lifestyle, and parkinson's disease: Implications for prevention in the next decade." Movement Disorders 34 (2019): 801-11.
- Mohebichamkhorami, F.; Niknam, Z.; Khoramjouy, M.; Heidarli, E.; Ghasemi, R.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Mohseni, S.S.; Hajikarim-Hamedani, A.; Heidari, A.; Ghane, Y.; et al. Brain Homogenate of a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease Modifies the Secretome of 3D Cultured Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: A Potential Neuroregenerative Therapy. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2022, 21, e133668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, S.W.; Huisman, M.H.B.; Sutedja, N.A.; van der Kooi, A.J.; de Visser, M.; Schelhaas, H.J.; Fischer, K.; Veldink, J.H.; Berg, L.H.v.D. Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, and the Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Population-based Study. Am. J. Epidemiology 2012, 176, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, A.; Oraii, A.; Jalali, A.; Alaeddini, F.; Saadat, S.; Masoudkabir, F.; Tajdini, M.; Ashraf, H.; Omidi, N.; Heidari, A.; et al. Epidemiology and prevalence of tobacco use in Tehran; a report from the recruitment phase of Tehran cohort study. BMC Public Heal. 2023, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, N., S. M. Fanaei, S. Hosseini and M. Mohseny. "The prevalence of anxiety and its associated factors among medical interns during the covid-19 outbreak in iran." International Journal of Body, Mind and Culture 9 (2022): 343-50. Available online: https://ijbmc.org/index.php/ijbmc/article/view/387.
- Banerjee, N. Neurotransmitters in alcoholism: A review of neurobiological and genetic studies. Indian J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 20, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; de Timary, P.; Delzenne, N.M.; Stärkel, P. The link between inflammation, bugs, the intestine and the brain in alcohol dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1048–e1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.A. Update on neuropharmacological treatments for alcoholism: Scientific basis and clinical findings. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Roige, S.; Palmer, A.A.; Clarke, T.-K. Recent Efforts to Dissect the Genetic Basis of Alcohol Use and Abuse. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 87, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.Y.; Sharma, V.K. DRD2 methylation and regional grey matter volumes in young adult offspring from families at ultra-high risk for alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2019, 286, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishamcar, S.; Chen, J.; Feil, D.; Kilanowski, A.; Koen, N.; Vanker, A.; Wedderburn, C.J.; Donald, K.A.; Zar, H.J.; Stein, D.J.; et al. DNA methylation as a potential mediator of the association between prenatal tobacco and alcohol exposure and child neurodevelopment in a South African birth cohort. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miozzo, F.; Arnould, H.; de Thonel, A.; Schang, A.-L.; Sabéran-Djoneidi, D.; Baudry, A.; Schneider, B.; Mezger, V. Alcohol exposure promotes DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A upregulation through reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanisms. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2018, 23, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.C.; Kyzar, E.J.; Zhang, H. Epigenetic basis of the dark side of alcohol addiction. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, I. Epigenetic Control of Gene Expression in the Alcoholic Brain. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2013, 35, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Gangisetty, O.; Sinha, R.; Sarkar, D.K. Hypermethylation of Proopiomelanocortin and Period 2 Genes in Blood Are Associated with Greater Subjective and Behavioral Motivation for Alcohol in Humans. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafre', S.; Carito, V.; Ferraguti, G.; Greco, A.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Fiore, M.; Ceccanti, M. How alcohol drinking affects our genes: an epigenetic point of view. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, F.T.; Vetreno, R.P.; Broadwater, M.A.; Robinson, D.L. Adolescent Alcohol Exposure Persistently Impacts Adult Neurobiology and Behavior. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 1074–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kyzar, E.J.; Bohnsack, J.P.; Kokare, D.M.; Teppen, T.; Pandey, S.C. Adolescent alcohol exposure epigenetically regulates CREB signaling in the adult amygdala. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzar, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Sakharkar, A.J.; Pandey, S.C. Adolescent alcohol exposure alters lysine demethylase 1 (LSD1) expression and histone methylation in the amygdala during adulthood. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Philibert, R.; Penaluna, B.; White, T.; Shires, S.; Gunter, T.; Liesveld, J.; Erwin, C.; Hollenbeck, N.; Osborn, T. A pilot examination of the genome-wide DNA methylation signatures of subjects entering and exiting short-term alcohol dependence treatment programs. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, R.; Dogan, M.; Noel, A.; Miller, S.; Krukow, B.; Papworth, E.; Cowley, J.; Knudsen, A.; Beach, S.R.H.; Black, D. Genome-wide and digital polymerase chain reaction epigenetic assessments of alcohol consumption. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B: Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2018, 177, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Herman, A.I.; Kranzler, H.R.; Anton, R.F.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, W.; Gelernter, J. Array-Based Profiling of DNA Methylation Changes Associated with Alcohol Dependence. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, E108–E115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Sjöholm, L.K.; Kononenko, O.; Tay, N.; Zhang, D.; Sarkisyan, D.; Geske, J.R.; Ing, A.; Qiu, W.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Genotype-dependent epigenetic regulation of DLGAP2 in alcohol use and dependence. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 26, 4367–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillemacher, T.; Rhein, M.; Burkert, A.; Heberlein, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Glahn, A.; Muschler, M.A.N.; Kahl, K.G.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; et al. DNA-methylation of the dopamin receptor 2 gene is altered during alcohol withdrawal. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschler, M.A.N.; Hillemacher, T.; Kraus, C.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Frieling, H. DNA methylation of the POMC gene promoter is associated with craving in alcohol dependence. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasteva, M.; Koycheva, Y.; Taseva, T.; Simeonova, S. Changes in the Expression of DNA Methylation Related Genes in Leukocytes of Persons with Alcohol and Drug Dependence. Acta Medica Bulg. 2020, 47, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Yamada, H.; Munetsuna, E.; Fujii, R.; Yamazaki, M.; Ando, Y.; Mizuno, G.; Ishikawa, H.; Ohashi, K.; Tsuboi, Y.; et al. Association of drinking behaviors with TXNIP DNA methylation levels in leukocytes among the general Japanese population. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2022, 48, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugue, P.A.; Wilson, R.; Lehne, B.; Jayasekara, H.; Wang, X.; Jung, C.H.; Joo, J.E.; Makalic, E.; Schmidt, D.F.; Baglietto, L.; et al. Alcohol consumption is associated with widespread changes in blood DNA methylation: Analysis of cross-sectional and longitudinal data. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, S.; Agrawal, A.; Purushottam, M.; Anand, S.D.; Shankarappa, B.; Sharma, P.; Jain, S.; Murthy, P. Changes in DNA methylation persist over time in males with severe alcohol use disorder—A longitudinal follow-up study. Am. J. Med Genet. Part B: Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2021, 186, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Liao, Y.; Tang, J.; Miao, Q.; Hao, W. Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in discordant sib pairs with alcohol dependence. Asia-Pacific Psychiatry 2013, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, B.; Reulbach, U.; Kornhuber, J.; Bleich, S.; Bönsch, D. Homocysteine associated genomic DNA hypermethylation in patients with chronic alcoholism. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.L.; Chan, R.F.; Zhao, M.; Xie, L.Y.; Copeland, W.E.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Aberg, K.A.; Oord, E.J.C.G.v.D. Dual methylation and hydroxymethylation study of alcohol use disorder. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13114–e13114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, M.; Bollepalli, S.; Cazaly, E.; Salvatore, J.E.; Barr, P.; Rose, R.J.; Dick, D.; Kaprio, J.; Ollikainen, M. Associations of Alcohol Consumption With Epigenome-Wide DNA Methylation and Epigenetic Age Acceleration: Individual-Level and Co-twin Comparison Analyses. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xueying, Q.; Hexiang, P.; Wenjing, G.; Hägg, S.; Weihua, C.; Chunxiao, L.; Canqing, Y.; Jun, L.; Zengchang, P.; et al. Genome-wide associations between alcohol consumption and blood DNA methylation: evidence from twin study. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohoff, F.W.; Roy, A.; Jung, J.; Longley, M.; Rosoff, D.B.; Luo, A.; O’connell, E.; Sorcher, J.L.; Sun, H.; Schwandt, M.; et al. Epigenome-wide association study and multi-tissue replication of individuals with alcohol use disorder: evidence for abnormal glucocorticoid signaling pathway gene regulation. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2224–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzardo, A.; Henkhaus, R.; Butler, M. Global DNA promoter methylation in frontal cortex of alcoholics and controls. Gene 2012, 498, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarev, I.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Harris, R.A.; Mayfield, R.D. Gene Coexpression Networks in Human Brain Identify Epigenetic Modifications in Alcohol Dependence. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnsack, J.P.; Teppen, T.; Kyzar, E.J.; Dzitoyeva, S.; Pandey, S.C. The lncRNA BDNF-AS is an epigenetic regulator in the human amygdala in early onset alcohol use disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouko, L.A.; Shantikumar, K.; Knezovich, J.; Haycock, P.; Schnugh, D.J.; Ramsay, M. Effect of Alcohol Consumption on CpG Methylation in the Differentially Methylated Regions ofH19andIG-DMRin Male Gametes-Implications for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautman, A.; Gurumoorthy, A.; Hansen, K.A. Effects of alcohol use on sperm chromatin structure, a retrospective analysis. Basic Clin. Androl. 2023, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaseg, E.; Von Wald, T.; Hansen, K.A. Vitamin D levels and human sperm DNA fragmentation: a prospective, cohort study. Basic Clin. Androl. 2022, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieting, J.; Rhein, M.; Hillemacher, T.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Hoppe, V.; Müschen, L.; Glahn, A.; Frieling, H.; Bleich, S.; Muschler, M. DNA Methylation of the Leptin Gene Promoter is Altered by Chronic Alcohol Exposure in an Animal Model for Alcohol Dependence. Eur. Addict. Res. 2019, 25, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakharkar, A.J.; Kyzar, E.J.; Gavin, D.P.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Krishnan, H.R.; Grayson, D.R.; Pandey, S.C. Altered amygdala DNA methylation mechanisms after adolescent alcohol exposure contribute to adult anxiety and alcohol drinking. Neuropharmacology 2019, 157, 107679–107679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokare, D.M.; Kyzar, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Sakharkar, A.J.; Pandey, S.C. Adolescent Alcohol Exposure-Induced Changes in Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone and Neuropeptide Y Pathways via Histone Acetylation in the Brain During Adulthood. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera-Juanes, R.; Wilhelm, L.J.; Park, B.; A Grant, K.; Ferguson, B. Alcohol-dose-dependent DNA methylation and expression in the nucleus accumbens identifies coordinated regulation of synaptic genes. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e994–e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.; Tapocik, J.D.; Juergens, N.; Pitcairn, C.; Borich, A.; Schank, J.R.; Sun, H.; Schuebel, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, Q.; et al. DNA Methylation in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Regulates Alcohol-Induced Behavior and Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6153–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastain, L.G.; Franklin, T.; Gangisetty, O.; Cabrera, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Shrivastava, P.; Jabbar, S.; Sarkar, D.K. Early life alcohol exposure primes hypothalamic microglia to later-life hypersensitivity to immune stress: possible epigenetic mechanism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, J.; Pascual, M.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Miñarro, J.; Guerri, C. Involvement of tlr4 in the long-term epigenetic changes, rewarding and anxiety effects induced by intermittent ethanol treatment in adolescence. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 53, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sahota, P.; Thakkar, M.M. Chronic alcohol exposure reduces acetylated histones in the sleep-wake regulatory brain regions to cause insomnia during withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 2020, 180, 108332–108332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkel, T.D.M.; Zhang, H.; Teppen, T.; Sakharkar, A.J.; Pandey, S.C. Essential Role of Histone Methyltransferase G9a in Rapid Tolerance to the Anxiolytic Effects of Ethanol. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzar, E.J.; Bohnsack, J.P.; Zhang, H.; Pandey, S.C. MicroRNA-137 Drives Epigenetic Reprogramming in the Adult Amygdala and Behavioral Changes after Adolescent Alcohol Exposure. eneuro 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzar, E.J.; Zhang, H.; Pandey, S.C. Adolescent Alcohol Exposure Epigenetically Suppresses Amygdala Arc Enhancer RNA Expression to Confer Adult Anxiety Susceptibility. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, T.M.; Vore, A.S.; Deak, T. Acute Ethanol Challenge Differentially Regulates Expression of Growth Factors and miRNA Expression Profile of Whole Tissue of the Dorsal Hippocampus. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 884197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, I.; Cagnon, V.; Lizarte, F.; Tirapelli, L.; Tirapelli, D.; Arantes, R.; Chuffa, L.; Martinez, F.; Martinez, M. Ethanol and caffeine consumption modulates the expression of miRNAs in the cerebellum and plasma of UChB rats. Life Sci. 2019, 229, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielawski, D.M.; Zaher, F.M.; Svinarich, D.M.; Abel, E.L. Paternal alcohol exposure affects sperm cytosine methyltransferase messenger RNA levels. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezovich, J.G.; Ramsay, M. The Effect of Preconception Paternal Alcohol Exposure on Epigenetic Remodeling of the H19 and Rasgrf1 Imprinting Control Regions in Mouse Offspring. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finegersh, A.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal Alcohol Exposure Reduces Alcohol Drinking and Increases Behavioral Sensitivity to Alcohol Selectively in Male Offspring. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e99078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Diao, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Huang, G.; Ma, D. Paternal ethanol exposure and behavioral abnormities in offspring: Associated alterations in imprinted gene methylation. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorko, D.; Bekdash, R.A.; Zhang, C.; Sarkar, D.K. Male Germline Transmits Fetal Alcohol Adverse Effect on Hypothalamic Proopiomelanocortin Gene Across Generations. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimipour, M.; Talebi, A.R.; Anvari, M.; Sarcheshmeh, A.A.; Omidi, M. Effects of different doses of ethanol on sperm parameters, chromatin structure and apoptosis in adult mice. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 170, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompala, G.R.; Mounier, A.; Wolfe, C.M.; Lin, Q.; Lefterov, I.; Homanics, G.E. Heavy Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure Alters Small Noncoding RNAs in Mouse Sperm and Epididymosomes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Tian, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Highly sensitive sequencing reveals dynamic modifications and activities of small RNAs in mouse oocytes and early embryos. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501482–1501482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiajie, T.; Yanzhou, Y.; Hoi-Hung, A.C.; Zi-Jiang, C.; Wai-Yee, C. Conserved miR-10 family represses proliferation and induces apoptosis in ovarian granulosa cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, Y.S.; Wang, H.; Thomas, K.N.; Basel, A.; Prunier, J.; Robert, C.; Golding, M.C. Alcohol induced increases in sperm Histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation correlate with increased placental CTCF occupancy and altered developmental programming. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, E.P.; McGee, C.L. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: An Overview with Emphasis on Changes in Brain and Behavior. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbar, S.; Chastain, L.G.; Gangisetty, O.; A Cabrera, M.; Sochacki, K.; Sarkar, D.K. Preconception Alcohol Increases Offspring Vulnerability to Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Diao, L.; Liu, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Huang, G.; Ma, D. Paternal ethanol exposure and behavioral abnormities in offspring: Associated alterations in imprinted gene methylation. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, C.L.; Burling, T.A.; Lochry, E.A.; Sutker, P.B. The effect of paternal alcohol consumption on fetal development in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1982, 9, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Jamerson, P.; Wulser, M.J.; Kimler, B.F. Neurobehavioral effects in rat pups whose sires were exposed to alcohol. Dev. Brain Res. 2004, 149, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccurello, R.; Carito, V.; Ciafrè, S.; Ferraguti, G.; Giacovazzo, G.; Mancinelli, R.; Tirassa, P.