Submitted:
01 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental procedures
2.2.1. CBDV administration at adulthood (Study 1)
2.2.2. CBDV administration at weaning (Study 2)
2.2.3. Behavioral assessment (studies 1 and 2)
2.2.4. Brain assessment of inflammatory and plasticity markers through RT-PCR (Studies 1 and 2)
2.3. Statistical analysis
3. Results
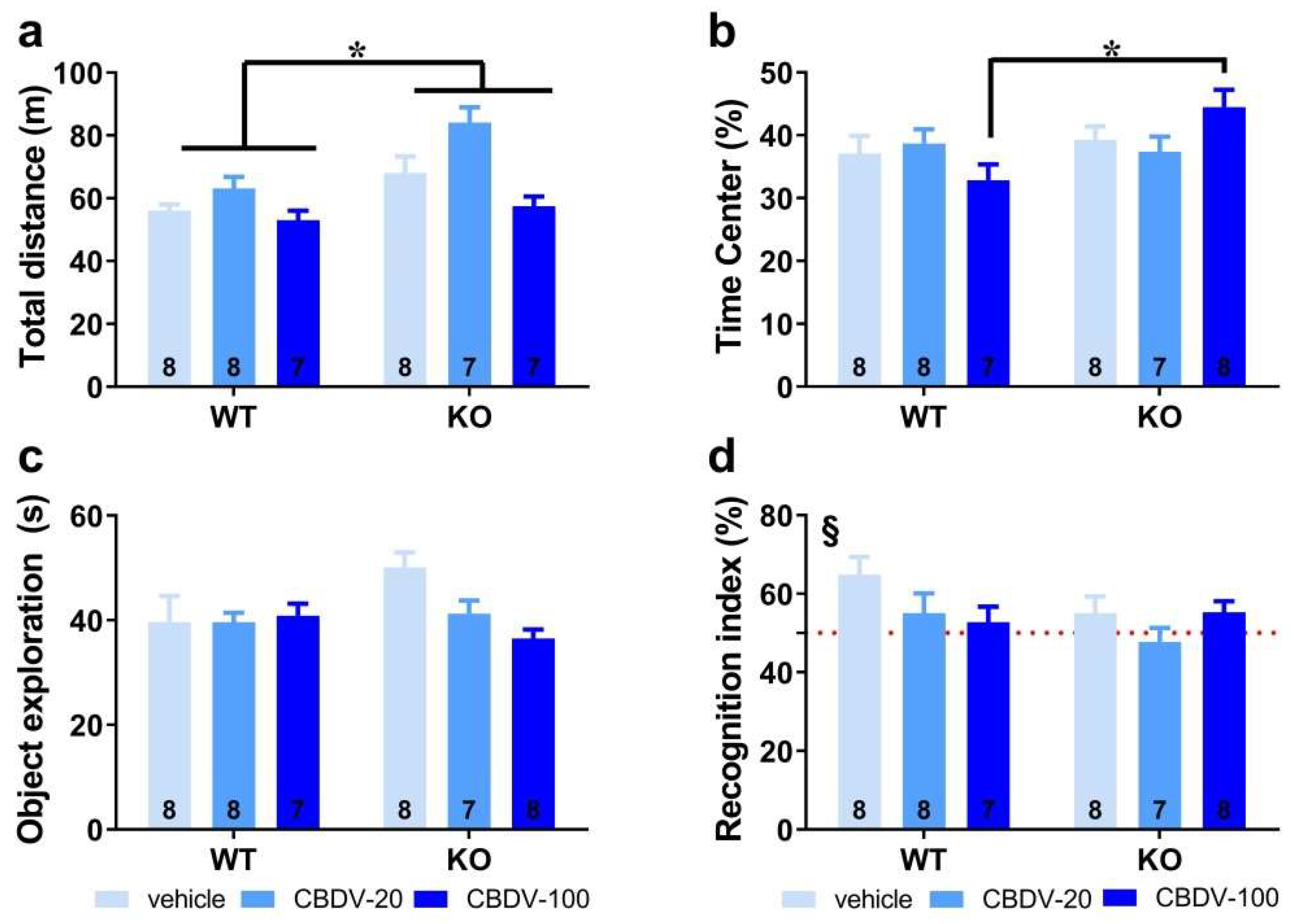
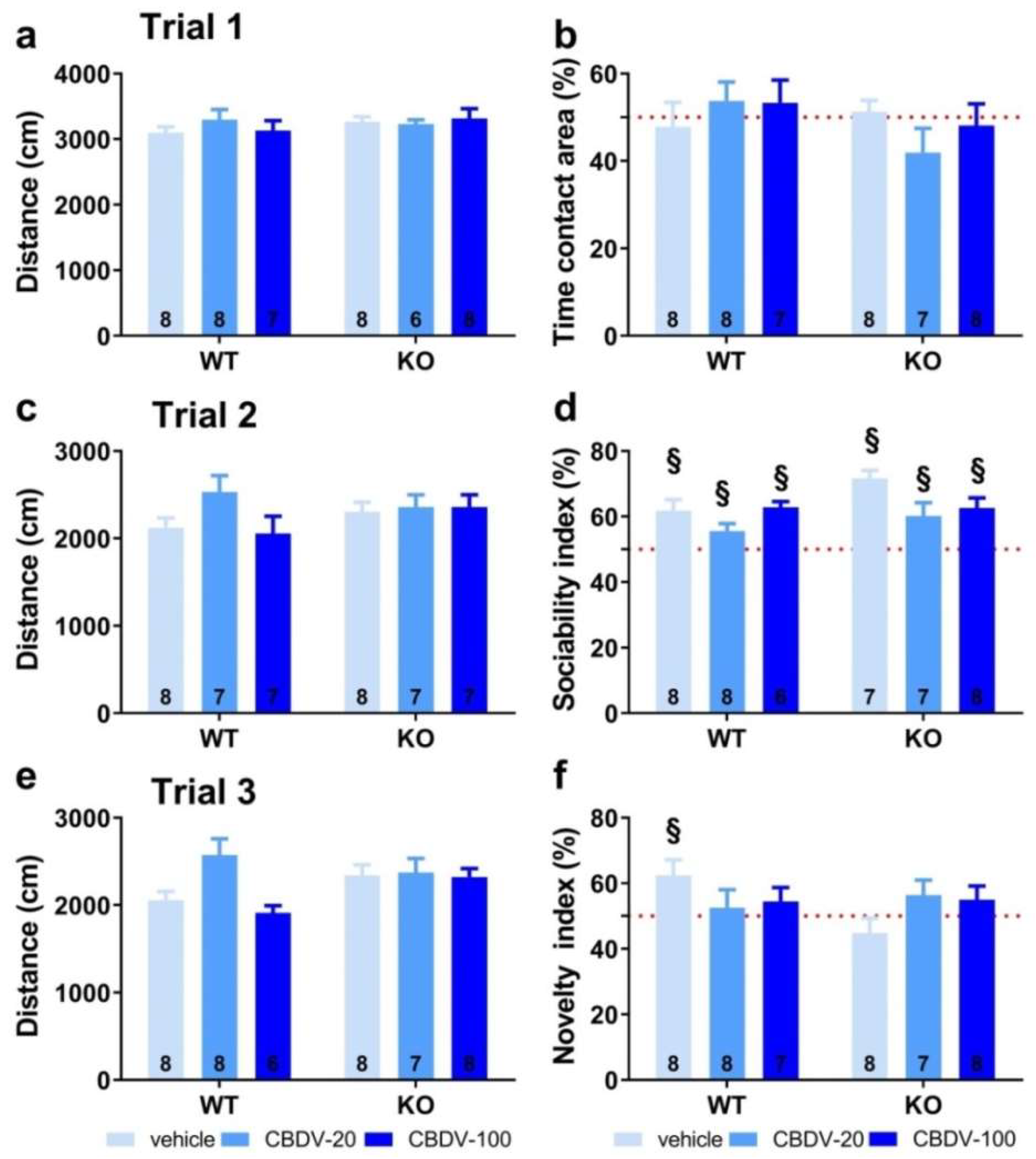
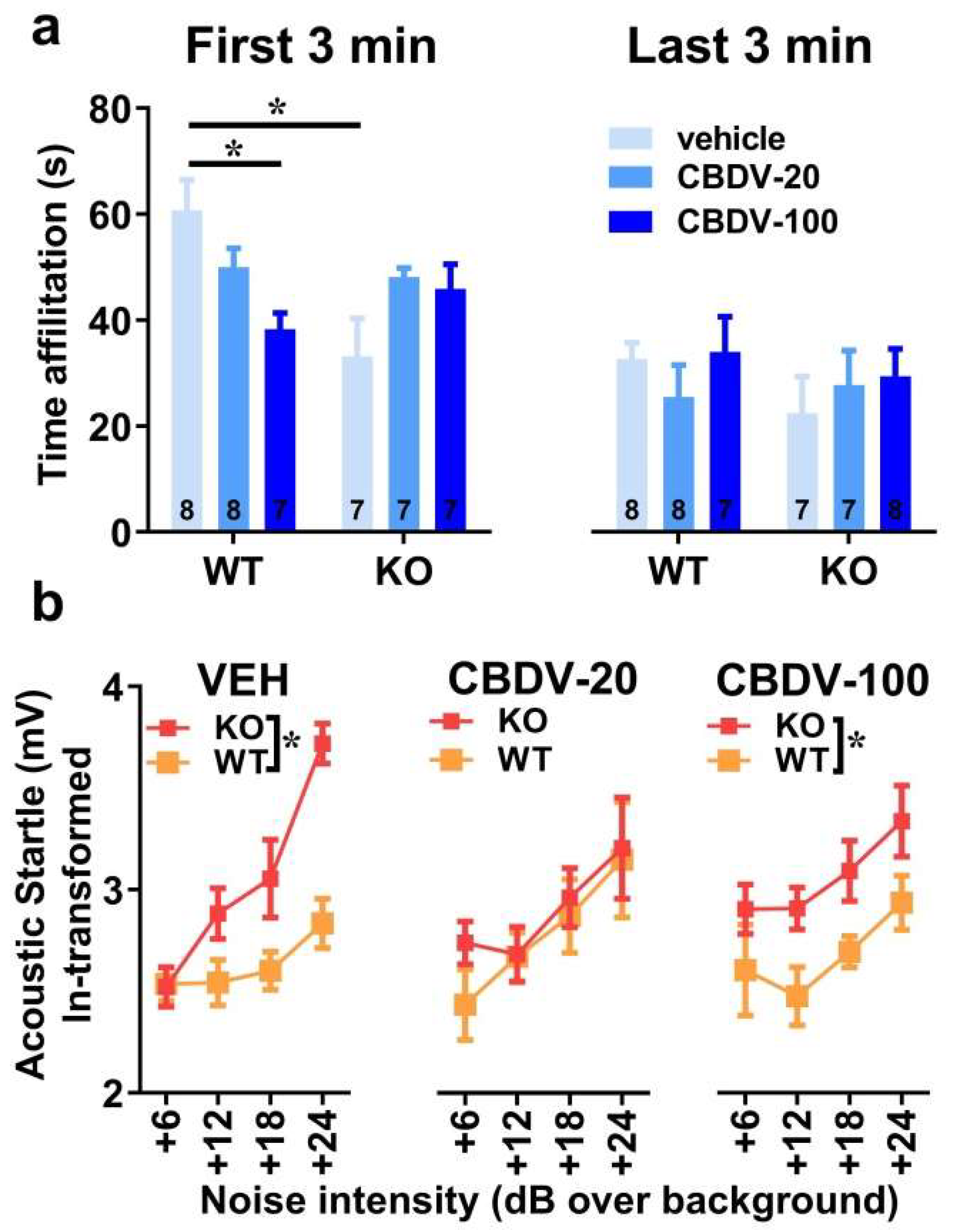
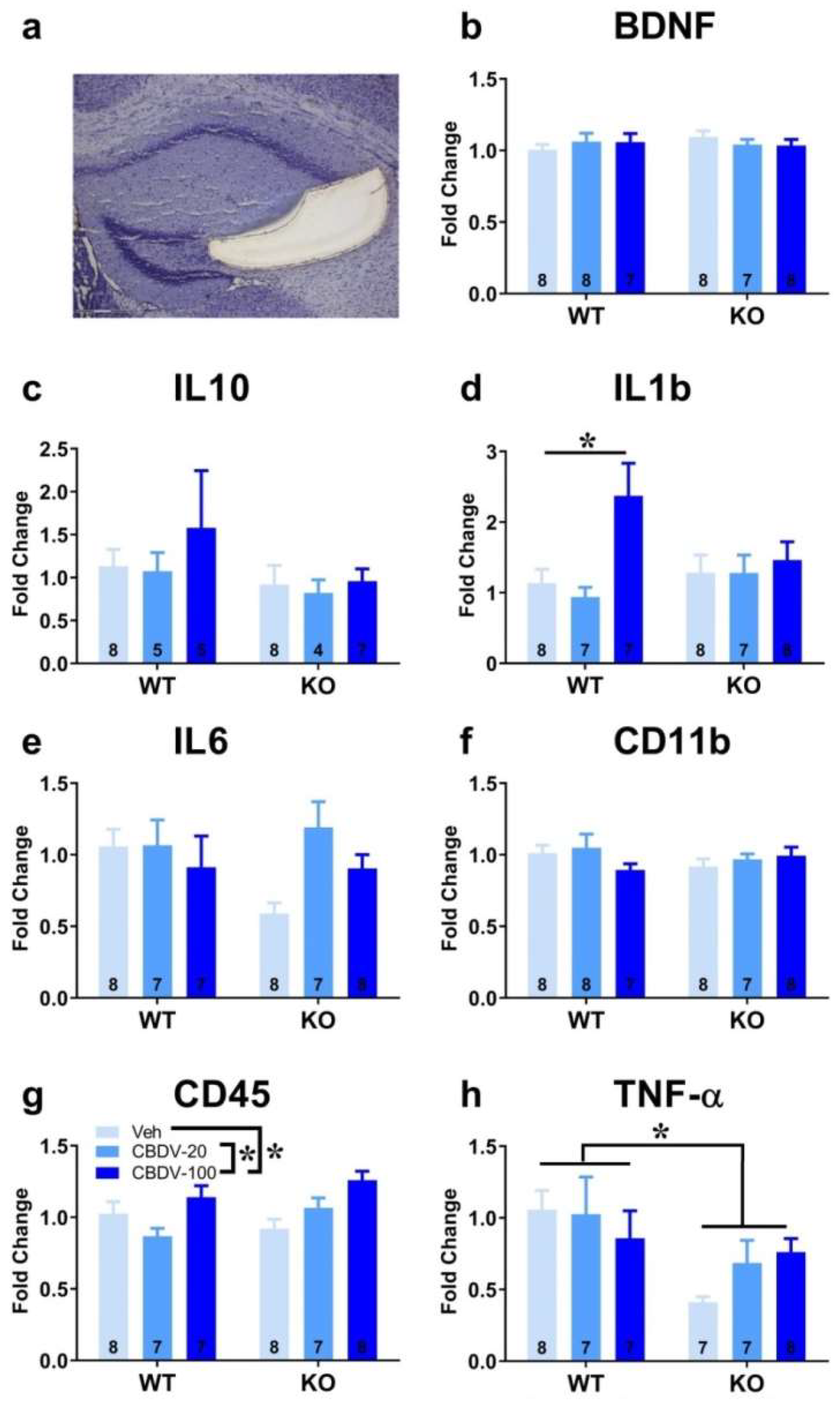
3.1. Study 1: Effects of subchronic administration of CBDV at adulthood
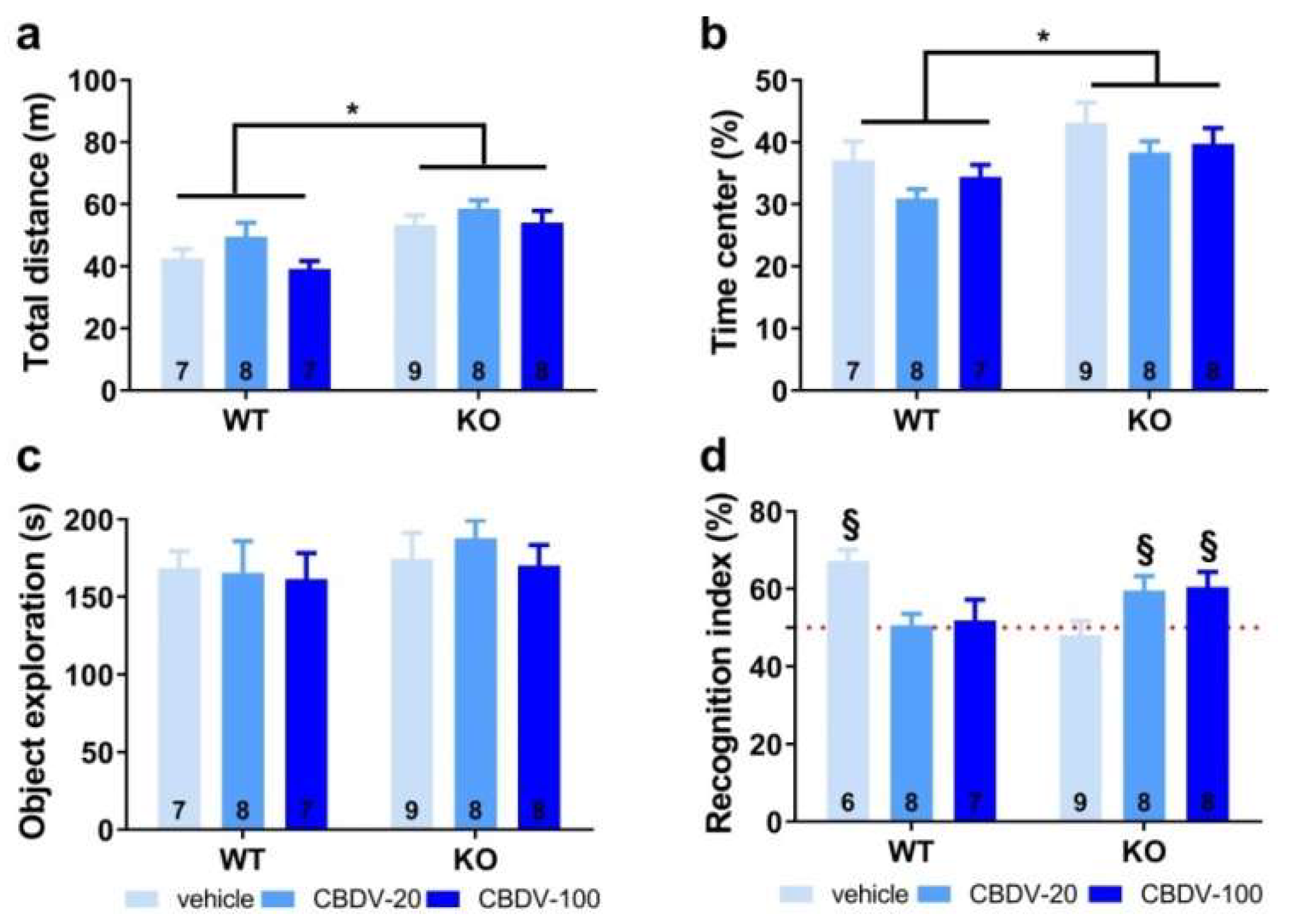
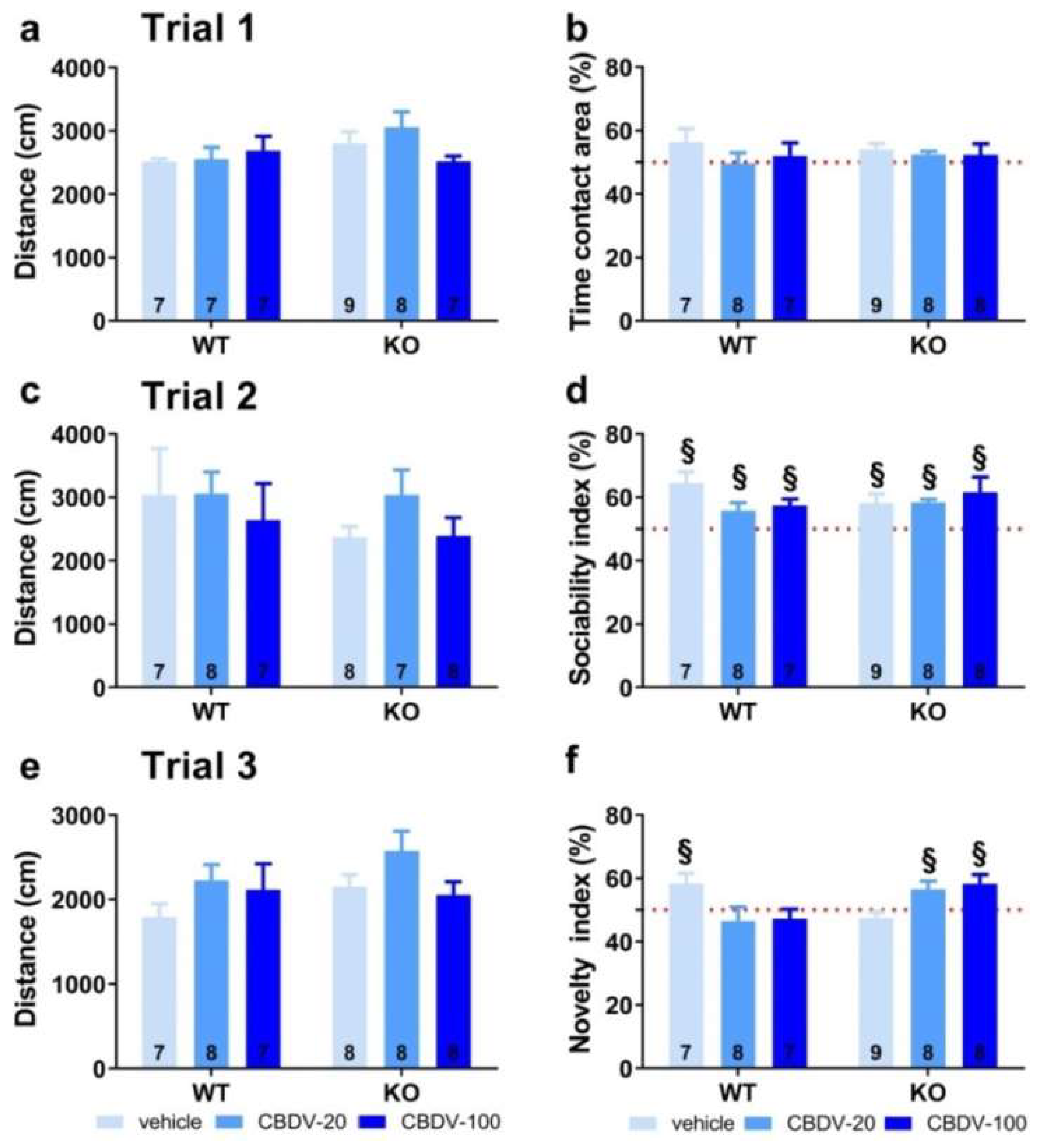
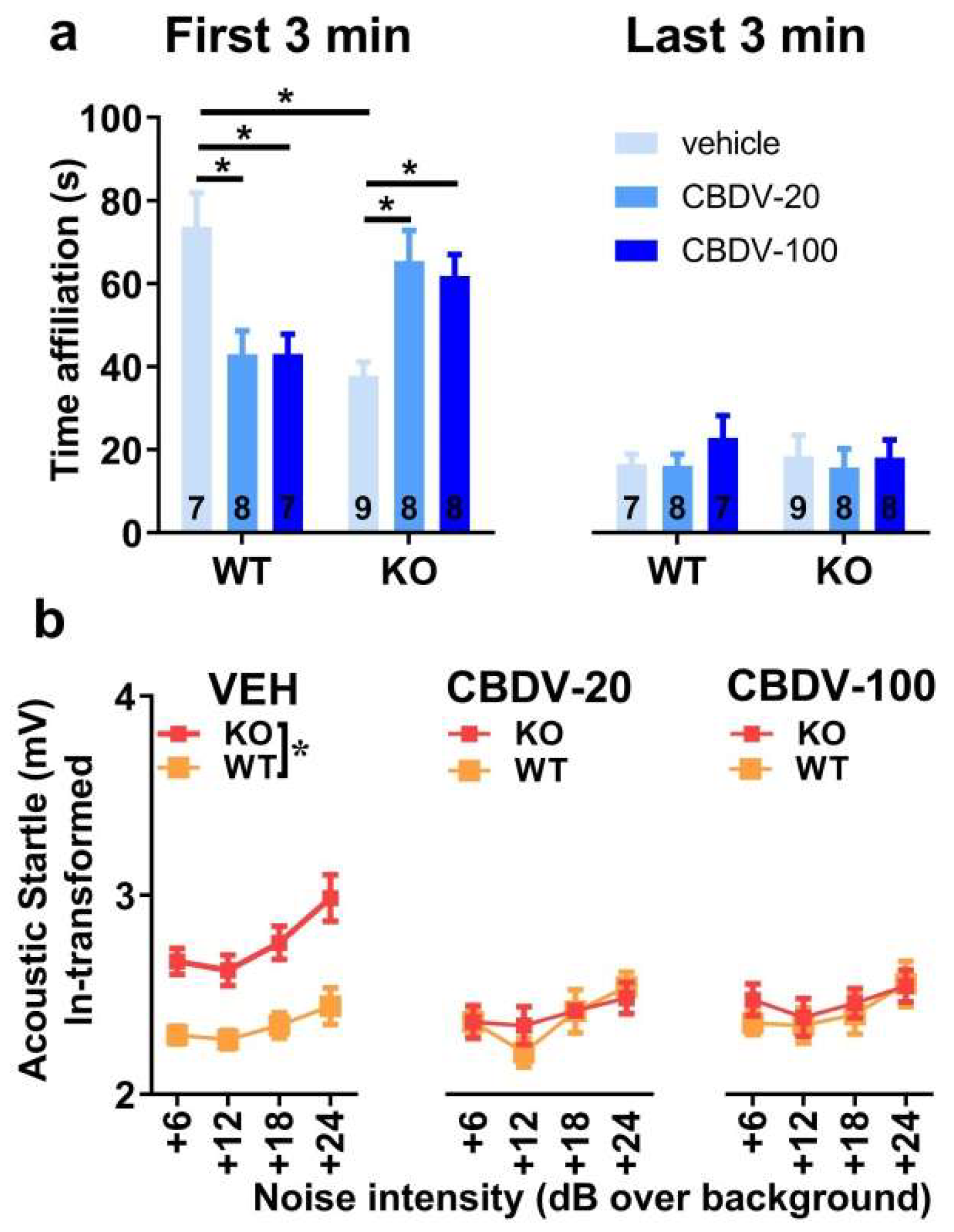
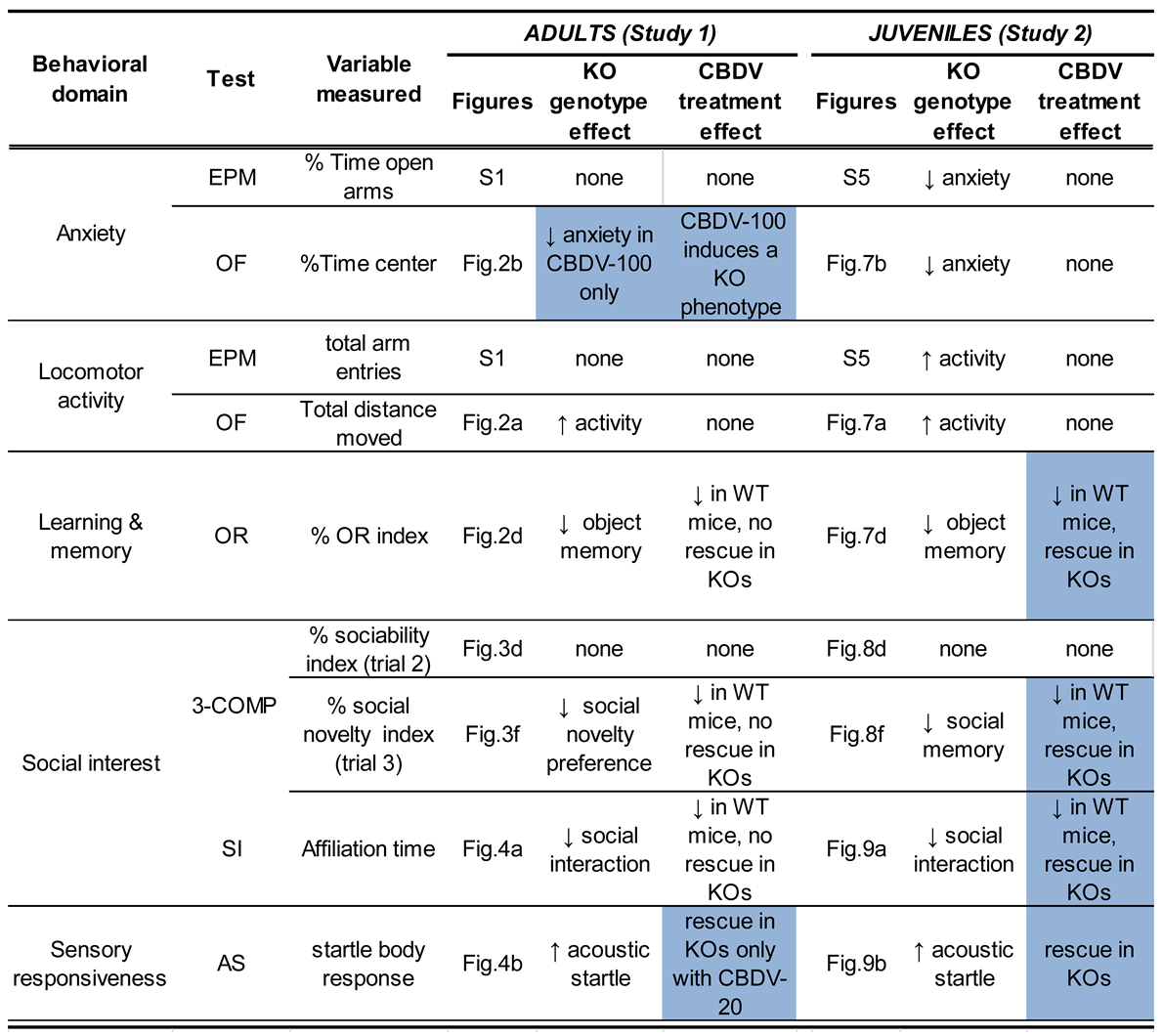
3.1.1. Behavioral profiling
- Elevated plus maze
- Object recognition test
- Three-compartment test for sociability and social novelty
- Direct social interaction with an adult female
- Acoustic startle
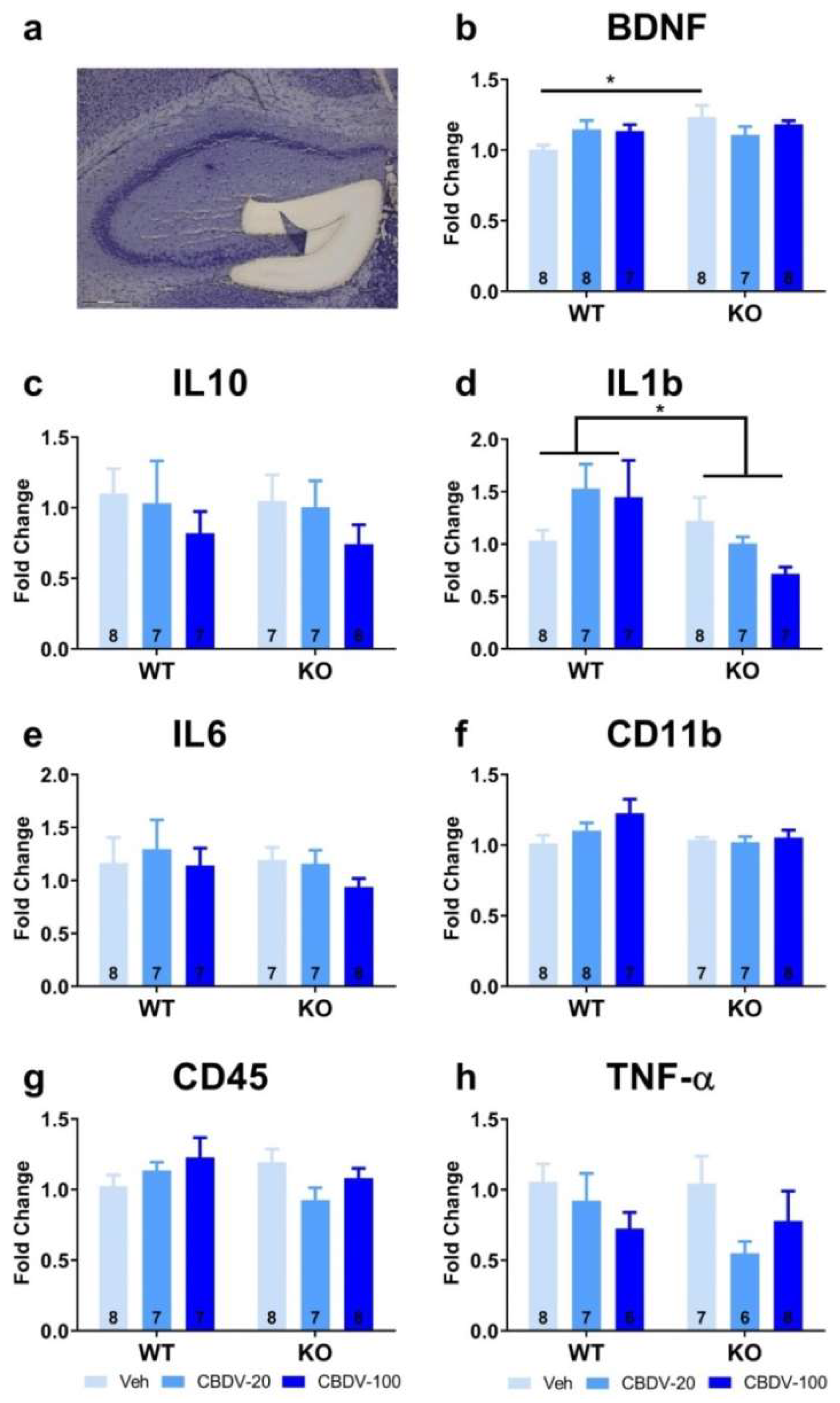
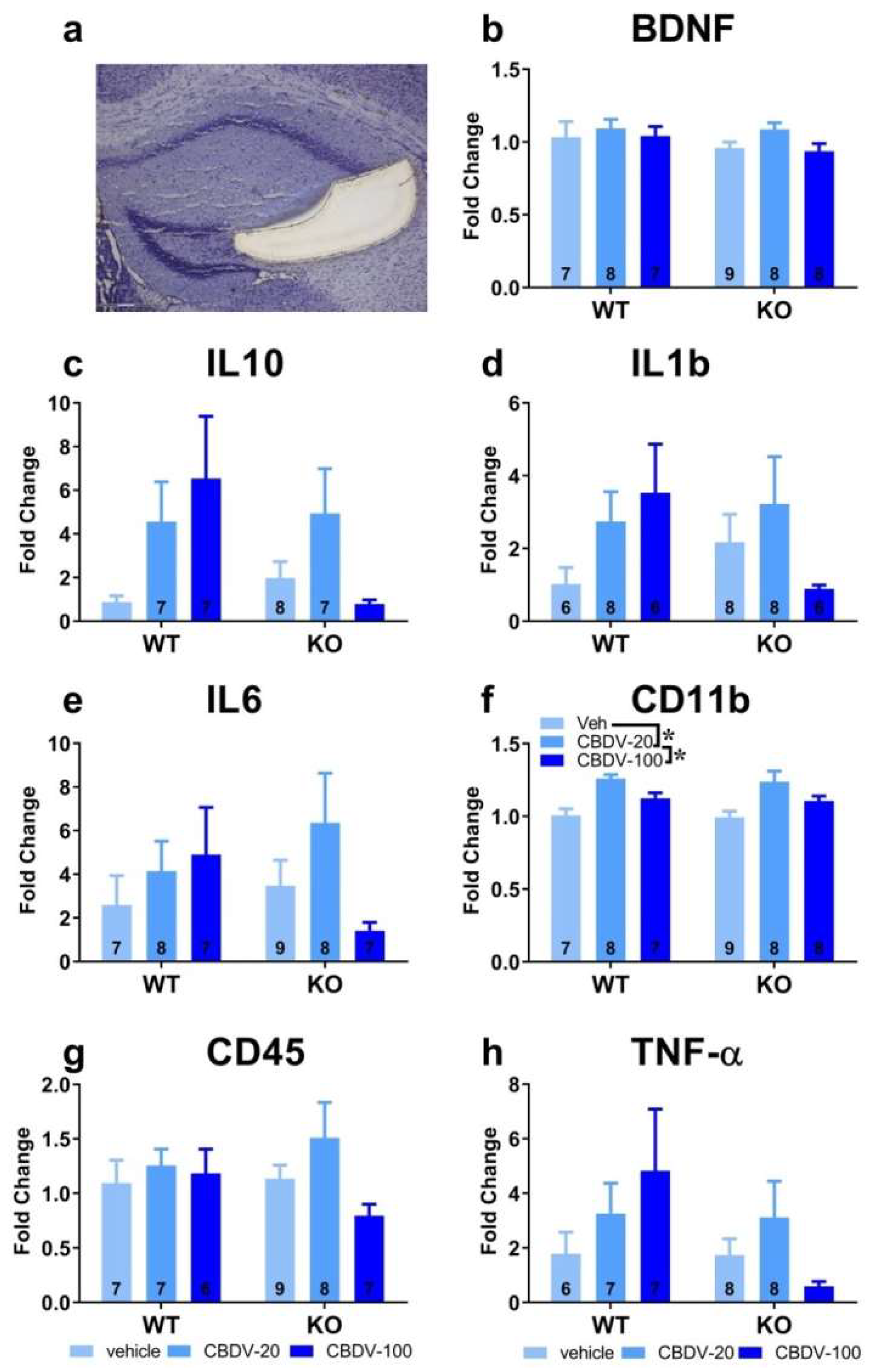
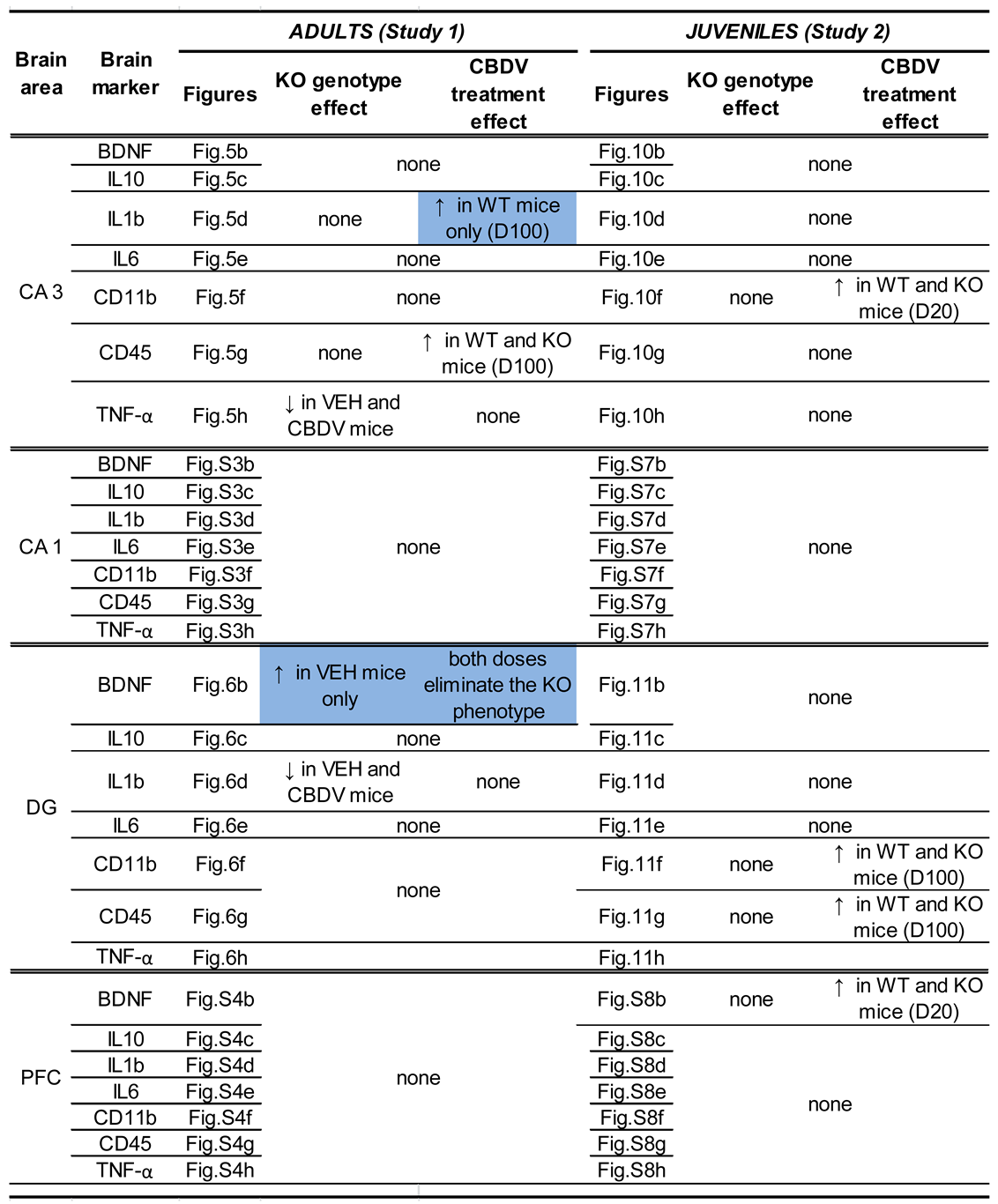
3.1.2. Brain analyses
- Hippocampus
- Prefrontal cortex
3.2. Study 2: Effects of chronic administration of CBDV at weaning
3.2.1. Behavioral profiling
- Elevated plus maze
- Object recognition test
- Three-compartment test for sociability and social novelty
- Direct social interaction with an adult female
