Submitted:
26 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
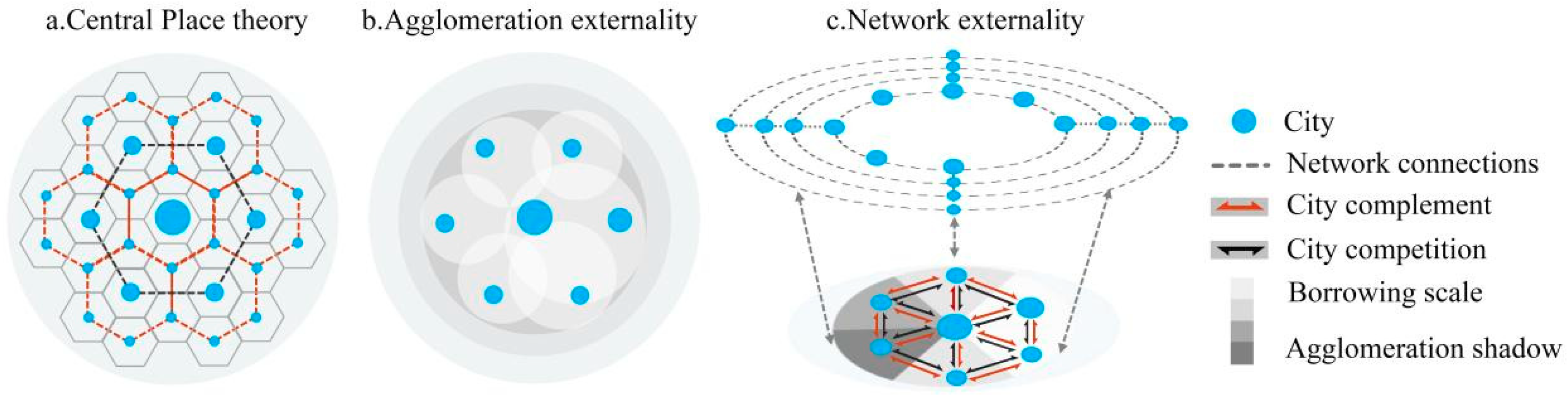
2. Study Area, Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
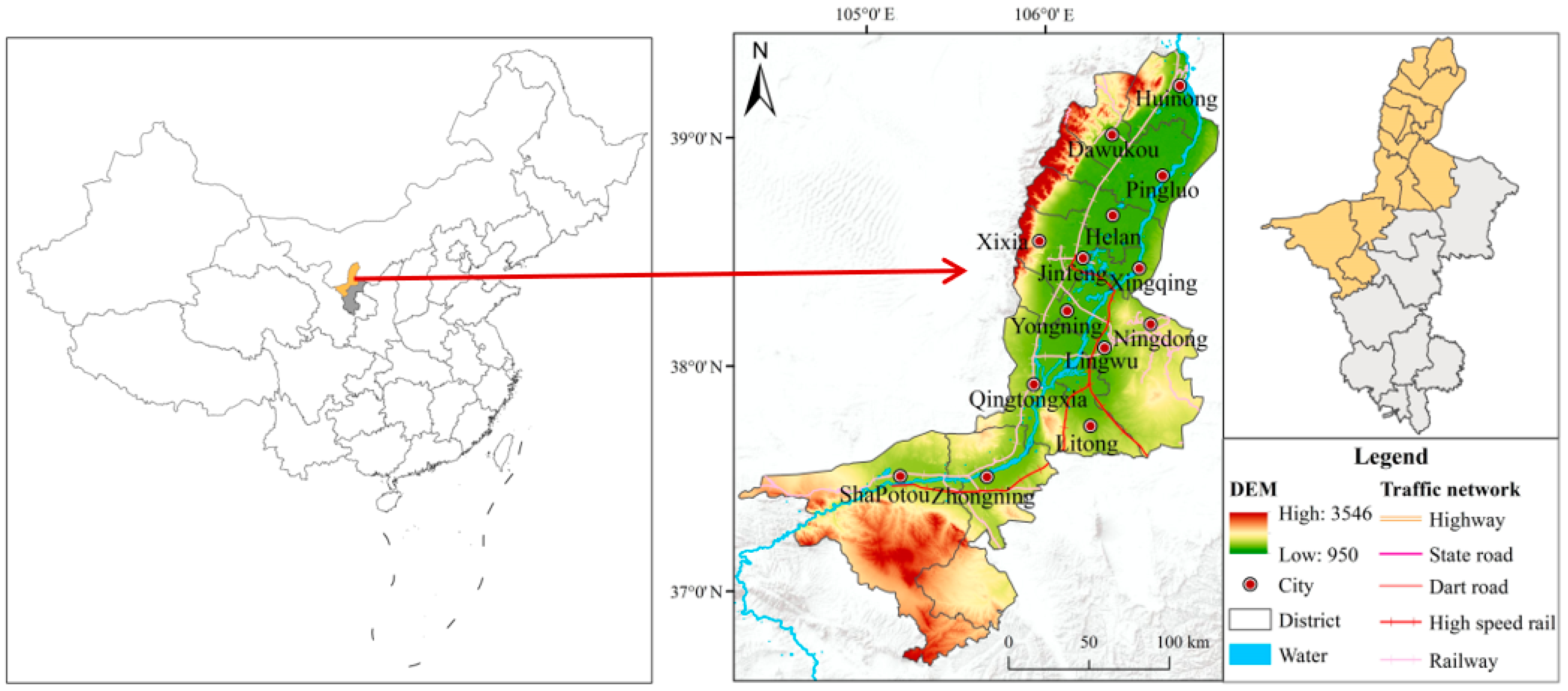
2.2. Study Data
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Enterprise connections value assessment
2.3.2. Enterprise Interlocking Network Model
2.3.3. Social network analysis method
2.3.4. Spatial panel econometric model
| Original category | Quantity | Categorization | Original category | Quantity | Categorization |
| Education | 3146 | Living service industry (127142) |
Transportation, Storage, and Postal services | 8190 | Productive service industry (84433) |
| Residential services, Repairs, and Other services | 8590 | Information transmission, Software, and Information technology services | 12008 | ||
| Accommodation and Catering | 5356 | Finance | 3792 | ||
| Wholesale and Retail | 105278 | Real Estate | 7230 | ||
| Culture, Sports and Entertainment | 3856 | Rental and Business services | 39391 | ||
| Health and Social work | 916 | Scientific research and Technical services | 13822 | ||
| Mining industry | 1739 | Productive manufacturing industry (30221) |
Agriculture | 20708 | Other industries (47663) |
| Manufacturing | 26210 | Construction | 25199 | ||
| Production and supply of Electricity, Heat, Gas, and Water | 2272 | Water resources, Environmental, and Public facilities management | 1492 | ||
| —— | Public administration, Social security, and Social organizations | 264 | |||
| Classification | Criteria for Classification | Valuation |
| Registered capital (Unit: 10,000 yuan) (va) |
Registered capital of the enterprise ∈ [0, 10) | 1 |
| Registered capital of the enterprise ∈ [10, 100) | 2 | |
| Registered capital of the enterprise ∈ [100, 1000) | 3 | |
| Registered capital of the enterprise ∈ [1000, 10000) | 4 | |
| Registered capital of the enterprise ∈ [10000, ∞] | 5 | |
| Innovation potential (vb) |
