Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. The Pathophysiology of Diabetes
4. Medicinal Plant-Based Foods Recommended for the Treatment of DM
4.1. Althaea officinalis L.
4.2. Anethum graveolens L.
4.3. Allium sativum
4.4. Brassica oleracea L.
4.5. Cicer arietinum L.
4.6. Cinnamomum verum J. Presl.
4.7. Crocus sativus L.
4.8. Cuminum cyminum L.
4.9. Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb.
4.10. Foeniculum vulgare Mill.
4.11. Hordeum vulgare L.
4.12. Juglans regia L.
4.13. Lens culinaris L.
4.14. Nigella sativa L.
4.15. Olea europaea L.
4.16. Pinus gerardiana Wall. ex D. Don
4.17. Piper nigrum L.
4.18. Pistacia vera L.
4.19. Vitis vinifera L.
4.20. Zingiber officinale Roscoe
| Medicinal plants | Plants parts | Traditional uses | Recipients | Pharmacological effects | Dose administered | Duration of treatment | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Althaea officinalis L. | Leaves, flowers, roots | Diabetes, inflammation, skin infection, digestive and respiratory disorders | Alloxan-induced diabetic rats | ↓Glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT), ↓cholesterol, ↓serum glucose levels, ↓ alkaline phosphate level (APL) | Powdered leaves (5% of the diet) | 28 days | [33] |
| Anethum graveolens L. | Leaves, stems and seeds | Diabetes, digestive disorders, cancer, microbial infections, inflammation, hyperlipidemia, | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓Inflammatory cytokines, ↓triglycerides, ↓ total cholesterol, ↓LDL-C, ↓VLDL-C, ↓ blood glucose, ↓ AGEs, ↓ protein glycation, ↓ fructosamine level, ↓ fasting blood glucose | 300 mg/mL | 8 weeks | [38,39] |
| Allium sativum L. | Pulp | Diabetes, respiratory tract disorders, bacterial and fungal infections, wounds, cancers, CVDs, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, cold, asthma, hay fever, inflammation, obesity | STZ-induced diabetic rats |
↓ LDL, ↓ total cholesterol, ↓ oxidative stress, ↑ HDL, ↓ blood glucose, ↓intestinal glucose absorption, ↓ ROS generation, ↑ intracellular GSH content, ↓ endothelial dysfunction | 200 mg/kg | 3 weeks | [43,44,45] |
| Brassica oleracea L. | Leaves | Inflammation, digestive disorders, cancer, peptic ulcer, gout, detoxification | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↑ Glucose homeostatic regulation, ↓ organ damage from T2DM, ↓ oxidative stress, ↓ obesity, ↓ LDL cholesterol, ↓ total cholesterol, ↓ lipid peroxidation, ↑ pancreatic β-cells functions | 250 mg/kg | 40 days | [52,53,55] |
| Cicer arietinum L. | Leaves, fruits, seeds | Diabetes, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, weight loss, inflammation, microbial infections | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↑ Glycemic control, ↓ total cholesterol, ↓ α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, ↑ insulin secretion and receptor activity, ↓ insulin deficiency, ↓LDL | 200 mg/kg | 30 days | [58,61,62] |
| Cinnamomum verum J. Presl. | Dried bark (inner part) | Diabetes, arthritis, diarrhea, hemorrhoids, toothache, cough, cold, menstrual irregularities, inflammation, bacterial infections | T2DM patients | ↓GI enzymes, ↑ insulin response and sensitivity, ↑ glucose uptake, ↑ glycogen synthesis, ↓ gluconeogenesis, ↓ AGE formation, ↑ phosphorylation, ↑ GLUT4 | 1000 mg/day | 12 weeks | [67,68,69] |
| Crocus sativus L. | Flower stigma | Diabetes, hepatic and cognitive disorders, lumbago, asthma, cough, bronchitis, CVDs, cancer, hyperlipidemia | Alloxan-induced diabetic rats | ↓ROS, ↓TG, ↓TC, ↓ blood glucose, ↓ insulin resistance, ↑ insulin secretion and sensitivity, ↓ LDL, ↑ HDL, ↑serum insulin, ↓body weight, ↓ lipid level | 25, 50, 100, 200 mg/kg | 2 months | [75,76] |
| Cuminum cyminum L. | Seeds | Diabetes, chronic diarrhea, dyspepsia, asthma, hypertension, inflammation, bronchitis, dizziness, eczema, gastrointestinal disturbances | T2DM patients | ↓Blood glucose, ↓ glycosylated hemoglobin, ↓ body weight, ↓phospholipid, ↓ cholesterol, ↓ free fatty acid, ↓ TG, ↑ insulin secretion, ↓ aldose reductase, ↓ α-amylase and ɑ-glucosidase activity, ↓ AGEs | 50,100 mg/kg | 8 weeks | [83,84,85,86] |
| Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb. | Unopened dried flower bud, stem, leaves and fruits | Nausea, hepatic, bowel and stomach disorders, vomiting, microbial and protozoal infections, cholera, malaria, tuberculosis | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓PEPCK, ↓ G6Pase gene expression, ↓AChE, ↓α-glycosidase, ↓α-amylase, ↓elevated blood sugar, ↓lipid peroxidation | 100 mg/kg | 15 weeks | [88,90,91,92] |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Seeds and fruits | Diabetes, lactation, menstruation irregularities, libido, tumor, inflammatory disease, cancer, hepatic disorders | STZ-induced diabetic male rats | ↑GSH, ↓α- amylase and α- glucosidase activity, ↓breakdown of carbohydrates, ↑glycemic control, ↓cholesterol, ↓TG, ↓LDL ↑HDL | 150 mg/kg | 4 weeks | [95,96,98] |
| Hordeum vulgare L. | Grains, leaves, sprouts | Diabetes, skin infections, arthritis, digestive diseases, weight loss, cancer, detoxification, lipid metabolism | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓Blood glucose, ↓ cholesterol, ↓ hepatic cholesterol synthesis, ↓ α-glucosidase, ↓ α-amylase, ↑ insulin secretion | 100, 250, 500 mg/kg | 11 days | [101,102,103,104] |
| Juglans regia L. | Husks, kernels, shells, seeds, flower, bark and leaves | Diabetes, asthma, arthritis, eczema, stomachache, sinusitis, diarrhea, astringent, antiseptic | T2DM patients | ↓ Blood glucose, ↑insulin, ↓ HbA1c, ↑ GLUT2, ↓ glucose intestinal absorption, ↓FBG, ↓ TG | 100 mg/kg | 3 months | [105,106,107] |
| Lens culinaris L. | Seeds and sprouts | Diabetes, meat substitute, obesity, inflammation, hyperlipidemia | STZ-induced diabetic mice | ↓ROS, ↑ lipoprotein metabolism improvement, ↑ glycemic control, ↓ fasting blood glucose, ↓serum blood glucose, ↑ gut motility, ↓body weight | 100, 200, 400 mg/kg | 3 weeks | [113,114,115,117] |
| Nigella sativa L. | Seeds | Diabetes, digestive disorders, diarrhea, warts, toothaches, swellings, dyspnea, microbial infections, fever, inflammation, hypertension, allergy, infertility, tumors | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↑Serum insulin , ↓serum glucose, ↓LDL, ↓TG, ↓total cholesterol, ↑proliferation of β-cells, ↓oxidative stress | 300, 400 mg/kg | 12 weeks | [118,119,120,121] |
| Olea europaea L. | Fruit, pulp, leaves | Diabetes, hypertension, inflammation, diarrhea, respiratory and urinary tract infections, hemorrhoids, rheumatism, laxative, intestinal diseases, asthma, hyper uremia, hyperlipidemia | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓ α-glucosidase and digestive enzymes activity, ↓ postprandial hyperglycemia, ↑insulin action, ↑functionality and survival of β-cells | 1mL/100 bw/day (oil) | 6 weeks | [127,128,129,131,163] |
| Pinus gerardiana Wall. ex D. Don | Seeds, leaves, barks | Diabetes, hypertension, sepsis, fungal and microbial infections | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓Body weight, ↓ oxidative stress, ↓ hyperglycemia, ↑expression of PPARγ gene, ↑Akt, ↑ insulin secretion, ↓malondialdehyde, ↓fasting glucose levels | 3% and 6% w/w, (Powder) | 6 weeks | [133,135] |
| Piper nigrum L. | Seeds, leaves, flower and fruits | Diabetes, menstrual problems, atrophic arthritis, digestive problems, influenza, bacterial infection, inflammation, fever, hypertension, cancer, depressants, diarrhea | Alloxan-induced diabetic rats | ↓ROS generation, ↓lipid peroxidation, ↓ lipogenesis, ↑insulin secretion, ↓blood glucose, ↓triglyceride, ↓ total cholesterol, ↑HDL, ↓ LDL, ↑ total antioxidant capacity | 50 mg/kg | 8 weeks | [137,141,143] |