- Acoustic startle
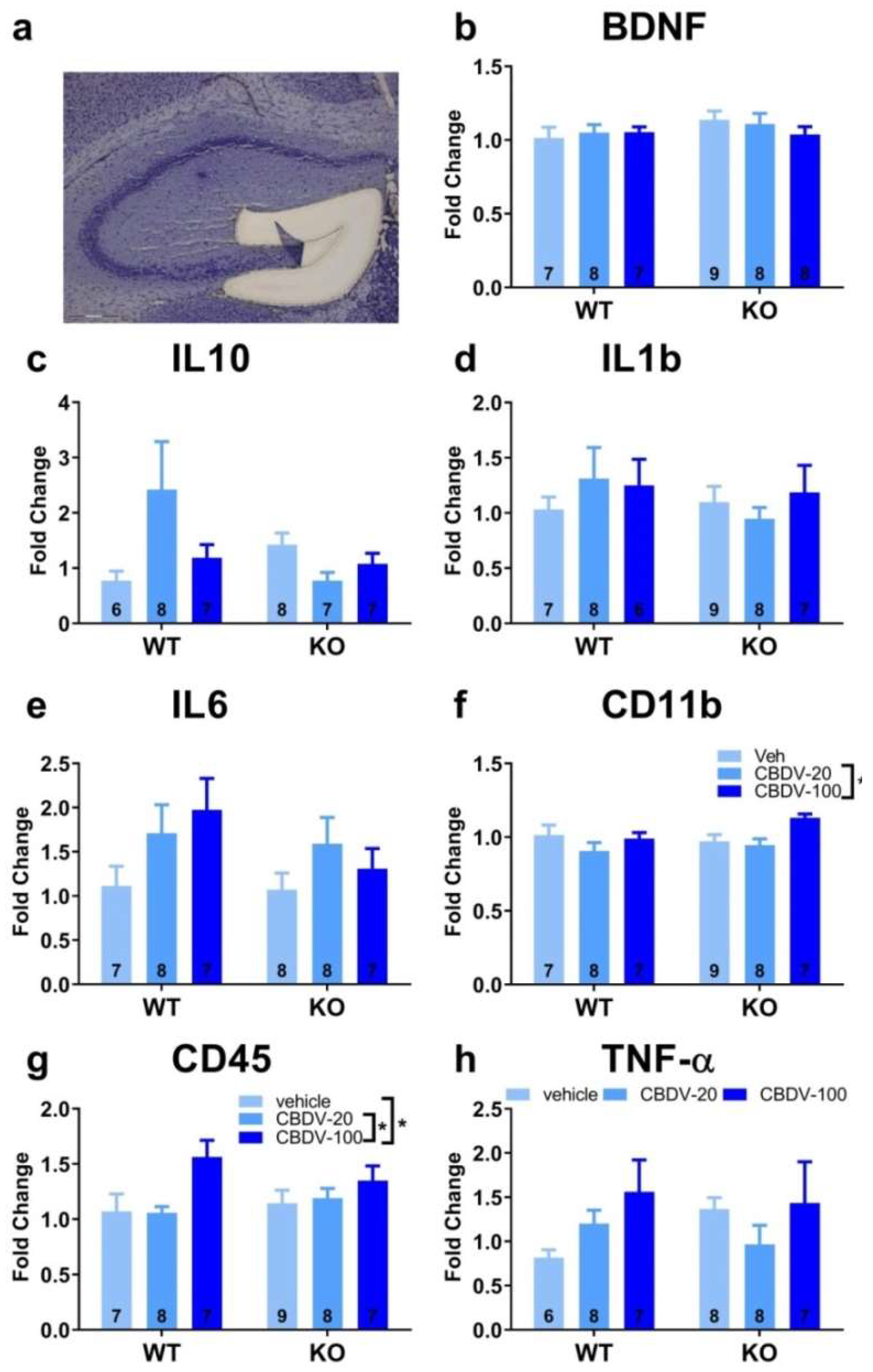
3.2.2. Brain analyses
- Hippocampus
- Prefrontal cortex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parolaro, D., N. Realini, D. Vigano, C. Guidali, and T. Rubino. “The Endocannabinoid System and Psychiatric Disorders.” Exp Neurol 224, no. 1 (2010): 3-14. [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K. “Distribution of Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System.” Handb Exp Pharmacol, no. 168 (2005): 299-325. [CrossRef]
- Basavarajappa, B. S., R. A. Nixon, and O. Arancio. “Endocannabinoid System: Emerging Role from Neurodevelopment to Neurodegeneration.” Mini Rev Med Chem 9, no. 4 (2009): 448-62. [CrossRef]
- Berghuis, P., A. M. Rajnicek, Y. M. Morozov, R. A. Ross, J. Mulder, G. M. Urban, K. Monory, G. Marsicano, M. Matteoli, A. Canty, A. J. Irving, I. Katona, Y. Yanagawa, P. Rakic, B. Lutz, K. Mackie, and T. Harkany. “Hardwiring the Brain: Endocannabinoids Shape Neuronal Connectivity.” Science 316, no. 5828 (2007): 1212-6. [CrossRef]
- Monory, K., F. Massa, M. Egertova, M. Eder, H. Blaudzun, R. Westenbroek, W. Kelsch, W. Jacob, R. Marsch, M. Ekker, J. Long, J. L. Rubenstein, S. Goebbels, K. A. Nave, M. During, M. Klugmann, B. Wolfel, H. U. Dodt, W. Zieglgansberger, C. T. Wotjak, K. Mackie, M. R. Elphick, G. Marsicano, and B. Lutz. “The Endocannabinoid System Controls Key Epileptogenic Circuits in the Hippocampus.” Neuron 51, no. 4 (2006): 455-66. [CrossRef]
