Submitted:
28 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Molecular mechanisms involved in the onset of neurodegenerative diseases
3. Limitations of current therapies used for the treatment of neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative disorders in early stages of disease
4. The potential role of Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases
| Effects on proinflammatory molecules and on oxidative stress mediators expression | Reduction of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, ROS and TBARS expression; reduction of Chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) release, phosphorylation of NFkB p65 and IkBa, as well as GFAP (Glial fibrillary acidic protein) induced by IL-1b; LPS-induced reduction of TLR4 expression and p-NFκB-p65 activation; reduction of the levels of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and MIP-1 (Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1); Increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines such as TGF-β and IL-10; reduction of pro-inflammatory molecules expression such as iNOS, COX-2, nitrates, NLRP3, caspase-1; improvement of SOD (Superoxide Dismutase), CAT (Catalase) and GSH (Glutathione) activity. |
|---|---|
| Effects on the hippocampus | Reduction of Cholinesterase activity induced by Lipopolysaccharide showing an anti-inflammatory activity and improving memory; increased expression of PSD-95 (Post Synaptic Density Protein 95) and synapsin which are involved in synaptic plasticity; increase in purinergic enzymes such as ATPdase, ADPdase. 5-Nucletidase and Adenosine Deaminase. |
| Effects in models of neuroinflammation | Reduction of cortical levels of chemokines such as CCL2, CCL5; |
| Effects on astrocytes | Increased Nrf2 levels and HO-1 expression through the p38 MAPK and ERK dependent pathway; anti-inflammatory effect in vitro; reduction of GFAP expression. |
| Effects on microglia | Reduction of CD-68 expression; increased levels of arginase-1. |
| Effects on prefrontal cortex | Reduction in β-amyloid, APP, ptau, BACE-1 (β-secretase-1) levels; activation of caspase-3 and bax; increased levels of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2. |
| Effects on the activity of neurotransmitters | Reduction of AChE and Buttyryl-Che, and of Monoamine Oxidases (MAO). |
| Effects on schizophrenia | Reduction of IL-1β and TNF-α, p-p65, p-IκBα, p-p38 and p-ERK1/2 levels in the prefrontal cortex; activation of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, CAT and GSH-Px; increased levels of NRF-2, HO-1 and NQO-1; increased locomotor activity. |
| Effects on stress-induced depression | Reduction of NO, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, p-p65, p-IκBα levels and NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in the prefrontal cortex; pro-autophagic action through an increase in Beclin-1 expression and a reduction in p-mTOR. |
| Effects in aluminum poisoning | Improved survival, locomotor performance, learning and memory through a reduction of AChE and MAO activity and increased catalase activity. |
| Effects on Multiple Sclerosis | Prevents the generation of peptide-MHC complexes required for T cell activation; inhibition of up-regulation of maturation markers I-Ab, CD40 and CD86 in LPS-treated dendritic cells. |
