Submitted:
23 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
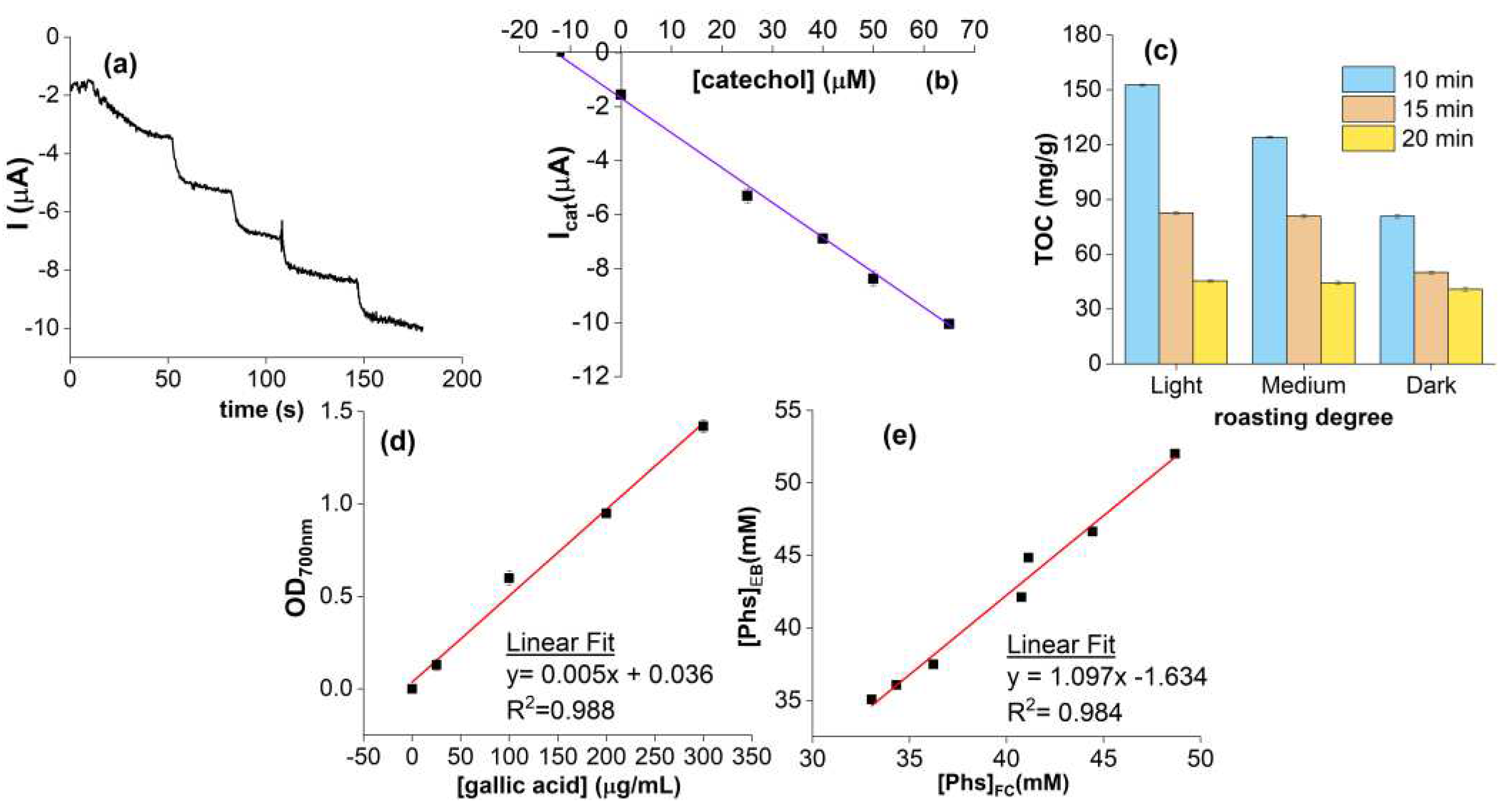
2. Results and Discussions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagentes and Samples
3.2. Electrochemical and Surface Characterization Apparatus
3.3. Real Sample Preparation and Treatment
3.4. Folin-Ciocâlteu Assay
3.5. TvLac-Based Biosensor Fabrication
3.6. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, M.; Rusling, J.F.; Dixit, C.K. Site-selective orientated immobilization of antibodies and conjugates for immunodiagnostics development. Methods 2017, 116, 95–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.11.010. [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.R.; Wang, C.; Younis, M.A.; Xia, X. Smartphone-Based Biosensors. Nanobiosensors From Des. to Appl. 2020, 357–387.