| Pistacia vera L. | Seeds, leaves, fruits | Diabetes, coughs, stomach diseases, asthma, sores, chest ailments, rheumatism, trauma, gynecological ailments, hemorrhoids | Pre-diabetic patients | ↓fasting blood glucose, ↓insulinemia, ↓Serum IL-6, and ↓fructosamine, ↓insulin resistance, ↓LDL, ↓ malondialdehyde , ↓proinflammatory cytokines, ↓glucose absorption | 57 g/day | 4 weeks | [145,146,149,164] |
| Vitis vinifera L. | Dried fruits | Diabetes, cancer, obesity, inflammation, hyperlipidemia | T2DM patients | ↓ LDL oxidation and LDL-cholesterol, ↓ blood glucose control, ↓postprandial glucose levels, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ blood pressure | 36 g/day | 24 weeks | [152,154,155] |
| Zingiber Officinale Roscoe | Roots and rhizomes | Diabetes, digestive disorders, nausea, rheumatism, respiratory tract infection, cough, hypercholesterolemia, neurological diseases, asthma, stroke, constipation, cancer | STZ-induced diabetic rats | ↓Superoxide anion, ↓hydroxyl radicals, ↓α-glucosidase and α-amylase activity, ↓cholesterol, ↓serum glucose, ↓ triglyceride, ↑HDL, ↑insulin sensitivity | 400 mg/kg | 8 weeks | [158,159,160] |
| Medicinal plants | Parts used | Phytoconstituent studied | Diabetic model | Dose administered | Duration of treatment | Pharmacological effects of the phytoconstituents used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Althaea officinalis L. | Leaves, roots, seeds | Lauric acid | Insulin resistance induced in macrophage THP-1 cells | 5μM-50μM | 24 h | Increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscles, Improves mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin sensitivity and GLUT-1, GLUT-3 expression | [165] |
| Anethum graveolens L. | Leaves, seeds |
Carvone | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 25,50,100 mg/kg | 30 days | Alleviates insulin resistance, improves insulin secretion, and reverses glycoprotein abnormalities | [166] |
| Allium sativum L. | Fruits | Allicin | STZ-induced diabetic rats |
15,30,45 mg/kg | 12 weeks | Improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance, ameliorates diabetes-induced morphological alterations in kidney and decreases FBG and triglyceride | [167] |
| Brassica oleracea L. | Leaves | Anthocyanin | T2DM patients | 160 mg/kg | 24 weeks | Improves lipid metabolism and insulin resistance, decreases LDL, total cholesterol and postprandial glucose, ameliorates diabetic complications | [168] |
| Cicer arietinum L. | Seeds | Quercetin | Alloxan-induced diabetic rats | 50 mg/kg | 30 days | Decreases blood glucose, total cholesterol, total bilirubin, creatinine and oxidative stress, regulates glucose homeostasis and improves insulin resistance | [169] |
| Cinnamomum verum J. Presl. | Bark | Cinnamaldehyde | STZ-induced diabetic rats |
5,10,20 mg/kg | 45 days | Elevates HDL level, plasma insulin, hepatic glycogen, decreases serum glucose, total cholesterol, triglyceride and LDL level | [170] |
| Crocus sativus L. | Flower stigma | Crocin | T2DM patients | 15 mg/kg | 12 weeks | Enhances GLUT-4 expression, inhibits TNF-α, IL-6, alleviates blood glucose, improves glucose homeostasis and insulin resistance | [171] |
| Cuminum cyminum L. | Seeds | Cuminaldehyde and cuminol | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 5, 10 mg/kg | 45 days | Increases insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity, lowers blood glucose, provides β-cell protection and improves lipid profile | [172] |
| Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb. | Flower buds, leaves, stem, fruits | Eugenol | STZ-induced diabetic mice | 100 mg/kg bw (I.P. route) |
45 days | Lowers blood glucose, blood lipids and AGEes formation, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase enzymes | [173] |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Seeds | Kaempferol | STZ-induced diabetic mice | 50 mg/kg | 12 weeks | Suppresses gluconeogenesis, enhances glucose uptake in skeletal muscles, restores hexokinase activity | [174] |
| Hordeum vulgare L. | Grains, leaves, sprouts | β-glucan | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 80 mg/kg | 4 weeks | Alleviates diabetic complications, reduces oxidative stress, lowers blood glucose, total cholesterol, total triglyceride and LDL level. | [175] |
| Juglans regia L. | Husks, kernels, seeds, flowers, bark, leaves | β-carotene | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 10, 20 mg/kg | 14 days | Improves glucose metabolism and lipid accumulation, lowers inflammatory cytokines, nitric oxide production and oxidative stress, enhances glucose uptake in skeletal muscle | [176] |
| Lens culinaris L. | Seeds, sprouts | Saponins | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 100,200 mg/kg | 2 weeks | Ameliorates postprandial hyperglycemia and diabetic complications, inhibits α-glucosidase and aldose reductase enzymes | [177] |
| Nigella sativa L. | seeds | Thymoquinone | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 50 mg/kg | 4 weeks | Attenuates blood glucose, lipid peroxidase, nitric oxide production, oxidative stress and alleviates diabetic nephropathy | [178] |
| Olea europaea L. | Fruits, leaves | Lutein | ARPE-19 cells | 0.5-1 μM | 24 h | Ameliorates diabetic retinopathy and hyperglycemia, Improves SOD2, HO-1, Nrf2, GSH and catalase regulation | [179] |
| Pinus gerardiana Wall. ex D. Don | Nuts | Linoleic acid | PTPN1, PTPN9, PTPN11 cell lines | 0.5-300 μM | 1 week | Inhibits the catalytic activity of PTPN1, PTPN9 and PTPN11, improves glucose uptake by activating AMPK and Akt pathway | [180] |
| Piper nigrum L. | Seeds, flowers fruits, leaves | β-caryophyllene | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 200 mg/kg | 42 days | Decreases glucose absorption and increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscles, ameliorates glucose tolerance, pancreatic cell damage, oxidative stress, lipid and blood glucose levels | [181] |
| Pistacia vera L. | Fruits, nuts, leaves | Procyanidins | STZ-induced db/db type 2 diabetic mice |
250 mg/kg | 45 days | Enhances GLUT-4 translocation and glucose uptake on skeletal muscles, possesses insulinotropic ad anti-hyperglycaemic effects | [182] |
| Vitis vinifera L. | Fruits | Ferulic acid | STZ-induced diabetic rats | 10 mg/kg | 14 days | Alleviates body weight, blood glucose, attenuates diabetes-associated symptom and lowers total triglyceride, total cholesterol, LDL and VLDL levels | [183] |
| Zingiber Officinale Roscoe | Roots | Gingerol | Type 2 diabetic mice (Leprdb/db) | 200 mg/kg | 4 weeks | Induces insulin secretion, elevates plasma GLP-1, activates cAMP, PKA, CREB in the pancreatic islets, enhances GLUT-4 translocation | [184] |
| Medicinal plant | Antidiabetic phytoconstituent | Chemical structure |
|---|---|---|
| Althaea officinalis L. | Lauric acid | 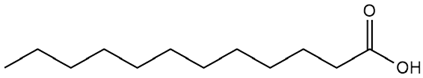 |
| Anethum graveolens L. | Carvone | 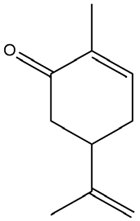 |
| Allium sativum L. | Allicin | 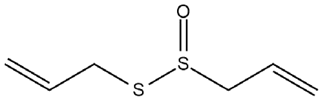 |
| Brassica oleracea L. | Anthocyanins | 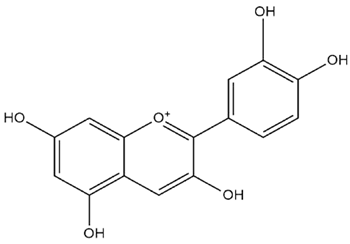 |
| Cicer arietinum L. | Quercetin | 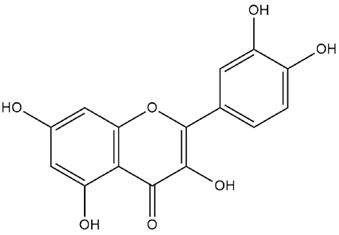 |
| Cinnamomum verum J. Presl. | Cinnamaldehyde |
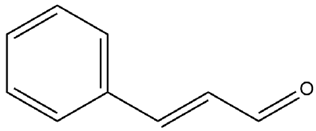 . . |
| Crocus sativus L. | Crocin | 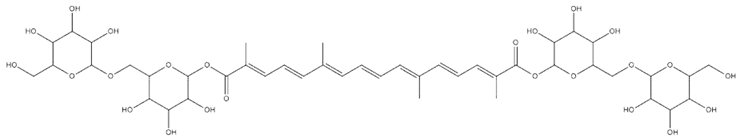 |
| Cuminum cyminum L. | Cuminaldehyde | 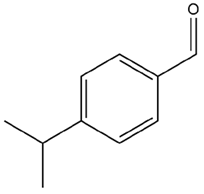 |
| Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb. | Eugenol | 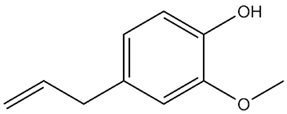 |