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Pascale, E.; Ceccanti, M.; et al. Paternal alcohol exposure in mice alters brain NGF and BDNF and increases ethanol-elicited preference in male offspring. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, L.R.; Myren, K.; Sturm, J.; Burau, D. Acute paternal alcohol use affects offspring development and adult behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimes, A.; Kim, C.K.; Cuarenta, A.; Auger, A.P.; Pak, T.R. Binge Drinking and Intergenerational Implications: Parental Preconception Alcohol Impacts Offspring Development in Rats. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompala, G.R.; Finegersh, A.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal preconception ethanol exposure blunts hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity and stress-induced excessive fluid intake in male mice. Alcohol 2016, 53, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.L.; Lee, J.A. Paternal Alcohol Exposure Affects Offspring Behavior but not Body or Organ Weights in Mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1988, 12, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Choi, C.S.; Park, J.H.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H.M.; Kim, K.C.; Jeon, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Han, S.-H.; et al. Chronic exposure to ethanol of male mice before mating produces attention deficit hyperactivity disorder-like phenotype along with epigenetic dysregulation of dopamine transporter expression in mouse offspring. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, M.; Misslin, R.; Vogel, E.; Holownia, A.; Copin, J.; Tholey, G. Paternal alcohol exposure: developmental and behavioral effects on the offspring of rats. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, D.F.; Cicero, T.J.; Kettinger, L.; Meyer, E.R. Paternal alcohol consumption in the rat impairs spatial learning performance in male offspring. Psychopharmacol. 1991, 105, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finegersh, A.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal Alcohol Exposure Reduces Alcohol Drinking and Increases Behavioral Sensitivity to Alcohol Selectively in Male Offspring. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e99078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottom, R.T.; Kozanian, O.O.; Rohac, D.J.; Erickson, M.A.; Huffman, K.J. Transgenerational Effects of Prenatal Ethanol Exposure in Prepubescent Mice. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 812429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koabel, J.; McNivens, M.; McKee, P.; Pautassi, R.; Bordner, K.; Nizhnikov, M. The offspring of alcohol-exposed sires exhibit heightened ethanol intake and behavioral alterations in the elevated plus maze. Alcohol 2021, 92, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeler, E.; Nobile, Z.L.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal Preconception Every-Other-Day Ethanol Drinking Alters Behavior and Ethanol Consumption in Offspring. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, S.J.; Harding, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Kosten, T.A. Paternal alcohol exposure has task- and sex-dependent behavioral effect in offspring. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 46, 2191–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Neurocircuitry in alcoholism: a substrate of disruption and repair. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 180, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, J.M.; Fergusson, D.M. Alcohol and depression. Addiction 2011, 106, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orford, J.; Velleman, R. Offspring of parents with drinking problems: drinking and drug-taking as young adults. Addiction 1990, 85, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rompala, G.R.; Finegersh, A.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal preconception ethanol exposure blunts hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity and stress-induced excessive fluid intake in male mice. Alcohol 2016, 53, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeler, E.; Nobile, Z.L.; Homanics, G.E. Paternal Preconception Every-Other-Day Ethanol Drinking Alters Behavior and Ethanol Consumption in Offspring. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, S.J.; Haile, C.N.; Quave, C.B.; Harding, M.J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Meisch, R.A.; Kosten, T.A. Paternal alcohol exposure reduces acquisition of operant alcohol self-administration and affects Bdnf DNA methylation in male and female offspring. Addict. Biol. 2022, 27, e13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Choi, C.S.; Park, J.H.; Joo, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H.M.; Kim, K.C.; Jeon, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Han, S.-H.; et al. Chronic exposure to ethanol of male mice before mating produces attention deficit hyperactivity disorder-like phenotype along with epigenetic dysregulation of dopamine transporter expression in mouse offspring. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, L.R.; Myren, K.; Sturm, J.; Burau, D. Acute paternal alcohol use affects offspring development and adult behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Abozaid, A.; Tsang, B.; Gerlai, R. Exposure of parents to alcohol alters behavior of offspring in zebrafish. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Yasari, A.; Jabbar, S.; A Cabrera, M.; Rousseau, B.; Sarkar, D.K. Preconception Alcohol Exposure Increases the Susceptibility to Diabetes in the Offspring. Endocrinology 2021, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimes, A.; Torcaso, A.; Pinceti, E.; Kim, C.K.