Company belongs to China’s Top 500 Private Enterprises, or Fortune China 500, or High-tech Enterprises. | 5 |
| Openness atmosphere (vc) |
The company belongs to foreign-invested or joint ventures with Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan. | 5 |
| Capital utilization (vd) |
The company belongs to listed companies or enterprise groups or state-owned enterprises. | 5 |
| Research Indicators | Research Methods | Meaning of Indicators |
| Urban connectivity | Taking the ratio of the node CS(i) to the maximum value in the same year, we obtain the relative level of inflow (i) and the relative level of outflow (i) within the internal network of city i. α and β are undetermined weights, with a default value of 0.5. The urban connectivity in the external network is also calculated using this formula. | |
| Dominant connections direction | represents the relative out-degree of a city in the network, indicating the city’s radiating capacity. represents the relative in-degree of a city in the network, indicating the city’s agglomeration capacity. N represents the number of cities. NSIi represents the dominant connections’ direction index of city i. |
3. Evolutionary characteristics of enterprise flow structure
3.1. The enterprise flow connections in the external network
3.1.1. The enterprise outflow connections in the external network
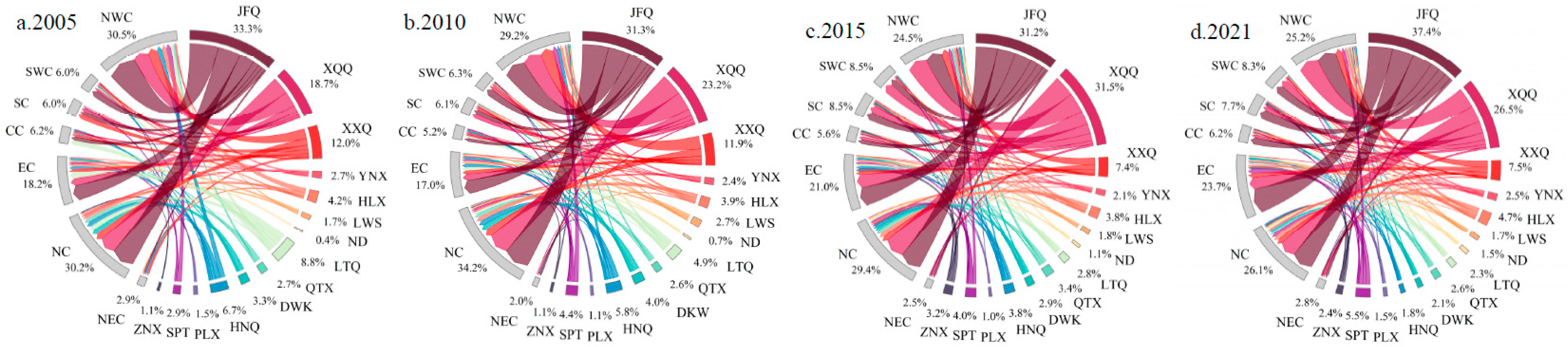
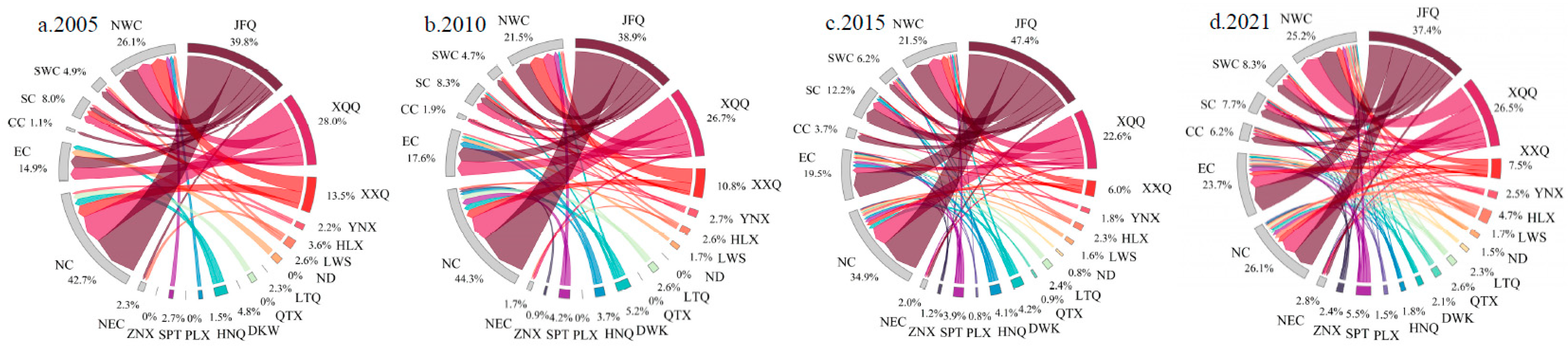
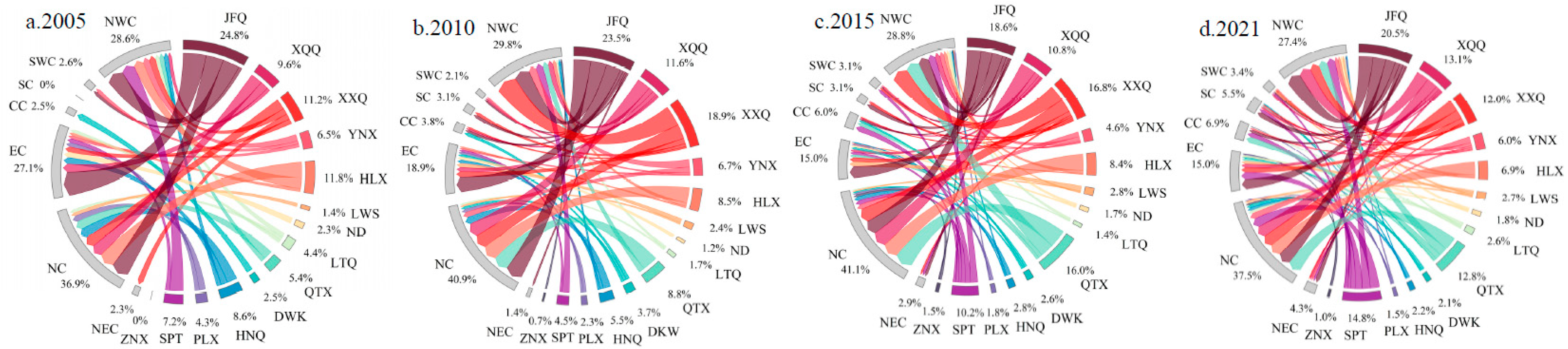
3.1.2. The enterprises inflow connections in the external network
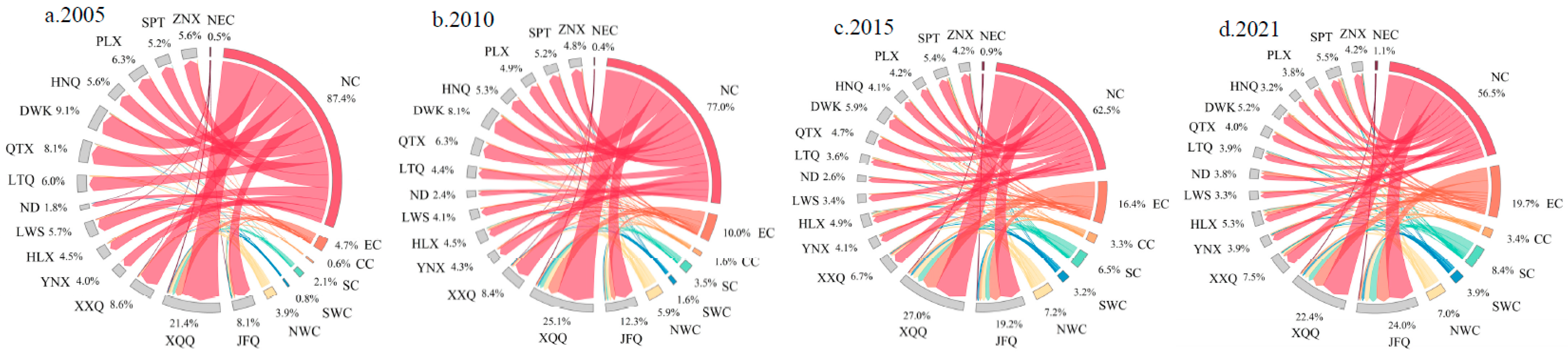
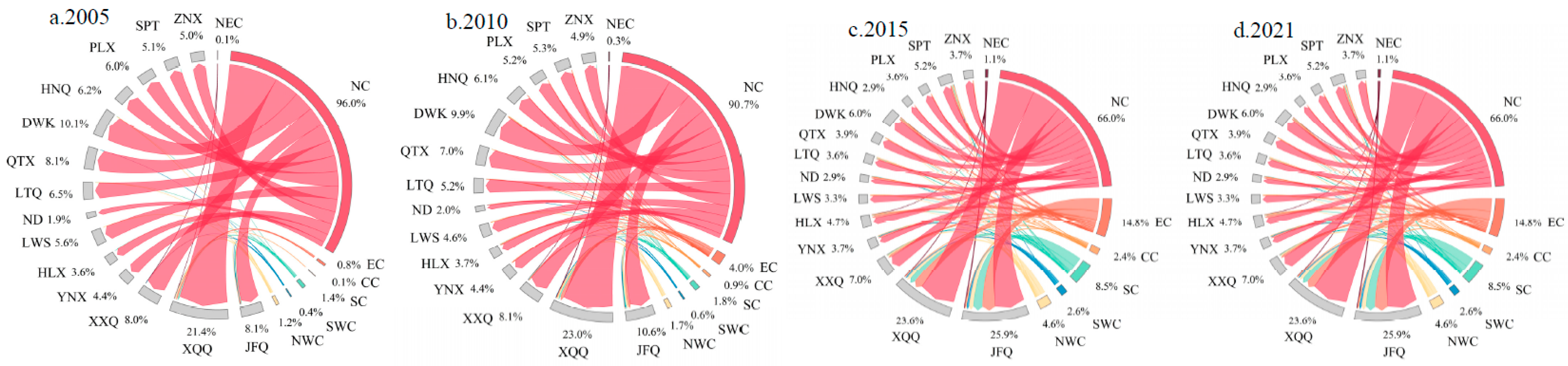
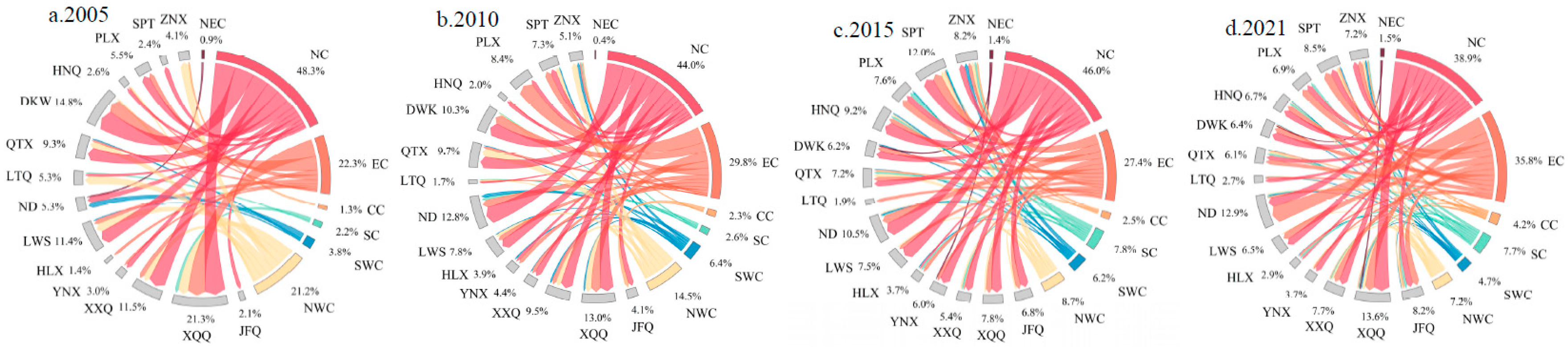
3.2. The enterprises flow connections in the internal network
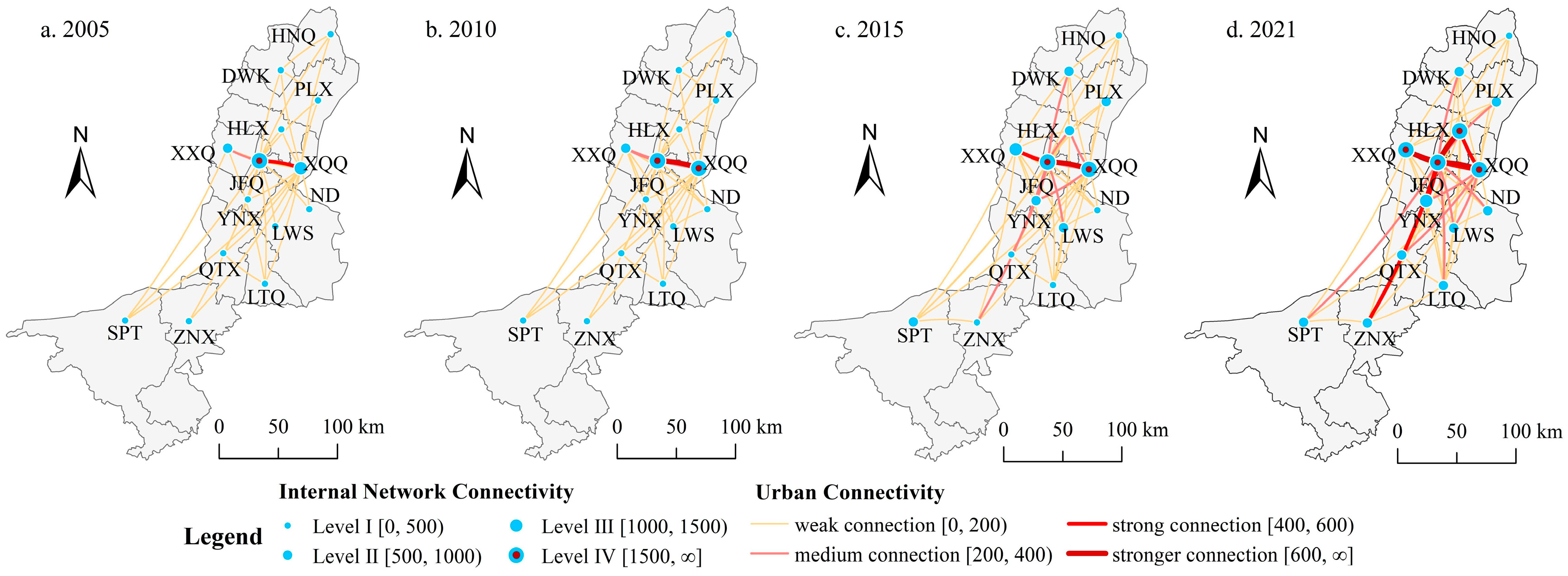
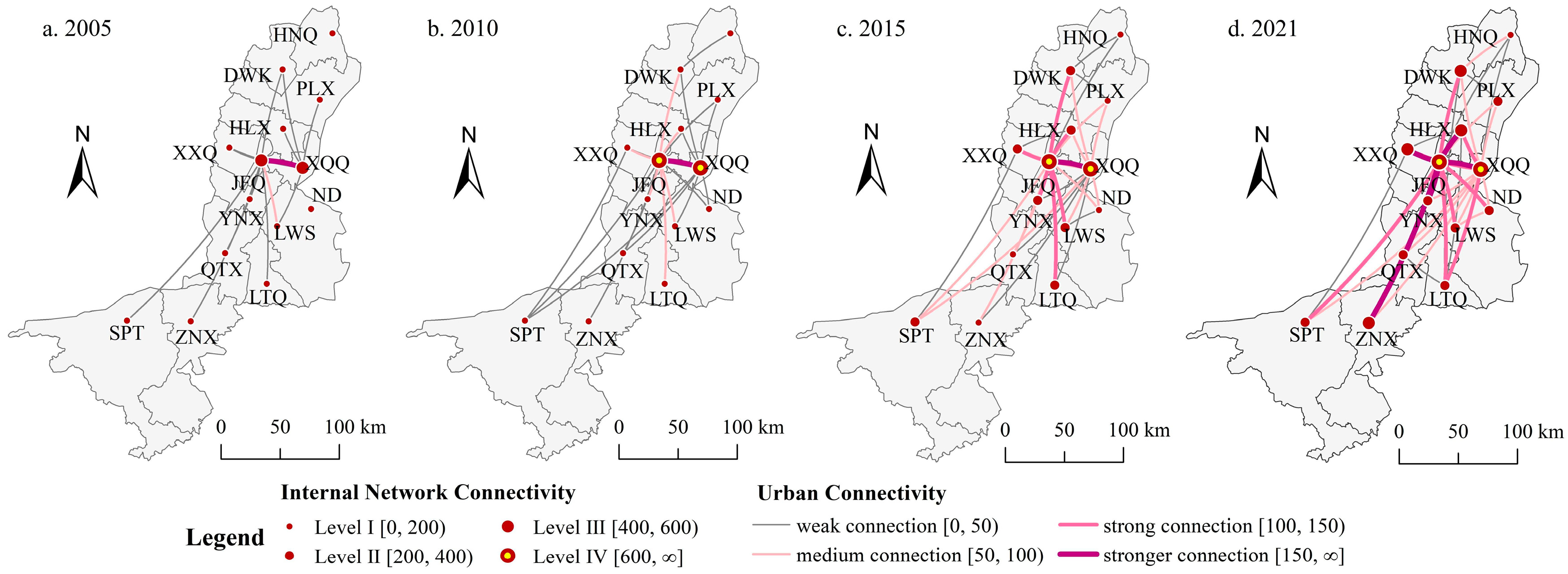
3.3. The enterprises flow connections in the internal network
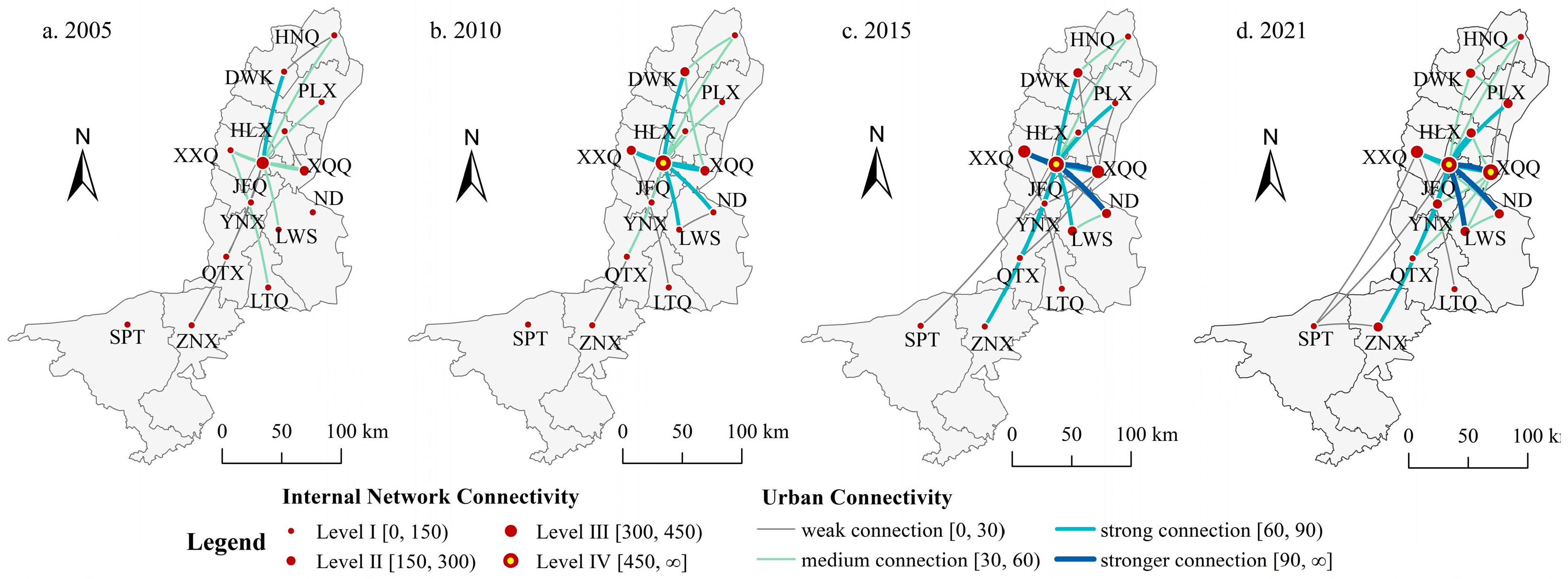
4. Analysis of the influence mechanism of enterprises flow