- Vigli, D., L. Cosentino, C. Raggi, G. Laviola, M. Woolley-Roberts, and B. De Filippis. “Chronic Treatment with the Phytocannabinoid Cannabidivarin (Cbdv) Rescues Behavioural Alterations and Brain Atrophy in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome.” Neuropharmacology 140 (2018): 121-29. [CrossRef]
- Zamberletti, E., M. Gabaglio, F. Piscitelli, J. S. Brodie, M. Woolley-Roberts, I. Barbiero, M. Tramarin, G. Binelli, N. Landsberger, C. Kilstrup-Nielsen, T. Rubino, V. Di Marzo, and D. Parolaro. “Cannabidivarin Completely Rescues Cognitive Deficits and Delays Neurological and Motor Defects in Male Mecp2 Mutant Mice.” J Psychopharmacol 33, no. 7 (2019): 894-907. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Romero, A., L. Galera-Lopez, P. Ortiz-Romero, A. Llorente-Ovejero, L. de Los Reyes-Ramirez, I. Bengoetxea de Tena, A. Garcia-Elias, A. Mas-Stachurska, M. Reixachs-Sole, A. Pastor, R. de la Torre, R. Maldonado, B. Benito, E. Eyras, R. Rodriguez-Puertas, V. Campuzano, and A. Ozaita. “Cannabinoid Signaling Modulation through Jzl184 Restores Key Phenotypes of a Mouse Model for Williams-Beuren Syndrome.” Elife 11 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Garcia, A., M. Gomis-Gonzalez, T. Guegan, C. Agustin-Pavon, A. Pastor, S. Mato, A. Perez-Samartin, C. Matute, R. de