Submitted:
17 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
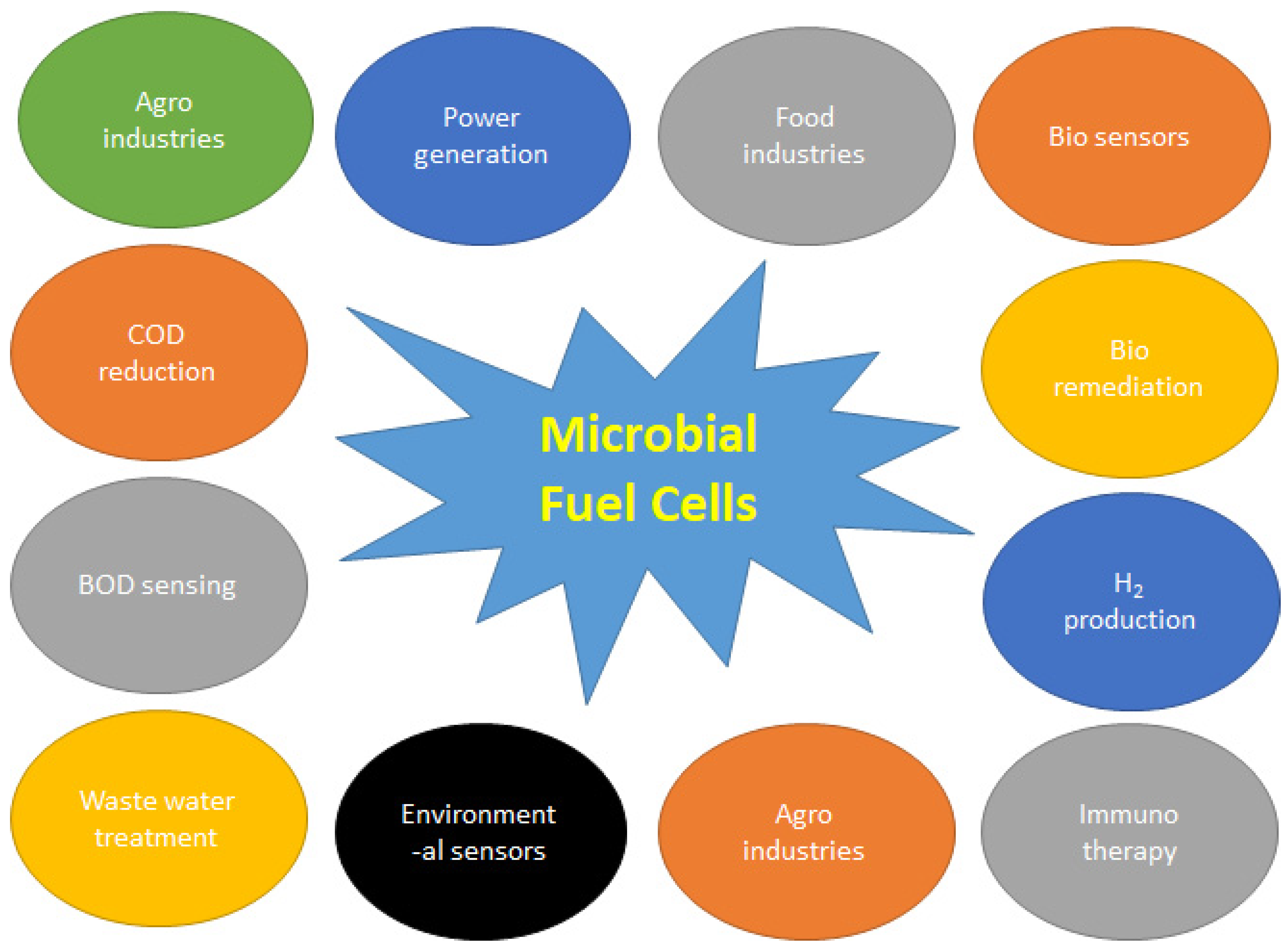
Introduction
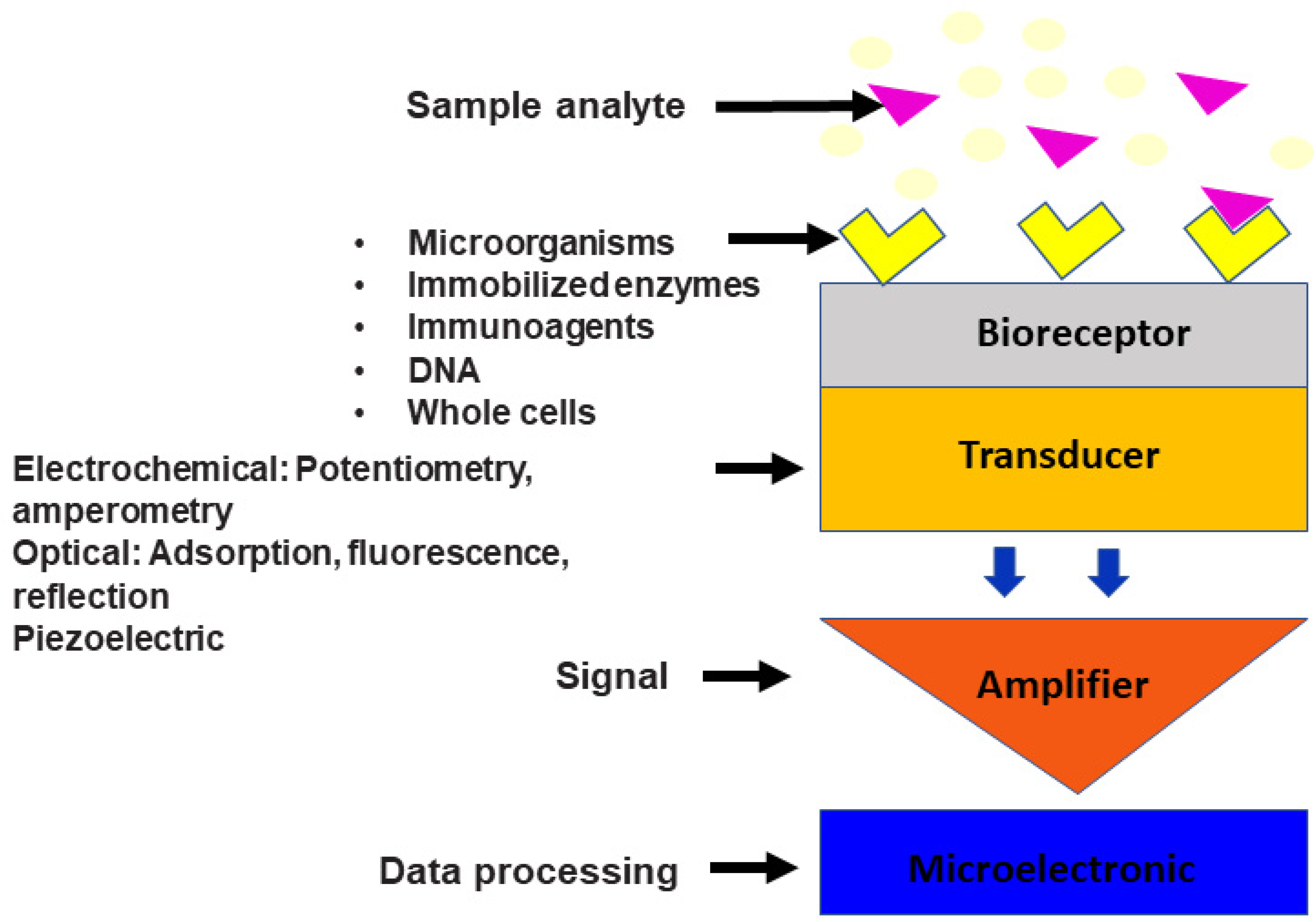
Microbial biosensors
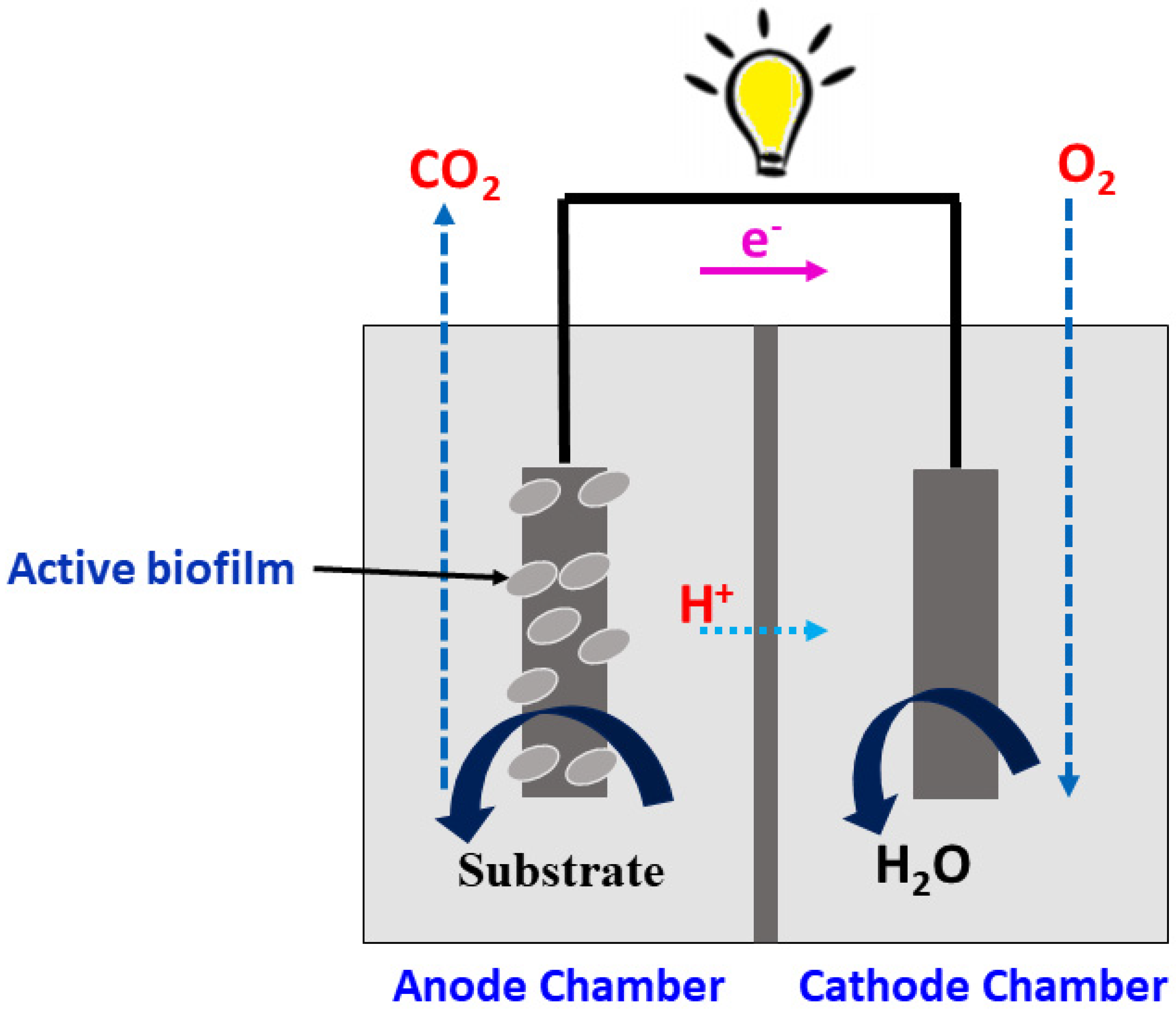
MFCs as an electrochemical sensor
MFC sensor design
MFCs as BOD sensors
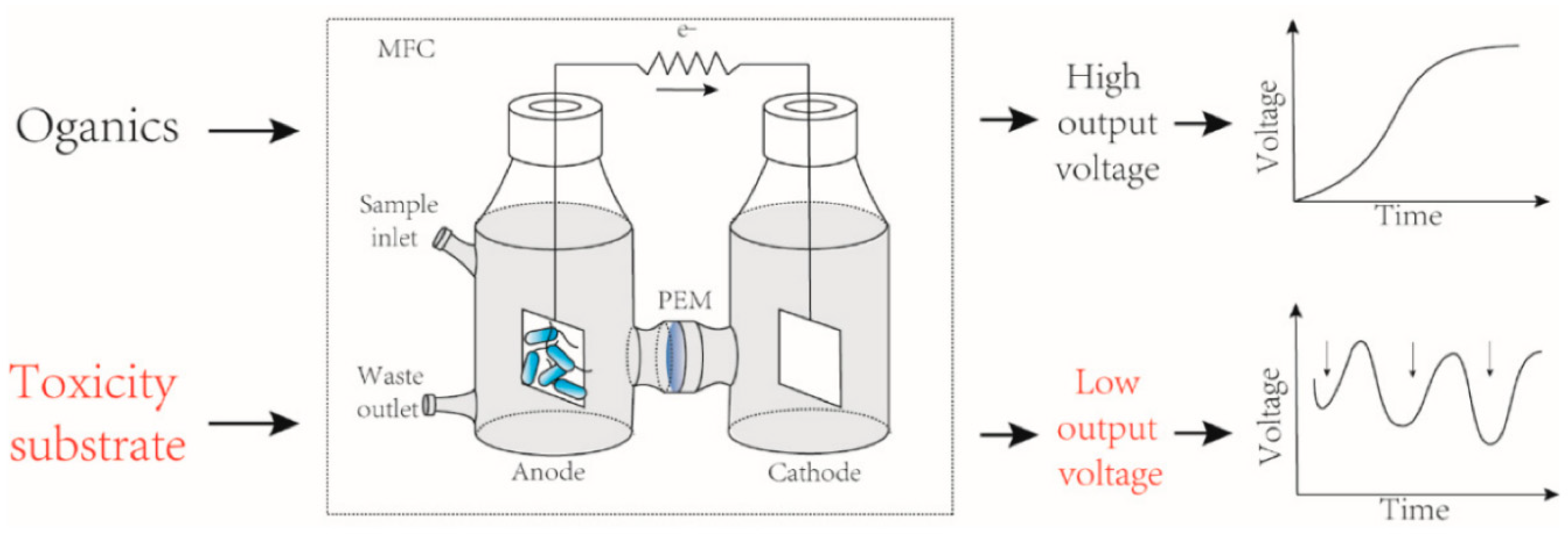
Detection of toxicants in water by MFCs
Conclusions
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Luo, S.; Sun, H.; Ping, Q.; Jin, R.; He, Z. A Review of Modeling Bioelectrochemical Systems: Engineering and Statistical Aspects. Energies 2016, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabangu, K.P.; Bakare, B.F.; Bwapwa, J.K. Microbial Fuel Cells for Electrical Energy: Outlook on Scaling-Up and Application Possibilities towards South African Energy Grid. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, M.; Riau, V.; Bonmatí, A. Recent Advances in Bioelectrochemical Systems for Nitrogen and Phosphorus Recovery Using Membranes. Membranes 2023, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsharian, Y.P.; Rahimnejad, M. Functional dynamics of microbial communities in bioelectrochemical systems: The importance of eco-electrogenic treatment of complex substrates. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 31, 100816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshova, T.; Rao, A.; Bhadra, S.; Garlapati, V.K.; Sharma, S.; Kaushik, A.; Goswami, P.; Sreekirshnan, T.; Sevda, S. Plant microbial fuel cells as an innovative, versatile agro-technology for green energy generation combined with wastewater treatment and food production. Biomass- Bioenergy 2022, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivars-Barceló, F.; Zuliani, A.; Fallah, M.; Mashkour, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Luque, R. Novel Applications of Microbial Fuel Cells in Sensors and Biosensors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minteer, S.D.; Liaw, B.Y.; Cooney, M.J. Enzyme-based biofuel cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckarift, H.R.; Atanassov, P.B.; Johnson, G.R. (Eds.) 2014. Enzymatic fuel cells: From fundamentals to applications. John Wiley & Sons.
- Ucar, D.; Zhang, Y.; Angelidaki, I. An Overview of Electron Acceptors in Microbial Fuel Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadzli, F.S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Microbial Fuel Cell: Recent Developments in Organic Substrate Use and Bacterial Electrode Interaction. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madondo, N.I.; Rathilal, S.; Bakare, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K. Application of Bioelectrochemical Systems and Anaerobic Additives in Wastewater Treatment: A Conceptual Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, J.V.; Oliveira, V.B.; Simões, M.; Pinto, A.M. Review on microbial fuel cells applications, developments and costs. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Hu, T.; Xiao, H.; Lu, W.; Jia, J. Progress on anodic modification materials and future development directions in microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2023, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-W.; Chung, Y.