4.1. Selecting model variables
4.1.1. Social-economic variables
| Variables | Description |
| Investment | Reflecting the intensity of internal urban construction, it is (the ratio of regional fixed asset investment / GDP). |
| GOV | Reflecting the intensity of government management over urban development, it is (the local government fiscal expenditure / GDP). |
| Demand | Reflecting the domestic demand of the city, it is (the total social retail sales / GDP). |
| Transition | Reflecting the adjustment of urban production structure, indicators such as energy consumption per unit of GDP, water consumption per unit of GDP, and construction land use per unit of GDP are selected, and the transformation development index is calculated using the entropy method. |
| Coordinate | Reflecting the coordinated development between regions, indicators such as regional income coordination, regional consumption coordination, urban-rural income coordination, and urban-rural consumption coordination are selected (Li Zhejin and Liu Qiang, 2021), and the coordination development index is calculated using the entropy method. |
4.1.2. Borrowing scale variables
4.1.3. Geographic spatial agglomeration variable
4.2. Analysis of estimation results
| Variables | CityCon | ProCon | ||||||
| GD weigh | ED weigh | GD weigh | ED weigh | GD weigh | ED weigh | GD weigh | ED weigh | |
| lnFun | 0.246*** | 0.336*** | 0.302*** | 0.405*** | ||||
| (0.089) | (0.089) | (0.075) | (0.071) | |||||
| lnEco | 2.740*** | 3.054*** | -1.762*** | -1.548*** | ||||
| (0.607) | (0.579) | (0.506) | (0.457) | |||||
| (lnEco)2 | -0.474*** | -0.523*** | 0.321*** | 0.288*** | ||||
| (0.100) | (0.094) | (0.083) | (0.075) | |||||
| lnBroFun | 1.516*** | 1.512*** | 0.788*** | 0.847** | ||||
| (0.453) | (0.495) | (0.188) | (0.349) | |||||
| lnBroEco | -2.215*** | -2.352*** | -1.163*** | -1.056*** | ||||
| (0.766) | (0.789) | (0.333) | (0.278) | |||||
| lnBroPop | 0.277 | 0.279 | 0.402 | 0.255 | ||||