| Foeniculum vulgare Mill. | Kaempferol | 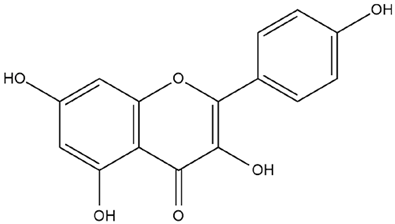 |
| Hordeum vulgare L. | β-glucan |
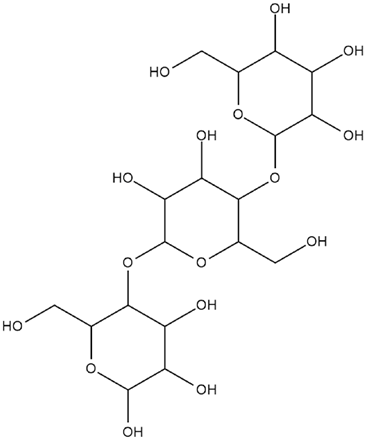 . . |
| Juglans regia L. | β-carotene | 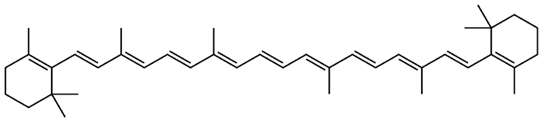 |
| Lens culinaris L. | Saponins | 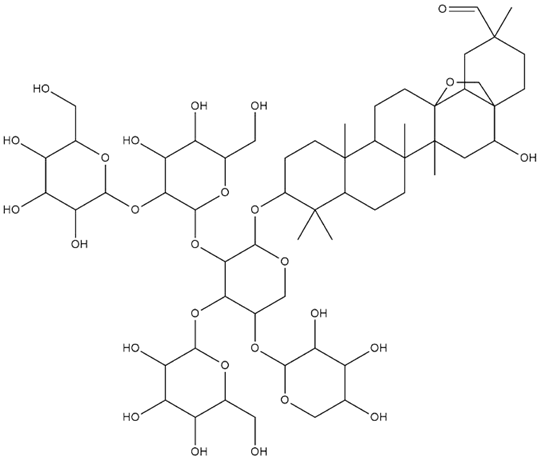 |
| Nigella sativa L. | Thymoquinone |  |
| Olea europaea L. | Lutein | 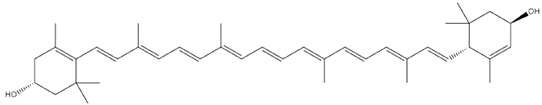 |
| Pinus gerardiana Wall. ex D. Don | Linoleic acid | 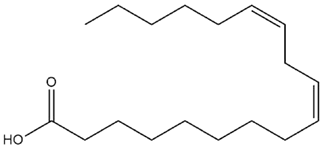 |
| Piper nigrum L. | β-caryophyllene |
 . . |
| Pistacia vera L. | Procyanidins | 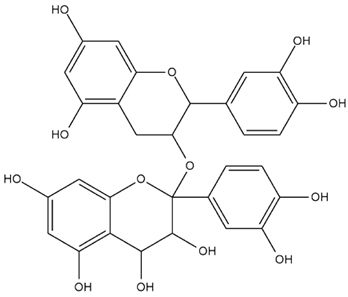 |
| Vitis vinifera L. | Ferulic acid | 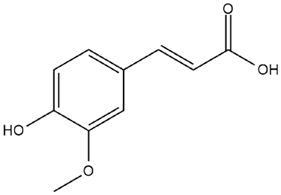 |
| Zingiber Officinale Roscoe | Gingerol | 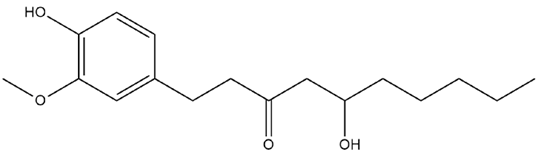 |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AchE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| Akt | Serine/threonine kinase |
| BW | Body weight |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CVDs | Cardiovascular disorders |
| CREB | cAMP-response element protein |
| FBG | Fasting blood glucose |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GLUT2 | Glucose transporter 2 |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| HDL | High density lipoprotein |
| LDL | Low density lipoprotein |
| PEPCK | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoprotein |
References
- Rashidi, A. A.; Mirhashemi, S. M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Sarkhail, P. Iranian Medicinal Plants for Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Pak J Biol Sci 2013, 16 (9), 401–411. [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Sarker, Md. M. R.; Sultana, T. N.; Chowdhury, Md. N. R.; Rashid, M. A.; Chaity, N. I.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, J.; Hafez, E. E.; Khan, S. A.; Mohamed, I. N. Antidiabetic Phytochemicals From Medicinal Plants: Prospective Candidates for New Drug Discovery and Development. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B. B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J. C. N.; Mbanya, J. C.; Pavkov, M. E.; Ramachandaran, A.; Wild, S. H.; James, S.; Herman, W. H.; Zhang, P.; Bommer, C.; Kuo, S.; Boyko, E. J.; Magliano, D. J. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 183, 109119. [CrossRef]
- Zarshenas, M. M.; Khademian, S.; Moein, M. Diabetes and Related Remedies in Medieval Persian Medicine. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2014, 18 (2), 142–149. [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Bancher-Todesca, D.; Pollak, A.; Repa, A.; Lechleitner, M.; Weitgasser, R. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2012, 124 Suppl 2,58–65. [CrossRef]
- Cade, W. T. Diabetes-Related Microvascular and Macrovascular Diseases in the Physical Therapy Setting. Phys Ther 2008, 88 (11), 1322–1335. [CrossRef]
- Dowarah, J.; Singh, V. P. Anti-Diabetic Drugs Recent Approaches and Advancements. Bioorg Med Chem 2020, 28 (5), 115263. [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Zielinski, A.; Roach, A. H.; Jende, J. A.; Householder, A. M.; Cole, E. E.; Atway, S. A.; Amornyard, M.; Accursi, M. L.; Shieh, S. W.; Thompson, E. E. Pharmacologic Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Oral Medications. Ann Pharmacother 2015, 49 (5), 540–556. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S. E.; Palumbo, P. J. Addition of Insulin to Oral Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Am J Med Sci 2006, 331 (5), 257–263. [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Hashempur, M. H.; Daneshfard, B.; Mosavat, S. H. Chapter 4 - Bioactive Foods as Dietary Intervention for Diabetes From the Perspective of Persian Medicine. In Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Diabetes (Second Edition); Watson, R. R., Preedy, V. R., Eds.; Academic Press, 2019, 49–68. [CrossRef]
- Osadebe, P.; Odoh, U.; Uzor, P. Natural Products as Potential Sources of Antidiabetic Drugs. British Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 4, 2075–2095. [CrossRef]
- Coulter-Parkhill, A.; McClean, S.; Gault, V. A.; Irwin, N; Therapeutic Potential of Peptides Derived from Animal Venoms: Current Views and Emerging Drugs for Diabetes. Clinical medicine insights. Endocrinology and diabetes, 2021, 14, 11795514211006071. [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, S. S.; Rachh, P. R. Review on Potent Anti-diabetic Plants or Herbs From Traditional Medicine. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 2018, 8 (5), 92–98. [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S. I.; Mishra, N. Traditional Indian medicines used for the management of diabetes mellitus. Journal of diabetes research, 2013, 712092. [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Pham, B.; Le, L. Bioactive Compounds in Anti-Diabetic Plants: From Herbal Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery. Biology, 2020, 9(9), 252. [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.; McClelland, A.; Hagiwara, S.; Godson, C.; Kantharidis, P. Chapter 31 - MiRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Diabetes and Their Value as Biomarkers. In Epigenetic Biomarkers and Diagnostics; García-Giménez, J. L., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, 2016, 643–661. [CrossRef]
- Lien, C. F.; Chen, S. J.; Tsai, M. C.; Lin, C. S. Potential Role of Protein Kinase C in the Pathophysiology of Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis. Frontiers in pharmacology, 2021, 12, 716332. [CrossRef]
- Koya, D.; King, G. L. Protein kinase C activation and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes, 1998, 47(6), 859–866. [CrossRef]
- Zaccardi, F.; Webb, D. R.; Yates, T.; Davies, M. J. Pathophysiology of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 90-year perspective. Postgraduate medical journal, 2016, 92(1084), 63–69. [CrossRef]
- Ohiagu, F. O., Chikezie, P. C.; Chikezie, C. M.. Pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus complications: Metabolic events and control. Biomedical Research and Therapy, 2021, 8(3), Article 3. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. P.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A. S. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic complications. The Korean journal of physiology & pharmacology: official journal of the Korean Physiological Society and the Korean Society of Pharmacology, 2014, 18(1), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S. P.; Dean, R. T. Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of 'autoxidative glycosylation' in diabetes. The Biochemical journal, 1987, 245(1), 243–250. [CrossRef]
- Chetyrkin, S.; Mathis, M.; Pedchenko, V.; Sanchez, O. A.; McDonald, W. H.; Hachey, D. L.; Madu, H.; Stec, D.; Hudson, B.; Voziyan, P. Glucose autoxidation induces functional damage to proteins via modification of critical arginine residues. Biochemistry, 2011, 50(27), 6102–6112. [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Chandra, H.; Banerjee, M. Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX1) expression in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A preliminary study from north India. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, 2016, 17(1), 41–45. [CrossRef]
- Banday, M. Z.; Sameer, A. S.; Nissar, S. Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna journal of medicine, 2020, 10(4), 174–188. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Pathophysiology. News-Medical.Net. 2021 https://www.news-medical.net/health/Diabetes-Mellitus-Type-2-Pathophysiology.aspx.