-P.; Liu, S.-H.; Chen, W.T.; Zhu, T.-J. Optimizing the parameters of microbial fuel cells using response surface methodology to increase Cr(VI) removal efficiency and power production. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Ahmad, I.; Zhao, T.; Maaza, M.; Bocchetta, P. Green Nanocomposite Electrodes/Electrolytes for Microbial Fuel Cells—Cutting-Edge Technology. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, A.N.; Farhat, I.; Irshad, M.; Hussain, M.A.; Usman, M.; Chaudhary, T.N.; Fouad, Y.; Raza, S.; Ashraf, W.M.; Krzywanski, J. Electrochemical Insight into the Use of Microbial Fuel Cells for Bioelectricity Generation and Wastewater Treatment. Energies 2023, 16, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Kishore, S.; Dhasmana, A.; Kumari, P.; Mitra, T.; Chaudhary, V.; Kumari, R.; Bora, J.; Ranjan, A.; Minkina, T.; et al. A Perspective Review on Microbial Fuel Cells in Treatment and Product Recovery from Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, S.; Logan, B.E. Production of Electricity from Acetate or Butyrate Using a Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Li, B. The variation of power generation with organic substrates in single-chamber microbial fuel cells (SCMFCs). Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimje, V.R.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, H.-R.; Tseng, M.-J.; Cheng, K.-C.; Shih, R.-C.; Chang, Y.-F. A Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell without an Air Cathode. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3933–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawale, H.D.; Ranveer, A.C.; Chavan, A.R. Electricity generation from wastewater using a microbial fuel cell by using mixed bacterial culture. Journal of Biochemical Technology 2017, 8, 1123. [Google Scholar]
- Abrevaya, X.C.; Sacco, N.J.; Bonetto, M.C.; Hilding-Ohlsson, A.; Cortón, E. Analytical applications of microbial fuel cells. Part II: Toxicity, microbial activity and quantification, single analyte detection and other uses. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkour, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Pourali, S.; Ezoji, H.; ElMekawy, A.; Pant, D. Catalytic performance of nano-hybrid graphene and titanium dioxide modified cathodes fabricated with facile and green technique in microbial fuel cell. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2017, 27, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-J.; Ubando, A.T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-X.; Culaba, A.B.; Lin, Y.-A.; Wang, C.-T. Modification of carbon based cathode electrode in a batch-type microbial fuel cells. Biomass- Bioenergy 2021, 145, 105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Haq, I.U.; Qaisar, K.; Gunes, B.; Raja, S.I.; Mohyuddin, K.; Amin, H. Microbial fuel cells: Insight into simultaneous wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 161, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubackar, H.N.; Biryol, I.; Ayol, A. Yeast industry wastewater treatment with microbial fuel cells: Effect of electrode materials