| Effects on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Significant reduction in the incidence of the disease as demonstrated by the reduced production of IFN and IL-2. |
4.1. Alzheimer Disease
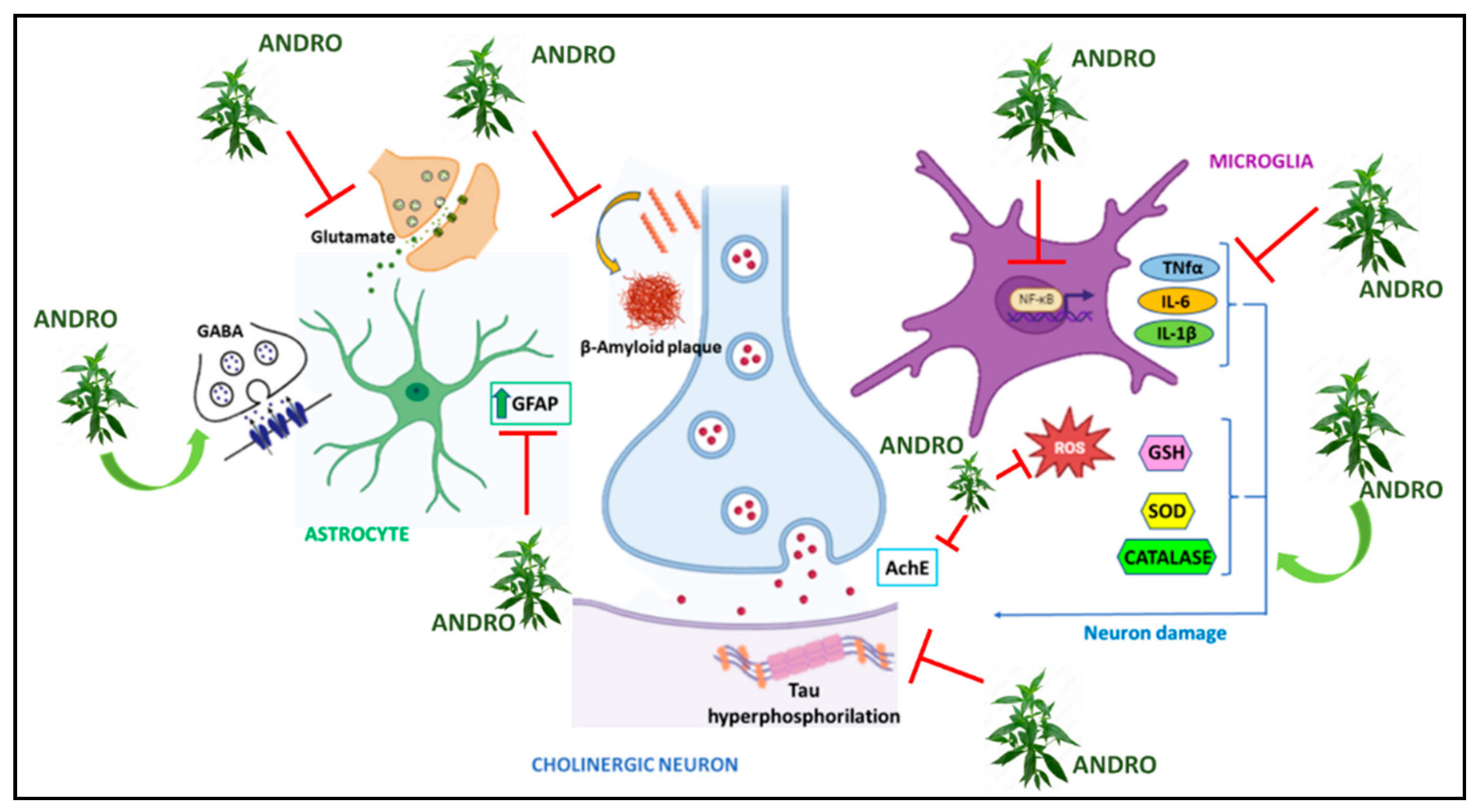
4.2. Parkinson’s disease
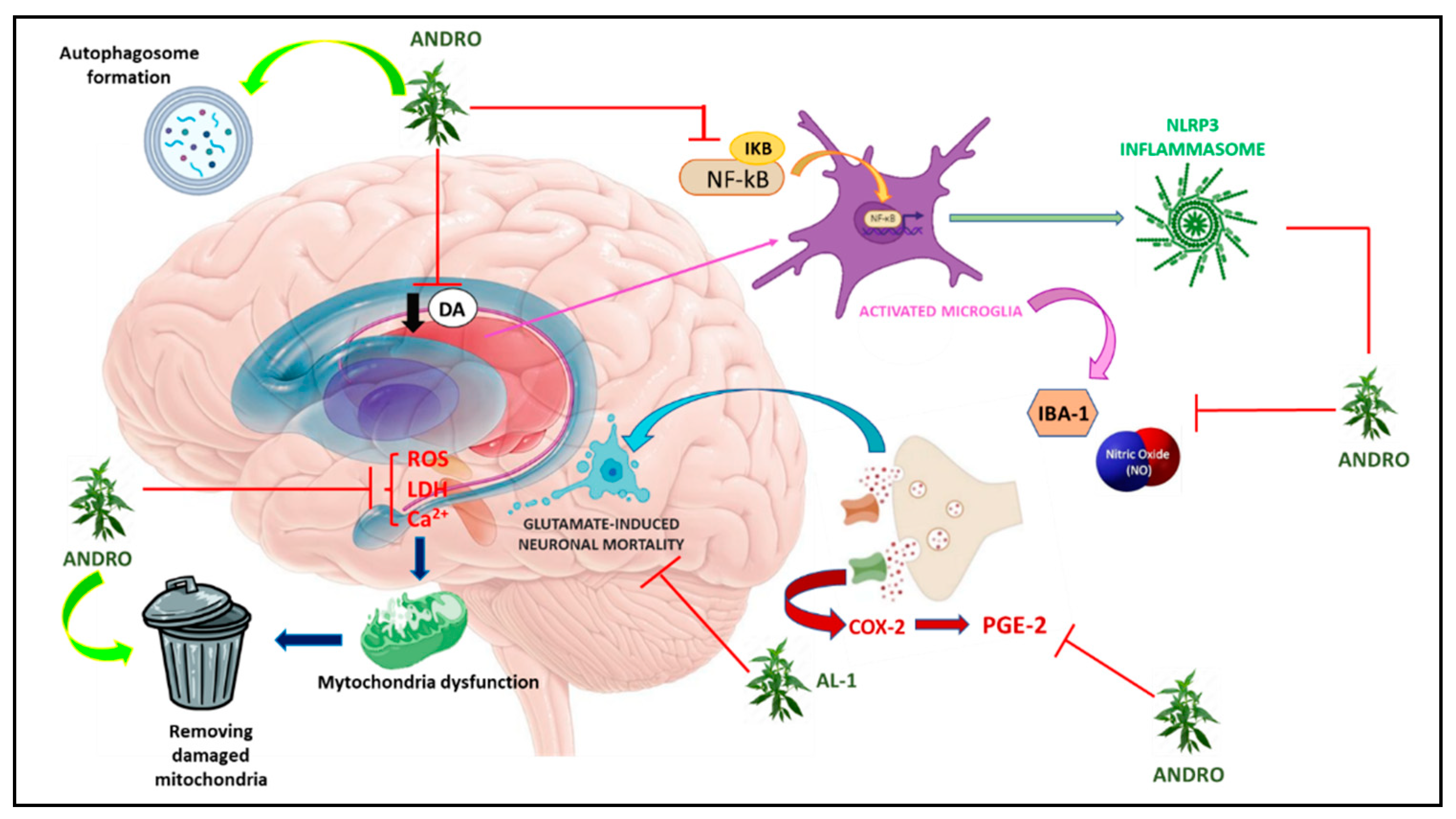
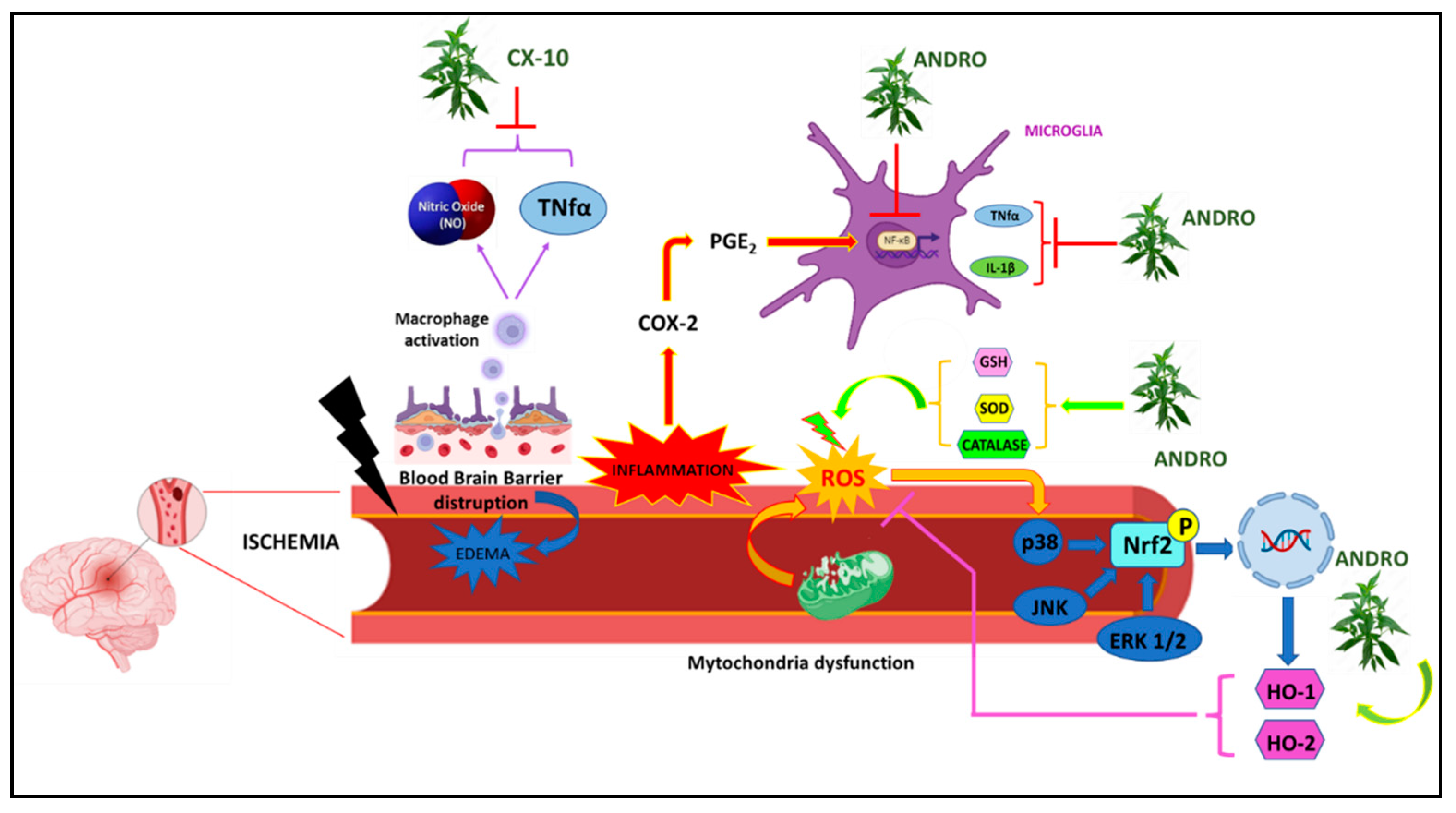
4.3. Brain Ischemia-reperfusion injury
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prusiner, S.B. Biology and genetics of prions causing neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Genet 2013, 47, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.F.; Serrano, G.; Adler, C.H.; Caviness, J.N.; Sue, L.I.; Beach, T.G. Altered Expression Patterns of Inflammation-Associated and Trophic Molecules in Substantia Nigra and Striatum Brain Samples from Parkinson’s Disease, Incidental Lewy Body Disease and Normal Control Cases. Front Neurosci 2015, 9, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C.; Rogaeva, E.; Foroud, T.; Farrer, L.A. Genetics and genomics of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease and its endophenotypes. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011, 2011, 284728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R.; Stern, Y. Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Ortiz, A.L.; Acosta-Castillo, I.; Prince, M.J. Epidemiology of dementias and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Med Res 2012, 43, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Álvarez-Álvarez, I.; Guillén-Grima, F.; Aguinaga-Ontoso, I. Prevalence and incidence of Alzheimer’s disease in Europe: A meta-analysis. Neurologia 2017, 32, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H.V. Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, F.; Kab, S.; Mohamed, F.; Canonico, M.; Le Guern, M.; Quintin, C.; Carcaillon, L.; Nicolau, J.; Duport, N.; Singh-Manoux, A. , et al. Parkinson disease male-to-female ratios increase with age: French nationwide study and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016, 87, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, C.F.; Knopman, D.S. Dementia: many roads, but not built in a day. Neurology 2007, 69, 2193–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson disease subtypes. JAMA Neurol 2014, 71, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.; Larsen, J.P.; Emre, M.; Wentzel-Larsen, T.; Aarsland, D. Changes in motor subtype and risk for incident dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2006, 21, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemels, M.T. Neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 2016, 539, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logroscino, G.; Urso, D.; Savica, R. Descriptive Epidemiology of Neurodegenerative Diseases: What Are the Critical Questions? Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H. [Alzheimer’s disease and the immune system response]. Nihon Rinsho 1994, 52, 2990–2994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Lio, D.; Candore, G.; Caruso, C. TLR4 polymorphisms and ageing: implications for the pathophysiology of age-related diseases. J Clin Immunol 2009, 29, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Ceruti, S.; Bramanti, P.; Abbracchio, M.P. Purinergic signalling in inflammation of the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 2009, 32, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Barger, S.; Barnum, S.; Bradt, B.; Bauer, J.; Cole, G.M.; Cooper, N.R.; Eikelenboom, P.; Emmerling, M.; Fiebich, B.L. , et al. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2000, 21, 383–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, L.; Hartley, O.; Dubois-Dauphin, M.; Krause, K.H. Chemokine receptors in the central nervous system: role in brain inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2005, 48, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.K.; Tansey, M.G. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, A.; Tsakiri, N.; Wang, P.; Rothwell, N.J. Interleukin-1 and inflammatory neurodegeneration. Biochem Soc Trans 2007, 35, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maida, C.D.; Norrito, R.L.; Daidone, M.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Pinto, A. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, S.D.; Philippou, E. Mediterranean Diet, Cognitive Function, and Dementia: A Systematic Review of the Evidence. Adv Nutr 2016, 7, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durães, F.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Old Drugs as New Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, J.S.; Harvey, R. Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003, CD001190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, J.; Schneider, L. Galantamine for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001, CD001747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.S.; Chong, L.Y.; Grimley Evans, J. Rivastigmine for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015, 9, CD001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, R.; McShane, R.; Lindesay, J.; Ritchie, C.; Baldwin, A.; Barber, R.; Burns, A.; Dening, T.; Findlay, D.; Holmes, C. , et al. Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 2012, 366, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisberg, B.; Doody, R.; Stöffler, A.; Schmitt, F.; Ferris, S.; Möbius, H.J.; Group, M.S. Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 2003, 348, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, R.; Areosa Sastre, A.; Minakaran, N. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006, CD003154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrimond, L.E.; Roberts, E.; McShane, R. Memantine and cholinesterase inhibitor combination therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. BMJ Open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemade, D.; Subramanian, T.; Shivkumar, V. An Update on Medical and Surgical Treatments of Parkinson’s Disease. Aging Dis 2021, 12, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, D.; Plastino, M.; Bosco, F.; Fava, A.; Rotondo, A. Daily motor performance after switching levodopa to melevodopa: an open-label on advanced Parkinson’s disease with “delayed-on” and/or”wearing-off”. Minerva Med 2011, 102, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Rascol, O.; Payoux, P.; Ory, F.; Ferreira, J.J.; Brefel-Courbon, C.; Montastruc, J.L. Limitations of current Parkinson’s disease therapy. Ann Neurol 2003, 53 Suppl 3, S3-12; discussion S12-15. 