| (0.252) | (0.259) | (0.259) | (0.298) | |||||
| lnInvestment | -0.112*** | -0.102*** | -0.115*** | -0.094** | -0.091*** | -0.066** | -0.031 | -0.016 |
| (0.038) | (0.038) | (0.034) | (0.042) | (0.032) | (0.030) | (0.030) | (0.058) | |
| lnGOV | 0.113*** | 0.114*** | 0.107*** | 0.092** | 0.033 | 0.035 | -0.013 | -0.010 |
| (0.034) | (0.033) | (0.035) | (0.037) | (0.028) | (0.026) | (0.031) | (0.054) | |
| lnConsumption | 0.281*** | 0.283*** | 0.210*** | 0.263*** | 0.199*** | 0.202*** | 0.165*** | 0.153*** |
| (0.051) | (0.051) | (0.079) | (0.064) | (0.043) | (0.040) | (0.051) | (0.044) | |
| lnTransition | 0.011 | 0.022 | -0.149** | -0.153** | -0.095** | -0.082** | -0.161*** | -0.149*** |
| (0.052) | (0.053) | (0.072) | (0.073) | (0.044) | (0.042) | (0.042) | (0.056) | |
| lnCoordination | 0.217*** | 0.243*** | 0.086* | 0.060 | 0.224*** | 0.212*** | 0.214*** | 0.190*** |
| (0.065) | (0.067) | (0.048) | (0.072) | (0.054) | (0.053) | (0.058) | (0.045) | |
| ρ/θ | 0.013*** | 0.013*** | 0.012*** | 0.012*** | 0.009*** | 0.008*** | 0.010*** | 0.009*** |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.002) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.002) | |
| Number | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 |
| R2 | 0.378 | 0.462 | 0.278 | 0.280 | 0.811 | 0.794 | 0.117 | 0.141 |
4.3. Spatial effect decomposition
| Variables | CityCon | ProCon | ||||
| Direct effect | Indirect effect | Total effect | Direct effect | Indirect effect | Total effect | |
| lnBroFun | 1.214*** | 3.086** | 4.300*** | 0.502 | 4.213*** | 4.715*** |
| (0.361) | (1.398) | (1.665) | (0.372) | (1.473) | (1.500) | |
| lnBroEco | -1.590** | -6.167*** | -7.757*** | -0.942*** | -3.242* | -4.185** |
| (0.638) | (2.053) | (2.571) | (0.195) | (1.689) | (1.788) | |
| lnBroPop | 0.126 | 1.348 | 1.474* | 0.585 | -2.598*** | -2.013*** |
| (0.306) | (0.880) | (0.758) | (0.359) | (0.574) | (0.620) | |
| lnInvestment | -0.118*** | 0.038 | -0.080 | -0.035 | 0.134 | 0.099 |