- Petroni, M. L.; Brodosi, L.; Marchignoli, F.; Sasdelli, A. S.; Caraceni, P.; Marchesini, G.; Ravaioli, F. Nutrition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Present Knowledge and Remaining Challenges. Nutrients, 2021, 13(8), 2748. [CrossRef]
- Ley, S. H.; Hamdy, O.; Mohan, V.; Hu, F. B. Prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: dietary components and nutritional strategies. Lancet (London, England), 2014, 383(9933), 1999–2007. [CrossRef]
- Kianitalaei, A.; Feyzabadi, Z.; Hamedi, S.; Qaraaty, M. Althaea Officinalis in Traditional Medicine and modern phytotherapy. J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res, 2019, 9, 155.
- Bonaterra, G. A.; Schmitt, J.; Schneider, K.; Schwarzbach, H.; Aziz-Kalbhenn, H.; Kelber, O.; Müller, J.; Kinscherf, R. Phytohustil® and Root Extract of Althaea Officinalis L. Exert Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Properties and Improve the Migratory Capacity of Endothelial Cells in Vitro. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 948248. [CrossRef]
- Basch, E.; Ulbricht, C.; Hammerness, P.; Vora, M. Marshmallow (Althaea officinalis L.) monograph. Journal of herbal pharmacotherapy, 2003, 3(3), 71–81. [CrossRef]
- Kayarohanam, S. Current Trends of Plants Having Antidiabetic Activity: A Review. Journal of Bioanalysis & Biomedicine, 2015, 07(02). [CrossRef]
- Khadr, S; Ahmed, A. Antidiabetic Effect of Marshmallow and Psyllium Leaves in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Journal of Home Economics-Menofia University, 2016, 26(3), 225–244. [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Malik, R.; Javaid, M.; Bibi, S. Ethonobotanical properties and uses of Medicinal plants of Morgah Biodiversity Park, Rawalpindi. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 2008, 40, 1897–1911.
- Yousaf, A.; Shahid, S. The study of Anethum graveolens L. (Dill) in the case of Diabetes mellitus (DM). Asian Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020, 10(4), 248–256. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N. Haematological and hypoglycemic potential Anethum graveolens seeds extract in normal and diabetic Swiss albino mice. Veterinary World, 2013, 6(8), 502. [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.; Nayebi, N.; Keshtkar, A.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Taheri, E.; Larijani, B. The effect of 12 weeks Anethum graveolens (dill) on metabolic markers in patients with metabolic syndrome; a randomized double blind controlled trial. Daru : journal of Faculty of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, 2012, 20(1), 47. [CrossRef]
- Oshaghi, E. A.; Tavilani, H.; Khodadadi, I.; Gobdarzi, M. T. Dill tablet: A potential antioxidant and anti-diabetic medicine. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2015, 5(9), 696–702. [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M. T.; Khodadadi, I.; Tavilani, H.; Abbasi Oshaghi, E. The Role of Anethum graveolens L. (Dill) in the Management of Diabetes. Journal of tropical medicine, 2016, 1098916. [CrossRef]
- Oshaghi, E. A.; Khodadadi, I.; Tavilani, H.; Goodarzi, M. T. Aqueous Extract of Anethum Graveolens L. has Potential Antioxidant and Antiglycation Effects. Iranian journal of medical sciences, 2016, 41(4), 328–333.
- Kazemi, T.; Panahi shahri, H.; Hossaini farash, M.; Darabi, M.; Kashanian, M.; Akbari, H. Effect of Dill Pearl on Serum Lipids. Journal of Arak University of Medical Sciences, 2006, 8(3), 35–41.
- Thomson, M.; Amin, Z.; Qattan, K. K. A.; Shaban, L. Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of garlic (Allium sativum) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Semantic scholar, 2007.
- Hosseini, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. A review on the effects of Allium sativum (Garlic) in metabolic syndrome. Journal of endocrinological investigation, 2015, 38(11),1147–1157. [CrossRef]
- Imo, C. Medicinal Properties of Ginger and Garlic: A Review. Current Trends in Biomedical Engineering & Biosciences, 2019, 18(2). [CrossRef]
- Londhe, V.; Gavasane, A.; Nipate, S; Bandawane, D.; Chaudhari, P. Role of garlic (Allium sativum) in various diseases: An overview. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Opinion, 2011, 1, 129–134.
- Liu, C. T.; Sheen, L. Y.; Lii, C. K. (2007). Does garlic have a role as an antidiabetic agent?. Molecular nutrition & food research, 51(11), 1353–1364. [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Magdy Beshbishy, A.; G Wasef, L.; Elewa, Y. H. A.; A Al-Sagan, A.; Abd El-Hack, M. E., Taha, A. E., M Abd-Elhakim, Y., & Prasad Devkota, H. Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Garlic (Allium sativum L.): A Review. Nutrients, 2020, 12(3), 872. [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Martínez, M.; Corzo, N.; Villamiel, M. Biological properties of onions and garlic. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2007, 18, 609–625. [CrossRef]
- Eidi, A.; Eidi, M.; Esmaeili, E. Antidiabetic effect of garlic (Allium sativum L.) in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology, 2006, 13(9-10), 624–629. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Upadhyay, A. K.; Bahadur, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, K. P.; Rai, M. Antioxidant phytochemicals in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. Capitata). Scientia Horticulturae, 2006, 108(3), 233. [CrossRef]
- Šamec, D.; Pavlović, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. White cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata f. alba): botanical, phytochemical and pharmacological overview. Phytochemistry reviews, 2017, 16, 117-135. [CrossRef]
- In Jaiswal, A. K. Nutritional composition and antioxidant properties of fruits and vegetables, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Uuh-Narvaez, J. J.; Segura-Campos, M. R. Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata): A food with functional properties aimed to type 2 diabetes prevention and management. Journal of food science, 2021, 86(11), 4775–4798. [CrossRef]
- Buko, V.; Zavodnik, I.; Kanuka, O.; Belonovskaya, E.; Naruta, E.; Lukivskaya, O.; Kirko, S.; Budryn, G.; Żyżelewicz, D.; Oracz, J.; Sybirna, N. Antidiabetic effects and erythrocyte stabilization by red cabbage extract in streptozotocin-treated rats. Food & function, 2018, 9(3), 1850–1863. [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeed, A. A.; Saif, M.; AlAmeer, M. A.; Al-Anazi, B. K. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Properties of Ethanolic Extract of Brassica oleracea in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2020, 9(2).