3. [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Daniele, A.; Albanese, A. Treatment of motor and non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease with deep brain stimulation. Lancet Neurol 2012, 11, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabid, A.L.; Pollak, P.; Louveau, A.; Henry, S.; de Rougemont, J. Combined (thalamotomy and stimulation) stereotactic surgery of the VIM thalamic nucleus for bilateral Parkinson disease. Appl Neurophysiol 1987, 50, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, J.; Lippitz, B. Bilateral chronic electrostimulation of ventroposterolateral pallidum: a new therapeutic approach for alleviating all parkinsonian symptoms. Neurosurgery 1994, 35, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, K.A.; Weaver, F.M.; Stern, M.; Hur, K.; Harris, C.L.; Luo, P.; Marks, W.J.; Rothlind, J.; Sagher, O.; Moy, C. , et al. Pallidal versus subthalamic deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 2010, 362, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odekerken, V.J.; Boel, J.A.; Schmand, B.A.; de Haan, R.J.; Figee, M.; van den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R.; de Bie, R.M.; group, N.s. GPi vs STN deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: Three-year follow-up. Neurology 2016, 86, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R. Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2004, 4, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guridi, J.; Rodriguez-Oroz, M.C.; Alegre, M.; Obeso, J.A. Hardware complications in deep brain stimulation: electrode impedance and loss of clinical benefit. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2012, 18, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouratian, N.; Thakkar, S.; Kim, W.; Bronstein, J.M. Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: efficacy and safety. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis 2012, 2012, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, D.P.; Adunuri, N.; Gill, S.S.; Gruneir, A.; Herrmann, N.; Rochon, P. Antidepressants for agitation and psychosis in dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011, CD008191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sink, K.M.; Holden, K.F.; Yaffe, K. Pharmacological treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. JAMA 2005, 293, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolini Paoletti, F.; Gaetani, L.; Parnetti, L. The Challenge of Disease-Modifying Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: Role of CSF Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotondo, A.; Bosco, D.; Plastino, M.; Consoli, A.; Bosco, F. Clozapine for medication-related pathological gambling in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 2010, 25, 1994–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, D.; Plastino, M.; Colica, C.; Bosco, F.; Arianna, S.; Vecchio, A.; Galati, F.; Cristiano, D.; Consoli, A.; Consoli, D. Opioid antagonist naltrexone for the treatment of pathological gambling in Parkinson disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 2012, 35, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K. Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep 2019, 20, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Quispe, C.; Hossain, R.; Islam, M.T.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Al-Rawahi, A.; Martorell, M.; Mamurova, A.; Seilkhan, A.; Altybaeva, N. , et al. Neuropharmacological Effects of Quercetin: A Literature-Based Review. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 665031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Miao, Q.W.; Zhu, C.X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; An, L. Sulforaphane ameliorates neurobehavioral deficits and protects the brain from amyloid β deposits and peroxidation in mice with Alzheimer-like lesions. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 2015, 30, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Bosco, F.; Guarnieri, L.; Nucera, S.; Ruga, S.; Oppedisano, F.; Tucci, L.; Muscoli, C.; Palma, E.; Giuffrè, A.M. , et al. Protective Role of an Extract Waste Product from. Plants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, S.R.; Chai, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Overview of pharmacological activities of. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2019, 59, S17–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, R.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Beltrán, J.F.; Islam, M.T.; Shaheen, S.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Martorell, M.; Kumar, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J. , et al. Neurobiological Promises of the Bitter Diterpene Lactone Andrographolide. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 3079577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, D.; Khatab, N.I.O.; Kirby, B.P.; Yong, A.; Hasan, S.; Basri, H.; Stanslas, J. A standardised. J Adv Res 2019, 16, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, R.; Ahmed, S.K.; Sarkar, L.; Sen, T.; Karmakar, S. Pharmacokinetic analysis and tissue distribution of andrographolide in rat by a validated LC-MS/MS method. Pharm Biol 2014, 52, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.Y.; Tan, M.G.; Banks, W.A.; Wong, W.S.; Wong, P.T.; Lai, M.K. Andrographolide attenuates LPS-stimulated up-regulation of C-C and C-X-C motif chemokines in rodent cortex and primary astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Chan, S.J.; Wong, W.S.; Wong, P.T.; Lai, M.K. Andrographolide attenuates interleukin-1β-stimulated upregulation of chemokine CCL5 and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes. Neuroreport 2014, 25, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mishra, K.P.; Ganju, L.; Singh, S.B. Andrographolide - A promising therapeutic agent, negatively regulates glial cell derived neurodegeneration of prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and working memory impairment. J Neuroimmunol 2017, 313, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedayo, B.C.; Jesubowale, O.S.; Adebayo, A.A.; Oboh, G. Effect of Andrographis paniculata leaves extract on neurobehavioral and biochemical indices in scopolamine-induced amnesic rats. J Food Biochem 2021, 45, e13280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, A. Neuroinflammation in Schizophrenia: The Key Role of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L.L.; Tizabi, Y. Neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, and depression. Neurotox Res 2013, 23, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Dai, Z.; Sui, Y. Andrographolide improves PCP-induced schizophrenia-like behaviors through blocking interaction between NRF2 and KEAP1. J Pharmacol Sci 2021, 147, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X.; Liu, W.; Guo, W. Andrographolide