- Xu, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, C.; Lin, S.; Liao, J. Cost-effective, wireless, and portable smartphone-based electrochemical system for on-site monitoring and spatial mapping of the nitrite contamination in water. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020, 319, 128221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128221. [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.C.; Hall, D.A. Point-of-care smartphone-based electrochemical biosensing. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 2–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800474. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liu, Q. Smartphone-based biosensors for portable food evaluation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.09.003. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Su, H.-M.; Imani, S.M.; Alkhaldi, K.; M. Filipe, C.D.; Didar, T.F. Intelligent food packaging: A review of smart sensing technologies for monitoring food quality. ACS sensors 2019, 4, 808–821. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00440. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Song, Y.; Tu, J.; Mukasa, D.; Ye, C.; Xu, C.; Heflin, N.; McCune, J.S. A wearable electrochemical biosensor for the monitoring of metabolites and nutrients. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-022-00916-z. [CrossRef]
- Irannejad, N.; Rezaei, B. Electrochemical sensors for food adulterants. In Biosensing and Micro-Nano Devices: Design Aspects and Implementation in Food Industries; Springer, 2022; pp. 69–90.
- Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, C.; Wu, J. Review of Electrochemical Biosensors for Food Safety Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110959. [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.; Krishnan, D.; Kalra, S.; Chawla, R.; Tiwaskar, M.; Saboo, B.; Baruah, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Makkar, B.M.; Jaggi, S. Insights on medical nutrition therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: an Indian perspective. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 520–547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-019-0872-8. [CrossRef]
- Nestel, P.J.; Beilin, L.J.; Clifton, P.M.; Watts, G.F.; Mori, T.A. Practical guidance for food consumption to prevent cardiovascular disease. Hear. Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 163–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2020.08.022. [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001. [CrossRef]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Visioli, F. Polyphenols and health: Moving beyond antioxidants. J. Berry Res. 2012, 2, 63–71. https://doi.org/10.3233/JBR-2012-028. [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, J. Review Article Regulation of Immune Function by Polyphenols. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018.
- Scalbert, A.; Johnson, I.T.; Saltmarsh, M. Polyphenols: antioxidants and beyond. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 215–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/81.1.215s. [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Han, Y.; Kayahara, M.; Watanabe, T.; Arishige, H.; Kato, N. Consumption of curcumin elevates fecal immunoglobulin A, an index of intestinal immune function, in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 2010, 56, 68–71. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.56.68. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Berezo, T.; Franch, A.; Castellote, C.; Castell, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J. Mechanisms involved in down-regulation of intestinal IgA in rats by high cocoa intake. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 838–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.04.008. [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, F.; Lemaur, V.; Cornil, J.; Lazzaroni, R.; Duroux, J.-L.; Olivier, Y.; Trouillas, P. Free radical scavenging by natural polyphenols: atom versus electron transfer. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 2082–2092. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3116319. [CrossRef]
- Król, K.; Gantner, M.; Tatarak, A.; Hallmann, E. The content of polyphenols in coffee beans as roasting, origin and storage effect. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-019-03388-9. [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.; Kempf, K.; Martin, S. Health effects of coffee: mechanism unraveled? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061842. [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, E.B.; Wardiana, E.; Hilmi, Y.S.; Komarudin, N.A. The changes in chemical properties of coffee during roasting: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 974. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/974/1/012115. [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Monteiro, M.C.; Calado, V.; Franca, A.S.; Trugo, L.C. Correlation between cup quality and chemical attributes of Brazilian coffee. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.032. [CrossRef]
- Perdani, C.G.; Pranowo, D. Total phenols content of green coffee (Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora) in East Java. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing, 2019; Vol. 230, p. 12093.
- Kwak, H.S.; Ji, S.; Jeong, Y. The effect of air flow in coffee roasting for antioxidant activity and total polyphenol content. Food Control 2017, 71, 210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.06.047. [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Lean, M.E.J.; Ashihara, H.; Crozier, A. Coffee: biochemistry and potential impact on health. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1695–1717. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4fo00042k. [CrossRef]
- Bunney, J.; Williamson, S.; Atkin, D.; Jeanneret, M.; Cozzolino, D.; Chapman, J.; Power, A.; Chandra, S. Current Research in Nutrition and Food Science The Use of Electrochemical Biosensors in Food Analysis. 2017, 5.