and reactor configurations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 12424–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanthi, K.; Madusanka, D.; Pathmalal, M.; Idroos, F. Emerging trends of cyanobacteria-based microbial fuel cells as an alternative energy source. In Development in Wastewater Treatment Research and Processes; Shah, M.P., Rodriguez-Couto, S., Nadda, A.K., Daverey, A., Eds. 2023; 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, P.J.; Malakar, B.; Mohanty, K. Self-sustaining bioelectricity generation in plant-based microbial fuel cells (PMFCs) with microalgae-assisted oxygen-reducing biocathode. Biomass- Convers. Biorefinery, 2023; 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Ng, K.H.; Papadopoulos, A.M.; Le, A.T.; Kumar, S.; Hadiyanto, H.; Pham, V.V. Microbial fuel cells for bioelectricity production from waste as sustainable prospect of future energy sector. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 132285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boas, J.V.; Oliveira, V.B.; Simões, M.; Pinto, A.M. Review on microbial fuel cells applications, developments and costs. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubackar, H.N.; Biryol, I.; Ayol, A. Yeast industry wastewater treatment with microbial fuel cells: Effect of electrode materials and reactor configurations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 12424–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Siddiqi, S.A.; Al-Mamun, A.; Jafary, T. Sustainable leachate pre-treatment using microbial desalination cell for simultaneous desalination and energy recovery. Desalination 2022, 532, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yi, K.; Hu, S.; Yang, W. Cathodic biofouling control by microbial separators in air-breathing microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2023, 15, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinovicius, A.; Rozene, J.; Merkelis, T.; Bruzaite, I.; Ramanavicius, A.; Morkvenaite-Vilkonciene, I. Evaluation of a Yeast–Polypyrrole Biocomposite Used in Microbial Fuel Cells. Sensors 2022, 22, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Okeke, S.I.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, L. Recent Implementations of Hydrogel-Based Microbial Electrochemical Technologies (METs) in Sensing Applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradian, J.M.; Yang, F.-Q.; Xu, N.; Wang, J.-Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Sha, C.; Ali, A.; Yong, Y.-C. Enhancement of bioelectricity and hydrogen production from xylose by a nanofiber polyaniline modified anode with yeast microbial fuel cell. Fuel 2022, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Sun, D.; Cao, G.; Wang, H.; Ren, N.; Wu, W.