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J.; Pak, T.R. Adolescent binge-pattern alcohol exposure alters genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the hypothalamus of alcohol-naïve male offspring. Alcohol 2017, 60, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, S.; Chastain, L.G.; Gangisetty, O.; A Cabrera, M.; Sochacki, K.; Sarkar, D.K. Preconception Alcohol Increases Offspring Vulnerability to Stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2782–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Rao, Y.S.; Prins, S.A.; Pak, T.R. Parental Binge Alcohol Abuse Alters F1 Generation Hypothalamic Gene Expression in the Absence of Direct Fetal Alcohol Exposure. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e89320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.C.; Skiles, W.M.; Chronister, S.S.; Wang, H.; Sutton, G.I.; Bedi, Y.S.; Snyder, M.; Long, C.R.; Golding, M.C. DNA methylation-independent growth restriction and altered developmental programming in a mouse model of preconception male alcohol exposure. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Species | Site of Investigation | DNA Methylation | Histone Modification | miRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trautman, 2023 [48] | Human | Sperm | Alcohol use did not show a significant association with the High DNA Stainability or DNA Fragmentation Index of sperm | N/A | N/A |
| Abrishamcar, 2022 [19] | Human | Cord blood samples | Identified 6 CpG sites associated with mQLT Hypermethylation of MAD1L1, CAMTA1, and ALDH1A genes |
N/A | N/A |
| Clark, 2022 [40] | Human | Post-mortem brain samples | Epigenomic deconvolution was utilized to conduct methylome-wide association studies specific to cell types within granulocytes, T-cells, B-cells, and monocytes in 1,132 blood samples. | N/A | N/A |
| Blaseg, 2022 [49] | Human/male | Serum and sperm | In non-drinkers, the levels of High DNA Stainability increased | N/A | N/A |
| Bedi, 2022 [72] | Mice/male | Sperm | No significant alterations in s-adenosylmethionine or DNA methylation levels were detected in the study | Widespread elevation in sperm H3K4me3 enrichment was observed | N/A |
| Barney, 2022 [61] | Rats | Blood and brain (amygdala and dorsal hippocampus) | N/A | N/A | Male and female rats were administered saline or ethanol (3.5 g/kg), and their brains were collected three hours after the injection. The purpose was to evaluate the expression of growth factor, cytokine, or miRNA |
| Maeda, 2021 [35] | Human | Blood samples(leukocytes) | A cross-sectional study was conducted on 404 individuals, comprising 176 males and 228 females. The participants were categorized into non-drinkers, moderate drinkers, and heavy drinkers based on their self-reported drinking habits. The pyrosequencing assay was utilized to determine the levels of TXNIP DNA methylation in leukocytes | N/A | N/A |
| Stephenson, 2021 [41] | Human | Whole-blood samples | The sample was comprised of individuals sourced from the Finnish Twin Cohorts. Participants self-reported their alcohol consumption within the previous week, and their epigenome-wide DNA methylation was evaluated in whole-blood samples | N/A | N/A |
| Soundararajan, 2021 [37] | Human/male | Blood samples | alterations in DNA methylation patterns within peripheral blood leukocytes of individuals with AUD who were actively seeking treatment •gene-specific methylation at ALDH2/MTHFR and global methylation |
N/A | N/A |
| Lu, 2021 [42] | Human | Whole blood samples | • Total of 57 pairs of monozygotic (MZ) twins who exhibited discordance in alcohol consumption, sourced from the Chinese National Twin Registry • 158 pairs of both monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic twins were assessed from the Swedish Adoption/Twin Study of Aging |
N/A | N/A |
| Lohoff, 2021 [43] | Human | Blood samples | • Extensive analysis of DNA methylation epigenome-wide association in AUD, comprising 625 participants. A cross-tissue/cross-phenotypic approach was employed to replicate the top hit (N = 4798) and identify novel epigenetic targets relevant to AUD | N/A | N/A |
| Sharma, 2020 [57] | Mice/male (C57BL/6J) |
Basal forebrain Lateral hypothalamus |
N/A | Expression of acetylated histones, H3 lysine 14 (AcH3K14), was examined in two major sleep-wake regulatory brain regions | N/A |
| Krasteva, 2020 [34] | Human | Blood samples | The expression pattern of genes associated with DNA methylation, such as DNMT1 and DNMT3a methyltransferases, as well as MeCP2, MBD1, MBD2, MBD3, and MBD4 methyl CpG binding domain proteins, was assessed in blood samples obtained from individuals with alcohol and drug dependence, in comparison to those who abstain from substance use and are in good health. | N/A | N/A |
| Dugué, 2019 [36] | Human | Blood samples | Using the Illumina HumanMethylation450 BeadChip, DNA methylation was measured in blood samples from 5606 Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study participants | N/A | N/A |
| Chastain, 2019 [55] | Rat/male | Hypothalamic microglia | Decreased global DNA methylation in PND 2–6 alcohol-exposed |
Increased global acetylation of histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9a) in PND 2–6 alcohol-exposed | N/A |
| Gangisetty, 2019 [23] | Human | Peripheral blood sample | Kyzar, 2019 [60] | Rat/male | Amygdala |
| Hillemacher, 2019 [32] | Human | Blood samples | A significant increase in DRD2-gene methylation during alcohol withdrawal/early abstinence | N/A | N/A |
| Rossetto, 2019 [62] | Rat | Cerebellum and plasma | N/A | N/A | Increased the levels of specific miRNAs, including miR-155-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-126-3p, and miR-132-3p, in the cerebellum |
| Kyzar, 2019 [61] | Rat | Amygdala | N/A | N/A | miRNA 137 was implicated in the process of chromatin remodeling at BDNF exon IV |
| Kyzar, 2019 [60] | Rat/male | Amygdala | Decreased Arc eRNA expression | Increased H3K27me3 occupancy at the Arc SARE site and five other locations across the Arc promoter and gene body in the amygdala of AIE adult rats compared with AIS rats | N/A |
| Meng, 2019 [31] | Cohort1: human/male Cohort2: human |
Cohort 1: Brain tissues Cohort 2: Whole blood samples |
Methylation within DMR-DLGAP2 | N/A | N/A |
| Sakharkar, 2019 [51] | Rat/male | Amygdala | One hour after exposure: decreased DNMT activity and DNMT3b expression, increased inducible protein 45 mRNA expressions in AIE rats compared to AIS rats 24 hours after exposure: increased DNMT activity but normalized Gadd45 and DNMT3b mRNA expression in AIE rats compared to AIS rats Adulthood: increased DNA methylation of Npy and BDNF exon IV is in the AIE compared to AIS |