la Torre, M. Dierssen, R. Maldonado, and A. Ozaita. “Targeting the Endocannabinoid System in the Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome.” Nat Med 19, no. 5 (2013): 603-7. [CrossRef]
- Jung, K. M., M. Sepers, C. M. Henstridge, O. Lassalle, D. Neuhofer, H. Martin, M. Ginger, A. Frick, N. V. DiPatrizio, K. Mackie, I. Katona, D. Piomelli, and O. J. Manzoni. “Uncoupling of the Endocannabinoid Signalling Complex in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Nat Commun 3 (2012): 1080. [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M., S. Rossi, M. Bari, V. De Chiara, C. Rapino, A. Musella, G. Bernardi, C. Bagni, and D. Centonze. “Abnormal Mglu 5 Receptor/Endocannabinoid Coupling in Mice Lacking Fmrp and Bc1 Rna.” Neuropsychopharmacology 35, no. 7 (2010): 1500-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. , and B. E. Alger. “Enhanced Endocannabinoid Signaling Elevates Neuronal Excitability in Fragile X Syndrome.” J Neurosci 30, no. 16 (2010): 5724-9. [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, M., F. P. Zhang, Y. H. Fu, S. T. Warren, B. A. Oostra, C. T. Caskey, and D. L. Nelson. “Absence of Expression of the Fmr-1 Gene in Fragile X Syndrome.” Cell 66, no. 4 (1991): 817-22. [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, A. J., M. Pieretti, J. S. Sutcliffe, Y. H. Fu, D. P. Kuhl, A. Pizzuti, O. Reiner, S. Richards, M. F. Victoria, F. P. Zhang, and