| (0.033) | (0.170) | (0.165) | (0.051) | (0.166) | (0.188) | |
| lnGOV | 0.071** | 0.313*** | 0.384*** | -0.019 | 0.043 | 0.024 |
| (0.033) | (0.101) | (0.103) | (0.050) | (0.135) | (0.164) | |
| lnConsumption | 0.237*** | -0.163 | 0.074 | 0.099 | 0.926*** | 1.024*** |
| (0.085) | (0.354) | (0.336) | (0.063) | (0.249) | (0.269) | |
| lnTransition | -0.159** | 0.024 | -0.135 | -0.100** | -0.864*** | -0.964*** |
| (0.080) | (0.359) | (0.332) | (0.049) | (0.314) | (0.294) | |
| lnCoordination | 0.079* | 0.057 | 0.136 | 0.214*** | -0.007 | 0.208 |
| (0.061) | (0.222) | (0.200) | (0.048) | (0.228) | (0.219) | |
4.4. Geographical agglomeration effect
| Variables | CityCon | ProCon | ||
| GD weigh | ED weigh | GD weigh | ED weigh | |
| lnAgglomeration | 0.958*** | 0.941*** | 0.375*** | 0.270** |
| (0.137) | (0.131) | (0.133) | (0.126) | |
| Direct effect | 0.778*** | 0.815*** | 0.185 | 0.130 |
| (0.200) | (0.203) | (0.228) | (0.223) | |
| Indirect effect | 2.623** | 3.427*** | 2.454* | 2.398 |
| (1.098) | (1.318) | (1.453) | (1.482) | |
| Total effect | 3.401*** | 4.241*** | 2.639* | 2.529* |
| (1.252) | (1.492) | (1.517) | (1.529) | |
| Other variable | Control | Control | Control | Control |
| ρ/θ | 0.012*** | 0.013*** | 0.012*** | 0.012*** |
| (0.001) | (0.001) | (0.002) | (0.001) | |
| Number | 208 | 208 | 208 | 208 |
| R2 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.485 | 0.404 |
5. Conclusions and Discussions
5.1. Conclusions
- (1)
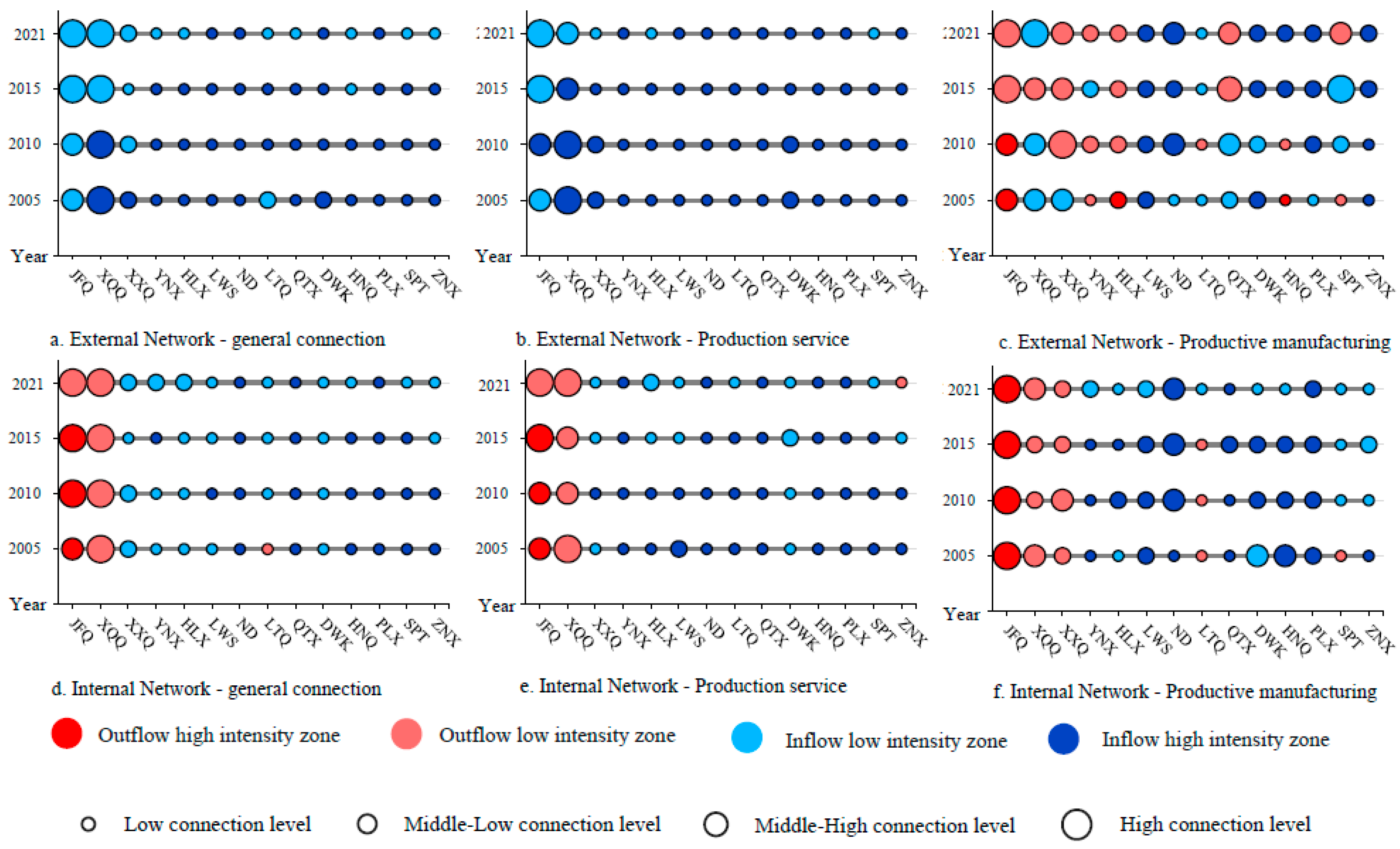
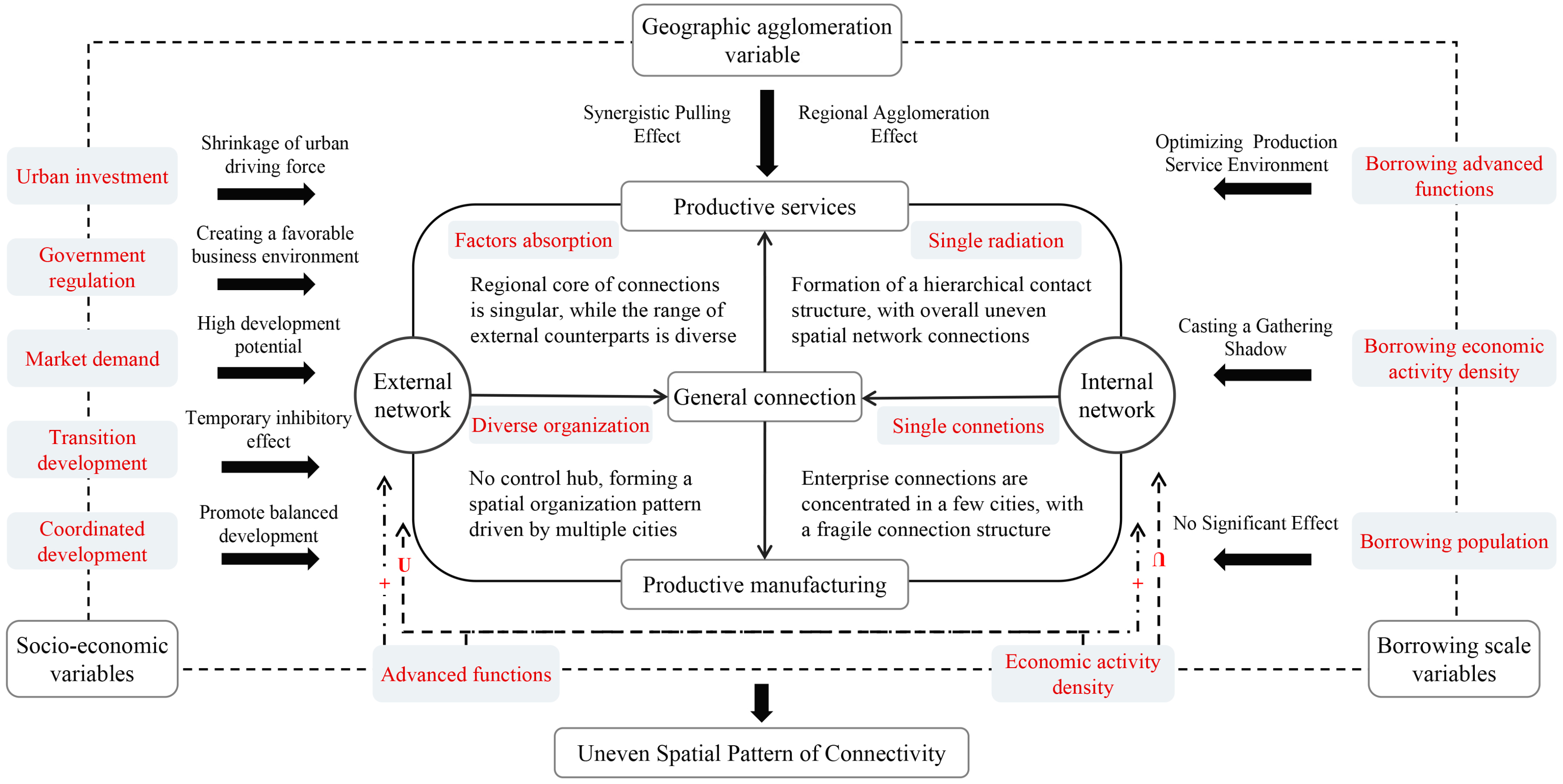
- With analysis of the spatial pattern evolution of external network connections through enterprise flows, the spatial organizational structure of Ningxia Urban Agglomeration along the Yellow River’s outflow investment demonstrates a trend of monopolar outflow from the investment sources and diversified inflows from various destinations. Jinfeng and Xingqing are the core hubs for regional enterprises investments, and the investments mainly flow