N/A | N/A |
| Wieting, 2019 [50] | Rat/male | Blood samples | Increased leptin gene promotor methylation | N/A | N/A |
| Bohnsack, 2019 [46] | Human | Amygdala | N/A | N/A | miRNA 137 was implicated in the process of chromatin remodeling at BDNF exon IV |
| Berkel, 2019 [58] | Rat/male | Amygdala | N/A | Decrease in the levels of H3K9me2 and G9a protein in the amygdala | N/A |
| Zhang, 2018 [26] | Rat/male | Amygdala | N/A | Lower occupancy of acetylated histone H3K9/14 proteins at particular sites in the Creb1, Cbp, and p300 gene promoter regions in amygdala | N/A |
| Philibert, 2018 [29] | Human | Whole blood DNA | Genome-wide methylation | N/A | N/A |
| Rompala, 2018 [69] | Mice/male | Sperm | N/A | N/A | Chronic intermittent alcohol exposure has induced changes in multiple miRNA and tDR (tRNA-derived RNA) species in sperm |
| Cervera-Juanes, 2017 [53] | Rhesus macaques/male | Nucleus accumbens | 17 DMRs, including 14 with methylation levels associated with alcohol consumption Decreased LRP5-DMR methylation Increased JAKMIP1-DMR and GPR39-DMR methylation |
N/A | N/A |
| Kyzar, 2017 [27] | Rat | Amygdala | N/A | Exposure to ethanol causes a reduction in the levels of messenger RNA (mRNA) associated with H3 lysine 9 demethylation (H3K9me2) in the amygdala | N/A |
| Jiajie, 2017 [71] | Human, mouse, and rat | Ovarian granulosa cells | N/A | N/A | miRNA is suggested to function as a posttranscriptional regulator of the alcohol-related gene BDNF |
| Kokare, 2017 [52] | Rat/male | Amygdala and hypothalamus | N/A | Decreased histone H3K9/14 acetylation in the neuropeptide Y promoter in the amygdala, increased histone H3K9/14 acetylation in the melanocortin four receptor gene promoter in the amygdala, and the melanocortin four receptor and pro-opiomelanocortin promoters in the hypothalamus of adolescent intermittent ethanol-exposed adult rats compared with controls | N/A |
| Montesinos, 2016 [56] | Mice/female | Medial prefrontal cortex | Increased expression of BDNF and FosB in wild-type mice | Up-regulated acetylation levels at H3 (K9)and H4 (K5, K12), decreased the tri-methylation of the H3 (K4) levels in adolescent mice after ethanol treatment in wild-type mice | N/A |
| Yang, 2016 [70] | Mice | Oocytes and early embryos | N/A | N/A | The small RNAs that exhibited increased levels of sperm due to alcohol exposure |
| Crews, 2016 [25] | Human | Review | Alcohol at different stages of life can disrupt chromatin function and DNA methylation | N/A | N/A |
| Barbier, 2015 [54] | Rat/male | Medial prefrontal cortex | Global DNA methylation in the medial prefrontal cortex Hypermethylation of the promoter region and exon 1 of Syt2 and on the promoter region of Cacna1a in the medial prefrontal cortex |
N/A | N/A |
| Philibert, 2014 [28] | Human | Blood cells | genome-wide DNA methylation analyses in mononuclear blood cells, finding significant changes in DNA methylation levels between patients with alcohol use disorder and healthy control subjects | N/A | N/A |
| Liang, 2014 [66] | Mice/male | Sperm and in the cerebral cortices | DNA methylation levels at imprinted gene loci are decreased in the sperm of mice subjected to chronic alcohol treatment | N/A | N/A |
| Finegersh, 2014 [65] | Mice/male | Sperm | DNA methylation levels at imprinted gene loci are decreased in the sperm of mice subjected to chronic alcohol treatment | N/A | N/A |
| Zhao, 2013 [38] | Human | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 865 hypomethylated and 716 hypermethylated CG sites in individuals who consumed alcohol | N/A | N/A |
| Zhang, 2013 [30] | Human | Peripheral blood cells | DNA methylation patterns based on ethnicity were observed in individuals with alcohol addiction | N/A | N/A |
| Ponomarev, 2012 [45] | Human | Amygdala and frontal cortex | evidenced by the association between DNA hypomethylation and increased histone H3K4 trimethylation in alcoholics | N/A | |
| Manzardo, 2012 [44] | Human | Human | No significant differences between alcohol-dependent individuals and controls in terms of global methylation parameters or most gene targets | DNA methylation was detected in various variants of histone proteins, particularly those associated with gene loci in the HIST2 domain of chromosome 1 | N/A |
| Knezovich, 2012 [64] | Mice/male | Sperm | DNA methylation levels at imprinted gene loci are decreased in the sperm of mice subjected to chronic alcohol treatment | N/A | N/A |
| Muschler, 2010 [33] | Human | Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in the brain | Different drinking patterns demonstrated an increase in DNA methylation of POMC genes among binge and heavy drinkers | N/A | N/A |
| Ouko, 2009 [47] | Human | Sperm | Increase methylation levels at the promoters of the POMC gene in sperm | N/A | N/A |
| Bönsch, 2004 [39] | Human | Peripheral blood cells | Global DNA hypermethylation in the mononuclear cells | N/A | N/A |
| Bielawski, 2002 [63] | Rat/male | Sperm | Decrease in the levels of DNMT1 in the sperm of rodents | N/A | N/A |
| Study | Species/Gender of Alcoholic Subjects | Ethanol Exposure Protocol | Abstinent Time | Studied Generation(s) | Phenotype and Molecular Changes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nieto, 2022 [96] | Rat/Male | 5 days each week for 6 weeks | Mating 8 weeks later | Male and female/ F1 | Lower levels of BDNF DNA methylation in the NAc and higher levels in the mPFC in alcohol-exposed sires. Aaberrant BDNF DNA methylation patterns in alcohol-sired offspring of both sexes compared to control-sired offspring. |
| Nieto, 2022 [90] | Rat/Male | For 6 weeks (5 days/week) | Mating 8 weeks after exposure | Male and female/F1 | EPM: Less anxiety-like behavior in alcohol-sired males that were not affected by alcohol administration. OFT: No significant differences in OFT results in both male and female offspring Paternal alcohol exposure provides protection against the initial reinforcing effects of alcohol. Anxiolytic effects of alcohol in the open field in male offspring only with no paternal alcohol effect No change in locomotor activity in either sex as a result of either paternal alcohol exposure or alcohol administration Sex-specific effects of paternal alcohol exposure in the rotarod test Blunted sensitivity to the alcohol's motor-impairing effects in alcohol-sired male offspring, enhanced sensitivity in alcohol-sired female offspring |