-M.; Logan, B.E. Integrated hydrogen production process from cellulose by combining dark fermentation, microbial fuel cells, and a microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4137–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Kumar, D.; Singh, N.; Katti, S.S.; Shah, Y.T. Electricigens and microbial fuel cells for bioremediation and bioenergy production: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2091–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Bose, D.; Yadav, J.; Sharma, B.; Sangli, E.; Patel, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Singh, A.A. Bioremediation and bioelectricity from Himalayan rock soil in sediment-microbial fuel cell using carbon rich substrates. Fuel 2023, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.D.; Yasasve, M.; Karthigadevi, G.; Aashabharathi, M.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Govarthanan, M. Efficiency of microbial fuel cells in the treatment and energy recovery from food wastes: Trends and applications - A review. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 132439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.N.A.; Sabri, M.N.I.M.; Tajarudin, H.A.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Shukor, H.; Makhtar, M.M.Z.; Abbas, S.Z.; Yong, Y.-C.; Rafatullah, M. Mixture of Sludge and Chicken Manure in Membrane-Less Microbial Fuel Cell for Simultaneous Waste Treatment and Energy Recovery. Catalysts 2022, 12, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutila, E.; Koivunen, R.; Bollström, R.; Gane, P. Fully inkjet-printed glucose assay fabricated on highly porous pigment coating. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics 2020, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, M.; Choi, S. Small-scale, storable paper biobatteries activated via human bodily fluids. Nano Energy 2022, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, U.; Nießen, J.; Scholz, F. A Generation of Microbial Fuel Cells with Current Outputs Boosted by More Than One Order of Magnitude. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2880–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Lissens, G.; Siciliano, S.D.; Verstraete, W. A microbial fuel cell capable of converting glucose to electricity at high rate and efficiency. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Verstraete, W. Microbial fuel cells: novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Boon, N.; Siciliano, S.D.; Verhaege, M.; Verstraete, W. Biofuel Cells Select for Microbial Consortia That Self-Mediate Electron Transfer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5373–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ramnarayanan, R.; Logan, B.E. Production of Electricity during Wastewater Treatment Using a Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2281–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivars-Barceló, F.; Zuliani, A.; Fallah, M.; Mashkour, M.; Rahimnejad, M.; Luque, R. Novel Applications of Microbial Fuel Cells in Sensors and Biosensors. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constructed Wetlands. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wetlands/constructed-wetlands (accessed on 17 July 2018).
- Corbella, C.; Puigagut, J.; Garfí, M. Life cycle assessment of constructed wetland systems for wastewater treatment coupled with microbial fuel cells. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584-585, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M. Use of microbial fuel cells in sensors. Microbial electrochemical and fuel cells 2016, 341–356. [Google Scholar]