et al. “Identification of a Gene (Fmr-1) Containing a Cgg Repeat Coincident with a Breakpoint Cluster Region Exhibiting Length Variation in Fragile X Syndrome.” Cell 65, no. 5 (1991): 905-14. [CrossRef]
- Bear, M. F., K. M. Huber, and S. T. Warren. “The Mglur Theory of Fragile X Mental Retardation.” Trends Neurosci 27, no. 7 (2004): 370-7. [CrossRef]
- Michalon, A., A. Bruns, C. Risterucci, M. Honer, T. M. Ballard, L. Ozmen, G. Jaeschke, J. G. Wettstein, M. von Kienlin, B. Kunnecke, and L. Lindemann. “Chronic Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Inhibition Corrects Local Alterations of Brain Activity and Improves Cognitive Performance in Fragile X Mice.” Biol Psychiatry 75, no. 3 (2014): 189-97. [CrossRef]
- Hoeffer, C. A., E. Sanchez, R. J. Hagerman, Y. Mu, D. V. Nguyen, H. Wong, A. M. Whelan, R. S. Zukin, E. Klann, and F. Tassone. “Altered Mtor Signaling and Enhanced Cyfip2 Expression Levels in Subjects with Fragile X Syndrome.” Genes Brain Behav 11, no. 3 (2012): 332-41. [CrossRef]
- Price, T. J., M. H. Rashid, M. Millecamps, R. Sanoja, J. M. Entrena, and F. Cervero. “Decreased Nociceptive Sensitization in Mice Lacking the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein: Role of Mglur1/5 and Mtor.” J Neurosci 27, no. 51 (2007): 13958-67.