- Quintero-Soto, M. F.; Chávez-Ontiveros, J.; Garzón-Tiznado, J. A.; Salazar-Salas, N. Y.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K. V., Delgado-Vargas, F., & López-Valenzuela, J. A. Characterization of peptides with antioxidant activity and antidiabetic potential obtained from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein hydrolyzates. Journal of food science, 2021, 86(7), 2962–2977. [CrossRef]
- Acevedo Martinez, K. A.; Yang, M. M.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Technological properties of chickpea (Cicer arietinum): Production of snacks and health benefits related to type-2 diabetes. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety, 2021, 20(4), 3762–3787. [CrossRef]
- Ramadhani, U. P.; Chandra, B.; Rivai, H. Overview of phytochemistry and pharmacology of chickpeas (Phaseolus vulgaris). World journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences, 2020, 9(9), 442-61.
- Roy, F.; Boye, J. I.; Simpson, B. K. Bioactive proteins and peptides in pulse crops: Pea, chickpea and lenti. Food Research International (Ottawa, Ont.), 2010, 43(2), 432–442. [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.A.; Grusak, M.A. Nutritional value of chickpea. In: Yadav, S.S., Redden, B., Chen, W. and Sharma, B., Eds., Chickpea Breeding and Management, CAB International, Wallingford, 2007, 101-142. [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Gahlot, K. Pharmacognostical and Pharmacological Importance of Cicer arietinum Linn -A Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 2018, 11(10), 4755–4763. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Magaña, L. M.; Cuevas-Rodríguez, E. O.; Gutiérrez-Dorado, R.; Ayala-Rodríguez, A. E.; Valdez-Ortiz, A.; Milán-Carrillo, J.; Reyes-Moreno, C. Solid-state bioconversion of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by Rhizopus oligosporus to improve total phenolic content, antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic functionality. International journal of food sciences and nutrition, 2014, 65(5), 558–564. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R. K.; Gupta, K.; Sharma, A.; Das, M.; Ansari, I. A.; Dwivedi, P. D. Health Risks and Benefits of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) Consumption. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 2017, 65(1), 6–22. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Li, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Qin, L.; Sun, W.; Xu, Y.; Shi, H.; Xu, T.; Liu, T. Study of the Hypoglycemic Activity of Derivatives of Isoflavones from Cicer arietinum L. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2017, 8746823. [CrossRef]
- Charles, D.J. Antioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other Sources. Antioxidant Properties of Spices, Herbs and Other Sources. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Rafehi, H.; Ververis, K.; Karagiannis, T. C. Controversies surrounding the clinical potential of cinnamon for the management of diabetes. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 2012, 14(6), 493–499. [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Uluwaduge, I.; Jansz, E. R. Bioactivity of cinnamon with special emphasis on diabetes mellitus: a review. International journal of food sciences and nutrition, 2012, 63(3), 380–386. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mandal, A.; Kant, R.; Jachak, S.; Jagzape, M. Is Cinnamon Efficacious for Glycaemic Control in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus?. JPMA. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association, 2020, 70(11), 2065–2069.
- Sahib A. S. Anti-diabetic and antioxidant effect of cinnamon in poorly controlled type-2 diabetic Iraqi patients: A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of intercultural ethnopharmacology, 2016, 5(2), 108–113. [CrossRef]
- Hayward, N. J.; McDougall, G. J.; Farag, S.; Allwood, J. W.; Austin, C.; Campbell, F.; Horgan, G.; Ranawana, V. Cinnamon Shows Antidiabetic Properties that Are Species-Specific: Effects on Enzyme Activity Inhibition and Starch Digestion. Plant foods for human nutrition (Dordrecht, Netherlands), 2019, 74(4), 544–552. [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, S.; Akilen, R.; Sharma, S.; Tsiami, A. The potential of cinnamon to reduce blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 2009, 11(12), 1100–1113. [CrossRef]
- Elgazar, A. F.; Rezq, A. A.; Bukhari, H. M. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Saffron Extract in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Journal of Medicinal Plants. 2013.
- Pandey, D. K.; Nandy, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dey, A. Chapter 10 - Advances in Bioactive Compounds from Crocus Sativus (Saffron): Structure, Bioactivity and Biotechnology. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Bioactive Natural Products; Elsevier, 2020, 66, 273–304. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Razavi, B. M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Saffron (Crocus sativus) petal as a new pharmacological target: a review. Iranian journal of basic medical sciences, 2018, 21(11), 1091–1099. [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and its ingredients on the management of diabetes mellitus and dislipidemia. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 2014, 8, 541–549. [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Saffron: a promising natural medicine in the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Journal of the science of food and agriculture, 2017, 97(6), 1679–1685. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Ahmed, H.; Dixit, R. K.; Dharamveer; Saraf, S. A. Crocus sativus L.: A comprehensive review. Pharmacognosy reviews, 2010, 4(8), 200–208. [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N. P. E.; Christodoulou, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. The cardiovascular-protective properties of saffron and its potential pharmaceutical applications: A critical appraisal of the literature. Phytotherapy research : PTR, 2021, 35(12), 6735–6753. [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Zare, V.; Butler, A. E.; Barreto, G. E.; Sahebkar, A. Antidiabetic potential of saffron and its active constituents. Journal of cellular physiology, 2019, 234(6), 8610–8617. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Khan, A.; Aldebasi, Y.; Aldebasi, Y. Saffron (Crocus sativus) and its Active Ingredients: Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Pharmacognosy Journal, 2017, 9(6), 873–879. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) and black cumin (Nigella sativa) seeds: traditional uses, chemical constituents, and nutraceutical effects. Food Quality and Safety, 2018, 2(1), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Allaq, A. A.; Sidik, N. J.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Ahmed, I. A. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.): A review of its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry. Biomedical Research and Therapy, 2020, 7(9), Article 9. [CrossRef]
- Mnif, S.; Aifa, S. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) from traditional uses to potential biomedical applications. Chemistry & biodiversity, 2015, 12(5), 733–742. [CrossRef]
- Siow, H.-L.; Gan, C.-Y. Functional protein from cumin seed (Cuminum cyminum): Optimization and characterization studies. Food Hydrocolloids. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Yadav, S. S.; Kumar, S.; Narashiman, B. A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical research of dietary spice Cuminum cyminum L. Phytotherapy research : PTR, 2021, 35(9), 5007–5030. [CrossRef]
- Ebada, M. E. Cuminaldehyde: A Potential Drug Candidate. Journal of Pharmacology & Clinical Research, 2017, 2(2). [CrossRef]
- Milind, P.; Deepa, K. Clove: A champion spice. International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy (IJRAP), 2011, 2(1), 47–54.
- Hussain, S.; Rahman, R.; Mushtaq, A.; Zerey-Belaskri, A. E. Clove: A review of a precious species with multiple uses. 2017.
- Cortés-Rojas, D. F.; de Souza, C. R.; Oliveira, W. P. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): a precious spice. Asian Pacific journal of tropical biomedicine, 2014, 4(2), 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G. E.; Alkazmi, L. M.; Wasef, L. G.; Beshbishy, A. M.; Nadwa, E. H.; Rashwan, E. K. Syzygium aromaticum L. (Myrtaceae): Traditional Uses, Bioactive Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological and Toxicological Activities. Biomolecules, 2020, 10(2), 202. [CrossRef]
- Bouchentouf, S.; Said, G.; Noureddine, M.; Allali, H.; Bouchentouf, A. A Note Study on Antidiabetic Effect of Main Molecules Contained in Clove Using Molecular Modeling Interactions with DPP-4 Enzyme. International Journal of Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2017, 5, 9–13. [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, K.; Hajlaoui, H.; Zmantar, T.; Kahla-Nakbi, A. B.; Rouabhia, M.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. The chemical composition and biological activity of clove essential oil, Eugenia caryophyllata (Syzigium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae): a short review. Phytotherapy research: PTR, 2007, 21(6), 501–506. [CrossRef]
- Topal, F. Anticholinergic and antidiabetic effects of isoeugenol from clove (Eugenia caryophylata) oil. International Journal of Food Properties, 2019, 22(1), 583-592. [CrossRef]
- Helal, E. G. E.; AL Jalaud, N. A.A.; El-Aleem, M. A.; Ahmed, S. S. Effect of Phytoestrogen (Fennel) on Some Sex Hormones and Other Physiological Parameters in Male Albino Rats. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine, 2019, 74(7), 1616–1620. [CrossRef]
- Abou, N.; Abou El-Soud, N.; El-Laithy N.; El-Saeed, G.; Wahby, M. S.; Khalil, M.; Morsy, F.; Shaffie, N.; Abou, C.; Wahby, S. Antidiabetic Activities of Foeniculum Vulgare Mill. Essential Oil in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Jun Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences Jun Maced J Med Sci Jun, 2011, 150173, 139–146139. [CrossRef]
- Samadi-Noshahr, Z.; Hadjzadeh, M. A.; Moradi-Marjaneh, R.; Khajavi-Rad, A. The hepatoprotective effects of fennel seeds extract and trans-Anethole in streptozotocin-induced liver injury in rats. Food science & nutrition, 2020, 9(2), 1121–1131. [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, S. B.; Patel, V. V.; Bandivdekar, A. H. Foeniculum vulgare Mill: a review of its botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, contemporary application, and toxicology. BioMed research international, 2014, 842674. [CrossRef]
- Osman, N. N.; Jambi, E. J.; Aseri, N. H. Assessment of antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of Cassia angustifolia and Feoniculum vulgare in diabetic rats. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences, 2017, 6(2).