towards North China, East China, and Northwest China. The overall inflow of enterprises has formed a multi-source structure, with North China as the dominant region and East China as the secondary region. A spatial pattern of enterprise inflow is formed in terms of overall connections and Productive service industry, with Jinfeng and Xingqing at its core. And a spatial organizational pattern driven by multiple cities is formed in the Productive manufacturing industry.
- (2)
- In the internal network, a connection structure centered around Jinfeng and Xingqing has been formed. However, the overall spatial network connections are imbalanced, and the hierarchical system of network nodes is incomplete. In different types of enterprise flows, on one hand, there is a relatively active flow of connections in the Productive service industry, and the driving capacity of core cities is beginning to emerge. On the other hand, the connections in the Productive manufacturing industry are relatively concentrated between Jinfeng, Xingqing, Ningdong, and Lingwu.
- (3)
- In terms of regional network structural characteristics, the external network primarily manifests as absorbing external elements to foster developmental momentum. In terms of overall connections and Productive service industry, each city is in a net inflow state, while in the Productive manufacturing industry, the network node connection structure presents a diversified organizational pattern and achieves a net outflow. In the internal network, Jinfeng and Xingqing serve as connection radiation sources and exert influence on each cities. However, their driving capacity is weak, the main manifestation is that the core nodes maintain a considerable communication with neighboring cities and promote the upgrading of their connection levels. And the radiation does not extend to peripheral cities, keeping them in a weak connectivity.
- (4)