| Bottom, 2022 [87] | Mice/Male | Prenatally exposed | Mate during adulthood | Male and female/F1, F2 | Sensory processing deficits, increased risk-taking behavior CD1 mice exposed to ethanol prenatally resulted in no change in anxiety-like behavior in offspring male CD1 mice prenatally exposed to ethanol, the depressive-like behavior increased Behavioral abnormalities are linked to parental ethanol exposure in mice, including abnormal sensorimotor processing No evidence of heritable, transgenerational phenotypes following a multi-level analysis of several key neocortical components, including sensory area connectivity, gene expression, and spine density analysis Decreased brain/body weights, altered Id2 expression, and reduced spine density in S1 neurons in F1 |
| Al-Yasari, 2021 [100] | Rat/Female | 30 days of treatment | 3 weeks after the last exposure | Male and female/ F1 | An altered stress gene network involving glucose metabolism in oocytes in female rats fed with alcohol in the liquid diet, but not with the isocaloric liquid diet, prior to conceptionF1: Significant hyperglycemia and hypoinsulinemia in the offspring born from preconception alcohol-fed mothers when they were adults, increased levels of inflammatory cytokines and cellular apoptosis in the pancreas, altered insulin production and actions in the liver, and a reduced number of proopiomelanocortin neurons in the hypothalamus |
| Suresh, 2021 [99] | Zebrafish/Female and male | For 7 days | Mating 7 hours after last exposure | Male and female/F1 | Increased duration and reduced frequency of immobility, increased turn angle, and increased intra-individual variance of turn angle in offspring of alcohol-exposed parents displayed anxiety and exploratory behavior alterations. |
| Koabel, 2021 [88] | Rat/Male | For 6 weeks, 5 days per week | Mating 8 weeks after last exposure | Male and female/F1 | Ethanol administration decreased anxiety in male progenies of ethanol-sired rats but not in female progenies OFT: Paternal alcohol exposure does not affect rats of either sex's baseline anxiety-like behavior |
| Rossetto, 2019 [62] | UChB rat/Male | Ethanol: 70 days Caffeine: 55 days |
NA | NA | Expression of miRNAs associated with the inflammatory process in the tissue and plasma of the UChB rats after ethanol and caffeine exposure. Increased expression of the analyzed miRNAs155-5p, -146a-5p, -126-3p, -132-3p for the cerebellar tissue in the Ethanol group, reduced expression of them in the Ethanol+caffeine groupو elevated levels of miR-126-3p and miR-132-3p and decreased levels of miR-155-5p in plasma as a result of caffeine exposure |
| Hill, 2019 [18] | Human | NA | NA | Third-generation offspring (F3) with and without a family background of alcoholdependence | Familial diathesis for alcohol dependence confers changes in methylation of the DRD2 gene that have implications for the reduction of volumes of the fusiform, insula, and temporal regions in the left hemisphere, structures involved in social cognition. Strong collinearity between prenatal use of substances and familial risk for alcohol dependence; it is unlikely that these would have been responsible for the reduction in volume seen in these regions. |
| Chang, 2019 [104] | Mice/Male | For 70 days | Mating after the final exposure | Male and female/ F1 | Fetal growth restriction, decreased placental efficiency, abnormalities in cholesterol trafficking, sex-specific alterations in the genetic pathways regulating hepatic fibrosis, and disruptions in the regulation of imprinted genes (decreased expression of Gnas and Grb10 within the placentas of male offspring and Sgce in the female offspring of EtOH-exposed males, significant reductions in transcripts encoding Cdkn1c, Dcn, and Gnas in male offspring and Meg3 in female offspring in the fetal liver) |
| Beeler, 2019 [89] | B6 mice/Male | For 12 weeks, every other day two bottle choice | Mating 48 hours after the last exposure | Male and female/F1 | OFT: distance did not change. In male: duration time in center increased. No change in total resting time, increased resting time in center and decreased in periphery EPM: no change in parameters DID: reduced ethanol binge-like drinking in male, but not female offspring No preference for sweet and bitter taste |
| Asimes, 2018 [80] | Rat/Male and female | PND 37-44 and PND 67-74 | Mating 24 hours after the last treatment | Male and female/F1 | Hypothalamic GnRH mRNA decreased (male and female)Circulating LH: decreased only in male Circulating testosterone decreased in male and female Tetis: No change in gross morphology or number of elongated spermatids Corticosterone decreased in males but not females, with no change in GR, CRF, AVP Both parents exposed to ethanol 24 hours before mating resulted in significantly lower pup body weights during adolescence and adulthood (PND 37-44 and PND 67-74) Small body weight, fewer play behavior |
| Asimes, 2017 [101] | Rat/Male and female | binge-ethanol exposure paradigm during early (postnatal day 37-44) and late (67-74) adolescent development | Mating 24 hours after the last ethanol dose | Male and female/F1 | Differential DNA methylation patterns in the hypothalamus in offsprings of alcohol-exposed parents DMCs were distinct between offspring depending on which parent was exposed to ethanol. Novel DMCs in offspring with both parents exposed to ethanol DMCs mostly in intergenic, intronic and coding functional regions, no direct correlation between DMCs and gene mRNA expression No change in sex ratio and litter size |
| Rompala, 2016 [94] | C57 mice/Male | 5 weeks of exposure (inhalation) | Mating after the final exposure | Male and female/F1 | Decreased corticosterone secretion after restrain stress only in male Increased fluid intake in response to restrain stress (only in male) CPP: No change in ethanol preference during chronic variable stress No change in bodyweight Polydipsia induced by stress was not observed in male offspring |