- Zeng, Y.; Pu, X.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, T. Preventive and Therapeutic Role of Functional Ingredients of Barley Grass for Chronic Diseases in Human Beings. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2018, 3232080. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. H.; Kim, J. H.; Kim, S. H.; Oh, J. Y.; Seo, W. D.; Kim, K. M.; Jung, J. C.; Jung, Y. S. Barley Sprouts Extract Attenuates Alcoholic Fatty Liver Injury in Mice by Reducing Inflammatory Response. Nutrients, 2016, 8(7), 440. [CrossRef]
- Minaiyan, M.; Ghannadi, A.; Movahedian, A.; Hakim-Elahi, I. Effect of Hordeum vulgare L. (Barley) on blood glucose levels of normal and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Research in pharmaceutical sciences, 2014, 9(3), 173–178.
- Rashid, K.; Kumar, C. S.; Haleel, P. M. M. Healthcare Benefits of Hordeum vulgare L (Barley): A Phyto-Pharmacological Review. Research Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacodynamics, 2017, 9(4), 207–210. [CrossRef]
- Boantă, A.; Muntean, L.; Russu, F.; Ona, A.; Porumb, I.; Filip, E. Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.): Medicinal and Therapeutic Uses - Review. Hop Med. Plants, 2019, 1-2.
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland barley: Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, health effects, and applications. Food research international (Ottawa, Ont.), 2021, 140, 110065. [CrossRef]
- Delaviz, H.; Mohammadi, J.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Mohammadi, B.; Farhadi, N. A Review Study on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology Applications of Juglans Regia Plant. Pharmacognosy reviews, 2017, 11(22), 145–152. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Su, C.; Xu, Y.; Shang, K.; Sun, K.; Li, C.; Lu, J. Identifying potential active components of walnut leaf that action diabetes mellitus through integration of UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS and network pharmacology analysis. Journal of ethnopharmacology, 2020, 253, 112659. [CrossRef]
- Forino, M.; Stiuso, P.; Lama, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Tenore, G. C.; Novellino, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Bioassay-guided identification of the antihyperglycaemic constituents of walnut (Juglans regia) leaves. Journal of Functional Foods, 2016, 26, 731–738. [CrossRef]
- Kamyab, H.; Hejrati, S.; Khanavi, M.; Malihi, F.; Mohammadirad, A.; Baeeri, M.; Esmaily, H.; Abdollahi, M. Hepatic mechanisms of the Walnut antidiabetic effect in mice. Open Life Sciences, 2010, 5 (3). [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Parkhideh, S.; Solhpour, A.; Madani, H.; Mahzouni, P.; Rahimi, P. Effect of ethanolic extract of Juglans regia L. on blood sugar in diabetes-induced rats. Journal of medicinal food, 2008, 11(3), 533–538. [CrossRef]
- Magro, A. E. A.; Silva, L. C.; Rasera, G. B.; Ferreira, L. R.; Faria, J. A. F.; Teixeira, J. A. Solid-state fermentation as an efficient strategy for the biotransformation of lentils: Enhancing their antioxidant and antidiabetic potentials. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 2019, 6(1), 38. [CrossRef]
- Singhal, P.; Kaushik, G.; Mathur, P. Antidiabetic potential of commonly consumed legumes: a review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 2014, 54(5), 655–672. [CrossRef]
- Świeca, M.; Baraniak, B.; Gawlik-Dziki, U. In vitro digestibility and starch content, predicted glycemic index and potential in vitro antidiabetic effect of lentil sprouts obtained by different germination techniques. Food chemistry, 2013, 138(2-3), 1414–1420. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Polyphenol-Rich Lentils and Their Health Promoting Effects. International journal of molecular sciences, 2017, 18(11), 2390. [CrossRef]
- Tefera, M. M.; Altaye, B. M.; Yimer, E. M.; Berhe, D. F.; Tadesse Bekele, S. Antidiabetic Effect of Germinated Lens culinaris Medik Seed Extract in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Journal of experimental pharmacology, 2020, 12, 39–45. [CrossRef]
- Casarin, A. L. F.; Rasera, G. B.; de Castro, R. J. S. Combined biotransformation processes affect the antioxidant, antidiabetic and protease inhibitory properties of lentils. Process Biochemistry, 2021, 102, 250-260 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2021.01.011.
- Faris, M. A.-I. E.; Takruri, H. R.; Issa, A. Y. Role of lentils (Lens culinaris L.) in human health and nutrition: A review. Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2013, 6(1), 3–16. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Gao, C.; Han, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Lu, F. Co-fermentation of lentils using lactic acid bacteria and Bacillus subtilis natto increases functional and antioxidant components. Journal of Food Science, 2021, 86(2), 475-483. [CrossRef]
- Rchid, H.; Chevassus, H.; Nmila, R.; Guiral, C.; Petit, P.; Chokaïri, M.; Sauvaire, Y. Nigella sativa seed extracts enhance glucose-induced insulin release from rat-isolated Langerhans islets. Fundamental & clinical pharmacology, 2004, 18(5), 525–529. [CrossRef]
- Benhaddou-Andaloussi, A.; Martineau, L. C.; Spoor, D.; Vuong, T.; Leduc, C.; Joly, E.; Burt, A.; Meddah, B.; Settaf, A.; Arnason, J. T.; Prentki, M.; Haddad, P. S. Antidiabetic Activity of Nigella sativa Seed Extract in Cultured Pancreatic β-cells, Skeletal Muscle Cells, and Adipocytes. Pharmaceutical Biology, 2008, 46(1–2), 96–104. [CrossRef]
- Yarnell, E.; Abascal, K. Nigella sativa: Holy Herb of the Middle East. Alternative and Complementary Therapies, 2011, 17, 99–105. [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M. L.; Gaur, J.; Sharma, R.; Haldiya, K. R. Antidiabetic Properties of a Spice Plant Nigella sativa. Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2011, 1(1). [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M. F. Nutritional value, functional properties and nutraceutical applications of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.): An overview. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2007, 42(10), 1208–1218. [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M. T.; Qadir, R., Bukhari, I.; Ashraf, R. A.; Malik, Z.; Zahoor, S.; Murtaza, M. A.; Siddique, F.; Shah, S. N. H.; Saadia, M. Antidiabetic potential of Nigella sativa L seed oil in alloxan induced diabetic rabbits. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2020, 19(2), 283-289. [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M. A.; Khan, A.; Hanif, M.; Farooq, U.; Perveen, S. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Olea europaea (Olive). Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2015, 541591. [CrossRef]
- Caramia, G. Virgin olive oil. From legend to scientific knowledge of the nutraceutical aspects. Pediatr Med Chir, 2006, 28 (1–3), 9–23.
- Acar-Tek, N.; Ağagündüz, D. Olive Leaf (Olea europaea L. folium): Potential Effects on Glycemia and Lipidemia. Annals of nutrition & metabolism, 2020, 76(1), 10–15. [CrossRef]
- Waterman, E.; Lockwood, B. Active components and clinical applications of olive oil. Alternative medicine review : a journal of clinical therapeutic, 2007, 12(4), 331–342.