- Sharma, A., C. A. Hoeffer, Y. Takayasu, T. Miyawaki, S. M. McBride, E. Klann, and R. S. Zukin. “Dysregulation of Mtor Signaling in Fragile X Syndrome.” J Neurosci 30, no. 2 (2010): 694-702. [CrossRef]
- Kano, M., T. Ohno-Shosaku, Y. Hashimotodani, M. Uchigashima, and M. Watanabe. “Endocannabinoid-Mediated Control of Synaptic Transmission.” Physiol Rev 89, no. 1 (2009): 309-80. [CrossRef]
- Varma, N., G. C. Carlson, C. Ledent, and B. E. Alger. “Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Drive the Endocannabinoid System in Hippocampus.” J Neurosci 21, no. 24 (2001): RC188. [CrossRef]
- Puighermanal, E., A. Busquets-Garcia, R. Maldonado, and A. Ozaita. “Cellular and Intracellular Mechanisms Involved in the Cognitive Impairment of Cannabinoids.” Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367, no. 1607 (2012): 3254-63. [CrossRef]
- Puighermanal, E., G. Marsicano, A. Busquets-Garcia, B. Lutz, R. Maldonado, and A. Ozaita. “Cannabinoid Modulation of Hippocampal Long-Term Memory Is Mediated by Mtor Signaling.” Nat Neurosci 12, no. 9 (2009): 1152-8. [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo S., L. Bellocchio, Oddi D., D’Amato F.R., G. Marsicano, and Crusio W.E. “The Fmr1 Mouse Line as a Model for Autism: The Relevance of the Genetic Background and of the Endocannabinoid System.” Paper presented at the FENS Annual Meeting, Amsterdam, The Netherlands,, 3-7 July 2010 2010.