- In terms of the role of socio-economic variables, market demand and coordinated development demonstrate significant promotion effects on both internal network connection and external network connection. The transformation and development exhibit significant negative impacts, which are attributed to the temporary negative effects caused by the inadequate adjustment and transition of industrial structure. The role of urban investment activities and the government management is reflected in the internal network connections. The uneven development pattern of cities restricts the driving effect of urban investment activities to the cities themselves. However, efficient government management is beneficial for creating a favorable business environment and generating positive spatial spillover effects.
- (5)
- In terms of the role of borrowing scale variables, the improvement of urban management and service functions, as well as external borrowing, can optimize the regional production service environment and promote enterprise connections among different network. In the scenario of imbalanced development within the internal network, improving economic activity will amplify the agglomeration shadow effect of core cities on other cities, and will have a negative impact on the enterprise connections in different networks. However, in the external network, economic activity exhibits a U-shaped relationship, which is the result of urban green development transformation and corresponds to the emergence of green industry enterprises.
- (6)
- In terms of the role of geographic spatial agglomeration variable, industrial agglomeration can significantly enhance the internal network connections of cities in different networks and exert spatial driving effects in surrounding cities. This reflects that a rational spatial distribution of production factors can effectively promote the enterprises flow in different networks, and the coordinated development of cities is an important foundation for regional urban network connections.