triggers autophagy-mediated inflammation inhibition and attenuates chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS)-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2019, 379, 114688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedayo, B.C.; Ogunsuyi, O.B.; Akinniyi, S.T.; Oboh, G. Effect of. Drug Chem Toxicol 2022, 45, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iruretagoyena, M.I.; Tobar, J.A.; González, P.A.; Sepúlveda, S.E.; Figueroa, C.A.; Burgos, R.A.; Hancke, J.L.; Kalergis, A.M. Andrographolide interferes with T cell activation and reduces experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2005, 312, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.; Fu, J. Andrographolide ameliorates neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2021, 96, 107808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Huang, C. A review for the neuroprotective effects of andrographolide in the central nervous system. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 117, 109078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Chen, R.; Li, F.; Maitra, S.; Hernandez, J.F.; Zhou, G.C.; Vincent, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Andrographolide Derivatives as Regulators of βAPP Processing in Human Cells. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Pyo, E.; An, J.P.; Kim, J.; Sung, S.H.; Oh, W.K. Andrographolide Activates Keap1/Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 Pathway in HT22 Cells and Suppresses Microglial Activation by A. Mediators Inflamm 2017, 2017, 5906189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Kuo, F.H.; Chen, P.N.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Yu, N.Y.; Yang, W.E.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, S.F. Andrographolide suppresses the migratory ability of human glioblastoma multiforme cells by targeting ERK1/2-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105860–105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, D.; Wang, J.; Wei, H.; Gao, J. Neuroprotection of Andrographolide Against Microglia-Mediated Inflammatory Injury and Oxidative Damage in PC12 Neurons. Neurochem Res 2019, 44, 2619–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, C.; Killick, R.; Lovestone, S. The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 2008, 104, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Rojas, C.; Schüller, A.; Lindsay, C.B.; Ureta, R.C.; Mejías-Reyes, C.; Hancke, J.; Melo, F.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide activates the canonical Wnt signalling pathway by a mechanism that implicates the non-ATP competitive inhibition of GSK-3β: autoregulation of GSK-3β in vivo. Biochem J 2015, 466, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, S.B.; Valenzuela-Bezanilla, D.; Mardones, M.D.; Varela-Nallar, L. Role of Wnt Signaling in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerda-Canals, G.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Güell-Bosch, J.; Villegas, S. Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2017, 57, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Fuentes, R.; Socas-Pérez, R. Octodon degus: a strong attractor for Alzheimer research. Basic Clin Neurosci 2013, 4, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Varela-Nallar, L.; Arredondo, S.B.; Tapia-Rojas, C.; Hancke, J.