- Unal, Y.D.; Pazarlioglu, N.K. Production and Gelatin Entrapment of Laccase from Trametes versicolor and its Application to Quantitative Determination of Phenolic Contents of Commercial Fruit Juices. Food Biotechnol. 2011, 25, 351–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/08905436.2011.617258. [CrossRef]
- Castrovilli, M.C.; Bolognesi, P.; Chiarinelli, J.; Avaldi, L.; Calandra, P.; Antonacci, A.; Scognamiglio, V. The convergence of forefront technologies in the design of laccase-based biosensors–An update. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.07.026. [CrossRef]
- Aroca, R.F.; Ross, D.J.; Domingo, C. Surface-Enhanced Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2004, 58, 324A-338A.
- Romero-Arcos, M.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Martínez-Flores, H.E. Electrochemical study and characterization of an amperometric biosensor based on the immobilization of laccase in a nanostructure of TiO2 synthesized by the sol-gel method. Materials (Basel). 2016, 9, 8–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9070543. [CrossRef]
- Tavares, A.P.M.; Silva, C.G.; Dražić, G.; Silva, A.M.T.; Loureiro, J.M.; Faria, J.L. Laccase immobilization over multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Kinetic, thermodynamic and stability studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 454, 52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.054. [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Maqbool, A.; Sun, K.; Si, Y. Immobilization of Trametes versicolor laccase on Cu-alginate beads for biocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A in water: Optimized immobilization, degradation and toxicity assessment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.107089. [CrossRef]
- Patro, T.U.; Wagner, H.D. Influence of graphene oxide incorporation and chemical cross-linking on structure and mechanical properties of layer-by-layer assembled poly(Vinyl alcohol)-Laponite free-standing films. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 2377–2387. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.24226. [CrossRef]
- García-Miranda Ferrari, A.; Foster, C.W.; Kelly, P.J.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Determination of the electrochemical area of screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms. Biosensors 2018, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020053. [CrossRef]
- Tortolini, C.; Di Fusco, M.; Frasconi, M.; Favero, G.; Mazzei, F. Laccase-polyazetidine prepolymer-MWCNT integrated system: Biochemical properties and application to analytical determinations in real samples. Microchem. J. 2010, 96, 301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2010.05.004. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Luo, L.; Ullah, N.; Wei, Q.; Huang, F. Facile fabrication of gold nanoparticle on zein ultrafine fibers and their application for catechol biosensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 328, 444–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.12.070. [CrossRef]
- Kizling, M.; Dzwonek, M.; Wieckowska, A.; Bilewicz, R. Gold nanoparticles in bioelectrocatalysis – The role of nanoparticle size. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 12, 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.05.021. [CrossRef]
- Kizling, M.; Dzwonek, M.; Więckowska, A.; Bilewicz, R. Size Does Matter—Mediation of Electron Transfer by Gold Clusters in Bioelectrocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1988–1992. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201800032. [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, D.; Sundberg, R.; Suyatin, D.B.; Sotres, J.; Barrantes, A.; Ruzgas, T.; Maximov, I.; Montelius, L.; Shleev, S. The influence of nanoparticles on enzymatic bioelectrocatalysis. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 38164–38168. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra08107b. [CrossRef]
- Silveira, C.M.; Zumpano, R.; Moreira, M.; de Almeida, M.P.; Oliveira, M.J.; Bento, M.; Montez, C.; Paixão, I.; Franco, R.; Pereira, E.; et al. Star-Shaped Gold Nanoparticles as Friendly Interfaces for Protein Electrochemistry: the Case Study of Cytochrome c. ChemElectroChem 2019, 6, 4696–4703. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201901393. [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.R.; Marzuki, N.H.C.; Buang, N.A.; Huyop, F.; Wahab, R.A. An overview of technologies for immobilization of enzymes and surface analysis techniques for immobilized enzymes. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 205–220. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2015.1008192. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Y. Laccase immobilization for water purification: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126272. [CrossRef]
- Hanefeld, U.; Gardossi, L.; Magner, E. Understanding enzyme immobilisation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 453–468. https://doi.org/10.1039/b711564b. [CrossRef]
- Ashkan, Z.; Hemmati, R.; Homaei, A.; Dinari, A.; Jamlidoost, M.; Tashakor, A. Immobilization of enzymes on nanoinorganic support materials: An update. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 708–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.127. [CrossRef]
- Ciogli, L.; Zumpano, R.; Poloznikov, A.A.; Hushpulian, D.M.; Tishkov, V.I.; Andreu, R.; Gorton, L.; Mazzei, F.; Favero, G.; Bollella, P. Highly Sensitive Hydrogen Peroxide Biosensor Based on Tobacco Peroxidase Immobilized on p-Phenylenediamine Diazonium Cation Grafted Carbon Nanotubes: Preventing Fenton-like Inactivation at Negative Potential. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 2495–2504. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202100341. [CrossRef]
- Lavín, Á.; de Vicente, J.; Holgado, M.; Laguna, M.F.; Casquel, R.; Santamaría, B.; Maigler, M.V.; Hernández, A.L.; Ramírez, Y. On the determination of uncertainty and limit of detection in label-free biosensors. Sensors (Switzerland) 2018, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072038. [CrossRef]
- Dybkowska, E.; Sadowska, A.; Rakowska, R.; Dębowska, M.; Świderski, F.; Świąder, K. Assessing polyphenols content and antioxidant activity in coffee beans according to origin and the degree of roasting. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2017, 68, 347–353.