- Figueiredo-González, M.; Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; González-Barreiro, C.; Simal-Gándara, J.; Valentão, P.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Andrade, P. B.; Cancho-Grande, B. Evaluation of the neuroprotective and antidiabetic potential of phenol-rich extracts from virgin olive oils by in vitro assays. Food research international (Ottawa, Ont.), 2018, 106, 558–567. [CrossRef]
- Collado-González, J.; Grosso, C.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P. B.; Ferreres, F.; Durand, T.; Guy, A.; Galano, J. M.; Torrecillas, A.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á. Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase by Spanish extra virgin olive oils: The involvement of bioactive compounds other than oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. Food chemistry, 2017, 235, 298–307. [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lozano, J. M.; Rada, M., Lapetra, J.; Guinda, Á.; Jiménez-Rodríguez, M. C.; Cayuela, J. A.; Ángel-Lugo, A.; Vilches-Arenas, Á.; Gómez-Martín, A. M.; Ortega-Calvo, M.; Castellano, J. M. Prevention of type 2 diabetes in prediabetic patients by using functional olive oil enriched in oleanolic acid: The PREDIABOLE study, a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes, obesity & metabolism, 2019, 21(11), 2526–2534. [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Davalos, A.; López de Las Hazas, M. C.; Crespo, M. C.; Tomé-Carneiro, J. An overview of the pharmacology of olive oil and its active ingredients. British journal of pharmacology, 2020, 177(6), 1316–1330. [CrossRef]
- Alami, K.; Mousavi, S. Y. Afghan Chehelghoza (Pinus gerardiana L.) pine nut diet enhances the learning and memory in male rats. Nutrition and Dietary Supplements, 2020, 12, 277-288. [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, D.; Dash, A. K. Pinus gerardiana Wallichex. D. Don.-a review. Phytomedicine Plus, 2021, 1(2), 100024. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S. A.; Vali, M.; Haghighi-Zade, M. H.; Siahpoosh, A.; Malihi, R. The Effect of Chilgoza Pine Nut (Pinus gerardiana Wall.) on Blood Glucose and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Rats. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity : targets and therapy, 2020, 13, 2399–2408. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Sharma, R.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Valko, M.; Upadhyay, N. K.; Kuča, K.; Bhardwaj, P. Studies of Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities of Pinus gerardiana and Pinus roxburghii Seed Extracts. BioMed Research International, 2022, e5938610. [CrossRef]
- Zulfqar, F.; Akhtar, M. F.; Saleem, A.; Akhtar, B.; Sharif, A.; Saleem, U. Chemical characterization, antioxidant evaluation, and antidiabetic potential of Pinus gerardiana (Pine nuts) extracts. Journal of food biochemistry, 2020, 44(6), e13199. [CrossRef]
- Takooree, H.; Aumeeruddy, M. Z.; Rengasamy, K. R. R.; Venugopala, K. N.; Jeewon, R.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M. F. A systematic review on black pepper (Piper nigrum L.): from folk uses to pharmacological applications. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 2019, 59(sup1), S210–S243. [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, V. A.; Chempakam, B.; Zachariah, T. J. Chemistry of spices. CABI Pub. 2008.
- Peter, K. V. Handbook of herbs and spices. Woodhead publishing. 2006, 3.
- Abukawsar, M.; Saleh-E-In, M.; Ahsan, M.; Rahim, M.; Nurul, M.; Huda Bhuiyan, M. N.; Sudhangshu, Roy; K., Ghosh, A.; Naher, S. Chemical, pharmacological and nutritional quality assessment of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) seed cultivars. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 2018, 42. [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, K.; Murugan, M.; Dhanya, M. K.; Pandian, A.; Warkentin, T. D. Phytochemistry and therapeutic potential of black pepper [Piper nigrum (L.)] essential oil and piperine: A review. Clinical Phytoscience, 2021, 7(1), 52. [CrossRef]
- Jeena, K.; Liju, V. B.; Umadevi, N. P.; Kuttan, R. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive properties of black pepper essential oil (Piper nigrum Linn). Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants, 2014, 17(1), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Khaliq, T.; Hafizur, R. M.; Raza, S. A.; Ullah, H. Effect of black pepper, turmeric and ajwa date on the endocrine pancreas of the experimentally induced diabetes in wister albino rats: A histological and immunohistochemical study. Endocrine and Metabolic Science, 2021, 4, 100098. [CrossRef]
- Shityakov, S.; Bigdelian, E.; Hussein, A. A.; Hussain, M. B.; Tripathi, Y. C.; Khan, M. U.; Shariati, M. A. Phytochemical and pharmacological attributes of piperine: A bioactive ingredient of black pepper. European journal of medicinal chemistry, 2019, 176, 149–161. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M.; Islam, M. R.; Akash, S.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Ray, T. K.; Rahaman, M. S.; Wilairatana, P. Recent advancements of nanoparticles application in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: At a glance. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2022, 153, 113305. [CrossRef]
- Napoli, E.; Gentile, D.; Ruberto, G. GC–MS analysis of terpenes from Sicilian Pistacia vera L. oleoresin. A source of biologically active compounds. Biomedical Chromatography, 2019, 33(2), e4381. [CrossRef]
- Emlik, H.; Simitcioglu, B.; Cakir, A.; Kilic, I. H.; Karagoz, I. D. Evaluation of Pistacia vera Sap Waste Sections and Its Potential Role on Treatment. The Eurasia Proceedings of Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics, 2020, 10, 12-16.
- Ozçelik, B.; Aslan, M.; Orhan, I.; Karaoglu, T. Antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral activities of the lipophylic extracts of Pistacia vera. Microbiological research, 2005, 160(2), 159–164. [CrossRef]
- Gok, H. N.; Pekacar, S.; Deliorman Orhan, D. Investigation of Enzyme Inhibitory Activities, Antioxidant Activities, and Chemical Properties of Pistacia vera Leaves Using LC-QTOF-MS and RP-HPLC. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research: IJPR, 2022, 21(1), e127033. [CrossRef]
- Noguera-Artiaga, L.; Pérez-López, D.; Burgos-Hernández, A.; Wojdyło, A.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á. A. Phenolic and triterpenoid composition and inhibition of α-amylase of pistachio kernels (Pistacia vera L.) as affected by rootstock and irrigation treatment. Food chemistry, 2018, 261, 240–245. [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Cruz, J. F.; Zhu, M.; Kinghorn, A. D.; Wu, C. D. Antimicrobial constituents of Thompson seedless raisins (Vitis vinifera) against selected oral pathogens. Phytochemistry Letters, 2008, 1(3), 151–154. [CrossRef]
- Olmo-Cunillera, A.; Escobar-Avello, D.; Pérez, A. J.; Marhuenda-Muñoz, M.; Lamuela-Raventós, R. M.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A. Is Eating Raisins Healthy? Nutrients, 2020, 12(1), Article 1. [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P. Grapes and Their Derivatives in Functional Foods. Foods, 2021, 10(3), 672. [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, P. T.; Kaliora, A. C.; Tentolouris, N. K.; Argiana, V.; Perrea, D.; Kalogeropoulos, N.; Kountouri, A. M.; Karathanos, V. T. A pilot, randomized controlled trial to examine the health outcomes of raisin consumption in patients with diabetes. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.), 2014, 30(3), 358–364. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R. H.; He, X. Novel triterpenoids isolated from raisins exert potent antiproliferative activities by targeting mitochondrial and Ras/Raf/ERK signaling in human breast cancer cells. Food & function, 2016, 7(7), 3244–3251. [CrossRef]
- Aderonke Otunola, G.; Jide Afolayan, A. A Review of the Antidiabetic Activities of Ginger. IntechOpen. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Anh, N. H.; Kim, S. J.; Long, N. P.; Min, J. E.; Yoon, Y. C.; Lee, E. G.; Kim, M.; Kim, T. J.; Yang, Y. Y.; Son, E. Y.; Yoon, S. J.; Diem, N. C.; Kim, H. M.; Kwon, S. W. Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 2020, 12(1), 157. [CrossRef]
- Račková, L.; Cupáková, M.; Tažký, A.; Mičová, J.; Kolek, E.; Košt'álová, D. Redox properties of ginger extracts: Perspectives of use of Zingiber officinale Rosc. as antidiabetic agent. Interdisciplinary toxicology, 2013, 6(1), 26–33. [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, Z.; Thomson, M.; Al-Qattan, K.; Peltonen-Shalaby, R.; Ali, M. Anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The British Journal of Nutrition, 2006, 96, 660–666. [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, K. R.; Mallikarjuna, K.; Nishanth, K.; Ku, C. H.; Reddy, K. S. Protective effect of dietary ginger on antioxidant enzymes and oxidative damage in experimental diabetic rat tissues. Food Chemistry, 2011, 124(4), 1436–1442. [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, A. O.; Akindele, A. J.; Ahmed, Z. Modulation of antioxidant enzymes and inflammatory cytokines: possible mechanism of anti-diabetic effect of ginger extracts. African Journal of Biomedical Research, 2011, 14(3), 195-202. [CrossRef]
- Adefegha, A. O. A. S. A.; Oboh, G., Akinyemi, A. J.; Ademiluyi, A. Inhibitory effects of aqueous extract of two varieties of ginger on some key enzymes linked to type-2 diabetes in vitro. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research, 2010, 49(1), 14-20.