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide Stimulates Neurogenesis in the Adult Hippocampus. Neural Plast 2015, 2015, 935403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, F.G.; Tapia-Rojas, C.; Carvajal, F.J.; Hancke, J.; Cerpa, W.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide reduces cognitive impairment in young and mature AβPPswe/PS-1 mice. Mol Neurodegener 2014, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, D.S.; Lindsay, C.; Codocedo, J.F.; Morel, I.; Pinto, C.; Cisternas, P.; Bozinovic, F.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide recovers cognitive impairment in a natural model of Alzheimer’s disease (Octodon degus). Neurobiol Aging 2016, 46, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, C.B.; Zolezzi, J.M.; Rivera, D.S.; Cisternas, P.; Bozinovic, F.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide Reduces Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in Aged Octodon degus. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Colica, C.; Plastino, M.; Messina, D.; Cristiano, D.; Opipari, C.; Vaccaro, A.; Gorgone, G.; Bosco, F.; Fratto, A. , et al. Cognitive impairment is correlated with insulin resistance degree: the “PA-NICO-study”. Metab Brain Dis 2017, 32, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Liang, J.; Zhou, B. Glucose Metabolic Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases-New Mechanistic Insights and the Potential of Hypoxia as a Prospective Therapy Targeting Metabolic Reprogramming. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Metabolic Dysregulation Contributes to the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 530219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, P.; Sabater, L.; Mathieu, E.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C. Why the Ala-His-His Peptide Is an Appropriate Scaffold to Remove and Redox Silence Copper Ions from the Alzheimer’s-Related Aβ Peptide. Biomolecules 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Sieber, C.C.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Mild cognitive impairment: when nutrition helps brain energy rescue-a report from the EuGMS 2020 Congress. Eur Geriatr Med 2021, 12, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, D.; Plastino, M.; Bosco, F.; Consoli, A.; Labate, A.; Pirritano, D.; Consoli, D.; Fava, A. Bell’s palsy: a manifestation of prediabetes? Acta Neurol Scand 2011, 123, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Kaur, K.; Singh, S. Protective effect of andrographolide against STZ induced Alzheimer’s disease in experimental rats: possible neuromodulation and Aβ. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Rai, G.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Kumar, V. Beneficial effects of an Andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide on cognitive functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 2016, 54, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardelli, C.; Cisternas, P.; Gutiérrez, J.; Martinez, M.; Inestrosa, N.C. Andrographolide restores glucose uptake in rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem 2021, 157, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, T.B.; Greenland, J.C. Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. 2018.