- Marzorati, S.; Schievano, A.; Colombo, A.; Lucchini, G.; Cristiani, P. Ligno-cellulosic materials as air-water separators in low-tech microbial fuel cells for nutrients recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilajeliu-Pons, A.; Puig, S.; Salcedo-Dávila, I.; Balaguer, M.D.; Colprim, J. Long-term assessment of six-stacked scaled-up MFCs treating swine manure with different electrode materials. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E. Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, C.; Mollica, A.; Féron, D.; Basséguy, R.; Etcheverry, L.; Bergel, A. Marine microbial fuel cell: Use of stainless steel electrodes as anode and cathode materials. Electrochimica Acta 2007, 53, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.S.; Jang, J.K.; Gil, G.C.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, B.W.; Kim, B.H. Continuous determination of biochemical oxygen demand using microbial fuel cell type biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalathil, S.; Patil, S.; Pant, D. Microbial Fuel Cells: Electrode Materials. Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry 2018, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uria, N.; Ferrera, I.; Mas, J. Electrochemical performance and microbial community profiles in microbial fuel cells in relation to electron transfer mechanisms. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimje, V.R.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, H.-R.; Tseng, M.-J.; Cheng, K.-C.; Shih, R.-C.; Chang, Y.-F. A Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell without an Air Cathode. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3933–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, J. Development of biosensor technologies for analysis of environmental contaminants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Jia, W.; Hou, C.; Lei, Y. Microbial biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1788–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Youn, S.M.; Shin, S.H.; Jang, J.G.; Han, S.H.; Hyun, M.S.; Gadd, G.M.; Kim, H.J. Practical field application of a novel BOD monitoring system. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biran, I.; Babai, R.; Levcov, K.; Rishpon, J.; Ron, E.Z. Online and in situ monitoring of environmental pollutants: electrochemical biosensing of cadmium. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Mulchandani, P.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Direct Determination of p-Nitrophenyl Substituent Organophosphorus Nerve Agents Using a Recombinant Pseudomonas putida JS444-Modified Clark Oxygen Electrode. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 53, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J., Jr.; van der Schalie, W.H. Biological monitoring Part I—Early warning systems. Water Research 1980, 14, 1179–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.H.; Byung, H.K. A microbial fuel cell type lactate biosensor using a metal-reducing bacterium, Shewanella putrefaciens. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 1999, 9, 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, I.S.; Jang, J.K.; Gil, G.C.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, B.W.; Kim, B.H. Continuous determination of biochemical oxygen demand using microbial fuel cell type biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mattiasson, B. Microbial BOD sensors for wastewater analysis. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3786–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lei, Y.; Li, B. A batch-mode cube microbial fuel cell based “shock” biosensor for wastewater quality monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila, D.; Esquivel, J.; Sabaté, N.; Mas, J. Silicon-based microfabricated microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Thomson, A.R.; Schneider, K.; Cameron, P.J.; Ieropoulos, I. A small-scale air-cathode microbial fuel cell for on-line monitoring of water quality. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Kjeang, E. A perspective on microfluidic biofuel cells. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Chae, J. Miniaturizing microbial fuel cells for potential portable power sources: promises and challenges. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2012, 13, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMekawy, A.; Hegab, H.M.; Dominguez-Benetton, X.; Pant, D. Internal resistance of microfluidic microbial fuel cell: Challenges and potential opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yadav, D.; Singh, S.; Kumar, M.; Song, M. Insights into the Domestic Wastewater Treatment (DWWT) Regimes: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.A.; Zouidi, F.; Kumar, P.; Fayssal, S.A.; Adelodun, B.; Goala, M.; Kumar, V.; Širić, I.; Eid, E.M. Impact of Irrigation with Contaminated Water on Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Water Chestnut (Trapa natans L.). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, A.; Sharma, L.; Pandit, C.; Gupta, P.K.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Pandit, S.; Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Upadhye, V.J. Microbial Fuel Cell–Based Biosensors and Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 195, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesarwani, S.; Panwar, D.; Mal, J.; Pradhan, N.; Rani, R. Constructed Wetland Coupled Microbial Fuel Cell: A Clean Technology for Sustainable Treatment of Wastewater and Bioelectricity Generation. Fermentation 2022, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Curtis, T.P.; Head, I.M.; Scott, K. A single-chamber microbial fuel cell as a biosensor for wastewaters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, I.; Matsunaga, T.; Mitsuda, S.; Suzuki, S. Microbial electrode BOD sensors. Biotechnology and bioengineering 1977, 19, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.H.; Byung, H.K. A microbial fuel cell type lactate biosensor using a metal-reducing bacterium, Shewanella putrefaciens. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 1999, 9, 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.H.; Chang, I.S.; Gil, G.C.; Park, H.S.; Kim, H.J. Novel BOD (biological oxygen demand) sensor using mediator-less microbial fuel cell. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Jang, J.K.; Pham, T.H.; Moon, H.; Chang, I.S.; Kim, B.H. A microbial fuel cell with improved cathode reaction as a low biochemical oxygen demand sensor. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.S.; Moon, H.; Jang, J.K.; Kim, B.H. Improvement of a microbial fuel cell performance as a BOD sensor using respiratory inhibitors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.; Thomson, A.R.; Schneider, K.; Cameron, P.J.; Ieropoulos, I. A small-scale air-cathode microbial fuel cell for on-line monitoring of water quality. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumlanghan, A.; Liu, J.; Thavarungkul, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Mattiasson, B. Microbial fuel cell-based biosensor for fast analysis of biodegradable organic matter. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Han, H.; Liu, P.; Xiong, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X. Microbial Fuels Cell-Based Biosensor for Toxicity Detection: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-X.; Sun, Y.-M.; Kong, X.-Y.; Zhen, F.; Li, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Lei, T.-Z.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Chen, G.-Y. Factors affecting the performance of a single-chamber microbial fuel cell-type biological oxygen demand sensor. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Angelidaki, I. Submersible microbial fuel cell sensor for monitoring microbial activity and BOD in groundwater: Focusing on impact of anodic biofilm on sensor applicability. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gard-Terech, A.; Palla, J. Comparative kinetics study of the evolution of freshwater aquatic toxicity and biodegradability of linear and branched alkylbenzene sulfonates. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1986, 12, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Waly, H.; Abou-Setta, M.M.; Nigg, H.N.; Mallory, L.L. Growth response of freshwater algae, Anabaena flos-aquae and Selenastrum capricornutum to atrazine and hexazinone herbicides. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology 1991, 46, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sik Hyun, M.; Gadd, G.M.; Joo Kim, H. A novel biomonitoring system using microbial fuel cells. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, N.E.; Hamelers, H.V.; Buisman, C.N. Stabilizing the baseline current of a microbial fuel cell-based biosensor through overpotential control under non-toxic conditions. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 78, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golitsch, F.; Bücking, C.; Gescher, J. Proof of principle for an engineered microbial biosensor based on Shewanella oneidensis outer membrane protein complexes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Tang, X.; Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M.; Liu, A. Direct energy conversion from xylose using xylose dehydrogenase surface displayed bacteria based enzymatic biofuel cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Han, H.; Liu, P.; Xiong, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X. Microbial Fuels Cell-Based Biosensor for Toxicity Detection: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila, D.; Esquivel, J.; Sabaté, N.; Mas, J. Silicon-based microfabricated microbial fuel cell toxicity sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, N.; Zhou, Q. Concentration responses of toxicity sensor with Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 growing in bioelectrochemical systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, N.E.; Hamelers, H.V.; Buisman, C.N. The effect of different control mechanisms on the sensitivity and recovery time of a microbial fuel cell based biosensor. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2012, 171-172, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lei, Y.; Li, B. A batch-mode cube microbial fuel cell based “shock” biosensor for wastewater quality monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Entry | Configuration | Source of carbon | Volume of anodic chamber (cm3) |
Sensitivity (μA mM21 cm22) |
Linearity rangea |
Time for response | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Two chambers | Glucose and glutamic acid | 25 | ND | 80–150 ppma | 30 min | [64] |
| 2 | Single chamber | Glucose | 12.6 | 0.08 |
50–350 ppma 100–500 ppmb |
40 min | [81] |
| 3 | Two chambers | Wastewater from a starch processing plant |
25 | ND | 0–206 ppmb | 30 min–1 h | [84] |
| 4 | Two chambers | Glucose and glutamic acid Glucose |
20 | 0.15 | 20–100 ppma | 1 h | [86] |
| 5 | Single chamber | Single chamber | 2 | 0.05 | 3–164 ppma | 2.8 min | [87] |
| 6 | Two chambers MFC coupled with an anaerobic reactor that provides a stable anaerobic consortium |
Glucose | 100 | ND | 1–25 g l—1c | 3 min | [88] |
| 7 | Single chamber | Glucose and glutamic acid |
73 | ND | 5–120 ppma | 2.2 h | [90] |
| 8 | Submerged anode coupled with a cathode chamber |
Acetate, glucose, wastewater |
NA | 0.1 | 10–250 ppm | 40 min | [91] |
| Entry | Device | Dynamic range | Bioreceptor | Time of Measurement | Pollutant | Control | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Air- cathode single chamber |
1–25 μg l—1 | Mixed bacteria | 6 min | Cd | External resistance (1 kΩ) | [87] |
| 2 | Two- chamber MFC |
ND | Mixed bacteria | 20 min–2 h | Diazin, Pb, Hg, PCBs | External resistor (500 Ω) | [94] |
| 3 | Two- chamber MFC |
0–200 mg l—1 | Mixed bacteria | 2 h | Ni, Cu | Poised anode potential (—0.4 V) | [95] |
| 4 | Two- chamber MFC |
ND |
Geobacter sulfurreducens |
3 min | Formaldehyde | Fixed current of 1 μA | [99] |
| 5 | Three electrode set-up |
0.01–0.10% (in volume) |
S. oneidensis MR-1 |
2–18 h | Formaldehyde | Poised anode potential (0 mV) |
[100] |
| 6 | Two- chamber MFC |
ND | Mixed bacteria | 2 h | Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) |
Poised anode potential (—470 to 400 mV), external resistance (0–1000 Ω), and fixed current (0.05 mA) |
[101] |
| 7 | Air- cathode single chamber |
ND | Mixed bacteria | 1.2 h | Cr6+ | External resistance (480 Ω) | [102] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