- Balamash, K. S.; Alkreathy, H. M.; Al Gahdali, E. H.; Khoja, S. O.; Ahmad, A. Comparative Biochemical and Histopathological Studies on the Efficacy of Metformin and Virgin Olive Oil against Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Journal of diabetes research, 2018, 4692197. [CrossRef]
- Mandalari, G.; Barreca, D.; Gervasi, T.; Roussell, M. A.; Klein, B.; Feeney, M. J.; Carughi, A. Pistachio Nuts (Pistacia vera L.): Production, Nutrients, Bioactives and Novel Health Effects. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(1), 18. [CrossRef]
- Tham, Y. Y.; Choo, Q. C.; Muhammad, T. S. T.; Chew, C. H. Lauric acid alleviates insulin resistance by improving mitochondrial biogenesis in THP-1 macrophages. Molecular biology reports, 2020, 47(12), 9595–9607. [CrossRef]
- Muruganathan, U.; Srinivasan, S.; Indumathi, D. Antihyperglycemic effect of carvone: Effect on the levels of glycoprotein components in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Acute Disease, 2013, 2(4),. https://cyberleninka.org/article/n/476314. [CrossRef]
- Abdulghafoor, H. A.; Ramadhan, S. J.; Nawfal, A. J. Therapeutic Effects of Allicin against the Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Streptozotocin in Male Rats. NVEO-NATURAL VOLATILES & ESSENTIAL OILS Journal| NVEO, 2021, 8934–8945.
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Purified anthocyanin supplementation reduces dyslipidemia, enhances antioxidant capacity, and prevents insulin resistance in diabetic patients. The Journal of nutrition, 2015, 145(4), 742–748. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Choudhury, S. T.; Seidel, V.; Rahman, A. B.; Aziz, M. A.; Richi, A. E.; Rahman, A.; Jafrin, U. H.; Hannan, J. M. A.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. A. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin in the Management of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Life (Basel, Switzerland), 2022, 12(8), 1146. [CrossRef]
- Subash Babu, P.; Prabuseenivasan, S.; Ignacimuthu, S. Cinnamaldehyde--a potential antidiabetic agent. Phytomedicine : international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology, 2007, 14(1), 15–22. [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, V.; Dastkhosh, A.; Hedayati, M.; Sedaghat, M.; Sharafkhah, M.; Sohrab, G. The effect of crocin supplementation on glycemic control, insulin resistance and active AMPK levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a pilot study. Diabetology & metabolic syndrome, 2020, 12, 59. [CrossRef]
- Patil, S. B.; Takalikar, S. S.; Joglekar, M. M.; Haldavnekar, V. S.; Arvindekar, A. U. Insulinotropic and β-cell protective action of cuminaldehyde, cuminol and an inhibitor isolated from Cuminum cyminum in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The British journal of nutrition, 2013, 110(8), 1434–1443. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Jayaramaiah, R. H.; Agawane, S. B.; Vannuruswamy, G.; Korwar, A. M.; Anand, A.; Dhaygude, V. S.; Shaikh, M. L.; Joshi, R. S.; Boppana, R.; Kulkarni, M. J.; Thulasiram, H. V.; Giri, A. P. Potential Dual Role of Eugenol in Inhibiting Advanced Glycation End Products in Diabetes: Proteomic and Mechanistic Insights. Scientific reports, 2016, 6, 18798. [CrossRef]
- Alkhalidy, H.; Moore, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; McMillan, R. P.; Zhen, W.; Zhou, K.; Liu, D. The Flavonoid Kaempferol Ameliorates Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes by Suppressing Hepatic Glucose Production. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2018, 23(9), 2338. [CrossRef]
- Mirjana, M.; Jelena, A.; Aleksandra, U.; Svetlana, D.; Nevena, G.; Jelena, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Ana, Š. D.; Goran, P.; Melita, V. β-Glucan administration to diabetic rats reestablishes redox balance and stimulates cellular pro-survival mechanisms. Journal of Functional Foods, 2013, 5(1), 267–278. [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, V.; Joshi, U.; Shinde, S.; Pawar, G. In-vivo and in-vitro evaluation of therapeutic potential of β- Carotene in diabetes. Journal of diabetes and metabolic disorders, 2021, 20(2), 1621–1630. [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S. M.; Abdel Motaal, A.; El Awdan, S. A. W. In vitro and in vivo antidiabetic potential of extracts and a furostanol saponin from Balanites aegyptiaca. Pharmaceutical biology, 2017, 55(1), 1931–1936. [CrossRef]
- Faisal Lutfi, M.; Abdel-Moneim, A. H.; Alsharidah, A. S.; Mobark, M. A.; Abdellatif, A. A. H.; Saleem, I. Y.; Al Rugaie, O.; Mohany, K. M.; Alsharidah, M. Thymoquinone Lowers Blood Glucose and Reduces Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Diabetes. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 26(8), 2348. [CrossRef]
- Shivarudrappa, A. H.; Ponesakki, G. Lutein reverses hyperglycemia-mediated blockage of Nrf2 translocation by modulating the activation of intracellular protein kinases in retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells. Journal of cell communication and signaling, 2020, 14(2), 207–221. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Ahn, D.; Hwang, J. Y.; Kang, M. J.; Chung, S. J. Linoleic acid exerts antidiabetic effects by inhibiting protein tyrosine phosphatases associated with insulin resistance. Journal of Functional Foods, 2021, 83, 104532. [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, V. S.; Kaur, G. Insulinotropic and antidiabetic effects of β-caryophyllene with l-arginine in type 2 diabetic rats. Journal of food biochemistry, 2020, 44(4), e13156. [CrossRef]
- Pinent, M.; Blay, M.; Bladé, M. C.; Salvadó, M. J.; Arola, L.; Ardévol, A. Grape seed-derived procyanidins have an antihyperglycemic effect in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and insulinomimetic activity in insulin-sensitive cell lines. Endocrinology, 2004, 145(11), 4985–4990. [CrossRef]
- Panwar, R.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Srivastava, A. K.; Sharma, A. K.; Pruthi, V. In-vivo sustained release of nanoencapsulated ferulic acid and its impact in induced diabetes. Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, 2018, 92, 381–392. [CrossRef]
- Samad, M. B.; Mohsin, M.; Bin, N. A.; Razu, B. A.; Hossain, M. T.; Mahzabeen, S.; Unnoor, N.; Muna, I. A.; Akhter, F.; Kabir, A. U. [6]-Gingerol, from Zingiber officinale, potentiates GLP-1 mediated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion pathway in pancreatic β-cells and increases RAB8/RAB10-regulated membrane presentation of GLUT4 transporters in skeletal muscle to improve hyperglycemia in Leprdb/db type 2 diabetic mice. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2017, 17(1), 1–13.
- Araújo, L. S.; da Silva, M. V.; da Silva, C. A.; Borges, M. F.; Palhares, H. M. D. C.; Rocha, L. P.; Corrêa, R. R. M.; Rodrigues Júnior, V.; Dos Reis, M. A.; Machado, J. R. Analysis of serum inflammatory mediators in type 2 diabetic patients and their influence on renal function. PloS one, 2020, 15(3), e0229765. [CrossRef]
- Sarian, M. N.; Ahmed, Q. U.; Mat So'ad, S. Z.; Alhassan, A. M.; Murugesu, S.; Perumal, V.; Syed Mohamad, S. N. A.; Khatib, A.; Latip, J. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Effects of Flavonoids: A Structure-Activity Relationship Based Study. BioMed research international, 2017, 8386065. [CrossRef]
- Sarian, M. N.; Ahmed, Q. U.; Mat So’ad, S. Z.; Alhassan, A. M.; Murugesu, S.; Perumal, V.; Syed Mohamad, S. N. A.; Khatib, A.; Latip, J. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Effects of Flavonoids: A Structure-Activity Relationship Based Study. BioMed Research International 2017, e8386065. [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Tang, Y. The Effect of Polyhydroxylated Alkaloids on Maltase-Glucoamylase. PLOS ONE, 2013, 8(8), e70841. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