- Pajares, M.; I Rojo, A.; Manda, G.; Boscá, L.; Cuadrado, A. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wilson, B.; Hong, J.S. Andrographolide reduces inflammation-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mesencephalic neuron-glia cultures by inhibiting microglial activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004, 308, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterman, A.J.; Wongtrakul, J.; Saisawang, C. Phytochemical andrographolide modulates NF-κB and JNK in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, a cell model for Parkinson’s disease. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kwatra, M.; Ranjan Panda, S.; Murty, U.S.N.; Naidu, V.G.M. Andrographolide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia through induction of parkin-mediated mitophagy in in-vitro and in-vivo models of Parkinson disease. Brain Behav Immun 2021, 91, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lai, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, P.; Zhu, L.; Guo, B.; Xu, L.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y.; Lee, S.M. , et al. Neuroprotective effects of the andrographolide analogue AL-1 in the MPP⁺/MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model in vitro and in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014, 122, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Hyun, J.; Park, J.; Jung, S.; Oh, Y.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, E.I.; Jo, D.G. , et al. Aberrant role of pyruvate kinase M2 in the regulation of gamma-secretase and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Rep 2021, 37, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.; Varma, V.R.; Varma, S.; Casanova, R.; Dammer, E.; Pletnikova, O.; Chia, C.W.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Troncoso, J. , et al. Evidence for brain glucose dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2018, 14, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kim, S.H.; Bishayee, K. Dysfunctional Glucose Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease Onset and Potential Pharmacological Interventions. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, R. Cerebral Ischemia. 2021.
- Yen, T.L.; Hsu, W.H.; Huang, S.K.; Lu, W.J.; Chang, C.C.; Lien, L.M.; Hsiao, G.; Sheu, J.R.; Lin, K.H. A novel bioactivity of andrographolide from Andrographis paniculata on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury through induction of cerebral endothelial cell apoptosis. Pharm Biol 2013, 51, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.J.; Wong, W.S.; Wong, P.T.; Bian, J.S. Neuroprotective effects of andrographolide in a rat model of permanent cerebral ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol 2010, 161, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Yu, Q.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Yang, G. Neuroprotective effects of andrographolide derivative CX-10 in transient focal ischemia in rat: Involvement of Nrf2/AE and TLR/NF-κB signaling. Pharmacol Res 2019, 144, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, C.M.; Liou, K.T.; Wang, Y.H.; Liao, J.F.; Yen, J.C.; Shen, Y.C. Andrographolide inhibits PI3K/AKT-dependent NOX2 and iNOS expression protecting mice against hypoxia/ischemia-induced oxidative brain injury. Planta Med 2011, 77, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, T.L.; Chen, R.J.; Jayakumar, T.; Lu, W.J.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, M.J.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Lin, K.H. , et al. Andrographolide stimulates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-heme oxygenase 1 signaling in primary cerebral endothelial cells for definite protection against ischemic stroke in rats. Transl Res 2016, 170, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