- Busquets-Garcia, A., R. Maldonado, and A. Ozaita. “New Insights into the Molecular Pathophysiology of Fragile X Syndrome and Therapeutic Perspectives from the Animal Model.” Int J Biochem Cell Biol 53 (2014): 121-6. [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T., F. Howell, G. Williams, A. Minassi, M. G. Cascio, A. Ligresti, I. Matias, A. Schiano-Moriello, P. Paul, E. J. Williams, U. Gangadharan, C. Hobbs, V. Di Marzo, and P. Doherty. “Cloning of the First Sn1-Dag Lipases Points to the Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Endocannabinoid Signaling in the Brain.” J Cell Biol 163, no. 3 (2003): 463-8. [CrossRef]
- Hill, A. J., C. M. Williams, B. J. Whalley, and G. J. Stephens. “Phytocannabinoids as Novel Therapeutic Agents in Cns Disorders.” Pharmacol Ther 133, no. 1 (2012): 79-97. [CrossRef]
- Blessing, E. M., M. M. Steenkamp, J. Manzanares, and C. R. Marmar. “Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Anxiety Disorders.” Neurotherapeutics 12, no. 4 (2015): 825-36. [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S. “Cannabidiol (Cbd) and Its Analogs: A Review of Their Effects on Inflammation.” Bioorg Med Chem 23, no. 7 (2015): 1377-85. [CrossRef]
- Campos, A. C., M. V. Fogaca, A. B. Sonego, and F. S. Guimaraes. “Cannabidiol, Neuroprotection and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.” Pharmacol Res (2016). [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, B., J. Ravi, and R. K. Ganju. “Cannabinoids as Therapeutic Agents in Cancer: Current Status and Future Implications.” Oncotarget 5, no. 15 (2014): 5852-72. [CrossRef]
- Fasinu, P. S., S. Phillips, M. A. ElSohly, and L. A. Walker. “Current Status and Prospects for Cannabidiol Preparations as New Therapeutic Agents.” Pharmacotherapy 36, no. 7 (2016): 781-96. [CrossRef]
- Hill, A. J., M. S. Mercier, T. D. Hill, S. E. Glyn, N. A. Jones, Y. Yamasaki, T. Futamura, M. Duncan, C. G. Stott, G. J. Stephens, C. M. Williams, and B. J. Whalley. “Cannabidivarin Is Anticonvulsant in Mouse and Rat.” Br J Pharmacol 167, no. 8 (2012): 1629-42. [CrossRef]
- Deiana, S., A. Watanabe, Y. Yamasaki, N. Amada, M. Arthur, S. Fleming, H. Woodcock, P. Dorward, B. Pigliacampo, S. Close, B. Platt, and G. Riedel. “Plasma and Brain Pharmacokinetic Profile of Cannabidiol (Cbd), Cannabidivarine (Cbdv), Delta(9)-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (Thcv) and Cannabigerol (Cbg) in Rats and Mice Following Oral and Intraperitoneal Administration and Cbd Action on Obsessive-Compulsive Behaviour.” Psychopharmacology (Berl) 219, no. 3 (2012): 859-73.
- Zamberletti, E., M. Gabaglio, M. Woolley-Roberts, S. Bingham, T. Rubino, and D. Parolaro. “Cannabidivarin Treatment Ameliorates Autism-Like Behaviors and Restores Hippocampal Endocannabinoid System and Glia Alterations Induced by Prenatal Valproic Acid Exposure in Rats.” Front Cell Neurosci 13 (2019): 367. [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, S. , and E. Subashi. “Mouse Models of Fragile X Syndrome.” In Behavioral Genetics of the Mouse, edited by S. Pietropaolo, F. Sluyter and W.E. Crusio, 146-63. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014.
- Spear, L. P. “The Adolescent Brain and Age-Related Behavioral Manifestations.” Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24, no. 4 (2000): 417-63. [CrossRef]
- Hebert, B., S. Pietropaolo, S. Meme, B. Laudier, A. Laugeray, N. Doisne, A. Quartier, S. Lefeuvre, L. Got, D. Cahard, F. Laumonnier, W. E. Crusio, J. Pichon, A. Menuet, O. Perche, and S. Briault. “Rescue of Fragile X Syndrome Phenotypes in Fmr1 Ko Mice by a Bkca Channel Opener Molecule.” Orphanet J Rare Dis 9 (2014): 124. [CrossRef]
- Oddi, D., E. Subashi, S. Middei, L. Bellocchio, V. Lemaire-Mayo, M. Guzman, W. E. Crusio, F. R. D’Amato, and S. Pietropaolo. “Early Social Enrichment Rescues Adult Behavioral and Brain Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Neuropsychopharmacology 40, no. 5 (2015): 1113-22.
- Pietropaolo, S., M. G. Goubran, C. Joffre, A. Aubert, V. Lemaire-Mayo, W. E. Crusio, and S. Laye. “Dietary Supplementation of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Rescues Fragile X Phenotypes in Fmr1-Ko Mice.” Psychoneuroendocrinology 49 (2014): 119-29. [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, S., A. Guilleminot, B. Martin, F. R. D’Amato, and W. E. Crusio. “Genetic-Background Modulation of Core and Variable Autistic-Like Symptoms in Fmr1 Knock-out Mice.” PLoS ONE 6, no. 2 (2011): e17073.
- Zhang, Y., A. Bonnan, G. Bony, I. Ferezou, S. Pietropaolo, M. Ginger, N. Sans, J. Rossier, B. Oostra, G. LeMasson, and A. Frick. “Dendritic Channelopathies Contribute to Neocortical and Sensory Hyperexcitability in Fmr1(-/Y) Mice.” Nat Neurosci 17, no. 12 (2014): 1701-9.
- Khandjian, E. W. “Biology of the Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein, an Rna-Binding Protein.” Biochem Cell Biol 77, no. 4 (1999): 331-42.
- Bakker, C. E., Y. de Diego Otero, C. Bontekoe, P. Raghoe, T. Luteijn, A. T. Hoogeveen, B. A. Oostra, and R. Willemsen. “Immunocytochemical and Biochemical Characterization of Fmrp, Fxr1p, and Fxr2p in the Mouse.” Exp Cell Res 258, no. 1 (2000): 162-70.
- Dutch-Belgian Fragile X Consortium. “Fmr1 Knockout Mice: A Model to Study Fragile X Mental Retardation.” Cell 78, no. 1 (1994): 23-33.
- Moles, A. , and R. D’Amato F. “Ultrasonic Vocalization by Female Mice in the Presence of a Conspecific Carrying Food Cues.” Anim Behav 60, no. 5 (2000): 689-94.
- Gaudissard, J., M. Ginger, M. Premoli, M. Memo, A. Frick, and S. Pietropaolo. “Behavioral Abnormalities in the Fmr1-Ko2 Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome: The Relevance of Early Life Phases.” Autism Res 10, no. 10 (2017): 1584-96. [CrossRef]
- Gauducheau, M., V. Lemaire-Mayo, F. R. D’Amato, D. Oddi, W. E. Crusio, and S. Pietropaolo. “Age-Specific Autistic-Like Behaviors in Heterozygous Fmr1-Ko Female Mice.” Autism Res 10, no. 6 (2017): 1067-78.
- Pietropaolo, S. , and W. E. Crusio. “Strain-Dependent Changes in Acoustic Startle Response and Its Plasticity across Adolescence in Mice.” Behav Genet (2009). [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S. A., V. Benes, J. A. Garson, J. Hellemans, J. Huggett, M. Kubista, R. Mueller, T. Nolan, M. W. Pfaffl, G. L. Shipley, J. Vandesompele, and C. T. Wittwer. “The Miqe Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time Pcr Experiments.” Clin Chem 55, no. 4 (2009): 611-22. [CrossRef]
- Livak, K. J. , and T. D. Schmittgen. “Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative Pcr and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method.” Methods 25, no. 4 (2001): 402-8.
- Vandesquille, M., M. Baudonnat, L. Decorte, C. Louis, P. Lestage, and D. Beracochea. “Working Memory Deficits and Related Disinhibition of the Camp/Pka/Creb Are Alleviated by Prefrontal Alpha4beta2*-Nachrs Stimulation in Aged Mice.” Neurobiol Aging 34, no. 6 (2013): 1599-609.