5.2. Discussions
References
- Alonso, W. Urban zero population growth. Daedalus 1973, 109, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Bentlage, M.; Thierstein, A. Intra firm networks in the German knowledge economy: economic performance of German agglomerations from a relational perspective. European Regional Science Association 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Castells, M. The Rise of Network Society; Blackwell: Oxford, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Z.; Pan, S. Understanding the structure and determinants of city network through intra-firm service relationships: The case of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Cities 2020, 103, 102738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bai, Y.; Song, L.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Economic Link and Network Structure of the Four Urban Agglomerations in the Middle and Upper Yellow River Basin. Areal Research And Development 2021, 40, 18–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Su, X. Review on the urban network externalities. Progress in Geography 2021, 40, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, J.; Li, Y.; et al. The Structural Evolution And Influencing Factors of urban network in the Yellow River basin from The perspective of High-quality development. Human Geography 2023, 38, 87–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P.J. The cliquishness of world cities. Global Networks 2005, 5, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P.J.; Hoyler, M.; et al. Measurement and interpretation of connectivity of Chinese cities in world city network, 2010. Chinese Geographical Science 2013, 23, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Taylor, P.J. Central flow theory: Comparative connectivities in the world-city network. Regional Studies 2018, 52, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.P. City connectivity via global intra-firm linkages: An analysis of Indian cities. Journal of International Development 2023, 35, 312–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, J. The world city hypothesis. Development and Change 1986, 17, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.; Phelps, N.A. Revisiting the multinational enterprise in global production networks. Journal of Economic Geography 2018, 18, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; He, D.; Ning, Y.; et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics and factors of urban investment linkage level in the Yangtze River Delta. Geographical Research 2021, 40, 2760–2779. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.; Pain, K. The polycentric metropolis: Learning from mega-city regions in Europe. Routledge 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyler, M. External relations of German cities through intra-firm networks—A global perspective. Raumforschung und Raumordnung Spatial Research and Planning 2011, 69, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Study On The Urban Networkers Structure and its Changing Characteristics of The Yangtze River Economic Belt: based on Inter-Firm Linkages. Human Geography 2021, 36, 146–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraprahasta, G.S.; Derudder, B. The geographically variegated connections of the Jakarta metropolitan area as produced by manufacturing firms. Growth and Change 2019, 50, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krätke, S. Global pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms’ linkages in the world city network. Urban Studies 2014, 51, 1196–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, S.; Thierstein, A.; Goebel, V. Intra-firm and extra-firm linkages in the knowledge economy: The case of the emerging mega-city region of Munich. Global networks 2010, 10, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Measuring functional polycentricity of China’s urban regions based on the interlocking network model, 2006–15. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography 2018, 39, 382–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Gu, R.; Wang, J.; et al. From Agglomeration Externalities to Network Externalities of Crossing Borders: Frontier Progress of Agglomeration Economics. Urban Development Studies 2018, 25, 82–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi, S.; Thierstein, A.; Hoyler, M. The world city network: Evaluating top-down versus bottom-up approaches. Cities 2018, 72, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mao, W. The Rise of Urban Network Eyxternalities: A New Mechanism for the High-quality Integrated Development of Regional Economy. Economist 2020, 2020, 62–70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Gao, P.; et al. Coupling relationship and interactive response between ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Journal of Natural Resources 2021, 36, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q. Research on the impact of information flow on high-quality economic development and its spatial effects. Statistics & Decision 2021, 37, 97–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinus, K.; Sigler, T.J. Global city clusters: Theorizing spatial and non-spatial proximity in inter-urban firm networks. Regional studies 2018, 52, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xiu, C.; Feng, X. Urban Network Characteristics in the Three Provinces of the Northeastern China Based on Headquarter-affiliate Enterprises Connection. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2019, 39, 1129–1138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuduru, B.H.; Webster, C.J.; Chiaradia, A.J.F. Associating street-network centrality with spontaneous and planned subcentres. Urban Studies 2021, 58, 2059–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Bi, W.; Liu, X.; et al. Exploring financial centre networks through inter-urban collaboration in high-end financial transactions in China. Regional Studies 2018a, 54, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; He, Z.; Sigler, T.; et al. How Chinese financial centers integrate into global financial center networks: An empirical study based on overseas expansion of Chinese financial service firms. Chinese Geographical Science 2018b, 28, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, P.; et al. Research on the innovative network of Guangzhou,Dongguan and Shenzhen in the context of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area development. City Planning Review 2021, 45, 31–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sassen, S. The global city; Princeton University Press: USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Scholvin, S.; Breul, M.; Diez, J.R. Revisiting gateway cities: Connecting hubs in global networks to their hinterlands. Urban Geography 2019, 40, 1291–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, T.; Neal, Z.P.; Martinus, K. The brokerage roles of city-regions in global corporate networks. Regional Studies 2021, 57, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J. Specification of the world city network. Geographical analysis 2001, 33, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Derudder, B.; Faulconbridge, J.; et al. Advanced producer service firms as strategic networks, global cities as strategic places. Economic Geography 2014, 90, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Huang, Y.; Tao, H. Urban network externalities, agglomeration economies and urban economic growth. Cities 2020, 107, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fang, C.; Zhao, M. The spatial organization and structure complexity of Chinese intercity networks. Geographical Research 2015, 34, 711–728. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, R. The Spatial Structure and Evolution of Yangtze River Delta Urban Network:Analysis Based on Enterprise Connection. Urban Development Studies 2019, 26, 21–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Waiengnier, M.; Van Hamme, G.; Hendrikse, R. Metropolitan geographies of advanced producer services: Centrality and concentration in Brussels. Tijdschrift voor economische en sociale geografie 2020, 111, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qi, D.; Liu, W.; et al. Analysis of Urban Network Relationship from the Perspective of listed parents and Subsidiary Enterprises —— A Case Study Liaoning Province. Resource Development & Market 2021, 37, 1186–1191. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Yao, C. Exploring the association between shrinking cities and the loss of external investment: An intercity network analysis. Cities 2021, 119, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Study on the economic connection and network structure evolution of the Yellow River Basin. World Regional Studies 2022, 31, 527–537. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, L. Spatio-temporal evolution of urban network in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area —— Based on listed company organization relations. World Regional Studies 2019, 28, 83–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Duan, X. City network structure of the Yangtze River Delta region based on logistics enterprise network. Progress in Geography 2016, 35, 622–631. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; et al. Spatial pattern evolution of territorial space and its effects on ecological response in the Yellow River Basin during 2000-2020 Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 2023, 39, 217–228. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Multiple creators of knowledge-intensive service networks: A case study of the Pearl River Delta city-region. Urban Studies 2018a, 55, 2000–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y. Behind the scenes: The evolving urban networks of film production in China. Urban Geography 2018b, 39, 1510–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Xu, J. Evolution of the Urban Network Spatial Structure in Yangtze River Delta: Based on Enterprise Connections. Journal of Nantong University (Social Sciences Edition) 2021, 37, 33–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Ren, J.; et al. Spatial structure and influencing factors of urban network in the Yellow River Basin based on multiple flows. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2022, 42, 1778–1787. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