- Várady, M.; Hrušková, T.; Popelka, P. Effect of preparation method and roasting temperature on total polyphenol content in coffee beverages. Czech J. Food Sci. 2020, 38, 417–421. https://doi.org/10.17221/122/2020-CJFS. [CrossRef]
- Król, K.; Gantner, M.; Tatarak, A.; Hallmann, E. The effect of roasting, storage, origin on the bioactive compounds in organic and conventional coffee (Caffea arabica). Eur. Food Res. Technol 2019, 246, 33–39.
- Sunarharum, W.B.; Yuwono, S.S.; Aziza, O.F. Study on the effect of roasting temperature on antioxidant activity of early-roasted Java coffee powder (Arabica and Robusta). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 230. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/230/1/012045. [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.J.; Pablos, F.; González, A.G. Discrimination between arabica and robusta green coffee varieties according to their chemical composition. Talanta 1998, 46, 1259–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(97)00409-8. [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.R.; Park, K.W.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, J. Influence of Roasting Conditions on the Antioxidant Characteristics of C olombian Coffee (C offea arabica L.) Beans. J. Food Biochem. 2014, 38, 271–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12045. [CrossRef]
- Somporn, C.; Kamtuo, A.; Theerakulpisut, P.; Siriamornpun, S. Effects of roasting degree on radical scavenging activity, phenolics and volatile compounds of Arabica coffee beans (Coffea arabica L. cv. Catimor). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 2287–2296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2011.02748.x. [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.; Donangelo, C.M. Phenolic compounds in coffee. Brazilian J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 18, 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202006000100003. [CrossRef]
- Bicho, N.C.; Lidon, F.C.; Ramalho, J.C.; Leitão, A.E. Quality assessment of Arabica and Robusta green and roasted coffees - A review. Emirates J. Food Agric. 2013, 25, 945–950. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.v25i12.17290. [CrossRef]
- Bobková, A.; Hudáček, M.; Jakabová, S.; Belej, Ľ.; Capcarová, M.; Čurlej, J.; Bobko, M.; Árvay, J.; Jakab, I.; Čapla, J.; et al. The effect of roasting on the total polyphenols and antioxidant activity of coffee. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. - Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2020, 55, 495–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2020.1724660. [CrossRef]
- Folin, O.; Denis, W. on Phosphotungstic-Phosphomolybdic Compounds As Color Reagents. J. Biol. Chem. 1912, 12, 239–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)88697-5. [CrossRef]
- A Agbor, G.; Vinson, J.A.; Donnelly, P.E. Folin-Ciocalteau Reagent for Polyphenolic Assay. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 147–156. https://doi.org/10.19070/2326-3350-1400028. [CrossRef]
- Ovemair Barbosa, Claudia Ortiz, Angel Berenguer-Murcia, Rodrigo Torres, Rafael C. Rodrigues, R.F.-L. GLUTARALDEHYDE IN BIO-CATALYSTS DESIGN: A useful crosslinker and a versatile tool in enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1583–1600. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45991h. [CrossRef]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. BioTecniques 2004, 37, 790–802. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA07211A.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