- Kat, R., M. Arroyo-Araujo, R. B. M. de Vries, M. A. Koopmans, S. F. de Boer, and M. J. H. Kas. “Translational Validity and Methodological Underreporting in Animal Research: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Fragile X Syndrome (Fmr1 Ko) Rodent Model.” Neurosci Biobehav Rev 139 (2022): 104722. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A., H. Kaphzan, A. C. Alvarez-Dieppa, J. P. Murphy, P. Pierre, and E. Klann. “Genetic Removal of P70 S6 Kinase 1 Corrects Molecular, Synaptic, and Behavioral Phenotypes in Fragile X Syndrome Mice.” Neuron 76, no. 2 (2012): 325-37.
- Dahlhaus, R. , and A. El-Husseini. “Altered Neuroligin Expression Is Involved in Social Deficits in a Mouse Model of the Fragile X Syndrome.” Behav Brain Res 208, no. 1 (2010): 96-105. [CrossRef]
- de Diego-Otero, Y., Y. Romero-Zerbo, R. el Bekay, J. Decara, L. Sanchez, F. Rodriguez-de Fonseca, and I. del Arco-Herrera. “Alpha-Tocopherol Protects against Oxidative Stress in the Fragile X Knockout Mouse: An Experimental Therapeutic Approach for the Fmr1 Deficiency.” Neuropsychopharmacology 34, no. 4 (2009): 1011-26.
- Eadie, B. D., W. N. Zhang, F. Boehme, J. Gil-Mohapel, L. Kainer, J. M. Simpson, and B. R. Christie. “Fmr1 Knockout Mice Show Reduced Anxiety and Alterations in Neurogenesis That Are Specific to the Ventral Dentate Gyrus.” Neurobiol Dis 36, no. 2 (2009): 361-73. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M. L., B. S. Rao, J. S. Seo, H. S. Choi, B. M. Dolan, S. Y. Choi, S. Chattarji, and S. Tonegawa. “Inhibition of P21-Activated Kinase Rescues Symptoms of Fragile X Syndrome in Mice.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, no. 27 (2007): 11489-94. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. H., D. M. Chuang, and C. B. Smith. “Lithium Ameliorates Phenotypic Deficits in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Int J Neuropsychopharmacol (2011): 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Mineur, Y. S., F. Sluyter, S. de Wit, B. A. Oostra, and W. E. Crusio. “Behavioral and Neuroanatomical Characterization of the Fmr1 Knockout Mouse.” Hippocampus 12, no. 1 (2002): 39-46.
- Olmos-Serrano, J. L., J. G. Corbin, and M. P. Burns. “The Gaba(a) Receptor Agonist Thip Ameliorates Specific Behavioral Deficits in the Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Dev Neurosci 33, no. 5 (2011): 395-403.
- Peier, A. M., K. L. McIlwain, A. Kenneson, S. T. Warren, R. Paylor, and D. L. Nelson. “(over)Correction of Fmr1 Deficiency with Yac Transgenics: Behavioral and Physical Features.” Hum Mol Genet 9, no. 8 (2000): 1145-59. [CrossRef]
- Restivo, L., F. Ferrari, E. Passino, C. Sgobio, J. Bock, B. A. Oostra, C. Bagni, and M. Ammassari-Teule. “Enriched Environment Promotes Behavioral and Morphological Recovery in a Mouse Model for the Fragile X Syndrome.” Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, no. 32 (2005): 11557-62. [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C. M., O. Alekseyenko, S. M. Hamilton, A. M. Thomas, E. Serysheva, L. A. Yuva-Paylor, and R. Paylor. “Modifying Behavioral Phenotypes in Fmr1ko Mice: Genetic Background Differences Reveal Autistic-Like Responses.” Autism Res 4, no. 1 (2011): 40-56. [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C. M., O. Alekseyenko, E. Serysheva, L. A. Yuva-Paylor, and R. Paylor. “Altered Anxiety-Related and Social Behaviors in the Fmr1 Knockout Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Genes Brain Behav 4, no. 7 (2005): 420-30. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. M., N. Bui, D. Graham, J. R. Perkins, L. A. Yuva-Paylor, and R. Paylor. “Genetic Reduction of Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Alters Select Behaviors in a Mouse Model for Fragile X Syndrome.” Behav Brain Res 223, no. 2 (2011): 310-21. [CrossRef]
- Uutela, M., J. Lindholm, V. Louhivuori, H. Wei, L. M. Louhivuori, A. Pertovaara, K. Akerman, E. Castren, and M. L. Castren. “Reduction of Bdnf Expression in Fmr1 Knockout Mice Worsens Cognitive Deficits but Improves Hyperactivity and Sensorimotor Deficits.” Genes Brain Behav 11, no. 5 (2012): 513-23. [CrossRef]
- Mineur, Y. S., L. X. Huynh, and W. E. Crusio. “Social Behavior Deficits in the Fmr1 Mutant Mouse.” Behav Brain Res 168, no. 1 (2006): 172-5. [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, A. M., A. K. Roth, L. Nawrocki, C. C. Wrenn, and M. G. Valdovinos. “Brief Report: Altered Social Behavior in Isolation-Reared Fmr1 Knockout Mice.” J Autism Dev Disord (2012). [CrossRef]
- Mines, M. A., C. J. Yuskaitis, M. K. King, E. Beurel, and R. S. Jope. “Gsk3 Influences Social Preference and Anxiety-Related Behaviors During Social Interaction in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome and Autism.” PLoS One 5, no. 3 (2010): e9706. [CrossRef]
- Michalon, A., M. Sidorov, T. M. Ballard, L. Ozmen, W. Spooren, J. G. Wettstein, G. Jaeschke, M. F. Bear, and L. Lindemann. “Chronic Pharmacological Mglu5 Inhibition Corrects Fragile X in Adult Mice.” Neuron 74, no. 1 (2012): 49-56. [CrossRef]
- Ventura, R., T. Pascucci, M. V. Catania, S. A. Musumeci, and S. Puglisi-Allegra. “Object Recognition Impairment in Fmr1 Knockout Mice Is Reversed by Amphetamine: Involvement of Dopamine in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex.” Behav Pharmacol 15, no. 5-6 (2004): 433-42.
- Bilousova, T. V., L. Dansie, M. Ngo, J. Aye, J. R. Charles, D. W. Ethell, and I. M. Ethell. “Minocycline Promotes Dendritic Spine Maturation and Improves Behavioural Performance in the Fragile X Mouse Model.” J Med Genet 46, no. 2 (2009): 94-102. [CrossRef]
- Heulens, I., C. D’Hulst, D. Van Dam, P. P. De Deyn, and R. F. Kooy. “Pharmacological Treatment of Fragile X Syndrome with Gabaergic Drugs in a Knockout Mouse Model.” Behav Brain Res 229, no. 1 (2012): 244-9. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, D. M., W. J. Derber, D. A. McClellan, and L. S. Crnic. “Alterations in the Auditory Startle Response in Fmr1 Targeted Mutant Mouse Models of Fragile X Syndrome.” Brain Res 927, no. 1 (2002): 8-17. [CrossRef]
- Qin, M., Z. Xia, T. Huang, and C. B. Smith. “Effects of Chronic Immobilization Stress on Anxiety-Like Behavior and Basolateral Amygdala Morphology in Fmr1 Knockout Mice.” Neuroscience 194 (2011): 282-90. [CrossRef]
- Veeraragavan, S., D. Graham, N. Bui, L. A. Yuva-Paylor, J. Wess, and R. Paylor. “Genetic Reduction of Muscarinic M4 Receptor Modulates Analgesic Response and Acoustic Startle Response in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome (Fxs).” Behav Brain Res 228, no. 1 (2011): 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Spear, L. P. “Adolescent Brain Development and Animal Models.” Ann N Y Acad Sci 1021 (2004): 23-6. [CrossRef]
- Spear, L. P. , and S. C. Brake. “Periadolescence: Age-Dependent Behavior and Psychopharmacological Responsivity in Rats.” Dev Psychobiol 16, no. 2 (1983): 83-109. [CrossRef]
- Gantois, I., A. Khoutorsky, J. Popic, A. Aguilar-Valles, E. Freemantle, R. Cao, V. Sharma, T. Pooters, A. Nagpal, A. Skalecka, V. T. Truong, S. Wiebe, I. A. Groves, S. M. Jafarnejad, C. Chapat, E. A. McCullagh, K. Gamache, K. Nader, J. C. Lacaille, C. G. Gkogkas, and N. Sonenberg. “Metformin Ameliorates Core Deficits in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” Nat Med 23, no. 6 (2017): 674-77. [CrossRef]
- Lemaire-Mayo, Valerie, Marion Piquemal, Wim E. Crusio, Eric Louette, and Susanna Pietropaolo. “Therapeutic Effects of Chlorzoxazone, a Bkca Channel Agonist, in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome.” bioRxiv (2020): 2020.12.11.389569.
- Cheng, D., J. K. Low, W. Logge, B. Garner, and T. Karl. “Chronic Cannabidiol Treatment Improves Social and Object Recognition in Double Transgenic Appswe/Ps1e9 Mice.” Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231, no. 15 (2014): 3009-17. [CrossRef]
- Zupan, B. , and M. Toth. “Wild-Type Male Offspring of Fmr-1+/- Mothers Exhibit Characteristics of the Fragile X Phenotype.” Neuropsychopharmacology 33, no. 11 (2008): 2667-75.

 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