| Jabbar, 2016 [74] | Rat/Female | For 4 weeks | Mating 3 weeks after the last treatment | Male and female/F1 | Plasma corticosterone increased in male, ACTH no change After LPS: plasma corticosterone and ACTH increased in both male and female Hypothalamus: CRH increased, β-endorphin decreased, AVP no change CRF mRNA increased, POMC mRNA increasedHippocampus and amygdala: Crfr1 decreased normalize after administration of methylation-blocker Maternal ethanol exposure three weeks before mating did not affect the behavior of mothers in terms of licking, grooming, and arched-back nursing Maternal exposure to alcohol resulted in a longer pregnancy duration and decreased body weight Maternal exposure to alcohol did not affect mothers' care Anxiety: increased in males but not females (EPM and OFT), normalized after administration of methylation-blocker |
| Ceccanti, 2016 [78] | CD1 mice/Male | For 60 days | Mating 2 months after the last exposure | Male/F1 | PFC: BDNF increased, P75 and NGF decreased, Trk, DAT, D1 and D2DR no change Hippocampus: TrkA increased, BDNF, NGF, TrkB, P75, D1D2DR, DAT no change Hypothalamus: No change Olfactory bulb: DAT increased, other no change The number of pups, sex ratio, and mortality rate of pups were not affected by paternal alcohol exposure Ethanol CPP: condition with low dose (0.5) but not high dose (1.5) Bodyweight decreased, mortality rate and number of pups did not change. |
| Liang, 2014 [66] | Mice/Male | Every 2 days for 4 weeks | Mating after one month | Male and female/F1 | F0: sperms: increased methylation of H19, Peg3 F1 cerebral cortex: No change in methylation of H19, Peg 3, Ndn, decreased methylation of Snrpn Mortality rate increased among the offspring of ethanol-exposed sires The offspring's body weight was not affected by paternal alcohol exposure before gestation Weight and sex ratio no change EPM: Increased anxiety only in females Depressive-like behavior: increased only in females MWM: memory and learning impaired in males and females |
| Kim, 2014 [97] | ICR mice/Male | For 7 weeks (at 5 weeks of age) | Mating 1 week after the final treatment | Male/F1 | DAT decreased in mPFC and striatum DNMT1 and MeCP2 decreased in mPFC and striatumMethylation in DAT promoter increased The offspring's body weight was not affected by paternal alcohol exposure before gestation OFT: increased locomotor activity Electro-foot shock aversive water drinking: increased impulsivity Attention/spontaneous alternation behavior in Y-maze test increased (ADHD-like behavior) |
| Finegersh, 2014 [86] | C57 mice/Male | 5 weeks of exposure (inhalation) | Mating after the final exposure | Male and female/ F1 | F0: Decreased DNA methylation at the BDNF exon Ixa F1 (VTA): Decreased methylation at the bdnf exon IXa, no change in bdnf exon IV, dlk-1 F1 VTA: Increased BDNF expression in exon IX only in male offspring mPFC: no change |
| Finegersh, 2014 [65] | C57 mice/Male | 5 weeks of exposure (inhalation) | Mating after the final exposure | Male and female/F1 | TBC test: decrease ethanol preference in male-but, not femalesEPM: no change in basal anxiety-like behavior The increased anxiolytic effect of ethanol only in male OFT: no change accelerating rotarod: no change Ethanol clearance: no change |
| Przybycien-Szymanska, 2014 [103] | Rat/ Male and female | PND 37-44 | Mating on PND 75 | Male and female/ F1 | Genome-wide microarray analysis: changes in gene expression involved in neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity in the hypothalamus on PND 7 FGF 13 decreased, BMP1 increased in males, RELN increased in females, SERPINI1 increased in males, PAK3 decreased, IGF2R increased in males, VAMP3 increased in males, GnRH increased in males, and ApoE decreased. |
| Knezovich, 2012 [64] | Mice/Male | For 5 weeks | Mating at week 6 | Male/ F1 | Two paternally methylated ICRs (H19 and Rasgrf1): decreased in somatic DNA |
| Meek, 2007 [79] | Mice/Male | A single dose | Mating 12-24 hours after exposure | Male and female/F1 | Male mice exposed to ethanol 12 hours before mating had a higher mortality rate and fewer pups Delay in: surface righting, clinging, the tail-pull reflex, rotation, linear movement, climbing an inclined surface, stretched attention, flatback, freezing, and defensive burying Increased aggressive behavior Decreased defensive/fearful behaviors |
| Ledig, 1998 [84] | Rat/Male | For 3 months | Mating 2 months after the exposure | Male and female/F1 | Male mice exposed to acute ethanol 12 hours before mating exhibited a reduced total number of pups In the cultured glia: protein levels did not change during 3 weeks after culture but decreased in 4th week Enolase increased in the first week, with no change until 4th week Glutamine synthase decreased in the first and second weeks SOD decreased in the second week but did not change on remained weeks OFT: locomotion increased Novelty-seeking: locomotion and rearing increased, the latency decreased Light-dark test: time in light increased |
| Wozniak, 1991 [85] | Rat/Male | PND 30, For 39 days | Mating 2 weeks after last treatment | Male and female/F1 | adolescent exposure to ethanol in male rats (2 weeks before mating) resulted in no alteration in developmental landmarks and body weight No change in the NOR test Impaired spatial learning performance in males, but not female in T-maze and RAM |
| Abel, 1988 [82] | Randall, 1982 | Mice/Male | For 5 weeks | Mating 24 hours after the last exposure | Male F1: Decreased serum testosterone level The offspring's body weight was not affected by paternal alcohol exposure before gestation PAT: Memory impairment in offspring following paternal ethanol exposure Decreased required trials to learn a passive avoidance task Longer latencies to reach the choice point in a T-maze paternal ethanol exposure increased locomotion, decreased latency in the novelty-seeking test, and increased time spent in the light compartment during the light-dark test. |
| Randall, 1982 [76] | Mice/Male | For 5 weeks | Mating 24 hours after the last exposure | Male and female/F1 | The number of pups, sex ratio, and mortality rate of pups were not affected by paternal alcohol exposure No change in weight gain, sex ratio, and malformation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





